Submitted:
25 November 2025
Posted:
26 November 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Coupling Coordination Mechanism and Driving Factors Between GF and GTI
2.1. Relevant Study on the Relationship Between GF and GTI
2.1.1. Relevant Studies on GF and GTI
2.1.2. Study on the Relationship Between GF and GTI
2.2. Analysis of the Coupling Coordination Mechanism
2.3. Impact of Different Development Situations of GF and GTI on Coupling Coordination
2.4. Analysis of Driving Factors for the Coupling Coordination Between GF and GTI
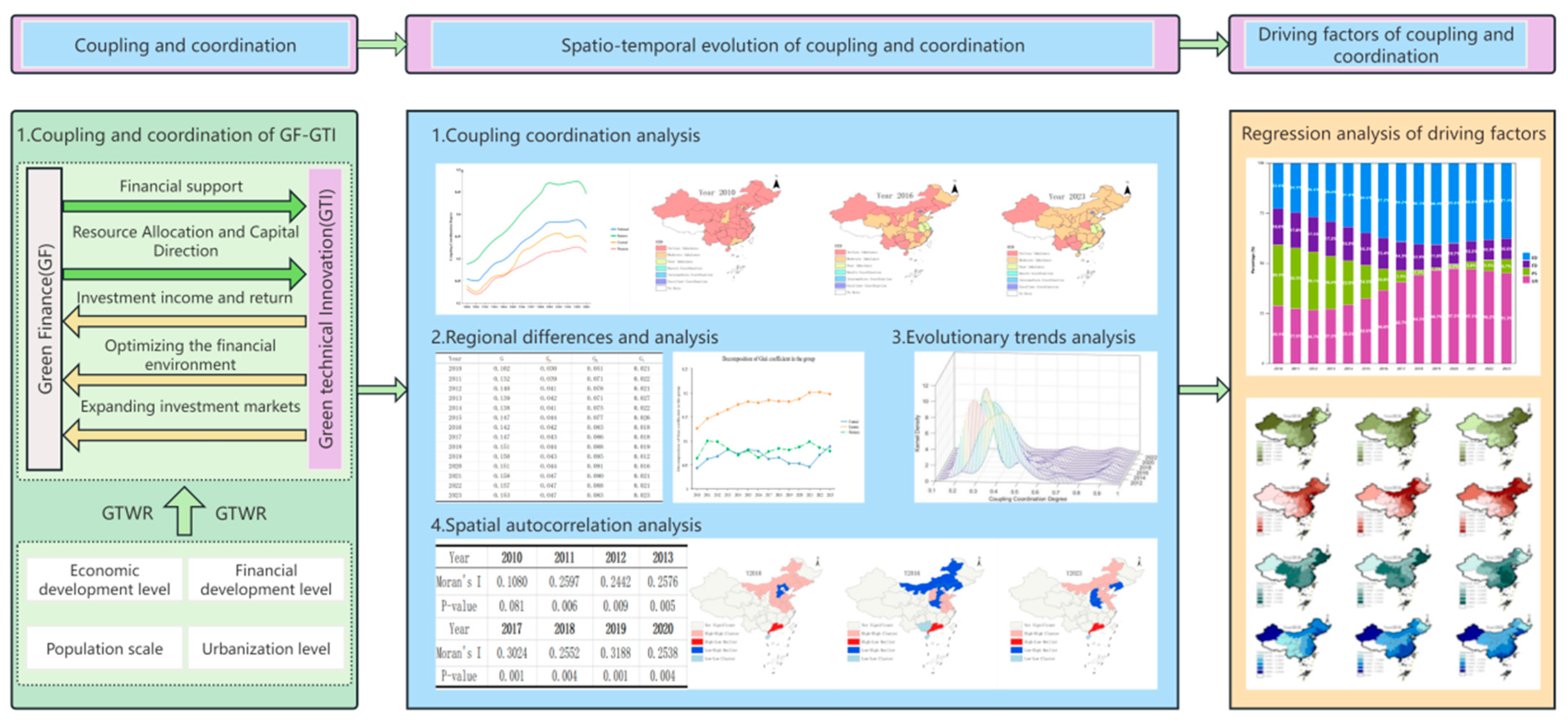
3. Data Sources and Research Methods
3.1. Data Sources and Construction of Index System
3.1.1. Data Sources
3.1.2. Construction of the Evaluation Index System
3.2. Research Methods
3.2.1. Entropy-Weighted TOPSIS Method
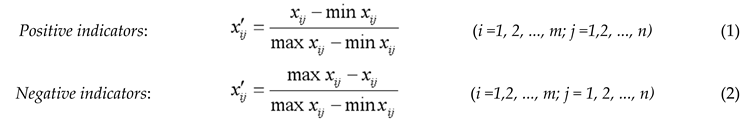
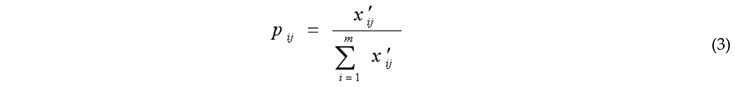
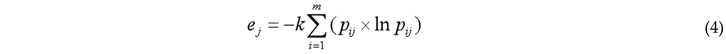
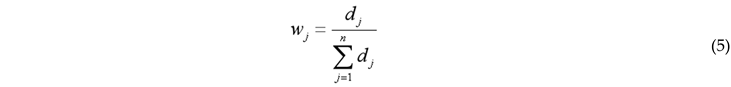
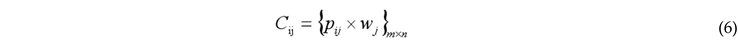
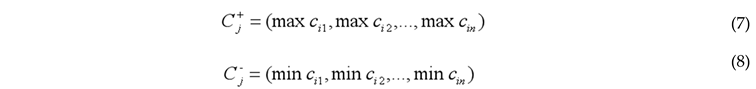
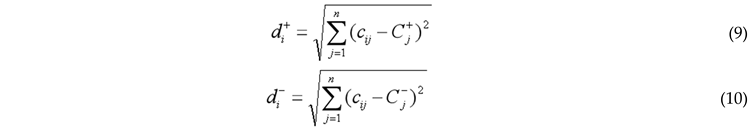
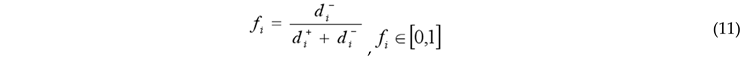
3.2.2. Coupling Coordination Degree Model
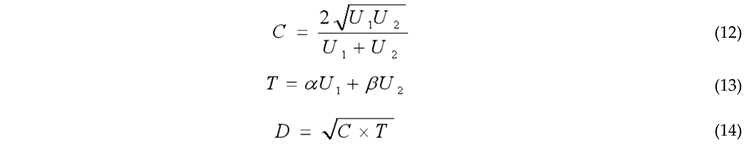
3.2.3. Dagum Gini Coefficient
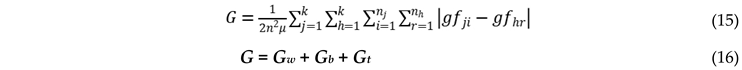
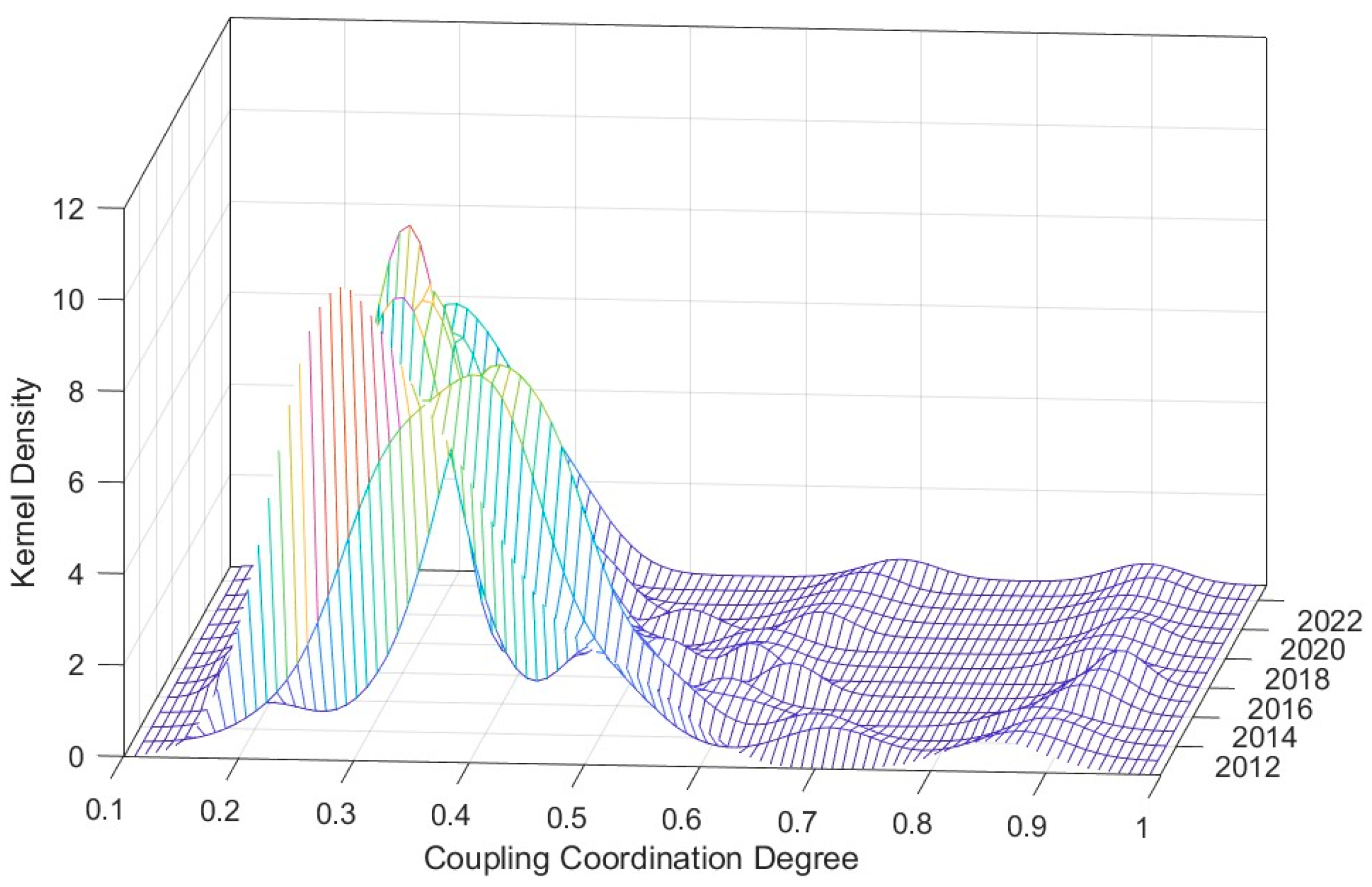
3.2.4. Kernel Density Estimation
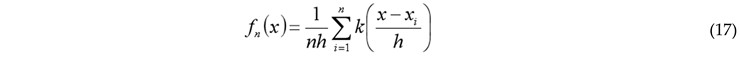
3.2.5. Spatial Autocorrelation Model
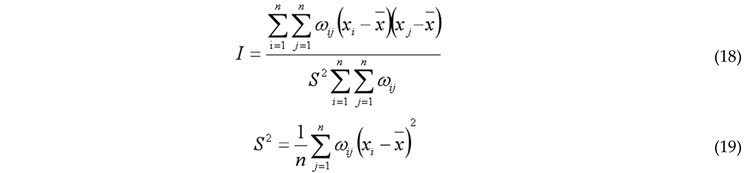
3.2.6. Spatio-Temporal Geographically Weighted Regression (GTWR)
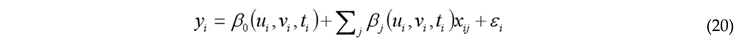
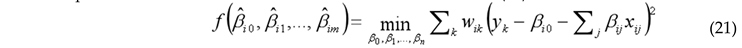
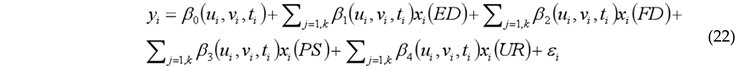
4. Results and Discussions
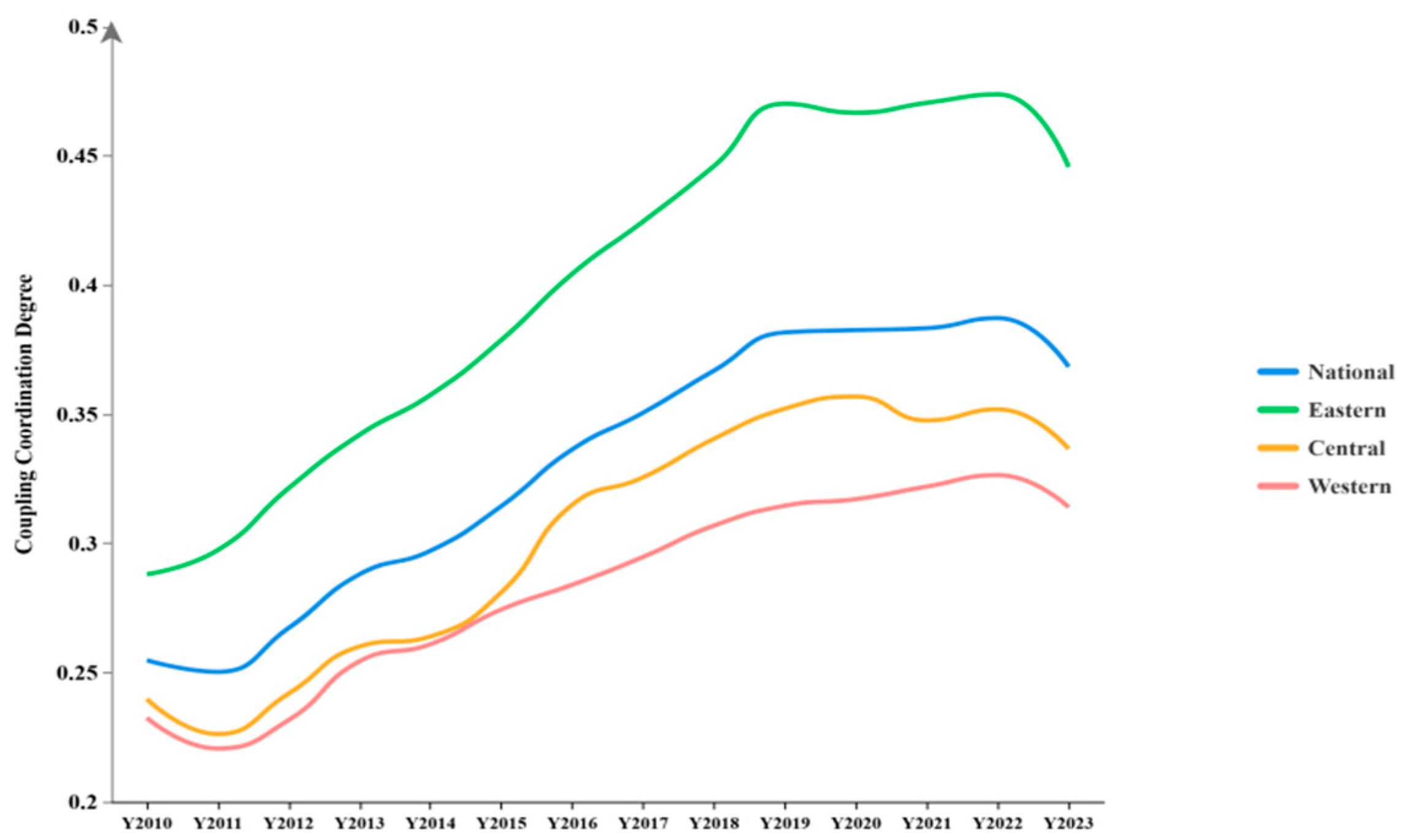
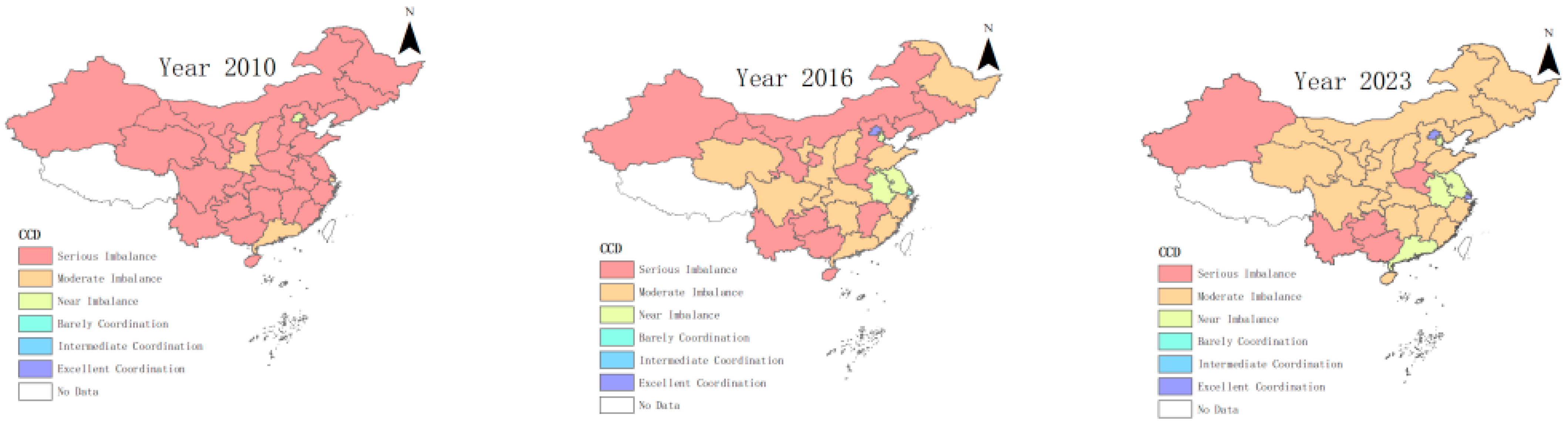
4.1. The Coupling Coordination Degree Between GF and GTI
4.2. Regional Differences in the Degree of the Coupling Coordination
4.2.1. Analysis of Regional Differences
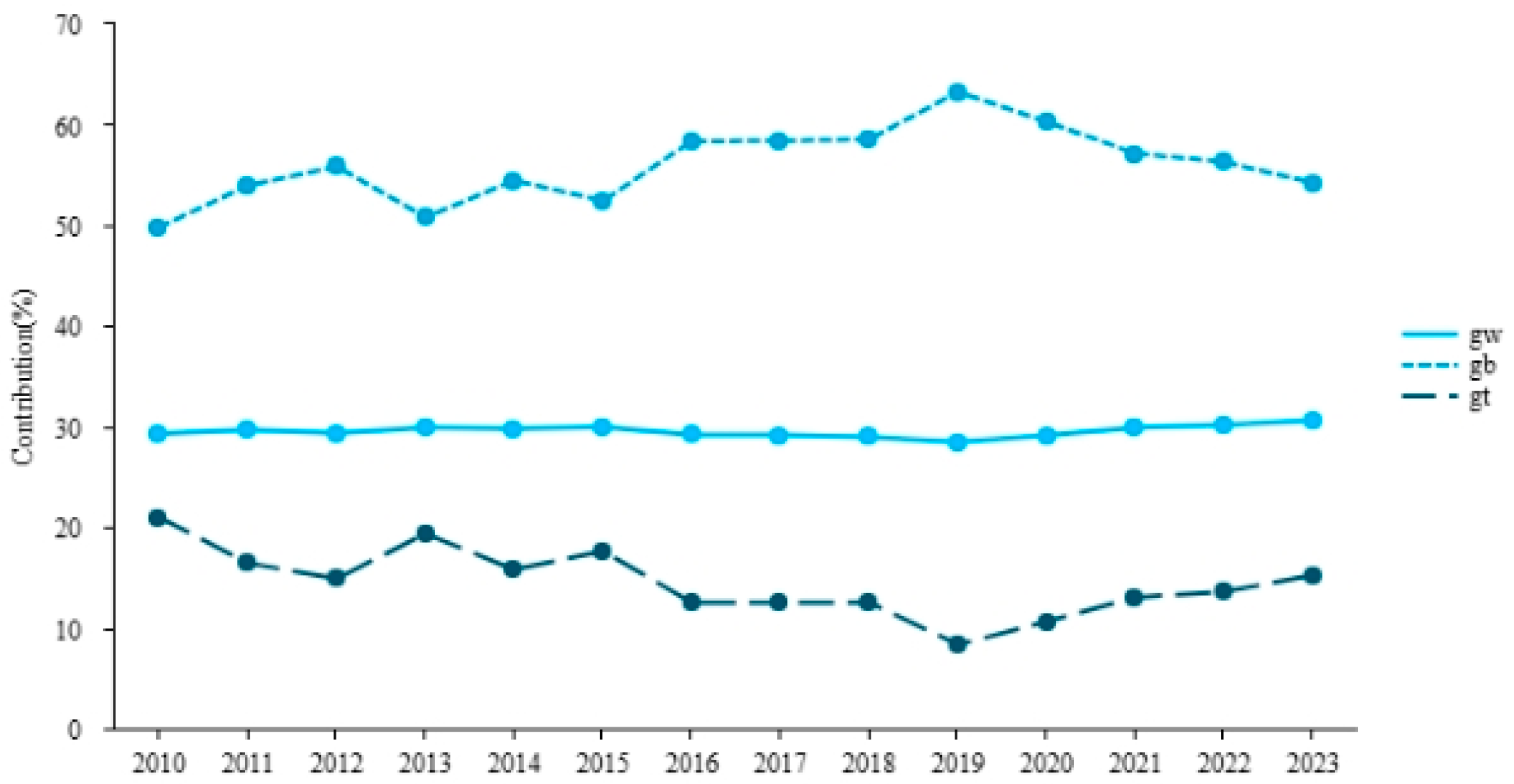
4.2.2. Analysis of Inter-Regional Differences
4.3. The Evolutionary Trends of Coupling Coordination
4.4. Spatial Correlation Analysis
4.5. Analysis of Driving Factors
4.5.1. Model Selection and Validation
4.5.2. Analysis of Driving Factors
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GF | Green Finance |
| GTI | Green Technology Innovation |
| GTWR | Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression |
| CCD | Coupling Coordination Degree |
References
- Pudryk, D.; Kwilinski, A.; Lyulyov, O.; Pimonenko, T. Towards achieving sustainable development: Interactions between migration and education. Forum Sci. Oecon. 2023, 11, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lyulyov, O.; Pimonenko, T.; Kwilinski, A. Green development of the country: The role of macroeconomic stability. Energy Environ. 2023, 35, 2273–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzwigol, H.; Kwilinski, A.; Lyulyov, O.; Pimonenko, T. The role of environmental regulations, renewable energy, and energy efficiency in finding the path to green economic growth. Energies 2023, 16, 3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.Y.; Ong, S.L.; Ooi, D.B.Y.; et al. The impact of green finance on environmental degradation in BRI region. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidance on building a green financial system. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/gwy/201611/t20161124_36 8163.htm (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Wei, H.; Li, Y.H. Research on the relationship between economic growth and environmental quality from the perspective of green finance. Shandong Soc. Sci. 2023, 131–140. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Research on green credit policy promoting green innovation. Manag. World 2021, 37, 173–188. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y. Green financial policy and green technology innovation: Evidence from green financial reform and innovation pilot zones. Fujian Trib. 2021, 126–138. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, X.E. The impact of green finance development on green technology innovation of industrial enterprises: Empirical evidence from listed companies. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2025, 45, 185–196. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Deng, J. How green finance drives the synergy of pollution reduction and carbon mitigation: Evidence from Chinese A-share firms. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Gao, W.; Lee, C.C. Does China’s Green Credit Interest Subsidies Policy Promote Enterprises’ Green Technology Innovation Quality? Based on the Perspective of Financial and Fiscal Coordination. J. Environ. Manage. 2025, 390, 126366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, N.; Lyu, R. The Dynamic Coupling and Spatio-Temporal Differentiation of Green Finance and Industrial Green Transformation: Evidence from China Regions. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.J.; Cui, L.Y.; Wang, Z.L.; et al. Research on the impact of green finance pilot policy on technological innovation of new energy enterprises. J. Nanjing Univ. Financ. Econ. 2024, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.B. Research on the impact of green finance on enterprise technological innovation efficiency: Resource allocation and innovation incentive. Ecol. Civiliz. Res. 2025, 90–106. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Wang, Z.P.; Du, R.; et al. Measurement of coupling coordination development level of green finance and digital technology, spatio-temporal evolution and pollution reduction effect. Inq. Econ. Issues 2024, 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.J.; Li, X.L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Research on the coupling coordination characteristics and influencing factors of green finance development and green low-carbon transformation: A case study of Hunan Province. Prog. Geogr. 2025, 44, 144–156. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Luo, Y.; Fang, J. Spatial-temporal evolution and driving factors of the synergistic development of green finance and low-carbon innovation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Zhang, H.Y. Research on the spatio-temporal pattern evolution and convergence of the coupling coordination between green finance and high-quality economic development in China. Chin. J. Manag. Sci. 2025, 33, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.A. Environmental finance: Value and risk in an age of ecology. Bus. Strategy Environ. 1996, 5, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnenluecke, M.K.; Smith, T.; McKnight, B. Environmental finance: A research agenda for interdisciplinary finance research. Econ. Model. 2016, 59, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green Finance Study Group. G20 green finance synthesis report. G20 Hangzhou Summit. Hangzhou, China, September 2016.
- Wang, Z.; Teng, Y.-P.; Wu, S.; Chen, H. Does Green Finance Expand China’s Green Development Space? Evidence from the Ecological Environment Improvement Perspective. Systems 2023, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhong, W.; Yan, S. Unlocking Green Growth: How Digital Finance Fosters Urban Sustainability via Innovation and Policy Synergy. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; He, X.; Zhu, T.; et al. Does green finance reform promote corporate green innovation? Evidence from China. Pac.-Basin Financ. J. 2023, 82, 102165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Liu, J.H.; Zhao, Y.X. Effectiveness measurement of green finance reform and innovation pilot zone. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2021, 38, 107–127. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, X.L.; Li, W.T. Does green finance affect the fulfillment of social responsibility of heavily polluting enterprises? Yuejiang Acad. J. 2023, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q. Green Bond Issuance and the Spillover Effect of Green Technology Innovation from the Perspective of Market Attention: Evidence from China. Systems 2024, 12, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yan, Y.; Wang, T.X. Research on the micro effects of green credit policy: From the perspective of technological innovation and resource reallocation. China Ind. Econ. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, K.; Cui, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhuang, R. Can Green Credit Improve the Innovation of Enterprise Green Technology: Evidence from 271 Cities in China. Systems 2024, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, X. Intelligent manufacturing, green technological innovation and environmental pollution. J. Innov. Knowl. 2023, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.Q. Research on the coupling between green technology innovation and green finance system development. Financ. Theory Pract. 2021, 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liao, G.; Wang, Z.; et al. Green loan and subsidy for promoting clean production innovation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiakui, C.; Abbas, J.; Najam, H.; et al. Green technological innovation, green finance, and financial development and their role in green total factor productivity: Empirical insights from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 382, 135131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, L.Q. Green finance and corporate green innovation. Wuhan Univ. J. 2021, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Mahmood, R.; Nassir, A.M.; Zhang, L. Digital Finance and Green Technology Innovation: A Dual-Layer Analysis of Financing and Governance Mechanisms in China. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Lin, B. Nexus between green finance development and green technological innovation: A potential way to achieve the renewable energy transition. Renew. Energy 2023, 218, 119295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.B.; Sun, X.Q.; Xing, M.Y. Research on the impact of green finance development on green total factor productivity. Stat. Decis. 2021, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, C.; Lei, L.; et al. Impacts of green finance on green innovation: A spatial and nonlinear perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.Z. Research on the relationship between green finance development and green technology innovation efficiency: An empirical analysis based on spatial spillover perspective. Price Theory Pract. 2020, 144–147, 178. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.D.; Huang, Y.Y.; Zhu, S.J.; Huang, H.F. The impact of green finance on technological innovation of polluting industries and its spatial differences in China. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2021, 41, 777–787. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, N. Does green credit promote regional green technology innovation? Based on regional green patent data. On Econ. Probl. 2021, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Wu, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. Green Finance, Green Technology Innovation and the Upgrading of China’s Industrial Structure: A Study from the Perspective of Heterogeneous Environmental Regulation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Yao, D.; Qian, Y.; et al. How does Fintech influence carbon emissions: Evidence from China's prefecture-level cities. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2023, 87, 102655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, W. Micro green technology innovation effects of green finance pilot policy: From the perspectives of action points and green value. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 159, 113724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.H.; Wang, B. Research on the development of green finance under the background of financial supply-side structural reform. Seek. Truth 2020, 47, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Falcone, P.M. Environmental regulation and green investments: The role of green finance. Int. J. Green Econ. 2020, 14, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Sun, C. Analysis of the spatial synergistic effect of green finance and high-quality economic development under the background of industrial structure upgrading. J. Hebei Univ. Eng. 2025, 42, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.B.; Zhang, R.X. Research on the impact of green finance on enterprise green technology innovation: A quasi-natural experiment based on green bond issuance. J. Henan Univ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 43, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Tao, L.; Chen, Y. Decoding the green code: Digital technology, talent re-structuring, and the path to green innovation efficiency. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wen, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, X. A Study on the Spatiotemporal Coupling Characteristics and Driving Factors of China’s Green Finance and Energy Efficiency. Systems 2025, 13, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sun, Z.C. Evaluation of the development level of new urbanization in Western China based on entropy method. On Econ. Probl. 2015, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Y.T.; Shi, B.F. Research on the impact of green finance on high-quality economic development. Front. Sci. Technol. Eng. Manag. 2023, 42, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.W.; Chen, M.Y.; Chen, N.X. Digital economy, green technology innovation and industrial structure upgrading. On Econ. Probl. 2023, 19–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.C.; Lee, C.C. How does green finance affect green total factor productivity? Evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2022, 107, 105863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.B.; Gao, C.L.; Zang, Y.T. Research on the coupling coordination mechanism of green technology innovation, environmental regulation and green finance. Sci. Technol. Manag. Res. 2021, 39, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, X.F.; Fang, T.S. Analysis of the coupling coordination degree between regional green finance and industrial structure: From the perspective of new institutional economics. J. Ind. Technol. Econ. 2021, 40, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.H.; Wang, H.J.; Zheng, P. Research on the coupling coordination development of circular economy and green finance in Guizhou Province. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.B.; Li, Y.J. Evolution of manufacturing spatial pattern and its driving factors in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Prog. Geogr. 2021, 40, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Xie, X.J.; Liang, H.Y.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation and spatial analysis of county economy in Chongqing based on entropy weight TOPSIS and GIS. Econ. Geogr. 2014, 34, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Wu, B.; Barry, M. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in house prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
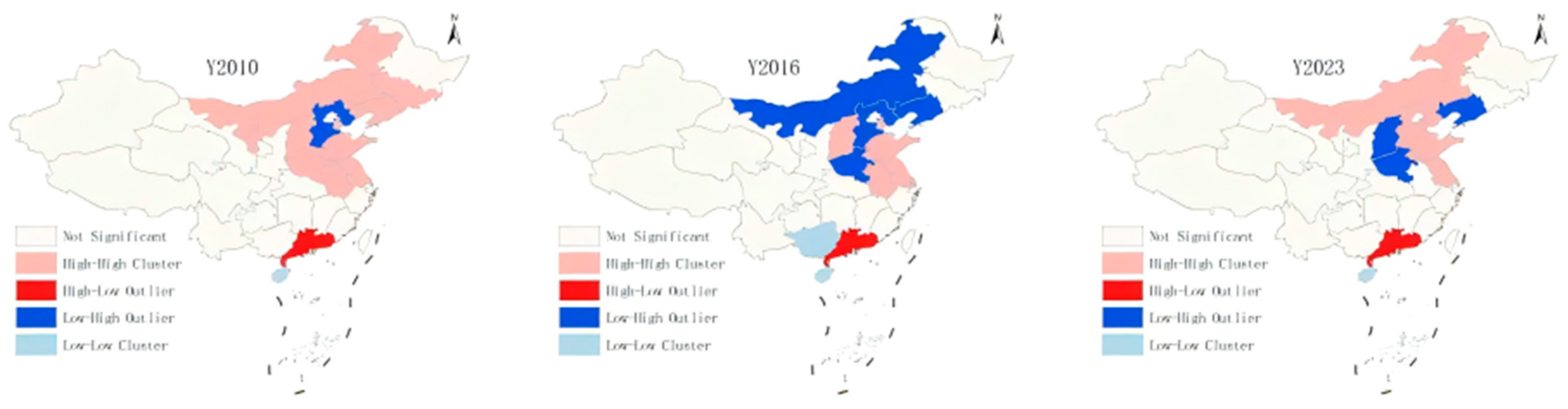
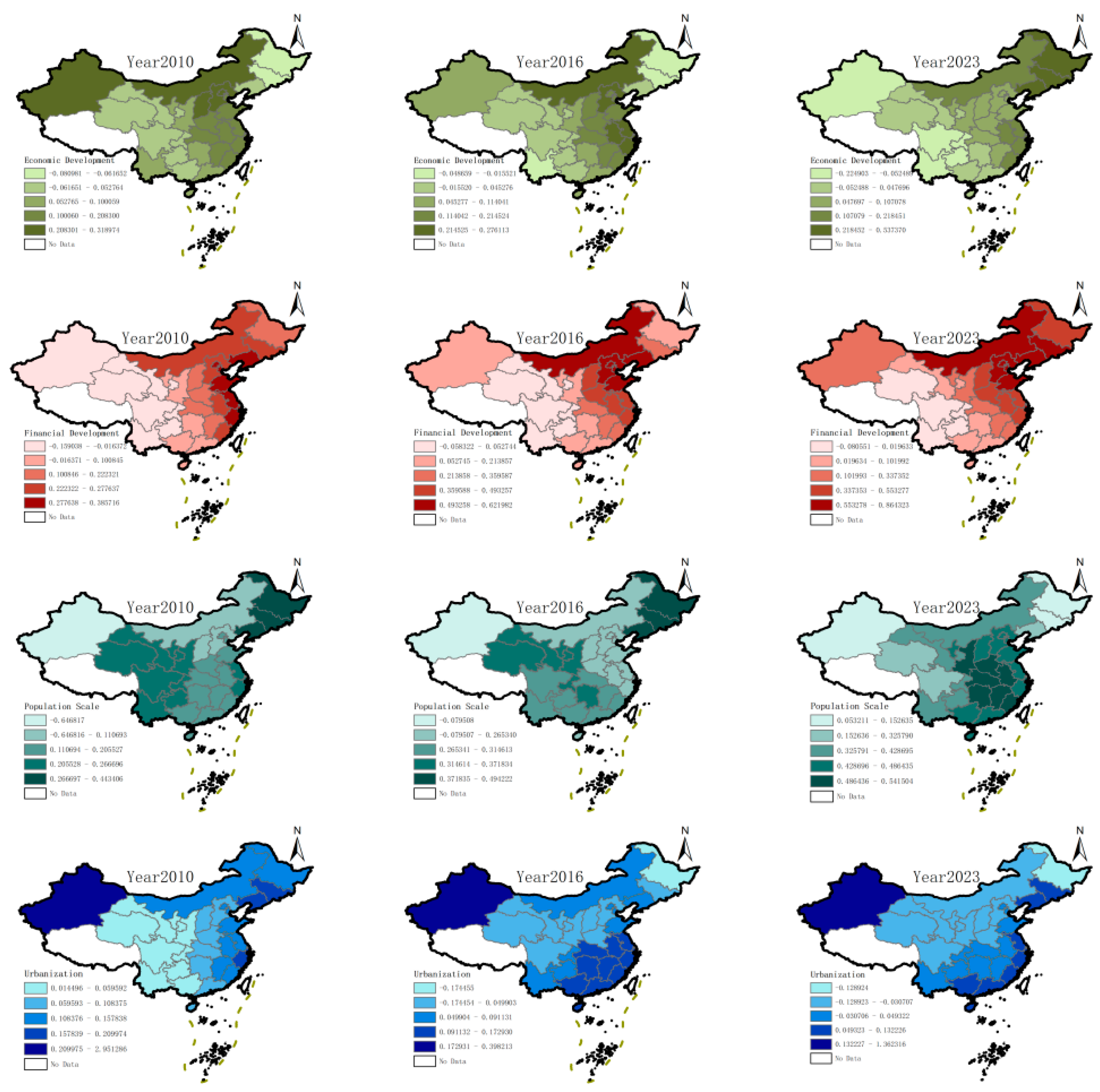
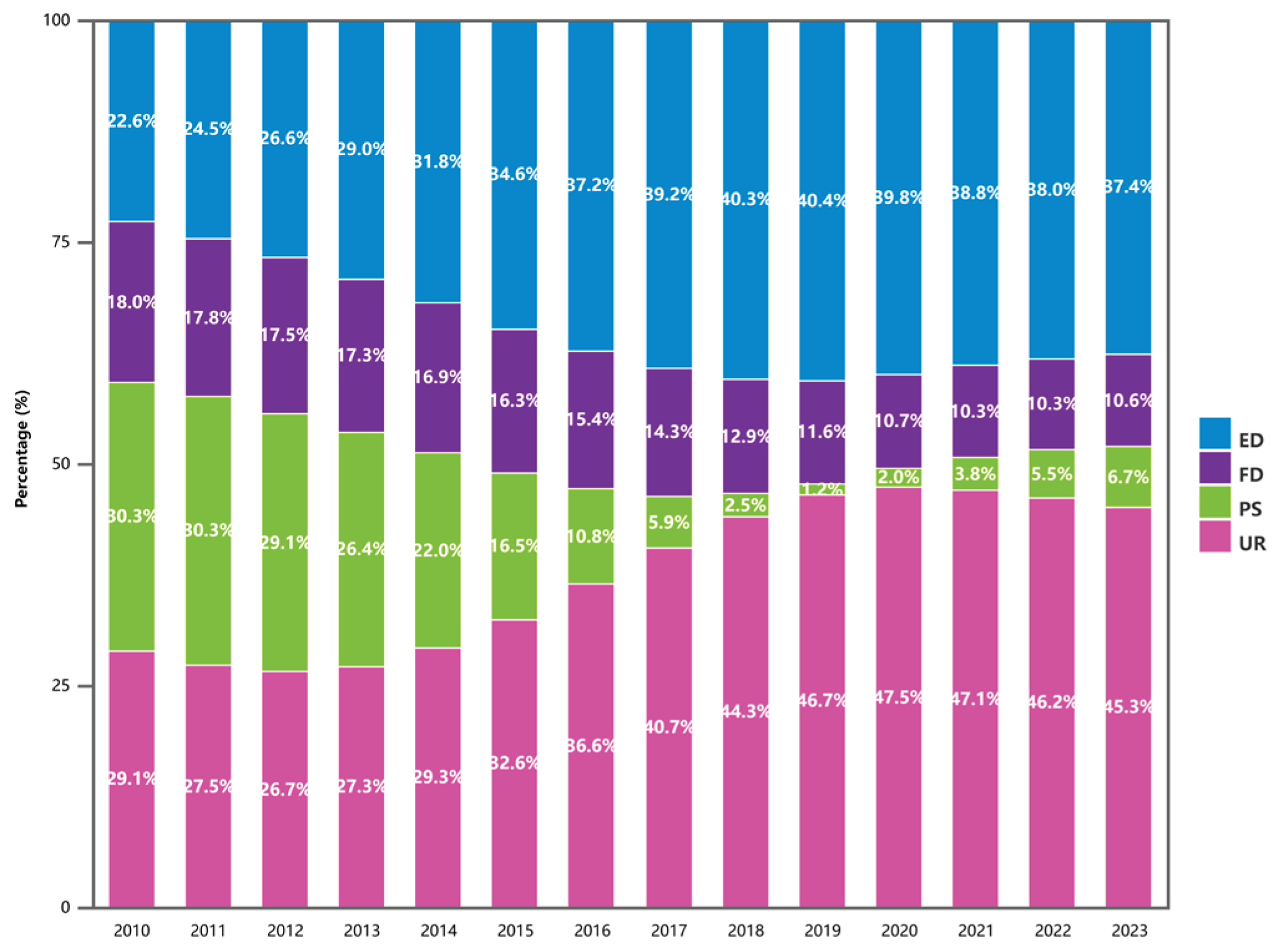
| System | Primary Indicators | Secondary Indicators | +/- | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green Finance (GF) |
Green Credit | proportion of interest in high-energy-consumption industries | - | 0.084 |
| Green Investment | share of investment in environmental pollution control | + | 0.252 | |
| share of environmental protection expenditure | + | 0.115 | ||
| Green Insurance | agricultural insurance density | + | 0.430 | |
| agricultural insurance loss ratio | + | 0.102 | ||
| Carbon Finance | carbon emission intensity | - | 0.017 | |
| Green Technology Innovation (GTI) | number of green patents granted per 10,000 persons | / | / | |
| CCD | Classification Criteria |
|---|---|
| 0≤C<0.2 | Serious Imbalance |
| 0.2≤C<0.4 | Moderate Imbalance |
| 0.4≤C<0.5 | Near Imbalance |
| 0.5≤C<0.6 | Barely Coordination |
| 0.6≤C<0.8 | Intermediate Coordination |
| 0.8≤C≤1 | Excellent Coordination |
| Driving Factors | Symbol | Definition Of Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Development | ED | ln GDP/ln Resident Population (10,000 persons) |
| Financial Development | FD | ln (Total Deposits & Loans) / GDP |
| Population Scale | PS | ln (Year-End Resident Population) |
| Urbanization | UR | Urban Population / Resident Population |
| Year | G | Gw | Gb | Gt | Eastern | Central | Western |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 0.102 | 0.030 | 0.051 | 0.021 | 0.125 | 0.043 | 0.063 |
| 2011 | 0.132 | 0.039 | 0.071 | 0.022 | 0.146 | 0.062 | 0.100 |
| 2012 | 0.140 | 0.041 | 0.078 | 0.021 | 0.155 | 0.068 | 0.098 |
| 2013 | 0.139 | 0.042 | 0.071 | 0.027 | 0.165 | 0.082 | 0.084 |
| 2014 | 0.138 | 0.041 | 0.075 | 0.022 | 0.175 | 0.073 | 0.070 |
| 2015 | 0.147 | 0.044 | 0.077 | 0.026 | 0.181 | 0.082 | 0.080 |
| 2016 | 0.142 | 0.042 | 0.083 | 0.018 | 0.179 | 0.079 | 0.065 |
| 2017 | 0.147 | 0.043 | 0.086 | 0.018 | 0.185 | 0.062 | 0.077 |
| 2018 | 0.151 | 0.044 | 0.088 | 0.019 | 0.182 | 0.065 | 0.085 |
| 2019 | 0.150 | 0.043 | 0.095 | 0.012 | 0.182 | 0.053 | 0.081 |
| 2020 | 0.151 | 0.044 | 0.091 | 0.016 | 0.187 | 0.053 | 0.087 |
| 2021 | 0.158 | 0.047 | 0.090 | 0.021 | 0.200 | 0.046 | 0.098 |
| 2022 | 0.157 | 0.047 | 0.088 | 0.021 | 0.201 | 0.071 | 0.086 |
| 2023 | 0.153 | 0.047 | 0.083 | 0.023 | 0.197 | 0.088 | 0.079 |
| Mean | 0.143 | 0.042 | 0.081 | 0.021 | 0.176 | 0.066 | 0.082 |
| Max | 0.158 | 0.047 | 0.095 | 0.027 | 0.201 | 0.088 | 0.1 |
| Min | 0.102 | 0.03 | 0.051 | 0.012 | 0.125 | 0.043 | 0.063 |
| Year | Central & Western | Eastern & Central | Eastern & Western |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 0.063 | 0.118 | 0.133 |
| 2011 | 0.087 | 0.149 | 0.169 |
| 2012 | 0.085 | 0.163 | 0.182 |
| 2013 | 0.085 | 0.167 | 0.174 |
| 2014 | 0.075 | 0.173 | 0.175 |
| 2015 | 0.086 | 0.179 | 0.184 |
| 2016 | 0.081 | 0.166 | 0.189 |
| 2017 | 0.082 | 0.169 | 0.199 |
| 2018 | 0.088 | 0.170 | 0.203 |
| 2019 | 0.082 | 0.167 | 0.209 |
| 2020 | 0.086 | 0.164 | 0.208 |
| 2021 | 0.086 | 0.175 | 0.213 |
| 2022 | 0.087 | 0.180 | 0.206 |
| 2023 | 0.090 | 0.178 | 0.194 |
| Mean | 0.083 | 0.166 | 0.188 |
| Max | 0.09 | 0.18 | 0.213 |
| Min | 0.063 | 0.118 | 0.133 |
| Year | Y2010 | Y2011 | Y2012 | Y2013 | Y2014 | Y2015 | Y2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran's I | 0.108 | 0.260 | 0.244 | 0.258 | 0.265 | 0.269 | 0.326 |
| P-value | 0.081 | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.001 |
| Year | Y2017 | Y2018 | Y2019 | Y2020 | Y2021 | Y2022 | Y2023 |
| Moran's I | 0.302 | 0.255 | 0.319 | 0.254 | 0.186 | 0.160 | 0.127 |
| P-value | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.023 | 0.044 | 0.100 |
| Parameters | OLS | GWR | GTWR |
|---|---|---|---|
| R² | 0.690 | 0.883 | 0.911 |
| R² Adjusted | - | 0.882 | 0.910 |
| AICc | -1067.049 | -1405.481 | -1487.161 |
| RSS | 1.893 | 0.714 | 0.543 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





