Submitted:
20 December 2025
Posted:
22 December 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Over the past two decades, the transition from conventional power networks to smart grids has accelerated, driven by advances in digital communication and intelligent control technologies. Smart grids integrate sensing devices, automated metering, and data-driven management systems, producing large volumes of heterogeneous information across all operational layers. This review examines 220 publications from the last twenty years, highlighting major research trends, classifying works by publication type, and identifying the most influential journals and conferences. It also summarizes the contribution of each reviewed work and categorizes the analytical methods and smart-grid-related topics addressed. Finally, the paper outlines emerging challenges and future research directions that can further enhance the role of big data analytics in next-generation smart grids.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
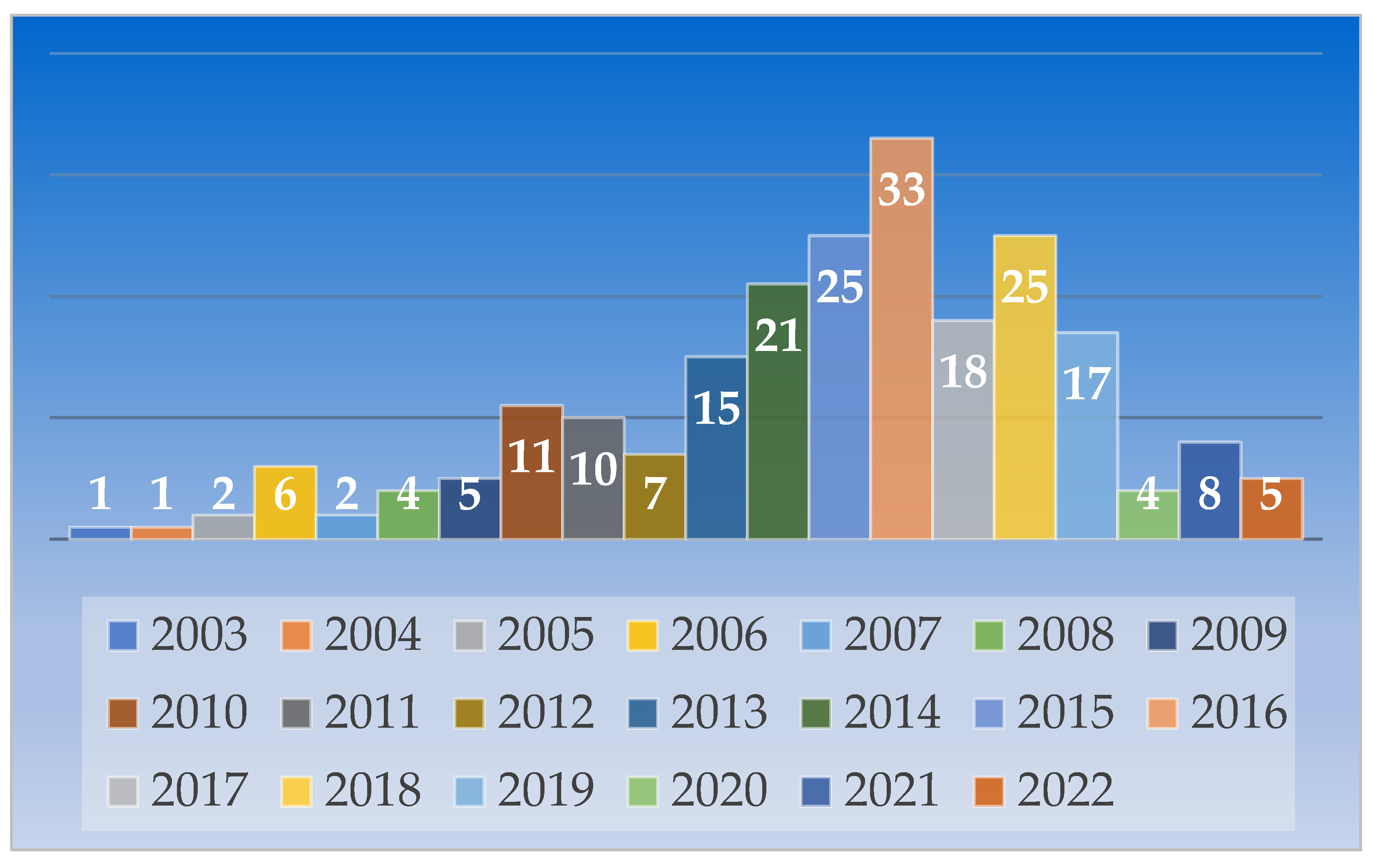
- The publications are chronologically distributed to highlight the research interest on the last 20 years. This allows researchers to determine whether or not the topic merits further investigation.
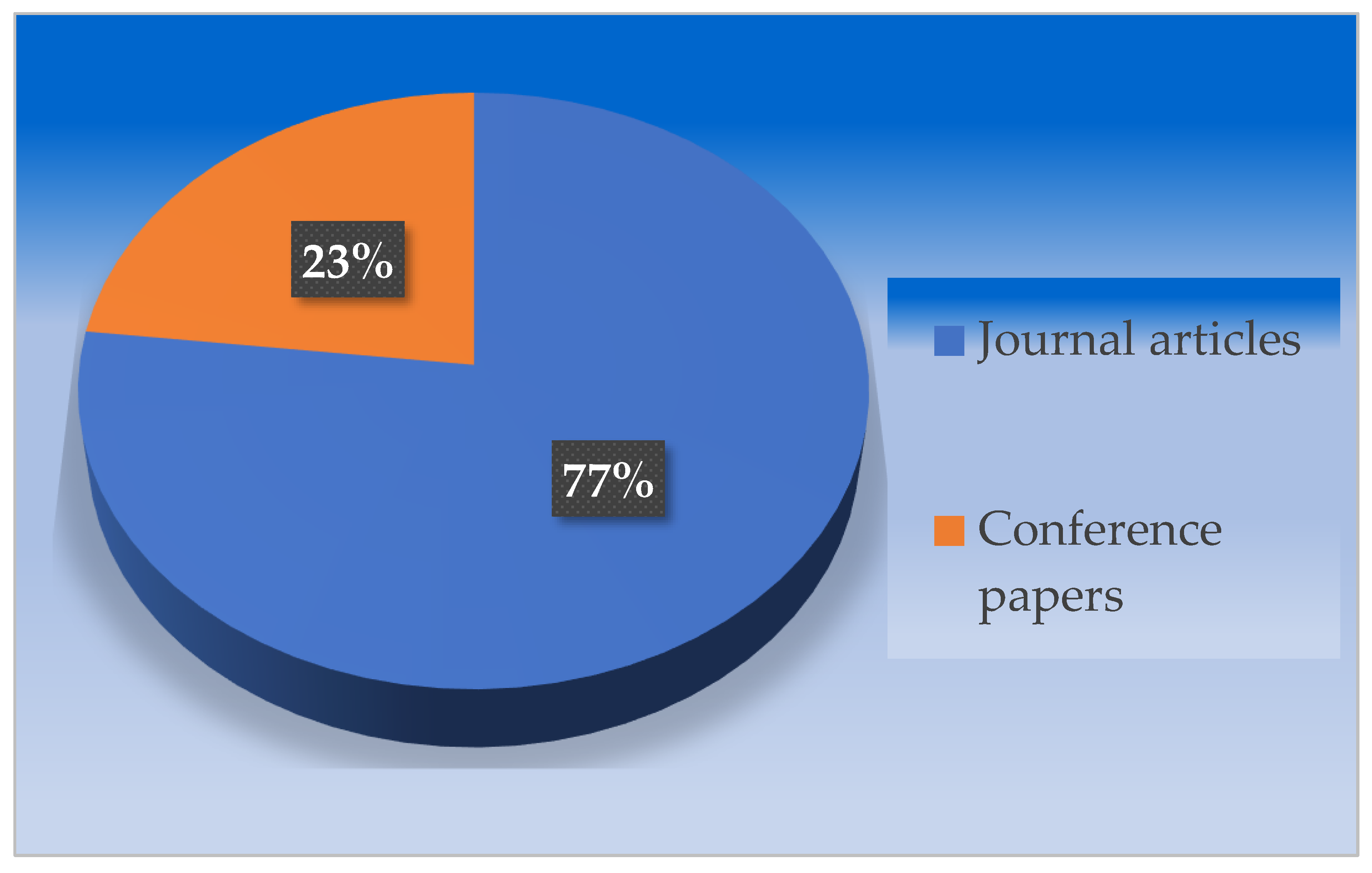
- All mentioned publications are classified into two major categories, namely journal articles and conference papers.
- The impact of the journals and conferences that have the highest influence is estimated based on the total number of publications per journal or conference. This provides the researcher with information regarding the frequency of publishing (announcement) in a journal (conference) and facilitates the selection of a journal or conference at which he/she can publish (present) a research work.
- The contribution of each work is given analytically in a table, allowing the researcher to quickly grasp the topic of the work and gain a general understanding of it.
- A categorization taking into consideration the various methods or techniques employed with big data is carried out.
- A classification considering the big data topics in smart grids is conducted.
- Future works and challenges of big data analytics applications and topics in smart grids are pointed out.
2. Chronological Distribution, Classification of Works and Impacts
3. Contribution of Published Works
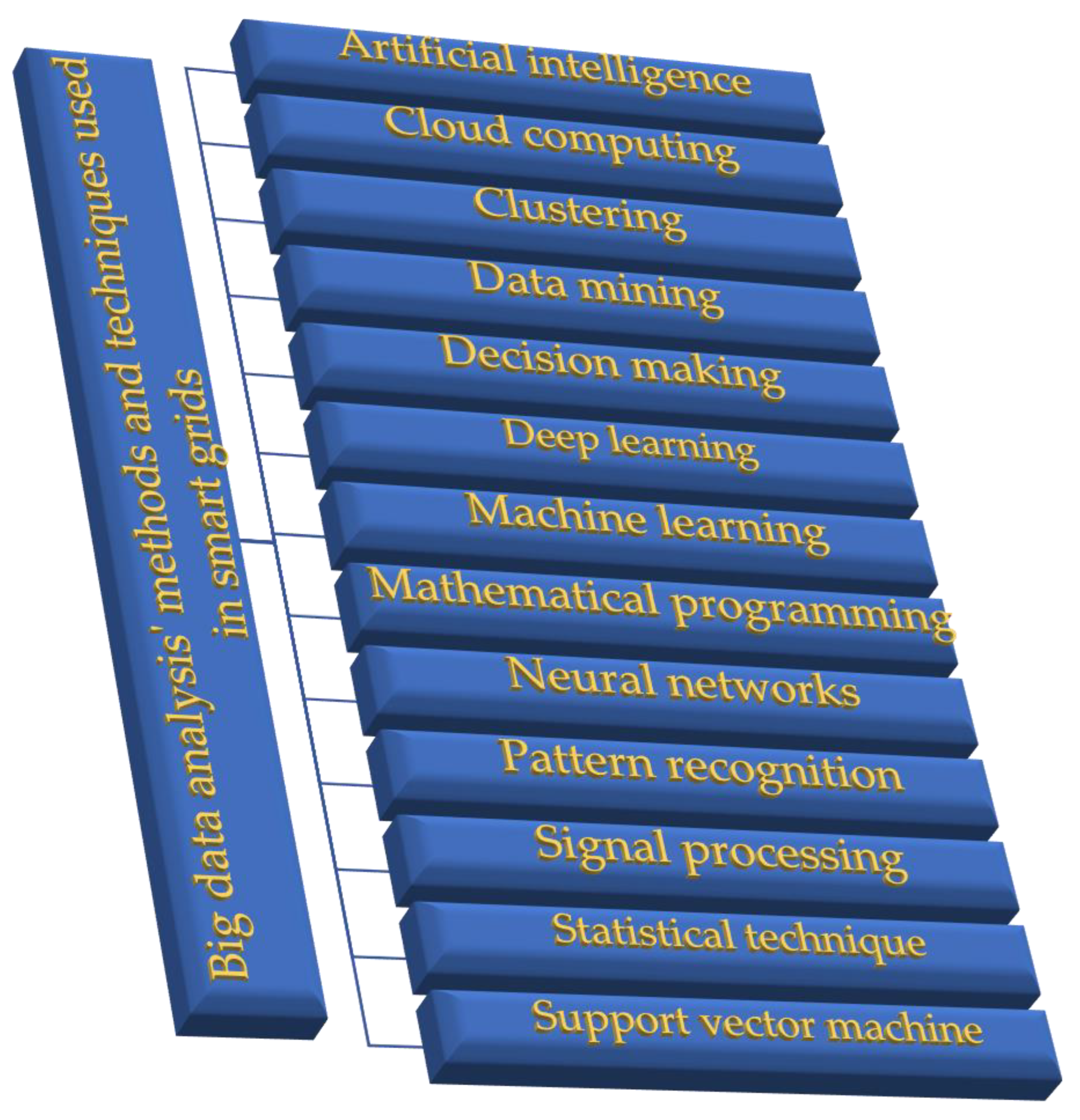
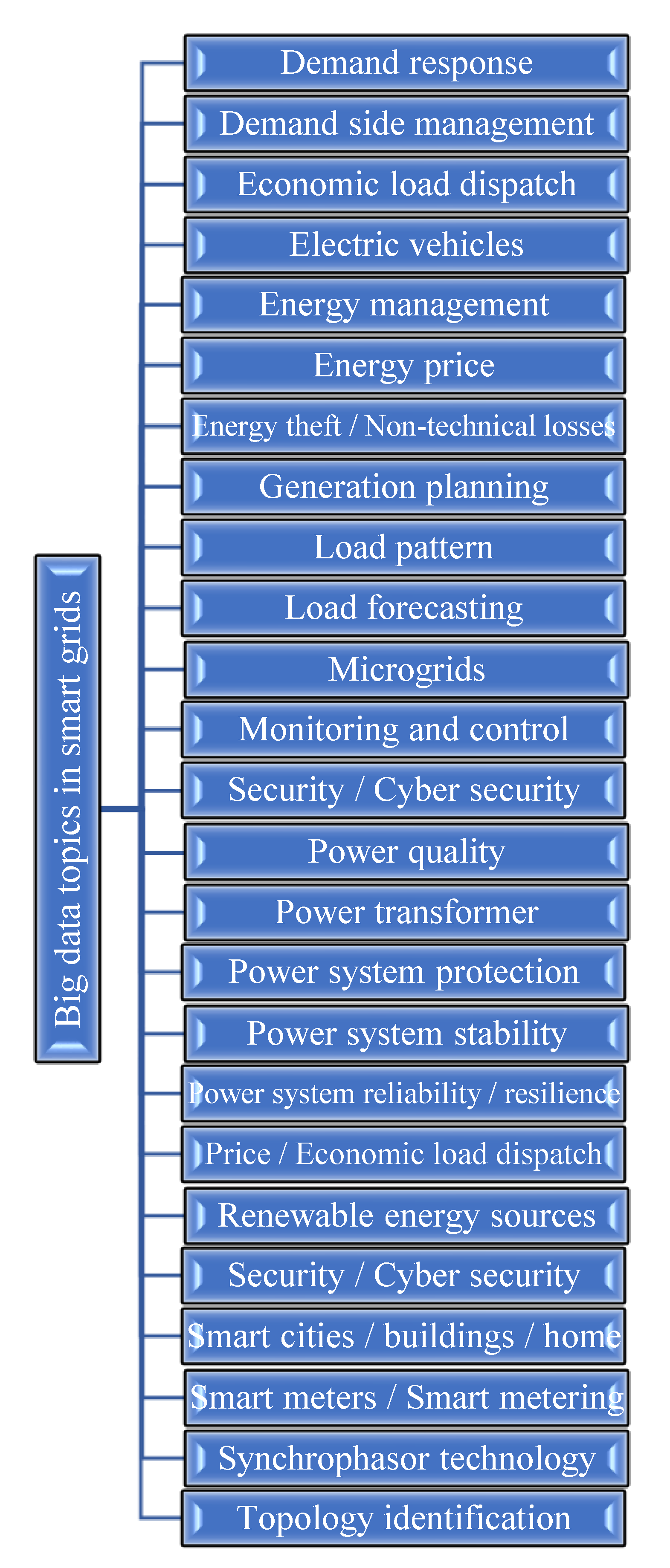
4. Classification of Publications Considering Big Data Analysis Methods or Techniques and Big Data Topics in Smart Grids
5. Future Research Works and Challenges of Big Data Analytics Applications and Topics in Smart Grids
- Study of electromagnetic disturbances, which affect the electronically based equipment of smart grids.
- Innovative strategies and fresh points of view to effectively solve the problem of power quality in smart grids.
- Determination of the fundamental components of smart meter analytics, which will allow the vast variety of smart metering solutions to be linked together and the primary analytical endeavors to be identified.
- New processes and workflows for diagnostics in real time.
- Customer engagement in initiatives utilizing demand response.
- Study of the interconnected system’s economic and financial growth.
- Techniques that are focused on the decrease of losses in various smart grid’s communication technologies.
- Analysis of the energy sustainability based on consumers effectively and cooperatively control the amount of energy they use and then communicate relevant information with one another.
- Addressing issues with traffic engineering, economic models, energy portfolio management, and conceptualizing process-level energy use.
- Sustainability to the big data industry in terms of smart grid.
- Techniques for protection of smart grids to guarantee their reliability and stability.
- Load control and demand response analysis as well as real-time pricing applications.
- Analysis of electrical load patterns and forecasting techniques for demand and generation (renewable or not).
- Techniques reducing security risks and improving the disaster recovery ability of smart grids.
- Techniques that incorporate renewable energy sources to smart grids.
- Efficient cryptographic schemes.
- Penalty and incentive mechanisms.
- Optimal allocation of smart metering devices.
- Advanced security and data communication techniques for integration, control, and monitoring of smart grid.
- A unified and complete standard for smart grids.
- Defending mechanisms against cyber attacks.
- Predictive models for different climatic and topographic conditions.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, X.; Misra, S.; Xue, G.; Yang, D. Smart Grid — The New and Improved Power Grid: A Survey. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2012, 14, 944–980. [CrossRef]
- Tuballa, M.L.; Abundo, M.L. A Review of the Development of Smart Grid Technologies. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016, 59, 710–725. [CrossRef]
- Farhangi, H. The Path of the Smart Grid. IEEE Power and Energy Magazine 2010, 8, 18–28. [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Chen, H.-H.; Huang, Y.-R.; Meng, W. Smart Grid Communication: Its Challenges and Opportunities. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2013, 4, 36–46. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, B.; Rabelo, L.; Gutierrez-Franco, E.; Clavijo-Buritica, N. Machine Learning for Short-Term Load Forecasting in Smart Grids. Energies 2022, 15, 8079. [CrossRef]
- Gerasopoulos, S.I.; Manousakis, N.M.; Psomopoulos, C.S. Smart Metering in EU and the Energy Theft Problem. Energy Efficiency 2022, 15. [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Mao, S.; Liu, Y. Big Data: A Survey. Mobile Networks and Applications 2014, 19, 171–209. [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Yaqoob, I.; Hashem, I.A.T.; Inayat, Z.; Mahmoud Ali, W.K.; Alam, M.; Shiraz, M.; Gani, A. Big Data: Survey, Technologies, Opportunities, and Challenges. The Scientific World Journal 2014, 2014, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Kaisler, S.; Armour, F.; Espinosa, J.A.; Money, W. Big Data: Issues and Challenges Moving Forward. 2013 46th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences 2013. [CrossRef]
- Saggi, M.K.; Jain, S. A Survey towards an Integration of Big Data Analytics to Big Insights for Value-Creation. Information Processing & Management 2018, 54, 758–790. [CrossRef]
- Aalami, H.A.; Moghaddam, M.P.; Yousefi, G.R. Modeling and Prioritizing Demand Response Programs in Power Markets. Electric Power Systems Research 2010, 80, 426–435. [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Nasser, M.; Mahmoud, K. Accurate Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Models Using Deep LSTM- RNN. Neural Computing and Applications 2017, 31, 2727–2740. [CrossRef]
- Abdoos, A.A.; Khorshidian Mianaei, P.; Rayatpanah Ghadikolaei, M. Combined VMD-SVM Based Feature Selection Method for Classification of Power Quality Events. Applied Soft Computing 2016, 38, 637–646. [CrossRef]
- Abuella, M.; Chowdhury, B. Solar Power Probabilistic Forecasting by Using Multiple Linear Regression Analysis. SoutheastCon 2015 2015. [CrossRef]
- Achlerkar, P.D.; Samantaray, S.R.; Sabarimalai Manikandan, M. Variational Mode Decomposition and Decision Tree Based Detection and Classification of Power Quality Disturbances in Grid-Connected Distributed Generation System. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2018, 9, 3122–3132. [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Balance, J.; Bhargava, B.; Dyer, J.; Martin, K.; Mo, J. Real Time Dynamics Monitoring System (RTDMS®) for Use with SynchroPhasor Technology in Power Systems. 2011 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting 2011. [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Tsoukalas, L.H. Smart Grids: Importance of Power Quality. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering 2011, 136–143. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.W.; Mourshed, M.; Rezgui, Y. Trees vs Neurons: Comparison between Random Forest and ANN for High-Resolution Prediction of Building Energy Consumption. Energy and Buildings 2017, 147, 77–89. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Awais, M.; Naeem, M.; Iqbal, M.; Ejaz, W.; Anpalagan, A.; Kim, H. Multiple Power Line Outage Detection in Smart Grids: Probabilistic Bayesian Approach. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 10650–10661. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Krishnan, V.V.G.; Foroutan, S.A.; Touhiduzzaman, M.; Srivastava, A.; Wu, Y.; Hahn, A.; Sindhu, S. Cyber Physical Security Analytics for Anomalies in Transmission Protection Systems. 2018 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting (IAS) 2018. [CrossRef]
- Aizpurua, J.I.; Garro, U.; Muxika, E.; Mendicute, M.; Gilbert, I.P.; Stewart, B.G.; McArthur, S.D.J.; Lambert, B. Probabilistic Power Transformer Condition Monitoring in Smart Grids. 2019 6th International Advanced Research Workshop on Transformers (ARWtr) 2019. [CrossRef]
- Akbari, E.; Teimouri, A.R.; Saki, M.; Rezaei, M.A.; Hu, J.; Band, S.; Pai, H.-T.; Mosavi, A. A Fault-Tolerant Cascaded Switched-Capacitor Multilevel Inverter for Domestic Applications in Smart Grids. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 110590–110602. [CrossRef]
- Alahakoon, D.; Yu, X. Smart Electricity Meter Data Intelligence for Future Energy Systems: A Survey. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2016, 12, 425–436. [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Dong, Z.Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, P. RSA-Grid: A Grid Computing Based Framework for Power System Reliability and Security Analysis. 2006 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting 2006. [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.M.; Jawad, M.; Khan, B.; Mehmood, C.A.; Zeb, N.; Tanoli, A.; Farid, U.; Glower, J.; Khan, S.U. Wide Area Smart Grid Architectural Model and Control: A Survey. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016, 64, 311–328. [CrossRef]
- Allen, W.H.; Rubaai, A.; Chawla, R. Fuzzy Neural Network-Based Health Monitoring for HVAC System Variable-Air-Volume Unit. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2016, 52, 2513–2524. [CrossRef]
- Alrasheedi, A.; Almalaq, A. Hybrid Deep Learning Applied on Saudi Smart Grids for Short-Term Load Forecasting. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2666. [CrossRef]
- Aman, S.; Simmhan, Y.; Prasanna, V.K. Energy Management Systems: State of the Art and Emerging Trends. IEEE Communications Magazine 2013, 51, 114–119. [CrossRef]
- Amin, M. Challenges in Reliability, Security, Efficiency, and Resilience of Energy Infrastructure: Toward Smart Self-Healing Electric Power Grid. 2008 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting - Conversion and Delivery of Electrical Energy in the 21st Century 2008. [CrossRef]
- Amjady, N. Short-Term Bus Load Forecasting of Power Systems by a New Hybrid Method. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2007, 22, 333–341. [CrossRef]
- Amjady, N.; Keynia, F. A New Neural Network Approach to Short Term Load Forecasting of Electrical Power Systems. Energies 2011, 4, 488–503. [CrossRef]
- Arif, A.; Alghamdi, T.A.; Khan, Z.A.; Javaid, N. Towards Efficient Energy Utilization Using Big Data Analytics in Smart Cities for Electricity Theft Detection. Big Data Research 2022, 27, 100285. [CrossRef]
- Asad, Z.; Rehman Chaudhry, M.A. A Two-Way Street: Green Big Data Processing for a Greener Smart Grid. IEEE Systems Journal 2017, 11, 784–795. [CrossRef]
- Azimi, R.; Ghayekhloo, M.; Ghofrani, M. A Hybrid Method Based on a New Clustering Technique and Multilayer Perceptron Neural Networks for Hourly Solar Radiation Forecasting. Energy Conversion and Management 2016, 118, 331–344. [CrossRef]
- Babakmehr, M.; Simoes, M.G.; Wakin, M.B.; Harirchi, F. Compressive Sensing-Based Topology Identification for Smart Grids. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2016, 12, 532–543. [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.; Vu, Q.H.; Liu, J.K.; Huang, X.; Xiang, Y. A Secure Cloud Computing Based Framework for Big Data Information Management of Smart Grid. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing 2015, 3, 233–244. [CrossRef]
- Baltas, G.N.; Perales-Gonzalez, C.; Mazidi, P.; Fernandez, F.; Rodriguez, P. A Novel Ensemble Approach for Solving the Transient Stability Classification Problem. 2018 7th International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA) 2018. [CrossRef]
- Bansal, S.K. Towards a Semantic Extract-Transform-Load (ETL) Framework for Big Data Integration. 2014 IEEE International Congress on Big Data 2014. [CrossRef]
- Basu, C.; Agrawal, A.; Hazra, J.; Kumar, A.; Seetharam, D.P.; Beland, J.; Guillon, S.; Kamwa, I.; Lafond, C. Understanding Events for Wide-Area Situational Awareness. ISGT 2014 2014. [CrossRef]
- Bei Xu; Abur, A. Observability Analysis and Measurement Placement for Systems with PMUs. IEEE PES Power Systems Conference and Exposition, 2004.. [CrossRef]
- Ben Taieb, S.; Huser, R.; Hyndman, R.J.; Genton, M.G. Forecasting Uncertainty in Electricity Smart Meter Data by Boosting Additive Quantile Regression. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2448–2455. [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.; Highfill, D. Networking AMI Smart Meters. 2008 IEEE Energy 2030 Conference 2008. [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.; Misra, S.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. Cloud Computing Applications for Smart Grid: A Survey. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems 2015, 26, 1477–1494. [CrossRef]
- Berrisford, A.J. A Tale of Two Transformers: An Algorithm for Estimating Distribution Secondary Electric Parameters Using Smart Meter Data. 2013 26th IEEE Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE) 2013. [CrossRef]
- Bessa, R.J.; Trindade, A.; Silva, C.S.P.; Miranda, V. Probabilistic Solar Power Forecasting in Smart Grids Using Distributed Information. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2015, 72, 16–23. [CrossRef]
- Bharothu, J.N.; Sridhar, M.; Rao, R.S. A Literature Survey Report on Smart Grid Technologies. 2014 International Conference on Smart Electric Grid (ISEG) 2014. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Chattopadhyay, P.K. Biogeography-Based Optimization for Different Economic Load Dispatch Problems. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2010, 25, 1064–1077. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Chattopadhyay, P.K. Hybrid Differential Evolution With Biogeography-Based Optimization for Solution of Economic Load Dispatch. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2010, 25, 1955–1964. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Chattopadhyay, P.K. Solving Complex Economic Load Dispatch Problems Using Biogeography-Based Optimization. Expert Systems with Applications 2010, 37, 3605–3615. [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, B.P.; Paudyal, S.; Luo, Y.; Mohanpurkar, M.; Cheung, K.; Tonkoski, R.; Hovsapian, R.; Myers, K.S.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, P.; et al. Big Data Analytics in Smart Grids: State-of-the-art, Challenges, Opportunities, and Future Directions. IET Smart Grid 2019, 2, 141–154. [CrossRef]
- Botte, B.; Cannatelli, V.; Rogai, S. The Telegestore Project in ENEL’s Metering System. 18th International Conference and Exhibition on Electricity Distribution (CIRED 2005) 2005. [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Gu, J.; Ma, J.; Jin, Z. Probabilistic Wind Power Forecasting Approach via Instance-Based Transfer Learning Embedded Gradient Boosting Decision Trees. Energies 2019, 12, 159. [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chow, M.-Y. Exploratory Analysis of Massive Data for Distribution Fault Diagnosis in Smart Grids. 2009 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting 2009. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Song, H.; Kaiwartya, O.; Zhou, B.; Zhuang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, X. Mobile Edge Computing for Big-Data-Enabled Electric Vehicle Charging. IEEE Communications Magazine 2018, 56, 150–156. [CrossRef]
- Catalao, J.P.S.; Pousinho, H.M.I.; Mendes, V.M.F. An Artificial Neural Network Approach for Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting in Portugal. 2009 15th International Conference on Intelligent System Applications to Power Systems 2009. [CrossRef]
- Cavraro, G.; Kekatos, V. Graph Algorithms for Topology Identification Using Power Grid Probing. IEEE Control Systems Letters 2018, 2, 689–694. [CrossRef]
- Chahine, K.; Drissi, K.E.K.; Pasquier, C.; Kerroum, K.; Faure, C.; Jouannet, T.; Michou, M. Electric Load Disaggregation in Smart Metering Using a Novel Feature Extraction Method and Supervised Classification. Energy Procedia 2011, 6, 627–632. [CrossRef]
- Chaouch, M. Clustering-Based Improvement of Nonparametric Functional Time Series Forecasting: Application to Intra-Day Household-Level Load Curves. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2014, 5, 411–419. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Ghoshal, S.P.; Mukherjee, V. Solution of Combined Economic and Emission Dispatch Problems of Power Systems by an Opposition-Based Harmony Search Algorithm. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2012, 39, 9–20. [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Wang, J. Short-Term Load Forecasting Using a Kernel-Based Support Vector Regression Combination Model. Applied Energy 2014, 132, 602–609. [CrossRef]
- Chehri, A.; Fofana, I.; Yang, X. Security Risk Modeling in Smart Grid Critical Infrastructures in the Era of Big Data and Artificial Intelligence. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3196. [CrossRef]
- Chelmis, C.; Kolte, J.; Prasanna, V.K. Big Data Analytics for Demand Response: Clustering over Space and Time. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data) 2015. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Duan, S.; Cai, T.; Liu, B. Online 24-h Solar Power Forecasting Based on Weather Type Classification Using Artificial Neural Network. Solar Energy 2011, 85, 2856–2870. [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Giannakis, G.B. Robust Workload and Energy Management for Sustainable Data Centers. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2016, 34, 651–664. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, L.; Kumar, P.R. Power System Event Classification via Dimensionality Reduction of Synchrophasor Data. 2014 IEEE 8th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop (SAM) 2014. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Wang, J.; Dominguez-Garcia, A.D.; Sauer, P.W. Measurement-Based Estimation of the Power Flow Jacobian Matrix. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2507–2515. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, M.; Ji, T.; Wu, Q. Real-time Recognition of Power Quality Disturbance-based Deep Belief Network Using Embedded Parallel Computing Platform. IEEJ Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering 2020, 15, 519–526. [CrossRef]
- Chicco, G. Overview and Performance Assessment of the Clustering Methods for Electrical Load Pattern Grouping. Energy 2012, 42, 68–80. [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Qiu, R.; He, X.; Ling, Z.; Liu, Y. Massive Streaming PMU Data Modelling and Analytics in Smart Grid State Evaluation Based on Multiple High-Dimensional Covariance Test. IEEE Transactions on Big Data 2018, 4, 55–64. [CrossRef]
- Chung-Hsiao Wang; Min, K.J. Electric Power Generation Planning for Interrelated Projects: A Real Options Approach. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management 2006, 53, 312–322. [CrossRef]
- Cindy Tan, H.F.; Lok Woo, W.; Sharma, A.; Logenthiran, T.; Kumar, D.S. Study of Smart Condition Monitoring Using Deep Neural Networks with Dropouts and Cross-Validation. 2019 IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies - Asia (ISGT Asia) 2019. [CrossRef]
- Coelho, I.M.; Coelho, V.N.; Luz, E.J. da S.; Ochi, L.S.; Guimarães, F.G.; Rios, E. A GPU Deep Learning Metaheuristic Based Model for Time Series Forecasting. Applied Energy 2017, 201, 412–418. [CrossRef]
- Dahal, N.; Abuomar, O.; King, R.; Madani, V. Event Stream Processing for Improved Situational Awareness in the Smart Grid. Expert Systems with Applications 2015, 42, 6853–6863. [CrossRef]
- Dahal, N.; King, R.L.; Madani, V. Online Dimension Reduction of Synchrophasor Data. PES T&D 2012 2012. [CrossRef]
- Dahal, O.P.; Brahma, S.M.; Cao, H. Comprehensive Clustering of Disturbance Events Recorded by Phasor Measurement Units. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 2014, 29, 1390–1397. [CrossRef]
- Daki, H.; El Hannani, A.; Aqqal, A.; Haidine, A.; Dahbi, A. Big Data Management in Smart Grid: Concepts, Requirements and Implementation. Journal of Big Data 2017, 4. [CrossRef]
- Dang-Ha, T.-H.; Olsson, R.; Wang, H. The Role of Big Data on Smart Grid Transition. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Smart City/SocialCom/SustainCom (SmartCity) 2015. [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Paramasivam, M.; Vaidya, U.; Ajjarapu, V. PMU-Based Model-Free Approach for Real-Time Rotor Angle Monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2015, 30, 2818–2819. [CrossRef]
- De Santis, E.; Livi, L.; Sadeghian, A.; Rizzi, A. Modeling and Recognition of Smart Grid Faults by a Combined Approach of Dissimilarity Learning and One-Class Classification. Neurocomputing 2015, 170, 368–383. [CrossRef]
- de Souza, J.C.S.; Assis, T.M.L.; Pal, B.C. Data Compression in Smart Distribution Systems via Singular Value Decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2017, 8, 275–284. [CrossRef]
- Depuru, S.S.S.R.; Wang, L.; Devabhaktuni, V. Support Vector Machine Based Data Classification for Detection of Electricity Theft. 2011 IEEE/PES Power Systems Conference and Exposition 2011. [CrossRef]
- Diamantoulakis, P.D.; Kapinas, V.M.; Karagiannidis, G.K. Big Data Analytics for Dynamic Energy Management in Smart Grids. Big Data Research 2015, 2, 94–101. [CrossRef]
- Dieb Martins, A.; Gurjao, E.C. Processing of Smart Meters Data Based on Random Projections. 2013 IEEE PES Conference on Innovative Smart Grid Technologies (ISGT Latin America) 2013. [CrossRef]
- Fallah, S.; Deo, R.; Shojafar, M.; Conti, M.; Shamshirband, S. Computational Intelligence Approaches for Energy Load Forecasting in Smart Energy Management Grids: State of the Art, Future Challenges, and Research Directions. Energies 2018, 11, 596. [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Chen, L. Short-Term Load Forecasting Based on an Adaptive Hybrid Method. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2006, 21, 392–401. [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Hyndman, R.J. Short-Term Load Forecasting Based on a Semi-Parametric Additive Model. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2012, 27, 134–141. [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Yin, X.; Tan, Y.; Li, C.; Gao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, J. The Contributions of Cloud Technologies to Smart Grid. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016, 59, 1326–1331. [CrossRef]
- Fei, S.; Zhang, X. Fault Diagnosis of Power Transformer Based on Support Vector Machine with Genetic Algorithm. Expert Systems with Applications 2009, 36, 11352–11357. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.M.S.; Cavalcante, C.A.M.T.; Fontes, C.H.O.; Marambio, J.E.S. A New Method for Pattern Recognition in Load Profiles to Support Decision-Making in the Management of the Electric Sector. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2013, 53, 824–831,.
- Fu-lin, M.; Hong-yang, L. Power Load Classification Based on Spectral Clustering of Dual-Scale. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Control Science and Systems Engineering 2014. [CrossRef]
- Gerbec, D.; Gasperic, S.; Gubina, F. Determination and Allocation of Typical Load Profiles to the Eligible Consumers. 2003 IEEE Bologna Power Tech Conference Proceedings. [CrossRef]
- Ghamkhari, M.; Mohsenian-Rad, H. Energy and Performance Management of Green Data Centers: A Profit Maximization Approach. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2013, 4, 1017–1025. [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Luh, P.B.; Michel, L.D.; Wang, Y.; Friedland, P.B. Very Short-Term Load Forecasting: Wavelet Neural Networks With Data Pre-Filtering. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2013, 28, 30–41. [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Du, X. Achieving Efficient and Secure Data Acquisition for Cloud-Supported Internet of Things in Smart Grid. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2017, 4, 1934–1944. [CrossRef]
- Gulbinas, R.; Khosrowpour, A.; Taylor, J. Segmentation and Classification of Commercial Building Occupants by Energy-Use Efficiency and Predictability. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2015, 6, 1414–1424. [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.K.; Alkhalifah, A.; Islam, S.; Babiker, N.B.M.; Habib, A.K.M.A.; Aman, A.H.M.; Hossain, Md.A. Blockchain Technology on Smart Grid, Energy Trading, and Big Data: Security Issues, Challenges, and Recommendations. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing 2022, 2022, 1–26, doi.org:10.1155/2022/9065768.
- Hashemipour, S.; Aghaei, J.; Kavousi-fard, A.; Taher, N.; Salimi, L.; Granado, P.C. del; Shafie-Khah, M.; Wang, F.; Catalao, J.P.S. Optimal Singular Value Decomposition Based Big Data Compression Approach in Smart Grids. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2021, 57, 3296–3305. [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Guan, L.; Mo, W. A Method for Transient Stability Assessment Based on Pattern Recognition. 2016 International Conference on Smart Grid and Clean Energy Technologies (ICSGCE) 2016. [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Kumar, N.; Zeadally, S.; Vinel, A.; Yang, L.T. Efficient and Privacy-Preserving Data Aggregation Scheme for Smart Grid Against Internal Adversaries. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2017, 8, 2411–2419. [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Murugesan, S.; Zhang, J. Multiple Timescale Dispatch and Scheduling for Stochastic Reliability in Smart Grids with Wind Generation Integration. 2011 Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM 2011. [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Ai, Q.; Qiu, R.C.; Huang, W.; Piao, L.; Liu, H. A Big Data Architecture Design for Smart Grids Based on Random Matrix Theory. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2015, 1–1. [CrossRef]
- Hernández, L.; Baladrón, C.; Aguiar, J.M.; Carro, B.; Sánchez-Esguevillas, A.; Lloret, J. Artificial Neural Networks for Short-Term Load Forecasting in Microgrids Environment. Energy 2014, 75, 252–264. [CrossRef]
- Hocaoglu, F.O.; Serttas, F. A Novel Hybrid (Mycielski-Markov) Model for Hourly Solar Radiation Forecasting. Renewable Energy 2017, 108, 635–643. [CrossRef]
- Hong, T. Big Data Analytics: Making the Smart Grid Smarter [Guest Editorial]. IEEE Power and Energy Magazine 2018, 16, 12–16. [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.-C. Application of Chaotic Ant Swarm Optimization in Electric Load Forecasting. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 5830–5839. [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.-C. Electric Load Forecasting by Seasonal Recurrent SVR (Support Vector Regression) with Chaotic Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm. Energy 2011, 36, 5568–5578. [CrossRef]
- Hossain, E.; Khan, I.; Un-Noor, F.; Sikander, S.S.; Sunny, Md.S.H. Application of Big Data and Machine Learning in Smart Grid, and Associated Security Concerns: A Review. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 13960–13988. [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, Z.S.; Mahoor, M.; Khodaei, A. AMI-Enabled Distribution Network Line Outage Identification via Multi-Label SVM. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2018, 9, 5470–5472. [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Ning, Z.; Guo, L.; Zhang, X. Temporal, Functional and Spatial Big Data Computing Framework for Large-Scale Smart Grid. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing 2019, 7, 369–379. [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Vasilakos, A.V. Energy Big Data Analytics and Security: Challenges and Opportunities. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2423–2436. [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zareipour, H.; Rosehart, W.D.; Amjady, N. Data Mining for Electricity Price Classification and the Application to Demand-Side Management. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2012, 3, 808–817. [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, S.; Davis, K. Energy Theft Detection Via Artificial Neural Networks. 2018 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference Europe (ISGT-Europe) 2018. [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, N.E.; Ruschmann, M.C. Data-Availability-Constrained Placement of PMUs and Communication Links in a Power System. IEEE Systems Journal 2014, 8, 483–492. [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Md.M.; Beg, M.M.S.; Alam, M.S. Fog Computing for Big Data Analytics in IoT Aided Smart Grid Networks. Wireless Personal Communications 2020, 114, 3395–3418. [CrossRef]
- Jakubiec, J.A.; Reinhart, C.F. A Method for Predicting City-Wide Electricity Gains from Photovoltaic Panels Based on LiDAR and GIS Data Combined with Hourly Daysim Simulations. Solar Energy 2013, 93, 127–143. [CrossRef]
- Jaradat, M.; Jarrah, M.; Bousselham, A.; Jararweh, Y.; Al-Ayyoub, M. The Internet of Energy: Smart Sensor Networks and Big Data Management for Smart Grid. Procedia Computer Science 2015, 56, 592–597. [CrossRef]
- Javaid, N.; Jan, N.; Javed, M.U. An Adaptive Synthesis to Handle Imbalanced Big Data with Deep Siamese Network for Electricity Theft Detection in Smart Grids. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing 2021, 153, 44–52. [CrossRef]
- Je, S.; Huh, J. Estimation of Future Power Consumption Level in Smart Grid: Application of Fuzzy Logic and Genetic Algorithm on Big Data Platform. International Journal of Communication Systems 2019, 34. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Dai, X.; Gao, D.W.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, Y.; Muljadi, E. Spatial-Temporal Synchrophasor Data Characterization and Analytics in Smart Grid Fault Detection, Identification, and Impact Causal Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2525–2536. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhang, Y. Energy Big Data: A Survey. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 3844–3861. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Mu, Y.; Jia, H.; Lu, N.; Yuan, H.; Yan, J.; Li, W. A Novel Dominant Mode Estimation Method for Analyzing Inter-Area Oscillation in China Southern Power Grid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2549–2560. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, C.-C.; Diedesch, M.; Lee, E.; Srivastava, A.K. Outage Management of Distribution Systems Incorporating Information From Smart Meters. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2016, 31, 4144–4154. [CrossRef]
- Jindal, A.; Dua, A.; Kaur, K.; Singh, M.; Kumar, N.; Mishra, S. Decision Tree and SVM-Based Data Analytics for Theft Detection in Smart Grid. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2016, 12, 1005–1016. [CrossRef]
- Jindal, A.; Kumar, N.; Singh, M. A Unified Framework for Big Data Acquisition, Storage, and Analytics for Demand Response Management in Smart Cities. Future Generation Computer Systems 2020, 108, 921–934. [CrossRef]
- Jokar, P.; Arianpoo, N.; Leung, V.C.M. Electricity Theft Detection in AMI Using Customers’ Consumption Patterns. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2016, 7, 216–226. [CrossRef]
- Jota, P.R.S.; Silva, V.R.B.; Jota, F.G. Building Load Management Using Cluster and Statistical Analyses. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2011, 33, 1498–1505. [CrossRef]
- Kamwa, I.; Beland, J.; Trudel, G.; Grondin, R.; Lafond, C.; McNabb, D. Wide-Area Monitoring and Control at Hydro-Quebec: Past, Present and Future. 2006 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting 2006. [CrossRef]
- Kezunovic, M.; Xie, L.; Grijalva, S. The Role of Big Data in Improving Power System Operation and Protection. 2013 IREP Symposium Bulk Power System Dynamics and Control - IX Optimization, Security and Control of the Emerging Power Grid 2013. [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.U.; Javaid, N.; Taylor, C.J.; Gamage, K.A.A.; Ma, X. Big Data Analytics for Electricity Theft Detection in Smart Grids. 2021 IEEE Madrid PowerTech 2021. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Li, M.; Ashton, P.; Taylor, G.; Liu, J. Big Data Analytics on PMU Measurements. 2014 11th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (FSKD) 2014. [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, J.; Fan, L.; Jiang, W.; Manjure, D. Distributed Prony Analysis for Real-World PMU Data. Electric Power Systems Research 2016, 133, 113–120. [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A.; Nahavandi, S.; Creighton, D. Quantifying Uncertainties of Neural Network-Based Electricity Price Forecasts. Applied Energy 2013, 112, 120–129. [CrossRef]
- Klump, R.; Agarwal, P.; Tate, J.E.; Khurana, H. Lossless Compression of Synchronized Phasor Measurements. IEEE PES General Meeting 2010. [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Dong, Z.Y.; Jia, Y.; Hill, D.J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Short-Term Residential Load Forecasting Based on LSTM Recurrent Neural Network. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2019, 10, 841–851. [CrossRef]
- Kotsiopoulos, T.; Sarigiannidis, P.; Ioannidis, D.; Tzovaras, D. Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Smart Manufacturing: The Smart Grid Paradigm. Computer Science Review 2021, 40, 100341. [CrossRef]
- Kusiak, A.; Haiyang Zheng; Zhe Song Short-Term Prediction of Wind Farm Power: A Data Mining Approach. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2009, 24, 125–136. [CrossRef]
- Kwac, J.; Rajagopal, R. Data-Driven Targeting of Customers for Demand Response. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2199–2207. [CrossRef]
- Lazzaretti, A.E.; Tax, D.M.J.; Vieira Neto, H.; Ferreira, V.H. Novelty Detection and Multi-Class Classification in Power Distribution Voltage Waveforms. Expert Systems with Applications 2016, 45, 322–330. [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Shiyan, L.; Chuanwen, J.; Hongling, L.; Yan, Z. A Review on the Forecasting of Wind Speed and Generated Power. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2009, 13, 915–920. [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jayaweera, S.K. Machine-Learning Aided Optimal Customer Decisions for an Interactive Smart Grid. IEEE Systems Journal 2015, 9, 1529–1540. [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xu, M.; Cao, W.; Gao, P. Researches on Data Processing and Data Preventing Technologies in the Environment of Big Data in Power System. 2015 5th International Conference on Electric Utility Deregulation and Restructuring and Power Technologies (DRPT) 2015. [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhu, W.; Saunders, C.; Gao, F.; Yu, Y. Real-Time Complex Event Processing and Analytics for Smart Grid. Procedia Computer Science 2015, 61, 113–119. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ning, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.T. Aggregated-Proofs Based Privacy-Preserving Authentication for V2G Networks in the Smart Grid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2012, 3, 1722–1733. [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Fan, W.; Liu, J. A Hybrid Forecasting Model with Parameter Optimization for Short-Term Load Forecasting of Micro-Grids. Applied Energy 2014, 129, 336–345. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Markham, P.N.; Zhou, D.; Guo, J.; Lei, Y.; Kou, G.; Yao, W.; Chai, J.; et al. Wide-Area-Measurement System Development at the Distribution Level: An FNET/GridEye Example. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 2016, 31, 721–731. [CrossRef]
- López, J.J.; Aguado, J.A.; Martín, F.; Muñoz, F.; Rodríguez, A.; Ruiz, J.E. Hopfield–K-Means Clustering Algorithm: A Proposal for the Segmentation of Electricity Customers. Electric Power Systems Research 2011, 81, 716–724. [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, K.; Li, Y.; Cai, D.; Zhao, C.; Meng, Q. Three-Layer Bayesian Network for Classification of Complex Power Quality Disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2018, 14, 3997–4006. [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Luo, X.; Litvinov, E. Cloud Computing for Power System Simulations at ISO New England—Experiences and Challenges. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2596–2603. [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Fang, S.; Yuan, D.; Wang, X. The Design of Power Security System in Smart Home Based on the Stream Data Mining. Advanced Data Mining and Applications 2014, 716–724. [CrossRef]
- Macedo, M.N.Q.; Galo, J.J.M.; de Almeida, L.A.L.; de C. Lima, A.C. Demand Side Management Using Artificial Neural Networks in a Smart Grid Environment. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2015, 41, 128–133. [CrossRef]
- Markovic, D.S.; Zivkovic, D.; Branovic, I.; Popovic, R.; Cvetkovic, D. Smart Power Grid and Cloud Computing. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2013, 24, 566–577. [CrossRef]
- Mayilvaganan, M.; Sabitha, M. A Cloud-Based Architecture for Big-Data Analytics in Smart Grid: A Proposal. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research 2013. [CrossRef]
- Meier, R.; Cotilla-Sanchez, E.; McCamish, B.; Chiu, D.; Histand, M.; Landford, J.; Bass, R.B. Power System Data Management and Analysis Using Synchrophasor Data. 2014 IEEE Conference on Technologies for Sustainability (SusTech) 2014. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.P.; Samantaray, S.R.; Joos, G. A Combined Wavelet and Data-Mining Based Intelligent Protection Scheme for Microgrid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2295–2304. [CrossRef]
- Moghaddass, R.; Wang, J. A Hierarchical Framework for Smart Grid Anomaly Detection Using Large-Scale Smart Meter Data. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2018, 9, 5820–5830. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Refaat, S.S.; Abu-Rub, H. A Review on Big Data Management and Decision-Making in Smart Grid. Power Electronics and Drives 2019, 4, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Monedero, I.; Biscarri, F.; León, C.; Guerrero, J.I.; Biscarri, J.; Millán, R. Detection of Frauds and Other Non-Technical Losses in a Power Utility Using Pearson Coefficient, Bayesian Networks and Decision Trees. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2012, 34, 90–98. [CrossRef]
- Moslehi, K.; Kumar, R. A Reliability Perspective of the Smart Grid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2010, 1, 57–64. [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, N.; Ramadan, H.S.M.; Elfarouk, O. Renewable Energy Management in Smart Grids by Using Big Data Analytics and Machine Learning. Machine Learning with Applications 2022, 9, 100363. [CrossRef]
- Munshi, A.A.; Mohamed, Y.A.-R.I. Big Data Framework for Analytics in Smart Grids. Electric Power Systems Research 2017, 151, 369–380. [CrossRef]
- Munshi, A.A.; Mohamed, Y.A.-R.I. Data Lake Lambda Architecture for Smart Grids Big Data Analytics. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 40463–40471. [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.; Shabbir, A.; Ul Hassan, N.; Yuen, C.; Ahmad, A.; Tushar, W. Understanding Customer Behavior in Multi-Tier Demand Response Management Program. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 2613–2625. [CrossRef]
- Nagi, J.; Mohammad, A.M.; Yap, K.S.; Tiong, S.K.; Ahmed, S.K. Non-Technical Loss Analysis for Detection of Electricity Theft Using Support Vector Machines. 2008 IEEE 2nd International Power and Energy Conference 2008. [CrossRef]
- Neuhoff, K.; Ehrenmann, A.; Butler, L.; Cust, J.; Hoexter, H.; Keats, K.; Kreczko, A.; Sinden, G. Space and Time: Wind in an Investment Planning Model. Energy Economics 2008, 30, 1990–2008. [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.D. Power Load Forecasting Using Support Vector Machine and Ant Colony Optimization. Expert Systems with Applications 2010, 37, 2531–2539. [CrossRef]
- Nizar, A.H.; Dong, Z.Y.; Jalaluddin, M.; Raffles, M.J. Load Profiling Method in Detecting Non-Technical Loss Activities in a Power Utility. 2006 IEEE International Power and Energy Conference 2006. [CrossRef]
- Nuchprayoon, S. Electricity Load Classification Using K-Means Clustering Algorithm. 5th Brunei International Conference on Engineering and Technology (BICET 2014) 2014. [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, D.; Levorato, M.; Goldsmith, A.; Mitra, U. Residential Demand Response Using Reinforcement Learning. 2010 First IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications 2010. [CrossRef]
- Oldewurtel, F.; Ulbig, A.; Parisio, A.; Andersson, G.; Morari, M. Reducing Peak Electricity Demand in Building Climate Control Using Real-Time Pricing and Model Predictive Control. 49th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) 2010. [CrossRef]
- Palomares-Salas, J.C.; Gonzalez de la Rosa, J.J.; Aguera-Perez, A.; Sierra-Fernandez, J.M. Smart Grids Power Quality Analysis Based in Classification Techniques and Higher-Order Statistics: Proposal for Photovoltaic Systems. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT) 2015. [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Morris, T.; Adhikari, U. Developing a Hybrid Intrusion Detection System Using Data Mining for Power Systems. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2015, 6, 3104–3113. [CrossRef]
- Panapakidis, I.; Asimopoulos, N.; Dagoumas, A.; Christoforidis, G.C. An Improved Fuzzy C-Means Algorithm for the Implementation of Demand Side Management Measures. Energies 2017, 10, 1407. [CrossRef]
- Pappu, S.J.; Bhatt, N.; Pasumarthy, R.; Rajeswaran, A. Identifying Topology of Low Voltage Distribution Networks Based on Smart Meter Data. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2018, 9, 5113–5122. [CrossRef]
- Peppanen, J.; Reno, M.J.; Thakkar, M.; Grijalva, S.; Harley, R.G. Leveraging AMI Data for Distribution System Model Calibration and Situational Awareness. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2015, 6, 2050–2059. [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Chacón, R.; Luna-Romera, J.; Troncoso, A.; Martínez-Álvarez, F.; Riquelme, J. Big Data Analytics for Discovering Electricity Consumption Patterns in Smart Cities. Energies 2018, 11, 683. [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Ketter, W.; Saar-Tsechansky, M.; Collins, J. A Reinforcement Learning Approach to Autonomous Decision-Making in Smart Electricity Markets. Machine Learning 2013, 92, 5–39. [CrossRef]
- Pignati, M.; Zanni, L.; Sarri, S.; Cherkaoui, R.; Le Boudec, J.-Y.; Paolone, M. A Pre-Estimation Filtering Process of Bad Data for Linear Power Systems State Estimators Using PMUs. 2014 Power Systems Computation Conference 2014. [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, M.; Niknam, T.; Aghaei, J.; Shafie-Khah, M.; Catalao, J.P.S. Probabilistic Load Forecasting Using an Improved Wavelet Neural Network Trained by Generalized Extreme Learning Machine. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2018, 9, 6961–6971. [CrossRef]
- Rahmatian, M.; Chen, Y.C.; Palizban, A.; Moshref, A.; Dunford, W.G. Transient Stability Assessment via Decision Trees and Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines. Electric Power Systems Research 2017, 142, 320–328. [CrossRef]
- Räsänen, T.; Voukantsis, D.; Niska, H.; Karatzas, K.; Kolehmainen, M. Data-Based Method for Creating Electricity Use Load Profiles Using Large Amount of Customer-Specific Hourly Measured Electricity Use Data. Applied Energy 2010, 87, 3538–3545. [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.Q.; Khosravi, A. A Review on Artificial Intelligence Based Load Demand Forecasting Techniques for Smart Grid and Buildings. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2015, 50, 1352–1372. [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.I.; Rabie, A.H.; Abo-Al-Ez, K.M. A Data Mining Based Load Forecasting Strategy for Smart Electrical Grids. Advanced Engineering Informatics 2016, 30, 422–448. [CrossRef]
- Sancho-Asensio, A.; Navarro, J.; Arrieta-Salinas, I.; Armendáriz-Íñigo, J.E.; Jiménez-Ruano, V.; Zaballos, A.; Golobardes, E. Improving Data Partition Schemes in Smart Grids via Clustering Data Streams. Expert Systems with Applications 2014, 41, 5832–5842. [CrossRef]
- Schuelke-Leech, B.-A.; Barry, B.; Muratori, M.; Yurkovich, B.J. Big Data Issues and Opportunities for Electric Utilities. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2015, 52, 937–947. [CrossRef]
- Selakov, A.; Cvijetinović, D.; Milović, L.; Mellon, S.; Bekut, D. Hybrid PSO–SVM Method for Short- Term Load Forecasting during Periods with Significant Temperature Variations in City of Burbank. Applied Soft Computing 2014, 16, 80–88. [CrossRef]
- Seunghyoung Ryu; Jaekoo Noh; Hongseok Kim Deep Neural Network Based Demand Side Short Term Load Forecasting. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm) 2016. [CrossRef]
- Shaker, H.; Zareipour, H.; Wood, D. A Data-Driven Approach for Estimating the Power Generation of Invisible Solar Sites. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2466–2476. [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.; Hou, H.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y. A Novel Association Rule Mining Method of Big Data for Power Transformers State Parameters Based on Probabilistic Graph Model. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2018, 9, 695–702. [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Xu, M.; Li, R. Deep Learning for Household Load Forecasting—A Novel Pooling Deep RNN. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2018, 9, 5271–5280. [CrossRef]
- Short, T.A. Advanced Metering for Phase Identification, Transformer Identification, and Secondary Modeling. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2013, 4, 651–658. [CrossRef]
- Shyam R.; Ganesh H.B., B.; Kumar S., S.; Poornachandran, P.; Soman K.P. Apache Spark a Big Data Analytics Platform for Smart Grid. Procedia Technology 2015, 21, 171–178. [CrossRef]
- Sideratos, G.; Hatziargyriou, N.D. An Advanced Statistical Method for Wind Power Forecasting. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2007, 22, 258–265. [CrossRef]
- Simmhan, Y.; Aman, S.; Kumbhare, A.; Liu, R.; Stevens, S.; Zhou, Q.; Prasanna, V. Cloud-Based Software Platform for Big Data Analytics in Smart Grids. Computing in Science & Engineering 2013, 15, 38–47. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Yassine, A. Mining Energy Consumption Behavior Patterns for Households in Smart Grid. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing 2019, 7, 404–419. [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.; Borges, N.; Fotouhi Ghazvini, M.A.; Vale, Z.; de Moura Oliveira, P.B. Scenario Generation for Electric Vehicles’ Uncertain Behavior in a Smart City Environment. Energy 2016, 111, 664–675. [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, Z.; Carrington, N.; Liao, J. Data-Driven Power Outage Detection by Social Sensors. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2516–2524. [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan, A.; Hernandez, A.S.; Sarwat, A.I. Adapting Big Data Standards, Maturity Models to Smart Grid Distributed Generation: Critical Review. IET Smart Grid 2020, 3, 508–519. [CrossRef]
- Syed, D.; Abu-Rub, H.; Ghrayeb, A.; Refaat, S.S.; Houchati, M.; Bouhali, O.; Banales, S. Deep Learning-Based Short-Term Load Forecasting Approach in Smart Grid With Clustering and Consumption Pattern Recognition. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 54992–55008. [CrossRef]
- Syed, D.; Refaat, S.S.; Abu-Rub, H.; Bouhali, O.; Zainab, A.; Xie, L. Averaging Ensembles Model for Forecasting of Short-Term Load in Smart Grids. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data) 2019. [CrossRef]
- Syed, D.; Zainab, A.; Ghrayeb, A.; Refaat, S.S.; Abu-Rub, H.; Bouhali, O. Smart Grid Big Data Analytics: Survey of Technologies, Techniques, and Applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 59564–59585. [CrossRef]
- Tannahill, B.K.; Jamshidi, M. System of Systems and Big Data Analytics – Bridging the Gap. Computers & Electrical Engineering 2014, 40, 2–15. [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Kang, C.; Xia, Q. Smart Metering Load Data Compression Based on Load Feature Identification. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2414–2422. [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; He, X.; Shuai, Z.; Jiang, F. Big Data Issues in Smart Grid – A Review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2017, 79, 1099–1107. [CrossRef]
- Tureczek, A.; Nielsen, P.; Madsen, H. Electricity Consumption Clustering Using Smart Meter Data. Energies 2018, 11, 859. [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.U.; Faruque, Md.O. Validation of a PMU-based Fault Location Identification Method for Smart Distribution Network with Photovoltaics Using Real-time Data. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution 2018, 12, 5824–5833. [CrossRef]
- Verdu, S.V.; Garcia, M.O.; Senabre, C.; Marin, A.G.; Franco, F.J.G. Classification, Filtering, and Identification of Electrical Customer Load Patterns Through the Use of Self-Organizing Maps. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2006, 21, 1672–1682. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Fang, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y. Power System Transient Stability Assessment Based on Big Data and the Core Vector Machine. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2561–2570. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, B.; Peng, J. A Review of Deep Learning for Renewable Energy Forecasting. Energy Conversion and Management 2019, 198, 111799. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, P.; Sun, L. Big Data and Intelligent Agent Based Smart Grid Architecture. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Agents (ICA) 2017. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, H. A Novel Deep Learning Method for the Classification of Power Quality Disturbances Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Applied Energy 2019, 235, 1126–1140. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Kang, C.; Xia, Q.; Luo, M. Sparse and Redundant Representation-Based Smart Meter Data Compression and Pattern Extraction. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2017, 32, 2142–2151. [CrossRef]
- Wei Sun; Jian-Chang Lu; Yu-Jun He; Jian-Qiang Li Application of Neural Network Model Combining Information Entropy and Ant Colony Clustering Theory for Short-Term Load Forecasting. 2005 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics 2005. [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Negi, R.; Faloutsos, C.; Ilic, M.D. Robust Data-Driven State Estimation for Smart Grid. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2017, 8, 1956–1967. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ota, K.; Dong, M.; Li, J.; Wang, H. Big Data Analysis-Based Security Situational Awareness for Smart Grid. IEEE Transactions on Big Data 2018, 4, 408–417. [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Chen, Y.; Kumar, P.R. Dimensionality Reduction of Synchrophasor Data for Early Event Detection: Linearized Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2014, 29, 2784–2794. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Yu, W. A Gaussian-Mixture Model Based Detection Scheme against Data Integrity Attacks in the Smart Grid. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2016, 1–1. [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Wen, M.; Liang, X.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Yang, B. Energy Theft Detection With Energy Privacy Preservation in the Smart Grid. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2019, 6, 7659–7669. [CrossRef]
- Yigit, M.; Gungor, V.C.; Baktir, S. Cloud Computing for Smart Grid Applications. Computer Networks 2014, 70, 312–329. [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.J.Q.; Hou, Y.; Lam, A.Y.S.; Li, V.O.K. Intelligent Fault Detection Scheme for Microgrids With Wavelet-Based Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2019, 10, 1694–1703. [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Shah, S.; Johnson, R.; Sherick, R.; Hong, M.; Loparo, K. Big Data Analytics in Power Distribution Systems. 2015 IEEE Power & Energy Society Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT) 2015. [CrossRef]
- Zainab, A.; Ghrayeb, A.; Syed, D.; Abu-Rub, H.; Refaat, S.S.; Bouhali, O. Big Data Management in Smart Grids: Technologies and Challenges. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 73046–73059. [CrossRef]
- Zainab, A.; Refaat, S.S.; Syed, D.; Ghrayeb, A.; Abu-Rub, H. Faulted Line Identification and Localization in Power System Using Machine Learning Techniques. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data) 2019. [CrossRef]
- Žarković, M.; Stojković, Z. Analysis of Artificial Intelligence Expert Systems for Power Transformer Condition Monitoring and Diagnostics. Electric Power Systems Research 2017, 149, 125–136. [CrossRef]
- Zendehboudi, A.; Baseer, M.A.; Saidur, R. Application of Support Vector Machine Models for Forecasting Solar and Wind Energy Resources: A Review. Journal of Cleaner Production 2018, 199, 272–285. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, X.; Li, P.; Shi, F.; Yu, Z. ELM Model for Power System Transient Stability Assessment. 2017 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC) 2017. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, G.; Das, K.; Korres, G.N.; Manousakis, N.M.; Sinha, A.K.; He, Z. Power System Real-Time Monitoring by Using PMU-Based Robust State Estimation Method. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2016, 7, 300–309. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Niu, X.; Dai, H.-N.; Zhou, Y. Wide and Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Electricity-Theft Detection to Secure Smart Grids. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2018, 14, 1606–1615. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Arghandeh, R.; Spanos, C.J. Partial Knowledge Data-Driven Event Detection for Power Distribution Networks. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2018, 9, 5152–5162. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wu, Q.H.; Li, M.S.; Jiang, L.; Smith, J.S. Support Vector Regression-Based Short-Term Wind Power Prediction with False Neighbours Filtered. 2013 International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications (ICRERA) 2013. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Gong, X.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y. Power Quality Disturbances Classification via Fully-Convolutional Siamese Network and k-Nearest Neighbor. Energies 2019, 12, 4732. [CrossRef]
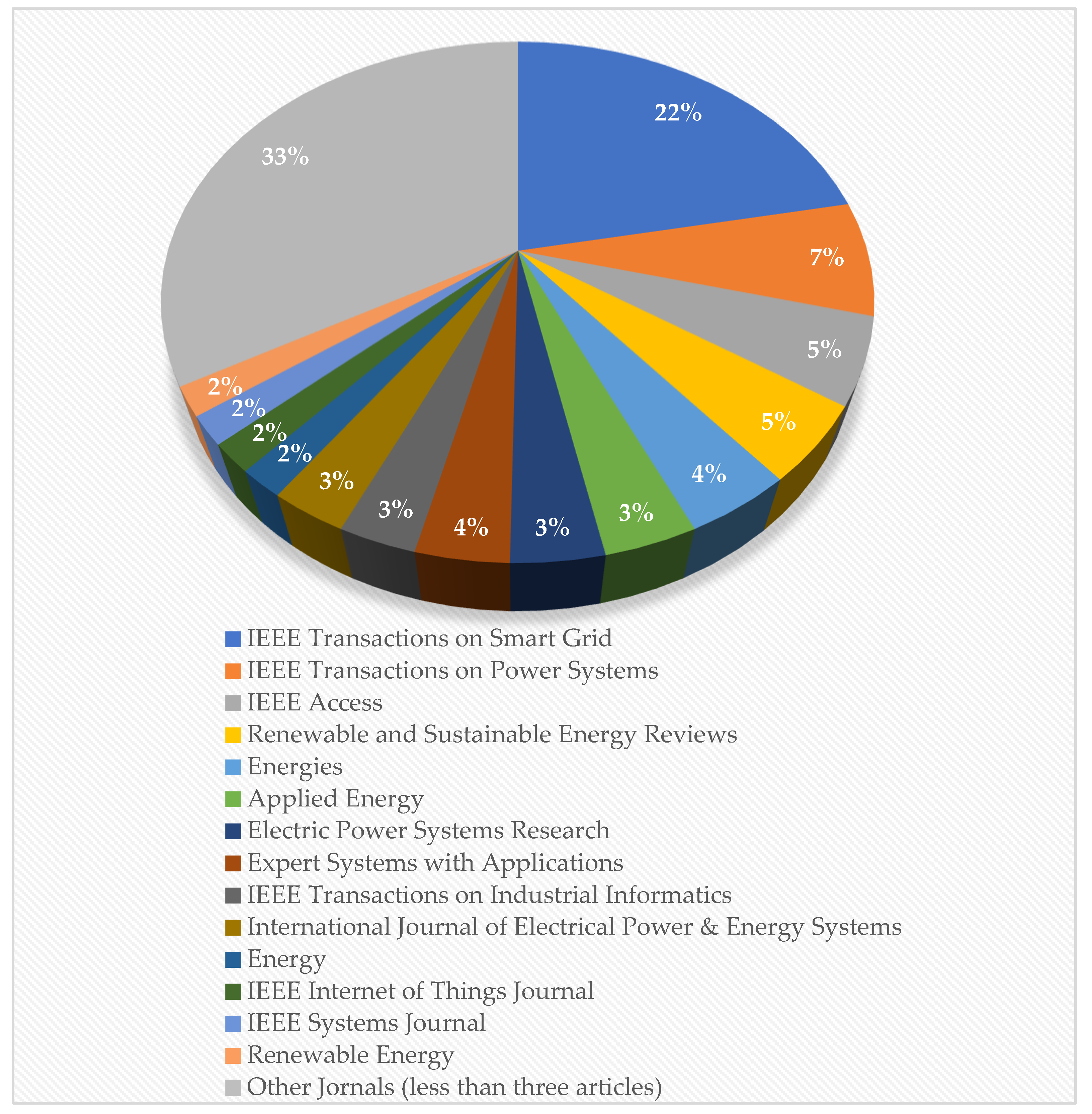
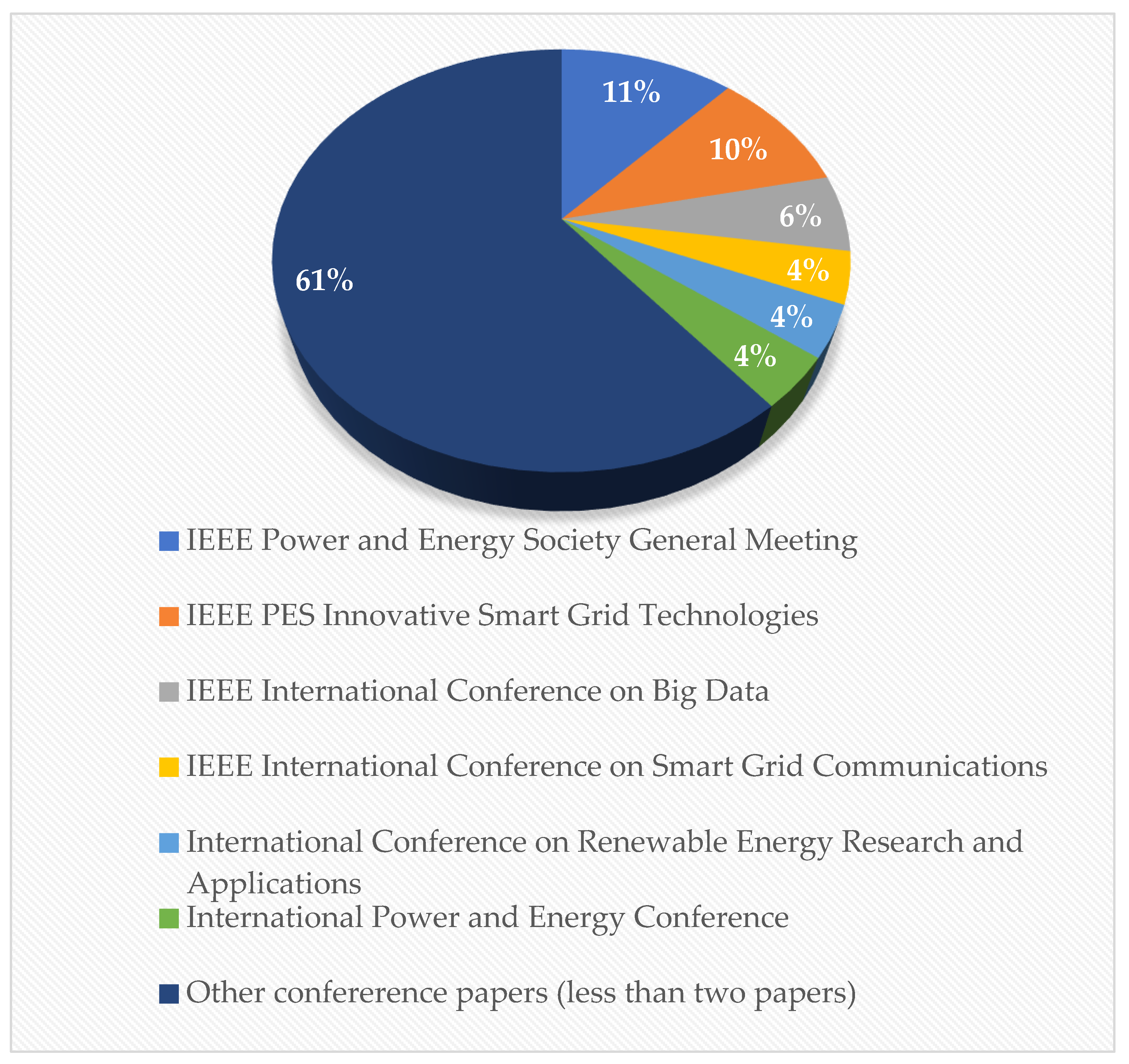
| Rank | Journal | Publisher | Number of publications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid | IEEE | 37 |
| 2 | IEEE Transactions on Power Systems | IEEE | 12 |
| 3 | IEEE Access | IEEE | 9 |
| 4 | Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews | ELSEVIER | 8 |
| 5 | Energies | MDPI | 7 |
| Rank | Conference | Number of publications |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting | 6 |
| 2 | IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies | 5 |
| 3 | IEEE International Conference on Big Data | 3 |
| 4 | IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications | 2 |
| 4 | International Conference on Renewable Energy Research and Applications | 2 |
| 4 | International Power and Energy Conference | 2 |
| Reference | Contribution |
|---|---|
| [11] | A price elasticity and customer benefit function-based extended responsive load economic model. |
| [12] | A deep long short-term memory recurrent neural network is used to forecast photovoltaic output power. |
| [13] | A hybrid algorithm for detecting power quality disturbances in electrical power systems that includes simulation of power quality events, feature extraction, selection of dominant features, and classification of selected features. |
| [14] | A multiple linear regression analysis model to make probabilistic forecasts of solar energy |
| [15] | Single and mixed power quality disturbances in distributed generation systems connected to the grid can be detected and categorized automatically with the help of a variational mode decomposition and a decision tree algorithm. |
| [16] | Description of the Real Time Dynamics Monitoring System (RTDMS®) for SynchroPhasor System Technology (SPST). |
| [17] | A review of the different levels of power quality problems in smart grids, as well as their structure, importance, and requirements. |
| [18] | Comparison of the efficiency of a random forest and an artificial neural network in predicting the amount of electricity used by the Heating, Venting, and Air Conditioning system in a hotel in Madrid, Spain. |
| [19] | The Bayesian probability theory is applied to solve the multiple line outage detection problem in linear time. |
| [20] | A data analytics-based technique for monitoring and detecting malicious activity on a cyber-physical transmission protection system. |
| [21] | A probabilistic health state estimation framework for smart grid power transformer lifetime management that integrates probabilistic forecasting models with Monte Carlo-based Bayesian filtering methods. |
| [22] | Based on the reliability priority of the components of the proposed fault-tolerant switched capacitor cascaded multilevel inverter, a novel fault location technique is presented, which results in a significant reduction in fault location detection time. |
| [23] | A thorough examination of smart electricity meters and their application, focusing on key aspects of the metering process, the various stakeholder interests, and the technologies used to satisfy stakeholder interests. |
| [24] | Development of a general computing grid framework for probabilistic-based reliability and security assessment of power systems. |
| [25] | A survey for wide area smart grid’s architectural model and control. |
| [26] | Using fuzzy logic to detect abnormal operating conditions and to generate fault signatures for various fault types, a novel health monitoring system for a variable air volume unit is created. An artificial neural network classification technique is then applied to fault signatures to classify the fault type. |
| [27] | Hybrid deep learning methods to enhance the outcomes in Saudi smart grid load forecasting. |
| [28] | A review of current energy management systems, applications, and frameworks. |
| [29] | A strategic vision of a self-healing smart grid. |
| [30] | A hybrid method for short-term bus load forecasting of power systems based on a forecast-aided state estimator and a multilayer perceptron neural network. |
| [31] | A neural network approach for hort-term load forecast having a novel learning algorithm based on a new modified harmony search technique. |
| [32] | Detection of fraudulent consumers by only observing electricity consumption records using a Tomek Link Borderline Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique with Support Vector Machine and a Temporal Convolutional Network with Enhanced Multi-Layer Perceptron. |
| [33] | Description of the role of the big data enterprise in envisioning the smart grid, based on a six-plane model that explains the factors necessary to transform the “brown-tussle” between the smart grid and the big data enterprise into a “greener-win-win” resolution. |
| [34] | The clustering yields consistent results across multiple iterations of the algorithm, and it is combined with a time-series analysis, a novel cluster selection algorithm, and a multilayer perceptron neural network to create a hybrid solar radiation forecasting method for varying time horizons. |
| [35] | An efficient dynamic solution for online smart grid topology identification and monitoring by combining concepts from compressive sensing and graph theory. |
| [36] | A cloud-computing-based universal framework for big data information management in smart grids. |
| [37] | An approach for transient stability assessment incorporating diversity by modifying it explicitly. |
| [38] | A semantic Extract-Transform-Load system that integrates and publishes data from many sources as open linked data using semantic technologies. |
| [39] | An event comprehension framework that analyses PMU data and develops high-level interpretations of the data with minimal latency to offer grid operators with greater situational awareness. |
| [40] | An integer programming based formulation for solution of the PMU placement problem. |
| [41] | An additive quantile regression model for a set of future distribution quantiles using a boosting approach. |
| [42] | Three major components for a public utilities demand response system are discussed. |
| [43] | A summary of current efforts to integrate cloud computing into the existing smart grid architecture in order to ensure the reliability, efficiency, and security of energy distribution. |
| [44] | A linear programming optimization algorithm based on the average hourly voltage and load data from the smart meters as well as the distribution topology data as given by the geographic information system. |
| [45] | A framework for very short-term probabilistic solar power estimates utilizing data acquired by a smart grid infrastructure. |
| [46] | A literature review of smart infrastructure and smart management techniques. |
| [47] | An algorithm that searches for the global optimum mainly through migration and mutation. |
| [48] | A differential evolution with biogeography-based optimization method for solving different convex and non-convex economic load dispatch problems. |
| [49] | A biogeography-based optimization algorithm for solving both convex and nonconvex economic load dispatch problems of thermal generators. |
| [50] | A review of the current state of big data analytics and its applications in power grids, identifying problems and potential from utility, industry, and research standpoints. |
| [51] | The “telegestore” project in ENEL metering system. |
| [52] | Instance-based transfer learning algorithm for wind power quantile regression. |
| [53] | Integration and analysis of data from many sources based on the geographic information system that provides a framework for integrating these data via spatial and temporal relationships. |
| [54] | A mobile edge computing-based system enabled by big data analytics for the electric vehicle charging use. |
| [55] | An artificial neural network approach for forecasting short-term wind power in Portugal. |
| [56] | Active sensing paradigm for inverter-enabled grid topology identification. |
| [57] | Smart metering electric load disaggregation using a novel feature extraction method and supervised classification. |
| [58] | A prediction of the intraday load curve at the residential level. |
| [59] | An opposition-based harmony search algorithm for the solution of combined economic and emission dispatch issues in power systems. |
| [60] | A kernel-based support vector regression combination model for solving the problem of short-term load forecasting. |
| [61] | Security risk modeling in critical smart grid infrastructures in the era of big data and artificial intelligence. |
| [62] | A clustering approach for identifying natural consumer segmentation and temporal consumption patterns. |
| [63] | An online forecasting model for a photovoltaic power system that uses a radial basis function network. |
| [64] | A framework for systematically incorporating renewable energy sources, distributed storage units, cooling facilities, and dynamic pricing into the workload and energy management activities of a data center network. |
| [65] | A method for rapidly identifying power system events using online synchrophasor measurements based on the reduction of the dimensionality of emergent ambient phasor measurement unit data. |
| [66] | A measurement-based methodology to compute the power flow Jacobian matrix and infer important information about the system’s topology in almost real time. |
| [67] | An integrated solution for the real-time power quality disturbance analysis based on an optimized deep belief network taking raw data of signals directly and an embedded parallel computing platform. |
| [68] | A summary of the clustering approaches used to construct appropriate customer grouping, as part of a larger system for analyzing data on electrical demand patterns. |
| [69] | The huge streaming PMU data were represented by utilizing the fluctuations in the covariance matrix of the large streaming PMU data and by developing a unique power state assessment technique based on the numerous high-dimensional covariance matrix tests. |
| [70] | The interrelated generation planning projects used to derive a unique -branch lattice process and approximate interrelated geometric Brownian motion processes that describes the evolution of market values of the completed projects. |
| [71] | Development and analysis of a computational intelligence algorithm for smart condition monitoring based on the ability to predict if a particular machine is in working condition or not and considering a dataset provided. |
| [72] | The performance of a metaheuristic-based n-steps-ahead time series forecasting model was evaluated using a multithreaded method. |
| [73] | A stream mining algorithm in order for the synchrophasor data to fulfill the speedy decision-making requirements of power system situational awareness. |
| [74] | A method for reducing the dimensionality of synchrophasor data in real-time by finding correlations between synchrophasor measurements and representing the data with their primary components without losing too much information. |
| [75] | Actual disturbance files acquired by PMUs were exhaustively grouped and mapped to a variety of disturbance occurrences using agglomerative hierarchical clustering. |
| [76] | A summary of the prospects, ideas, and problems of data management in smart grids, as well as a summary of the Big Data technologies and methods that may be utilized to manage smart grid requirements, including as processing, storage, and even visualization. |
| [77] | The importance of big data for smart grid implementation. |
| [78] | A model-free technique that uses high-resolution phasor measurement unit data to deliver accurate and fast information on the stability of the system. |
| [79] | Modelling of localized faults in the smart grid of a multi-utility by means of several heterogeneous features using an one-class classifier based on an interaction among clustering and dissimilarity measure learning techniques where specialized measures have been designed to deal with each feature type (e.g., categorical, metric, and time series). |
| [80] | A method for compressing data in smart distribution systems utilizing singular value decomposition. |
| [81] | Detection of electricity theft by comparing the energy consumption patterns of customers based on the historical data and support vector machines trained with the data collected from smart meters to represent all possible forms of theft. |
| [82] | Utilization of big data techniques for dynamic energy management on smart grid systems. |
| [83] | The application of random projections in order to tackle the problem of the huge quantity of data generated in smart grids by using a data sketching procedure to obtain a summarized version of original data. |
| [84] | State-of-the-art computationally intelligent approaches used in load forecasting in terms of their categorization and assessment for the sustainable functioning of the entire energy management system. |
| [85] | An approach for short-term load forecasting that utilizes an adaptive two-stage hybrid network with self-organized map and support vector machine. |
| [86] | A bootstrap approach that incorporates randomness from the model and external factors for generating forecasting distributions. |
| [87] | A review of cloud technologies to smart grids. |
| [88] | Diagnostics of a power transformer are performed using a support vector machine with genetic algorithm. |
| [89] | A technique for recognizing patterns in load profiles to aid in the management of the electric sector. |
| [90] | A dual-scale similarity function algorithm based on the combination of Euclidean distance and the shape of the curve to describe the similarity between the power load curves and a clustering of load curves according to the principle of spectral clustering to make the algorithm insensitive to the data distribution and data dimension and to ensure convergence to the global optimal solution. |
| [91] | Clusters determination of the typical load profiles based on the fuzzy c-means and hierarchical clustering algorithms along with probability neural networks used as a classification tool for assign consumers’ type of activity to the particular cluster. |
| [92] | A two-case optimization-based profit maximizing technique for data centers without and with renewable generators behind the meter. |
| [93] | A technique using wavelet neural networks and data pre-filtering to predict extremely short-term loads 1 hour into the future in 5-minute increments using a moving window. |
| [94] | An efficient and secure data acquisition scheme based on ciphertext policy attribute based encryption. |
| [95] | Three metrics, namely, the building occupant energy-use efficiency, entropy, and intensity enable the design of more targeted energy conservation campaigns introduced for the classification of building occupants according to their energy-use patterns. |
| [96] | Security issues, challenges, and recommendations for block chain technology in smart grid, energy trading, and big data. |
| [97] | A rank reduction optimization approach for singular value decomposition-based data compression. |
| [98] | A method for the intelligent recognition of transient instability pattern based on power grid topology. |
| [99] | A data aggregation approach that protects privacy against internal attackers using Boneh-Goh-Nissim public key encryption. |
| [100] | Various timeframe dispatch and scheduling, such as day-ahead and real-time scheduling, to address the difficulty of integrating variable wind energy into the bulk electricity system. |
| [101] | A method that performs a high-dimensional analysis and compares the results to random matrix theory predictions in order to discover anomalies. |
| [102] | A technique for short-term load forecasting in microgrids based on pattern recognition using a self-organizing map, clustering of the prior partition using the k-means algorithm, and demand forecasting for each cluster using a multilayer perceptron. |
| [103] | A Mycielski - Markov hybrid model for the the prediction of solar radiation. |
| [104] | Big data analytics for the enhancement of the smart grid. |
| [105] | A support vector regression-based electric load forecasting model based on a chaotic ant swarm optimization technique to enhance the forecasting performance by looking for the optimal combination of parameters. |
| [106] | A load forecasting model that improves forecasting performance by combining the seasonal recurrent support vector regression model with the chaotic artificial bee colony method. |
| [107] | Analysis, protection and security concerns associated with IoT generated big data of smart grids. |
| [108] | A multi-label support vector machine to identify distribution lines outages in response to extreme weather events by leveraging advanced metering infrastructure data. |
| [109] | A framework for temporal, functional, and geographical big data processing for large-scale smart grids. |
| [110] | A review of the most recent advancements in energy big data analytics and security/privacy. |
| [111] | A study of the applicability and efficacy of many data mining techniques for energy market price classification, as well as a data model for generating the initial data set for price classification. |
| [112] | An artificial neural network method for energy theft detection in distribution systems. |
| [113] | A redundancy architectural design for measuring network deployment in a power system including PMUs. |
| [114] | A mathematical framework for a typical fog-based smart grid design that describes the placement and planning of fog computing in smart grid. |
| [115] | A technique for forecasting city-wide power gains from solar panels using precise 3D urban massing models in conjunction with Daysim-based hourly irradiance simulations, average meteorological year climatic data, and hourly estimated rooftop temperatures. |
| [116] | A study of the applications of Internet of Things technology in the power grid, as well as the integration of renewable energy sources, in order to achieve sustainable energy and avert climate change. |
| [117] | An approach for detecting theft that combines a convolutional neural network, long-short term memory, and a deep siamese network. |
| [118] | A strategy based on both fuzzy theory and game theory for presenting a system that can effectively avoid a prisoner’s dilemma in an environment where electricity is created autonomously via the use of new and renewable energy and then exchanged for consumption. |
| [119] | A two-layer dynamic optimum synchrophasor measuring devices selection technique for the spatial characterization of the synchrophasor measurement system coupled with a matching pursuit decomposition for characterization of the signals in the time domain. To study defect detection and identification, a hidden Markov model-based SG situational awareness technique is developed. |
| [120] | A survey on big data and the power grid that provides background information on relevant studies, approaches, and tools for big data in energy. |
| [121] | A technique that uses PMU measurement data to predict the inter-area dominating oscillation modes in a bulk power system and to handle both ringdown data and ambient data with robust performance. |
| [122] | An approach for outage management in distribution systems based on the multiple-hypothesis method and the extended protection tree that handles complicated outage situations involving numerous failures, missing outage notifications from fault indicators and smart meters, and protection miscoordination. |
| [123] | Adopting a top-down approach with decision tree and support vector machine classifiers for the detection of consumers that actively steal power. |
| [124] | A tensor-based large data processing approach in the Internet of Everything context of a smart city using support vector machine. |
| [125] | A consumption pattern-based energy theft-detecting algorithm and a support vector machine utilized to forecast the normal and fraudulent usage patterns of clients. |
| [126] | A method for synthesizing load curves and estimating the equation of the typical load curve in a building. |
| [127] | A study of damping/firstswing stability control and wide-area secondary voltage regulation. |
| [128] | Utilization of extraordinarily big data sets that are difficult to analyze with conventional database tools in power system operation, control, and protection. |
| [129] | A two-module strategy that combines data preprocessing and categorization into a single framework. The first module includes data imputation, outliers management, standardization, and class balance stages to provide quality data for classifier training, while the second module separates honest and dishonest users using a support vector machine classifier. |
| [130] | A parallel-detrended fluctuation analysis technique leveraging a computer cluster for the rapid identification of transient events on enormous PMU data. |
| [131] | A method for distributed Prony analysis utilizing consensus and subgradient updating. |
| [132] | Utilization of prediction interval creation techniques in the forecasting of power prices. |
| [133] | A method for the lossless compression of voltage magnitude and phase data in which power system features are employed to improve upon conventional compression techniques. |
| [134] | A procedure for solving the short-term load forecasting problem for residential households. |
| [135] | The new industrial revolution and the significance of Artificial Intelligence are reviewed and addressed. |
| [136] | Data mining methods were used to create four time series models with varying prediction horizons. |
| [137] | A scalable technique expressed as a stochastic knapsack problem including projected customer reactions for demand response program targeting using unique data obtainable from smart meters at the individual level. |
| [138] | A formulation based on a variant of the conventional support vector data description for multi-class classification with novelty detection that yields precise results for the classification of actual waveforms. |
| [139] | A bibliographical review of the broad background of wind speed and wind power forecasting research and development. |
| [140] | The smart home idea was expanded to general consumer units with immediate and distributed decision-making capabilities. |
| [141] | Analysis of the requirements for protecting the privacy of big data in smart grids and proposal of associated approaches. |
| [142] | A Lambda-based big data architecture for smart grids, including a Real-Time CEP engine incorporated in the Speed layer and utilizing Spark Streaming. |
| [143] | A privacy-preserving authentication technique based on aggregated proofs (AP3A) for achieving simultaneous identification and safe identification for varied working mode battery vehicles. |
| [144] | Micro-grid load forecasting using a hybrid model built of empirical mode decomposition (EMD), extended Kalman filter (EKF), and extreme learning machine with Kernel (KELM). |
| [145] | A cost-effective situational awareness tool (FNET/GridEye) for the development of wide-area monitoring system in electric power grids. |
| [146] | A precise categorization of electric consumers enabling electric utilities to set individualized tariffs for each customer category. |
| [147] | A classification strategy for the detection and categorization of complex power quality disturbances (PQDs) utilizing a three-level Bayesian-Network with multiple connections. |
| [148] | Development of a cloud computing platform including the system architecture design and a cyber security scheme. |
| [149] | A power security system based on stream data mining that consists primarily of an intelligent electric outlet, a coordinator, and a server, with a ZigBee module serving as a link between the traditional power grid and the coordinator. |
| [150] | An artificial neural network tool for the rating of the load curves of all consumers of a power utility in data centres and from various consumer profiles, together with the registration data and analysis of each load feeder. |
| [151] | Cloud computing model can be used for developing smart grid solutions |
| [152] | Establishment of a cloud-based smart grid for evaluating big data and making decisions to balance consumer demand. |
| [153] | A method for analyzing synchrophasor data that use statistical correlation techniques to uncover data inconsistencies inconsistencies and power system contingencies. |
| [154] | A protection strategy for microgrids with inverter-interfaced distributed generating units based on the wavelet transform and a data-mining algorithm. |
| [155] | A platform for real-time anomaly detection based on smart meter data obtained at the users’ premises. |
| [156] | A review on big data management and decision making in smart grids. |
| [157] | Detection of customers with anomalous drops in their consumed energy by means of a windowed analysis with the use of the Pearson coefficient, Bayesian networks and decision trees. |
| [158] | A comprehensive analysis of the reliability impacts of major smart grid resources, including renewables, demand response, and storage. |
| [159] | A framework for the prospective deployment of big data analytics for smart grids and renewable energy power utilities based on five distinct machine learning techniques for forecasting the stability of the smart grid. |
| [160] | The implementation of a large data framework for smart grids on a secure Google Service cloud platform. |
| [161] | A big data ecosystem for the smart grid that is built on the cutting-edge Lambda architecture and is capable of executing parallel batch and real-time operations on distributed data. |
| [162] | A study of the elements that impact a customer’s decision to subscribe to a certain demand response management system, as well as a classification of consumer types to non-green comfort seeking behavior (NCSB) and green incentive seeking behavior (GISB). |
| [163] | Support vector machine (SVM)-based methodology for non-technical loss analysis for electric utilities. |
| [164] | A technique for capturing geographic variation in wind production alongside transmission restrictions. |
| [165] | A system for power load forecasting using support vector machine and ant colony optimization. |
| [166] | A review of non-technical losses, load profiles, and data mining strategies utilized to decrease non-technical loss activities. |
| [167] | The K-means clustering approach is used to categorize data on power load into five groups: super-peak, peak, cycling, intermediate, and base. |
| [168] | A consumer automated energy management system (CAES) used to reduce residential energy costs and smooth energy usage, which is based on an online learning application that implicitly estimates the impact of future energy prices and consumer decisions on long-term costs and schedules residential device usage. |
| [169] | A method to reduce peak electricity demand in building climate control by using real-time electricity pricing and applying model predictive control (MPC) along with least-squares support vector machine for electricity tariff price forecasting. |
| [170] | Comparison of classification techniques, namely Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA), Nearest Neighbor Method (kNN), Learning Vector Quantization (LVQ), and Support Vector Machine (SVM), to identify several power quality disturbances in the context of smart metering design for smart grids with high penetration of photovoltaic (PV) systems. |
| [171] | A systematic and automated approach to build a hybrid intrusion detection system that learns temporal state-based specifications for power system scenarios including disturbances, normal control operations, and cyber-attacks based on a data mining technique called common path mining. |
| [172] | A process that employs a collection of unsupervised machine learning algorithms and selects the Fuzzy C-Means (FCM) algorithm for clustering load curves. |
| [173] | A data-driven method for determining the underlying network architecture for low voltage (LV) distribution networks, including load phase connection, based on energy measurement time series. |
| [174] | Intelligent methods for detecting and dealing with missing or inaccurate smart meter data, as well as methods for processing the data for various applications, and a method for parameter estimation based on the voltage drop equation and regression analysis to improve the accuracy of distribution system models. |
| [175] | A methodology to extract electric energy consumption patterns in big data time series, based on the study of four clustering validity indices in their parallelized versions along with the application of a distributed version of the k-means algorithm included in Apache Spark’s Machine Learning Library. |
| [176] | A class of autonomous broker agents for retail power trading that can operate in a broad variety of smart electricity markets utilizing reinforcement learning with function approximation and can derive long-term, profit-maximizing strategies. |
| [177] | A bad data pre-estimation filtering algorithm of PMU-based linear state estimators coupled with a Discrete Kalman Filter (DKF) state estimator that uses only PMU measurements and an AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) process combined with the outcome of the adopted DKF state estimator. |
| [178] | A hybrid method for probabilistic electrical load forecasting that employs a generalized extreme learning machine (GELM) for training an enhanced wavelet neural network (IWNN), wavelet preprocessing, and bootstrapping. |
| [179] | Tools for online transient stability assessment that use classification and regression trees (CART) and multivariate adaptive regression splines (MARS) models in combination with high-speed synchronized phasor data derived from phasor measurement units. |
| [180] | A self-organizing maps (SOM) and clustering methods (K-means and hierarchical clustering) methodology, capable of handling large amounts of time-series data in the context of electricity load management research. |
| [181] | A literature review of short-term load forecasting strategies based on artificial intelligence. |
| [182] | A load forecasting strategy by employing a distance based outlier rejection (DBOR) methodology and a hybrid technique combining evidence from Genetic Based Feature Selector (GBFS) and Rough set Base Feature Selector (RBFS). |
| [183] | The deployment of an online version of the eXtended Classifier System for Clustering (XCSc) on top of the smart grid using a multi-agent system architecture with the goal of generating a dynamic data partitioning scheme for the smart grid storage repository. |
| [184] | An assessment of both the concerns of big data for electric utilities and the use of data analytics to determine if data is relevant to regulatory and policy considerations regarding electric utilities. |
| [185] | A hybrid model based on particle swarm optimization (PSO) and support vector machine (SVM) for anticipating short term electricity load. |
| [186] | Deep neural network (DNN)-based load forecasting models for demand side empirical load database, trained by pre-training limited Boltzmann machine and rectified linear unit without pre-training, respectively. |
| [187] | A data-driven methodology for the estimation the power generation of invisible solar power sites by using the measured values from a small number of representative sites including a data dimension reduction engine and a mapping function and additionally proposing a hybrid method based on k-means clustering and principal component analysis. |
| [188] | A data-driven technique of association rule mining for transformer state parameters that combines the Apriori algorithm with a probabilistic graphical model. |
| [189] | A pooling-based deep recurrent neural network that groups a collection of customers’ load profiles into a pool of inputs in order to construct a customized deep learning application for residential load forecasting. |
| [190] | A technique for identifying the phasing of transformers and single-phase taps as well as creating or verifying meter-to-transformer mappings utilizing voltage and kilowatt-hour readings from advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) based on linear regression and fundamental voltage drop relationships. |
| [191] | Apache spark is presented as a unified cluster computing platform appropriate for storing and analyzing large data on smart grid data for applications such as autonomous demand response and real-time pricing. |
| [192] | A combination of neural networks and fuzzy logic approaches is used to accurately estimate the production of a wind farm. |
| [193] | A cloud-based software platform for big data analytics in smart grids. |
| [194] | A proposal for mining patterns of residential energy consumption behavior in smart grids. |
| [195] | A framework and methods for estimating the various states of electric cars with respect to their demand, location, and grid connection durations, based on Monte Carlo simulation and fuzzy logic probability. |
| [196] | A technique for detecting and localizing power outages based on social media data (Twitter). |
| [197] | A review of big data standards and maturity models for smart grid distributed generation. |
| [198] | A hybrid model comprised of k-Medoids clustering and deep learning models for hourly load forecasting one day in advance at the level of distribution transformers. |
| [199] | Various approaches of machine learning have been utilized for load forecasting. |
| [200] | In-depth analysis of the various big data technologies and big data analytics in the context of the smart grid, as well as a discussion of the difficulties and opportunities presented by the arrival of machine learning and big data from smart grids. |
| [201] | A high-level overview of some of the Matlab tools that allow the user to extract relevant information from big data sources. |
| [202] | A smart metering load data compression approach based on the detection of load features using the general extreme value (GEV) distribution characteristic of residential load data. |
| [203] | A review of big data issues in smart grid. |
| [204] | K-Means methods to improve clustering by harvesting inherent structure from the smart meter data. |
| [205] | A fault location identification method for smart distribution network based on a state estimation algorithm which uses real-time data from simulated phasor measurement units placed in the distribution network. |
| [206] | A self-organizing map methodology to achieve the segmentation and demand patterns classification for electrical customers on the basis of database measurements. |
| [207] | The online power system Transient Stability Assessment (TSA) problem is represented as a two-class classification problem, and a novel data mining approach, Core Vector Machine (CVM), based on PMU large data is proposed to tackle the problem. |
| [208] | A review of deep learning for renewable energy forecasting. |
| [209] | Intelligent agent and big data-based smart grid architecture. |
| [210] | Based on a deep convolutional neural network, a unique full closed-loop strategy to identify and categorize power quality problems is presented. A unit structure consisting of 1-D convolutional, pooling, and batch-normalization layers is meant to capture multi-scale features and reduce overfitting in the context of the power quality disturbances problem. |
| [211] | A K-SVD sparse representation approach is utilized to breakdown load profiles into linear combinations of various partial use patterns (PUPs), enabling the compression of smart meter data and the extraction of concealed power consumption patterns. On the basis of the recovered patterns, a linear support vector machine (SVM)-based technique is utilized to categorize the load profiles into two groups: residential consumers and small and medium-sized companies (SMEs). |
| [212] | A hybrid neural network model for load forecasting that combines information entropy theory with ant colony clustering. |
| [213] | A system for cleaning historical data, doing supervised learning, and accelerating the learning process in order to enable online state estimates. |
| [214] | A security situational awareness mechanism based on the analysis of big data in the smart grid is seamlessly combined with a Fuzzy cluster-based analytical approach, game theory, and reinforcement learning to provide a security situational analysis for the smart grid. |
| [215] | An online application for early event detection using the reduced dimensionality and phasor measurement unit data. |
| [216] | By utilizing the Gaussian-Mixture model to cluster the historical data and learning minimum and maximum values or distance values to each center of individual clusters, we can obtain a narrower range of normal data compared to the scheme based on the Min-Max model, resulting in more accurate detection of false data. |
| [217] | An energy theft detection technique for the energy privacy protection in the smart grid based on convolutional neural networks (CNN) to identify abnormal behavior of the metering data from a long-period pattern observation and a Paillier algorithm to safeguard the energy privacy. |
| [218] | A review on cloud computing for smart grid applications |
| [219] | A microgrid fault detection strategy based on the wavelet transform and deep neural networks. |
| [220] | Applications as well as a comprehensive overview of the technological and regulatory obstacles and hazards associated with big data analytics in electricity distribution networks. |
| [221] | A study of large data management and management processes to assist in managing grid data. |
| [222] | A data-driven method for identifying and classifying faults in an electrical power system is comprised of an efficient analysis of the data using feature vectors including the region or zone of the bus and machine learning models to classify and identify the fault’s location. |
| [223] | Analysis of the use of the Mamdani-model and the Sugeno-model in a fuzzy expert system for defect diagnostics based on the current condition of the power transformer. |
| [224] | A survey of the uses of SVM modeling in the solar and wind energy industries. |
| [225] | Extreme learning machine method for power system transient stability assessment problem. |
| [226] | A phasor measurement unit-based robust state estimation method (PRSEM) for real-time monitoring of power systems under different operation conditions. |
| [227] | A method for detecting power theft based on the Wide & Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) model. |
| [228] | Application of micro-phasor measurement unit (PMU) data to power distribution network event detection using an unique data-driven event detection technique, namely Hidden Structure SemiSupervised Machine (HS3M). |
| [229] | A short-term wind power prediction approach based on a support vector regression (SVR)-based local predictor (LP) with false neighbours filtered (FNF-SVRLP). |
| [230] | Small sample-based classification of power quality disturbances using a hybrid method based on k-nearest neighbor and fully-convolutional Siamese network. |
| Big data analysis’ methods and techniques | Definition | References |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial intelligence | Artificial intelligence refers to a collection of computing technologies that, when combined, give computers the ability to carry out a wide range of complex tasks such as the ability to read, comprehend, and translate both spoken and written language, as well as to analyze data and provide recommendations. | [18,23,55,57,61,82,99,102,104,112,118,135,139,150,158,181,192,223] |
| Cloud computing | Cloud computing refers to the on-demand access, via the internet, to computing resources that are hosted at a remote data center that is managed by a cloud services provider. These computing resources include applications, servers (both physical and virtual servers), data storage, development tools, and networking capabilities, among other things. | [36,43,54,87,94,114,148,151,152,160,161,193,203] |
| Clustering | Clustering, often known as cluster analysis, is a method of machine learning that organizes the dataset without labeling it. It is a method for organizing the data points into distinct clusters, each of which is made up of data points that are quite similar to one another. | [34,58,62,68,75,79,89,90,91,95,109,111,118,121,126,130,146,153,161,166,167,172,175,180,183,184,187,191,204,212,214,216] |
| Data mining | The technique of using big data sets to search for anomalies, patterns, and correlations in order to make accurate predictions is known as data mining. This information may be utilized to enhance revenues, lower expenses, improve customer connections, reduce risks, and a variety of other things by employing a wide variety of ways. | [18,38,73,74,111,120,136,141,149,154,157,161,166,171,174,182,183,184,185,194,203,206,209,220,221] |
| Decision making | The process of selecting choices by recognizing a decision to be made, collecting relevant information, and analyzing potential solutions is referred to as decision making. | [11,155,156] |
| Deep learning | Deep learning is a subclass of machine learning that comprises neural networks with three or more layers. These neural networks seek to imitate the activity of the human brain, although inadequately, allowing them to “learn” from vast quantities of data. | [12,20,27,32,67,71,72,73,117,134,135,198,199,208,210,217,218,219,227,229] |
| Machine learning | Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence and computer science that focuses on the use of data and algorithms to emulate how people learn, while continually enhancing its accuracy. | [23,28,32,33,37,45,52,57,59,60,78,81,84,85,88,97,99,104,105,106,107,108,110,115,122,123,124,125,128,129,135,136,138,140,142,144,159,163,165,168,169,170,172,175,176,178,183,185,191,196,198,200,201,202,207,208,209,213,214,222,224,225,227,228,229,230] |
| Mathematical programming | Mathematical programming refers to the use of mathematical models to the solution of issues such as decision problems. The concepts are supposed to contrast with computer programming, which handles similar issues by creating methods that may be tailored to a particular situation. | [17,29,35,40,44,47,48,49,56,64,70,83,92,100,103,113,119,137,140,143,164,205] |
| Neural networks | Neural networks, commonly referred to as artificial neural networks or simulated neural networks, are a subset of machine learning and the foundation of deep learning methods. Their name and structure are derived from the human brain, emulating how organic neurons communicate with one another. | [12,25,26,27,30,31,55,63,71,91,93,102,112,132,134,146,150,178,181,186,198,199,219,227,229] |
| Pattern recognition | Pattern recognition is a mature yet interesting and rapidly expanding area that underlies advancements in related fields such computer vision, image processing, text and document analysis, and neural networks. It is similar to machine learning and has applications in rapidly developing fields. | [13,89,91,98,102,153,175,194,206,211,212] |
| Signal processing | Signal processing is the technology that enables the production, transformation, and interpretation of data. | [15,16,22,33,39,46,51,127,131,133,145] |
| Statistical technique | Statistical procedures include planning, designing, collecting data, analyzing, making relevant interpretations, and publishing the results of the research. The statistical analysis offers meaning to meaningless numbers and hence gives life to dead facts. | [14,17,19,21,24,41,53,65,66,69,80,86,101,147,153,162,169,170,173,177,179,184,188,189,190,192,195,202,215,226] |
| Support vector machine | It is a supervised machine learning model for two-group classification problems that employs classification techniques. Support vector machine models can classify fresh text after receiving labeled training data. | [13,32,81,85,88,108,123,124,125,129,163,165,169,170,185,211,224] |
| Big data topics in smart grids | References |
|---|---|
| Demand response | [62,72,137,142,162,191] |
| Demand side management | [11,76,84,111,146,150,167,168,169,172,194,204,206,207] |
| Economic load dispatch | [47,48,49] |
| Electric vehicles | [54,114,116,143,195] |
| Energy management | [28,33,64,82,84,159] |
| Energy price | [59,132,176,184] |
| Energy theft / Non-technical losses | [32,81,112,117,123,125,129,157,163,166,217,227] |
| Generation planning | [70] |
| Load forecasting | [27,30,31,58,60,84,85,89,90,91,93,95,102,105,106,134,144,165,178,181,182,185,189,193,198,199,212] |
| Load pattern | [68,180] |
| Microgrids | [43,102,144,154,201,219] |
| Monitoring and control | [25,28,38,39,40,42,50,66,69,71,80,82,138,184,203,213,226] |
| Power quality | [13,15,17,67,147,170,210,230] |
| Power transformer | [21,44,88,188,190,223] |
| Power system protection | [154] |
| Power system stability | [37,78,98,121,127,128,179,203,225] |
| Power system reliability / resilience | [19,22,24,29,53,79,87,100,122,156,158,196,219,222,228] |
| Renewable energy sources | [12,14,34,45,52,55,63,64,86,92,101,103,118,136,139,151,152,159,186,187,192,201,208,224,229] |
| Security / Cyber security | [20,24,29,36,38,50,61,87,94,96,97,99,107,110,135,141,143,148,149,171,214,216] |
| Smart cities / buildings / home | [18,26,32,95,115,124,126,140,175,181] |
| Smart meters / Smart metering | [23,41,42,43,44,46,51,57,77,83,96,97,104,108,110,116,122,137,142,155,160,161,170,173,174,183,197,200,202,203,209,211,218,220,221] |
| Synchrophasor technology | [16,39,40,65,66,69,73,74,75,78,104,109,113,119,120,121,128,130,131,133,145,153,164,177,205,215,226] |
| Topology identification | [35,56,173] |
| Reference | Chronological distribution | Classification per journal or conference | Methods and techniques | Topics in smart grids | Future works |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [17] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [23] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ‒ |
| [25] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [28] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [29] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ‒ |
| [33] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ‒ |
| [43] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [46] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [50] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [68] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ‒ |
| [76] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ‒ |
| [77] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [82] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [87] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ‒ |
| [96] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [104] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ‒ |
| [107] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [116] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ‒ |
| [120] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [135] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [139] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ‒ |
| [156] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [184] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [197] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [200] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [208] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| [224] | ‒ | ‒ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| This work | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





