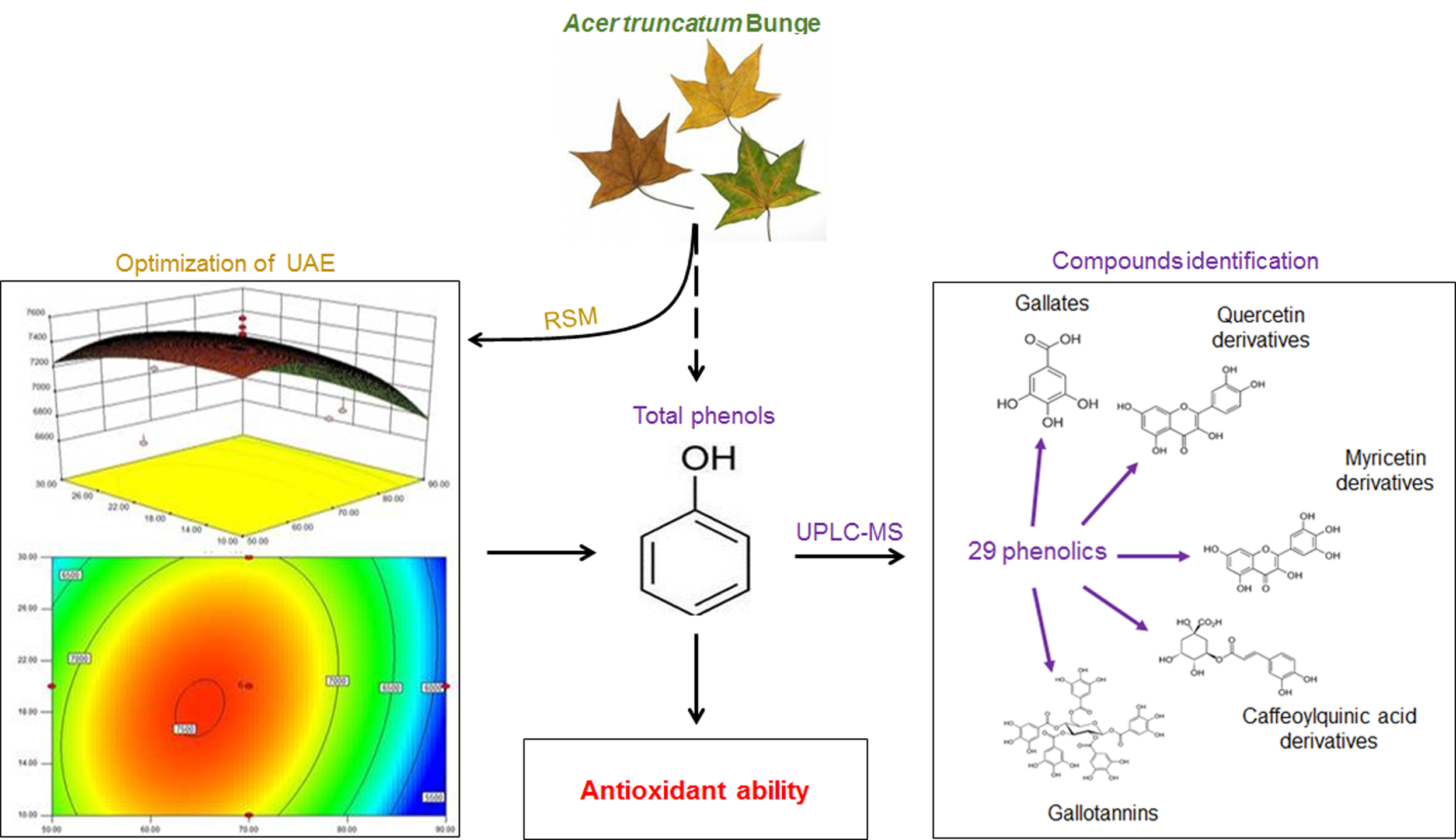
This study was designed for the first time to improve phenolic yield and antioxidant activity of ultrasonic-assisted extraction from Acer truncatum leaves (ATL) using response surface methodology, and phenolic composition in ATL extracted under the optimized condition were characterized by UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS. Solvent and extraction time were selected based on preliminary experiments, and a four-factors-three-levels central composite design was conducted to optimize solvent concentration (X1), material-to-liquid ratio (X2), ultrasonic temperature (X3) and power (X4) for an optimal total phenol yield (Y1) and DPPH• antioxidant activity (Y2). The results showed that the optimal combination was ethanol: water (v:v) 66.21%, material-to-liquid ratio 1:15.31 g/mL, ultrasonic temperature 60 °C, power 267.30 W, and time 30 min with three extractions, giving a maximal total phenol yield of 7593.62 mg gallic acid equivalent /100 g d.w. and a maximal DPPH• antioxidant activity of 74241.61 μmol Trolox equivalent/100 g d.w.. Furthermore, 22 phenolics were first identified in ATL extract obtained under the optimized conditions, indicating that gallates, gallotannins, quercetin, myricetin and chlorogenic acid derivatives were the main phenolic composition in ATL. What’s more, a gallotannins pathway existing in ATL from gallic acid to penta-O-galloyl-glucoside was interpreted. All these results provided practical information aiming at full utilization of phenolics in ATL, together with fundamental knowledge for further research.