2.1. Formation of a Thermodynamic Subsystem Model and a Thermodynamic Feedback Model
As it is known, the tool is in contact with the workpiece on its two rear faces, the main and auxiliary. From the point of view of temperature formation in the cutting area, the auxiliary rear face, which is in contact with the part in the feed direction, is in the sphere of interest. This is due to the fact that the temperature flow in the feed direction will preheat the future zone after one cutting revolution, which should significantly change the temperature in the primary deformation zone and the value of the coefficient of friction. It should be noted here that this factor (the effect on the cutting temperature, the temperature released during the cutting process earlier) has never been taken into account by anyone. This is due to the fact that the cutting speed, as a rule, significantly exceeds the rate of temperature propagation in metals. However, the movement of the tool in the feed direction is slower than the propagation speed of the temperature field in metals processed on metal-cutting machines.
To improve the quality of further reasoning, it is necessary to consider what the very concept of temperature flow is, which is disclosed in the methods of thermal conductivity. As it is known from the methods of thermal conductivity [193], the temperature at a specific point in space can be determined not only by the current heat output, but also by the factor of heat transfer, while in metals such transfer is called thermal conductivity (Fourier’s law), as it is associated with the thermal motion of atoms in the crystal lattice due to the inhomogeneous temperature distribution [
21].
where - heat flow density vector, - the coefficient of proportionality, called thermal conductivity (W/mK)), accordingly, the inverse value is called the thermal resistance of materials.
The energy release in the cutting zone has a complex structure and distribution in the areas adjacent to the tool (tool faces), as well as in the cutting zone itself [
22], but as mentioned earlier, the most significant is the temperature flow directed into the depth of the workpiece through the contact zone of the main back face of the tool and the part.
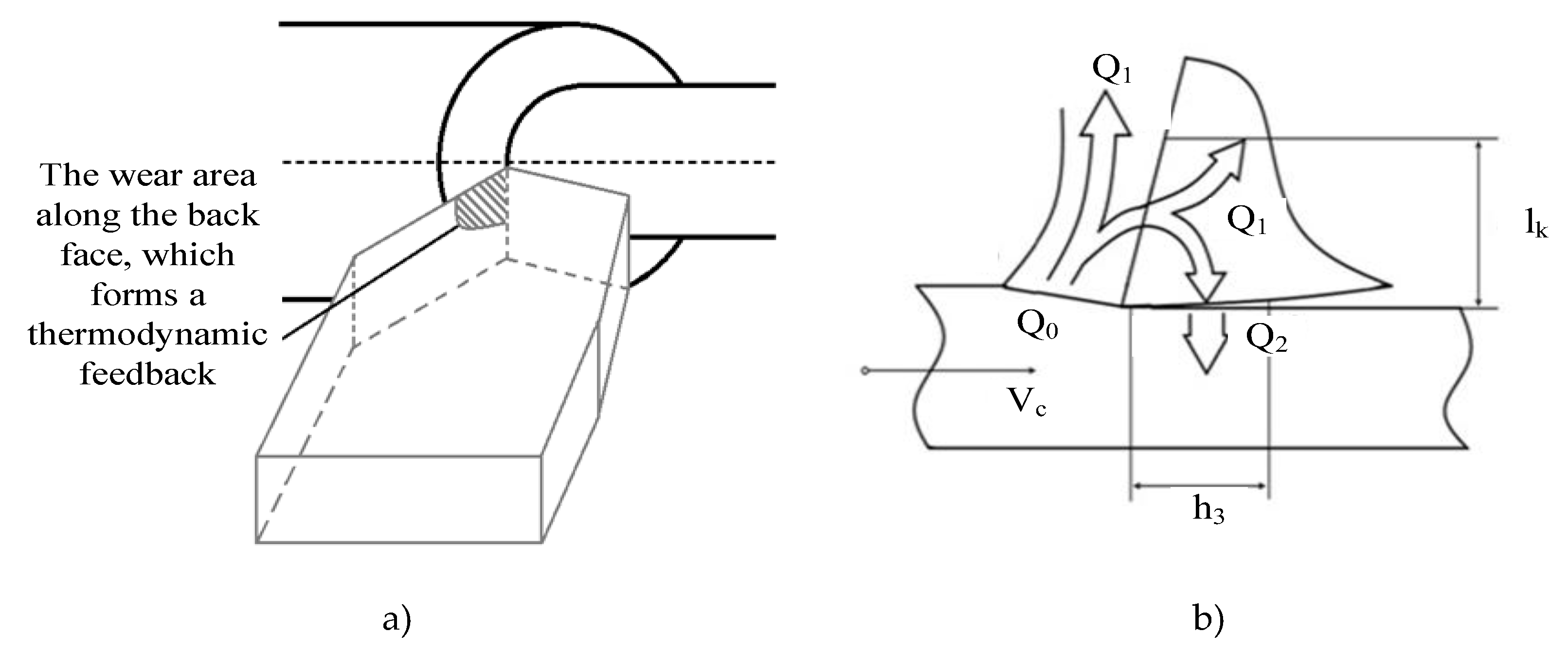
Figure 1 details the contact zone and its corresponding heat release zone.
As can be seen from
Figure 1, a heat transfer zone is formed during the cutting process, due to the formed wear area along the back face, it is through it that the temperature from the previous processing stages is transmitted. Due to this temperature transfer channel, a thermodynamic bond is formed that affects the force response from the cutting process to the shaping movements of the instrument.
Summarizing all of the above, and also taking into account the Fourier equation, we describe the thermodynamic relationship formed by the cutting system along the back face of the instrument as follows:
- the power of irreversible transformations released in the zone of primary deformation during metal cutting forms a temperature field in the cutting wedge through the contact of the chips and the front edge of the cutting wedge of the instrument, the gradient of which is directed towards the tool in the contact zone of the auxiliary rear edge of the tool and the workpiece. Due to this, the irreversible transformation power released in the contact of the back face of the tool and the workpiece (friction force) is converted into a temperature dissipated by the temperature current in the opposite direction to the temperature gradient in the contact zone, that is, in the direction of the workpiece.
Thus, summarizing the scheme shown in
Figure 1 (b), the temperature formed in the current cutting zone will be determined both by the transformation of the current cutting power and by the temperature flow formed by the cutting powers highlighted earlier. Based on this, the heat balance equation for the primary deformation zone will look like this:
where - current cutting temperature in the primary deformation zone, - the temperature obtained as a result of the conversion of cutting power in the primary deformation zone, and - the temperature obtained by the current primary deformation zone from the previous cutting stages (thermodynamic feedback).
The difference between the approach presented by equation (2) and the traditional approach to modeling the temperature field in the contact zone of the tool and the workpiece is that it takes into account only the current value of the power released during cutting and the associated temperature, while expression (2) allows to take into account previous transformations. To clarify the effect of the heat flow shown in
Figure 1b on the current cutting temperature, we assume that the temperature in the contact area of the tool and the workpiece will be determined not only by the current value of the allocated power, but by previous values, that is, by the entire temperature field formed in the workpiece during cutting. In defense of the traditional approach, it can be pointed out that while cutting, the heat source moves faster than the temperature field propagates in the workpiece. However, this is true only in the direction of the main movement, the direction in which the cutting itself is carried out, and in the feed direction, the speed of movement of the tool relative to the workpiece is small and this condition may not be fulfilled here. Earlier, we determined that when turning, the tool has contact with the workpiece along two rear faces, one of them is the main one, the second is auxiliary, so the main rear face rubs against the workpiece material in a place where, subsequently, through one revolution of the machine spindle, deformation and shearing of the workpiece will occur. Based on this, the heat released as a result of the interaction of the tool on the back surface with the part one revolution before the moment of the current cutting should be taken into account in the temperature of the current contact zone of the tool and the workpiece, and the heat released in two turns should be taken into account during the previous temperature calculation, etc ... In the conditions of the cutting process the heat flows in the workpiece will propagate not only in the feed direction, but also in all other directions. When calculating the current temperature in the processing area, it is this direction that is important, as it will determine the channel of the evolutionary influence of the temperature previously isolated during processing. Here, by the word evolution, we mean precisely the evolution of the instrument as the degree of wear increases along the back edge. This is due to the fact that the value of the temperature gradient in the contact area of the tool along the back face has a great influence here, since the heat flow is directed in the opposite direction from the direction of the temperature gradient (see expression 1). At the same time, the higher the value of the temperature gradient, the greater the heat flow in the opposite direction, and the greater the influence on the current temperature value of the entire previously formed temperature field. Taking into consideration that the heat removal from the tool is limited, all the accumulated and temperature-converted power released during the entire cutting process will be accumulated in the tool. Since the temperature previously allocated during the formation of tool wear along the back face will accumulate here, the magnitude of the temperature gradient in the area of current contact between the back face of the tool and the workpiece, directed towards the tool, will depend on the entire temperature previously allocated during processing.
Of great interest is the issue of temperature modeling using a simplified linear equation of the second order. To construct this equation, we use an approach that will be based on the theory of heat sources and sinks [
20]. Let us consider the formation of temperature in the contact zone of the cutting tool and the part,
which is based on the representation of the cutting tool as a one-parameter object with a concentrated container in which there is a source of heat production and the mechanism of its selection is described:
where - time constants of the thermodynamic subsystem [с], - a coefficient showing the conversion of cutting power (-[N*mm/s]) into the cutting temperature [Q*s/N*mm], - the period with which the workpiece being processed on the machine rotates, fixed in the spindle of the machine [s], - the dimensionless coefficient of thermodynamic feedback transmission.
Thus, the second-order differential equation (2) will describe the thermodynamics of the cutting process, taking into account the revealed thermodynamic feedback.
2.2. Synthesis of an Operator Forming an Elastic-Thermodynamic Interaction in a Finite-Dimensional System of Differential Equations
While cutting metals, a complex force bond is formed, which accumulates various physico-chemical reactions that occur during this process. The most important factor here is the temperature of the interaction, through which the interaction is formed in the expanded space of the physical states of the cutting system. Let us consider this interaction in the form of the following block diagram (see
Figure 2).
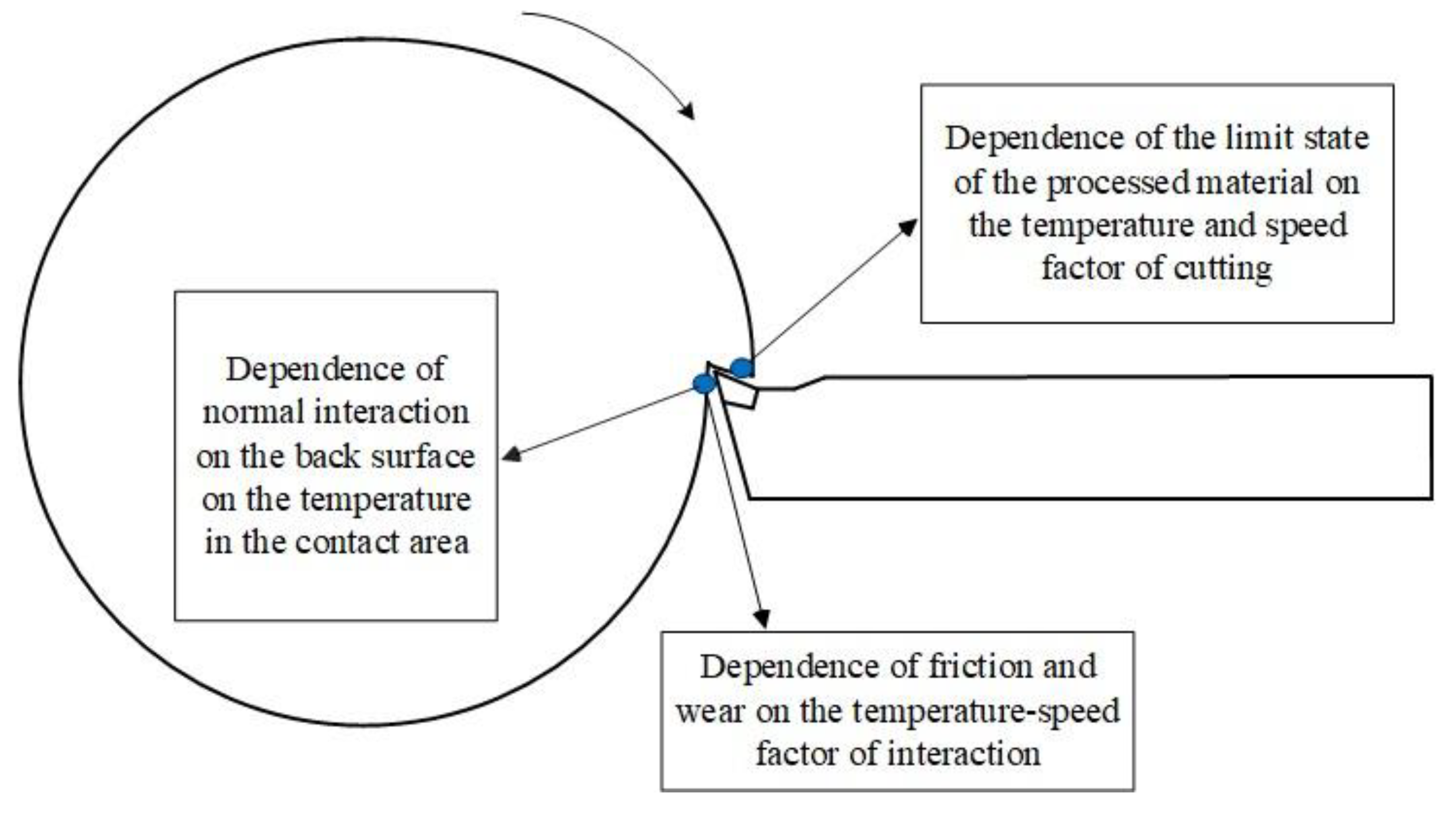
As can be seen from
Figure 2, the elastic-thermodynamic interaction causes multiple effects in metal cutting, including the dependence of the limiting state of the processed material on temperature, the dependence of friction and wear on the temperature-speed factor of cutting, and the dependence of normal interaction on temperature, etc. Separate studies have been conducted, but there is currently no general theory of elastic-thermodynamic interaction that systematically considers these and other effects.
According to the provisions of the synergetic concept [
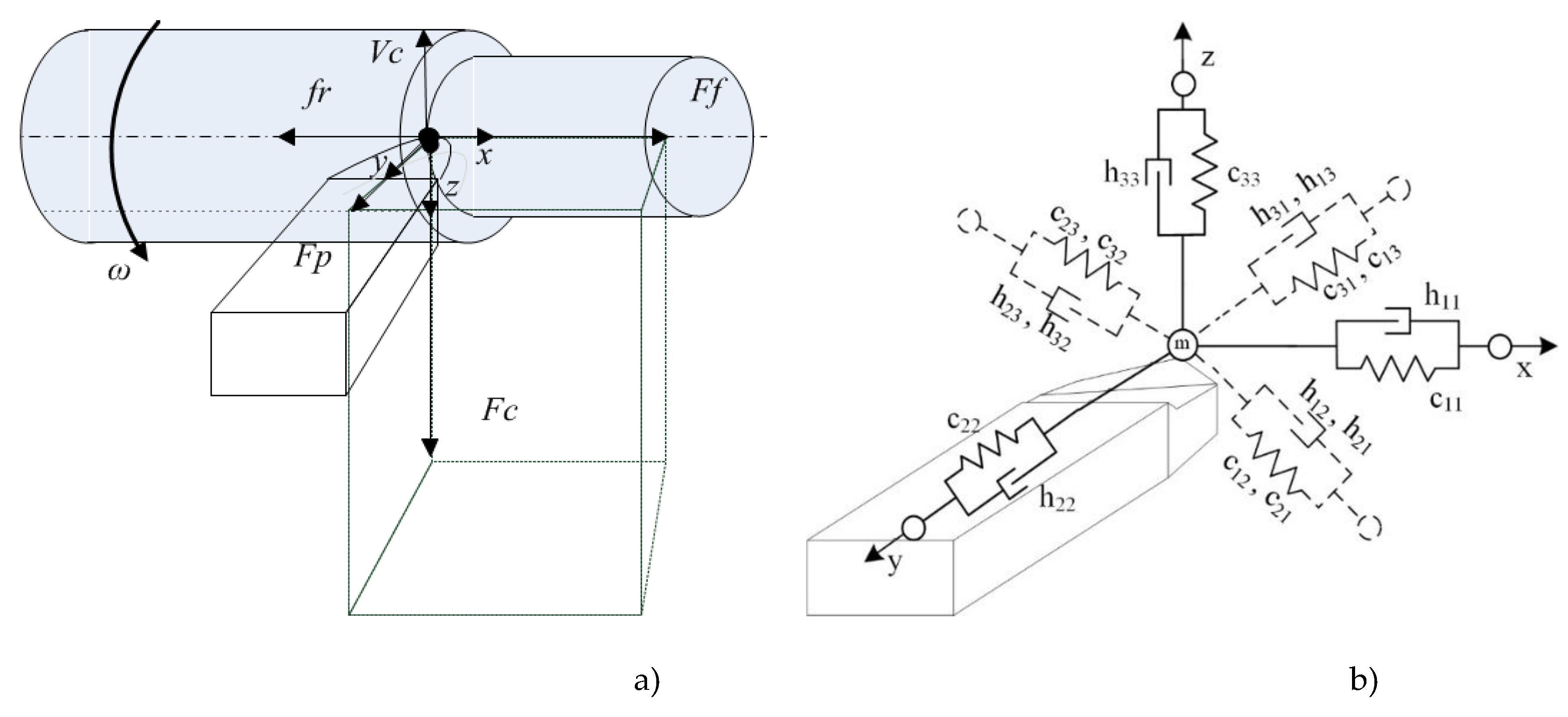
19], the forces that impede the shaping movements of the tool must be represented in the coordinates of the state, external influences, taking into account the accepted technological modes of processing. When modeling forces, it is necessary to take into account their properties known from the processing technology: the forces acting on the front surface of the tool depend on the area of the cut layer, they decrease with increasing cutting speed.; when the tool moves towards contact with the rear face (main or auxiliary), a velocity-dependent increase in the normal force component is observed]. To clarify this approach to the formation of a mathematical model of the force reaction from the process to the tool and the workpiece, we consider these forces and moments in the form of expansion along the axes of deformation of the tool (see
Figure 3).
For the convenience of further discussion, the coordinates entered in
Figure 3 (
) will be used as the coordinates of the tool tip deformations. Here and further, we will assume that the workpiece is not deformed.
Taking into account the proposed expression of the dependence of reaction forces, as well as based on the approach to modeling the dynamics of the deformation motion of a tool used in the scientific school of Zakorotny V.L. [
19,
20], we assume that the model of deformations of the tip of the tool will take the following form:
, (4)
where the vector of elastic deformations of the tool, - vector is a function of the forces acting on the tool (reaction to the shaping movements of the tool from the cutting process),[N*s2/mm]; [N*s/mm]; [N/mm] – symmetric and positively defined matrices of inertia coefficients, dissipation coefficients, and stiffness coefficients, respectively.
The formation of the tool wear area along the back face significantly affects the overall force response from the cutting process to the shaping movements of the tool. Based on these considerations, the overall force response of the machining process to the shaping movements of the tool can be represented as:
. (5)
where - reaction from the cutting process to shaping movements on the front edge of the cutting tool (cutting force), - a certain coefficient of decomposition of the total vector of reaction forces on i – tool deformation axis, - the reaction from the side of the processed part to the insertion of the cutting wedge of the tool into the processed part.
The cutting force model will be based on the hypothesis of the proportionality of the force of the area of the cut layer in the form of:
where -: a coefficient characterizing the dependence of the limiting state of the processed material on temperature, which can be described as the following dependence:
, (7)
where - some minimum value of the coefficient , - the coefficient showing the increase in value up to a certain maximum value, - the steepness coefficient of the value drop , Q – temperature in the cutting area.
The normal component of the force response from the cutting process to the tool embedded in the workpiece can be represented as a function of the force on the volume of the cutting wedge embedded in the part, that is, the product of the cutting depth by the instantaneous feed and the amount of wear along the back face.:
, (8)
where - the ultimate strength of the processed metal under compression in ; , - the amount of wear on the back of the tool [mm]. As a working hypothesis, we assume that with the increase in the temperature in the contact of materials on the back face of the tool and the resulting linear expansion of the part material, the normal component of the force will increase linearly, by:
, (8)
where - the coefficient of coupling of the normal component of the force with the contact temperature of the instrument and the workpiece along the back face, - a coefficient which value is less than one and shows how much of the previously released thermal energy is transmitted by thermodynamic feedback, and - the part of the contact temperature obtained from thermodynamic feedback.
To decompose the reaction from the cutting process in the normal direction on the deformation axis, we use the main angle in the plan - φ, in the following way:
. (9)
The force reaction in the direction of the z coordinate, in its essence, is nothing more than a friction force, which can be represented as:
, (10)
where - coefficient of friction.
The coefficient of friction also depends non-linearly on the temperature in contact between the instrument and the workpiece. We define the characteristic of the coefficient of friction by the following expression:
, (11)
where - some constant minimum value of the coefficient of friction, - the value of the increment of the coefficient of friction with a change in temperature in the contact area, и coefficients determining the steepness of the fall and growth characteristics of the coefficient of friction.
Thus, the general system of equations describing the dynamics of the deformation movements of the tip of the cutting tool, taking into account the thermodynamic feedback generated by the cutting process, is presented below.
(12)
The mathematical model formed here contains thermodynamic feedback, which has a twofold effect on the force interaction formed during cutting. On the one hand, along with the increase in the temperature of the rear face of the cutting tool transmitted in contact, the cutting force decreases from the previous cutting zones to the current one, which suggests the formation of a negative feedback. However, on the other hand, with the increase in the temperature of the rear face of the cutting tool transmitted in contact from the previous cutting zones to the current one, the normal component of the cutting force increases, which can be interpreted as positive feedback. Similar considerations are associated with a change in the coefficient of friction, which initially decreases with the increase in the temperature of the contact interaction, but subsequently begins to increase. In other words, the influence of thermodynamic feedback in the mathematical model of the cutting system leads to the appearance of both stabilizing feedback (negative feedback) and destabilizing effects (positive feedback).