Submitted:
07 December 2025
Posted:
09 December 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
We validate, through an example, the direct correspondence between the irreversibility of renormalization-group (RG) flow and entropy production thermodynamics imposed by Newell. Using the local RG framework of Osborn and Jack, we identify a scheme-invariant potential \( \tilde a(\mathbf g) \) and a positive-definite tensor \( \chi_{ij} \) satisfying an exact gradient formula, \( \partial_i\tilde a=\chi_{(ij)}\beta^j \). Mapping this structure onto the GENERIC formalism of Grmela and Öttinger reveals that RG evolution is a purely dissipative process in coupling space, governed by \( \dot g^i=M^{ij}\partial_j S \) with \( S=-\tilde a \). Numerical integration of a three-coupling gauge--Yukawa model confirms a strictly monotonic \( \tilde a(\sigma) \), verifying \( \dot{\tilde a}=\beta^i\chi_{ij}\beta^j\!\ge\!0 \) to machine precision. The result validates the thermodynamic interpretation of the four-dimensional a-theorem and confirms the imposed validity of RG irreversibility, validating the Newell's framework thermodynamics integration.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
Relation to the Unified Scientific Framework of Newell (2025)
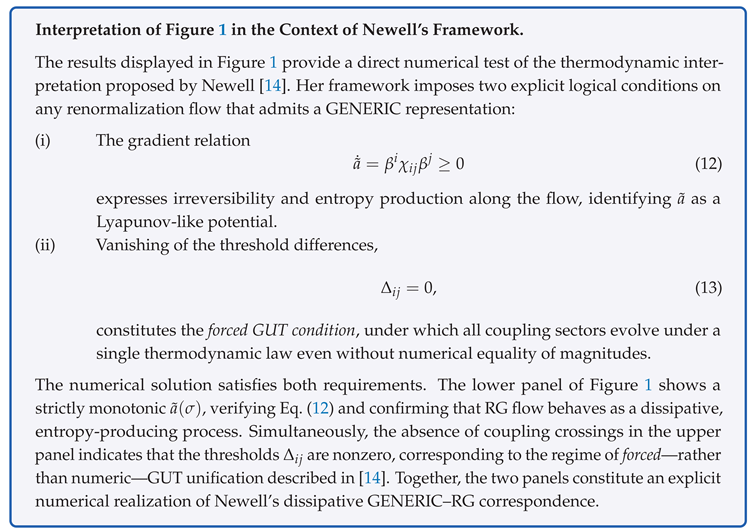
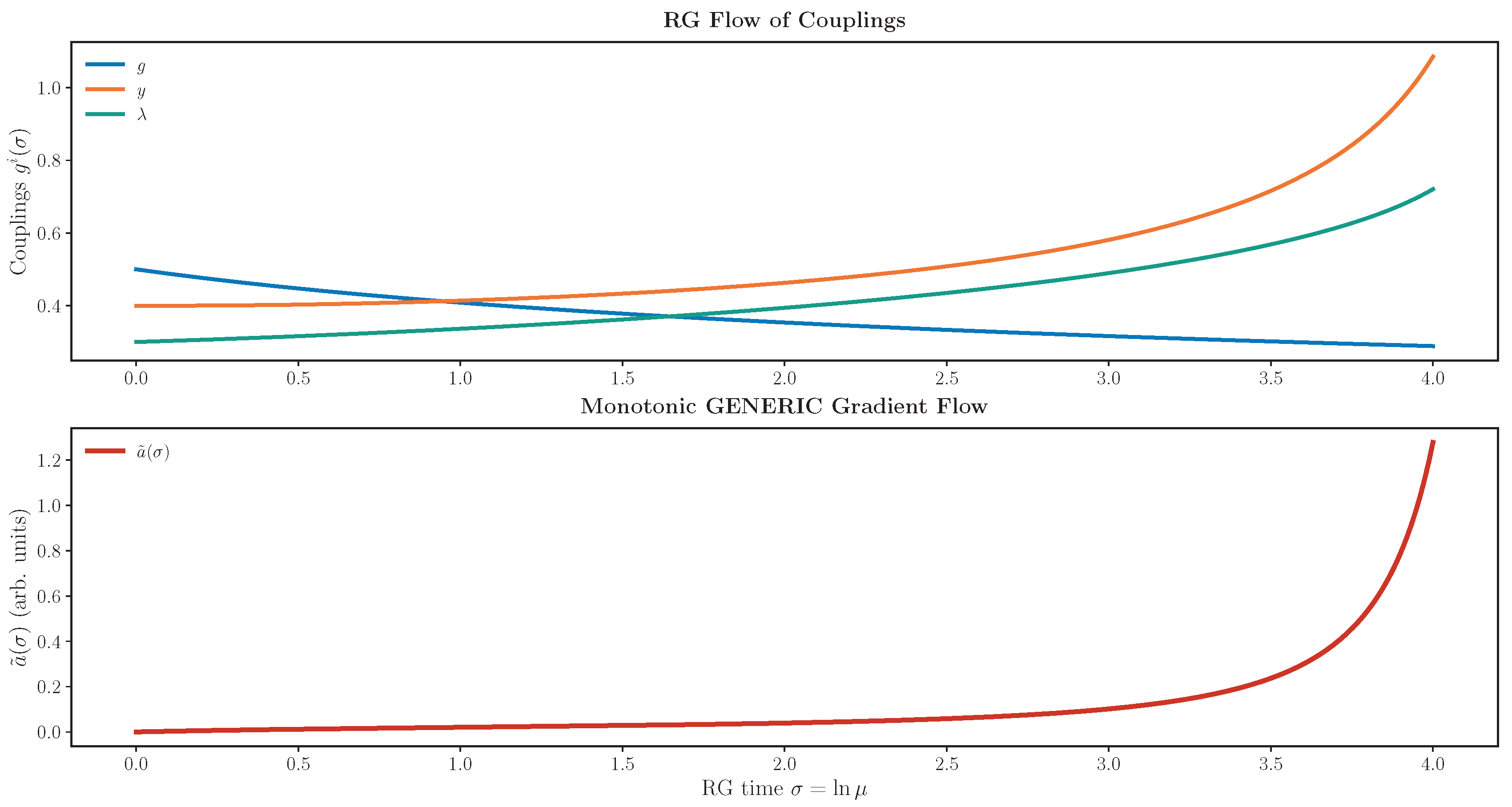
2. Local RG Structure and Gradient Formula
3. Positivity, GENERIC Mapping, and Geometric Interpretation
4. Gauge–Yukawa Example and Numerical Verification
5. Conclusions
References
- Wilson, K.G. Renormalization Group and Critical Phenomena. I. Renormalization Group and the Kadanoff Scaling Picture. Phys. Rev. B 1971, 4, 3174–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.G.; Kogut, J. The Renormalization Group and the ε Expansion. Phys. Rep. 1974, 12, 75–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigogine, I. From Being to Becoming: Time and Complexity in the Physical Sciences; W. H. Freeman, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Callen, H.B. Thermodynamics and an Introduction to Thermostatistics, 2nd ed.; Wiley, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Zamolodchikov, A.B. Irreversibility of the Flux of the Renormalization Group in a 2D Field Theory. JETP Lett. 1986, 43, 730–732. [Google Scholar]
- Komargodski, Z.; Schwimmer, A. On Renormalization Group Flows in Four Dimensions. JHEP 2011, 12, 099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komargodski, Z. The Constraints of Conformal Symmetry on RG Flows. JHEP 2012, 07, 069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, H. Derivation of a Four-Dimensional c Theorem. Phys. Lett. B 1989, 222, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, I.; Osborn, H. Analogs for the c Theorem for Four-Dimensional Renormalizable Field Theories. Nucl. Phys. B 1990, 343, 647–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, H. Weyl Consistency Conditions and a Local Renormalization Group Equation for General Renormalizable Field Theories. Nucl. Phys. B 1991, 363, 486–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grmela, M.; Öttinger, H.C. Dynamics and Thermodynamics of Complex Fluids. I. Development of a General Formalism. Phys. Rev. E 1997, 56, 6620–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öttinger, H.C.; Grmela, M. Dynamics and Thermodynamics of Complex Fluids. II. Illustrations of a General Formalism. Phys. Rev. E 1997, 56, 6633–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öttinger, H.C. Beyond Equilibrium Thermodynamics; Wiley, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, M.J. A Unified Scientific Framework, a Perspective Discovery of Hidden Fundamental Principles: Entropy Driven Stochastic-Based Emulation Framework. Preprints.org;Preprint 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, M.J. Twenty Years of the Weyl Anomaly. Class. Quantum Grav. 1994, 11, 1387–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luty, M.A.; Polchinski, J.; Rattazzi, R. The a-Theorem and the Asymptotics of 4D Quantum Field Theory. JHEP 2013, 01, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, G.M. The c, a, and b Theorems and the Local Renormalization Group. JHEP 2016, 12, 033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, I.; Osborn, H. Constraints on RG Flow for Four Dimensional Quantum Field Theories. Nucl. Phys. B 2014, 883, 425–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, R.; Matsuo, K. Statistical-Mechanical Theory of Irreversible Processes. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1966, 19, 2069–2090. [Google Scholar]
- ichi Amari, S.; Nagaoka, H. Methods of Information Geometry; American Mathematical Society, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda, H. Fisher Information and the Renormalization Group. J. Phys. A 2015, 48, 375401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V.Balasubramanian, M.B.M.; Raamsdonk, M.V. Momentum Space Entanglement and Renormalization in Quantum Field Theory. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 045014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machacek, M.E.; Vaughn, M.T. Two-Loop Renormalization Group Equations in a General Quantum Field Theory: (I) Wave Function Renormalization. Nucl. Phys. B 1983, 222, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machacek, M.E.; Vaughn, M.T. Two-Loop Renormalization Group Equations in a General Quantum Field Theory: (II) Yukawa Couplings. Nucl. Phys. B 1984, 236, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.k. NSVZ-Compatible Three-Loop Gauge β-Functions and Regulator-Driven Scheme Structure in Supersymmetric Theories with Exponential Higher Covariant Derivative Regularization 2025. [arXiv:hepth/2509.06799].
- Jensen, K.; Kapustin, A. Boundary and Defect C-Theorems in Four-Dimensional Quantum Field Theory. JHEP 2015, 05, 071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietro, L.D.; Komargodski, Z. Cardy Formulae for SUSY Theories in d=4 and d=6. JHEP 2016, 12, 031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Gopakumar, R. Information Geometry of Quantum Field Theories. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2023, 130, 081601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Simon, J. Quantum Information Geometry and RG Flows. JHEP 2021, 06, 025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




