Submitted:
22 January 2026
Posted:
23 January 2026
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
3. Discussion

4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- BUNDGAARD, E.; KREBS, F. Low Band Gap Polymers for Organic Photovoltaics. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells 2007, 91, 954–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, A.; Kawahara, H.; Yoshida, M.; Ohmori, Y.; Yoshino, K. Emission Enhancement in Electroluminescent Diode Utilizing Poly(3-Alkylthiophene) Doped with Oxadiazole Derivative. J Phys D Appl Phys 1995, 28, 2135–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valaski, R.; Moreira, L.M.; Micaroni, L.; Hümmelgen, I.A. The Electronic Behavior of Poly(3-Octylthiophene) Electrochemically Synthesized onto Au Substrate. Brazilian Journal of Physics 2003, 33, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoul, C.; Kim, N.-H. Polymer Light-Emitting Diodes Based on Poly(3-Hexyl Thiophene). Fibers and Polymers 2000, 1, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, D. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly(3-Alkylthiophene)s for Light-Emitting Diodes. Macromol Chem Phys 2001, 202, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yuan, C.; Lu, Z.; Wei, Y. Enhancement of Organic Electroluminescent Intensity by Charge Transfer from Guest to Host. J Lumin 1996, 68, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, K.; Manda, Y.; Sawada, K.; Onoda, M.; Sugimoto, R. Anomalous Dependences of Luminescence of Poly(3-Alkylthiophene) on Temperature and Alkyl Chain Length. Solid State Commun 1989, 69, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmori, Y.; Uchida, M.; Muro, K.M.K.; Yoshino, K.Y.K. Visible-Light Electroluminescent Diodes Utilizing Poly(3-Alkylthiophene). Jpn J Appl Phys 1991, 30, L1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncali, J. Conjugated Poly(Thiophenes): Synthesis, Functionalization, and Applications. Chem Rev 1992, 92, 711–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therézio, E.; Duarte, J.L.; Laureto, E.; Di Mauro, E.; Dias, I.; Marletta, A.; de Santana, H. Analysis of the Optical Properties of Poly(3-octylthiophene) Partially Dedoped. J Phys Org Chem 2011, 24, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therézio, E.M.; Franchello, F.; Dias, I.F.L.; Laureto, E.; Foschini, M.; Bottecchia, O.L.; de Santana, H.; Duarte, J.L.; Marletta, A. Emission Ellipsometry as a Tool for Optimizing the Electrosynthesis of Conjugated Polymers Thin Films. Thin Solid Films 2013, 527, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, T.N.M.; Bento, D.C.; Maia, E.C.R.; Fernandes, R.V.; Laureto, E.; Moore, G.J.; Louarn, G.; de Santana, H. The Influence of Different Electrolytes on the Electrical and Optical Properties of Polymer Films Electrochemically Synthesized from 3-Alkylthiophenes. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics 2014, 25, 1703–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, T.N.M.; Bento, D.C.; Maia, E.C.R.; Zaia, D.A.M.; Laureto, E.; da Silva, M.A.T.; Moore, G.J.; de Santana, H. In Situ and Ex Situ Spectroscopic Study of Poly(3-Hexylthiophene) Electrochemically Synthesized. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics 2012, 23, 1916–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Bento, C.; Laureto, E.; Zaia, M.; Therézio, M.; Moore, G.; de, S. Spectroscopic Analysis of the Structure and Stability of Two Electrochemically Synthesized Poly(3-Alkylthiophene)s. Journal of the Serbian Chemical Society 2013, 78, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, K.; Hayashi, S.; Sugimoto, R. Preparation and Properties of Conducting Heterocyclic Polymer Films by Chemical Method. Jpn J Appl Phys 1984, 23, L899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, A.Y.; El-Mossalamy, E.H.; Al-Thabaiti, S.A.; El-Hallag, I.S.; Hermas, A.A.; Asiri, A.M. Electrodeposition and Characterization of Polyaniline on Stainless Steel Surface via Cyclic, Convolutive Voltammetry and SEM in Aqueous Acidic Solutions. Int J Electrochem Sci 2014, 9, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.J.; Korzeniewski, C.; Franco, J.H.; Minteer, S.D.; Fritsch, I. Spatially Directed Functionalization by Co-Electropolymerization of Two 3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene Derivatives on Microelectrodes within an Array. J Electrochem Soc 2020, 167, 166511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, M.P.; Babu, R.S.; Samyn, L.M.; Barros, A.L.F. de Electrosynthesis of PolyFilm Modified Graphite Electrode and Its Application Towards Determination of Thymine. Materials Research 2025, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiseppi-Elie, A.; Pradhan, S.R.; Wilson, A.M.; Allara, D.L.; Zhang, P.; Collins, R.W.; Kim, Y.T. Growth of Electropolymerized Polyaniline Thin Films. Chemistry of Materials 1993, 5, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkili, C.; Deligiannakis, K.; Lappa, E.; Papoulia, C.; Sazou, D. Electrodeposition of Polyaniline on Tantalum: Redox Behavior, Morphology and Capacitive Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 7286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Pietrzyk-Le, A.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Electrochemically Synthesized Polymers in Molecular Imprinting for Chemical Sensing. Anal Bioanal Chem 2012, 402, 3177–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesi D’Alvise, T.; Sunder, S.; Hasler, R.; Moser, J.; Knoll, W.; Synatschke, C. V.; Harvey, S.; Weil, T. Preparation of Ultrathin and Degradable Polymeric Films by Electropolymerization of 3-Amino- l -tyrosine. Macromol Rapid Commun 2023, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-G.; Kim, S.Y. Increase in Interfacial Adhesion and Electrochemical Charge Storage Capacity of Polypyrrole on Au Electrodes Using Polyethyleneimine. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Österbacka, R.; An, C.P.; Jiang, X.M.; Vardeny, Z. V. Two-Dimensional Electronic Excitations in Self-Assembled Conjugated Polymer Nanocrystals. Science (1979) 2000, 287, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Hamazaki, J.; Kunugita, H.; Ema, K.; Endo, T.; Rikukawa, M.; Sanui, K. Coexistence of Photoluminescence from Two Intrachain States in Polythiophene Films. Phys Rev B 2003, 67, 205214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemoto, K.; Sudo, T.; Akai, I.; Hashimoto, H.; Karasawa, T.; Aso, Y.; Otsubo, T. Intrachain Photoluminescence Properties of Conjugated Polymers as Revealed by Long Oligothiophenes and Polythiophenes Diluted in an Inactive Solid Matrix. Phys Rev B 2006, 73, 235203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
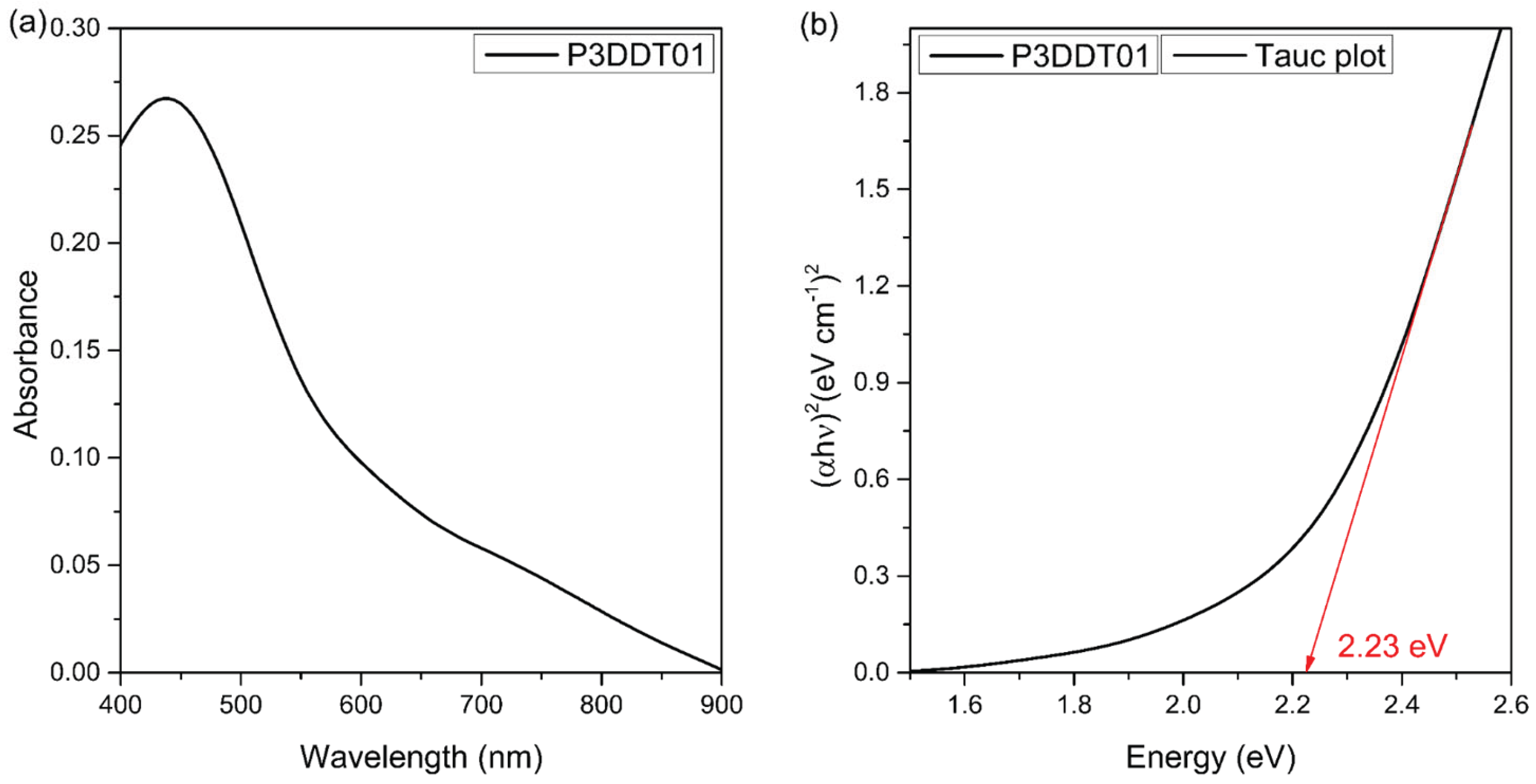
- Tauc, J.; Grigorovici, R.; Vancu, A. Optical Properties and Electronic Structure of Amorphous Germanium. physica status solidi (b) 1966, 15, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garai, A.; Kuila, B.K.; Samai, S.; Roy, S.; Mukherjee, P.; Nandi, A.K. Physical and Electronic Properties in Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube–Poly(3-dodecylthiophene) Nanocomposites. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 2009, 47, 1412–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Lu, J.; Ji, S.; Lu, C. Third-Order Nonlinear Optical Properties of P3DDT–CdS Nanocomposites. Synth Met 2011, 161, 2441–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therézio, E.; Piovesan, E.; Vega, M.L.; Silva, R.; Oliveira, O.; Marletta, A. Thickness and Annealing Temperature Effects on the Optical Properties and Surface Morphology of Layer-by-Layer Poly(p-Phenyline Vinylene) plus Dodecylbenzenesulfonate Films. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 2011, 49, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.H.; Barreira, S.V.P.; Moura, C.; Silva, F. Electrochemical Characterization of a Self-Assembled Polyelectrolyte Film. Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 2003, 21, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambo, E.C.; Kolbow, A.C.H.; Ramos, R.J.; Chagas, E.F.; de Santana, H.; Dalkiranis, G.G.; Marletta, A.; Therézio, E.M. Does the Substrate and a Buffer Layer Have a Greater Influence on Poly(3-Hexylthiophene) Films Deposited by the Chronocoulometry Technique? Phys Scr 2024, 99, 125967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schura, A.B.; Sá, S.; Silva, R.; de Santana, H.; Marletta, A.; Therézio, E. Energy Transfer Processes in Electrochemical P3HT Thin Films. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalkiranis, G.G.; Therézio, E.M.; Conte, G.; Gallardo, H.; Bechtold, I.H.; Marletta, A. Emission Ellipsometry as a Tool for Luminescent Liquid Crystal Phase Transition Identification. Phys Rev E 2018, 98, 022702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louarn, G.; Trznadel, M.; Buisson, J.P.; Laska, J.; Pron, A.; Lapkowski, M.; Lefrant, S. Raman Spectroscopic Studies of Regioregular Poly(3-Alkylthiophenes). J Phys Chem 1996, 100, 12532–12539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baibarac, M.; Lapkowski, M.; Pron, A.; Lefrant, S.; Baltog, I. SERS Spectra of Poly(3-Hexylthiophene) in Oxidized and Unoxidized States. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy 1998, 29, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Yao, Q.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Xu, K.; Zeng, H.; Shi, W.; Zhang, T.; Uher, C.; Chen, L. Highly Anisotropic P3HT Films with Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance via Organic Small Molecule Epitaxy. NPG Asia Mater 2016, 8, e292–e292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.A.; Sultan, A.A.; Obeid, M.T.; Abdulnabi, A.T.; Ali, M.T. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly (3-Hexylthiophene). International Journal of Scientific Engineering and Applied Science (IJSEAS)-Volume-1, Issue-7 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kolbow, A.C.H.; Rambo, E.C.; dos Santos, M.R.N.; Marchezi, P.E.; Nogueira, A.F.; Marletta, A.; Ramos, R.J.; Therézio, E.M. Emission Ellipsometry Study in Polymeric Interfaces Based on Poly(3-Hexylthiophene), [6,6]-Phenyl-C61-Butyric Acid Methyl Ester, and Reduced Graphene Oxide. C (Basel) 2024, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schura, A.B.; Kolbow, A.C.H.; Rambo, E.C.; Dalkiranis, G.G.; do Nascimento, C.A.; Ramos, R.J.; Marletta, A.; Pereira, L.; Germino, J.C.; Therézio, E.M. Investigating the Polarized Emission of P3HT Films and the Role of GO in the Interfacial Layer. Next Materials 2025, 9, 100976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therézio, E.M.; Rodrigues, P.C.; Tozoni, J.R.; Marletta, A.; Akcelrud, L. Energy-Transfer Processes in Donor–Acceptor Poly(Fluorenevinylene-Alt-4,7-Dithienyl-2,1,3-Benzothiadiazole). The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2013, 117, 13173–13180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förster, Th. Zwischenmolekulare Energiewanderung Und Fluoreszenz. Ann Phys 1948, 437, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Bagchi, B. Förster Energy Transfer in Thin Films of Conjugated Polymers and in Solution. Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society 2006, 53, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Bharti, V.; Kumar, M.; Chand, S.; Heeger, A.J. Polymer–Polymer Förster Resonance Energy Transfer Significantly Boosts the Power Conversion Efficiency of Bulk-Heterojunction Solar Cells. Advanced Materials 2015, 27, 4398–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



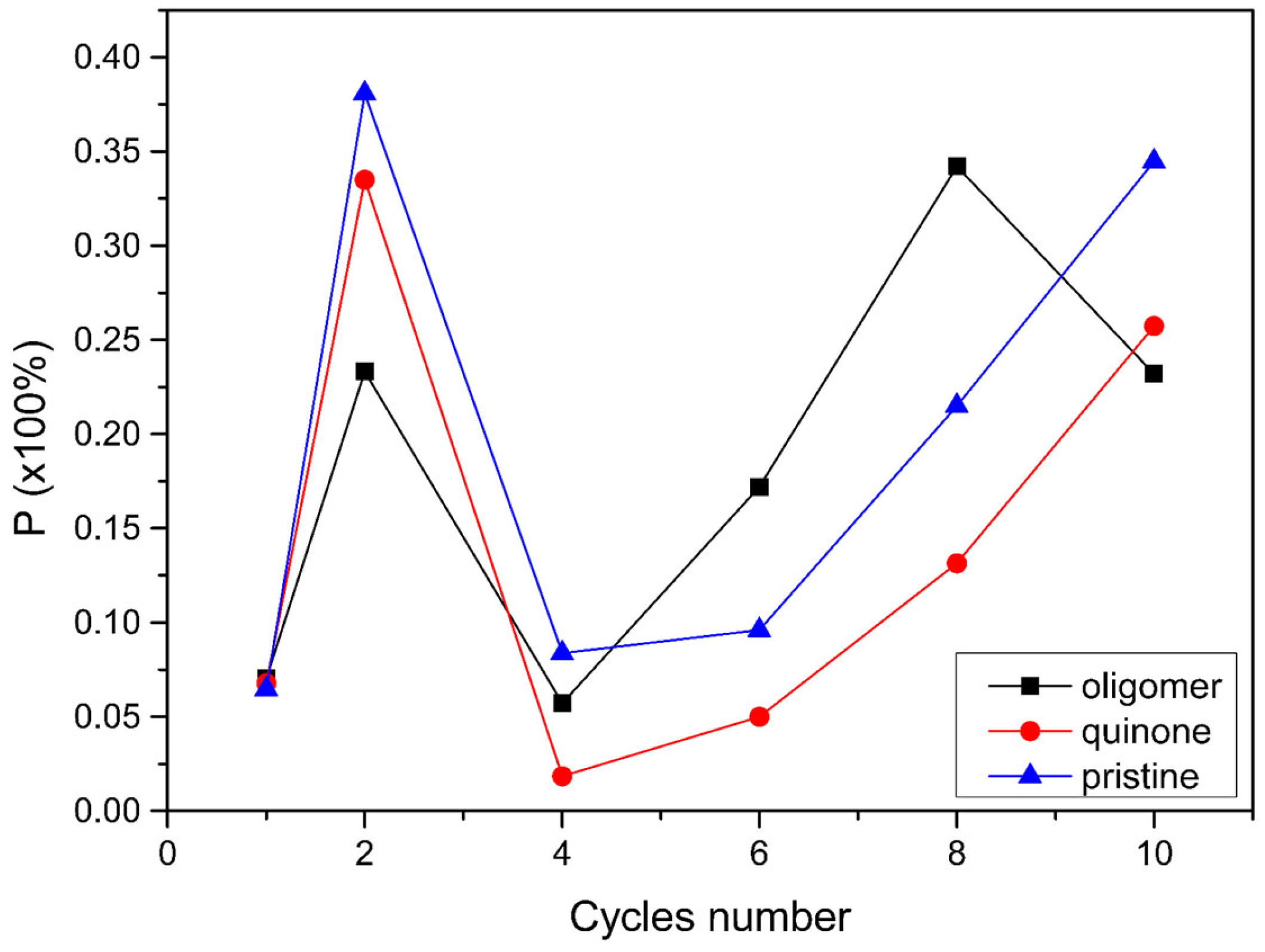
| Number of cycles | Cathodic peak (V) | Anodic peak (V) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | 0.84 |
| 2 | 1.25 | 0.80 |
| 4 | 1.44 | 0.70 |
| 6 | 1.62 | 0.68 |
| 8 | 1.76 | 0.55 |
| 10 | 1.82 | 0.55 |
| Film | Eg (eV) |
|---|---|
| P3DDT01 | 2.23 ± 0.02 |
| P3DDT02 | 2.23 ± 0.02 |
| P3DDT04 | 2.39 ± 0.02 |
| P3DDT06 | 2.46 ± 0.02 |
| P3DDT08 | 2.23 ± 0.02 |
| P3DDT10 | 2.38 ± 0.02 |
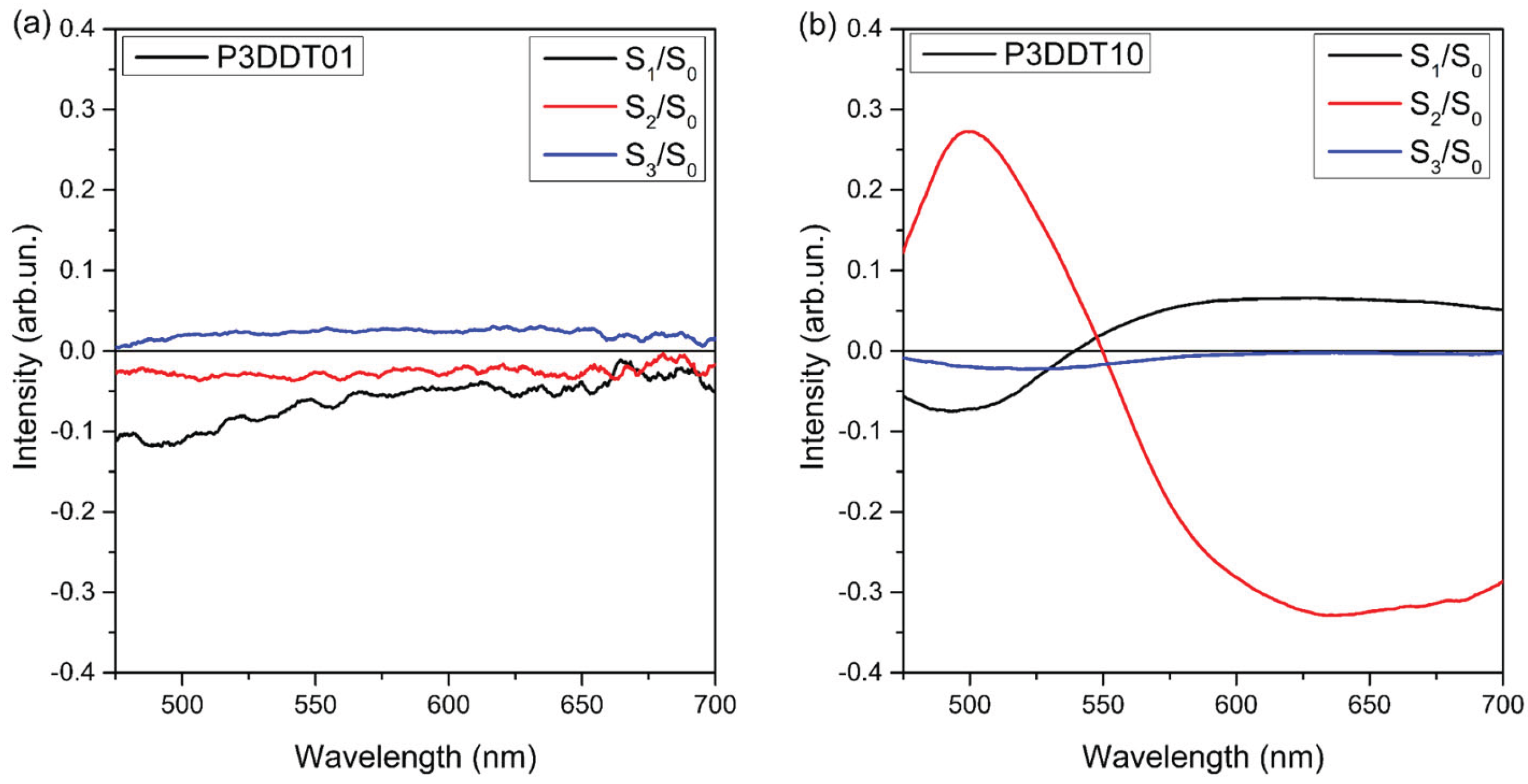
| Film | 1st oligomers band nm (eV) | 2nd oligomers band nm (eV) |
Quinone band nm (eV) | Pristine band nm (eV) | Vibrational replica nm (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3DDT01 | 465 (2.66) | 520 (2.38) | 568 (2.18) | 630 (1.96) | 684 (1.81) |
| P3DDT02 | 461 (2.68) | 515 (2.40) | 556 (2.22) | 610 (2.03) | 674 (1.83) |
| P3DDT04 | - | 500 (2.47) | 569 (2.17) | 638 (1.94) | 691 (1.79) |
| P3DDT06 | - | 499 (2.48) | 566 (2.19) | 625 (1.98) | 683 (1.81) |
| P3DDT08 | - | 512 (2.42) | 575 (2.15) | 632 (1.96) | 675 (1.83) |
| P3DDT10 | - | 516 (2.40) | 584 (2.12) | 638 (1.94) | 678 (1.82) |
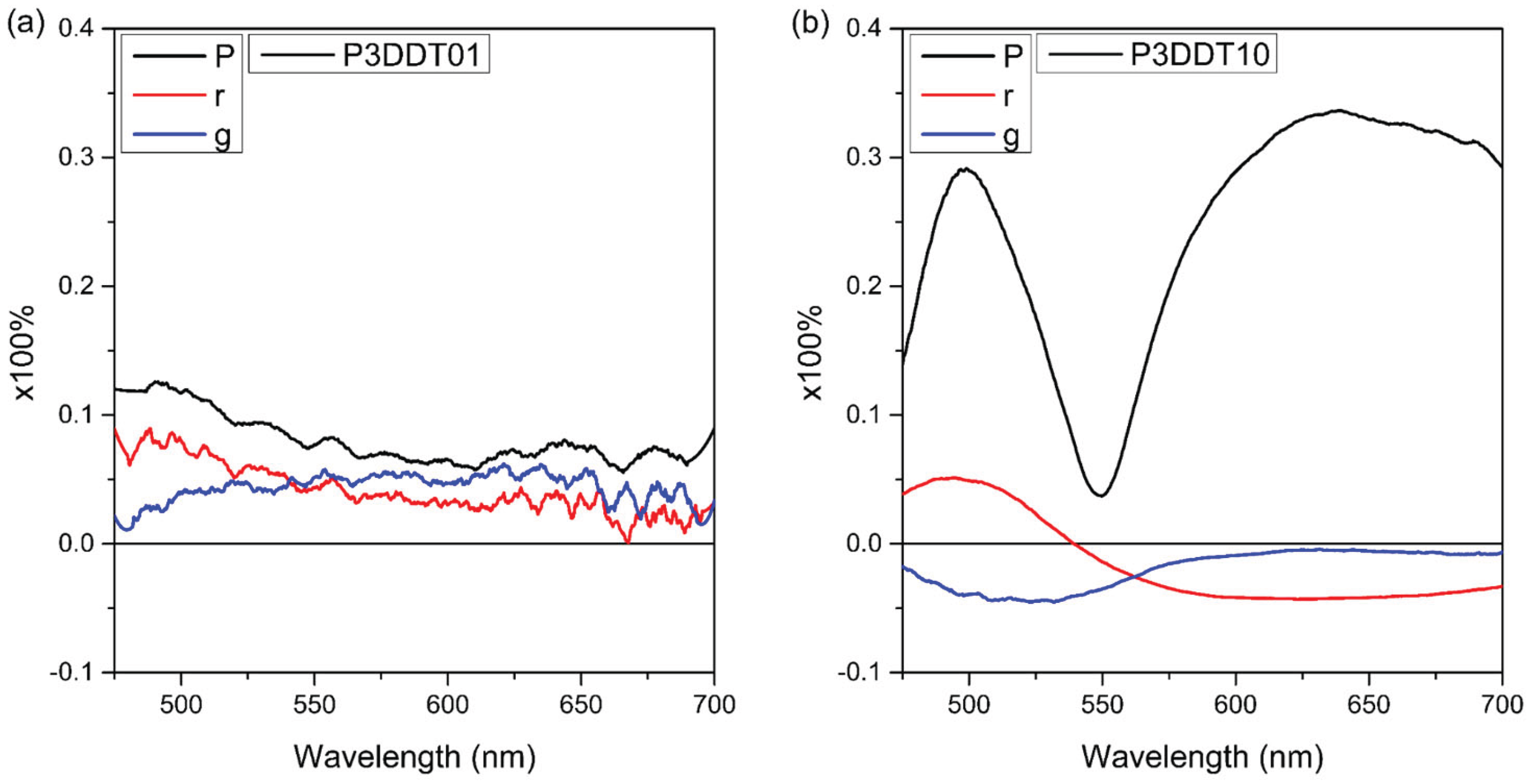
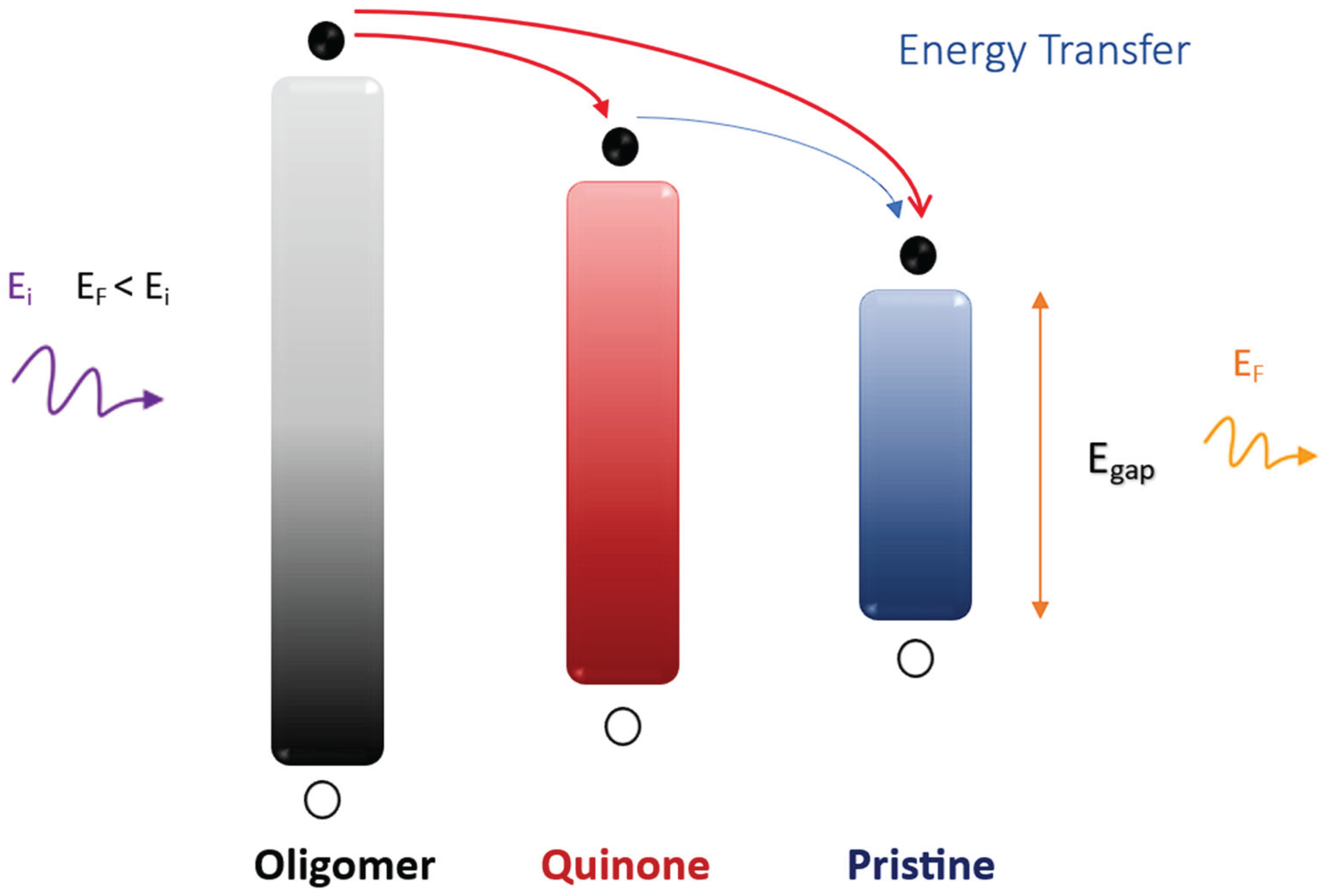
| Process | Photophysical description | Rate and assignment |
|---|---|---|
| π + 2 + hνex → π* + 2 | Oligomeric chains absorption | Excitation energy is absorbed (100%) |
| π* + 2 → π + 2 + hνo | Polarized fluorescence | 7% |
| π* + 2 → π + 2 + hνo or π* + 2 → π + 2 or π* + 2 → π* + 1 or π* + 2 → π* |
Non-polarized fluorescence; or internal conversion (oligomer) + vibrational relaxation; or Internal conversion to quinone chains; or internal conversion for pristine chains |
93% |
| π* + 1 → π + 1 + hνQ | Polarized fluorescence | 5-6% |
| π* + 1 → π + 1 + hνQ or π* + 1 → π + 1 or π* + 1 → π* |
Non-polarized fluorescence; or internal conversion (quinone chains) + vibrational relaxation; or internal conversion to pristine chains | Up to 95% |
| π* → π + hνp | Fluorescence | 6% |
| π* → π or π* → π + hνp | Internal conversion (quantum chains) + vibrational relaxation + non-polarized fluorescence | Up to 94% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





