Introduction
A published analysis established that the cosmic microwave background blackbody spectrum, its temperature redshift scaling, and photon number evolution can be reproduced under a frequency-independent redshift kernel without invoking metric expansion (Cody, 2026). That work demonstrated exact Planck preservation under collisionless Liouville evolution, enforced as a consequence of frequency-independent transport, and introduced an illustrative post-recombination relaxation form for the kernel dynamics. Within the same framework, background level consistency with luminosity distance relations, time dilation, and Tolman surface-brightness dimming was demonstrated observationally. Together, these results remove the classical background objections that historically excluded non-expansion interpretations of cosmological redshift. The present paper does not extend those results into a complete cosmological model. It instead examines limited, testable consequences of the established framework by confronting it with observational data, proving formal transport results where possible, and explicitly identifying inference boundaries beyond which additional dynamical assumptions are required. The objective is to determine precisely what current observations do and do not logically require once a frequency-independent redshift mechanism is admitted at the background level. The work is deliberately restricted in scope. It addresses only background level phenomenology and the collisionless transport of angular structure in the photon distribution. No attempt is made to derive structure formation, recombination microphysics, primordial nucleosynthesis, or gravitational dynamics. These topics are excluded explicitly. Where observational constraints depend on baryonic evolution, gravitational instability, or nonlinear growth, they are identified as external to the present analysis and treated as future discriminators rather than deficiencies. Within this limited scope, the goals are threefold. First, the framework is tested directly against observational data by treating the previously introduced kernel dynamics as a falsifiable hypothesis rather than an adjustable explanatory tool. Second, logical discriminators are examined explicitly, in particular whether the existence of CMB anisotropies constitutes, by itself, a necessary implication of metric expansion. Third, the paper formalizes inference boundaries by clarifying which observational statements follow from background thermodynamics and transport alone, and which require additional theoretical commitments.
This approach parallels earlier methodological interventions in cosmology where phenomenological consistency was separated from ontological interpretation. Modified Newtonian Dynamics provides a relevant example, having been framed initially not as a complete theory of gravity but as a targeted empirical modification isolating what galaxy rotation curves actually require (Milgrom, 1983). Regardless of its ultimate status, MOND altered the field by forcing a distinction between observational adequacy and theoretical completeness. The present work adopts a similar methodological posture, without asserting equivalence in scope or ambition. The analysis presented here is explicitly terminal with respect to this line of inquiry. No further extensions of the program are pursued after this paper. The stopping condition is stated unambiguously. If early-universe observations such as JWST timing impose empirical constraints on kernel dynamics, and if angular anisotropy transport is shown to be non-discriminatory at the level of collisionless evolution, then the analysis is complete. Any remaining questions necessarily concern dynamical structure formation, gravity, or matter evolution, and therefore lie outside the logical domain of the present framework.
Kernel-Based Redshift Framework
The present analysis relies on a background level redshift framework previously established and published, and only the minimal machinery required for the arguments that follow is restated here (Cody, 2026). The framework is treated strictly as an effective description of photon-sector kinematics after decoupling, with collisionless propagation and photon number conservation assumed throughout. Cosmological redshift is defined operationally through a time-dependent kernel
relating emission and observation epochs. For a photon emitted at time
and observed at time
, the redshift is given by
This definition does not assume metric expansion as the physical origin of redshift. It functions instead as a kinematic mapping between observed frequency ratios and an underlying time parameterization in the photon sector. All observable redshift relations used in this paper are derived from this operational definition alone. The instantaneous rate associated with the kernel is defined by
This quantity enters the redshift evolution algebraically in the same manner as a Hubble rate enters standard treatments, but here it is defined purely as a property of the kernel rather than of a spacetime scale factor. In the present work,
is used only as an operational rate governing frequency evolution and time–redshift mapping, without any assumption that it describes gravitational expansion (Dodelson, 2020; Weinberg, 1972). Photon propagation after decoupling is treated as collisionless. Let
denote the photon distribution function, where
p is the magnitude of the comoving momentum. Under a uniform, frequency-independent redshift action, the collisionless Boltzmann equation reduces to
This equation is standard in cosmological radiative transfer when collisions are negligible and the redshift action is homogeneous in frequency space. The form above is the only kinetic statement required in what follows (Dodelson, 2020; Weinberg, 1972). Solving this equation by the method of characteristics yields
where
is the distribution function evaluated at a reference time. If the initial photon distribution is Planckian,
then the solution remains exactly Planckian at all later times, with an effective temperature
Expressed in terms of redshift, this implies
identical in form to the temperature–redshift relation used in standard cosmology. In the present framework this scaling arises from frequency-independent Liouville transport rather than adiabatic expansion. The evolution of photon number and energy densities follows directly from this temperature scaling. The standard Stefan-Boltzmann integrals give
where
a and
b are constants determined by the Planck integral; their explicit forms are not required for the scaling argument. From
, differentiation yields
Applying the chain rule to
:
Similarly, for
:
These scaling laws are algebraically identical to those arising from adiabatic expansion in standard cosmology, where and . In the present framework, the same coefficients emerge from the temperature dependence of the integrals combined with frequency-independent Liouville transport, without invoking metric expansion. No assumption regarding spacetime expansion, metric dynamics, or gravitational degrees of freedom enters this derivation; only collisionless Liouville evolution and frequency-independent redshift are used. Observational determinations of the present CMB temperature and limits on spectral distortions are taken from COBE/FIRAS measurements and subsequent analyses (Mather et al., 1994; Fixsen et al., 1996; Fixsen, 2009). Because the redshift action is uniform in frequency, no chemical potential distortion is generated by the evolution described above. The chemical potential therefore remains identically zero under collisionless propagation governed by the kernel, consistent with the absence of observed -type distortions in the CMB spectrum. This statement aligns with the standard theory of spectral distortions when energy injection or frequency-dependent processes are absent (Hu & Silk, 1993; Chluba & Sunyaev, 2012).
At the background level, the kernel framework reproduces the same observable photon-sector scalings commonly attributed to expansion, including temperature evolution, photon number dilution, and the relations entering luminosity distance, time dilation, and surface-brightness tests. In this paper, that background level degeneracy is taken as an established premise rather than a claim of full cosmological equivalence. No attempt is made here to describe the generation of anisotropies, the growth of structure, or the microphysics of recombination. The only statements used in later sections concern collisionless photon transport and background kinematics. Predictions for anisotropy generation and acoustic structure require perturbation theory and coupling to matter and gravity, as in standard Boltzmann treatments, and are explicitly outside the scope of the present analysis (Ma & Bertschinger, 1995; Seljak & Zaldarriaga, 1996; Lewis et al., 2000).
JWST Timing
A recurring criticism of non-expansion redshift frameworks is that they are underconstrained by observation and therefore lack empirical falsifiability. This section addresses that criticism directly by using early galaxy timing inferred from James Webb Space Telescope observations as an empirical constraint on post-recombination kernel dynamics. The analysis is not framed as a resolution of the early-galaxy timing tension. Instead, it treats a specific, previously introduced kernel evolution as a concrete hypothesis and evaluates whether it is compatible with the minimum cosmic time implied by JWST observations. The kernel dynamics considered here are imported unchanged from the illustrative post-recombination relaxation model introduced in the CMB analysis (Cody, 2026). No new functional freedom is introduced at this stage. The effective rate governing redshift evolution is taken to be
where
is the present effective rate,
is the effective rate immediately after recombination,
denotes the recombination epoch, and
is the relaxation timescale. The exponential form is an ansatz, introduced previously as an illustrative post-recombination kernel dynamics rather than as a unique or derived solution. No claim is made that this form is unique or physically preferred; it is adopted solely to demonstrate how post-recombination kernel dynamics may be empirically constrained. In the companion CMB analysis, this relaxation form arises as the closed-form solution of a damped scalar field equation with
(Cody,2026); it is treated here as a testable post-recombination hypothesis. The parameter values are fixed by two independent background level conditions imposed by the CMB. First, the present-day effective rate is required to satisfy
. Second, the observed CMB temperature ratio requires
which fixes the integral of
between recombination and the present. For the illustrative choice
, enforcement of this boundary condition uniquely determines the relaxation timescale to be
. The relaxation timescale is therefore not an independently adjustable parameter once
and the CMB boundary conditions are specified. The time–redshift mapping follows directly from the operational definition of redshift. For photons observed at
and emitted at time
t, one has
This relation is exact within the kernel framework and does not rely on any approximation beyond collisionless propagation. Given , it uniquely determines the cosmic time associated with an observed redshift. The mapping is evaluated numerically for the parameter set specified above.
For comparison, a reference flat
CDM model is used to compute the corresponding cosmic times. The standard relation
is evaluated with
using
,
, and
, consistent with recent Planck determinations (Planck Collaboration, 2020). Radiation is neglected in this comparison, as the focus is restricted to relative timing differences at
-20. The cosmic times corresponding to redshifts
and 10 are computed under both the illustrative kernel dynamics and the reference
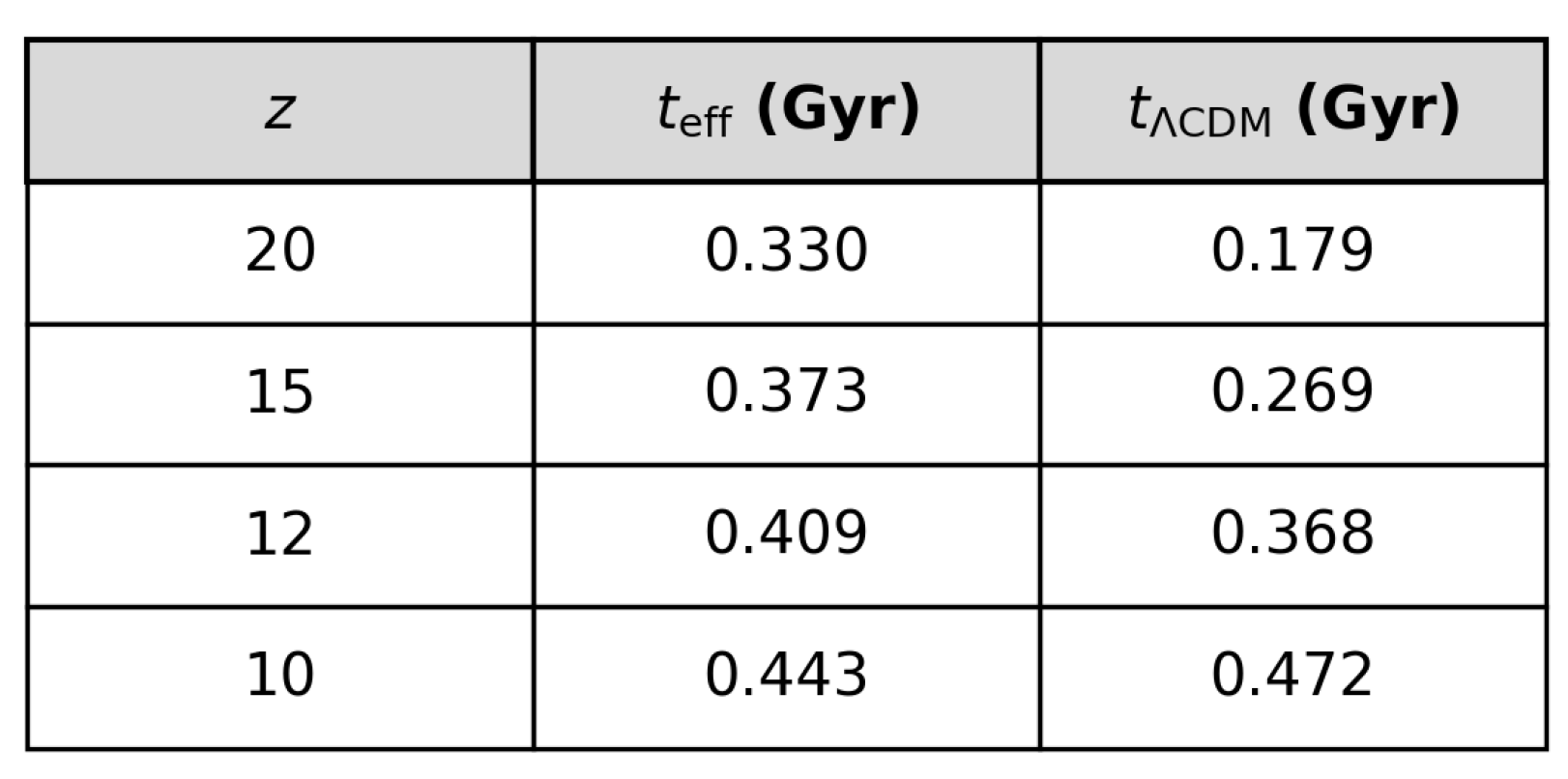
CDM model. The resulting values are summarized in
Figure 1.
From these values, the available assembly interval between
and
is
under the illustrative kernel dynamics, compared to
under the reference
CDM model. For the parameter set fixed by the CMB boundary conditions, the kernel framework therefore predicts a significantly shorter assembly interval over this redshift range. Observations with JWST have reported the presence of galaxies with inferred stellar masses of order
or greater at redshifts
, based on photometric and spectroscopic analyses of early deep-field data. While the interpretation of these masses and formation histories remains under active debate, multiple independent studies report assembly timescales of order a few hundred Myr or less (Adams et al., 2023; Curtis-Lake et al., 2023; Labbé et al., 2023; Robertson et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023). These results are cited here only as timing indicators and not as settled determinations of stellar mass or star-formation history. The comparison above shows that, if the illustrative exponential kernel dynamics are taken as physically realized, the framework predicts less cosmic time for early galaxy assembly than
CDM. JWST observations therefore act as an empirical constraint on the allowed kernel dynamics. Compatibility with the inferred timing requires either a sufficiently long relaxation timescale, a reduced initial effective rate, or alternative post-recombination kernel evolution. In this sense, JWST supplies an independent third constraint on the kernel ansatz, beyond the two background level conditions imposed by the CMB. This result strengthens rather than weakens the framework. The kernel-based description admits empirical exclusion at the background level, and specific kernel dynamics can be ruled out by early-universe timing data independently of CMB thermodynamics or angular transport. No claim is made that JWST observations favor the kernel framework over
CDM, nor that uncertainties in stellar mass estimates or baryonic physics have been resolved. The sole conclusion of this section is that early-galaxy timing provides a direct observational bound on post-recombination kernel dynamics. The same relaxation dynamics that fix
also determine the timing behavior at
-20, providing an internal consistency check across cosmic epochs. Any viable extension of the framework must satisfy this bound in addition to reproducing the observed CMB blackbody spectrum and background redshift relations. It is important to emphasize that the CMB constraint derived in this work fixes only the time-integrated redshift kernel,
and does not uniquely determine the functional form of
. The exponential relaxation profile adopted here arises naturally from the scalar-field dynamics developed in the companion CMB analysis (Cody, 2026) and serves as a concrete realization of the framework. Other admissible kernel shapes satisfying the same integral constraint may yield substantially different cosmic time-redshift mappings at
. Consequently, JWST observations should be interpreted as constraining the detailed kernel dynamics rather than falsifying the kinematic redshift mechanism itself.
Angular Anisotropy Transport
A common assertion in cosmology is that the existence of angular anisotropies in the cosmic microwave background constitutes a logical requirement for metric expansion. This section examines that claim directly by analyzing the transport of angular structure in the photon distribution under a frequency-independent redshift operator. The purpose is not to explain the origin of anisotropies, but to determine whether their mere existence discriminates between expansion and non-expansion redshift mechanisms at the level of collisionless transport. The analysis begins with the phase-space photon distribution retaining full angular dependence,
where
p is the photon momentum magnitude and
is the propagation direction. In the absence of collisions, gravitational lensing, or scattering, the evolution of
f is governed by the collisionless Liouville equation. For a frequency-independent redshift kernel, the evolution equation takes the form
where
is the effective redshift rate. The derivation does not depend on whether the redshift arises from metric expansion or from an alternative isotropic mechanism, only on the absence of angular dependence in the operator. Crucially, no angular derivatives appear in this equation. The redshift operator acts only on the momentum magnitude and is isotropic by construction. To track angular structure explicitly, the distribution is expanded in spherical harmonics,
which is standard in treatments of radiative transfer and CMB anisotropies (Weinberg, 1972; Dodelson, 2020). Substitution of this expansion into the Liouville equation yields, for each multipole coefficient,
The evolution equation is identical for all
and contains no coupling between different angular modes. In particular, there is no
ℓ- or
m-mixing introduced by the redshift operator. The equation is solved by the method of characteristics. Along characteristic curves defined by
the solution is
where
is the momentum at a reference time. Along these curves, the distribution function is conserved,
Projecting onto spherical harmonics gives
where
denotes the multipole coefficients at the reference time. Each multipole is transported independently, with its momentum dependence rescaled by the kernel
and its angular structure unchanged. This result establishes that angular anisotropies are transported, not generated, by a frequency-independent redshift operator. The preservation of multipole structure follows directly from the isotropy of the operator and the absence of angular derivatives in the Liouville equation. No assumption about metric expansion enters the derivation. It is worth emphasizing that the same transport structure arises in standard expanding cosmologies once collisions, metric perturbations, and source terms are neglected; the present result isolates the redshift operator itself rather than the full Boltzmann hierarchy (Ma & Bertschinger, 1995; Seljak & Zaldarriaga, 1996).
It follows that the existence of angular anisotropies in the CMB does not, by itself, constitute a logical test of expansion versus non-expansion redshift mechanisms. Anisotropies present at some initial time are preserved under collisionless propagation regardless of whether redshift is attributed to metric expansion or to a frequency-independent kernel. Any discrimination between models must therefore arise from the generation and statistical structure of anisotropies, or from their coupling to matter perturbations, not from their mere persistence. The limits of this result are explicit. No claim is made regarding the origin of anisotropies, acoustic oscillations, or the angular power spectrum. The analysis does not address gravitational instability, baryon–photon coupling, recombination microphysics, or the dynamics responsible for setting initial conditions. These effects enter through collision terms, metric perturbations, and source functions in the Boltzmann hierarchy, which lie outside the scope of collisionless Liouville transport (Hu & White, 1997; Challinor & Lasenby, 1999).Within its stated domain, the result is definitive. Under collisionless evolution with a frequency-independent redshift operator, angular multipoles are preserved exactly. There is no angular scrambling, no mode mixing, and no generation of structure. The presence of CMB anisotropies therefore cannot, at the level of angular transport alone, be taken as a logical requirement for metric expansion.
Conclusion
This work set out to determine what cosmological observations logically require once a frequency-independent redshift mechanism is admitted at the background level, and to identify the precise boundaries beyond which additional theoretical assumptions become necessary. That objective has been met. At the background level, cosmological redshift observables are shown to be degenerate under a broad class of redshift implementations that preserve collisionless Liouville evolution. The cosmic microwave background constrains phase-space preservation, Planck spectrum stability, temperature-redshift scaling, and photon number evolution, but does not uniquely determine the spacetime origin of redshift. These results close the classical objections historically raised against non-expansion redshift interpretations at the level of background thermodynamics and transport. When specific post-recombination kernel dynamics are treated as concrete hypotheses rather than explanatory devices, independent observational data provide meaningful constraints. In particular, early-galaxy timing inferred from JWST observations bounds the allowed parameter space of illustrative relaxation models, demonstrating that kernel dynamics are empirically testable and, in some cases, disfavored. This establishes falsifiability at the background level rather than explanatory freedom. The angular structure of the CMB has been addressed separately and rigorously. Under collisionless evolution, a frequency-independent redshift operator transports existing angular anisotropies without generating, suppressing, or mixing multipole structure. The existence of CMB anisotropies therefore does not, by itself, constitute a logical discriminator between expansion-based and non-expansion redshift mechanisms. Anisotropy generation, acoustic features, and power-spectrum morphology depend on additional physics not invoked here.
Taken together, these results show that metric expansion is sufficient to account for observed cosmological redshift phenomena, but it is not logically necessary at the level of background observables and angular transport. Claims to the contrary rely on auxiliary dynamical assumptions rather than on the redshift phenomenology itself. Further progress beyond this point requires either a concrete model of structure formation and gravitational dynamics within a non-expansion framework, or independent, physically motivated proposals for kernel dynamics capable of satisfying all observational constraints simultaneously. Such developments lie outside the scope of the present analysis. This work completes the background level analysis of the framework with respect to CMB thermodynamics, photon transport, and post-recombination timing constraints.
Not applicable.
Author Contributions
This article is the sole work of the author.
Funding
No external funding was received for this work.
Data Availability Statement
No original datasets were generated for this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Cody, M. A. Cosmic microwave background without expansion. Journal of Modern Physics 2026, 17(1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milgrom, M. A modification of the Newtonian dynamics as a possible alternative to the hidden mass hypothesis. The Astrophysical Journal 1983, 270, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodelson, S. Modern cosmology, 2nd ed.; Academic Press, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, S. Gravitation and cosmology: Principles and applications of the general theory of relativity; Wiley, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Mather, J. C.; Cheng, E. S.; Cottingham, D. A.; Eplee, R. E.; Fixsen, D. J.; Hewagama, T.; Isaacman, R. B.; Jensen, K. A.; Meyer, S. S.; Noerdlinger, P. D.; Read, S. M.; Rosen, L. P.; Shafer, R. A.; Wright, E. L.; Bennett, C. L.; Boggess, N. W.; Hauser, M. G.; Kelsall, T.; Moseley, S. H.; Wilkinson, D. T. Measurement of the cosmic microwave background spectrum by the COBE FIRAS instrument. The Astrophysical Journal 1994, 420, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fixsen, D. J.; Cheng, E. S.; Gales, J. M.; Mather, J. C.; Shafer, R. A.; Wright, E. L. The cosmic microwave background spectrum from the full COBE FIRAS data set. The Astrophysical Journal 1996, 473, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fixsen, D. J. The temperature of the cosmic microwave background. The Astrophysical Journal 2009, 707, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Silk, J. Thermalization and spectral distortions of the cosmic background radiation. Physical Review D 1993, 48, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chluba, J.; Sunyaev, R. A. The evolution of CMB spectral distortions in the early Universe. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 2012, 419, 1294–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.-P.; Bertschinger, E. Cosmological perturbation theory in the synchronous and conformal Newtonian gauges. The Astrophysical Journal 1995, 455, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seljak, U.; Zaldarriaga, M. A line-of-sight integration approach to cosmic microwave background anisotropies. The Astrophysical Journal 1996, 469, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.; Challinor, A.; Lasenby, A. Efficient computation of cosmic microwave background anisotropies in closed Friedmann-Robertson-Walker models. The Astrophysical Journal 2000, 538, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planck Collaboration. Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters. Astronomy & Astrophysics 2020, 641, A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, N. J.; et al. Discovery and properties of ultra-high redshift galaxies (9 <z <12) in the JWST ERO SMACS 0723 Field. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 2023, 518, 4755–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis-Lake, E.; et al. Spectroscopic confirmation of four metal-poor galaxies at z = 10.3-13.2. Nature Astronomy 2023, 7, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbé, I.; et al. A population of red candidate massive galaxies 600 Myr after the Big Bang. Nature 2023, 616, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, B. E.; et al. Identification and properties of intense star-forming galaxies at redshifts. Nature Astronomy 2023, 7, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; et al. UNCOVER: Illuminating the early Universe-JWST/NIRSpec confirmation of. The Astrophysical Journal Letters 2023, 957, L34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; White, M. CMB anisotropies: Total angular momentum method. Physical Review D 1997, 56, 596–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challinor, A.; Lasenby, A. Cosmic microwave background anisotropies in the cold dark matter model: A covariant and gauge-invariant approach. The Astrophysical Journal 1999, 513, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunyaev, R. A.; Zeldovich, Y. B. The interaction of matter and radiation in the hot model of the Universe, II. Astrophysics and Space Science 1970, 7, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chluba, J. Green’s function of the cosmological thermalization problem. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 2013, 434, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).