1. Methods and Scope
This work presents a narrative review aimed at providing a possible coherent theoretical framework. We integrate heterogeneous models of electromagnetic field (EMF) biological interactions that have remained disconnected in the literature. The review includes a focused examination of research conducted over roughly fifty years (1970-2025). The literature review was carried out using the PubMed and Web of Science databases, employing search terms such as "ELF-EMF," "extremely low frequencies,", “PEMF”, "ion cyclotron resonance," “parametric resonance”, "biological effects," "calcium signaling", “calmodulin”, “DNA signaling”, "coherence domains," and "thermomagnetic resonance". The selection process focused on peer-reviewed experimental and theoretical research that provided fundamental concepts or important mechanistic understanding of extremely low frequency and weak intensity EMF (ELF-EMF) biological effects. A narrative review approach was chosen to organize the diverse evidence into a logical framework. This method prioritizes studies aligned with established biological mechanisms, such as calcium's (Ca2+) role as a second messenger. Anchoring the analysis to known physiological processes is essential for building a cohesive model that illustrates the cascade of events from primary physical interactions to tissue response.
This work targets physicians and healthcare professionals with limited mathematical background rather than physicists and specialists. To prioritize conceptual framework and biological mechanism understanding, we present the model foundations in logical rather than mathematical-analytical form. The few formulas reported are included to remind medical category of the words of the great Galileo Galilei present in "Il Saggiatore" of 1623:
Philosophy is written in this great book that continuously stands open before our eyes (I mean the universe), but it cannot be understood unless one first learns to understand the language and know the characters in which it is written. It is written in mathematical language, and the characters are triangles, circles, and other geometric figures, without which it is impossible to understand a single word of it humanly; without these one wanders in vain through a dark labyrinth.
2. Background: The ICR-like Model
The interaction between EMFs and biological systems remains the subject of scientific investigation and controversy.
Key milestones include the works of Prof. William R. Adey [
1,
2] and Prof. Carl F. Blackman [
3,
4]. Starting in the 1970s, they observed how specific ELF-EMFs profoundly influenced Ca²⁺ transport in chick brain tissue. Adey observed that EMFs influence biological tissues differently. He hypothesized specific frequency and intensity ranges—"windows"—within which measurable biological effects occur [
2]. These ranges are termed "biologically active.
A fundamental contribution to understanding this phenomenon came in 1985 from Prof. Abraham R. Liboff [
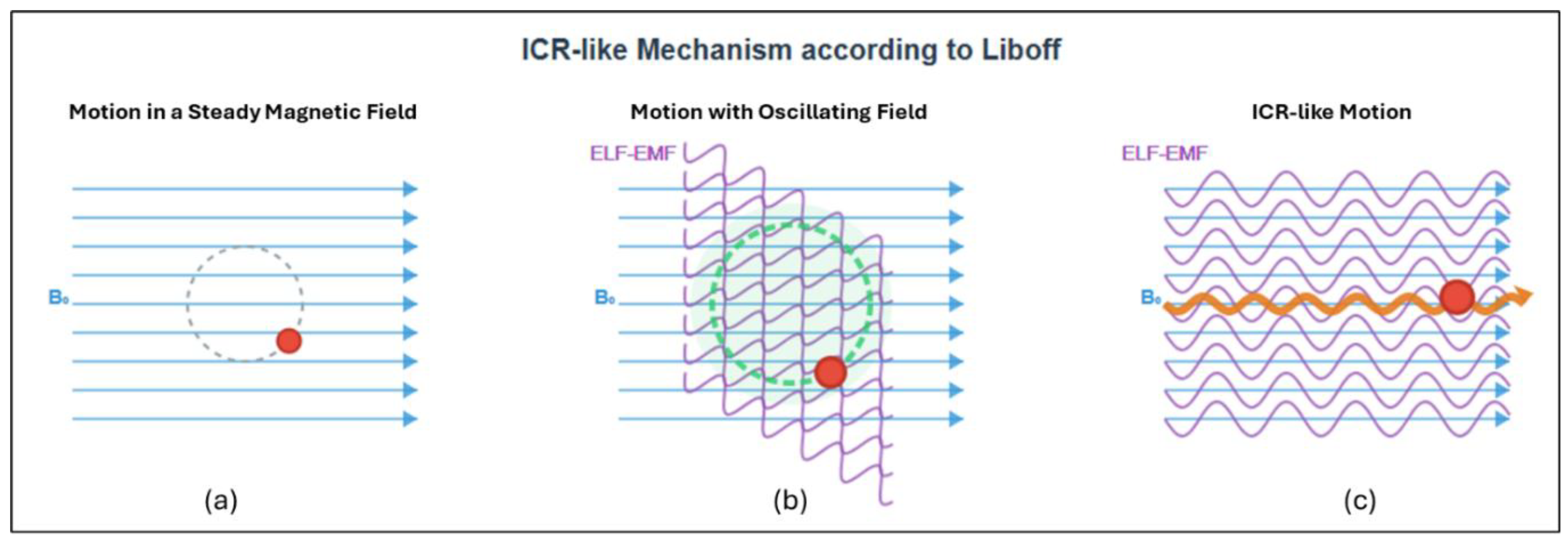
5]. He was the first to propose ion cyclotron resonance (ICR or ICR-like) as a mechanism explaining how biological systems interact with ELF-EMFs. This mechanism is especially relevant in Adey's lower window, where the applied field strengths are comparable to those of the Earth's magnetic field (the so-called Geomagnetic Field or GMF), and the frequencies fall within the ELF range.
Liboff's theory represented a conceptual breakthrough, providing the first coherent theoretical framework for understanding how ELF-EMFs could influence fundamental biological processes.
Liboff hypothesized that weak alternating EMFs produce resonance effects on biologically relevant positively charged ions [
5]. These fields have intensities similar to or lower than those in Adey and Blackman's experiments, or comparable to the GMF. This resonance effect increases the momentum of these ions (
Figure 1), much like the behavior observed in ICR experiments carried out in a vacuum [
5].
The theory found significant corroboration in third-party experimental evidence, most notably with the detection of the so-called "Zhadin effect" (1994-1998) [
6,
7]. This phenomenon confirmed that weak EMFs could indeed influence ionic motion in solution. Zhadin, indeed, observed how extremely weak alternating EMFs, when combined with the GMF at specific frequencies corresponding to the hypothetical ICR of amino acids, could induce measurable changes in aqueous solutions [
6,
7].
Subsequently, Liboff further developed his initial idea of ICR. He intuited that an endogenous electromagnetic phenomenon—linked to the natural electrical activity of the cell membrane and its interaction with the GMF—was possible. He proposed that this phenomenon is formally used by living beings as a regulatory system for biological processes [
8,
9,
10].
The ICR-like phenomenon (
Figure 1) occurs when the frequency of an alternating EMF corresponds to the characteristic frequency of circular motion of an ion in a static magnetic field [
5], according to the equation:
where
q is the ion charge,
m its mass and
B₀ the intensity of the static magnetic field expressed in µT (micro-Tesla).
What makes the ICR-like mechanism particularly relevant for biological systems is that the GMF (~50 μT) produces resonance frequencies in the ELF range (0.1-150 Hz) for biologically important cations, coinciding with many natural biological rhythms and cellular processes (see for example brain rhythms, hence Liboff's hypothesis about an endogenous regulatory phenomenon [
8,
9,
10]).
Although the ICR-like model has garnered support from several studies [
8,
9,
10,
11,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45], its reproducibility between different laboratories has remained inconsistent. This variability, as highlighted by Engström and Fitzsimmons, can be partly attributed to the lack of a universally accepted physical model, which makes it difficult to design standardized experiments and compare results [
12]. This highlights the need for a more systematic approach in future research.
4. Zhadin Effect and the kT Paradox
Mikhail N. Zhadin highlighted how ELF-EMFs, when combined with the GMF at specific frequencies corresponding to the ICR of polar amino acids, could induce measurable changes in aqueous solutions [
6,
7]. The effect, first reported by Novikov and Zhadin [
6] and subsequently by Zhadin et al. [
7], showed a transient increase in current flux through polar aminoacid solutions when exposed to ELF-EMFs of only 40 nT superimposed on a static field of 40 μT.
The significance of this observation is twofold. First, it corroborates with laboratory data the theoretical plausibility of the ICR/IPR hypothesis. Second, it reveals for the first time that even more complex and heavier positively charged systems—such as proteins or large biomolecules—can also be affected by specific ELF-EMFs.
The experimental basis for this effect has been strengthened by several independent replications, despite theoretical challenges. In 2004 In 2004, Pazur confirmed the resonance peak in glutamic acid solutions using non-linear dielectric spectroscopy [
19]. This validated the original results with a different methodology. Subsequently, in 2008, Alberto et al. observed and measured current peaks at the predicted ICR frequencies for different static magnetic fields, confirming the phenomenon under varied conditions [
20]. Nevertheless, the effect's reproducibility has been a subject of debate. Finally in 2009, Giuliani et al. directly addressed this issue. While acknowledging the "poor reproducibility" reported in some contexts, they demonstrated that "almost full" reproducibility could be achieved through meticulous control of the experimental parameters, thus suggesting that the effect is not a sporadic artifact but a real and controllable phenomenon [
21].
However, the Zhadin effect remains controversial, as broader discussions on magnetobiological effects (MBE) highlight related challenges. Binhi and Prato (2017) [
22] emphasized the difficulties in replicating nonspecific MBE, noting that most studies are unique and rarely independently reproduced, with effects influenced by multiple physiological factors and environmental interferences such as geomagnetic storms and background electromagnetic noise, making replication more of an accidental occurrence than a consistent outcome.
This variability suggests the phenomenon operates at the boundary of classical predictions. ELF-EMF interactions with complex ions should be negligible according to conventional physics. Yet they may involve additional uncharacterized mechanisms.
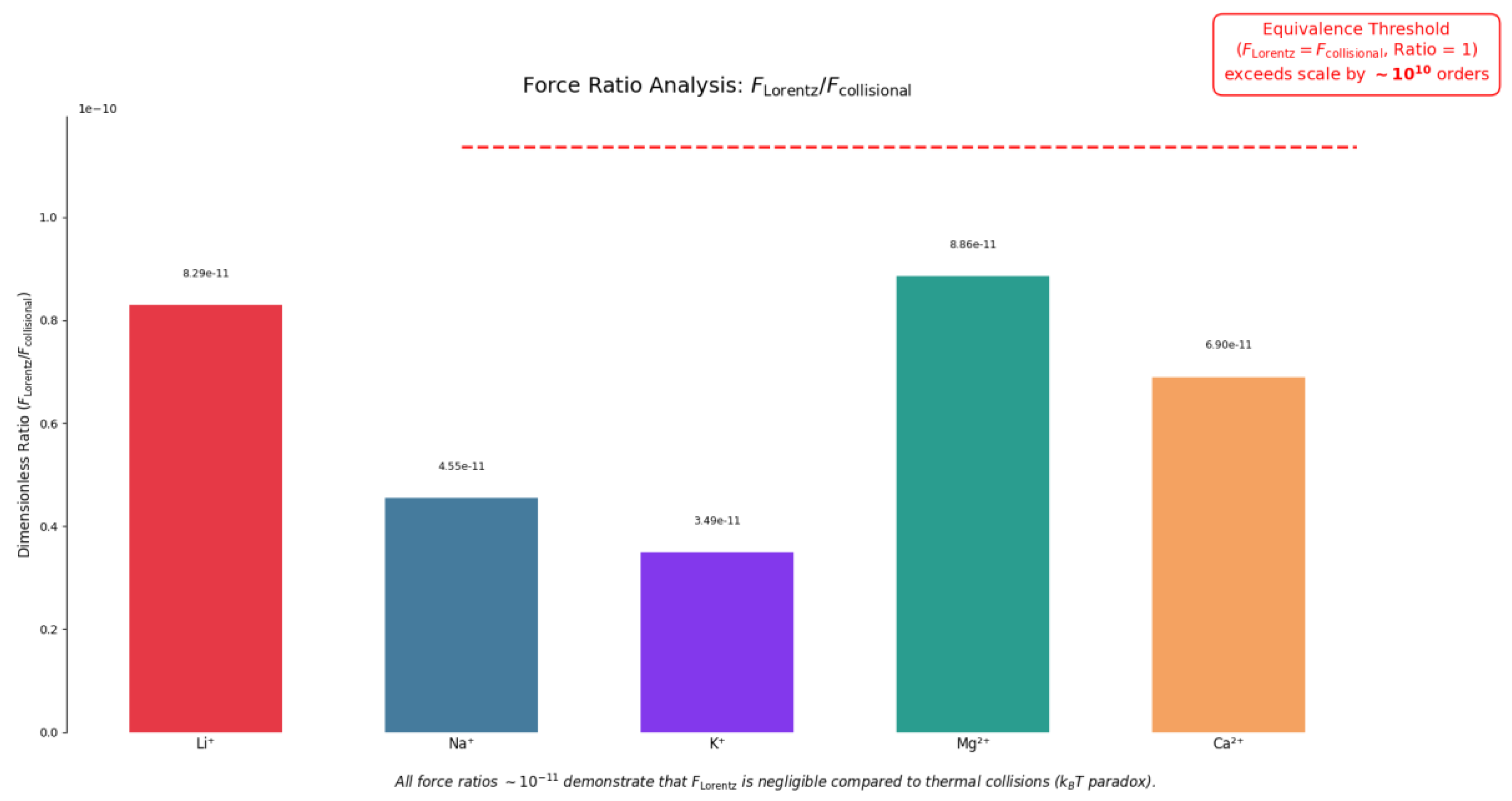
The work done by Comisso et al. [
23] cites this aspect as critical: for a glutamic acid ion (mass = 150 atomic units = 2.4 × 10⁻²² g) at room temperature, the thermal velocity can be calculated using the formula:
(where k is the Boltzman constant, T is the absolute temperature of gas measured in Kelvin, m is the mass of the particle) obtaining about 220 m/s. This result suggests that thermal motion dominates at this scale, making any ELF-EMF effect unexpected and reinforcing why the observed phenomenon is so remarkable within the context of biological systems.
In the presence of the GMF (B₀ = 0.5 Gauss = 50 µT), an ion with this velocity should follow a circular orbit with radius determined by the balance between Lorentz force and centripetal force. The radius r of the circular orbit is given by:
where m, q and v are respectively the mass, the charge and the velocity of the particle and B0 is the strength of GMF. In a uniform magnetic field, this relationship shows that increasing the particle’s velocity or mass will result in a larger orbit radius, while increasing the charge or the magnetic field strength will decrease the radius.
From this equation, a radius of 6.7 meters is derived, clearly incompatible with the dimensions of the electrolytic cell used in the experiment (about 1 cm³). Furthermore, the induced Lorentz force that would act on the ion (on the order of 10⁻²¹ N) is much weaker than collisional forces (on the order of 10⁻¹⁰ N). This apparently insurmountable problem, discussed by Adair in his works [
24,
25] is known as the kT paradox (
Table 1,
Figure 3).
The inability of classical models to resolve this paradox suggests that the key may lie not only in the properties of the ion, but in the environment in which it moves. A potential solution, in fact, could emerge from the peculiar organization of water in biological systems.
5. Coherence Domains and Water Organization
The key paradox requiring explanation: ELF-EMFs (few µT or nT) oscillating in Adey's window influence ionic currents in solution. This apparently occurs despite room temperature thermal energy (kT), which should completely interrupt any coherent ionic motion. Del Giudice et al. [
26] postulated that the so-called kT paradox cannot be resolved within classical frameworks that assume purely electrostatic interactions between independent particles, necessitating a different approach to explain coherent ionic behavior in aqueous systems.
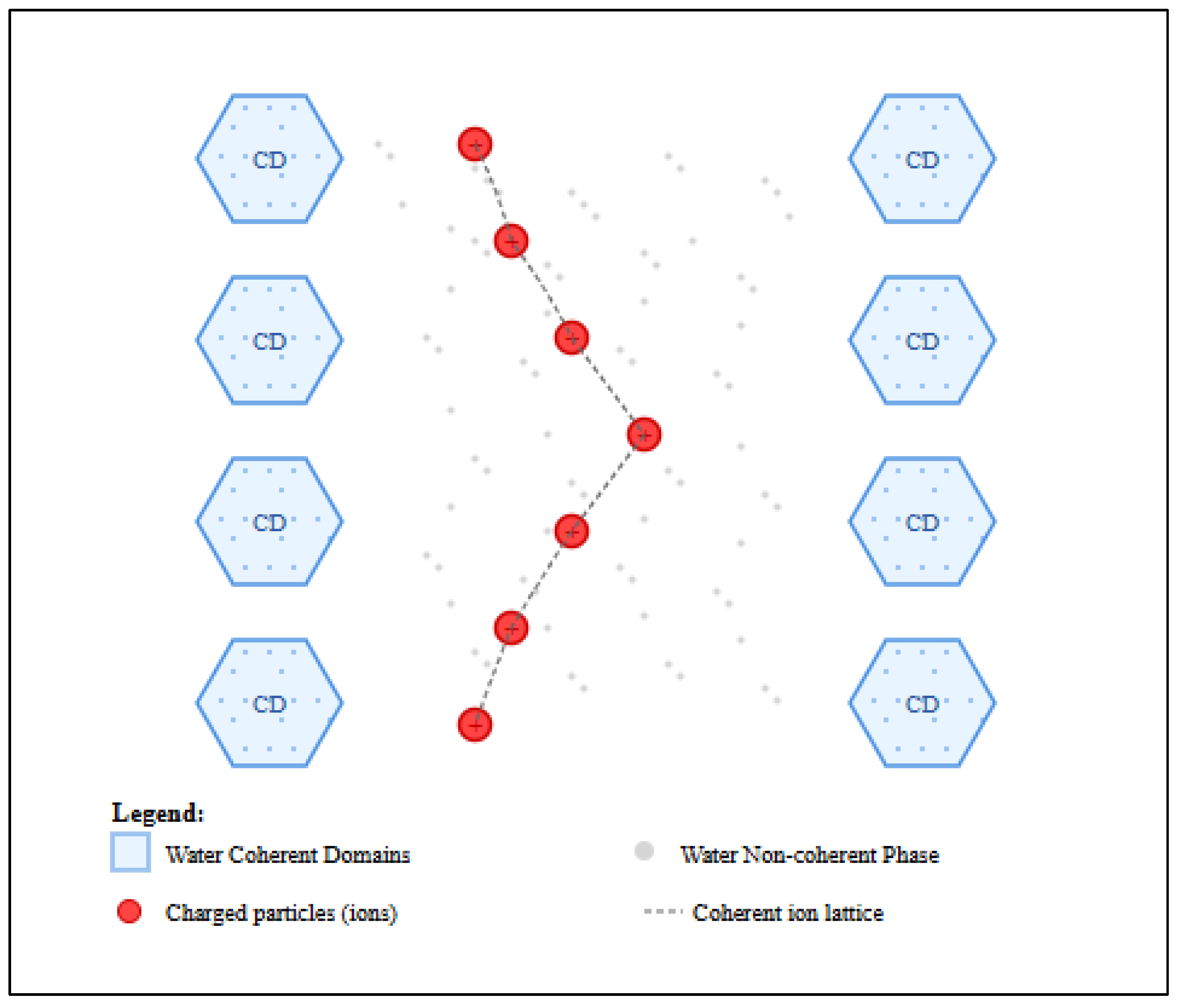
The theory of water coherence domains (CDs) provides several key mechanisms that can resolve this paradox. Del Giudice et al. [
27] and, earlier, by Del Giudice and Preparata [
28] elaborated these in detail: according to the authors, within the framework of Quantum ElectroDynamics (QED), water would be found in biological tissues in two distinct phases, defined as "coherent" and "non-coherent".
Table 2 reports the main properties of each phase. The coherent phase forms CDs where water molecules exhibit collective, synchronized oscillations. These results from coupling with an EMF that oscillates in phase with the molecules. In the non-coherent phase, instead, water molecules do not exhibit behavior like that described above, falling into the domain of thermal fluctuations (and therefore responding to classical physics). The two phases described above are defined as interpenetrating [
27], thus indicating a dynamic situation in which there is continuous exchange of water molecules between the two phases, in a context of continuous interaction.
In this dynamic framework created by interstitial water, positively charged ions are confined in the non-coherent regions of water [
26], where they form, in turn, a coherent system. The authors postulate that ions oscillate according to their individual properties as described by the Debye-Hückel law [
29]. According to the authors, it is precisely these oscillations, described within the framework of the Debye-Hückel theory [
29], that satisfy the conditions for QED coherence. This allows the ions to form their own coherent system, decoupled from the background thermal noise. A direct consequence of this QED coherence is that the ions, oscillating in phase, are protected from random inter-ionic collisions. Since it is precisely these collisions that generate the thermal background noise, their inhibition by the QED model provides a direct solution to the kT paradox (
Figure 4).
Quantitatively, within a coherence domain of ~25 nm radius at 300K (wavelength ~100 nm) containing ~10³-10⁴ water molecules [
28], the collective interaction energy Eint scales as N3/2 [
26], providing an amplification factor of √N ≈ 10¹·⁵-10² relative to individual contributions. This collective behavior creates an energy gap Δ sufficient to overcome thermal fluctuations (Δ > kT per molecule), effectively resolving the kT paradox through quantum collective dynamics rather than individual molecular motion.
The QED coherence domain model remains controversial, despite its theoretical appeal. Indeed, there are strong objections, such as those raised by Bier and Pravica (2018) [
30], according to which the rapid decoherence due to thermal collisions makes the existence of stable, large-scale coherent domains physically implausible.
Despite these criticisms, the model postulates a mechanism that, if valid, would resolve the kT paradox: the application of weak EMFs in resonance would induce a temporary stabilization of the coherent water regions. These regions would act as a transient "shield" against thermal decoherence, facilitating ion transport [
26].
6. Cell Membranes
The cell membrane constitutes the crucial interface where ICR mechanisms would perform their function, thus acquiring biological relevance. The structure of the cell membrane itself represents a true masterpiece of Nature, where chemistry and physics find equal space and application.
Hodgkin and Huxley’s milestone work [
31] on this fundamental structure has allowed us to understand in a solid manner the physical processes of ionic transport through the cell membrane, its electrical response nature and the propagation of action potentials, among other fundamental aspects. No one today disputes the behavioral nature both chemical and electrical of the cell membrane.
Focusing on electrical properties, key characteristics include high resistivity and capacitance (about 1 µF/cm² [micro-Farad per cm²]), constant for all mammalian cells [
32,
33,
34]. These properties enable local creation of intense transmembrane electric fields, on the order of about 10⁷ V/m [
32], fundamental for maintaining intra- and extracellular ionic homeostasis and as protection of cytoplasmic content.
This intense electric field renders the cell membrane susceptible to electrical perturbations. Consequently, variations in the field can modulate its permeability and directly influence cellular signaling pathways. In this context, the ICR-like mechanism proposed by Liboff [
32] provides a key insight: when an EMF is tuned to the cyclotron resonance frequency of specific ions, it increases their drift velocity through the Lorentz force. According to Liboff's hypothesis, ions with enhanced kinetic energy become more likely candidates for capture by channel gating mechanisms. This increased probability of ion-channel interaction represents one pathway through which weak EMFs can modulate transmembrane ion flux.
However, the ICR-mediated increase in ionic drift velocity represents only part of the mechanism. Experimental evidence indicates that ELF-EMFs can also directly modulate the properties of voltage-dependent channels themselves, creating a bidirectional enhancement: energized ions encounter channels that have become more receptive to their passage.
Particularly important in this dynamic is the role of voltage-dependent channels, especially those of Ca²⁺. T-type (transient) and L-type (long-lasting) channels represent two distinct classes of voltage-dependent Ca²⁺ channels that show different responses to ELF-EMF exposure. Experimental studies have demonstrated that exposure to ELF-EMFs can selectively modulate the activity of these channels through non-thermal mechanisms [
35,
36]. T-type channels, characterized by rapid inactivation, have been shown to mediate cellular responses to time-varying electromagnetic fields (TVEMFs), suggesting enhanced channel activity under these conditions [
37]. L-type channels, with their slower inactivation kinetics, respond to ELF-EMF primarily through increased protein expression and increased Ca²⁺ current via ERK-dependent pathways [
38,
39].
7. Calmodulin
Calmodulin is a fundamental protein present in all eukaryotic cells. Rare calmodulin-like proteins exist in some prokaryotes. This protein is characterized by a molecular weight of about 16,700 Daltons and a highly conserved structure among species. It consists of four homologous domains, each containing a Ca²⁺ binding site, organized in two globular lobes connected by a flexible α-helix region [
40]. The presence in each domain of a high-affinity region for Ca²⁺ called EF-hand [
40,
41], makes it the most important protein with second messenger function linked to free Ca²⁺ currents, serving as an intracellular sensor of Ca²⁺ variations; the binding between calmodulin and Ca2+ induces an important conformational change in the former that exposes hydrophobic regions, fundamental for second messenger activity [
40].
Important is its role in regulating cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels through direct activation of adenylyl cyclase (at low Ca²⁺ concentrations, with consequent cAMP synthesis) and calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase (at high Ca²⁺ concentrations, with relative cAMP degradation) [
40,
41,
42]. This system allows fine control of cAMP levels through a single messenger (Ca²⁺) and a single sensor (calmodulin), creating a feedback system that prevents excessive accumulation of cAMP in the cell [
41].
Calmodulin is also essential in controlling cytoplasmic Ca²⁺ concentration, through direct activity on Ca²⁺-ATPase, which then passes from an inactivation state to an active one, with expulsion against gradient of excess Ca²⁺ from the cell [
40,
41,
42].
Another key role of calmodulin is on Ca²⁺/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases, which represent a sophisticated Ca²⁺-linked signal transduction system [
41]. The activation mechanism is common: the Ca²⁺-calmodulin complex binds to a specific domain of the kinase, removing autoinhibition and allowing catalytic activity [
42]. These kinases form a hierarchical family with different specificities: CaMKII, abundant in the brain (1-2% of brain proteins), mainly regulate synaptic plasticity and memory [
42]. MLCK controls smooth muscle contraction through myosin light chain phosphorylation [
40]. Other kinases (CaMKI, III, IV) have broader roles in gene expression and metabolism regulation [
42].
These three examples demonstrate calmodulin's strategic importance for cellular life. Its evolutionary conservation and ubiquitous distribution across eukaryotic systems emphasize this role [
40,
41,
42]. The functional versatility of calmodulin positions it as a central hub in calcium-dependent signal transduction cascades.
Experimental evidence demonstrates that calmodulin serves as a primary sensor for weak EMFs perception through Ca²⁺-calmodulin signaling systems [
43]. The mechanistic pathway for ELF-EMF biological effects involves plasma membrane voltage changes that induce forced intracellular ionic vibrations, resulting in extracellular Ca²⁺ influx and enhanced calmodulin binding affinity, which constitutes the primary transduction pathway to secondary messengers including cAMP and cGMP [
44].
Given calmodulin's established role as the principal Ca²⁺ sensor and its demonstrated capacity to transduce electromagnetic signals into biochemical cascades, it follows as a natural consequence that the hypothesized ICR-like effects on Ca²⁺ currents would converge on calmodulin as the crucial biochemical node. This convergence enables the translation of weak electromagnetic perturbations into amplified cellular responses through calmodulin-dependent enzymatic pathways and downstream signaling cascades [
43,
44,
45], thereby providing a mechanistic foundation for the observed biological effects of ELF-EMF exposure across diverse experimental systems.
8. Ca²⁺ and ELF-EMF: From Liboff’s Proof to Latest Evidence
Building on Adey and Blackman's observations, Liboff first studied Ca²⁺ ion cyclotron resonance frequency (ICR-Ca²⁺) on biological substrates [
46,
47,
48,
49,
50]. We report below a noteworthy 2002 study [
50]. In this study, among other things, the effects of ICR-Ca²⁺ on bone cell cultures from chicken embryo were analyzed. ICR-Ca²⁺ stimulation increased diaphysis diameter by 10.6%, rudiment length by 4.1% and diaphyseal collar length by 28.3% [
50]. ICR-Ca²⁺ also led to an increase in Ca²⁺ content (measured by Alizarin Red-S, +26.0%) and glycosaminoglycan (GAG) content (+67.4%) [
50]. Conversely, ICR-K⁺ (Potassium ICR) stimulation produced opposite results: diameter decreased (-7.8%), length decreased (-5.7%), and diaphyseal collar length substantially reduced (-43.2%) [
50].
Liboff's vision opened the way to a broader and more systematic understanding of the interaction between EMF and biological systems mediated by Ca2+, as we will see chronologically below.
The therapeutic potential of ICR-Ca²⁺ was systematically explored by Lisi et al. (2008), who demonstrated applications in regenerative medicine using human epithelial cells [
51]. Exposure to ICR-Ca²⁺ enhanced cellular differentiation markers and promoted tissue repair processes. The authors identified ICR as a non-invasive tool for controlling stem cell fate, with implications for tissue engineering applications [
51].
Foletti et al. (2010) provided direct mechanistic validation using pituitary corticotrope-derived AtT20 D16V cells exposed to identical ICR-Ca²⁺ parameters (7.0 Hz, 9.2 µT) [
52]. Within 36 hours of exposure, cells exhibited enhanced neurite outgrowth with early expression and aggregation of neurofilament proteins. Remarkably, these morphological changes persisted for 72-168 hours after field removal, suggesting activation of long-term cellular memory mechanisms [
52].
In 2009, a large Italian team evaluated the effect of ICR-Ca²⁺ stimulation on human adult cardiac stem cells: regarding proliferation and metabolic activity, exposure led to an increase in metabolic activity and cell proliferation [
53]. On the cardiac differentiation front, a significant increase in cardiac markers expression was observed [
53].
In 2013, the same group shifted its attention to neuronal differentiation and tumorigenicity modulation of NT2 cells (a human pluripotent embryonal carcinoma cell line) [
54]. The cells developed neurite-like structures and showed reduced proliferation rate and metabolic activity, similar to those observed in cells treated with retinoic acid, used as a positive control [
54]. At the molecular level, exposure induced significant up-regulation of early and late neuronal differentiation markers, accompanied by down-regulation of transforming growth factor-α (TGF-α) and fibroblast growth factor-4 (FGF-4) [
54]. Of particular relevance was the decreased protein expression of the Cripto-1 gene, involved in tumor transformation, and the reduced capacity of exposed NT2 cells to form colonies in soft agar. These results suggest a reduction in tumorigenic potential [
54].
The effect on neurons is also demonstrated by Sun et al. (2016), who demonstrated that 8-10 days of ELF-EMF exposure dramatically increases presynaptic Ca²⁺ channel expression at central synapses [
55]. This effect improves all forms of vesicle endocytosis including slow, rapid, overshoot and bulk endocytosis without affecting the readily releasable pool size [
55].
A recent and comprehensive review by Ma et al. [
56] provided an updated synthesis of how EMFs regulate stem cell fate through Ca
2+ oscillations, confirming what has been reported so far about the crucial role of Ca
2+ in the biological activity of ELF-EMFs. The authors demonstrated how ELF-EMFs (0-75 Hz, 0-1 mT) selectively promote osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through activation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. Particularly relevant was the identification of dual mechanisms: for osteogenic differentiation, ELF-EMFs mainly activate voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels that promote pERK and Wnt/β-catenin pathways; for chondrogenic differentiation, ELF-EMFs act predominantly on cation receptor-like channels, including purinergic receptors and TRP channels [
56].
The central importance of Ca²⁺ in electromagnetically-mediated biological activity is further confirmed by innovative approaches that, while utilizing different frequencies and mechanisms from classical ICR, converge on the modulation of intracellular Ca²⁺.
Stanley et al. (2015) [
57] developed a genetically encoded system where ferritin nanoparticles, associated with TRPV1 channels, transduce radiofrequency fields (465 kHz) or static magnetic fields into channel activation and Ca²⁺ influx. Although this approach employs frequencies far above the ELF-EMF range (0.1-150 Hz) and field intensities in the millitesla range—orders of magnitude higher than those used in ICR studies—it demonstrates that remote control of Ca²⁺ flux can be achieved through diverse physical modalities, all converging on the activation of Ca²⁺-permeable channels. In vivo, this system enabled remote control of glucose homeostasis through Ca²⁺-dependent gene expression modulation.
This principle of magnetically-mediated transduction has been extended by Rosenfeld et al. (2020) [
58], demonstrating magnetothermal control of hormone secretion in adrenal chromaffin cells through TRPV1 activation.
At the subcellular level, Teranishi et al. (2024) revealed that chronic ELF-EMF exposure (10 µT, 10 days) enhances mitochondrial electron transport chain activities through upregulation of Complex I proteins in prefrontal cortex neurons [
59]. This mitochondrial response is coupled with increased SERCA2a expression in cardiomyocytes, suggesting a coordinated Ca²⁺-mitochondrial axis that extends beyond plasma membrane effects [
59].
Recent evidence further validates ICR principles in regenerative medicine. Wang et al. (2024) demonstrated that ELF-EMFs effectiveness in bone repair correlates with Ca2+ flux through membranes, emphasizing the central role of calmodulin activation and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways [
60].
Table 3 synthesizes these findings to demonstrate a fundamental principle: diverse electromagnetic interaction mechanisms—whether classical ICR, nanoparticle-mediated magnetothermal transduction, or direct mitochondrial modulation—converge on Ca²⁺ flux as the universal signaling pivot in cellular electromagnetic responsiveness.
9. Interaction Between ELF-EMFs and DNA
A fundamental theoretical contribution to understanding the molecular mechanisms of ELF-EMF and biology interaction is given by possible direct interaction with DNA, as hypothesized by Blank and Goodman [
61], who proposed a model based on electronic charge transfer directly in DNA structure. According to this theory, EMFs can displace electrons in hydrogen bonds that hold the two DNA chains together, causing a transient charging of small groups of base pairs and favoring local disaggregation that thus allows the beginning of transcription [
61]. The authors identified a specific DNA sequence (nCTCTn) associated with EMF response, characterized by low electron affinities that facilitate electron displacement [
61]. The proposed mechanism predicts that an electromagnetic force of just 10⁻²⁰ N is sufficient to activate DNA, displacing an isolated electron for 1 nm in 1 nsec, a distance greater than the length of a hydrogen bond (0.3 nm) [
61]. The displaced charge can create conditions that lead to disaggregation by overcoming cohesive forces, including hydrogen bonds, facilitating water molecule infiltration into the spaces created [
61,
62]. The hypothesis on which Blank and Goodman base their study suggests that DNA stability arises from a delicate balance: while repulsive electrostatic forces tend to push DNA chains apart, hydration forces counteract this repulsion and help maintain the structural integrity of the DNA molecule [
61]. When exogenous ELF-EMFs displace electrons, thus creating excessive local charge, electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged DNA backbones increases [
61]. If this charge exceeds a critical threshold, repulsive forces prevail over hydrogen bonds that hold base pairs together, causing transient chain separation [
61,
62,
63]. Blank and Goodman's geometric model demonstrates that DNA, due to its particular structure, is optimized for this disaggregation when local charge increase occurs: opening of 4 base pairs exposes about 8 additional faces to surrounding water, creating an energetically favorable environment for RNA polymerase entry and transcription initiation [
61]. This mechanism explains the specificity of the phenomenon: nCTCTn sequences, characterized by low electron affinities, are particularly susceptible to electron displacement and therefore local disaggregation, while the rest of DNA maintains its structural stability [
61].
Complementary to the Blank and Goodman model is the approach proposed by Elson [
64,
65], which explores the physical mechanisms through which TVEMF can generate mechanical forces sufficient to cause DNA strand separation. Elson postulates that pulsatile currents can flow along DNA through stacked bases (π-way), generating Lorentz and Faraday forces that act radially on complementary strands [
65]. The model predicts that currents on the order of 0.1 A can produce radial forces of 10-15 pN, comparable to those necessary for mechanical separation of complementary strands in solution [
64]. However, Elson acknowledges that this theoretical value substantially exceeds experimentally measured DNA currents (16-22 nA), suggesting that the model may be particularly relevant in regions of stress-induced duplex destabilization (SIDD), where DNA is on a "hair-trigger" and minimal force is required for strand separation [
65]. Particularly relevant is the observation that in the B-form structure of DNA (the most common physiological conformation), a pitch angle of 29° would determine that currents on the two strands have predominant transverse components in opposite directions compared to longitudinal components in the same direction [
65]. Since repulsive forces (transverse component) would exceed attractive forces (longitudinal component), a net force tending to separate strands would be generated, explaining why the natural geometry of DNA would favor opening when traversed by electromagnetic currents [
65]. This electromechanical approach provides a quantitative physical hypothesis for understanding how external EMFs can translate into direct mechanical effects on DNA structure, particularly in instability regions where the force required for strand separation is significantly reduced [
65]. Elson's model also identifies the importance of identifying a biological source for postulated currents, suggesting that cellular structures with capacitive properties could provide the energy necessary to sustain such electromechanical processes [
65]. A comparative summary of the two approaches is presented in
Table 4.
Therefore, the role of the nuclear envelope as an active bioelectric system in modulating DNA replication and gene expression becomes particularly relevant. Mazzanti et al. [
66] have demonstrated that the nuclear envelope possesses significant electrical dimensions, with ionic channels that show variable conductances (up to 200 pS [picosiemens]) and that changes in ionic conductance of the nuclear envelope are directly associated with DNA replication. The nuclear envelope, through its capacitive properties and the presence of K⁺-selective channels [
66], can generate local electrical potentials and intense EMFs (up to 10⁷ V/m) [
67]. The validity of this model is supported by Leno's experiments [
68], which demonstrate how the structural and functional integrity of the nuclear envelope is essential for temporal regulation of DNA replication, suggesting a direct electrical control mechanism on nuclear processes. Considering the documented electrical and capacitive properties of the nuclear envelope, it is postulated that it could act as an electromechanical transducer and field generator at the local level, similarly to what Liboff proposed for the cell membrane [
8,
9,
10]. In this hypothetical framework, the separation and oscillation of charges across the nuclear envelope would generate the necessary physical conditions — specifically, localized alternating and static electric fields — for the onset of resonance phenomena (such as IPR) directly at the genome level, thus providing a mechanistic explanation for electromagnetic field-mediated modulation of gene expression. This nuclear-level transduction mechanism would complement the direct electron transfer mechanisms proposed by Blank and Goodman [
61] and the electromagnetic force-based DNA strand separation described by Elson [
60,
65], creating a multi-scale framework for understanding ELF-EMF interactions with genetic material.
10. Thermomagnetic Resonance (TR)
While the previously described mechanisms - from ICR-like to calmodulin, from DNA interaction to cell membranes - provide specific explanations for different aspects of ELF-EMF/biological systems interaction, a more general and unifying approach has been developed in recent years by the research group led by Prof. Umberto Lucia of the Polytechnic University of Turin. This approach, based on fundamental thermodynamic principles, offers for the first time a predictive approach capable of calculating a priori the most effective electromagnetic frequencies for specific cell types [
69,
70]. The conceptual innovation of Lucia's approach lies in considering cells as open and complex thermodynamic systems, characterized by continuous flows of energy and matter through cell membranes [
71]. According to this vision, cells can be modeled as biochemical engines that execute a series of chemical reactions, where energy transformations, thermo-electro-chemical processes and transport phenomena through cell membranes occur [
69]. All living systems dissipate heat into the environment, resulting from their internal irreversibility, and this heat represents a form of information that flows from the cell to the environment, experimentally measurable [
72].
The heart of the thermodynamic approach lies in analyzing the entropy generation of the cell-environment system. Entropy generation (Sg) represents a quantitative measure of the irreversibility of cellular processes (for mathematical treatment refer to Lucia U et al., 2017) [
69]. According to this model, then experimentally verified, the application of an ELF-EMF at a specific frequency can induce a homeostatic response in cells that requires a shift in cellular energy conversion [
69]. The optimal frequency can be calculated considering cellular morphological characteristics and using a resistor-capacitor (RC) circuit model for the cell membrane [
69].
The natural evolution of the thermodynamic model led to the development of the concept of "thermomagnetic resonance" (TR) [
70,
73]. This represents a particular condition in which the EMF frequency corresponds to the characteristic response time of the cell to external thermal perturbations. The TR frequency is inversely proportional to the characteristic time τ defined as [
73]:
where α is the convection coefficient (measured in W⋅m
−2⋅K
−1 - Watts per square meter per Kelvin), ρ
cell the cell mass density, c
cell the specific heat and ⟨r⟩ the characteristic volume-area ratio of the cell (so their product is measured in J⋅m
−2⋅K
−1 - Joules per square meter per Kelvin).
Under TR conditions, heat flux modulation occurs which determines a variation in Gibbs potential, in turn generating changes in membrane potential [
70]. This mechanism seems to provide a unifying thermodynamic explanation for many of the previously described phenomena, including effects on voltage-dependent ionic channels and perturbations of transmembrane ionic fluxes.
The validity of Lucia’s thermodynamic approach was initially demonstrated on two-dimensional cultures of human tumor cell lines, specifically glioblastoma and breast cancer cells [
74]. The mathematical model at the core of this approach predicts that exposure to ELF-EMFs at specific resonance frequencies—determined by the biophysical properties of the cells—should induce measurable changes in cellular processes such as proliferation and energy metabolism [
74]. In line with these predictions, experiments showed that exposing the tumor cells to ELF-EMF at frequencies calculated by the model resulted in approximately a 30% reduction in proliferation rates, along with a marked increase in mitochondrial membrane potential, reflecting significant modulation of mitochondrial activity [
74]. These findings establish a clear link between the theoretical framework and the observed biological effects, lending credibility to the model’s predictive power. A fundamental advancement was subsequently obtained with extension of the approach to three-dimensional (3D) cancer models [
73]. In studies on 3D models, Bergandi et al. demonstrated that the thermodynamic approach can be successfully applied even to complex cell masses where cells show synergistic and complex interactions [
73]. The cell membrane was modeled as an RC circuit and the specific thermal resonance frequency was calculated and tested on two-dimensional and three-dimensional cultures of human pancreatic cancer, glioblastoma and breast cancer, with promising results on cell growth inhibition [
69].
Lucia's approach, although based on general thermodynamic principles, finds a direct correspondence with the biophysical properties of the cell membrane. This connection emerges clearly when the membrane is modeled as an RC circuit with typical mammalian parameters, according to Hodgkin & Huxley [
31] and Brantlov et al. [
75]. The membrane capacitance (Cm) is approximately 1 μF/cm², while the membrane resistance (Rm) ranges from 1 to 10 kΩ·cm², yielding a time constant, τ, equal to the product Cm × Rm, ranging from 1 to 10 milliseconds (ms). This time constant τ determines how quickly the membrane potential can respond to changes, which is crucial for physiological processes such as nerve impulse transmission and synaptic signaling. The characteristic frequency associated with this RC circuit can be calculated as f
c = 1/(2πτ), which corresponds to a range of approximately 16–160 Hz. This frequency range overlaps with both ICR frequencies for biologically relevant ions (1-100 Hz) and observed ELF-EMF biological effects, suggesting the membrane RC properties act as a natural band-pass filter for electromagnetic signals.
Lucia's thermodynamic approach provides a rigorous quantitative basis for analyzing ELF-EMF/biological systems interactions through application of mass, charge and energy conservation principles to cellular systems [
69]. The model is based on the entropic balance equation for open systems under non-equilibrium conditions:
where dS represents the total entropy variation, diS the variation due to internal irreversibility and deS the variation for interaction with the environment [
65].
Thermodynamic analysis establishes a direct relationship between entropy generation (Sg) of the cell-environment system and transmembrane ionic fluxes according to the relation [
68]:
where Jk represents the flux of the k-th ionic species and Xk the corresponding thermodynamic force.
While acknowledging limited competence in the nuances due to different professional backgrounds, we hypothesize that this mathematical formulation can provide a quantitative basis for understanding how external electromagnetic perturbations modulate the ionic fluxes described in ICR-like theory through modification of the transmembrane electrochemical gradient [
5].
11. NASA’s Contribution
A fundamental contribution to understanding the effects of ELF-EMF on biological systems comes from research conducted at NASA's Johnson Space Center by Thomas J. Goodwin and collaborators [
76]. This study represents a cornerstone in experimental validation of the theoretical mechanisms previously described, providing the first direct demonstration of TVEMF effects on normal human neuronal progenitor cells. The NASA study used a particularly innovative methodology, employing both two-dimensional and three-dimensional cell cultures through Rotating Wall Vessel (RWV) technology, which simulates some microgravity conditions.
TVEMF exposure produced a 2.5-4.0 fold increase in cell proliferation compared to controls, maintaining cell viability above 98%. This effect persisted for 72-168 hours after TVEMF removal, suggesting activation of long-term cellular memory mechanisms. Particularly relevant was the observation of organized neural-like structure formation, with development of "neural tubes" and preferential cellular orientation. In three-dimensional cultures, formation of three-dimensional tissue aggregates that emulate native neural tissue organization was observed. A distinctive phenomenon observed was termed the "Corona effect" by NASA researchers: cells exposed to TVEMF exhibited radial growth patterns emanating from tissue edges, creating concentric rings of actively proliferating cells. A particularly significant aspect is that the dramatic increase in cell proliferation was not accompanied by proportional increases in glucose consumption, lactate production or oxygen consumption. This suggests that ELF-EMFs can induce optimization of cellular metabolic efficiency, possibly through modulation of mitochondrial activity or transmembrane ionic transport systems.
NASA's observations provide crucial empirical support for an integrated model. The activation of complex processes such as neuronal differentiation and organized proliferation, achieved with weak fields, is difficult to explain by a single mechanism. These results, therefore, align with the hypothesis of a convergence of multiple processes (ICR/IPR, genomic activity, and TR) that act synergistically to translate a weak physical signal into a complex and coordinated biological response.
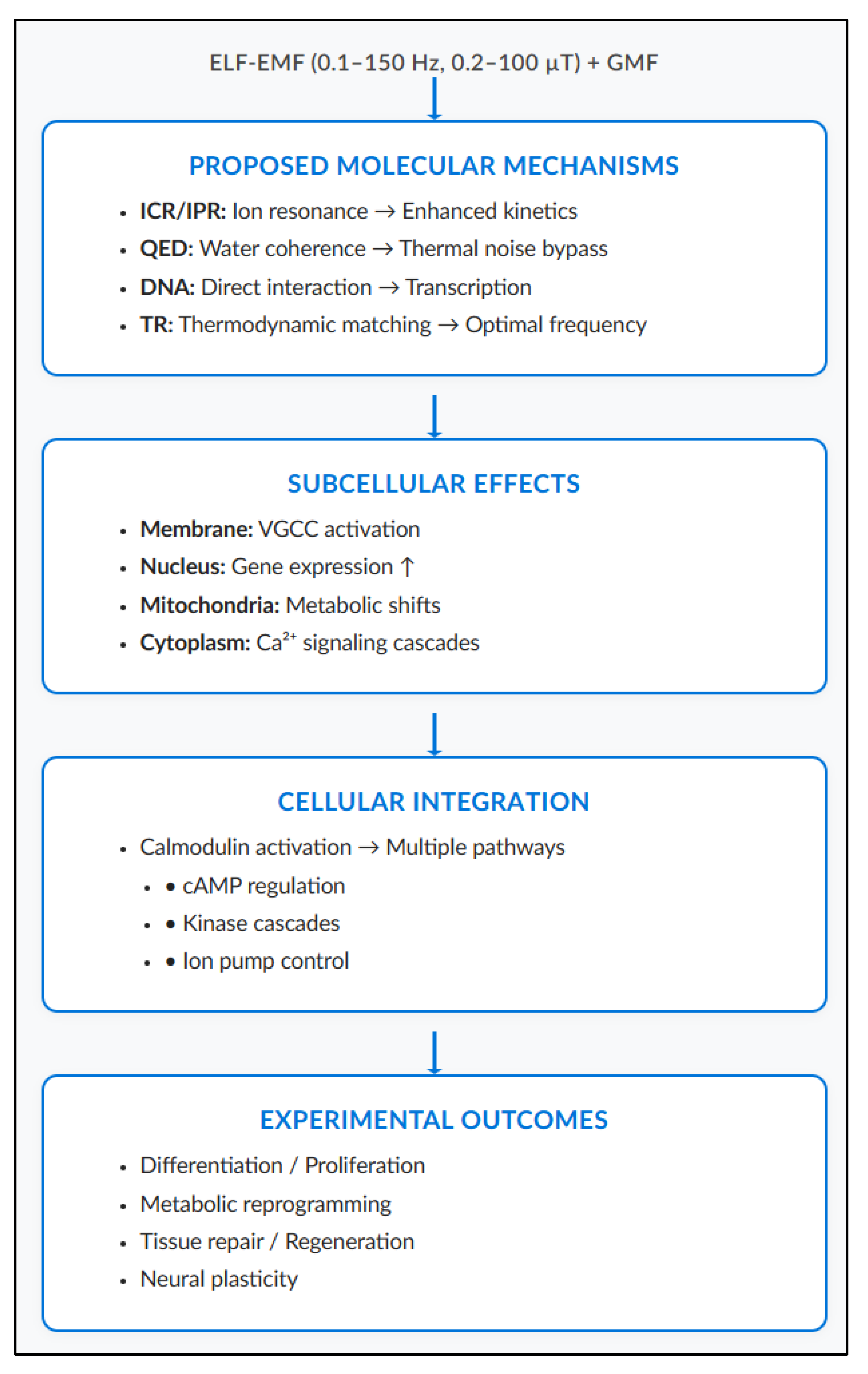
12. Discussion
This narrative review shows that ELF-EMF biological interactions involve multiple mechanisms. These operate as interconnected cascades across different scales rather than through a single pathway (
Figure 5). This cascade begins at the quantum-molecular level and propagates to cellular and probably tissue manifestations (
Figure 5).
The GMF provides the static stage for alternating electromagnetic signals (TVEMF in the ELF-EMF range). When the frequency of this signal corresponds to the ICR frequency of specific biologically relevant positive charge ions, the first critical event occurs: ions acquire additional kinetic energy selectively. This is not a chaotic thermal effect, but an ordered and coherent phenomenon. Liboff's intuition [
5] showed us that not all ions respond to the same stimulus: each has its "frequency signature" determined by the charge/mass ratio. Ca²⁺ seems to emerge as the main ionic actor for its centrality in biological processes, as demonstrated by Adey [
1,
2] and Blackman [
3,
4] and by its crucial calmodulin-mediated role [
38,
39,
40]. The evolution of this theory into Lednev's IPR [
13,
14,
15] and subsequent refinenement by Blackman et al. [
16,
17] has further refined understanding of the phenomenon, showing how cellular response follows oscillatory patterns predicted by Bloch functions [
18].
An apparent paradox emerges: how can such a weak field, with energy much lower than thermal noise, produce measurable biological effects? A potential solution to this paradox may lie in the unique organization of water in biological contexts. Water in living tissues is not merely a passive solvent: according to Del Giudice and Preparata's QED theory [
28], it organizes into CDs where millions of molecules oscillate in phase [
26,
27]. These CDs create "corridors" protected from thermal noise where ions stimulated by ICR can move coherently, as if shielded from surrounding thermal chaos, thus resolving the kT paradox [
24,
25]. The Zhadin effect [
6,
7], confirmed by multiple independent groups [
19,
20,
21], represents a first experimental proof of this phenomenon: measurable ionic currents emerge from incredibly weak EMFs, precisely as predicted by ICR theory.
In this context, the cell membrane works as a sophisticated signal transducer. With its intense transmembrane electric field (10^7 V/m) and capacitive nature (1 µF/cm²), it is intrinsically susceptible to electromagnetic perturbations [
32,
33,
34]. Voltage-dependent Ca²⁺ channels, particularly T and L types, function as sensitive "gates" that further amplify the initial signal. A small change in membrane potential, induced by coherent ion movement, can trigger the opening of many channels, creating an "avalanche" effect that leads to significant variations in intracellular Ca²⁺ concentration [
35,
36,
37,
38,
39]. This non-linear behavior implies that total biological effect cannot be calculated by simply adding individual effects. Instead, an integral formulation is needed that accounts for temporal and spatial interactions between mechanisms.
Once inside the cell, Ca²⁺ meets its main molecular partner: calmodulin [
40]. This ubiquitous protein appears as the "universal translator" that converts the Ca²⁺ signal into multiple biochemical responses [
40,
41,
42]. Ca²⁺-activated calmodulin regulates cAMP levels, protein kinase activity and calcium pumps, thus influencing countless metabolic pathways and maintaining cellular homeostasis [
43,
44,
45].
Several experimental validations strengthen this framework, after the various observations proposed by Liboff [
46,
47,
48,
49,
50]. Lisi et al. [
51] demonstrated ICR-Ca²⁺ enhanced differentiation markers in human epithelial cells. Foletti et al. [
52] showed that identical ICR-Ca²⁺ parameters induced neurite outgrowth, with morphological changes persisting 72-168 hours after field removal. Gaetani et al. [
53] observed increased metabolic activity, proliferation, and cardiac marker expression in human adult cardiac stem cells. Ledda et al. [
54] reported that NT2 cells developed neurite-like structures, showed reduced proliferation and metabolic activity, and exhibited decreased tumorigenic potential with down-regulation of Cripto-1 and reduced soft agar colony formation. Sun et al. [
55] demonstrated dramatic increases in presynaptic Ca²⁺ channel expression improving all forms of vesicle endocytosis. Teranishi et al. [
59] identified mitochondrial Complex I upregulation coupled with increased SERCA2a expression in cardiomyocytes, revealing coordination between Ca²⁺ signaling and mitochondrial function. Ma et al.'s comprehensive review [
56] synthesized how ELF-EMFs selectively promote osteogenic differentiation through voltage-dependent Ca²⁺ channel activation of pERK and Wnt/β-catenin pathways, and chondrogenic differentiation through purinergic receptors and TRP channels. These results with different outcomes, depending on cellular context, all converge on the Ca2+-calmodulin as the central transduction node, offering an initial confirmation of the cascade amplification model proposed here. (
Figure 5).
Parallel to the cytoplasmic Ca²⁺-calmodulin cascade, evidence emerges of direct interactions with DNA. Two complementary theoretical hypotheses address this mechanism. Blank and Goodman [
61] proposed that EMFs displace electrons in hydrogen bonds holding DNA strands together, creating transient local charge excess that increases electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged backbones. Elson's electromechanical model [
64,
65] provides a complementary physical mechanism, postulating that pulsatile currents flowing along DNA through stacked bases (π-way) generate Lorentz and Faraday forces acting radially on complementary strands. The nuclear envelope could provide a crucial link between EMFs and these DNA interaction mechanisms. Its intrinsic electrical properties [
31,
66,
67] are the basis for the local creation of an electric field [
67], suggesting it can work as transducer analogous to the cytoplasmic membrane [
8,
9,
10]. Charge separation and oscillation across the nuclear envelope could generate localized alternating and static electric fields sufficient to produce resonance phenomena (ICR/IPR) directly at the genome level. The nuclear envelope interacting with exogenous EMFs creates optimal conditions for gene expression modulation [
67,
68]. This would explain the long-term effects observed in NASA studies [
76], which persist even after field removal.
Lucia et al. [
69,
70,
71,
72,
73,
74] provide a unifying thermodynamic perspective. Modeling cells as open thermodynamic systems, they demonstrate that cells possess characteristic thermal resonance (TR) frequencies. When the frequency of external EMF corresponds to these natural frequencies (TR), optimization of energy exchange processes occurs, modulating membrane potential and cellular metabolism [
69]. This explains why different cells respond optimally to different frequencies and why it is possible to mathematically predict these frequencies based on cellular morphological characteristics, as demonstrated by Bergandi et al. [
73,
74].
The four most significant models here discussed are summarized, for a brief summary, in
Table 5.
An important integrative element is the role of ferritin and other endogenous superparamagnetic substances. These molecules function as "molecular antennas" that concentrate and locally amplify the magnetic field, creating microenvironments where resonant effects are enhanced [
56,
57,
58]. This mechanism explains cellular heterogeneity in electromagnetic responses. Ferritin acts as molecular antennas, amplifying local field strength through magnetothermal interactions with TRPV1 channels [
57,
58]. Cells with varying ferritin content show proportional sensitivity differences.
Despite these mechanistic insights, it is important to acknowledge that some of the foundational phenomena require further validation. The Zhadin effect, though replicated by several independent groups [
19,
20,
21], shows significant sensitivity to experimental conditions, with some studies reporting poor or null results when parameters deviate minimally from optimal ranges [
20,
22]. Similarly, while QED coherence domains provide an elegant theoretical framework for resolving the kT paradox, direct experimental observation of the predicted 100 nm structures in biological systems remains an open challenge. These considerations highlight the importance of developing standardized protocols and conducting systematic validation studies to fully establish the robustness of these phenomena.
Despite these experimental challenges and theoretical controversies, the convergent evidence reveals consistent multi-scale interactions. This integrative approach suggests that ELF-EMF/biological systems interaction represents a paradigmatic example of a complex adaptive system, displaying several key characteristics:
Emergence of macroscopic effects through non-linear microscopic interactions: macroscopic biological effects (differentiation, proliferation changes, metabolic shifts) emerge from non-linear coupling between quantum (QED coherence), atomic (ICR/IPR), molecular (calmodulin), organellar (mitochondria, nucleus), and cellular (membrane potential) scales.
Redundancy of mechanisms guarantees response robustness: multiple mechanisms (ICR/IPR, TR, direct DNA interaction) converge on common pathways (Ca²⁺ flux, calmodulin as second messenger, gene expression).
Resonance tuning enabling specificity: The frequency and intensity "windows" reflect resonance phenomena operating at multiple scales.
Cascade amplification transforms weak signals into significant biological response (
Figure 5): sequential amplification stages —voltage-gated channel avalanches, and calmodulin-dependent enzymatic cascades — combine to transform weak, sub-thermal signals into robust cellular responses.
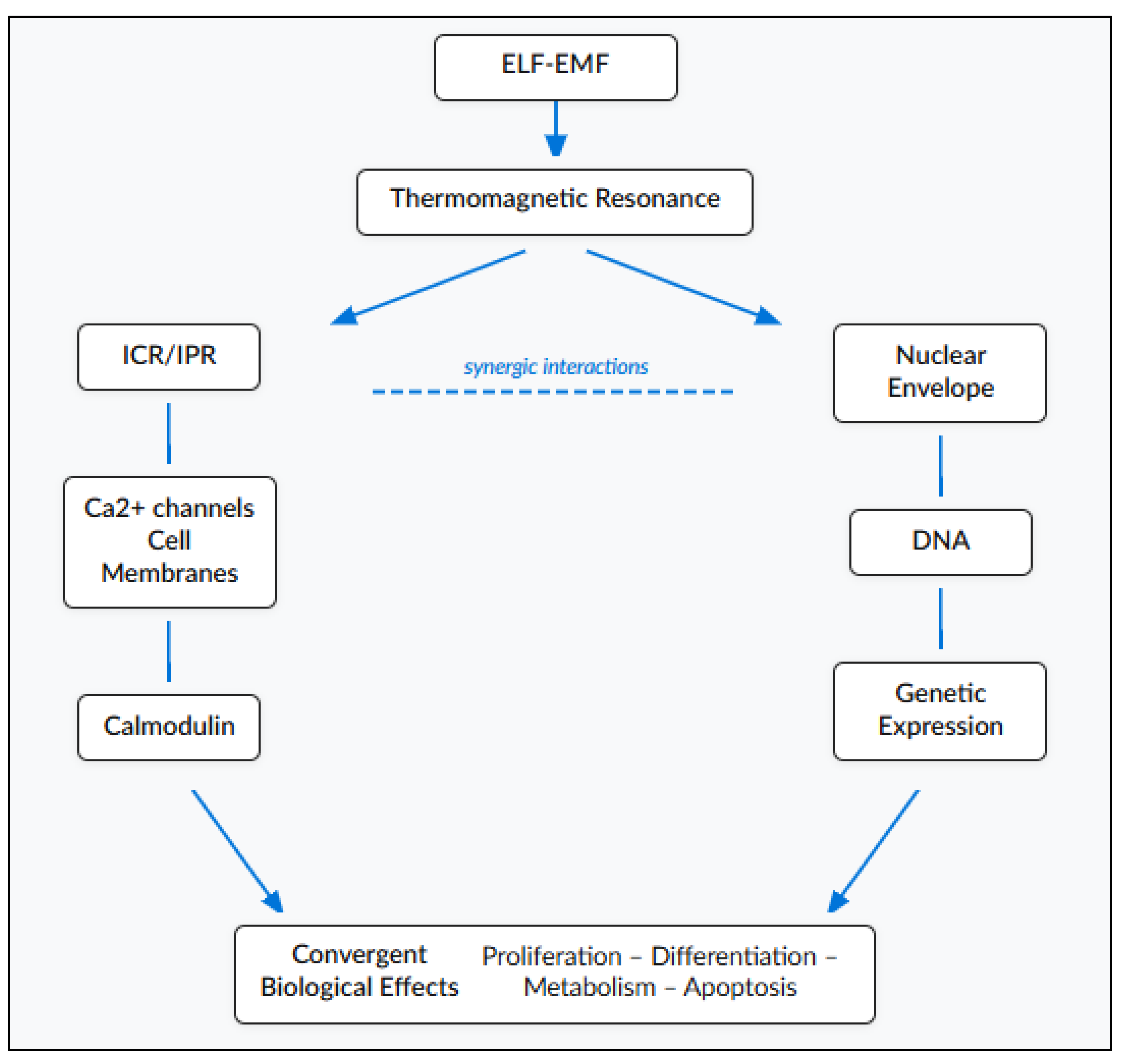
Convergence of multiple mechanisms toward common nodes: ICR/IPR, TR and DNA interactions, though operating through distinct physics, all converge on Ca²⁺ flux and membrane polarization as pivotal signaling nodes (
Figure 6). This convergence architecture explains why diverse electromagnetic parameters can produce similar biological outcomes: different mechanisms activate the same downstream biochemical pathways. Conversely, it explains why the same electromagnetic parameters produce different outcomes in different cell types: cells express different complements of calcium-responsive proteins, causing the converged signal to propagate through divergent pathways.
Cellular memory through sustained molecular changes: the persistence of effects hours after field removal [
52,
76] indicates activation of stable molecular states, particularly transcriptional programs and epigenetic modifications.
This multi-scale interaction model (
Figure 5) shows how extremely weak electromagnetic signals overcome the thermal noise problem through amplification mechanisms at each biological level. While the initial ELF-EMF energy is sub-thermal (~10⁻²² J per photon), non-linear biological amplifiers—including coherent water domains, voltage-gated channels, and enzymatic cascades—transform weak signals into measurable cellular responses.
The comparative analysis of major models (
Table 5) reveals complementary frequency ranges and mechanisms. ICR operates at 0.1-150 Hz, IPR refines resonance conditions through Bessel’s and Bloch’s functions, QED explains the kT paradox through coherent domains, and TR provides cell-specific frequency predictions. This convergence validates the multi-mechanism approach rather than single-pathway explanations.
This model proposes that living systems have evolved to use environmental EMFs as a fine regulation system, complementary to traditional chemical mechanisms. This idea was hypothesized by Liboff in his work on the endogenous resonance hypothesis [
8,
9,
10]. The hypothesis was anticipated by Lund [
77], who, as early as 1947, suggested the existence of a bioelectric system for controlling cellular metabolism. This system was seen as parallel and antecedent to the more specialized chemical control systems that evolved later, such as the endocrine and nervous systems [
77].
The GMF, from a biological perspective, represents an active component in cellular regulatory networks. The remarkable sensitivity of cells to weak EMFs suggests evolutionary selection for electromagnetic responsiveness. This sensitivity harnesses sophisticated physical principles—quantum coherence, parametric resonance, and non-linear amplification—that appear critical for maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating vital processes. This evolutionary perspective finds further support in De Ninno and Pregnolato's concept of "electromagnetic homeostasis" [
78], which describes the human body's ability to maintain equilibrium of complex internal electromagnetic interactions despite the noisy external electromagnetic environment, through a fundamental information network consisting of oscillatory frequencies of substances, enzymes, cell membranes and nucleic acids that controls cellular metabolism [
78].