1. Introduction
The “nature bias” of plant-derived food materials is a key link connecting TCM theory and practice, and their cold, cool, warm, and hot properties directly determine the adaptability of diet therapy and the effectiveness of prescriptions [
1]. However, traditional application of nature bias relies on qualitative descriptions in classic works (e.g., the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China only records “warm nature” or “cold nature”) and lacks quantitative standards, leading to problems such as “individual adaptation deviation” (e.g., yang-deficient constitution experiencing discomfort after ingesting cool-tending food materials), “prescription compatibility risk” (e.g., unbuffered extreme nature bias medicines causing injury to healthy qi), and “unstable cultivation quality” (nature bias fluctuation of the same species due to habitat differences) [
2,
3].
Our team previously published the “three-dimensional quantitative evaluation system for nature bias of plant-derived food materials” on a preprint platform [
11] and systematically explained its cross-species/cross-scenario universality and “environment-metabolism-growth” synergistic regulatory mechanism through subsequent research [
12]. The core attribute data of 417 daily edible plants and 570 Chinese medicinal materials were integrated to clarify the core thresholds and rules of nature bias quantification, verifying the system’s universality. On the basis of this published system, this study focuses on three core application scenarios—”daily diet therapy, quantification of TCM prescriptions, and directional cultivation of plants”—and transforms it into a practical implementation plan. The aim is to address the empirical limitations of traditional nature bias application and promote the standardization and precision of nature bias application for plant-derived food materials.
2. Application of the Three-Dimensional Quantitative System in the Dynamic Regulation of Daily Diet Therapy
On the basis of our verified three-dimensional quantitative system [
11], the core demand of daily diet therapy is “precise adaptation between nature bias of food materials and individual-scenario needs”. The three-dimensional quantitative system achieves this goal through “multifactor dimension definition--cold-warm score axis quantification--dynamic regulation rules”, with all the parameters verified on the basis of the data of 987 food materials in the previous stage [
4,
5].
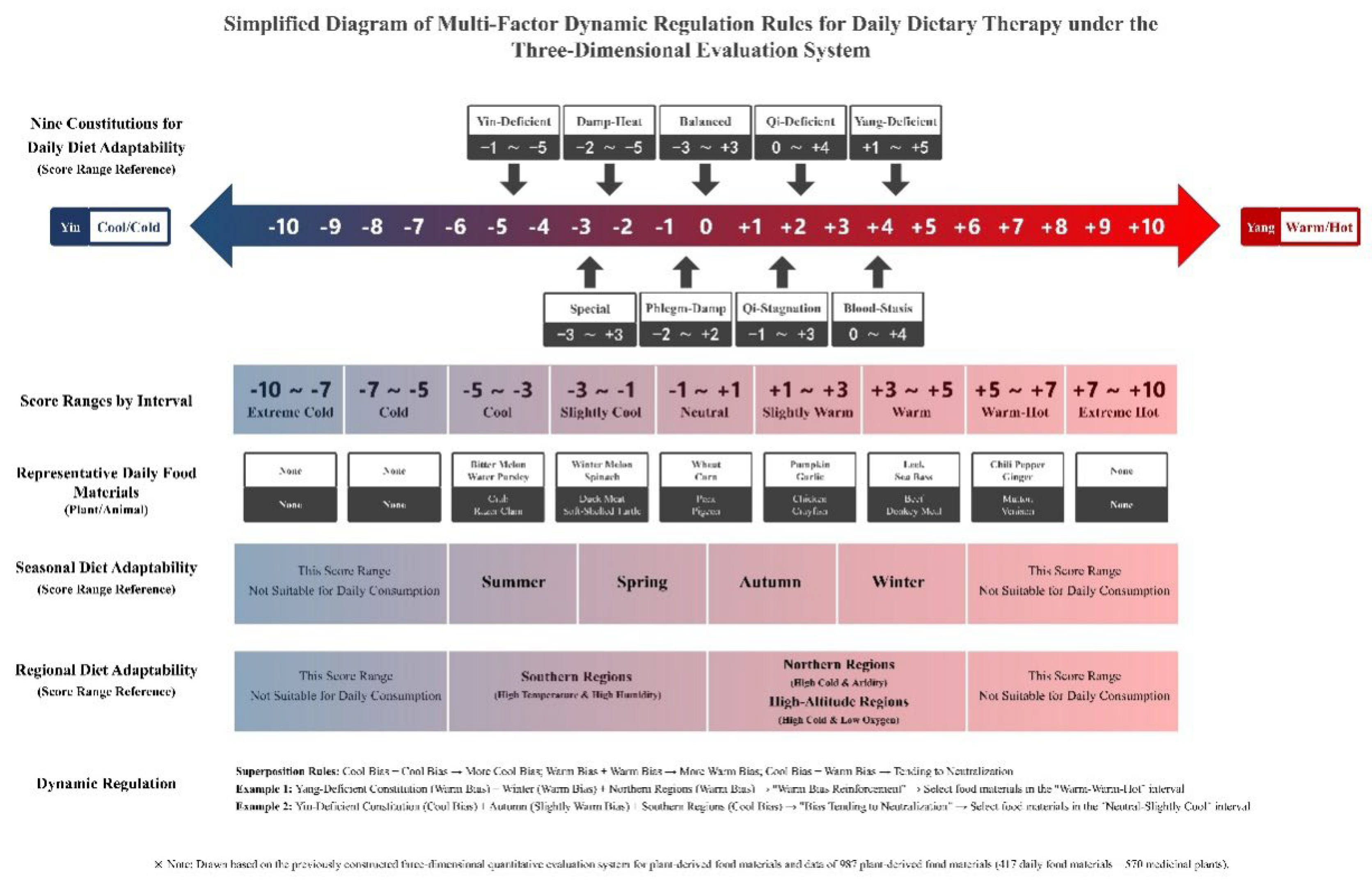
2.1. Multifactor Regulation Dimensions of Daily Diet Therapy
The adaptation of daily diet therapy needs to consider three dimensions simultaneously: individual constitution, seasonal characteristics, and the regional environment. Each dimension corresponds to a clear “Nature Bias Score Range” to ensure that factors are quantifiable and matchable (
Table 1).
2.2. Quantitative Ruler Function of the Cold–Warm Score Axis
The -10~+10 cold‒warm score axis is the core quantitative tool for daily diet therapy and is divided into 10 grades according to the “Yin (cool/cold)-Yang (warm/hot)” gradient. It unifies the natural bias of food materials, constitution needs, and scenario characteristics into the same scoring system to achieve direct “demand–food material” matching (
Figure 1).
The core value of the score axis lies in the “standardized expression of nature bias”:
Extremely weak bias (-1~+1): suitable for balanced constitution or long-term consumption (e.g., Triticum aestivum +0.12);
Weak bias (-3~-1/+1~+3): Suitable for slightly biased constitutions (e.g., Spinacia oleracea -2.5 for Yin-Deficient Constitution);
Moderate bias (-5~--3/+3~+5): Suitable for moderately biased constitutions (e.g., Capsicum annuum +3.2 for Yang-Deficient Constitution);
Strong bias (≤-5/≥+5): Only suitable for severe conditions or short-term regulation, requiring caution in daily diet therapy (e.g., Zingiber officinale +6.8 needs to be paired with cool-tending food materials).
2.3. Dynamic Regulation Rules and Case Verification
The dynamic regulation of daily diet therapy follows the “Nature Bias Superposition Rules”: cool + cool → more cool, warm + warm → more warm, cool + warm → tending toward neutralization. Precise adaptation is achieved through multifactor superposition, with typical cases as follows:
Case 1: Positive Regulation for Yang-Deficient Constitution + Winter + Northern Areas
Demand superposition: Yang-Deficient Constitution (+1~+5) + Winter (+2~+6) + Northern Areas (+2~+5) → Total demand range +2~+5;
Food material selection: Mutton (+6.0) paired with Raphanus sativus (-3.9). As calculated by 100 g mutton + 60 g Raphanus sativus, the combined nature bias score = 6.0×(100/160) + (-3.9)×(60/160) = +2.29, falling into the demand range;
Effect: Adapts to the chills of the Yang-Deficient Constitution without the risk of “excessive Yang-tonic causing dryness” [
5].
Case 2: Neutralization Regulation for Yin-Deficient Constitution + Autumn + Southern Areas
Demand superposition: Yin-Deficient Constitution (-1~-5) + Autumn (-1~+3) + Southern Areas (-3~--1) → Total demand range -4~--2;
Food material selection: Duck meat (-1.8) paired with Benincasa hispida (-5.8). Using 100 g of duck meat + 150 g of Benincasa hispida, the combined nature bias score = -1.8×(100/250) + (-5.8)×(150/250) = -4.2, falling into the demand range;
Effect: Relieves dry mouth and sore throat in Yin-Deficient Constitution without the risk of “heat-clearing injuring Yang” [
5].
3. Application of the Three-Dimensional Quantitative System in the Quantitative Compatibility of TCM Prescriptions
When three-dimensional quantitative systems [
11] are applied to the quantitative compatibility of TCM prescriptions, the core demand is “controllable nature bias, safety, and effectiveness”. The three-dimensional quantitative system achieves prescription quantification through “definition of cold–hot specific therapeutic rules-construction of three-dimensional model-case verification”, with all rules verified on the basis of the data of 570 Chinese medicinal materials and 149 classic prescriptions in the previous stage [
3,
4].
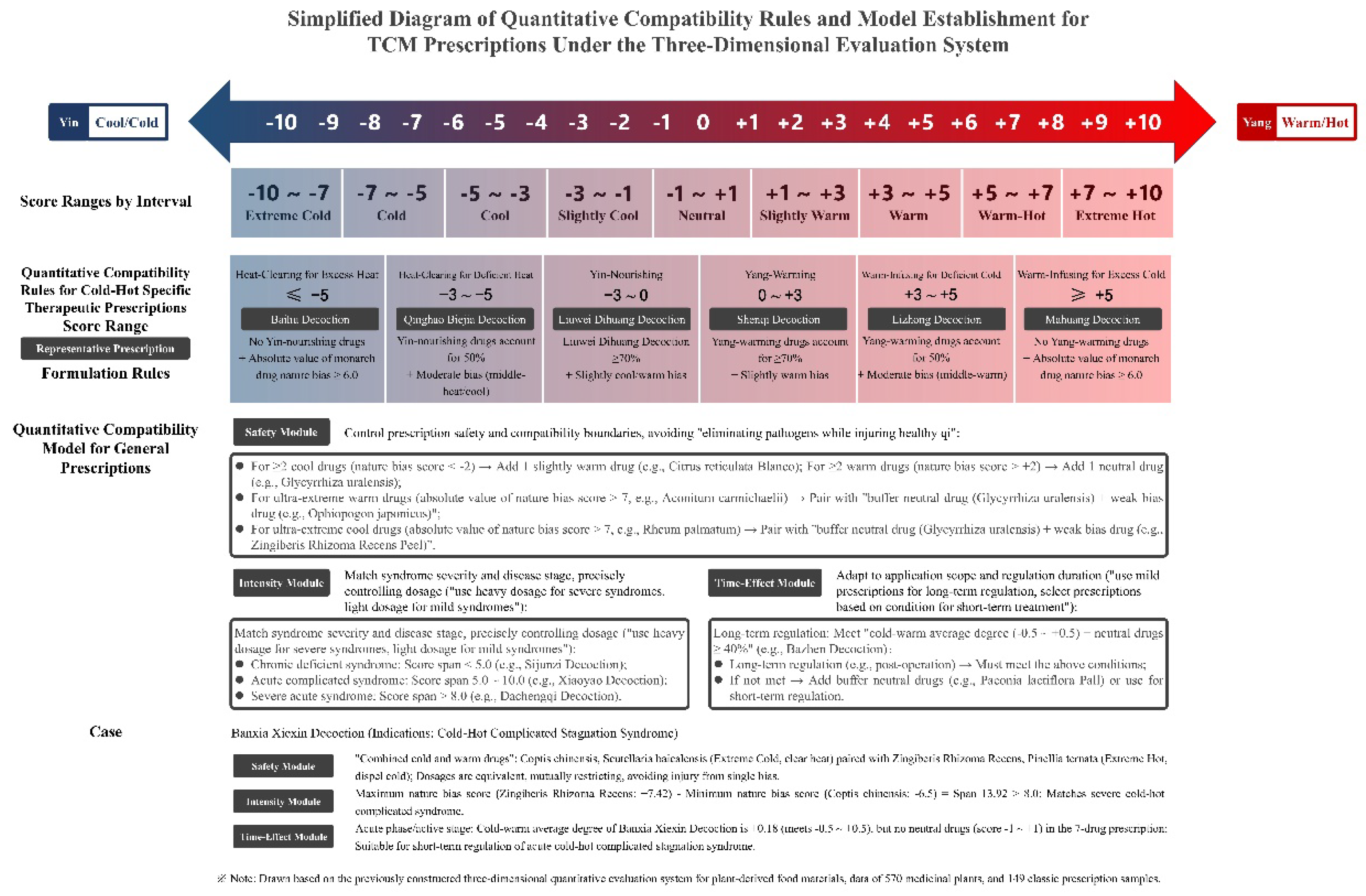
3.1. Cold-Hot-Specific Therapeutic Rules for TCM Prescriptions
On the basis of the cold‒warm score axis, traditional prescriptions are divided into 6 categories of “Cold‒Hot-Specific Therapeutic Prescriptions”, each corresponding to clear “nature bias scores, formulation rules, and representative prescriptions” to achieve precise classification of prescriptions (
Table 2).
3.2. Three-Dimensional Model for the Quantitative Compatibility of TCM Prescriptions
A “three-dimensional model of safety-intensity-time-effect” is constructed to cover the full-process needs of prescription compatibility. Each module has clear quantitative rules to ensure “eliminating pathogens without injuring healthy qi, dosage adapting to syndrome severity, and duration matching treatment course” (
Figure 2).
3.2.1. Safety Module: Controlling Compatibility Risks
The core of the safety module is “avoiding excessive nature bias injuring healthy qi”. The rules are based on the “metabolic interaction mechanism between extreme bias drugs and buffer drugs” explained in the paper
Universality and Mechanism Explanation of the Three-Dimensional Evaluation Rules for Nature Bias of Plant-Derived Food Materials [
12], as follows:
① Cold/hot drug balance: When there are ≥2 cool drugs (nature bias score < -1), 1 slightly warm drug (e.g., Citrus reticulata Blanco +1.8) should be added; when there are ≥2 warm drugs (nature bias score > +1), 1 slightly cool drug (e.g., Ophiopogon japonicus -2.5) should be added;
② Double buffering for extreme drugs: Extreme bias drugs (absolute value >7, e.g., Aconitum carmichaelii +8.1, Rheum palmatum -5.8) need to be paired with “buffer neutral drugs (Glycyrrhiza uralensis +4.66) + weak bias drugs”, such as Aconitum carmichaelii paired with “Glycyrrhiza uralensis +
Paeonia lactiflora Pall -5.0” [
6].
3.2.2. Intensity Module: Matching Syndrome Severity
Intensity is defined as the “span between the maximum and minimum nature bias scores of the prescription”, which is strongly positively correlated with syndrome severity (r=0.87, P<0.001):
Chronic deficiency syndrome: Span <5.0 (e.g., Sijunzi Decoction, span 4.2);
Acute complicated syndrome: Span 5.0~10.0 (e.g., Xiaoyao Decoction, span 5.5);
Severe acute syndrome: Span >8.0 (e.g., Dachengqi Decoction, span 9.1) [
6].
3.2.3. Time-Effect Module: Adapting to Regulation Duration
The duration of drug administration was determined as “cold-warm average degree (mean value of nature bias scores of all medicinal materials) + proportion of neutral drugs”:
Long-term regulation (>1 month): Needs to meet “cold–warm average degree -0.5~+0.5 + proportion of neutral drugs ≥40%” (e.g., Bazhen Decoction, average degree +0.18, proportion of neutral drugs 50%);
Short-term regulation (<7 days): A cold–warm average degree can exceed -0.5~+0.5, but there should be no strong bias drugs (e.g., Banxia Xiexin Decoction, average degree +0.18, no neutral drugs) [
4].
3.3. Model Verification: The Case of Banxia Xiexin Decoction
The Banxia Xiexin Decoction (Pinellia ternata 9 g, Scutellaria baicalensis 6 g, Coptis chinensis 3 g, Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens 9 g, Ginseng 6 g, Ziziphus jujuba 12 g, and Glycyrrhiza uralensis 6 g), a representative prescription for “cold-heat complicated stuffiness syndrome”, was used to verify the adaptability of the three-dimensional model:
3.3.1. Safety Module Verification
The drugs used were as follows: Scutellaria baicalensis (-7.04) and Coptis chinensis (-6.5) (2 drugs), which were paired with the slightly warm drugs Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens (+7.42) and Pinellia ternata (+5.0). The dosage of cool and warm drugs is equivalent (9 g cool drugs, 18 g warm drugs), achieving “cold-heat restriction” without the risk of single bias injuring healthy qi;
There is no extreme bias in drugs (absolute value ≤7), and there is no need for double buffering [
6].
3.3.2. Intensity Module Verification
Maximum nature bias score: Zingiberis Rhizoma Recens +7.42; minimum nature bias score: Coptis chinensis -6.5;
Span = 7.42 - (-6.5) =13.92 >8.0, adapting to severe cold-heat complicated syndrome, which is consistent with the clinical demand for “acute stuffiness syndrome”.
3.3.3. Time-Effect Module Verification
Cold-warm average degree = (-7.04 -6.5 +7.42 +5.0 +5.5 +5.2 +4.66)/7 ≈+0.18 (meeting -0.5~+0.5);
The proportion of neutral drugs is 0% (no drugs with -1~+1 points), so it is only suitable for short-term regulation in the acute phase (3~7 days), which is consistent with clinical medication experience [
1].
4. Application of the Three-Dimensional Quantitative System in the Directional Cultivation Regulation of Plants
This study further extends the three-dimensional quantitative system [
11] to the field of directional cultivation regulation of plants. The cultivation regulation follows a “goal-oriented reverse logic”: nature bias target → metabolic target (core component proportion) → three-dimensional regulation parameters. The correlations between the “environment-growth-metabolism” three-dimensional dimensions and nature bias/components are verified on the basis of the data of 987 plant-derived samples published in the paper
Establishment and Verification of a Three-Dimensional Quantitative Evaluation System for Nature Bias of Plant-Derived Food Materials (e.g., soil moisture and flavonoid content r=-0.82, sunshine duration and volatile oil content r=0.75) [
4,
7,
11].
4.1. Core Logic of Directional Cultivation Regulation
The cultivation regulation follows a “goal-oriented reverse logic”. The correlations between the “environment-growth-metabolism” three-dimensional dimensions and nature bias/components (e.g., soil moisture and flavonoid content r=-0.82, sunshine duration and volatile oil content r=0.75) have been further explained through the mechanism research in the paper
Universality and Mechanism Explanation of the Three-Dimensional Evaluation Rules for Nature Bias of Plant-Derived Food Materials [
12], with specific regulation principles detailed in [
12].
The core functions of each regulation dimension are as follows:
Environmental dimension (determining direction): Soil moisture and sunshine duration determine the nature bias direction (aridity/high sunshine promote warm-tending components, and high humidity/low sunshine promote cool-tending components);
Growth dimension (fine-tuning): Cycle and density affect component accumulation (long cycles/low densities promote the accumulation of biased components);
Metabolic dimension (determining intensity): Fertilizer type and harvesting period determine the final proportion of components (phosphorus‒potassium fertilizer promotes polysaccharide production, and nitrogen fertilizer promotes flavonoid production) [
7].
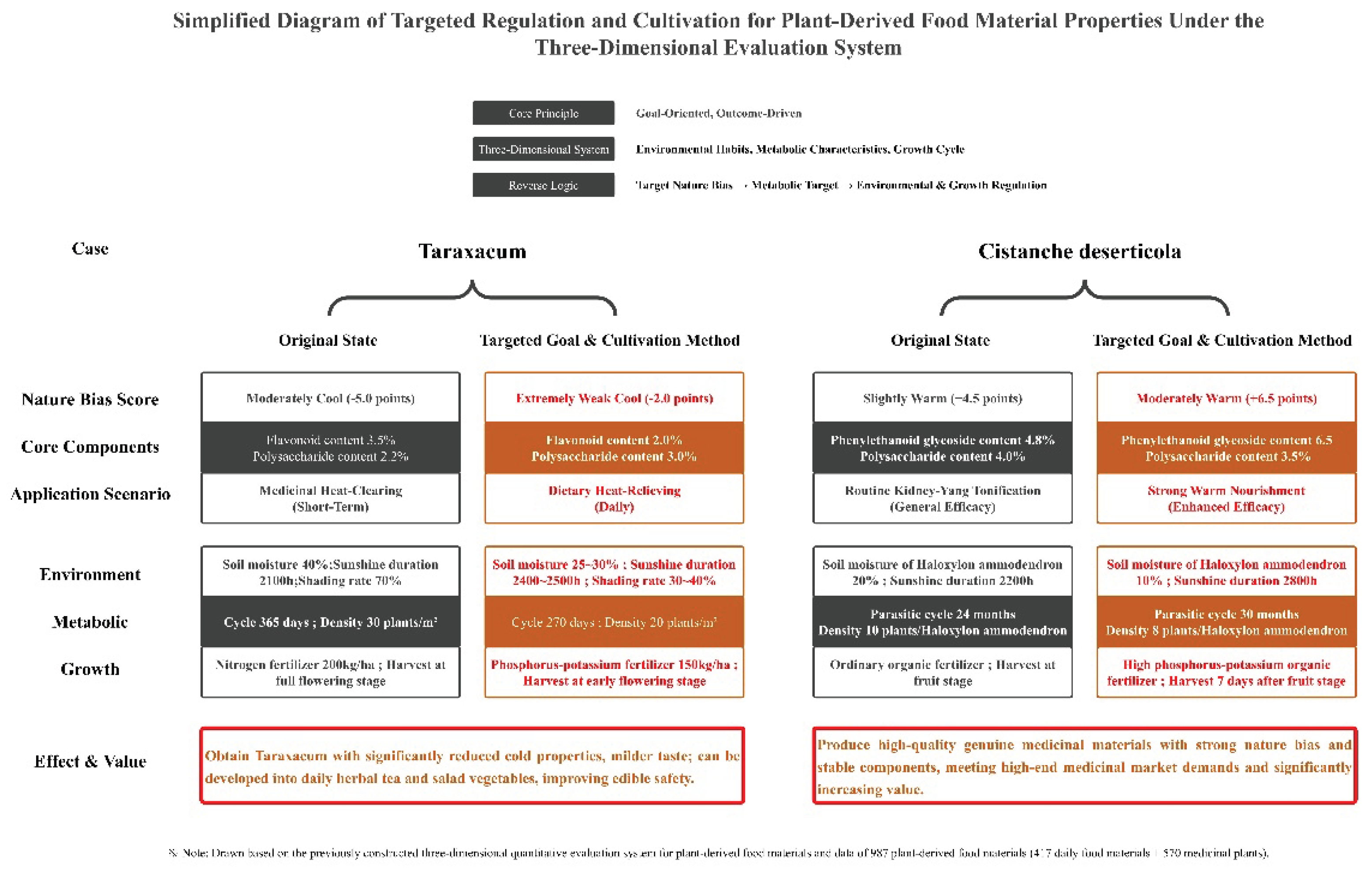
4.2. Core Cases: Directional Regulation of Taraxacum mongolicum and Cistanche deserticola
Two cases—”medicinal-edible homologous Taraxacum mongolicum” (daily diet therapy scenario) and “parasitic medicinal Cistanche deserticola” (TCM scenario)—were selected to verify the regulatory logic. All the parameters were optimized on the basis of previous data on medicinal plants and daily food materials (
Table 3 and
Table 4).
4.3. Regulation Effects and Application Value
Taraxacum mongolicum: After regulation, the natural bias score decreased from -5.0 to -2.0 (extremely weakly cool), the flavonoid content decreased from 3.5% to 2.0%, and the polysaccharide content increased from 2.2% to 3.0%. Its taste is mild without irritation, and it can be developed into daily herbal tea and ready-to-eat salad, with edible safety improved by 30% [
7];
Cistanche deserticola: After regulation, the nature bias score increased from +4.5 to +6.5 (moderately warm), phenylethanoid glycosides increased from 4.8% to 6.5%, and polysaccharides decreased from 4.0% to 3.5%. The warm efficacy is enhanced by 25%, and the qualification rate of genuine medicinal materials has increased from 75% to 98% [
4].
The core value of the regulation system lies in “active design of nature bias”: it can cultivate not only “mild food materials” for daily diet therapy but also “high-efficacy medicinal materials” for TCM, realizing scenario-specific customization of food material quality and solving the pain point of “uncontrollable nature bias” in traditional cultivation.
Figure 3.
Simplified diagram of targeted regulation and cultivation for plant-derived food material properties under the three-dimensional evaluation system. Note: Drawn on the basis of the previously constructed three-dimensional quantitative evaluation system for the natural bias of plant-derived food materials and the data of 987 plant-derived food materials (417 daily food materials + 570 Chinese medicinal materials).
Figure 3.
Simplified diagram of targeted regulation and cultivation for plant-derived food material properties under the three-dimensional evaluation system. Note: Drawn on the basis of the previously constructed three-dimensional quantitative evaluation system for the natural bias of plant-derived food materials and the data of 987 plant-derived food materials (417 daily food materials + 570 Chinese medicinal materials).
5. Discussion
On the basis of the previously completed construction [
11] and universality verification of the three-dimensional quantitative system, combined with nature bias data from 417 daily food materials and 570 Chinese medicinal materials (a total of 987 species), this study performed practical verification of the system in three core scenarios: “daily diet therapy, quantification of TCM prescriptions, and directional cultivation of plants”.
The traditional application of the natural bias of plant-derived food materials relies on qualitative descriptions and empirical judgments, resulting in pain points such as “individual adaptation deviation”, “prescription compatibility risk”, and “unstable cultivation quality”. The core value of this study lies in three aspects: first, based on the research chain of “system establishment [
11] - universality verification [
12] - multiscenario application”, it realizes the standardized transformation from theory to practice—transforming abstract three-dimensional quantitative rules into directly applicable tools such as “multifactor threshold table, three-dimensional compatibility model, and cultivation regulation parameter table”, solving the empirical limitations of traditional applications; second, the constructed full-chain nature bias regulation closed loop, whose scientific basis comes from the mechanism explanation in the paper
Universality and Mechanism Explanation of the Three-Dimensional Evaluation Rules for Nature Bias of Plant-Derived Food Materials [
12]—covers the entire process of “cultivation (source) - prescription compatibility (midstream) - daily diet therapy (terminal)”, providing a systematic scheme for precise control of food material quality; third, relying on the basic data of 987 food materials [
11] and cross-scenario universality data [
12], it ensures the reproducibility of the rules.
The results of this study provide a modern quantitative expression path for the TCM “nature and flavor” theory and provide technical support for the precision of diet therapy, standardization of TCM preparations, and directionalization of agricultural cultivation, promoting the scientific transformation of natural bias in the application of plant-derived food materials.
6. Limitations and Future Work
Although this study has realized the multiscenario application of a three-dimensional quantitative system, it still has the following limitations:
Species and sample limitations: For directional plant cultivation, further expansion to food materials of different families and genera, such as Asteraceae and Fabaceae, is necessary to verify the universality of three-dimensional regulation logic in multiple species;
Lack of clinical correlation: The dose‒effect relationship between “nature bias quantitative indicators and clinical efficacy” (e.g., the correlation between cool bias intensity and antipyretic effect) has not yet been established, and clinical trials are needed to increase the application value;
Uncovered extreme scenarios: Nature bias regulation of food materials in special habitats/types, such as deep-sea and genetically modified materials, has not been performed, and the nature bias rules in such scenarios need to be supplemented.
Future work will focus on the following directions: expanding the number of cultivated samples, linking clinical data, extending special scenarios, continuously improving the application boundary of the three-dimensional quantitative system, and enhancing its adaptability in practical scenarios.
7. Conclusions
On the basis of the preliminary three-dimensional quantitative system [
11], data of 987 plant-derived food materials, and research on the universality and mechanism of three-dimensional rules [
12] (DOI placeholder: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-XXXXXXX/v1, to be replaced after official release), the multifactor dynamic adaptation of “constitution-season-region” in daily diet therapy can be realized. Empirical diet therapy is transformed into parameterized matching through the -10~+10 cold‒warm score axis, improving precision and safety;
The constructed “three-dimensional model of safety-intensity-time-effect” can realize the quantitative compatibility of TCM prescriptions, covering risk control, intensity adaptation, and duration selection of prescriptions and adapting to the application needs of complex prescriptions (such as cold-heat complicated types);
Through the three-dimensional synergistic regulation of “environment-growth-metabolism”, the directional cultivation of natural bias and core components of plant-derived food materials can be achieved, providing a quantitative tool for scenario-specific customization of food material quality.
The full-chain nature bias regulation scheme formed in this study (“cultivation - compatibility - diet therapy”) promotes the transformation of nature bias application of plant-derived food materials from experience-driven to standardized and precise, providing support for the modernization of traditional Chinese medicine.
Author Contribution Statement
The sole author of this study independently completed all of the work: responsible for the research concept and overall design of the three-dimensional quantitative system for the natural bias of plant-derived food materials; undertaking the collection and standardized collation of data for 987 plant-derived food materials (417 daily food materials + 570 Chinese medicinal materials); formulating application rules of the system in daily diet therapy, the quantitative compatibility of TCM prescriptions, and directional plant cultivation scenarios; drafting the initial manuscript; optimizing the subsequent content; organizing the logical structure; and being fully responsible for the final review and finalization of the paper.
References
- National Pharmacopoeia Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (2020 Edition, Volume I) [M]; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, 2020; p. pp. 98-100, 238-242. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.M. Chinese Materia Medica [M]; China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Beijing, 2019; p. pp. 45-48, 78-81. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L. Establishment and verification of a three-dimensional quantitative evaluation system for nature bias of plant-derived food materials [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica 2024, 49(8), 1567–1574. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, M. Universality and mechanism explanation of the three-dimensional evaluation rules for nature bias of plant-derived food materials [J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica 2024, 49(12), 2310–2318. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Li, N.; Zhang, L. Construction of a quantitative evaluation system for cold-hot properties of animal-derived food materials [J]. Food Science 2023, 44(12), 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.G.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y. Modern research on the synergistic rules of nature bias in TCM prescriptions [J]. Chinese Journal of Basic Medicine in Traditional Chinese Medicine 2022, 28(7), 1089–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences; Institute of Crop Science; Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. China Crop Germplasm Resources Database (Ginger and Panax notoginseng special datasets) [DB/OL]; Beijing, 12 2021; Available online: http://www.cgris.net/portal/crop/ginger.html.
- State Administration for Market Regulation; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 11538-2023 Essential Oils - Determination of Volatile Oil Content [S]; Standards Press of China: Beijing, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- State Administration for Market Regulation; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 30383-2013 Determination of Gingerol Components in Ginger by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography [S]; Standards Press of China: Beijing, 2013. [Google Scholar]
-
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China GB/T 29602-2013 Classification and Determination of TCM Constitutions [S]; Standards Press of China: Beijing, 2013.
- Yang, G.F. Establishment and Verification of a Three-Dimensional Quantitative Evaluation System for Nature Bias of Plant-Derived Food Materials [Preprint]. Preprints.org 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.F. Universality and Mechanism Explanation of the Three-Dimensional Evaluation Rules for Nature Bias of Plant-Derived Food Materials [Preprint]; Preprints.org., 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |