1. Introduction
The beef industry is critical to the US economy, contributing significantly to the agricultural GDP and several sectors. According to the USDA, millions of direct and indirect jobs are linked to the beef industry, including producers, processors, distributors, and retailers. Beef export is also a massive trade stock for the US, and it is positioned as one of the top exporters globally, fostering economic growth. The US beef industry is valued at approximately
$100 billion based on production revenue, coming at about 20% of the total US agricultural market size [
1]. It is also noteworthy that the US beef industry makes up 20% of the global beef cattle sector, valued at 395.2 billion USD in 2021. Beef export alone constitutes 6% of all agricultural exports to other countries by the US. Since beef production is such a value provider for the US economy, numerous challenges persist that continue to threaten the industry’s growth and sustainability, chief among which is Bovine Respiratory Disease (BRD).
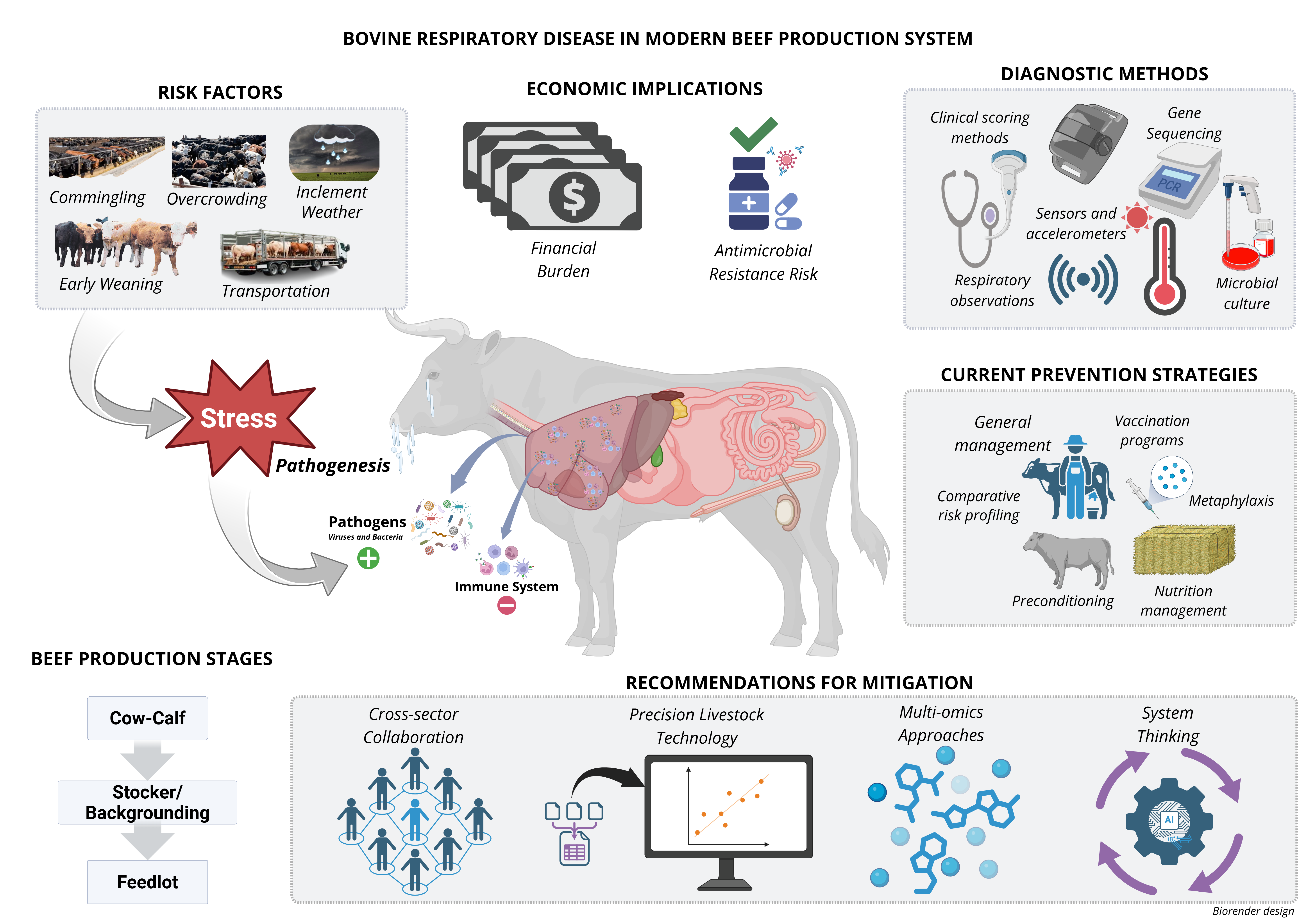
BRD is known to be endemic in North America, impeding the health, welfare, and economic productivity of the beef cattle industry. It is a disease complex that affects cattle, more pronounced in the feedlot phase of production. Its multifactorial etiology involves viral and bacterial agents, environmental stressors, and host factors. With the US beef industry being a cornerstone of the nation's agriculture, mitigating BRD is crucial for sustaining cattle health and ensuring economic stability. Common risk factors that predispose feedlot cattle to BRD include stressors such as transportation, commingling, and abrupt dietary changes. A spectrum of pathogens and microbial organisms has been incriminated as causative agents of the disease, including but not limited to Bovine Herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1), Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus (BVDV), and
Mannheimia haemolytica. Understanding the risk factors [
2] and causative agents is vital for implementing effective prevention and control measures.
BRD inflicts substantial economic losses on the US beef industry. Affected cattle exhibit reduced weight gain, decreased feed efficiency, and increased mortality rates. Additionally, there is a high cost involved in the management of a BRD-affected herd, including veterinary and treatment costs. These impacts not only compromise animal welfare but also affect the overall efficiency and profitability of beef production. The economic significance of BRD is underscored by its financial implications, costing the US beef industry billions of dollars annually. Understanding these economic implications highlights the urgency of investing in research and development for improved prevention and treatment methods. Preventing BRD involves a multifaceted approach, including vaccination programs, biosecurity measures, proper nutrition, and stress reduction techniques. Early detection and prompt treatment are also critical in minimizing the disease's impact. Additionally, research and investment in novel therapies and the deployment of precision livestock management tools and technologies contribute to improving prevention and management.
In the United States, at least one case of BRD is reported per year in about 21% of cattle operations in known cattle-producing states, according to a recent USDA study [
3]. This indicates that a significant number of cattle herds are affected by this disease across the country, making it an important challenge, with the trends in its prevalence presenting some fluctuation over time. Although it is impractical to single out a specific reason for this trend variation, there are numerous factors contributing to the intransigence and spread of BRD. A typically affected cattle herd may present morbidity and mortality rates as high as 80% and 50% respectively [
4].
Generally, producers face a daunting task in implementing effective management practices for BRD. These include the costs associated with diagnostic testing, treatment expenses, labor requirements for regular monitoring of the animal health status, and ensuring adequate nutrition/environmental conditions conducive to cattle well-being, especially during stressful periods like weaning/calving seasons or transportation events. The direct and indirect costs of managing the disease are substantial in that they not only rob producers of their margins but also position them for huge production losses that often threaten their entire operation. Although producers employ a range of strategies to manage and prevent BRD, these measures also come with their deleterious effects, which sometimes are worse than the immediate impact of the disease on the herd. These are referred to as ‘unintended consequences’, giving rise to numerous sustainability challenges plaguing not just the beef production industry but also the global economy. Putting these unintended outcomes in perspective, BRD poses the risk of antimicrobial resistance, which is heightened by the pressure to keep up with production in situations of outbreak, and not to mention, the huge economic sustainability issue arising from performance loss and disease management costs mentioned earlier.
This paper examines the epidemiological contributors to BRD incidence, spread, and prevalence, presents insight into its multifactorial pathogenesis and herd dynamics, discusses its economic implications, and proposes strategies for effective management and mitigation of the disease.
2. Epidemiology of BRD
2.1. Etiology, Pathogens, and Risk Factors
BRD is polymicrobial and multifactorial, with causative agents including viruses and pathogenic bacteria whose interactions elicit varying clinical signs [
5]. A spectrum of pathogens and microbial organisms has been incriminated as causative agents of the disease. This includes viral agents such as: Bovine Herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1), Bovine coronavirus, Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR) virus, Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus (BVDV), parainfluenza-3 (PI3), Bovine respiratory syncytial virus, and bacterial organisms, namely,
Mannheimia hemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, Histophilus somni, and Mycoplasma bovis [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10]. BRD affects cattle of all age groups from pre-weaning to finishing feedlot cattle. It is the main cause of mortality in beef calves from 3 weeks old to weaning, as well as in the beef feedlot system [
11].
The expression of BRD or an outbreak is a function of a complex relationship among various risk factors (including viral and bacterial pathogens), which remains difficult to understand [
2,
11,
12] Commonly associated risk factors that have been reported to predispose animals and exacerbate the observed clinical signs of the disease are transportation from one point to the other, commingling of the herd (e.g., in auction market), inclement weather conditions, hydration status of the animal, metabolic disturbances, age, gender, weight and the immune status of the animal among other risk factors [
11,
13,
14]. Insight into the interplay between the causative agent (pathogen), host (the animal), and the environment (external risk factors) is important in understanding the underlying systems that govern predisposition to BRD.
2.2. Pathogenesis of BRD
The progression of BRD is underlined by the activity of causative agents upon subjecting animals to the risk factors of the disease (
Figure 1). Under stress conditions like transportation and commingling, pathogens proliferate and are easily transmitted between animals. The resulting immunosuppression and damage to the respiratory mucous membrane by viruses lead to secondary bacterial infection [
15]. Stressors such as transportation, commingling, and environmental changes allow the invasion and propagation of microbial organisms in the respiratory system that are endogenous but capable of causing diseases. The proliferation of these organisms potentiates the resulting harm to the respiratory mucous membrane, leading to clinical infection. Virus-infected respiratory mucosal cells speed up bacterial adhesion. Bacterial agents involved in the BRD complex are normal commensal organisms normally found in the nasopharyngeal region. However, they produce virulence factors when they enter the lower respiratory tract, which promote further proliferation, tissue damage, and subsequent inflammatory responses [
16]. Essentially, stress and infectious agents are the leading culprits for the most fatal forms of BRD [
17].
2.3. Clinical Symptoms and Diagnosis
Cases of BRD are presented with various clinical signs, which are general symptoms of the disease, such as fever (>104°F), varying degrees of depression, and diminished or no appetite (animal is “off feed”). The disease also alters normal respiratory activity, manifesting as nasal discharge, rapid shallow breathing, and coughing. Other systemic clinical signs associated with the disease include diarrhea and loss of body condition[
18]. Due to the numerous etiologies of the disease, affected animals are not easily diagnosed, especially those with subclinical infection, since a prominent measure of identifying BRD-affected animals is by observing the rectal temperature [
19]. There have been several efforts to effectively diagnose the disease, but the complexity of its pathogenesis as well as associated risk factors has made the task herculean, leaving a ceaseless ‘burden of care’ for the livestock industry.
Clinical signs, animal/herd history, and laboratory testing are commonly used methods for the diagnosis of BRD (
Table 1). The prevailing technique in use in most field conditions in the US is the visual evaluation and clinical scoring by a Pen Rider, which mainly depends on observation of the rectal temperature, respiratory distress, reduced activity, discharges, and appetite of the animal. One such commonly used clinical scoring method is “DART scoring,” which measures the Depression, Appetite, Respiration, and Temperature of the animal. Laboratory techniques, including microbial culture, serology, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), and gene sequencing, are also gaining wider usage in the diagnosis of BRD, but an important consideration for the field efficacy or viability of these methods is the turnaround time, i.e., time lag between sampling and test results [
20].The popularity of PCR for etiological diagnosis of BRD is increasing, especially quantitative PCR, as it can be used to detect numerous viral and bacterial pathogens, making it possible for professionals to better establish treatment, prevention, or control measures [
20]. Recent research has explored various approaches for diagnosing BRD (
Table 1). One example is the work by [
21], which utilized blood 1H NMR metabolomics to identify BRD markers in animal blood samples and classify them as infected or not infected. Their work demonstrated high accuracy and potential for using the biomarker as a diagnostic tool.
Table 1 and
Figure 2 below present a comprehensive summary of the various methods employed in BRD diagnosis.
Essentially, owing to the continuous advocacy for the rational use of antimicrobial agents, there is an increasing application of laboratory diagnostic tests as tools for identifying BRD pathogens. Still, difficulty persists in interpreting the presence of incriminated pathogens of BRD-affected cattle individually and within a herd [
20] Hence, regardless of the utility of some of the laboratory diagnostic techniques and the advancements in arriving at more specific methods, there is still more to be desired, as none can pass as the gold standard for diagnosing BRD due to the cost and impracticality of use as methods for real-time diagnostic tools. In the wake of the adoption of cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning linked to agents [
35,
36] for solving big problems plaguing global economies, we might see a veritable application of these trends in combating BRD. However, the spate of unintended consequences from the lack of established diagnostic gold standards still leaves much to be desired.
2.4. Herd-Level Dynamics of BRD
BRD exhibits complex herd-level dynamics influenced by animal movements, pathogen load, stress physiology, and management practices [
37]. From an epidemiological standpoint, herds act as semi-closed populations where BRD transmission follows nonlinear contagion processes. The Susceptible – Infectious – Recovered (SIR) framework provides a foundational structure for modeling within-herd transmission of BRD, allowing researchers to characterize the rate at which susceptible animals (S) become infected (I) and subsequently recover (R). The classic equations are defined as:
where
represents the transmission coefficient and
the recovery rate. Extensions of this framework, such as SEIR (which includes an exposed latent class) and SIR-Q (incorporating quarantine or isolation compartments) [
38], are increasingly used to reflect the biological latency of BRD pathogens and the effects of intervention strategies.
Recent herd epidemiology modeling efforts have integrated system dynamics and network theory to capture the complex adaptive behavior of beef systems, where cattle flow between ranches, auction yards, and feedlots creates multiple infection pathways [
39]. These models have shown that disease propagation is not homogeneous; instead, “superspreading” herds emerge as critical nodes within cattle trade networks. In such models, herd-level effective reproduction numbers (Rₑ) often exceed individual-level estimates due to animal movement density and stress-induced immunosuppression during transport [
40]. These dynamics underscore the importance of network-informed epidemiological parameters when estimating the transmission potential of BRD in U.S. beef systems.
Pathogen-specific models have been developed to parameterize BRD-related agents such as
Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, and
Mycoplasma bovis. For instance, [
41] applied an SIR model to
M. bovis outbreaks, identifying strong seasonal variation in
and
values due to fluctuations in housing and temperature. Similarly, [
42] used time-homogeneous SIR modeling to estimate the force of infection for bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV), another key complex respiratory pathogen, finding that transient infections can sustain endemic transmission even in partially immune populations. These studies demonstrate that parameter estimates derived from empirical serosurveys can effectively calibrate BRD transmission models for assessing herd-level risk.
The integration of management interventions into epidemiological frameworks, such as vaccination, antimicrobial metaphylaxis, and quarantine, is gaining traction through modified SEIR and SIR-Q models [
37,
43]. To represent this biological and managerial complexity, contemporary models extend the basic SIR framework to include latent, quarantine, and intervention compartments. Such integration yields the controlled SEIR-Q model, formulated as:
Here,
represents vaccination efficacy (reducing susceptibility),
captures the effectiveness of quarantine or isolation (reducing transmission),
denotes metaphylactic or therapeutic treatment efficiency (shortening infectious duration),
is the rate of progression from exposure to infectiousness, and
represents disease-induced mortality [
38]. Quarantine compartments (Q) in particular allow simulation of management-imposed isolation, reflecting feedlot health protocols that remove clinically affected cattle from the transmission pool. These models help optimize vaccination timing and evaluate how biosecurity reduces
by interrupting direct and indirect contact pathways[
35,
36]. Dynamic simulation studies further highlight how delayed detection or inadequate isolation can prolong epidemic persistence at the herd level, even when vaccination coverage exceeds 70% [
44,
45].
To further help the understanding of the herd level dynamics of BRD, the growing incorporation of machine learning and parameter databases such as PARAMETRA [
38] is advancing predictive BRD epidemiology by merging mechanistic and data-driven approaches. Predictive algorithms trained on SIR and SEIR model outputs can anticipate outbreak peaks and inform adaptive management decisions. Collectively, these advances mark a paradigm shift in BRD epidemiology, from descriptive field studies to quantitative systems modeling, which integrates animal-level data, movement networks, and pathogen dynamics to understand and mitigate herd-level transmission in the U.S. beef industry.
2.5. Current BRD Prevention and Management Strategies
Due to the multifactorial nature of the disease, complete elimination of BRD is not currently guaranteed, but a holistic and integrated system-thinking approach can reduce the prevalence of the disease to a desirable level for producers to minimize associated losses. Formulation of prevention strategies may vary with the need to think of the disease from a system perspective and address specific problems associated with each junction of the observed challenges by iterating and taking feedback where necessary. Prevention strategies (
Figure 3) require a multifaceted approach that considers all relevant factors. However, current prevention and management strategies include vaccination, preconditioning, risk profiling, and segregation of high-risk animals on arrival, metaphylaxis, adopting proper biosecurity measures, stress management, and proper record keeping, etc.
2.5.1. Vaccination Programs
Several studies [
46,
47,
48,
49] have proven that vaccination is effective in preventing the BRD pathogens. Modified live vaccines and killed vaccines have been used against viral agents incriminated in the occurrence of BRD. Hence, the adoption of a proper scientific vaccination protocol can reduce the incidence and prevalence of BRD in the herd, but it must be noted that the timing of vaccination is crucial. Calves transported over a long distance, very close to the day of vaccination, soon after arrival, may show detrimental effects. Economic analysis of return on investment is also required before designing and adopting a vaccination protocol; otherwise, there may be economic losses that lead to long-term consequences.
2.5.2. Preconditioning
This is a management practice where newly weaned calves undergo a period of preparation and adjustments before entering the feedlot for further finishing. Precondition normally takes place soon after weaning, before transporting the animals to feedlots. During precondition, animals are provided with proper nutrition, vaccination, deworming, dehorning, castration, and other health management to adapt to the new condition. These practices help to reduce the stress associated with traveling. Various studies have identified that preconditioning is beneficial in reducing the incidence [
48,
50,
51] Preconditioning ideally should be done at least 3 weeks before the transportation of animals[
50].
2.5.3. Metaphylaxis
This is the mass medication of a group of animals to reduce the incidence rate of a disease in a population that already has some evidence of the disease [
8] i.e., a population at a high risk of progression towards clinical infection. In feedlot cattle, metaphylaxis is widely used to control BRD. Studies have identified that metaphylaxis of high-risk animals is very useful in controlling the disease [
52]. Still, the accurate segregation or classification of high-risk animals is the critical deciding factor here because it affects the overall cost of treatment. Any lack of accuracy may lead to overspending on antibiotics or missing potential animals that can spread the disease to the rest of the population. Implementation of metaphylactic protocols in beef cattle feedlot should be done based on an informed perspective to ensure that it is productive.
2.5.4. Comparative Risk Profiling & Segregation of Risk Factors
Categorizing animals based on BRD risk factors into high and low risk is an effective management tool in reducing the disease prevalence in a herd and thereby mitigating the economic and animal welfare impact associated with the disease. Currently, many producers use qualitative risk assessment based on information on commingling history, transportation duration, age, weight, extreme weather changes, prior history of concentrate feeding, vaccination history, etc. [
53,
54]. A quantitative risk profiling of BRD will help to classify the animals more accurately. A weighted ranking method of comparative risk classification, a Bayesian network model of risk classification, or a big data-based predictive model can be used for risk profiling. Once risk profiling is done, high-risk animals can be separated from the remaining herd, and a separate management method can be employed to keep them healthy.
2.5.5. Nutritional Management
Recent findings underscore the growing importance of nutrition in the prevention and management of Bovine Respiratory Disease (BRD), even though definitive causal links between specific nutrients and BRD incidence remain elusive. Modern feedlot studies have identified that cattle receiving diets supplemented with probiotics, such as
Bacillus subtilis, exhibit lower BRD morbidity and improved growth performance. This suggests that certain dietary components may positively influence gut health and immunity, indirectly reducing susceptibility to respiratory infections [
55]. Moreover, preconditioning practices that include nutritional support, like vitamin and mineral supplementation, particularly vitamin E, selenium, and zinc, are increasingly recognized for enhancing immune response and reducing BRD risk, especially during high-stress periods such as weaning and transportation [
56].
While the specific feed composition may not be a standalone factor, ensuring consistent feed intake and minimizing abrupt dietary changes are critical. [
57] emphasized that early feedlot acclimation, along with maintaining nutritional energy balance, helps reduce stress-related immunosuppression, thereby enhancing resilience to BRD pathogens. Additionally, calves with higher body condition scores at arrival, typically linked to sound nutritional backgrounds, demonstrated reduced BRD treatment rates, reinforcing the role of prior nutritional status. Thus, while nutrition alone may not entirely prevent BRD, its strategic role in immune modulation and stress reduction makes it an essential component of integrated BRD control programs [
58].
2.5.6. General Management Practices
Management practices may vary by region. It is important to prepare a standard operating procedure to deal with the disease. Ideally, it should consist of tailored prevention strategies and biosecurity measures, risk profiling and segregation of high-risk animals, metaphylaxis protocols for the high-risk animals, a tailored vaccination protocol, and nutritional guidelines to follow. It should be prepared by the collaborative effort of veterinarians, farm managers, nutritionists, and other key stakeholders. Focus should be on reducing stressors and improving immunity through nutrition and proper management practices to ensure the welfare of the animals. Record keeping and adequate information management [
59] should be the norm because only a data-driven approach potentially presents the most viable means to reduce disease incidence.
An effective yet challenging means of disease control is to reduce exposure of susceptible cattle to pathogens, which involves stringent management practices in the area of sanitation. Receiving and hospital pens, associated feed bunks, and water troughs should be frequently cleaned. Equipment used in manure management and dead stock removal should not be involved in the handling of feed sources. Lastly, controlling BRD must be managed through a comprehensive herd health immunization and management program that effectively addresses disease challenges common to the operation [
8].
3. Epidemiological Studies on BRD
3.1. BRD Incidence, Prevalence, and Epidemiological Patterns
Across multiple decades of epidemiological studies, reported morbidity has ranged from 10% to 87%, and mortality from 0.7% to 60% (
Table 1), underscoring the multifactorial nature of the syndrome and the influence of management, environment, and host susceptibility [
4,
13,
60]. Early studies in the Central Plains region described average feedlot morbidity near 8% and mortality below 1%, with respiratory disease responsible for three-quarters of all cases [
61]. However, subsequent feedlot surveillance and controlled research revealed much higher prevalence, particularly among high-risk and newly received calves [
62].
Temporal trends in disease expression suggest that BRD is not confined to the initial feeding period. Historically, approximately 65-80% of BRD cases were recorded within the first 45 days on feed, 13-22% between 45 and 90 days, and less than 15% thereafter [
60,
61]. More recent evidence indicates a gradual epidemiological shift toward mid and late feeding phase morbidity. In a multi-feedlot study of 13 commercial operations, [
40] observed that 5-10% of cohorts arriving during the second quarter of the year developed mid or late feeding stage BRD, suggesting a seasonal association with environmental transitions. Similarly, [
63] reported morbidity rates of 33.7% in high-performing cattle and 67.2% in high-risk cattle, noting that BRD onset occurred later in the feeding period for the former. These findings indicate that while early onset BRD remains dominant, the disease increasingly manifests in later feeding stages, particularly under high-performance or preconditioned production conditions.
Several demographic and management-related factors consistently influence disease occurrence. Lighter, newly weaned, or stressed calves, especially those sourced from multiple origins and transported long distances, exhibit markedly higher morbidity [
62] Steers are generally more affected than heifers, likely due to the added stress of castration before feedlot entry [
64] In contrast, older, heavier, and preconditioned cattle that are weaned for ≥45 days and vaccinated before shipment display significantly lower morbidity and mortality [
65,
66] Yet, as [
65] observed, BRD continues to occur even among high-performing and well-vaccinated cattle, implying that host-pathogen interactions, microbial ecology, and management intensity remain crucial determinants of disease risk.
Table 2.
Showing various research-based and author-reported Bovine Respiratory Disease morbidity and mortality in varying animal populations, risk profiles, and experimental conditions over 26 years. .
Table 2.
Showing various research-based and author-reported Bovine Respiratory Disease morbidity and mortality in varying animal populations, risk profiles, and experimental conditions over 26 years. .
| BRD Morbidity, % |
BRD Mortality, % |
Year |
Author |
| 75 |
50 |
1996 |
[61] |
| 75* |
45* |
1998 |
[60] |
| 20.60 |
5.90 |
2000 |
[66] |
| 10.52* |
13.1#* |
2005 |
[64] |
| 75* |
30* |
2008 |
[62] |
| 14.70 |
0.70 |
2009 |
[67] |
| 39 |
15.15* |
2010 |
[68] |
| 100** |
31.9** |
2013 |
[54] |
| 21 |
46.4#
|
2013 |
[69] |
| 75* |
45* |
2014 |
[4] |
| 11.43* |
3 |
2014 |
[70] |
| 22 |
3.50 |
2014 |
[71] |
| 35* |
9* |
2015 |
[72] |
| 87 |
33 |
2017 |
[73] |
| 61.90 |
12.90 |
2018 |
[13] |
| 33.90 |
5 |
2018 |
[74] |
| 18 |
2.10 |
2020 |
[21] |
| 12 |
5.60 |
2021 |
[75] |
| 67.2** |
4.83** |
2021 |
[63] |
| 75 |
60* |
2021 |
[65] |
| 14.15* |
2.73* |
2022 |
[40] |
| 44.50 |
3.30 |
2022 |
[76] |
Seasonal and regional differences further shape BRD epidemiology. [
54] reported culling and mortality risks reaching 100% and 31.9%, respectively, in a study encompassing over eight million animals, with higher disease risk between March and September. In contrast, [
75] identified elevated BRD morbidity (12%) and mortality (5.6%) in the fall, correlating with seasonal antimicrobial usage patterns. Auction-derived cattle experience a particularly high risk. [
13] recorded morbidity and mortality of 61.9% and 12.9%, respectively, reinforcing the impact of marketing, transport, and commingling stress. Despite such variability, long-term datasets reveal that while overall annual mortality from BRD remains stable [
77], its temporal clustering and within-feedlot heterogeneity have intensified [
63].
The epidemiological continuity of BRD extends beyond feedlot settings into cow-calf and dairy systems. In pre-weaned and nursing calves, reported respiratory morbidity ranges from 12% to 39%, and mortality from 3% to 17%, depending on passive transfer status, ventilation, and environmental management[
74,
78,
79]. Failure of passive transfer of immunity and poor colostrum management significantly increase disease susceptibility in calves and later influence feedlot performance [
68,
70]. These early-life vulnerabilities contribute to the overall population-level persistence of BRD in integrated beef systems.
Longitudinal analyses spanning more than two decades highlight BRD as an endemic, multifactorial syndrome characterized by variable morbidity (10-87%) and mortality (1-60%) across production systems and time (
Figure 4). While improved genetics, vaccination, and management have reduced early-feeding losses, chronic and late-feeding-stage cases are now proportionally increasing, reflecting changing production intensities and microbial adaptation. The evolving epidemiology of BRD emphasizes the necessity for integrated surveillance and predictive modeling that combine biological, environmental, and management variables to guide precision health interventions in U.S. beef feedlot systems.
3.2. Selected Studies and Contributions to the Understanding of BRD Epidemiology
3.2.1. Temporal Disease Patterns and Treatment Outcomes in Feedlot Cattle (Case Study I)
In [
80], the authors conducted one of the most extensive temporal analyses of BRD in feedlot systems, leveraging standardized event data from 25 commercial feedyards across the United States, comprising 567,989 cattle between 2015 and 2021. The study evaluated three key temporal indicators, timing of initial BRD treatment (Tx1), fatal disease onset (FDO), and days to death after treatment (DTD), to characterize the epidemiological distribution and variability of BRD events across quarters of arrival and gender. Using Wasserstein distances, a robust metric for comparing empirical distributions, the researchers identified significant quarterly variation in disease frequency, with the greatest differences between the second and third quarters and between the second and fourth quarters. Heifers arriving in the second quarter had an FDO distribution extending between 20 and 80 days post-arrival, underscoring the role of seasonality and animal demographics in disease onset.
Importantly, DTD exhibited a right-skewed distribution, suggesting that traditional arithmetic averages inadequately represent BRD progression or fatality timing [
80]. These findings have profound implications for feedlot management, emphasizing that BRD occurrence and outcomes follow complex temporal patterns rather than uniform trajectories. Understanding such skewed distributions allows veterinarians and feedyard managers to optimize disease monitoring windows and resource allocation. The study thus expands epidemiological understanding by linking the timing of clinical intervention with survival outcomes, an advancement that complements earlier epidemiological frameworks describing predisposing risk factors and infection dynamics [
67]. In [
80], the importance of precision-timed interventions and continuous disease surveillance in feedlot cattle populations is demonstrated through the heterogeneity of BRD timing across seasons, sex, and treatment responses
3.2.2. Predictive Modeling for BRD Outcomes in Commercial Feedyards (Case Study II)
Building upon the need for data-driven decision support, [
81] applied modern predictive analytics to estimate the likelihood of treatment outcomes in BRD cases using retrospective data from 96,382 animals across 12 U.S. feedlots in Kansas, Nebraska, Colorado, and Texas. The study sought to predict whether animals treated for BRD would successfully finish the feeding period based on variables known at first treatment, incorporating weather data and feedyard-specific balancing techniques to refine predictive accuracy. Five supervised learning models: averaged perceptron, decision forest, logistic regression, neural network, and boosted decision tree were trained and validated using standard performance metrics such as accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC). Results indicated that predictive performance was moderate, with a median AUC of 0.675 across models, but significant variability existed among individual feedyards. Incorporation of weather data modestly altered sensitivity and specificity but did not markedly improve predictive strength. Among models, the boosted decision tree consistently demonstrated superior performance in most feedyards [
81].
Despite the modest accuracy, this study represents a pivotal advancement in epidemiological modeling for BRD management by demonstrating the feasibility of machine learning approaches in real-world feedlot datasets. From an epidemiological perspective, the study underscores that disease prediction in large, heterogeneous populations remains inherently complex due to interactions among host factors, environmental conditions, and management systems. Nonetheless, the emergence of predictive tools offers a foundation for evidence-based clinical decision support systems that can enhance early diagnosis and optimize antimicrobial stewardship [
80]. As precision livestock technologies continue to evolve, integrating predictive modeling into feedlot health management could transform BRD control from reactive treatment toward proactive risk mitigation, marking a significant methodological contribution to modern veterinary epidemiology.
3.2.4. Economic Impacts and Performance Consequences of BRD (Case Study III)
In [
82], the economic burden of BRD was evaluated using a comprehensive feedlot study of 898 crossbred steers in Australia, focusing on animal performance, carcass characteristics, and financial outcomes under four diagnostic definitions: number of BRD treatments received, lung lesions, pleural lesions, and combined clinical diagnosis. This multi-parameter approach revealed a BRD morbidity rate of 18% and a mortality rate of 2.1%, both consistent with historical North American feedlot data. The authors quantified substantial performance losses in affected cattle, reporting carcass weight reductions of 16.0 kg in subclinical and 24.1 kg in clinically infected animals compared with healthy controls. Animals treated three or more times for BRD produced 39.6 kg lighter carcasses and generated AUD
$384.97 (
$252.30 USD) less net return than untreated counterparts. BRD mortality resulted in an average economic loss of AUD
$1,647.53 (
$1079.75 USD) per head [
21].
Beyond these economic metrics, the study offered key epidemiological insights by differentiating between clinical and subclinical BRD. Subclinical infections, often undetected through routine health checks, still resulted in measurable productivity and financial losses, emphasizing the need for improved diagnostic precision and continuous health surveillance. By linking pathological findings at slaughter (lung and pleural lesions) with on-feed performance and financial outcomes, the study illustrated that BRD’s economic impact extends well beyond acute morbidity events, encompassing chronic subclinical damage that erodes profitability
4. Economic Impact of BRD
4.1. Financial Burden and Animal Performance Consequences
The economic burden of BRD is multifactorial, encompassing direct treatment expenses, production losses due to morbidity and mortality, and long-term impacts on carcass quality and feed efficiency. Recent studies indicate that BRD continues to erode profitability within the U.S. cattle industry, accounting for losses exceeding
$1 billion annually in beef operations alone [
83] Although this figure represents a refinement from earlier broad estimates of global losses of around
$3 billion [
84]. It highlights the persistent economic gravity of the disease. The cost per clinical case of BRD has been estimated at approximately
$42 to
$90 per animal, depending on production phase and severity [
85,
86]. These per-head figures integrate both tangible and opportunity costs, such as reduced growth performance and the downstream impact on market returns.
Multiple studies show that both BRD severity and the number of antimicrobial treatments exert compounding negative effects on cattle performance and carcass outcomes[
83,
85,
87,
88], as shown in
Figure 5. [
89] demonstrated stepwise declines in carcass weight, dressing percentage, and total value as cattle move from zero to multiple BRD treatments, with cumulative losses exceeding
$230 per head. [
90] similarly, found that cattle receiving two or more treatments showed reduced marbling and quality grades, while [
87] linked higher lesion severity to lower carcass weights. These patterns align with [
21], who reported carcass value reductions of
$53-
$80 per head and mortality losses surpassing
$150. BRD also reduces average daily gain (ADG), feed efficiency, and carcass weight by 6-8 kg [
83], translating into substantial lost income and reduced operational efficiency in feedlots where carcass uniformity and throughput drive profitability.
Recent economic modeling emphasizes that integrating predictive analytics into BRD management can significantly mitigate financial losses. [
91] demonstrated that mortality prediction models deployed at the first or second treatment event reduced economic loss by
$59 per head, largely through more targeted therapy and reduced retreatment frequency. These models exemplify the growing utility of precision management tools in animal health economics, bridging epidemiological insight with cost optimization. The consistent message across contemporary literature is that BRD’s financial toll extends well beyond immediate treatment costs; it affects the entire production continuum from feeder cattle acquisition through carcass marketing, influencing both individual producer returns and broader market dynamics.
4.2. Economic Ramifications of Antimicrobial Usage and Stewardship in Managing BRD
The management of Bovine Respiratory Disease (BRD) in U.S. beef production systems remains fundamentally anchored in the use of antimicrobial agents. This reliance stems from the disease’s complex etiology, which involves the synergistic interaction of viral agents, such as
Bovine herpesvirus-1 and
Bovine respiratory syncytial virus, with bacterial pathogens like
Mannheimia haemolytica,
Pasteurella multocida, and
Mycoplasma bovis. These bacteria, often acting as secondary invaders, drive the acute inflammatory response responsible for pulmonary consolidation and subsequent production losses. The integration of metaphylactic and therapeutic antimicrobial interventions has long been central to limiting outbreaks and minimizing mortality in feedlots. Potent macrolides such as tulathromycin and tilmicosin have achieved therapeutic success rates exceeding 90% in controlled field studies, contributing significantly to feedlot profitability and the preservation of carcass quality [
84,
92]. However, the increasing dependence on these agents has concurrently accelerated the emergence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), posing profound challenges to both veterinary and public health domains.
Despite their proven efficacy, the continuous and often prophylactic use of antibiotics has exerted selective pressure on microbial populations, facilitating the proliferation of resistant strains. Recent surveillance data indicate a worrying trend: isolates of
M. haemolytica and
P. multocida from BRD-affected cattle demonstrate multidrug resistance (MDR) profiles, including reduced susceptibility to macrolides, tetracyclines, and fluoroquinolones [
75]. Of particular concern is
Mycoplasma bovis, whose intrinsic resistance to β-lactams and rising tolerance to macrolides threatens to render key antimicrobial classes ineffective. Studies such as those by [
93] and [
94] emphasize that this resistance dynamic not only diminishes therapeutic efficacy but also poses zoonotic risks through horizontal gene transfer and environmental dissemination of resistance determinants. The One Health implications are significant; resistant bacteria or resistance genes originating in feedlot environments can propagate through the food chain or via environmental pathways, thereby escalating the global AMR burden.
The growing recognition of AMR risk has catalyzed policy shifts and the evolution of antimicrobial stewardship frameworks in livestock production. Initiatives now prioritize targeted therapy, diagnostics-driven treatment, and biosecurity reinforcement to reduce prophylactic use [
95]. Artificial intelligence and predictive modeling are being explored to optimize antimicrobial decision-making, enabling earlier identification of at-risk cattle and minimizing unnecessary mass medication. This technological evolution aligns with recommendations by the World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH) and the U.S. FDA’s Guidance for Industry #263, which call for veterinary oversight and data-driven antimicrobial management. However, while stewardship policies are scientifically justified, their implementation has been met with economic resistance in the beef sector, where disease outbreaks can rapidly compromise profit margins if left unmanaged.
The economic implications of antimicrobial restriction are substantial. [
96] demonstrated through simulation modeling that limiting antimicrobial access, particularly metaphylaxis, could precipitate revenue declines of
$43 to
$139 per steer, effectively nullifying profit margins in high-risk feedlot systems. These results mirror findings from feedlot health economists who emphasize that antimicrobial use remains a critical stabilizing input, protecting the high-capital investments associated with intensive cattle feeding operations [
83]. The balance between maintaining herd health and mitigating AMR therefore embodies a central dilemma: while antimicrobial reduction aligns with societal and regulatory priorities, it risks destabilizing production efficiency and profitability, especially when alternative interventions such as rapid diagnostics or effective vaccines are limited in scalability or availability.
Beyond economic and clinical dimensions, antimicrobial usage in BRD management carries broader ethical and consumer-driven ramifications (
Figure 6). Public perception of antibiotic use in food animals has shifted markedly, with growing demand for “antibiotic-free” beef products driven by food safety concerns and AMR awareness [
97] This has prompted major beef producers to explore non-antibiotic disease prevention strategies, including precision feeding, microbiome modulation, and genetic selection for disease resilience. Nevertheless, the transition away from antimicrobial dependence is constrained by the absence of universally effective alternatives and the logistical complexities of implementing large-scale preventive systems. The resultant tension between consumer expectations and production realities underscores the necessity of nuanced policies that sustain both animal welfare and public health objectives.
Globally, antimicrobial use in livestock is projected to increase in parallel with the intensification of animal production. As [
98] notes, the global expansion of meat demand has quadrupled over the past half-century, with future growth concentrated in emerging economies. This expansion inherently heightens antimicrobial reliance to maintain productivity and disease control under dense stocking conditions. Consequently, strategic innovation, including vaccine development, improved environmental management, and digital epidemiological surveillance, will be indispensable to reconciling productivity goals with antimicrobial stewardship imperatives. The sustainability of BRD control programs will thus hinge on an integrative approach that aligns economic viability, epidemiological insight, and public health protection
4.3. Practical Implications for Farmers, Veterinarians, and Policymakers
The cumulative losses from BRD extend well beyond treatment costs, encompassing reduced feed efficiency, lower average daily gain, diminished carcass weight, and increased mortality, with per-head losses estimated at up to
$150 [
83], hence the need for decision support tools that optimize production and improve productivity [
99]. In addition, producers’ adoption of precision livestock technologies, including wearable sensors, automated feeding systems, and behavioral and physiological parameters monitoring platforms, offers an effective means to detect early disease onset, optimize antimicrobial use, and minimize performance losses [
100]. Despite high initial costs, these tools yield long-term savings by reducing morbidity, mortality, and antimicrobial dependence.
Veterinarians, meanwhile, face the dual challenge of diagnosing BRD in the absence of a universally accepted diagnostic gold standard and exercising responsible antimicrobial stewardship. Field diagnosis often depends on subjective indicators such as rectal temperature, respiratory effort, nasal discharge, and behavioral changes, which vary in diagnostic sensitivity and specificity [
20,
21]. Thus, veterinarians are not only clinicians but also educators, tasked with guiding producers in evidence-based diagnosis, prudent antimicrobial use, and the implementation of vaccination, biosecurity, and immunomodulatory strategies. At the policy level, BRD management intersects with public health and food system sustainability concerns, as the widespread antimicrobial use in cattle production contributes to the emergence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), a recognized One Health threat [
96]. Policymakers must therefore pursue balanced frameworks that incentivize judicious drug use, fund the development and subsidization of diagnostic and preventive technologies, and strengthen data integration and disease surveillance networks across the livestock sector
5. Recommendations
5.1. Areas Requiring Further Exploration and In-Depth Studies
Despite more than a century of intensive research into the complex dynamics of BRD, it continues to challenge scientists, veterinarians, and producers alike. Its persistence within U.S. beef production systems underscores gaps in the understanding of its multifactorial etiology, particularly concerning the interplay between host, pathogen, and environmental stressors. While conventional approaches, including vaccination, metaphylaxis, and biosecurity, remain central to control strategies, there is an evident shift toward advanced predictive and diagnostic technologies that integrate precision livestock management and systems biology. However, these emerging innovations remain in their infancy regarding validation, standardization, and practical field deployment, calling for continued exploration into scalable and cost-effective applications [
83]. Greater translational research linking laboratory findings with on-farm implementation is, therefore, essential to bridge the divide between scientific discovery and industry adoption.
A critical frontier for future BRD research lies in continued studies of the bovine respiratory microbiome and its role in disease pathogenesis. BRD arises not from a single etiologic agent but from a complex dysbiosis involving commensal and opportunistic microbes under immune or environmental stress [
101] Investigating microbial community dynamics in relation to host immune modulation may reveal new biomarkers and therapeutic targets. The integration of systems biology and multi-omics approaches, including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, offers an unprecedented opportunity to unravel host-pathogen interactions at the molecular level [
102]. For example, [
21] demonstrated the potential of ¹H NMR metabolomics in identifying blood biomarkers indicative of BRD, though they emphasized that these diagnostic signatures require extensive validation across diverse populations and production contexts. Advancing computational biology and data integration frameworks will be key to leveraging such datasets for predictive modeling and personalized disease management.
Equally promising is the application of precision livestock technologies (PLTs) and artificial intelligence (AI)-based diagnostic systems for the early detection of BRD [
103]. Traditional clinical scoring systems, though widely used, are limited by subjectivity and variable accuracy across operators and environments. Hybrid intelligent models combining machine learning algorithms with behavioral and physiological sensor data can enhance diagnostic precision and timeliness [
104] Multi-modal sensor systems capable of monitoring parameters such as body temperature, rumination, movement, and respiratory rate, when combined with pathogen detection and biomarker analysis, could establish a new standard for real-time, predictive health surveillance in feedlot settings. Nonetheless, the economic feasibility of such technologies remains a major constraint, particularly for small and medium-scale operations. Future research must therefore address not only the technological refinement of PLTs but also cost reduction strategies, industry-specific calibration, and demonstration of return on investment under commercial conditions.
Ultimately, the next phase of BRD research demands multidisciplinary integration, bringing together veterinarians, molecular biologists, engineers, and data scientists under a systems-thinking framework. Emphasis should be placed on creating adaptable models that capture the epidemiological, immunological, and environmental complexity of BRD within intensive beef production. Funding mechanisms that support large-scale field trials, computational tool development, and open-access data sharing will be pivotal in accelerating progress. As climate variability, production intensification, and antimicrobial stewardship pressures converge, refining the predictive, preventive, and precision-oriented BRD management strategies will define the future of sustainable beef health systems globally.
5.2. Suggestions for Refining Preventive Measures and Management Strategies
An effective BRD prevention requires leveraging environmental and epidemiological intelligence to forecast and manage disease risk. Outbreaks frequently coincide with stress-inducing events such as weaning, transport, and abrupt environmental changes. Integrating weather patterns, transport data, and nutritional factors into predictive models enables producers to anticipate risk periods and implement timely interventions [
105]. Incorporating animal-level parameters such as age, breed susceptibility, and immune status further enhances predictive precision and enables risk-based stratification of management actions. Structured intake procedures, including quarantine and gradual acclimatization of new arrivals, are particularly effective in reducing BRD morbidity [
100].
Enhancing diagnostic capabilities remains a pivotal element in modernizing BRD management. Traditional diagnostic approaches, based on clinical observation and pen rider assessments, are constrained by low sensitivity and specificity, often leading to underdiagnosis or overtreatment [
46] Emerging pen-side diagnostic tools, biomarker assays, and precision monitoring technologies [
103,
106] can detect subclinical infections earlier, facilitating targeted therapy and minimizing antimicrobial misuse. Integrating these diagnostic innovations with data-driven decision systems allows veterinarians and producers to link disease detection with performance monitoring, enabling stratified interventions that optimize animal health outcomes and preserve antimicrobial efficacy.
Sustainable refinement of BRD prevention strategies ultimately depends on cross-sector collaboration among producers, veterinarians, researchers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders. Systems-thinking approaches that view BRD epidemiology across the entire beef production system, from cow-calf to feedlot and processing, enhance understanding of transmission dynamics and intervention efficacy [
97]. For example, improvements in preconditioning and weaning practices at the cow-calf stage can markedly reduce downstream BRD incidence in feedlots. Policymakers play a critical enabling role by supporting the development of surveillance infrastructure, rapid diagnostics, and economic incentives for producers who adopt best-practice health protocols. Given the financial vulnerability of feedlot operations to disease outbreaks, policies must balance public health imperatives with economic sustainability, ensuring that regulatory shifts consider producer profitability [
96]. Aligning epidemiological insight, technological innovation, and policy support will be key to achieving a resilient, low-disease-risk beef production system
6. Conclusion
BRD remains a defining constraint to the health, welfare, and economic sustainability of U.S. beef production systems. Its persistence, despite decades of research and technological progress, reflects the intricate connection of microbial, host, environmental, and management determinants that drive its epidemiology. BRD exemplifies the complexity of contemporary livestock health challenges, where biological heterogeneity intersects with production intensification, climate variability, and antimicrobial resistance. Addressing this burden requires reframing BRD not as a discrete clinical syndrome, but as an emergent property of the production ecosystem, one demanding system-level interventions that integrate epidemiology, economics, and ethics (policy).
Emerging innovations in precision livestock monitoring, molecular diagnostics, and data-driven epidemiology are redefining what is possible in BRD control. These technologies offer unprecedented opportunities for early detection, predictive modeling, and individualized management, enabling a shift from reactive treatment to proactive disease prevention. Yet, their transformative potential will only be realized through cross-sector integration, linking on-farm data streams with veterinary expertise, genomic surveillance, and policy frameworks that incentivize responsible antimicrobial use. Sustainable progress will depend not only on technological adoption but also on the development of equitable regulatory environments and knowledge-sharing networks that empower producers to implement evidence-based health strategies.
Bridging mechanistic understanding with system-wide application presents a potential next frontier in the quest for BRD mitigation. Advances in microbiome science, immunogenomics, and computational biology hold promise for elucidating host-pathogen-environment interactions and translating them into actionable prevention models. Achieving this translation will require sustained collaboration between producers, scientists, veterinarians, and policymakers. Ultimately, overcoming BRD’s enduring impact will require a paradigm shift, from managing disease consequences to anticipating and preventing its emergence. A future in which BRD is predictably mitigated rather than persistently endured will depend on aligning technological innovation with policy foresight and cooperative governance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A. and K.K.; validation, A.A. and K.K.; formal analysis, A.A.; investigation, A.A.; resources, K.K.; data curation, A.A.; writing – original draft preparation, A.A.; review and editing, K.K.; visualization, A.A.; supervision, K.K.; project administration, K.K.; funding acquisition, K.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by AgriLife Research and Texas A&M College of Agricultural and Life Sciences’ doctoral research funding and 2024 Texas A&M Institute of Data Science Early Career Collaborative grant.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not Applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Baldwin, K.; Williams, B.; Turner, D.; Tsiboe, F.; Raszap Skorbiansky, S.; Sichko, C.; Jones, J.W.; Toossi, S. U.S. Agricultural Policy Review, 2023. 2024 Available online: https://ageconsearch.umn.edu/record/349026 (accessed on Oct 27, 2025).
- Adekunle A.J., Gaines A., Estefano N., Lenin D., Hole P., Khandelwal R., Cooke R., Kaniyamattam K. Mapping Risk Factor Variability and Disease Dynamics of Bovine Respiratory Disease in Beef Production Systems: A Scoping Review. 2025, DOI: In press.
- USDA Feedlot 2011 Part IV Health and health mgt on US feedlot with capacity 1000 above. 2013.
- Hilton, W.M. BRD in 2014: where have we been, where are we now, and where do we want to go? Animal health research reviews 2014, 15, 120–122. [CrossRef]
- Dubrovsky, S.A.; Van Eenennaam, A.L.; Karle, B.M.; Rossitto, P.V.; Lehenbauer, T.W.; Aly, S.S. Epidemiology of bovine respiratory disease (BRD) in preweaned calves on California dairies: The BRD 10K study. Journal of Dairy Science 2019, 102, 7306–7319. [CrossRef]
- Brodersen, B.W. Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus. The Veterinary Clinics of North America. Food animal practice 2010, 26, 323–333. [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Capik, S.F.; Kegley, B.; Richeson, J.T.; Powell, J.G.; Zhao, J. Bovine respiratory microbiota of feedlot cattle and its association with disease. Veterinary research (Paris) 2022, 53, 4. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, T.A. Control Methods for Bovine Respiratory Disease for Feedlot Cattle. The Veterinary Clinics of North America. Food animal practice 2010, 26, 273–284. [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.; Chengappa, M.M.; Kuszak, J.; McVey, D.S. Bacterial Pathogens of the Bovine Respiratory Disease Complex. The Veterinary Clinics of North America. Food animal practice 2010, 26, 381–394. [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.F.F.; Kondov, N.O.; Deng, X.; Van Eenennaam, A.; Neibergs, H.L.; Delwart, E. A Metagenomics and Case-Control Study To Identify Viruses Associated with Bovine Respiratory Disease. Journal of Virology 2015, 89, 5340–5349. [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.A.; Step, D.L.; Woolums, A.R. Bovine Respiratory Disease. The Veterinary Clinics of North America. Food animal practice 2020, 36, 239–251. [CrossRef]
- Adekunle, A.J.; Kaniyamattam, K.; Cooke, R.F. 388 Epidemiological risk factor dynamics of Bovine Respiratory Disease in U.S. beef production systems. J Anim Sci 2025, 103, 47–48. [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, K.J.; DVM, A.R.; Woolums, DVM; Karisch, B.B.; Blanton, J.R.; Epperson, W.B.; DVM, D.R.; Smith; Smith, D.R. Case report: Analysis of risk factors and production effects following an outbreak of bovine respiratory disease in Stocker cattle. 2018.
- Rojas, H.A.; White, B.J.; Amrine, D.E.; Larson, R.L. Predicting Bovine Respiratory Disease Risk in Feedlot Cattle in the First 45 Days Post Arrival. Pathogens (Basel) 2022, 11, 442. [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.A. Update on viral pathogenesis in BRD. Animal Health Research Reviews 2009, 10, 149–153. [CrossRef]
- Muggli-Cockett, N.E.(.S.U., Logan); Cundiff, L.V.; Gregory, K.E. Genetic analysis of bovine respiratory disease in beef calves during the first year of life. Journal of animal science 1992, 70, 2013–2019. [CrossRef]
- Panciera, R.J.; Confer, A.W. Pathogenesis and Pathology of Bovine Pneumonia. The Veterinary Clinics of North America. Food Animal Practice 2010, 26, 191–214. [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, S.; Fecteau, G.; Dubuc, J.; Francoz, D.; Rousseau, M.; Roy, J.; Buczinski, S. Scoping review on clinical definition of bovine respiratory disease complex and related clinical signs in dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Science 2021, 104, 7095–7108. [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D. The monster we don't see: subclinical BRD in beef cattle. Animal health research reviews 2014, 15, 138–141. [CrossRef]
- Buczinski, S.; Pardon, B. Bovine Respiratory Disease Diagnosis. The Veterinary Clinics of North America. Food animal practice 2020, 36, 399–423. [CrossRef]
- Blakebrough-Hall, C.; Dona, A.; D’occhio, M.J.; McMeniman, J.; González, L.A. Diagnosis of Bovine Respiratory Disease in feedlot cattle using blood 1H NMR metabolomics. Scientific Reports 2020, 10, 115. [CrossRef]
- Berman, J.; Francoz, D.; Abdallah, A.; Dufour, S.; Buczinski, S. Evaluation of inter-rater agreement of the clinical signs used to diagnose bovine respiratory disease in individually housed veal calves. Journal of Dairy Science 2021, 104, 12053–12065. [CrossRef]
- Flöck, M. Diagnostic ultrasonography in cattle with thoracic disease. The Veterinary Journal 2004, 167, 272–280. [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.; Stieger-Vanegas, S.M.; Vanegas, J.A.; Bobe, G.; Poulsen, K.P. Comparison of Thoracic Radiography and Computed Tomography in Calves with Naturally Occurring Respiratory Disease. Front Vet Sci 2017, 4. [CrossRef]
- Galland, J.C.; House, J.K.; Hyatt, D.R.; Hawkins, L.L.; Anderson, N.V.; Irwin, C.K.; Smith, B.P. Prevalence of Salmonella in beef feeder steers as determined by bacterial culture and ELISA serology. Veterinary Microbiology 2000, 76, 143–151. [CrossRef]
- Goto, Y.; Fukunari, K.; Suzuki, T. Multiplex RT-qPCR Application in Early Detection of Bovine Respiratory Disease in Healthy Calves. Viruses 2023, 15, 669. [CrossRef]
- Conrad, C.C.; Daher, R.K.; Stanford, K.; Amoako, K.K.; Boissinot, M.; Bergeron, M.G.; Alexander, T.; Cook, S.; Ralston, B.; Zaheer, R.; Niu, Y.D.; McAllister, T. A Sensitive and Accurate Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Detection of the Primary Bacterial Pathogens Causing Bovine Respiratory Disease. Front Vet Sci 2020, 7. [CrossRef]
- Jiminez, J.; Timsit, E.; Orsel, K.; van der Meer, F.; Guan, L.L.; Plastow, G. Whole-Blood Transcriptome Analysis of Feedlot Cattle With and Without Bovine Respiratory Disease. Front Genet 2021, 12. [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.T.; Spire, M.F. Near infrared spectroscopy as a potential method to detect bovine respiratory disease. Kansas Agricultural Experiment Station Research Reports 2004, 97–99. [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.L.; Cook, N.J.; Church, J.S.; Basarab, J.; Perry, B.; Miller, C.; Tong, A.K.W. The use of infrared thermography as an early indicator of bovine respiratory disease complex in calves. Research in Veterinary Science 2007, 83, 376–384. [CrossRef]
- Cantor, M.C.; Casella, E.; Silvestri, S.; Renaud, D.L.; Costa, J.H.C. Using Machine Learning and Behavioral Patterns Observed by Automated Feeders and Accelerometers for the Early Indication of Clinical Bovine Respiratory Disease Status in Preweaned Dairy Calves. Front Anim Sci 2022, 3. [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, L.; Berckmans, D.; Youssef, A.; Berckmans, D.; van Waterschoot, T.; Johnston, D.; Ferguson, N.; Earley, B.; Fontana, I.; Tullo, E.; Guarino, M.; Vranken, E.; Norton, T. Automatic cough detection for bovine respiratory disease in a calf house. Biosystems Engineering 2018, 173, 45–56. [CrossRef]
- Haddadi, S.; Koziel, J.A.; Engelken, T.J. Analytical approaches for detection of breath VOC biomarkers of cattle diseases -A review. Analytica Chimica Acta 2022, 1206, 339565. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, M. Application of machine learning based genome sequence analysis in pathogen identification. Front Microbiol 2024, 15. [CrossRef]
- Adekunle, A.J.; Rahimifar, A.; Kaniyamattam, K. 48. An agent-based modeling framework for bovine respiratory disease management in integrated beef supply chains. Animal - Science proceedings 2025, 16, 579–581. [CrossRef]
- Kniffen, E.; Adekunle, A.; Agnoor, P.; Akpenyi, O.; Bose, S. Stochastic Modeling of Bovine Respiratory Disease Using Agent-Based Modeling, AMS: 2026/01/06.
- Sanguinetti, V. Disease control practices used to prevent morbidity and mortality in preweaned beef calves. UCalgary 2025 Available online: https://chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/https://ucalgary.scholaris.ca/server/api/core/bitstreams/5be2208e-1b17-4c09-88da-21521c95a017/content.
- Antonopoulos, A.; Ciria, N.; Regan, Á; Tubay, J.; Ciaravino, G.; Hayes, B.; Lambert, S.; Vergne, T.; Velkers, F.; Biebaut, E.; Viltrop, A.; Dewulf, J.; Charlier, J.; Fischer, E.; Palau, A.A. PARAMETRA: A transmission modelling database for livestock diseases. Preventive Veterinary Medicine 2025, 245, 106668. [CrossRef]
- Computational and analytical approaches towards epidemic spread containment of temporal animal trade networks. (Accessed on Oct 27, 2025).
- Smith, K.J.; Amrine, D.E.; Larson, R.L.; Theurer, M.E.; White, B.J. Determining relevant risk factors associated with mid- and late-feeding-stage bovine respiratory disease morbidity in cohorts of beef feedlot cattle. Applied Animal Science 2022, 38, 373–379. [CrossRef]
- Biesheuvel, M.M.; Ward, C.; Penterman, P.; van Engelen, E.; van Schaik, G.; Deardon, R.; Barkema, H.W. Within-herd transmission of Mycoplasma bovis infections after initial detection in dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 2024, 107, 516–529. [CrossRef]
- Isoda, N.; Sekiguchi, S.; Ryu, C.; Notsu, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Hamaguchi, K.; Hiono, T.; Ushitani, Y.; Sakoda, Y. Serosurvey of Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus in Cattle in Southern Japan and Estimation of Its Transmissibility by Transient Infection in Nonvaccinated Cattle. Viruses 2025, 17, 61. [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Smith, R.L.; Pongolini, S.; Bolzoni, L. Modelling farm-to-farm disease transmission through personnel movements: from visits to contacts, and back. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 2375. [CrossRef]
- Hill, E.M.; Prosser, N.S.; Ferguson, E.; Kaler, J.; Green, M.J.; Keeling, M.J.; Tildesley, M.J. Modelling livestock infectious disease control policy under differing social perspectives on vaccination behaviour. PLOS Computational Biology 2022, 18, e1010235. [CrossRef]
- Chumachenko, D. A theoretical framework for agent-based modelling of infectious disease dynamics under misinformation and vaccine hesitancy. Radioelectronic and Computer Systems 2025, 2025, 6–28. [CrossRef]
- Kamel, M.S.; Davidson, J.L.; Verma, M.S. Strategies for Bovine Respiratory Disease (BRD) Diagnosis and Prognosis: A Comprehensive Overview. Animals 2024, 14, 627. [CrossRef]
- Gorden, P.J.; Plummer, P. Control, Management, and Prevention of Bovine Respiratory Disease in Dairy Calves and Cows. The Veterinary Clinics of North America. Food Animal Practice 2010, 26, 243–259. [CrossRef]
- Lalman, D.; Ward, C.E. Effects of Preconditioning on Health, Performance and Prices of Weaned Calves. American Association of Bovine Practitioners. Conference. Proceedings of the ... Annual Conference 2005, 44–50. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.D.; Fulton, R.W.; Lehenbauer, T.W.; Step, D.L.; Confer, A.W. The epidemiology of bovine respiratory disease: what is the evidence for preventive measures? Canadian Veterinary Journal 2010, 51, 1351–1359. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21358927.
- Schunicht, O.C. Preconditioning beef calves is an economic no-brainer. American Association of Bovine Practitioners. Conference. Proceedings of the ... Annual Conference 2017, 59–62. [CrossRef]
- Hodder, A., Impact on feeding behavior of beef calves preconditioning on ranch and commingling. Masters, University of Calgary, 2022.
- Nickell, J.S.; White, B.J. Metaphylactic Antimicrobial Therapy for Bovine Respiratory Disease in Stocker and Feedlot Cattle. The Veterinary Clinics of North America. Food animal practice 2010, 26, 285–301. [CrossRef]
- Maier, G.U.; Love, W.J.; Karle, B.M.; Dubrovsky, S.A.; Williams, D.R.; Champagne, J.D.; Anderson, R.J.; Rowe, J.D.; Lehenbauer, T.W.; Van Eenennaam, A.L.; Aly, S.S. A novel risk assessment tool for bovine respiratory disease in preweaned dairy calves. Journal of Dairy Science 2020, 103, 9301–9317. [CrossRef]
- Babcock, A.H.; Cernicchiaro, N.; White, B.J.; Dubnicka, S.R.; Thomson, D.U.; Ives, S.E.; Scott, H.M.; Milliken, G.A.; Renter, D.G. A multivariable assessment quantifying effects of cohort-level factors associated with combined mortality and culling risk in cohorts of U.S. commercial feedlot cattle. Preventive veterinary medicine 2013, 108, 38–46. [CrossRef]
- Lehtoranta, L.; Latvala, S.; Lehtinen, M.J. Role of Probiotics in Stimulating the Immune System in Viral Respiratory Tract Infections: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3163. [CrossRef]
- Palomares, R.A. Trace Minerals Supplementation with Great Impact on Beef Cattle Immunity and Health. Animals 2022, 12, 2839. [CrossRef]
- Markey, J., Evaluation of NutraGen®, an Immunomodulatory Feed Additive, in Calves Subjected to a Combination Viral and Bacterial Bovine Respiratory Disease Challenge - ProQuest. PhD, Oklahoma State University, 2024.
- Voland, L.; Ortiz-Chura, A.; Tournayre, J.; Martin, B.; Bouchon, M.; Nicolao, A.; Pomiès, D.; Morgavi, D.P.; Popova, M. Duration of dam contact had a long effect on calf rumen microbiota without affecting growth. Front Vet Sci 2025, 12. [CrossRef]
- Sweiger, S.H.; Nichols, M.D. Control Methods for Bovine Respiratory Disease in Stocker Cattle. The Veterinary Clinics of North America. Food animal practice 2010, 26, 261–271. [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.A. Impact of disease on feedlot performance: a review. Journal of Animal Science 1998, 76, 272. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, A. Respiratory diseases of feedlot cattle in central USA. The Bovine Practitioner 1996, 5–7. [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, M.W.; Wagner, B.A.; Dargatz, D.A. Risk factors for initial respiratory disease in the United States' feedlots based on producer-collected daily morbidity counts. 2008.
- Theurer, M.E.; Johnson, M.D.; Fox, T.; McCarty, T.M.; McCollum, R.M.; Jones, T.M.; Alkire, D.O. Bovine respiratory disease during the mid-portion of the feeding period: Observations of frequency, timing, and population from the field. Applied Animal Science 2021, 37, 52–58. [CrossRef]
- Snowder, G.; Van Vleck, L. D.,; Cundiff, L. V.,; Bennett, G. L. Bovine respiratory disease in feedlot cattle environmental, genetic, and economic factors. American Society of Animal Science 2005, 84, 1999–2008. [CrossRef]
- Hicks, B. BEEF CATTLE RESEARCH UPDATE. 2021.
- Faber, R.; Hartwig, N.; Busby, D.; BreDahl, R. The Costs and Predictive Factors of Bovine Respiratory Disease in Standardized Steer Tests. Iowa State University Animal Industry Report 2000, 1. Available online: https://www.iastatedigitalpress.com/air/article/id/7342/ (accessed on Oct 27, 2025).
- Taylor, J.D.; Fulton, R.W.; Lehenbauer, T.W.; Step, D.L.; Confer, A.W. The epidemiology of bovine respiratory disease: What is the evidence for predisposing factors? Public Health 2010, 51.
- Stokka, G.L. Prevention of Respiratory Disease in Cow/Calf Operations. The Veterinary Clinics of North America. Food Animal Practice 2010, 26, 229–241. [CrossRef]
- Woolums, A.R.; Berghaus, R.D.; Smith, D.R.; White, B.J.; Engelken, T.J.; Irsik, M.B.; Matlick, D.K.; Jones, A.L.; Ellis, R.W.; Smith, I.J.; Mason, G.L.; Waggoner, E.R. Producer survey of herd-level risk factors for nursing beef calf respiratory disease. J Am Vet Med Assoc 2013, 243, 538–547. [CrossRef]
- Guterbock, W.M. The impact of BRD: the current dairy experience. Anim Health Res Rev 2014, 15, 130–134. [CrossRef]
- Windeyer, M.C.; Leslie, K.E.; Godden, S.M.; Hodgins, D.C.; Lissemore, K.D.; LeBlanc, S.J. Factors associated with morbidity, mortality, and growth of dairy heifer calves up to 3 months of age. Preventive Veterinary Medicine 2014, 113, 231–240. [CrossRef]
- DeDonder, K.D.; Apley, M.D. A review of the expected effects of antimicrobials in bovine respiratory disease treatment and control using outcomes from published randomized clinical trials with negative controls. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract 2015, 31, 97–111, vi. [CrossRef]
- Baptista, A.L.; Rezende, A.L.; Fonseca, P.d.A.; Massi, R.P.; Nogueira, G.M.; Magalhães, L.Q.; Headley, S.A.; Menezes, G.L.; Alfieri, A.A.; Saut, J.P.E. Bovine respiratory disease complex associated mortality and morbidity rates in feedlot cattle from southeastern Brazil. J Infect Dev Ctries 2017, 11, 791–799. [CrossRef]
- Urie, N.J.; Lombard, J.E.; Shivley, C.B.; Kopral, C.A.; Adams, A.E.; Earleywine, T.J.; Olson, J.D.; Garry, F.B. Preweaned heifer management on US dairy operations: Part V. Factors associated with morbidity and mortality in preweaned dairy heifer calves. Journal of Dairy Science 2018, 101, 9229–9244. [CrossRef]
- Andrés-Lasheras, S.; Ha, R.; Zaheer, R.; Lee, C.; Booker, C.W.; Dorin, C.; Van Donkersgoed, J.; Deardon, R.; Gow, S.; Hannon, S.J.; Hendrick, S.; Anholt, M.; McAllister, T.A. Prevalence and risk factors associated with antimicrobial resistance in bacteria related to bovine respiratory disease—a broad cross-sectional study of beef cattle at entry into Canadian feedlots. Frontiers in Veterinary Science 2021, 8, 692646. [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.J.; Amrine, D.E.; Larson, R.L.; Theurer, M.E.; Szaz, J.I.; Bryant, T.; White, B.J. Risk factors for mid- and late-feeding-stage bovine respiratory morbidity and mortality based on individual animal treatments of beef feedlot cattle. Applied Animal Science 2022, 38, 360–372. [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Wills, R.W.; Woodruff, K.A. Epidemiology’s Adoption of System Dynamics is a Natural Extension of Population Thinking. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Food Animal Practice 2022, 38, 245–259. [CrossRef]
- Windeyer, M.C.; Timsit, E.; Barkema, H. Bovine respiratory disease in pre-weaned dairy calves: Are current preventative strategies good enough? Vet J 2017, 224, 16–17. [CrossRef]
- Woolums, A.R.; Karisch, B.B.; Frye, J.G.; Epperson, W.; Smith, D.R.; Blanton, J.; Austin, F.; Kaplan, R.; Hiott, L.; Woodley, T.; Gupta, S.K.; Jackson, C.R.; McClelland, M. Multidrug-resistant Mannheimia haemolytica isolated from high-risk beef stocker cattle after antimicrobial metaphylaxis and treatment for bovine respiratory disease. Veterinary Microbiology 2018, 221, 143–152. [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.J.; White, B.J.; Amrine, D.E.; Larson, R.L.; Theurer, M.E.; Szasz, J.I.; Bryant, T.C.; Waggoner, J.W. Evaluation of First Treatment Timing, Fatal Disease Onset, and Days from First Treatment to Death Associated with Bovine Respiratory Disease in Feedlot Cattle. Veterinary Sciences 2023, 10. [CrossRef]
- Heinen, L.; White, B.J.; Amrine, D.E.; Larson, R.L. Evaluation of predictive models to determine final outcome for feedlot cattle based on information available at first treatment for bovine respiratory disease. American journal of veterinary research 2023, 84, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Blakebrough-Hall; McMeniman, J.P.; González, L.A. An evaluation of the economic effects of bovine respiratory disease on animal performance, carcass traits, and economic outcomes in feedlot cattle defined using four BRD diagnosis methods. Journal of animal science 2020, 98, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- White, B.J.; Larson, B.L. Impact of bovine respiratory disease in U.S. beef cattle. Animal health research reviews 2020, 21, 132–134. [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.L.; Sweeney, M.T. Antimicrobial Resistance in Bovine Respiratory Disease Pathogens: Measures, Trends, and Impact on Efficacy. The Veterinary Clinics of North America. Food animal practice 2010, 26, 79–88. [CrossRef]
- Dubrovsky, S.A.; Van Eenennaam, A.L.; Aly, S.S.; Karle, B.M.; Rossitto, P.V.; Overton, M.W.; Lehenbauer, T.W.; Fadel, J.G. Preweaning cost of bovine respiratory disease (BRD) and cost-benefit of implementation of preventative measures in calves on California dairies: The BRD 10K study. Journal of Dairy Science 2020, 103, 1583–1597. [CrossRef]
- Overton, M.W. Economics of respiratory disease in dairy replacement heifers. Animal Health Research Reviews 2020, 21, 143–148. [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.J.; Tait, R.G.; Busby, W.D.; Reecy, J.M. An evaluation of bovine respiratory disease complex in feedlot cattle: Impact on performance and carcass traits using treatment records and lung lesion scores. J Anim Sci 2009, 87, 1821–1827. [CrossRef]
- Brooks, K.R.; Raper, K.C.; Ward, C.E.; Holland, B.P.; Krehbiel, C.R.; Step, D.L. Economic effects of bovine respiratory disease on feedlot cattle during backgrounding and finishing phases1. The Professional Animal Scientist 2011, 27, 195–203. [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.K.; Step, D.L.; Maxwell, C.L.; Gifford, C.A.; Richards, C.J.; Krehbiel, C.R. Effect of bovine respiratory disease during the receiving period on steer finishing performance, efficiency, carcass characteristics, and lung scores. Prof Anim Sci 2017, 33, 24–36. [CrossRef]
- Roeber, D.L.; Speer, N.C.; Gentry, J.G.; Tatum, J.D.; Smith, C.D.; Whittier, J.C.; Jones, G.F.; Belk, K.E.; Smith, G.C. Feeder Cattle Health Management: Effects on Morbidity Rates, Feedlot Performance, Carcass Characteristics, and Beef Palatability12. The Professional Animal Scientist 2001, 17, 39–44. [CrossRef]
- Heinen, L.; White, B.J.; Larson, R.L.; Kopp, D.; Pendell, D.L. Economic impact of mortality prediction by predictive model at first and second treatment for bovine respiratory disease. American Journal of Veterinary Research 2024, 85. [CrossRef]
- De Koster, J.; Tena, J.; Stegemann, M.R. Treatment of bovine respiratory disease with a single administration of tulathromycin and ketoprofen. Veterinary record 2022, 190, no. [CrossRef]
- Magouras, I.; Dürr, S.; Martínez-López, B.; Brookes, V.J. Editorial: Insights in veterinary epidemiology and economics: 2023. Front Vet Sci 2025, 12. [CrossRef]
- Soares Filipe, J.F.; Ciliberti, M.G.; Attard, G.; Ratti, G.; Rocchi, M.S.L. Editorial: Biosecurity of infectious diseases in veterinary medicine. Front Vet Sci 2025, 12, 1665683. [CrossRef]
- Cazer, C.L.; Basran, P.; Ivanek-Miojevic, R. From bark to bytes: artificial intelligence transforming veterinary medicine. Am J Vet Res 2025, 86, S4–S5. [CrossRef]
- Lhermie, G.; Sauvage, P.; Tauer, L.W.; Chiu, L.V.; Kanyiamattam, K.; Ferchiou, A.; Raboisson, D.; Scott, H.M.; Smith, D.R.; Grohn, Y.T. Economic effects of policy options restricting antimicrobial use for high-risk cattle placed in U.S. feedlots. PloS one 2020, 15, e0239135. [CrossRef]
- Kaniyamattam, K.; Tauer, L.W.; Gröhn, Y.T. System Economic Costs of Antibiotic Use Elimination in the US Beef Supply Chain. Frontiers in Veterinary Science 2021, 8, 606810. [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.J.; Wellington, M.; Shah, R.M.; Ferreira, M.J. Antibiotic Stewardship in Food-producing Animals: Challenges, Progress, and Opportunities. Clinical therapeutics 2020, 42, 1649–1658. [CrossRef]
- Adekunle, A.J.; Kaniyamattam, K. Feedlot economic visualization decision support tool for sustainable beef production. J Anim Sci 2025, 103, 246–247. [CrossRef]
- Abell, K.M.; Theurer, M.E.; Larson, R.L.; White, B.J.; Apley, M. A mixed treatment comparison meta-analysis of metaphylaxis treatments for bovine respiratory disease in beef cattle. J Anim Sci 2017, 95, 626–635. [CrossRef]
- Centeno-Martinez, R.E.; Klopp, R.N.; Koziol, J.; Boerman, J.P.; Johnson, T.A. Dynamics of the nasopharyngeal microbiome of apparently healthy calves and those with clinical symptoms of bovine respiratory disease from disease diagnosis to recovery. Front Vet Sci 2023, 10. [CrossRef]
- Munir, S.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Qasim, M.; Fatima, T.; Aslam, S.; Sarfraz, M.H.; Kober, A.K.M.H.; Khurshid, M. Chapter 4 - Molecular omics: a promising systems biology approach to unravel host-pathogen interactions. In Systems Biology Approaches for Host-Pathogen Interaction Analysis; Ashraf, M.T.; Khan, A.A.; Aldakheel, F.M., Eds.; Academic Press: 2024; pp. 81–102.
- Kaniyamattam, K.; Adekunle, A.; Vettil, V.K.; Rejimon, S.P.; Pi, Y.; Tao, J.; Mendes, E.D.M.; Tedeschi, L.O. 400 Design and development of artificial intelligence-driven decision support systems for sustainable livestock systems in the United States. J Anim Sci 2025, 103, 109–110. [CrossRef]
- Puig, A.; Ruiz, M.; Bassols, M.; Fraile, L.; Armengol, R. Technological Tools for the Early Detection of Bovine Respiratory Disease in Farms. Animals (Basel) 2022, 12, 2623. [CrossRef]
- Theurer, M.E.; White, B.J.; Renter, D.G. Optimizing Feedlot Diagnostic Testing Strategies Using Test Characteristics, Disease Prevalence, and Relative Costs of Misdiagnosis. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Food Animal Practice 2015, 31, 483–493. [CrossRef]
- Vysyaraju, U.S.R.; Moon, S.; Mendes, E.D.M.; Adekunle, A.J.; Kaniyamattam, K.; Pi, Y. 47. Activity recognition in beef cattle Calan gate using CLIP and YOLO v11. Animal - Science proceedings 2025, 16, 578–579. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Pathway of BRD Development: This figure summarizes how multiple stressors, such as transport, commingling, weaning, and inclement weather exposure, compromise immune function and increase susceptibility to respiratory pathogens. Elevated stress facilitates viral and bacterial proliferation in the upper and lower respiratory tract. When pathogen load exceeds the weakened immune defenses, clinical BRD emerges, characterized by respiratory inflammation, reduced performance, and increased morbidity.
Figure 1.
Pathway of BRD Development: This figure summarizes how multiple stressors, such as transport, commingling, weaning, and inclement weather exposure, compromise immune function and increase susceptibility to respiratory pathogens. Elevated stress facilitates viral and bacterial proliferation in the upper and lower respiratory tract. When pathogen load exceeds the weakened immune defenses, clinical BRD emerges, characterized by respiratory inflammation, reduced performance, and increased morbidity.
Figure 2.
Diagnostic approaches for Bovine Respiratory Disease (BRD): This figure outlines the major diagnostic pathways used to identify BRD in cattle, including clinical observation methods (e.g., thoracic auscultation, behavior monitoring), laboratory-based techniques (bacterial culture, PCR/qPCR, serology, metabolomics, and pathogen sequencing), and clinical scoring methods e.g., DART scoring. Together, these complementary approaches support early detection, confirmatory diagnosis, and differentiation of pathogen types, enabling more accurate case identification and informed treatment decisions.
Figure 2.
Diagnostic approaches for Bovine Respiratory Disease (BRD): This figure outlines the major diagnostic pathways used to identify BRD in cattle, including clinical observation methods (e.g., thoracic auscultation, behavior monitoring), laboratory-based techniques (bacterial culture, PCR/qPCR, serology, metabolomics, and pathogen sequencing), and clinical scoring methods e.g., DART scoring. Together, these complementary approaches support early detection, confirmatory diagnosis, and differentiation of pathogen types, enabling more accurate case identification and informed treatment decisions.
Figure 3.
Preventive and control strategies for BRD: This figure summarizes key measures used to reduce BRD risk, including preconditioning, vaccination, metaphylaxis, and good nutrition. It also highlights management practices such as improved ventilation, reduced commingling, and biosecurity, alongside timely treatment and health monitoring to limit disease onset and severity.
Figure 3.
Preventive and control strategies for BRD: This figure summarizes key measures used to reduce BRD risk, including preconditioning, vaccination, metaphylaxis, and good nutrition. It also highlights management practices such as improved ventilation, reduced commingling, and biosecurity, alongside timely treatment and health monitoring to limit disease onset and severity.
Figure 4.
Research-based and author-reported Bovine Respiratory Disease morbidity and mortality in varying animal populations, risk profiles, and experimental conditions over 26 years. Single asterisked ‘*’ records were reported rates averages, double asterisked ‘**’ records were reported as risk levels and not actual morbidity or mortality rates, and pound sign ‘#’ are for case fatality rates, not mortality.
Figure 4.
Research-based and author-reported Bovine Respiratory Disease morbidity and mortality in varying animal populations, risk profiles, and experimental conditions over 26 years. Single asterisked ‘*’ records were reported rates averages, double asterisked ‘**’ records were reported as risk levels and not actual morbidity or mortality rates, and pound sign ‘#’ are for case fatality rates, not mortality.
Figure 5.
Heatmap illustrating the combined effects of BRD severity and number of treatments on carcass outcomes: Increasing treatment frequency and disease severity are associated with progressively greater carcass weight penalties and carcass value reductions, and quality grade loss, consistent with reported feedlot performance trends [
73,
78,
80,
81].
Figure 5.
Heatmap illustrating the combined effects of BRD severity and number of treatments on carcass outcomes: Increasing treatment frequency and disease severity are associated with progressively greater carcass weight penalties and carcass value reductions, and quality grade loss, consistent with reported feedlot performance trends [
73,
78,
80,
81].
Figure 6.
Drivers and Consequences of Antimicrobial Use in Beef Production: Systems-level interactions linking antimicrobial use in cattle production with animal welfare, economic sustainability, and public health, illustrating the reinforcing pathways that influence antimicrobial resistance development.
Figure 6.
Drivers and Consequences of Antimicrobial Use in Beef Production: Systems-level interactions linking antimicrobial use in cattle production with animal welfare, economic sustainability, and public health, illustrating the reinforcing pathways that influence antimicrobial resistance development.
Table 1.
BRD Diagnostic Methods: Showing a list of scientific and general methods for the diagnosis of BRD in cattle.
Table 1.
BRD Diagnostic Methods: Showing a list of scientific and general methods for the diagnosis of BRD in cattle.
| Method |
Principle/Target |
Advantages |
Limitations |
Key
References |
| DART Scoring |
Subjective clinical signs: depression, appetite, respiration, temperature |
Low-cost; easy to implement quickly in the field |
Low sensitivity/specificity (<70%); high inter-observer variability. |
[19,20,22] |
| Thoracic Auscultation |
Detects abnormal lung sounds via a stethoscope |
Simple, immediate insights |
Requires expertise; limited sensitivity, especially for lower lung lesions |
[20] |
| Thoracic Ultrasound (TUS) |
Visualizes lung consolidations and pleural lesions |
High sensitivity (~85%); early lesion detection |
Equipment cost, operator dependency, and animal handling are needed |
[23] |
| Thoracic Radiography |
X-ray imaging of lung structures |
Can detect deep parenchymal lesions |
Superimposition issues require anesthesia or restraint |
[24] |
| Bacterial Culture & Serology |
Identification of pathogen presence and immune response |
Gold standard for pathogen ID; supports antimicrobial sensitivity testing |
Takes days; may miss fastidious pathogens; serology may lack specificity |
[25] |
| Multiplex PCR and qPCR |
Detects DNA/RNA of multiple pathogens (viral & bacterial) |
High sensitivity/specificity; can detect co-infections; quantitative |
Infrastructure and cost barriers; positives may reflect colonization, not disease |
[26] |
| Isothermal Amplification (LAMP, RPA) |
Rapid on-site detection of specific pathogens |
Field-friendly; colorimetric readout; ~1 hr results |
Requires primer design; possible false positives; early-stage tool |
[27] |
| ¹H NMR Metabolomics |
Identifies systemic metabolic biomarkers in blood |
High accuracy (~85%); reveals host response patterns |
High cost; requires lab and ML models; less field-ready |
[21] |
| Blood Transcriptomics (DEGs) |
Uses gene-expression profiling to detect immune response |
Early detection potential; highly specific insights |
Requires RNA sequencing; high cost; technical demands |
[28] |
| Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) |
Measures biochemical fingerprint in fluids/tissues |
Non-invasive; potential rapid testing without a blood draw |
Early research stage; needs standardization |
[29] |
| Infrared Thermography |
Measures surface temperature (eye/orbit) |
Non-contact; early fever detection |
Variable with ambient conditions; needs calibration |
[30] |
| Accelerometers and Behavior Sensors |
Detect changes in activity and rumination |
Can detect illness ~3 days before clinical signs |
Initial cost, data noise; requires algorithms |
[31] |
| Acoustic Monitoring (Cough sensors) |
Detects cough frequency in pens |
Automated, non-invasive; early outbreak detection |
Background noise interference |
[32] |
| Breath Analysis (e.g., NO, VOCs) |
Measures volatile biomarkers linked to inflammation |
Non-invasive; rapid results |
Technical complexity; needs calibration |
[33] |
| Metagenomic Sequencing & AI-based Pathogen Profiling |
Deep sequencing with ML models for pathogen signature |
Potential for high-throughput, sensitive detection |
High cost; bioinformatics demands; emerging technology |
[34] |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).