Submitted:
17 December 2025
Posted:
23 December 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
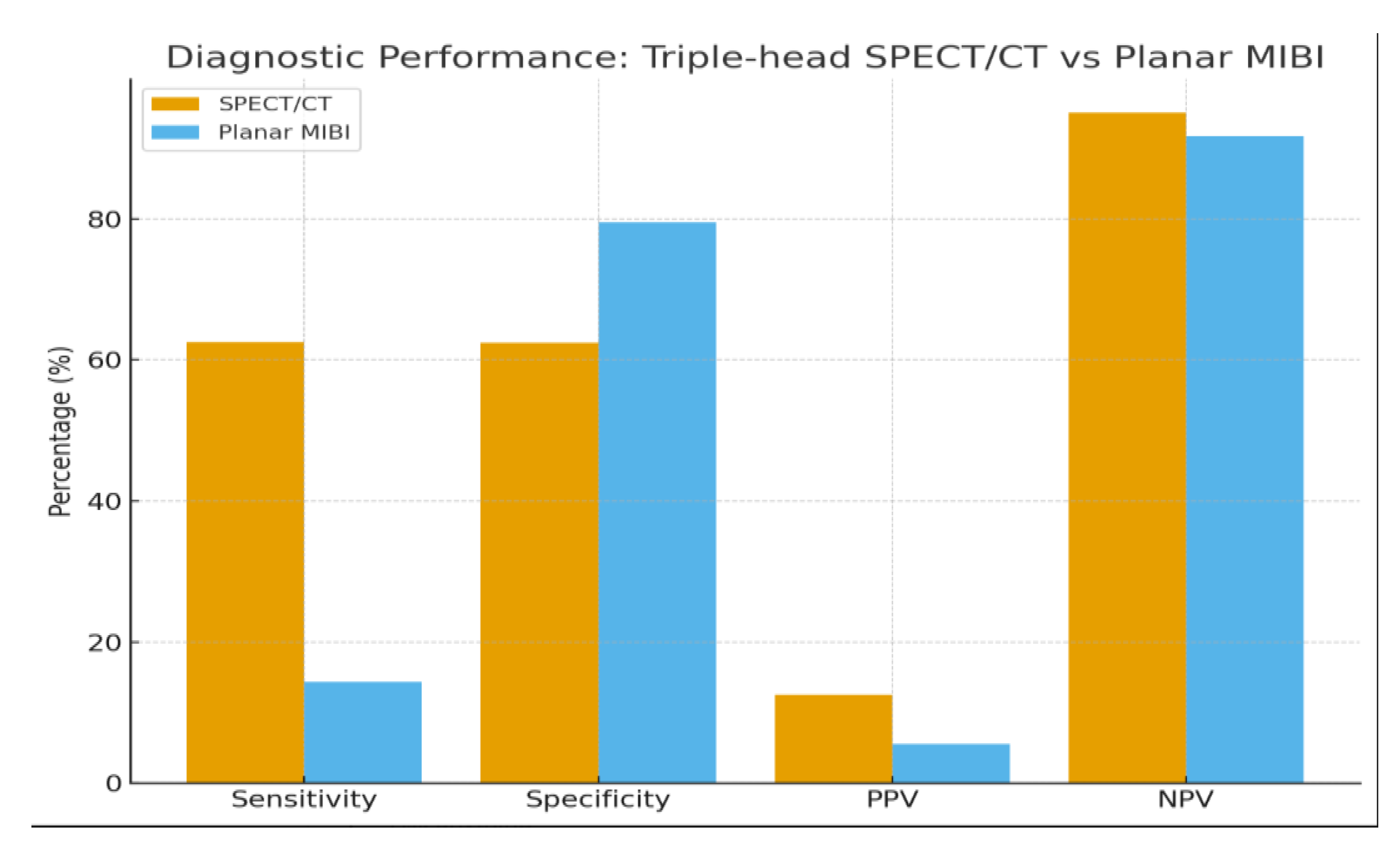
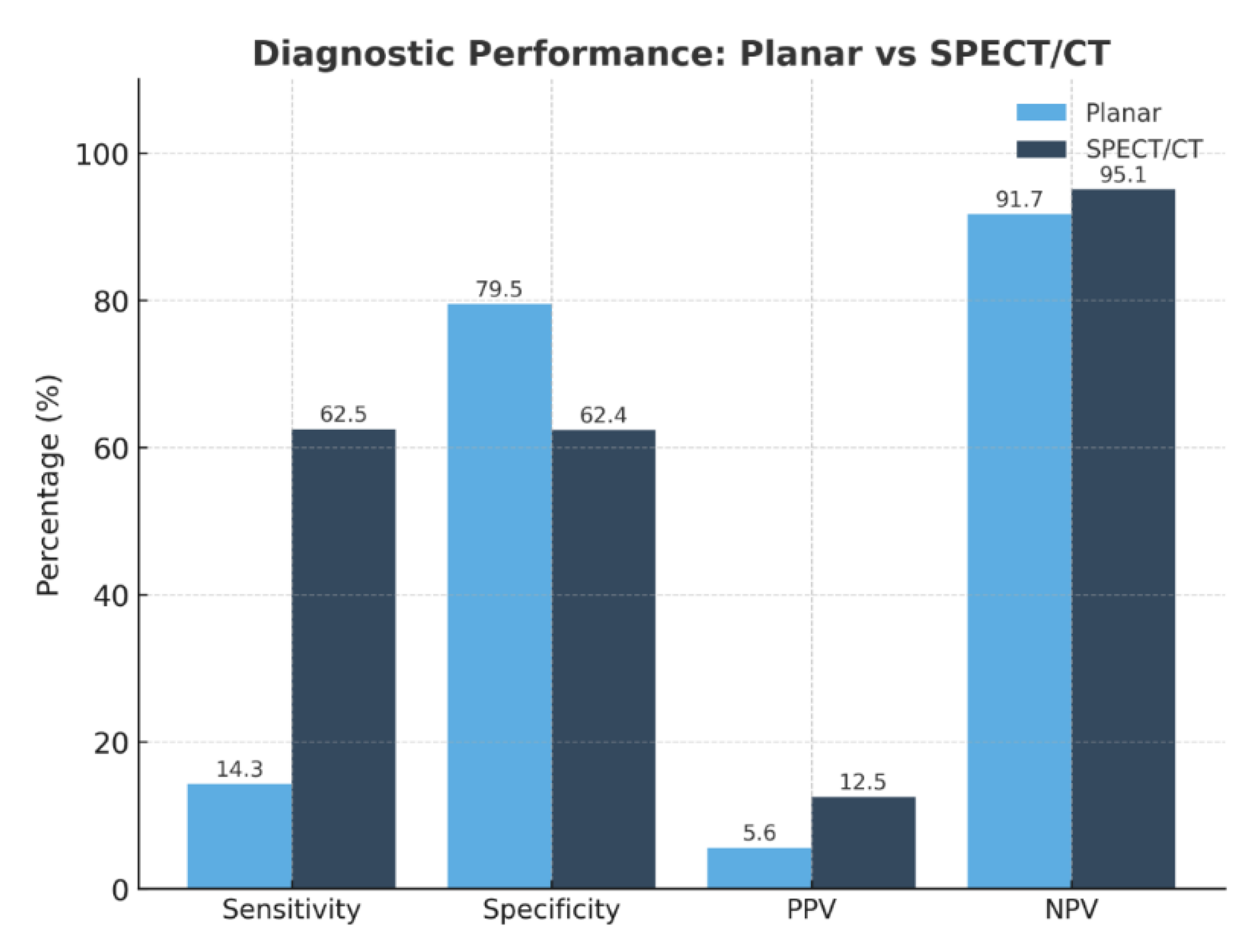
Background/Objectives: Accurate preoperative localization of hyperfunctioning parathyroid tissue is essential for minimally invasive parathyroidectomy. Conventional planar dual-phase 99mTc-sestamibi scintigraphy is widely used but shows reduced diagnostic accuracy in patients with thyroid nodules or ectopic glands. Hybrid triple-head SPECT/CT integrates functional and anatomical imaging and may improve lesion detection. This study evaluated the diagnostic performance of triple-head SPECT/CT compared with planar scintigraphy and explored correlations between biochemical markers and imaging positivity. Methods: A retrospective single-center study included 90 adults referred for suspected primary hyperparathyroidism between January 2021 and August 2025. Demographic data, laboratory parameters (PTH, total and ionized calcium, 25-hydroxyvitamin D), and imaging results were collected. Diagnostic accuracy was assessed in patients with surgical confirmation or robust clinical verification. Correlations between biochemical markers and imaging positivity were analyzed using Pearson correlation coefficients. Results: SPECT/CT demonstrated significantly higher sensitivity than planar scintigraphy (62.5% vs. 14.3%) and an excellent negative predictive value (95.1%), whereas planar imaging showed slightly higher specificity (79.5%). Ionized calcium correlated significantly with SPECT/CT positivity (r = 0.39; p = 0.009), while PTH and 25-hydroxyvitamin D showed no significant association. SPECT/CT accurately localized ectopic parathyroid glands and lesions in patients with coexisting thyroid nodularity, overcoming limitations of planar imaging. Several lesions undetected by planar scintigraphy were identified on SPECT/CT, supporting its role in anatomically complex or subtle cases. Conclusions: Triple-head SPECT/CT provided superior diagnostic performance over planar scintigraphy for preoperative localization in primary hyperparathyroidism, particularly in patients with thyroid nodularity or ectopic glands. Ionized calcium may serve as a complementary predictor of lesion detectability. These findings support hybrid SPECT/CT as the preferred first-line imaging modality, facilitating targeted minimally invasive surgery and optimizing surgical planning.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Radiopharmaceutical Preparation and Radiolabeling Procedure
2.3. Imaging Equipment
2.4. Imaging Protocols
2.5. Endpoints and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Characteristics
3.2. Diagnostic Performance
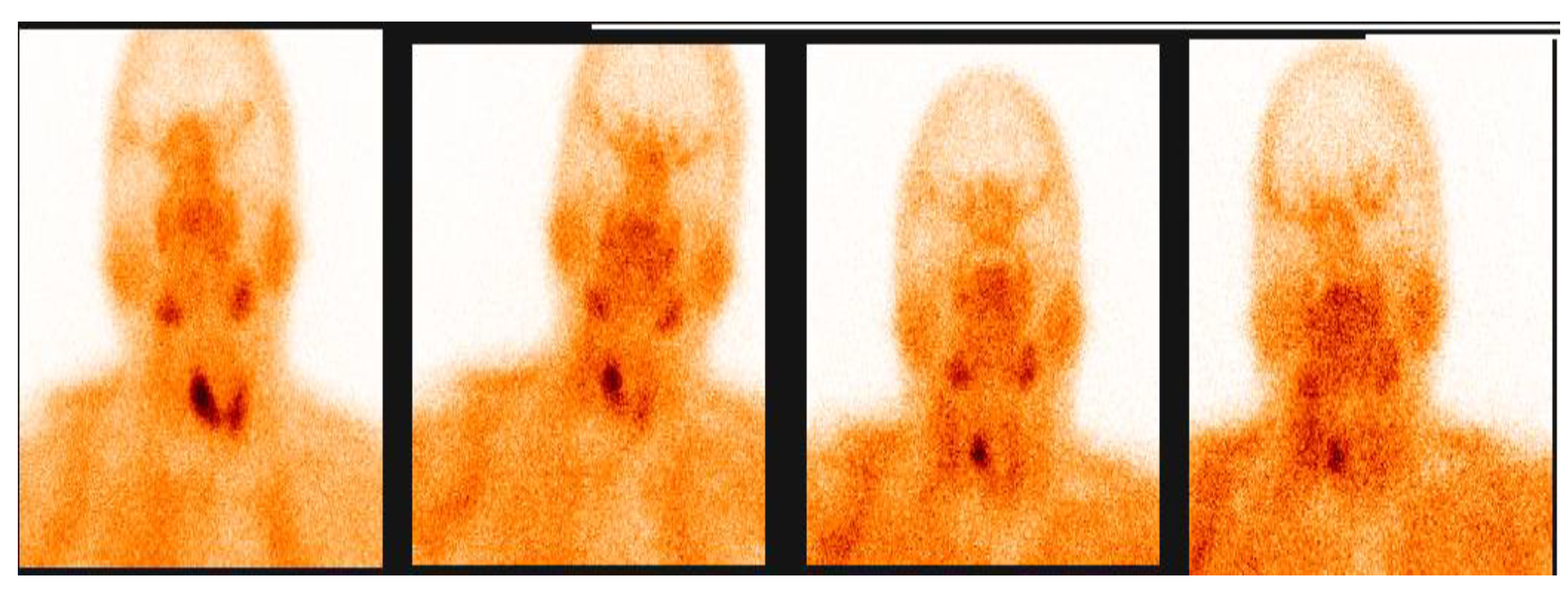
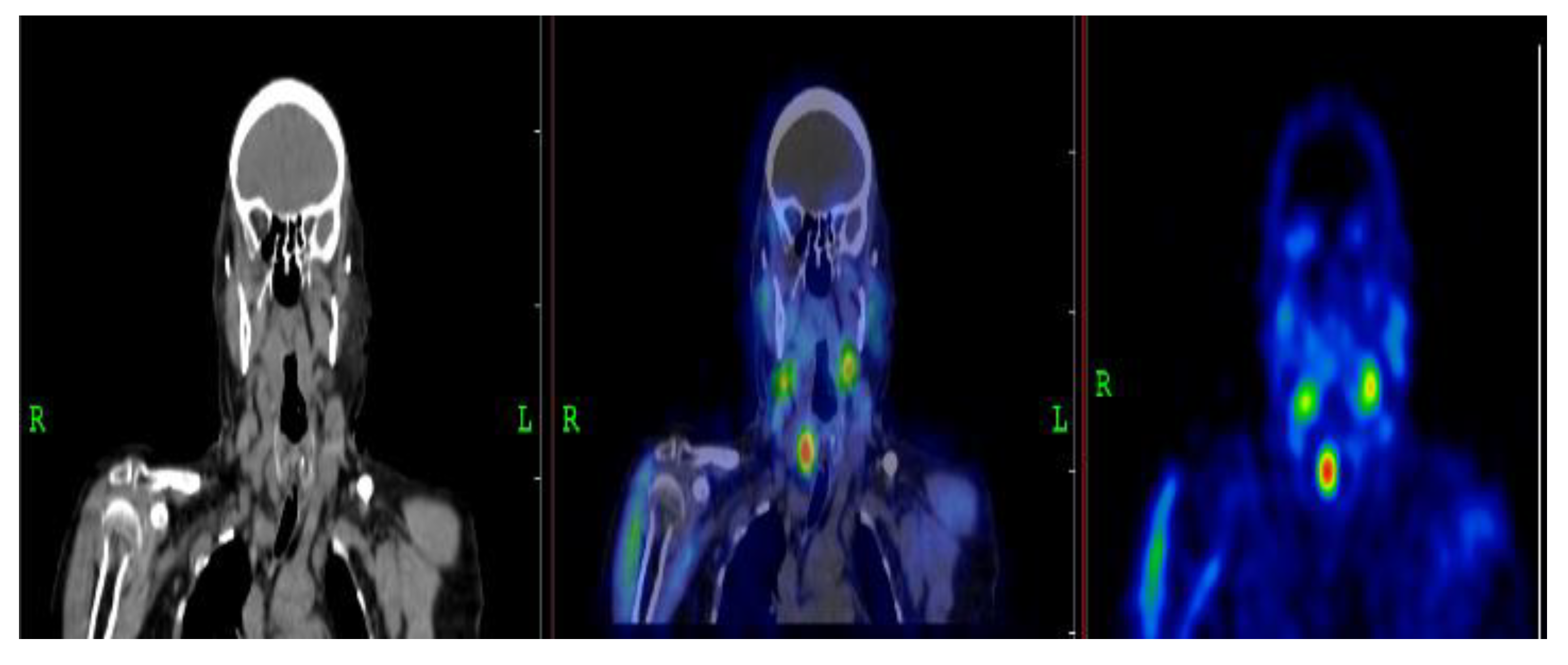
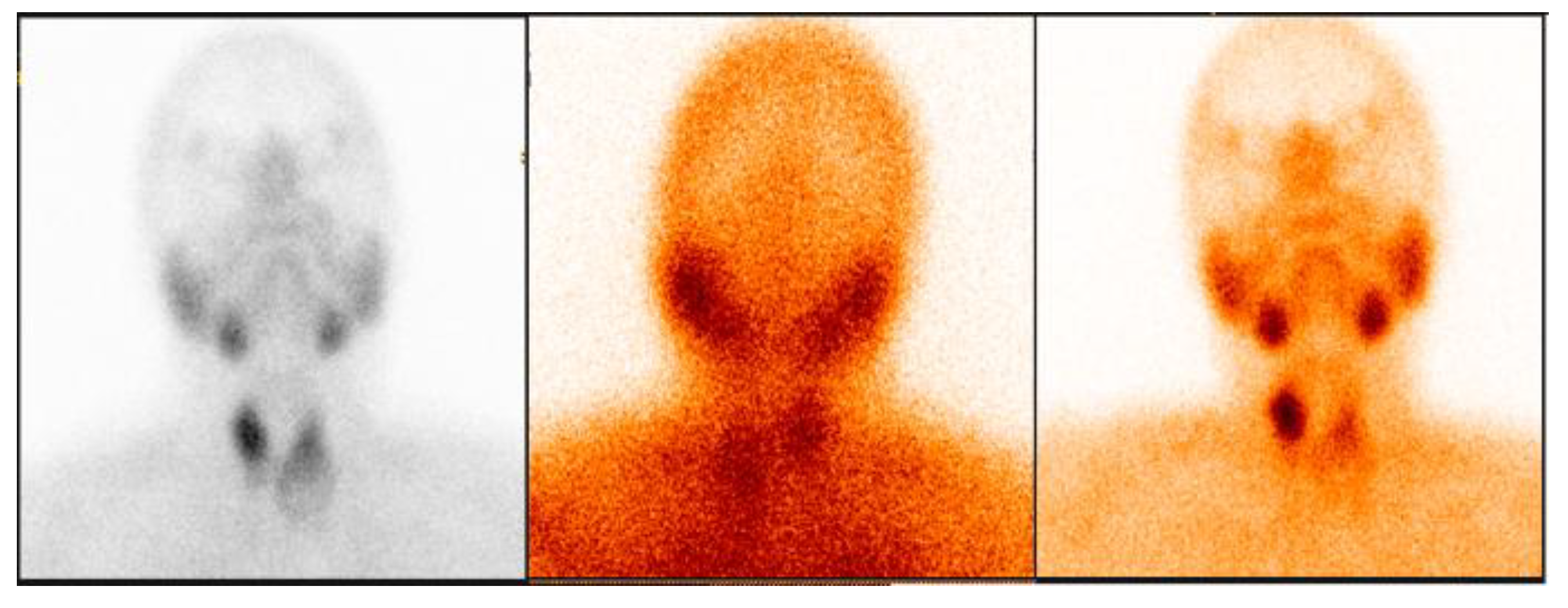
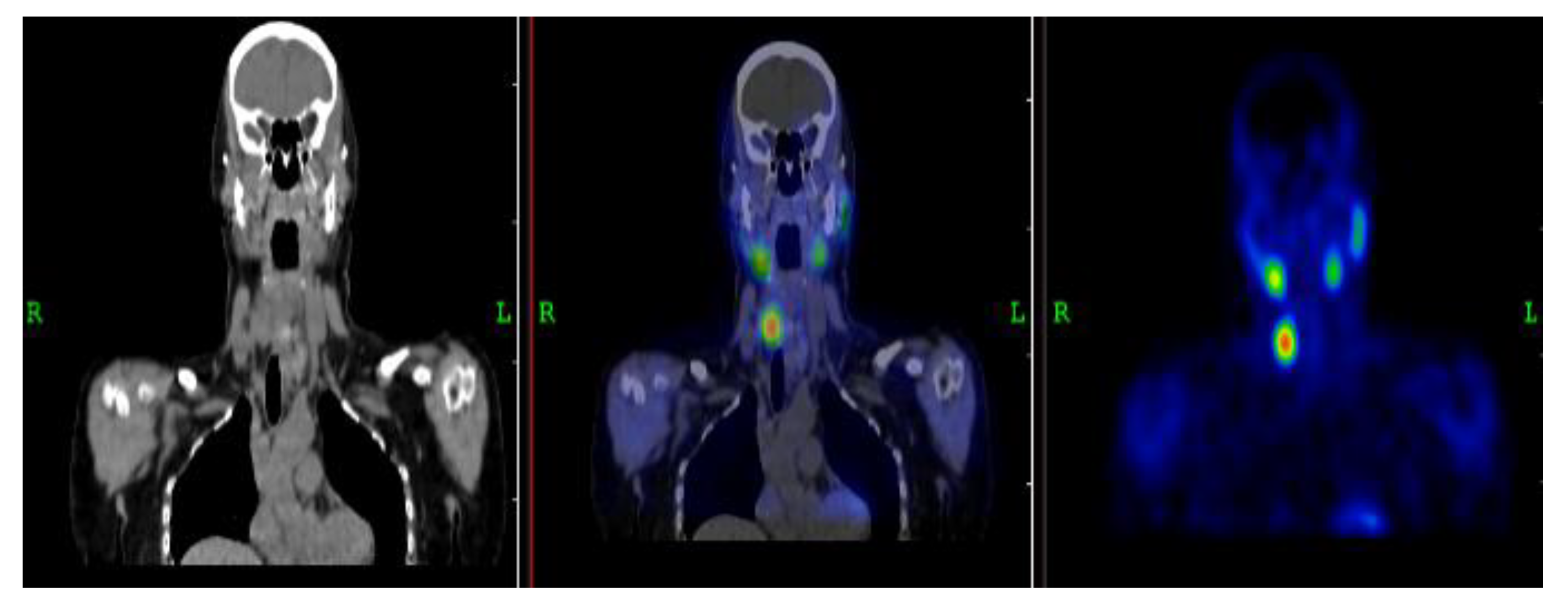
3.2.1. Representative Clinical Case 1
3.2.2. Representative Clinical Case 2
3.3. Diagnostic Performance
3.4. Biochemical Correlations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palermo, A.; Tabacco, G.; Makras, P.; Zavatta, G.; Trimboli, P.; Castellano, E.; Anastasilakis, A.D. Primary Hyperparathyroidism: From Guidelines to Outpatient Clinic. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2024, 25, 875–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilezikian, J.P.; Cusano, N.E.; Khan, A.A.; Liu, J.M.; Marcocci, C.; Bandeira, F. Primary Hyperparathyroidism. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLellis, R.A.; Mazzaglia, P.; Mangray, S. Primary Hyperparathyroidism: A Current Perspective. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2008, 132, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, G.J.; Buła, G.; Żądło, D.; Gawrychowska, A.; Gawrychowski, J. Primary Hyperparathyroidism. Endokrynol. Pol. 2020, 71, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindié, E.; Schwartz, P.; Avram, A.M.; Imperiale, A.; Sebag, F.; Taïeb, D. Primary Hyperparathyroidism: Defining the Appropriate Preoperative Imaging Algorithm. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 3S–12S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, G.; Gulec, S.A.; Rubello, D.; Boni, G.; Puccini, M.; Pelizzo, M.R.; Giuliano, A.E. Preoperative Localization and Radioguided Parathyroid Surgery. J. Nucl. Med. 2003, 44, 1443–1458. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kunstman, J.W.; Kirsch, J.D.; Mahajan, A.; Udelsman, R. Parathyroid Localization and Implications for Clinical Management. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özçevik, H.; Tamam, M.Ö.; Tatoğlu, M.T.; Mülazımoğlu, M. Comparison of Dual-Phase Tc-99m-Sestamibi Planar Imaging and SPECT/CT in Hyperparathyroidism. Mol. Imaging Radionucl. Ther. 2022, 31, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lu, X.; Zhou, P.; Gao, Z.; Ding, C.; Weng, W.; Su, X. Comparison of Four-Dimensional CT and Sestamibi SPECT/CT in the Localization Management of Primary Hyperparathyroidism. Cancer Imaging 2025, 25, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Xu, K.; Zhang, W. Quantitative Application of Dual-Phase 99mTc-Sestamibi SPECT/CT for Parathyroid Lesions: Identification of Optimal Timing in Secondary Hyperparathyroidism. EJNMMI Phys. 2023, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavely, W.C.; Goetze, S.; Friedman, K.P.; Leal, J.P.; Zhang, Z.; Garret-Mayer, E.; Ziessman, H.A. Comparison of SPECT/CT, SPECT, and Planar Imaging Using 99mTc-Sestamibi. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papathanassiou, D.; Bruna-Muraille, C.; Jouannaud, C.; Gagneux-Lemoussu, L.; Eschard, J.P.; Liehn, J.C. SPECT/CT in Bone Diseases. Joint Bone Spine 2009, 76, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Yaman, A.; Alwan, M.; El Ghazawi, A.; Al-Mallah, M.H.; Al Rifai, M. Advances in Nuclear Hybrid Imaging in Cardiovascular Diseases. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, D.; Kotian, R.P. Hybrid Imaging: Physics, Principles, and Quality Control. In Fundamentals of X-ray Imaging, 2nd ed.; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2025; pp. 417–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Even-Sapir, E.; Keidar, Z.; Bar-Shalom, R. Hybrid Imaging Improving Diagnostic Accuracy. In Semin. Nucl. Med.; WB Saunders, July 2009; Vol. 39, pp. 264–275. [Google Scholar]
- Mariani, G.; Bruselli, L.; Kuwert, T.; Kim, E.E.; Flotats, A.; Israel, O.; Watanabe, N. Clinical Uses of SPECT/CT—A Review. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 1959–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, A.; Schillaci, O.; Piras, B.; Madeddu, G. SPECT/CT in Hyperparathyroidism. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2014, 2, 537–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scerrino, G.; Paladino, N.C.; Graceffa, G.; Melfa, G.; Orlando, G.; Di Vuolo, R.; Lo Casto, A. 18F-Fluorocholine PET/CT vs 4D-CT for Parathyroid Identification. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latge, A.; Riehm, S.; Vix, M.; Bani, J.; Ignat, M.; Pretet, V.; Imperiale, A. 18F-Fluorocholine PET and 4D-CT in Persistent Primary Hyperparathyroidism. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hraishawi, H.K. Comparison of Metabolic and Characteristic Features of PHPT Patients with Different PTH Levels. Master’s Thesis, Rutgers University, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bhan, A.; Athimulam, S.; Kumari, P.; Pal, R.; Bhadada, S.K.; Cook, B.C.; Rao, S.D. Large Parathyroid Adenomas: Reconciling Adenoma Size and Phenotype. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1009516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakou, P.; Vrachnis, D.; Paschou, S.A.; Nastos, K.; Sarlani, H.; Kantreva, K.; Saltiki, K. Giant Parathyroid Adenoma with Carcinoma-like Presentation: Case Report. Hormones 2025, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Shin, E.; Ha, S.; Oh, J.S.; Song, D.E.; Ryu, J.S. Dual- vs. Single-Phase SPECT/CT for Parathyroid Lesion Localization. Medicine 2020, 99, e19989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanella, L.; Hindie, E.; Huellner, M.W.; Talbot, J.N.; Verburg, F.A. Summary of the New EANM Guidelines for Parathyroid Imaging. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 66, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavely, W.C.; Goetze, S.; Friedman, K.P.; Leal, J.P.; Zhang, Z.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; Ziessman, H.A. Tc-99m Sestamibi Planar, SPECT, and SPECT/CT Comparison. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacene, H.A.; Goetze, S.; Patel, H.; Wahl, R.L.; Ziessman, H.A. Advantages of Hybrid SPECT/CT. Open Med. Imaging J. 2008, 2, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durma, A.D.; Saracyn, M.; Kołodziej, M.; Jóźwik-Plebanek, K.; Kamiński, G. Use of [11C]C-Methionine in Endocrine Diagnostics. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.K.; Fig, L.M.; Gross, M.D.; Dwamena, B.A. Parathyroid Adenoma Localization with Sestamibi SPECT/CT: Meta-analysis. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2015, 36, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayed, I.W.; Kim, E.E.; Broussard, W.F.; Evans, D.; Lee, J.; Broemeling, L.D.; Podoloff, D.A. Value of SPECT/CT Over SPECT in Parathyroid Imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2005, 46, 248–252. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.A.; Saboury, B.; Ahlman, M.; Malayeri, A.A.; Jones, E.C.; Chen, C.C.; Millo, C. Parathyroid Imaging: Past, Present, and Future. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12, 760419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitha, T.; Staudenherz, A. Hybrid PET/CT and SPECT/CT Imaging. In Computed Tomography—Clinical Applications; InTech, 2012; pp. 269–294. [Google Scholar]
- Israel, O.; Goldsmith, S.J. (Eds.) Hybrid SPECT/CT Imaging in Clinical Practice; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Pata, G.; Casella, C.; Magri, G.C.; Lucchini, S.; Panarotto, M.B.; Crea, N.; Salerni, B. Financial and Clinical Implications of Low-Energy CT with 99mTc-MIBI SPECT. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 2555–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, D.; Das, J.P.; Yeh, R. Preoperative Localization for PHPT: A Clinical Review. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandqvist, P. Preoperative Localisation of Parathyroid Adenoma Using Tc-99m-Sestamibi SPECT/CT. Thesis, Karolinska Institutet, Sweden, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hindie, E.; Ureña-Torres, P.A.; Taïeb, D. Parathyroid Imaging in Renal Hyperparathyroidism. In Parathyroid Glands in Chronic Kidney Disease; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.D.; Jani, A.G.; Mai, V.Q.; Tuamokumo, F.O.; Shakir, M.K. Associations of Biochemical Markers with Parathyroid Scans. Endocr. Pract. 2019, 25, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, T.W.; Chan, S.K.; Jones, S.J.; Bugis, S.; Irvine, R.; Belzberg, A.; Wiseman, S.M. Determinants of Sestamibi SPECT Sensitivity. Am. J. Surg. 2010, 199, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, D.A.; Deacu, L.G.; Caragheorgheopol, A.; Popescu, N.; Ghemigian, A.; Procopiuc, C.; Poiana, C. Effects of Vitamin D, Renal Function and Age on PTH. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 657991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, P.; Downs, J.; Skene, T.; Evans, A.; Richardson, T.; Parekh, A. Factors Associated with Successful Parathyroid Localization. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2025, 2025, 3922886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sencar, M.E.; Sakiz, D.; Unsal, I.O.; Hepsen, S.; Calapkulu, M.; Gumus, P.; Cakal, E. Vitamin D Does Not Affect Parathyroid Imaging Sensitivity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mshelia, D.S.; Hatutale, A.N.; Mokgoro, N.P.; Nchabaleng, M.E.; Buscombe, J.R.; Sathekge, M.M. Serum Calcium and Dual-Phase Sestamibi Sensitivity. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2012, 32, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silov, G.; Erdogan Ozbodur, S. Relationship between SPECT/CT Parameters and Functional Markers. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petranović Ovčariček, P.; Giovanella, L.; Carrió Gasset, I.; Hindié, E.; Huellner, M.W.; Luster, M.; Verburg, F.A. EANM Practice Guidelines for Parathyroid Imaging. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 2801–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krausz, Y.; Bettman, L.; Guralnik, L.; Yosilevsky, G.; Keidar, Z.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Israel, O. Tc-99m MIBI SPECT/CT in Primary Hyperparathyroidism. World J. Surg. 2006, 30, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taubman, M.L.; Goldfarb, M.; Lew, J.I. Role of SPECT and SPECT/CT in Parathyroid Surgery. Int. J. Mol. Imaging 2011, 2011, 141593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.G.; Saunders, N.D.; Jamshed, S.; Weber, C.J.; Sharma, J. Multimodal Localization Improves Reoperative Parathyroidectomy Outcomes. Am. Surg. 2019, 85, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandedkar, S.S.; Dixit, M.; Malukani, K.; Varma, A.V.; Gambhir, S. Evaluation of Thyroid Lesions with FNAC Using Bethesda System. Int. J. Appl. Basic Med. Res. 2018, 8, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nockel, P.; Millo, C.; Keutgen, X.; Klubo-Gwiezdzinska, J.; Shell, J.; Patel, D.; Kebebew, E. Incidental Thyroid Uptake on 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT. Thyroid 2016, 26, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnier, S.; Mahéo, C.; Potard, G.; Cavarec, M.B.; Roudaut, N.; Thuillier, P.; Leclere, J.C. Value of 18F-Fluorocholine PET-CT in Localizing Parathyroid Adenoma. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavely, W.; Goetze, S.; Friedman, K.; Leal, J.; Zhang, Z.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; Ziessman, H. Dual-Phase Tc-99m Sestamibi Planar and SPECT/CT for Parathyroid Localization. Unpublished Work. 2006; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.R.; Oates, M.E. Radionuclide imaging of the parathyroid glands: Patterns, pearls, and pitfalls. Radiographics 2004, 24, 1101–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizsan, A.K.; Kukuts, K.; Al-Muhanna, W.; Szoboszlai, Z.; Balazs, L.; Szabo, B.; Forgacs, A.; et al. Performance evaluation of a novel multipinhole collimator on a triple–NaI-detector SPECT/CT system for dedicated myocardial imaging. EJNMMI Physics 2023, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willowson, K.P.; Bailey, D.L. Evolving SPECT/CT technology. Br. J. Radiol. 2024, tqae200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseb, A.; Benider, H.; Treglia, G.; Cusumano, C.; Bessac, D.; Trimboli, P.; Imperiale, A.; et al. Refining the role of presurgical PET/4D-CT in a large series of patients with primary hyperparathyroidism undergoing [18F]fluorocholine PET/CT. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 55, e14336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchareb, Y.; AlSaadi, A.; Zabah, J.; Jain, A.; Al-Jabri, A.; Phiri, P.; Sirasanagandla, S.R.; et al. Technological advances in SPECT and SPECT/CT imaging. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Mean ± SD | Range | Units |
| Age | 56.7 ± 13.0 | 23–82 | Years |
| Female sex | — | — | 75 (83.3%) |
| PTH | 336.1 ± 564.3 | 1.98–3144 | pg/mL |
| Total calcium | 2.55 ± 1.46 | — | mmol/L |
| Ionized calcium | 1.35 ± 0.21 | — | mmol/L |
| 25-OH Vitamin D | 20.7 ± 8.8 | — | ng/mL |
| Modality | TP | FP | TN | FN | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planar 99mTc-MIBI | 1 | 17 | 66 | 6 | 14.3 | 79.5 | 5.6 | 91.7 |
| SPECT/CT | 5 | 35 | 58 | 3 | 62.5 | 62.4 | 12.5 | 95.1 |
| Parameters | r | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| PTH | +0.18 | 0.099 |
| Total calcium | +0.26 | 0.054 |
| Ionized calcium | +0.39 | 0.009 |
| 25-OH Vitamin D | +0.12 | 0.428 |
| Parameters | r | p-value |
|---|---|---|
| PTH | +0.09 | 0.423 |
| Total calcium | +0.03 | 0.834 |
| Ionized calcium | +0.27 | 0.083 |
| 25-OH Vitamin D | −0.09 | 0.524 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.





