Submitted:
01 December 2025
Posted:
04 December 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
In this study, we report the development of a recombinant human G-CSF fused with apolipoprotein A-I. The chimeric protein was expressed in Pichia pastoris. Using human bone marrow cells, the fusion protein was shown to retain the granulocyte activity of authentic G-CSF, more effectively inducing the differentiation and maturation of segmented neutrophils and maintaining the viability of progenitor cells. Using human mononuclear cells and THP cells, the resulting protein demonstrated monocytic activity, manifested by an increase in both total and CD14+ cell counts. By maintaining cell viability, the chimeric protein reduced the number of cells expressing caspase 3/7. G-CSF-ApoAI demonstrated accelerated cytokine regulation, promoting a more rapid transition of inflammation phases, accompanied by increased phagocytosis of latex particles, compared with G-CSF, increasing phagocytosis by 1.4-fold in the LPS-induced inflammation model. This suggests that this new pleotropic factor may be useful for pathogen clearance in infected wounds.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Creation of the Recombinant P. pastoris Strain Capable of Producing rhG-CSF-АpoA-I
2.2. Analysis of the Biological Activity of G-CSF-АpoA-I
2.2.1. Flow Cytometry Analysis of Human BMCs
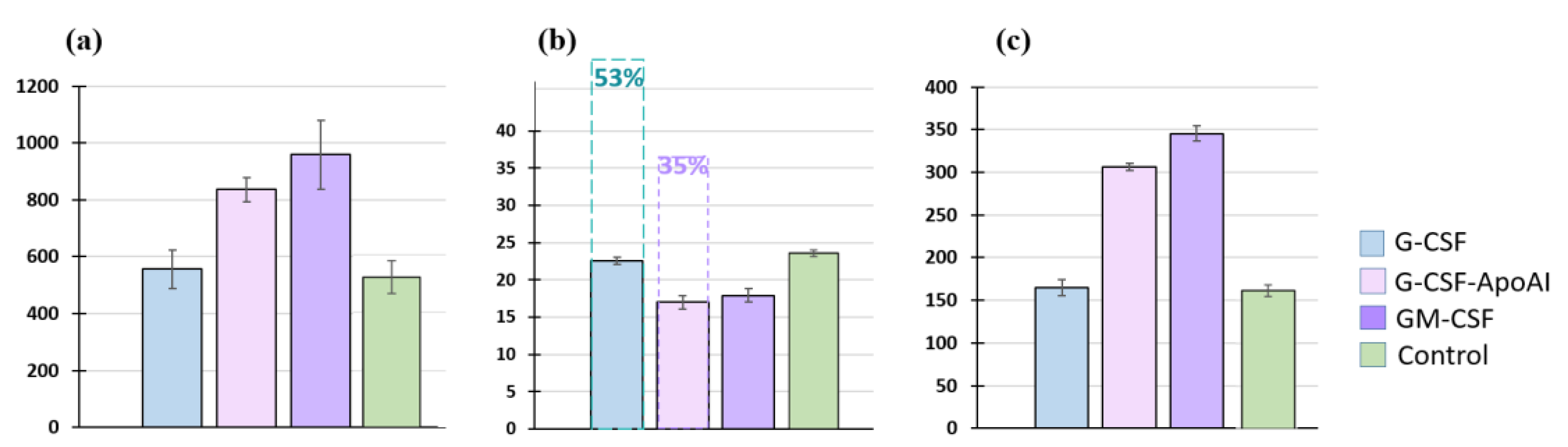
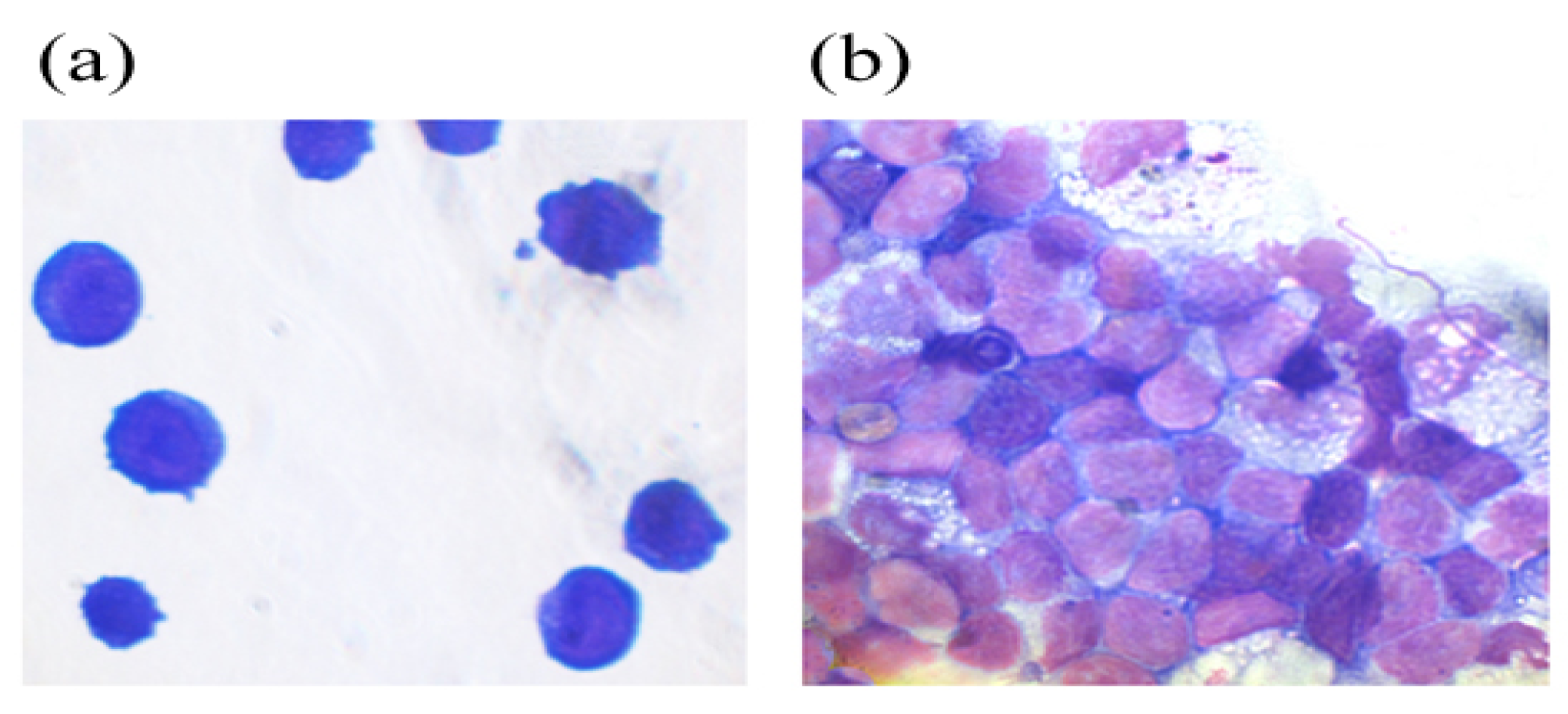
2.2.2. Аnalysis of the Cellular Composition of the Granulocyte Series of Human BMC Treated with G-CSF and G-CSF-ApoAI
2.2.3. Study of the Proliferative Activity of Human BMCs Treated with G-CSF and G-CSF-АpoAI
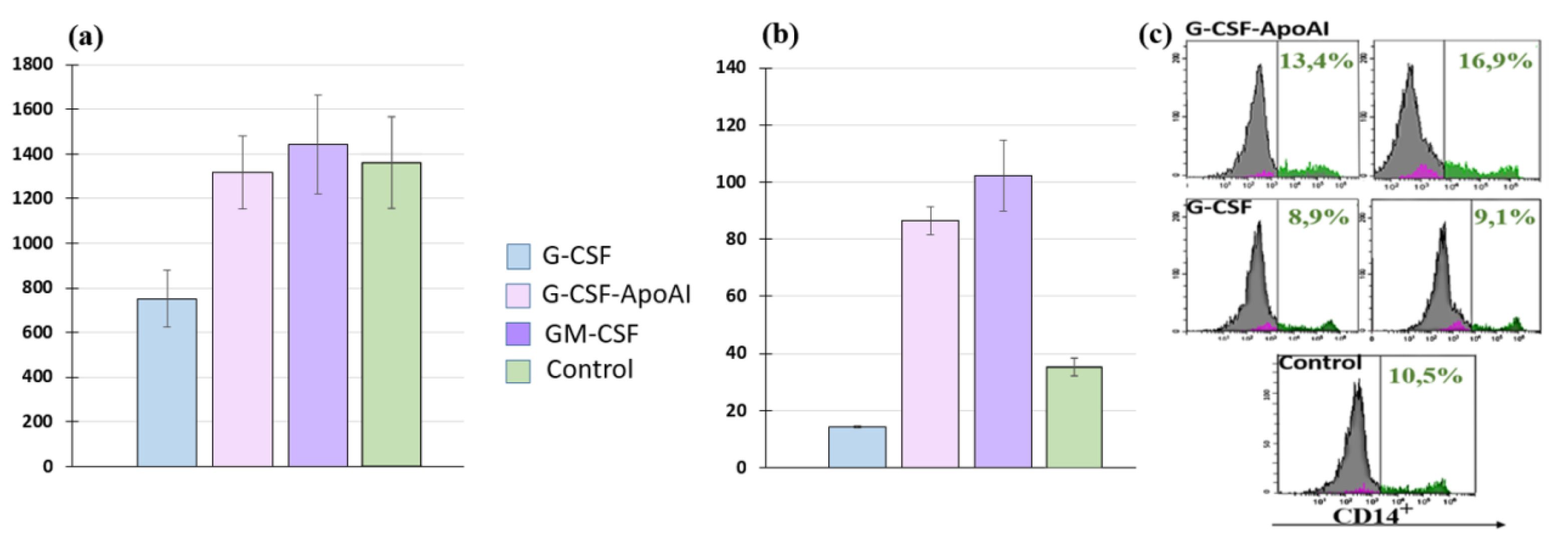
2.2.4. Study of Monocyte Activity G-CSF-ApoAI on Human MNCs
2.2.5. Study of Monocyte Activity of G-CSF-ApoAI on the THP-1 Cell Line
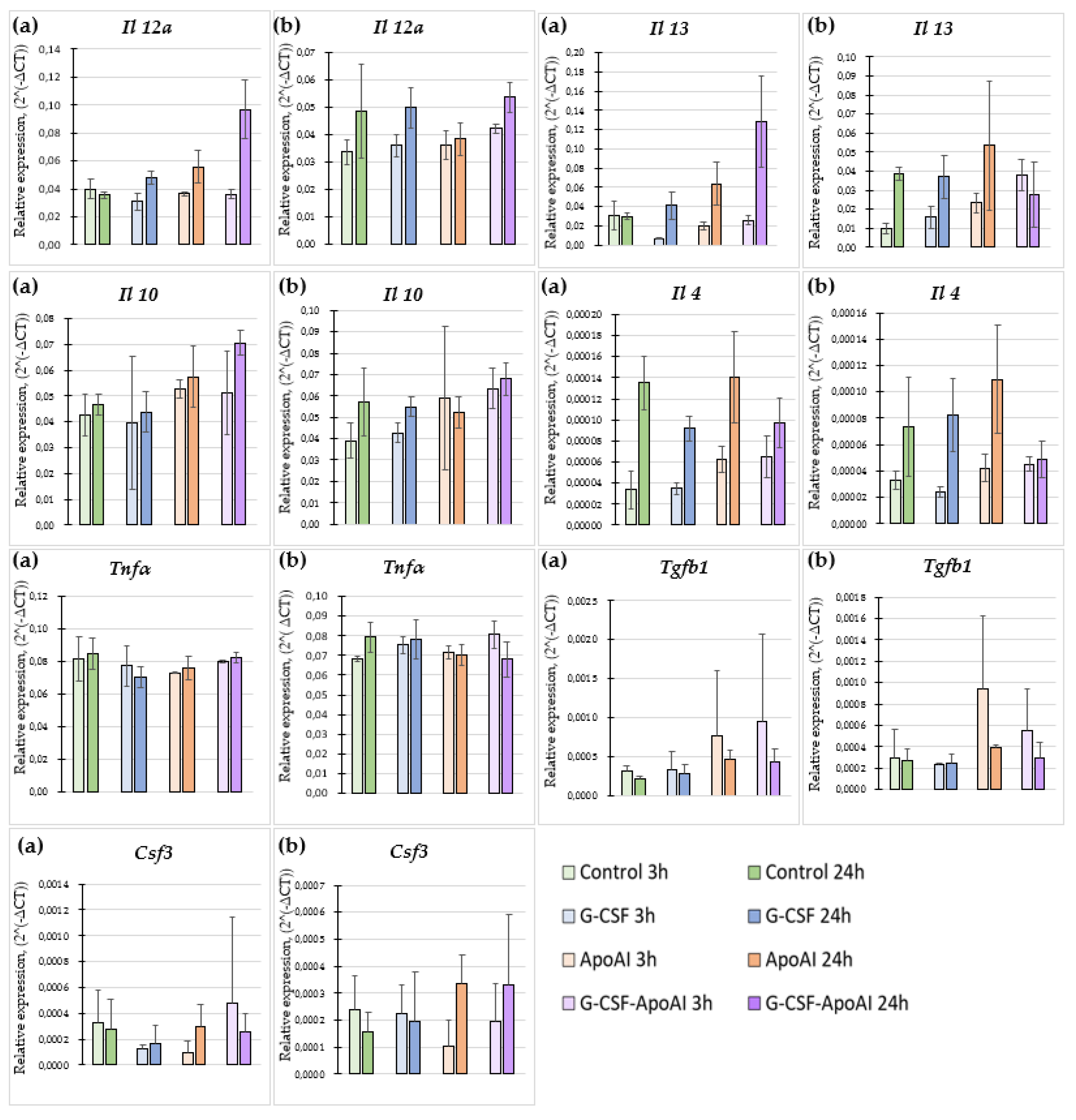
2.2.6. The Effect of Recombinant Proteins on Cytokine Expression and Phagocytic Activity of Mouse Bone Marrow Cells
2.2.6.1. Evaluation of the Expression Level of Proinflammatory and Inflammatory Cytokines
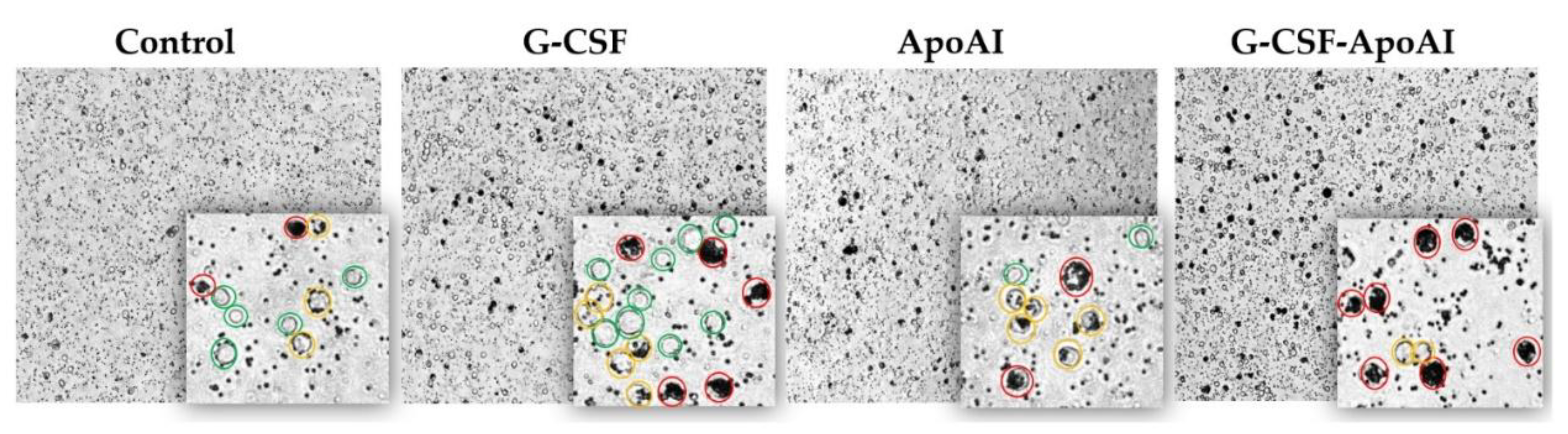
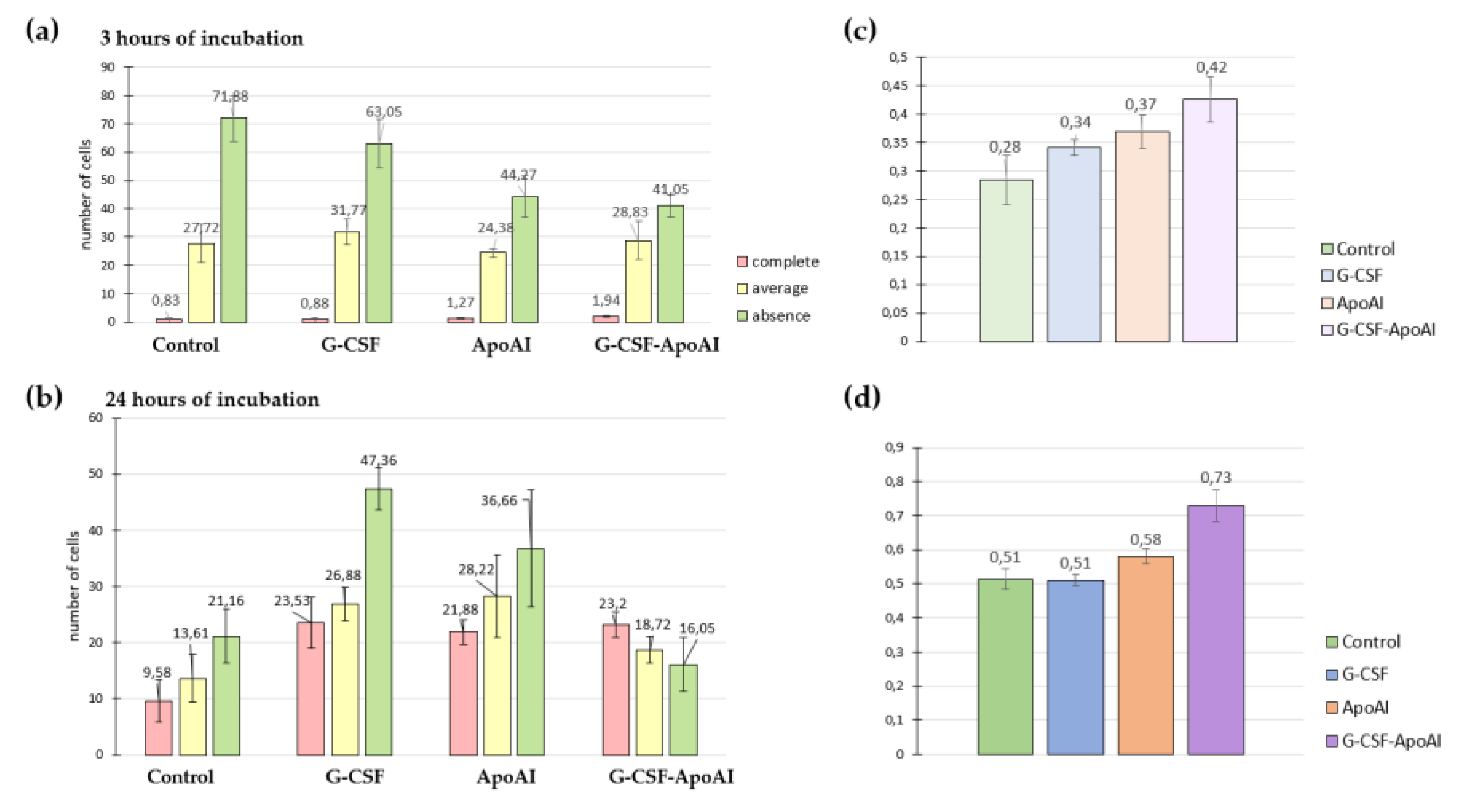
2.2.6.2. Evaluation of Phagocytic Activity of Mouse Bone Marrow Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Development of P. pastoris Strain Producing the Chimeric Protein G-CSF-АpoAI
4.2.2. Bone Marrow Cell Isolation and Culture
4.2.3. Isolation of Mononuclear Cells
4.2.4. Сulturing of TНP Cell Line
4.2.5. Flow Cytometry
4.2.6. Myelography
4.2.7. Cytokine Expression
4.2.8. Assessment of Phagocytic Activity
4.2.9. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salamone, P.; Fuda, G.; Casale, F.; Marrali, G.; Lunetta, C.; Caponnetto, C.; Mazzini, L.; La Bella, V.; Mandrioli, J.; Simone, I. L.; Moglia, C.; Calvo, A.; Tarella, C.; Chio, A. STEMALS-II Study Group. G-CSF (filgrastim) treatment for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: protocol for a phase II randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group, multicentre clinical study (STEMALS-II trial). BMJ Open. 2020, 10, 034049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Ramos, J.; Song, S.; Sava, V.; Catlow, B.; Lin, X.; Mori, T.; Cao, C.; Arendash, G. W. Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) Decreases Brain Amyloid Burden and Reverses Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer’s Mice. Neuroscience 2009, 163, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnerup, J.; Sevimli, S.; Schäbitz, W.R. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor for stroke treatment: mechanisms of action and efficacy in preclinical studies. Exp. Transl. Stroke Med. 2009, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.J.; Jambaldorj, E.; Lee, J.G.; Jang, J.Y.; Shim, J.M.; Han, M.; Koo, T.Y.; Ahn, C.; Yang, J. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor treatment ameliorates lupus nephritis through the expansion of regulatory T cells. BMC Nephrology 2016, 17, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Н.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Hao, Н.; Jiang, C.; Han, W. Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) Accelerates Wound Healing in Hemorrhagic Shock Rats by Enhancing Angiogenesis and Attenuating Apoptosis. Med. Sci Monit. 2017, 23, 2644–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, S.S.; Aghmiyuni, Z.F.; Mohammad, N.; Anissian, A.; Azimi, M.; Majidpour, А.; Nasirinezhad, F.; Roham, М. Histological Survey of the Effect of Granulocyte-colony-stimulating Factor (G-CSF) on Bacterial Translocation and Wound Healing in Burned Mice. Trauma Res. 2019, 8, 149–54. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Sati, S.; Murphy, C.; Spencer, C.A.; Rapp, E.; Prouty, S.M.; Korte, S.; Ahart, O.; Sheng, E.; Jones, P.; Kersh, A.E.; Leung, D.; Leung, T.H. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor promotes scarless tissue regeneration. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, A.; Clapperton, M.; Rolando, N.; Foster, A.V.; Philpott-Howard, J.; Edmonds, M.E. Randomised placebo-controlled trial of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor in diabetic foot infection. Lancet. 1997, 350, 855–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lalla, F.; Pellizzer, G.; Strazzabosco, M.; Martini, Z.; Du Jardin, G.; Lora, L.; Fabris, P.; Benedetti, P.; Erle, G. Randomized prospective controlled trial of recombinant granulocyte colony-stimulating factor as adjunctive therapy for limb-threatening diabetic foot infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 1094–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruciani, M.; Lipsky, B.A.; Mengoli, C.; de Lalla, F.; Are granulocyte colony-stimulating factors beneficial in treating diabetic foot infections? A meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2 Smith, J.; Rai, V. Novel Factors Regulating Proliferation, Migration, and Differentiation of Fibroblasts, Keratinocytes, and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells during Wound Healing. Biomedicines. 2024, 12, 1939. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.; Rai, V. Novel Factors Regulating Proliferation, Migration, and Differentiation of Fibroblasts, Keratinocytes, and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells during Wound Healing. Biomedicines. 2024, 12, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartung, T. Anti-inflammatory effects of granulocyte colony stimulating factor. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 1998, 5, 221–5.005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawa, Y.; Teshima, T.; Sunami, K.; Hiramatsu, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Yano, T.; Shinagawa, K.; Ishimaru, F.; Omoto, E.; Harada, M. G-CSF reduces IFN- and IL-4 production by T cells after allogeneic stimulation by indirectly modulating monocyte function. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000, 25, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Kiyokawa, N.; Taguchi, T.; Suzuki, K.; Sekino, T.; Mimori, K.; Suzuki, T.; Nakajima, H.; Katagiri, Y.U.; Fujimura, J.; Fujita, H.; Ishimoto, K.; Yamashiro, Y.; Fujimoto, J. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor directly affects human monocytes and modulates cytokine secretion. Exp. Hematol. 2002, 30, 1115–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.S.; Wen, X.F.; Yang, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, L.F. Development and characterization of a novel fusion protein of a mutated granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and human serum albumin in Pichia pastoris. PLoS One. 2014, 9, e115840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikravesh, F.Y.; Shirkhani, S.; Bayat, E.; Talebkhan, Y.; Mirabzadeh, E.; Sabzalinejad, M.; Aliabadi, HAM.; Nematollahi, L.; Ardakani, Y.H; Sardari, S. Extension of human GCSF serum half-life by the fusion of albumin binding domain. Sci Rep. 2022, 12, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Ann, D.K.; Shen, W.C. Recombinant granulocyte colony stimulating factor-transferrin fusion protein as an oral myelopoietic agent. Proc. Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005, 102, 7292–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, G.N.; Smith, D.J.; Carlson, S.J.; Bendele, A.M.; Chlipala, E.A.; Doherty, D.H. Enhanced circulating half-life and hematopoietic properties of a human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor/immunoglobulin fusion protein. Exp. Hematol. 2004, 32, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, B.H.; Kang, H.J.; Song, J.A.; Nguyen, M.T.; Park, S.; Yoo, J.; Nguyen, A.N.; Kwon, G.G.; Jang, J.; Jang, M.; Lee, S.; So, S.; Sim, S.; Lee, K.J.; Osborn, M.J.; Choe, H. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (GCSF) fused with Fc Domain produced from E. coli is less effective than Polyethylene Glycol-conjugated GCSF. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nardo, D.; Labzin, L.I.; Kono, H.; Seki, R.; Schmidt, S.V.; Beyer, M.; Xu, D.; Zimmer, S.; Lahrmann, C.; Schildberg, F.A.; et al. High-density lipoprotein mediates anti-inflammatory reprogramming of macrophages via the transcriptional regulator ATF3. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 5, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakaki, A.; Marsche, G. Current Understanding of the Immunomodulatory Activities of High-Density Lipoproteins. Biomedicines. 2021, 9, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Pecchi, V.; Valdés, S.; Pons, V.; Honorato, P.; Martinez, L.O.; Lamperti, L.; Aguayo, C.; Radojkovic, C. Apolipoprotein A-I enhances proliferation of human endothelial progenitor cells and promotes angiogenesis through the cell surface ATP synthase. Microvasc. Res. 2015, 98, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usynin, I.F.; Dudarev, A.N.; Gorodetskaya, A.Y.; Miroshnichenko, S.M.; Tkachenko, T.A.; Tkachenko, V.I. Apolipoprotein A-I Stimulates Cell Proliferation in Bone Marrow Cell Culture. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 164, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miroshnichenko, S.; Usynin, I.; Dudarev, A.; Nimaev, V.; Solovieva, A. Apolipoprotein A-I Supports MSCs Survival under Stress Conditions. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21, 4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioravanti, J.; González, I.; Medina-Echeverz, J.; Larrea, E.; Ardaiz, N.; González-Aseguinolaza, G.; Prieto, J.; Berraondo, P. Anchoring interferon alpha to apolipoprotein A-I reduces hematological toxicity while enhancing immunostimulatory properties. Hepatology. 2011, 53, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Echeverz, J.; Vasquez, M.; Gomar, C.; Ardaiz, N.; Berraondo, P. Overexpression of apolipoprotein A-I fused to an anti-transforming growth factor beta peptide modulates the tumorigenicity and immunogenicity of mouse colon cancer cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2015, 64, 717–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardaiz, N.; Gomar, C.; Vasquez, M.; Tenesaca, S.; Fernandez-Sendin, M.; Di Trani, C.A.; Belsué, V.; Escalada, J.; Werner, U.; Tennagels, N.; Berraondo, P. Insulin Fused to Apolipoprotein A-I Reduces Body Weight and Steatosis in DB/DB Mice. Front Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 591293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pykhtina, M.B.; Romanov, V.P.; Miroshnichenko, S.M; Beklemishev, A.B. Construction of a Pichia pastoris strain efficiently producing recombinant human granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (rhG-CSF) and study of its biological activity on bone marrow cells. Mol Biol Rep. 2020, 47, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pykhtina, M.; Miroshnichenko, S.; Romanov, V.; Grazhdantseva, A.; Kochneva, G.; Beklemishev, A. Construction of Recombinant Human GM-CSF and GM-CSF-ApoA-I Fusion Protein and Evaluation of Their Biological Activity. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2021, 14, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidez, L.I.; Miller, G.J.; Burstein, M.; Slagle, S.; Eder, H.A. Separation and quantitation of subclasses of human plasma high density lipoproteins by a simple precipitation procedure. J. Lipid Res. 1982, 23, 1206–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroshnichenko, S.; Pykhtina, M.; Kotliarova, A.; Chepurnov, A.; Beklemishev, A. Engineering a New IFN-ApoA-I Fusion Protein with Low Toxicity and Prolonged Action. Molecules. 2023, 28, 8014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, M.U.; Ahmed, N.; Khan, M.A.; Tahir, S.; Zafar, A.U. Production of potent long-lasting consensus interferon using albumin fusion technology in Pichia pastoris expression system. Protein Expr. Purif. 2020, 166, 105509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, B.L.; Sekut, L.; Corcoran, M.; Poortman, C.; Sturm, B.; Chen, G.; Mather, D.; Lin, H.L.; Parry, T.J. Albutropin: a growth hormone–albumin fusion with improved pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in rats and monkeys. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 456, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Liao, X.L; Lou, B.; Wu, M.P. Role of apolipoprotein A-I in protecting against endotoxin toxicity. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin (Shanghai) 2004, 36, 419–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedzka-Sarek, M.; Metso, J.; Kateifides, A.; Meri, T.; Jokiranta, T.S.; Muszyński, A.; Radziejewska-Lebrecht, J.; Zannis, V.; Skurnik, M.; Jauhiainen, M. Apolipoprotein A-I exerts bactericidal activity against Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:3. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 38211–38219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClean, C.M.; Tobin, D.M. Macrophage form, function, and phenotype in mycobacterial infection: Lessons from tuberculosis and other diseases. Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74, ftw068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, D.N.; Kremer, L.; Guérardel, Y.; Molano, A.; Jacobs, W.R., Jr.; Porcelli, S.A.; Briken, V. Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipomannan induces apoptosis and interleukin-12 production in macrophages. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 2067–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peignier, A.; Kim, J.; Lemenze, A.; Parker, D. Monocyte-regulated interleukin 12 production drives clearance of Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, S.Y.; Wang, X.; Vijayan, S.; Tang, Y.; Kim, Y.O.; Padberg, K.; Regen, T.; Molokanova, O.; Chen, T.; Bopp, T.; et al. IL-4 Receptor Alpha Signaling through Macrophages Differentially Regulates Liver Fibrosis Progression and Reversal. EBioMedicine. 2018, 29, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnegan, A.; Grusby, M.J.; Kaplan, C.D.; O’Neill, S.K.; Eibel, H.; Koreny, T.; Czipri, M.; Mikecz, K.; Zhang, J. IL-4 and IL-12 regulate proteoglycan-induced arthritis through Stat-dependent mechanisms. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 3345–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardilo-Reis, L.; Gruber, S.; Schreier, S.M.; Drechsler, M.; Papac-Milicevic, N.; Weber, C.; Wagner, O.; Stangl, H.; Soehnlein, O.; Binder, C.J. Interleukin-13 protects from atherosclerosis and modulates plaque composition by skewing the macrophage phenotype. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 1072–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
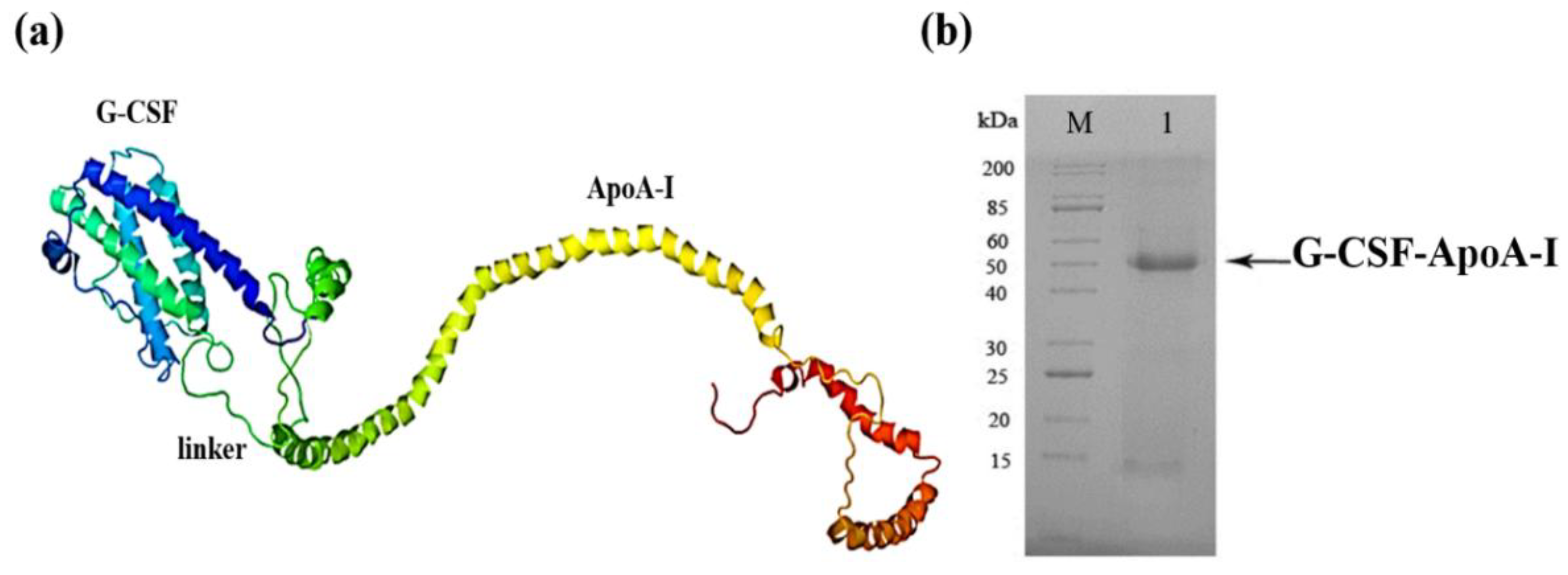
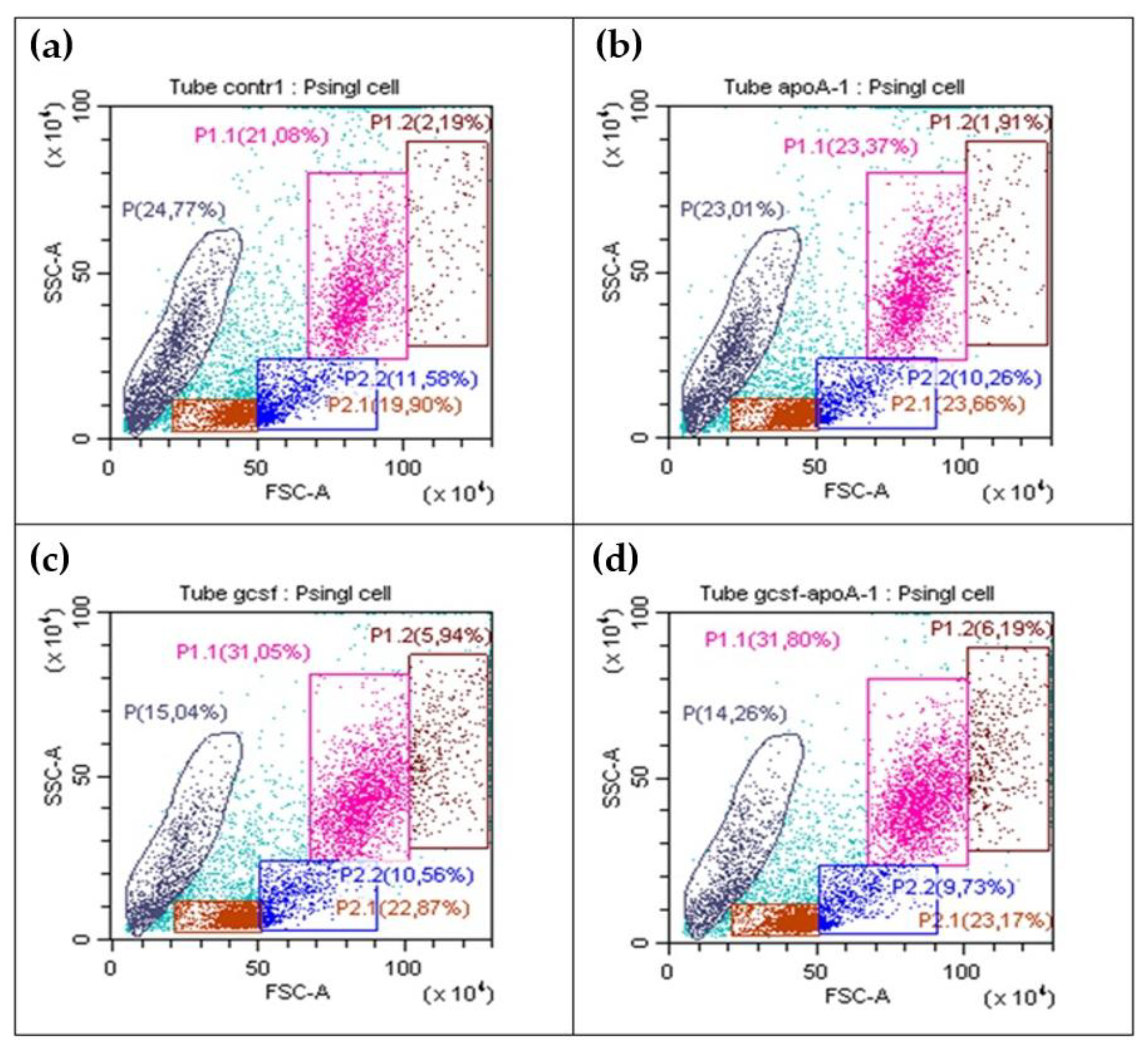
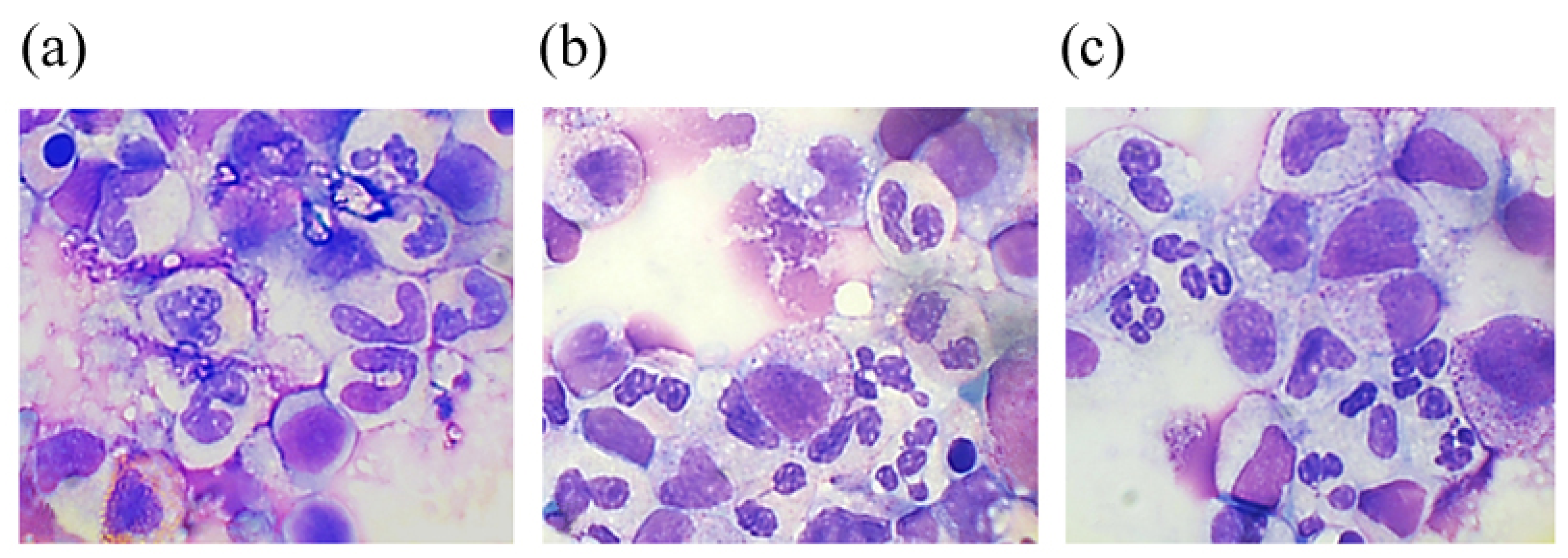
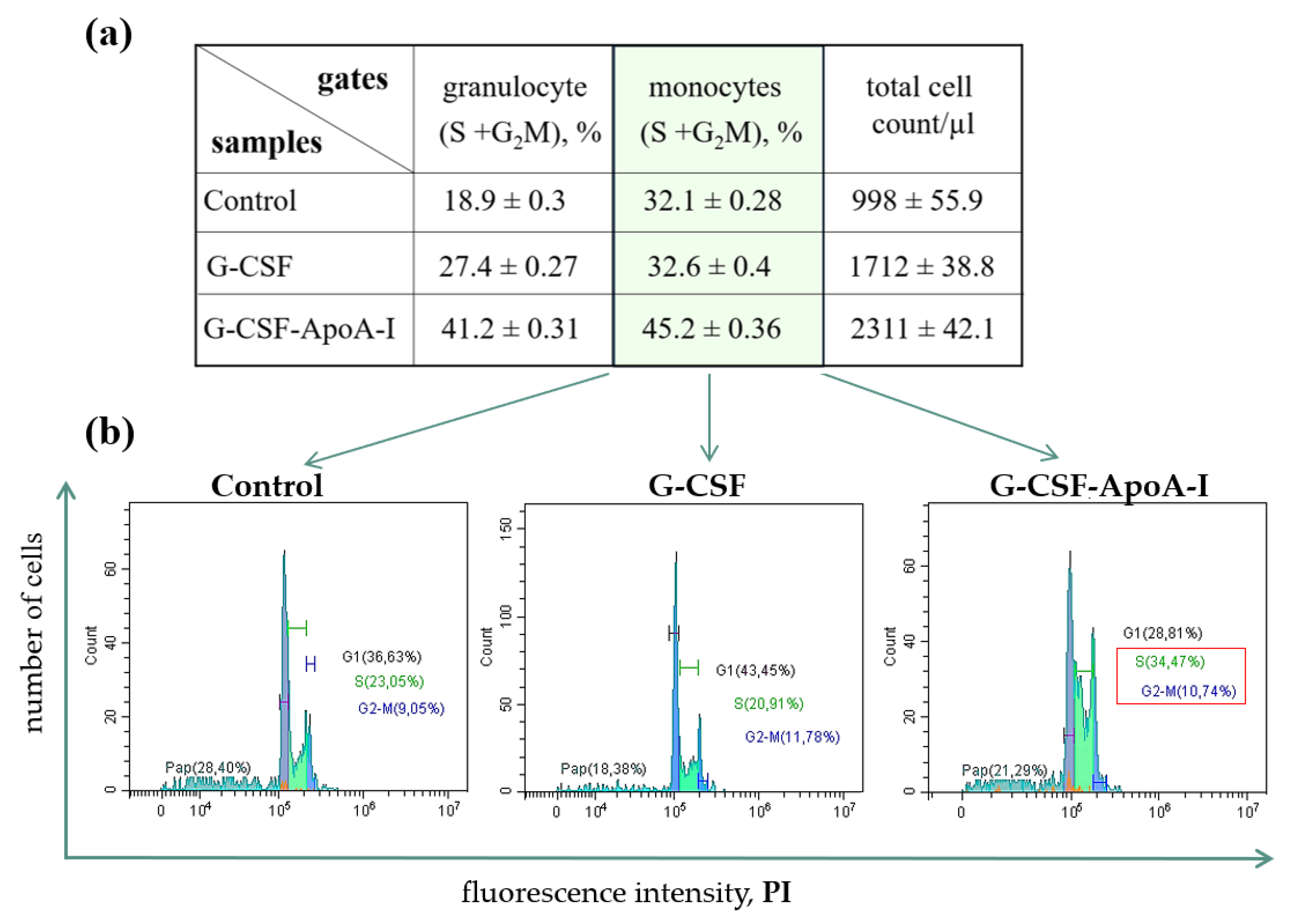
| Cell maturation phases, (%) | 24 hours of incubation | 48 hours of incubation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | G-CSF | G-CSF-ApoAI | Control | G-CSF | G-CSF-ApoAI | |
| blast/promyeloblast | 8.9±0.2 | 3.2±0.15 | 3.2±0.2 | 3.4±0.2 | 3.5±0.15 | 4.7±0.15 |
| myelocyte | 16.1±0.25 | 10.2±0.25 | 8.4±0.22 | 13.2±0.25 | 8.8±0.22 | 13.5±0.25 |
| metamyelocyte | 13.4±0.33 | 8.0±0.22 | 7.3±0.2 | 11.1±0.27 | 6.6±0.2 | 9.8±0.2 |
| band neutrophil | 11±0.5 | 5.6±0.25 | 11.6±0.3 | 19.1±0.2 | 7.6±0.2 | 6.6±0.15 |
| segmented neutrophil | 21.3±0.3 | 56.8±0.4 | 58.1±0.36 | 26.2±0.25 | 57.1±0.33 | 53.8±0.3 |
| segmentation anomalies | 26±0.35 | 16.4±0.27 | 10.8±0.25 | 27.3±0.3 | 15.7±0.2 | 11.1±0.2 |
| granulocyte content of all BMC, (%) | 27±3 | 41±2.1 | 36±2.6 | 20±2.5 | 35±2.7 | 34±2.5 |
| Gene | Organism | Primer sequences | Annealing temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gapdh | mouse | F: 5' – TAGACAAAATGGTGAAGGTCGG – 3' R: 5'- CCTGGAAGATGGTGATGGG – 3' |
57-64,5oС |
| Il12a | mouse | F: 5' –AGTGTGGCACTGATGCTGATG– 3' R: 5' – GTAGCCAGGCAACTCTCGTT – 3' |
63,9oС |
| Il10 | mouse | F: 5' – TGGGTTGCCAAGCCTTATCG – 3' R: 5' – CTCTTCACCTGCTCCACTGC – 3' |
63oС |
| Il4 | mouse | F: 5’ – TGAACGAGGTCACAGGAGAA – 3’ R: 5’ – CGAGCTCACTCTCTGTGGTG – 3’ |
59oС |
| Il13 | mouse | F: 5’ – TGTGTCTCTCCCTCTGACCC – 3’ R: 5’ – CACACTCCATACCATGCTGC – 3’ |
64,5oС |
| Tnfα | mouse | F: 5' – TGAGCACAGAAAGCATGATCC – 3' R: 5' – GGAACTTCTCATCCCTTTGGG – 3' |
60oС |
| Tgfb1 | mouse | F: 5' – TGATACGCCTGAGTGGCTGTCT – 3' R: 5' – CACAAGAGCAGTGAGCGCTGAA – 3' |
58oС |
| Csf3 | mouse | F: 5' – GAGCAGTTGTGTGCCACC – 3' R: 5' – CCAGCTGAAGCAAGTCCAAG – 3' |
58oС |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




