Submitted:
15 November 2025
Posted:
18 November 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
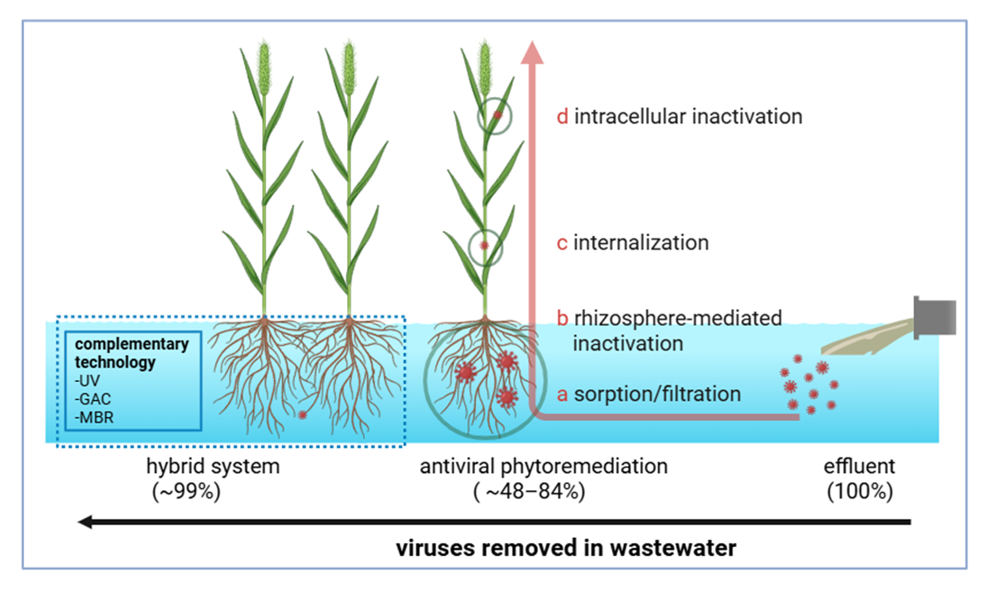
2. Mechanistic Basis of Antiviral Phytoremediation
2.1. Phytoremediation Mechanisms
2.2. Antiviral-Specific Mechanisms
2.3. Comparative Analysis of Viral Particles and Heavy Metals
|
Mechanism/Parameter |
Virus (Antiviral Mechanism) |
Heavy Metal (co-Removal) |
Performance Metrics |
Critical Variables |
Example Systems |
Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary removal | electrostatic/hydrophobic adsorption; aggregation; enzymatic inactivation | ion exchange; surface complexation; chelation; precipitation | virus: ~1–2 log₁₀ capture, up to 7 log₁₀ with polishing; metal: ~70–100% removal | charge density, DOC, pH, root potential, ionic strength | Pistia stratiotes, Typha latifolia, Phragmites australis beds | [80,81,90] |
|
Rhizosphere biochemistry |
exudate oxidation, proteolysis; polyphenol virion destabilization (ΔG ≈ -10 kcal/mol) | organic acid complexation; phytochelatin synthesis; redox cycling | inactivation rate: k = ~0.02–0.07 h⁻¹ (25°C); infectivity loss: 65 ± 12% (48 h) | root activity, flavonoid flux (~0.8–1.5 mg g⁻¹ DW), microbial profile, T-sensitivity | natural/ changed wetlands | [83,96,119] |
| Particle stability | capsid/envelope disruption, genome cleavage; enveloped viruses removed ~2–5× better | speciation-dependent stability; vacuolar sequestration post-uptake | enveloped removal: >90%; RNA decay: ~65–84% (~48–72 h) | temperature, pH, oxidative potential, virion charge | macrophyte–biofilm systems | [83,87] |
|
Adsorption/ partitioning |
Freundlich Kₙ = ~2×10³–2.7×10⁵ mL g⁻¹; mean capture: 58 ± 20% | surface complexation log K = ~4–8 (pH-driven) | capture efficiency: ~58 ± 20% (n=16); K = ~10³–10⁴ mL g⁻¹ for bacteriophages | ionic strength, DOC competition, surface pKa, hydrophobicity | rhizofiltration, periphyton-root systems | [88,89] |
| HRT requirement (d) | ~3–6 d for viral attenuation; ideal ~5–10 d | ~2–4 d for metal sorption equilibrium | virus: ~1–2 log₁₀ per stage; metal: ~70–100% removal | flow uniformity, aeration regime, recirculation, temperature effects | hybrid wetland + UV, VSSF units | [93,106] |
| Chemical aids | polyphenols (ΔG); electrocoagulation (EC) → ~2–3× capture boost | biochar, zeolite, Fe(OH)₃, molecular imprinted polymers composites | virus capture: +1–1.5 log₁₀ gain with EC; metal removal: +15–30% with media | coagulant dose (FeCl₃ ~5–20 mg/L), pH, oxidation reduction potential (ORP) | modular wetland-filter hybrids |
[109,120,121] |
| Microbial contribution | lytic enzymes, quorum-regulated proteases (Bacillus); ROS generation | extracellular polymeric substance matrix, siderophore secretion, biosorption | +0.5–1.0 log₁₀ increment; peroxidase activity ↑25–60%. | microbial diversity, nutrient ratio (C:N:P ≈ 100:10:1), rhizosphere age | engineered consortia | [41,116,122] |
| Seasonal sensitivity | strong T-dependence (−0.3 log₁₀ per 10°C drop); dissolved organic carbon (DOC) competition | moderate; resilient under redox/pH shift | winter: retains ~70–85% of summer rate with thermal buffering | temperature, DOC level, biofilm maturity, flow fluctuation | aerated/intermittent-flow constructed wetland systems | [91,92,123] |
| AI control | adaptive flow/dosing for dual targeting; real-time viral prediction (~12–18 h lead time) | dynamic ligand control via real-time speciation | ±10% variance reduction under fluctuating loads | pH/ORP sensors, metabolite biosensors, AI feedback | smart AI-integrated wetlands | [114,124] |
3. Recent Advancements in Antiviral Phytoremediation
3.1. Plant Selection and Optimization
3.2. System Optimization
| Scientific Name (Common Name) |
Functional Traits (Key Mechanisms) |
Optimal Configurations |
Viral Removal Performance (log₁₀ Reduction) |
Co-Removal Benefits |
Critical Constraints |
Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monoculture systems | ||||||
| Phragmites australis (Common reed) | fine root area (>300 cm² g⁻¹); dense periphyton; strong O₂ transfer; high porosity (~25–35%) | VSSF (intermittent loading); baffled FWS | 1.2 ± 0.3 log₁₀ (capture-dominant); field stability ~60–75% | high N/P removal (~70–99%); stable heavy metal uptake (~70–90% Zn/Cu) | seasonal dormancy (winter); requires periodic harvest (~2–4× yr⁻¹); establishment time 4–6 wks | [40,138,156] |
| Ocimum basilicum (Sweet basil) | high phenolic/flavonoid exudates (0.8–1.5 mg g⁻¹ DW); elevated oxidase/peroxidase activity | horizontal/free-water flow with aeration; mixed beds (2:1 ratio) | 2.3 ± 0.4 log₁₀ (chemical inactivation); +40% for enveloped viruses | volatile oil antimicrobial effects; phenolic anti-biofilm agents; biomass valorization potential | high T-sensitivity (~20–30°C ideal); short lifespan (requires replacement ~2–3× yr⁻¹) | [83,139,140] |
| Strobilanthes cusia (Assam indigo) | indole alkaloid production (Tryptanthrin 10–50 µM IC₅₀); elevated RNase/protease activity | floating macrophytes; warm shallow beds (~20–28°C) | +0.7 ± 0.2 log₁₀ gain over baseline (intracellular enzymatic defense) | medicinal/commercial value co-product potential; strong nucleic acid hydrolysis capability | tropical requirement (dies <10°C); limited geographic deployment; alkaloid bioaccumulation risk | [104,139,140] |
|
Pistia stratiotes (Water lettuce) |
extensive adventitious root system; rapid biomass production; high transpiration | floating-bed systems; rhizofiltration units | ~0.5–1.0 log₁₀ per pass; ~3–5 log₁₀ in CWs–UV hybrid (high sorption capacity, K = ~10³–10⁴ mL g⁻¹) | high heavy metal uptake (~70–85%); scalable for rapid deployment | Invasive potential (requires containment); sensitive to low DOC/high shear; capture-dominant mechanism | [83,157,158] |
| Optimized polyculture systems | ||||||
| Phragmites + Typha + Ocimum (triculture) | trait complementarity: max surface area + diverse exudate chemistry + functional redundancy | coupled VSSF–free-surface system | 2.8 ± 0.5 log₁₀ reduction; 85 ± 10% infectivity loss (capture–inactivation synergy) | superior stability; buffering seasonal/load variations; showed performance over 3+ yrs | higher complexity in operation and maintenance (O&M); longer initial establishment (~8 wks); requires strict nutrient control | [138,143,159] |
3.3. Hybrid Systems and Technology Integration
| Factor/Strategy | Target Parameters | Key Action/Specification | Performance Metric | Mechanistic Rationale | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic loading rate (HLR) | HLR & distribution uniformity | VSSF: 0.05–0.15 m³ m⁻² d⁻¹; perforated manifold dosing | ~1–2 log₁₀ removal; HRT = ~4–15 d | maximizes root–water contact and filtration efficiency; prevents short-circuiting | [59,154,198] |
| Flow configuration | flow pattern & dead-zone control | baffled FWS/staged islands; dispersion index >0.7 | HRT efficiency ~70–95%; channeling causes up to −30% loss | promotes plug flow (extended home time); increases uniform virion–biofilm interaction | [161,199] |
| Hydraulic retention time (HRT) | retention stability & redundancy | design: ~4–10 d (+20–40% safety margin for low T) | stable up to 3 log₁₀ removal | sustains contact time for adsorption/inactivation kinetics; reduces desorption risk | [123,162] |
| Rhizosphere aeration | intermittent air cycles & DO | ON/OFF ~1–2 h cycles; DO > 2 mg L⁻¹ at inlet. | enzyme gain ~20–45%; redox maintained (+50 to +200 mV) | boosts oxidative/enzymatic antiviral activity (peroxidases, ROS); prevents anoxic clogging | [165,200] |
| Redox / nutrient balance | C:N:P Ratio & ORP | C:N:P ≈ 100:10:1; ORP target: +100–+250 mV | infectivity loss 2.5 ± 0.4 log₁₀ | optimizes synthesis of antiviral exudates and enzymatic function; stabilizes microbial consortia | [169,171] |
| Temperature buffering | seasonal heat retention | raise water depth ~10–20% (winter); optional geothermal loop (<10°C differential) | keeps ~70–85% of summer rate; viral loss: –0.3 log₁₀ per 10°C drop | counteracts T-dependent reduction in enzymatic/adsorption kinetics; ensures year-round stability | [123,176] |
| Biomass management | harvest fraction & frequency | remove ~20–40% biomass ~2–4× yr⁻¹ | +0.5–0.8 log₁₀ improvement post-harvest | renews roots and exudation capacity (young plants are more active); prevents DOC release from senescence | [178,179] |
| Pretreatment (chemical) | charge neutralization & aggregation | FeCl₃ 5–20 mg L⁻¹ or EC ~1–2 mA cm⁻² | +1–1.5 log₁₀ viral gain (primary capture); +20% DOC tolerance. | strengthens primary capture by neutralizing negative virion charge; flocculation enhances settling/adsorption | [121,185] |
| Polishing/disinfection | secondary oxidation | UV ~30–60 mJ cm⁻²; ferrate ~0.5–1 mg L⁻¹; ozone ~0.2–0.5 mg L⁻¹ | ~5–7 log₁₀ total removal; low phytotoxicity | eliminates residual, recalcitrant infectivity (non-enveloped viruses); ensures safety for reuse standards | [188,191] |
4. Practical Applications and Implementation
4.1. Constructed Wetland Systems (CWs)
| Components | Configuration Description | Primary Antiviral Mechanisms | Demonstrated Performance | Innovation Value/Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWS wetland | shallow vegetated channels (~0.3–0.6 m); open photic zone | photolysis, oxidation, biofilm sorption (low shear) | ~0.5–1.0 log₁₀ baseline; up to 2.0 with baffling | simple, low-cost system; sensitive to temperature and climate variability | [202,217] |
| HSSF wetland | saturated porous bed; laminar flow | filtration and anoxic biofilm degradation (stable pH) | 1.0 ± 0.3 log₁₀ (n=15); high stability across pH changes | filtration-dominant removal; good hydraulic control; limited oxidative capacity | [81,220] |
| VSSF wetland | intermittent dosing (alt-day); aerated percolation | adsorptive capture and oxidative decay on roots/media (high O₂) | ~2–3 log₁₀ at HRT ~5–10 d | high efficiency (~2–3× HSSF); reduces land area; requires mechanical dosing/aeration | [59,227] |
| Multistage hybrid CWs | sequential VSSF–FWS or VSSF–UV trains (multi-barrier approach) | combined filtration, oxidation, photolysis, enzymatic action | ~3–7 log₁₀ total removal (highest efficacy) | meets stringent reuse standards; functional redundancy buffers system failures | [113,161] |
| Substrate innovation | gravel, slag, zeolite, biochar, ferric media | enhanced adsorption; pH ~10–11 microzones; ROS generation | +10–30% extra removal from reactive layers | increases specific surface area; biochar adds catalytic/adsorptive properties; controls metal mobility | [224,225,226] |
| Vegetation selection | Phragmites, Typha, Ocimum, Strobilanthes (targeted functional traits). | O₂ release, enzyme induction, antiviral metabolite exudation | ~2–4 log₁₀ (field mean); 85–95% infectivity loss | shifts CWs from simple filtration to biochemically active reactors; cost-effective performance boost | [138,228] |
| Digital monitoring/AI | IoT sensors (DO, ORP, metabolites, microbial activity) | predictive control and early alerting (machine learning integration) | ~12–18 h lead time before viral breakthrough prediction | improves reliability/uptime; enables adaptive dosing/flow control; important for fluctuating loads. | [229,230] |
|
Synthetic biology integration |
engineered microbial consortia & biosensors (PGPR, lytic strains) | self-regulated enzymatic capture loops; enhanced proteolysis | +1–2 log₁₀ added potential (proof-of-concept) | high potential for targeted virus/pathogen removal; highly specific mechanism; requires regulatory acceptance | [137,231,232] |
4.2. Modular and Scalable Designs
4.3. Hybrid Treatment Systems and Economic Considerations
5. Challenges and Prospects
5.1. Current Challenges and Persistent Gaps
5.2. Prospects and Emerging Innovations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOPs | Advanced Oxidation Processes |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| CAPEX | Capital Expenditure |
| C:N:P | Carbon:Nitrogen:Phosphorus Ratio |
| COD | Chemical Oxygen Demand |
| CRISPR | Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats |
| CRISPR-Cas | Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats [CRISPR]-associated [Cas] nuclease |
| CWs | Constructed Wetland Systems |
| DEWATS | Decentralisation of Wastewater Treatment |
| DO | Dissolved Oxygen |
| DOC | Dissolved Organic Carbon |
| EC | Electrocoagulation |
| e-MBRs | Electrochemically Enhanced Membrane Bioreactors |
| EPS | Extracellular Polymeric Substance |
| FWS | Free-Water Surface (or Free-Water Surface cells/systems) |
| GAC | Granular Activated Carbon |
| GH19 | Glycoside Hydrolase Family 19 |
| GMO | Genetically Modified Organism |
| HAA | Haloacetic Acids |
| HLR | Hydraulic Loading Rate |
| HO· | Hydroxyl Radical |
| HRT | Hydraulic Retention Time |
| HSSF | Horizontal Subsurface-Flow |
| IC₅₀ | Inhibitory Concentration 50% |
| IFITM3 | Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Protein 3 |
| MBRs | Membrane Bioreactors |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| O&M | Operation and Maintenance |
| ORP | Oxidation-Reduction Potential |
| PGPR | Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria |
| PPP | Public-Private Partnerships |
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
| RNAi | RNA Interference |
| RNase | Ribonuclease |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| RT-RPA | Reverse Transcription Recombinase Polymerase Amplification |
| SA | Salicylic Acid |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
| SSF | Subsurface-Flow |
| THM | Trihalomethanes |
| TOC | Total Organic Carbon |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| UVC | Ultraviolet C |
| VSSF | Vertical Subsurface-Flow |
References
- Carmo Dos Santos, M.; Cerqueira Silva, A.C.; Dos Reis Teixeira, C.; Pinheiro Macedo Prazeres, F.; Fernandes Dos Santos, R.; de Araújo Rolo, C.; de Souza Santos, E.; Santos da Fonseca, M.; Oliveira Valente, C.; Saraiva Hodel, K.V.; et al. Wastewater Surveillance for Viral Pathogens: A Tool for Public Health. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Ahmad, M.; Usman, A.R.A.; Al-Wabel, M.I. Prevalence of Human Pathogenic Viruses in Wastewater: A Potential Transmission Risk as Well as an Effective Tool for Early Outbreak Detection for COVID-19. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 298, 113486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivins, A.; Greaves, J.; Fischer, R.; Yinda, K.C.; Ahmed, W.; Kitajima, M.; Munster, V.J.; Bibby, K. Persistence of SARS-CoV-2 in Water and Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girón-Guzmán, I.; Falcó, I.; Cuevas-Ferrando, E.; Ballesteros, S.; Barranquero, R.; Sánchez, G. Survival of Viruses in Water Microcosms. Science of The Total Environment 2025, 963, 178416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahler, A.M.; Cromeans, T.L.; Roberts, J.M.; Hill, V.R. Effects of Source Water Quality on Chlorine Inactivation of Adenovirus, Coxsackievirus, Echovirus, and Murine Norovirus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5159–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanrewaju, A.A.; Enitan-Folami, A.M.; Sabiu, S.; Swalaha, F.M. A Review on Disinfection Methods for Inactivation of Waterborne Viruses. Frontiers in Microbiology 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, R.M.; Nelson, K.L.; Drewes, J.E. Mechanisms of Pathogenic Virus Removal in a Full-Scale Membrane Bioreactor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2815–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Guo, L.; Yang, Y.; Oguma, K.; Hou, L. Comparative Effectiveness of Membrane Technologies and Disinfection Methods for Virus Elimination in Water: A Review. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 801, 149678–149678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzeminski, P.; van der Graaf, J.H.J.M.; van Lier, J.B. Specific Energy Consumption of Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) for Sewage Treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skouteris, G.; Arnot, T.C.; Jraou, M.; Feki, F.; Sayadi, S. Modeling Energy Consumption in Membrane Bioreactors for Wastewater Treatment in North Africa. Water Environment Research 2014, 86, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, A.A.; Amoah, I.D.; Stenström, T.A.; Verbyla, M.E.; Mihelcic, J.R. Epidemiological Evidence and Health Risks Associated With Agricultural Reuse of Partially Treated and Untreated Wastewater: A Review. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haramoto, E.; Malla, B.; Thakali, O.; Kitajima, M. First Environmental Surveillance for the Presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Wastewater and River Water in Japan. Science of The Total Environment 2020, 737, 140405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Kapoor, D.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Bhatia, D.S.; Jan, S.; Singh, N.; Romero, R.; Ramamurthy, P.C.; Singh, J. Detection and Disinfection of COVID-19 Virus in Wastewater. Environmental Chemistry Letters 2021, 19, 1917–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandukar, S.; Sthapit, N.; Thakali, O.; Malla, B.; Sherchan, S.P.; Shakya, B.M.; Shrestha, L.P.; Sherchand, J.B.; Joshi, D.R.; Lama, B.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Wastewater, River Water, and Hospital Wastewater of Nepal. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingare, R.P.; Nanekar, S.V.; Thawale, P.R.; Karthik, R.; Juwarkar, A.A. Comparative Study on Removal of Enteric Pathogens From Domestic Wastewater Using Typha Latifolia and Cyperus Rotundus Along With Different Substrates. 2017, 19, 899–908. [CrossRef]
- Rosendo, J.C.M.; da Paz, G.M.; Rosendo, A. Constructed Wetlands Applied on Domestic Wastewater for Decetralized Systems: Concepts, Processes, Modalities, Combinations and Enhancements; A Review. 2022, 21, 371–397. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Jing, Y.; Liu, C.; Xiao, Y.; Li, C.; Jiao, C.; Xu, M. Research Progress on the Removal of Contaminants from Wastewater by Constructed Wetland Substrate: A Review. Water 2024, 16, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-F.; Mitch, W.A. Drinking Water Disinfection Byproducts (DBPs) and Human Health Effects: Multidisciplinary Challenges and Opportunities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salt, D.E.; Smith, R.D.; Raskin, I. PHYTOREMEDIATION. Annu. Rev. Plant. Physiol. Plant. Mol. Biol. 1998, 49, 643–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilon-Smits, E. PHYTOREMEDIATION. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2005, 56, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.; Willby, N.; Oliver, D.M.; Quilliam, R.S. Phytoremediation Using Aquatic Plants. In Phytoremediation; Shmaefsky, B.R., Ed.; Concepts and Strategies in Plant Sciences; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 205–260. ISBN 978-3-030-00098-1. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.B. Phytoremediation in Wetland Ecosystems: Progress, Problems, and Potential. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences 2002, 21, 607–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bais, H.P.; Weir, T.L.; Perry, L.G.; Gilroy, S.; Vivanco, J.M. The Role of Root Exudates in Rhizosphere Interactions with Plants and Other Organisms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourav Kumar, P.; Surajit, D. Potential of Plant Growth-Promoting Microbes for Improving Plant and Soil Health for Biotic and Abiotic Stress Management in Mangrove Vegetation. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 23, 801–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, M.K.; Ali, S.; Abbas, Z.; Zaheer, I.E.; Riaz, M.A.; Malik, A.; Hussain, A.; Rizwan, M.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Zhu, S.J. Potential of Duckweed ( Lemna Minor ) for the Phytoremediation of Landfill Leachate. Journal of Chemistry 2018, 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.; Khan, A.N.; Waris, A.; Ilyas, M.; Zamel, D. Phytoremediation of Pollutants from Wastewater: A Concise Review. Open Life Sciences 2022, 17, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, M. Phytoremediation Strategies for Mitigating Environmental Toxicants. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, A.K. An Overview of Antimicrobial Properties of Different Classes of Phytochemicals. In Dietary Phytochemicals and Microbes; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, 2012; pp. 1–32. ISBN 978-94-007-3925-3. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, L.; Sleiman, A.; Abdel-Massih, R.M. Antimicrobial Activity of Polyphenols and Alkaloids in Middle Eastern Plants. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangl, J.L.; Jones, J.D. Plant Pathogens and Integrated Defence Responses to Infection. Nature 2001, 411, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nürnberger, T.; Lipka, V. Non-Host Resistance in Plants: New Insights into an Old Phenomenon. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2005, 6, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.A.; Lee, H.Y.; Seo, E.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.B.; Oh, S.; Choi, E.; Choi, E.; Lee, S.E.; Choi, D. Current Understandings of Plant Nonhost Resistance. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 2017, 30, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Hunag, Z.; Wang, X.; Cui, L. Pennisetum Sinese Roxb and Pennisetum Purpureum Schum. as Vertical-Flow Constructed Wetland Vegetation for Removal of N and P from Domestic Sewage. Ecological Engineering 2015, 83, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.-F.; Tsai, H.-P.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chang, T.-Y.; Hsieh, C.-F.; Lin, C.-Y.; Lin, G.-H.; Chen, Y.-L.; Jheng, J.-R.; Liu, P.-C.; et al. Perilla (Perilla Frutescens) Leaf Extract Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 via Direct Virus Inactivation. Biomedical Journal 2021, 44, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wang, H.; Pan, S.; Liu, Y. The Antiviral Potential of Perilla Frutescens: Advances and Perspectives. Molecules 2024, 29, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, D.W.; Porter, S.J.; Herzog, C. Dimensions: Building Context for Search and Evaluation. Front. Res. Metr. Anal. 2018, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Bote, V.P.; Chinchilla-Rodríguez, Z.; Mendoza, A.; de Moya-Anegón, F. Comparative Analysis of the Bibliographic Data Sources Dimensions and Scopus: An Approach at the Country and Institutional Levels. Front. Res. Metr. Anal. 2020, 5, 593494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, P.; Karmakar, M.; Leta, J.; Mayr, P. The Journal Coverage of Web of Science, Scopus and Dimensions: A Comparative Analysis. Scientometrics 2021, 126, 5113–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlec, R.H.; Wallace, S. Treatment Wetlands; 0 ed.; CRC Press, 2008. ISBN 978-0-429-13795-2.
- Vymazal, J. Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment: Five Decades of Experience. 2010, 45, 61–69. [CrossRef]
- Saeed, T.; Sun, G. A Review on Nitrogen and Organics Removal Mechanisms in Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands: Dependency on Environmental Parameters, Operating Conditions and Supporting Media. 2012, 112, 429–448. [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Yu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Clogging Development and Hydraulic Performance of the Horizontal Subsurface Flow Stormwater Constructed Wetlands: A Laboratory Study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2017, 24, 9210–9219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bais, H.P.; Weir, T.L.; Perry, L.G.; Gilroy, S.; Vivanco, J.M. THE ROLE OF ROOT EXUDATES IN RHIZOSPHERE INTERACTIONS WITH PLANTS AND OTHER ORGANISMS. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ávila, F. Treatment of Municipal Wastewater by Vertical Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetland: Data Collection on Removal Efficiency Using Phragmites Australis and Cyperus Papyrus. Data in Brief 2020, 30, 105584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ávila, F. Treatment of Municipal Wastewater by Vertical Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetland: Data Collection on Removal Efficiency Using Phragmites Australis and Cyperus Papyrus. Data in Brief 2020, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlec, R.H.; Wallace, S. Treatment Wetlands. 2008. [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Ghosh, G.K.; Avasthe, R. Biochar Application for Environmental Management and Toxic Pollutant Remediation. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 13, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Liang, S.; Fan, J.; Lu, S.; Wu, H. Optimizations on Supply and Distribution of Dissolved Oxygen in Constructed Wetlands: A Review. Bioresource Technology 2016, 214, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, S.K.; Srivastava, A.K.; Rajput, V.D.; Chauhan, P.K.; Bhojiya, A.A.; Jain, D.; Chaubey, G.; Dwivedi, P.; Sharma, B.; Minkina, T. Root Exudates: Mechanistic Insight of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria for Sustainable Crop Production. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 916488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vinent, N.; Cruz-Alcalde, A.; Santacruz, A.P.; Sans, C. Green Approach for Micropollutants Removal: Study of Constructed Wetlands as Pretreatment of Solar Photo-Fenton Catalyzed by Organic Fertilizers. Catal. Today 2024, 430, 114540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruttens, A.; Boulet, J.; Weyens, N.; Smeets, K.; Adriaensen, K.; Meers, E.; Van Slycken, S.; Tack, F.; Meiresonne, L.; Thewys, T.; et al. Short Rotation Coppice Culture of Willows and Poplars as Energy Crops on Metal Contaminated Agricultural Soils. International Journal of Phytoremediation 2011, 13, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiodar, E.D.; Văcar, C.L.; Podar, D. Phytoremediation and Microorganisms-Assisted Phytoremediation of Mercury-Contaminated Soils: Challenges and Perspectives. IJERPH 2021, 18, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manorama Thampatti, K.C.; Beena, V.I.; Meera, A.V.; Ajayan, A.S. Phytoremediation of Metals by Aquatic Macrophytes. In Phytoremediation; Shmaefsky, B.R., Ed.; Concepts and Strategies in Plant Sciences; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 153–204. ISBN 978-3-030-00098-1. [Google Scholar]
- Gersberg, R.M.; Gearheart, R.A.; Ives, M. Pathogen Removal in Constructed Wetlands. In Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment; Hammer, D.A., Ed.; CRC Press, 2020; pp. 431–445. ISBN 978-1-003-06985-0.
- Gersberg, R.M.; Lyon, S.R.; Brenner, R.; Elkins, B.V. Fate of Viruses in Artificial Wetlands. Appl Environ Microbiol 1987, 53, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasper, J.T.; Nguyen, M.T.; Jones, Z.L.; Ismail, N.S.; Sedlak, D.L.; Sharp, J.O.; Luthy, R.G.; Horne, A.J.; Nelson, K.L. Unit Process Wetlands for Removal of Trace Organic Contaminants and Pathogens from Municipal Wastewater Effluents. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2013, 30, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, G.; Chi, T.; Du, C.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, K.; Long, Y.; et al. Enhanced Removal of Heavy Metals and Metalloids by Constructed Wetlands: A Review of Approaches and Mechanisms. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 821, 153516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Long, Y.; Yu, G.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, S. A Review on Microorganisms in Constructed Wetlands for Typical Pollutant Removal: Species, Function, and Diversity. Frontiers in Microbiology 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, S.; Yang, K.; Zeng, X.; Li, Y.; Zou, M.; Deng, Y.; Qian, W. CFD-Based Study of Flow Field Characteristics and Clogging in Horizontal Flow Constructed Wetlands. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghermandi, A.; Bixio, D.; Traverso, P.; Cersosimo, I.; Thoeye, C. The Removal of Pathogens in Surface-Flow Constructed Wetlands and Its Implications for Water Reuse. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 56, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badri, D.V.; Vivanco, J.M. Regulation and Function of Root Exudates. Plant Cell & Environment 2009, 32, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Wang, B.; Qi, M.; Lin, R.; Chen, H.; Xie, C.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, J.; Du, H.; Ge, Y. Medicinal Plant Root Exudate Metabolites Shape the Rhizosphere Microbiota. IJMS 2024, 25, 7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacka, K.; Moustakas, K.; Mikulewicz, M. The Combined Rhizoremediation by a Triad: Plant-Microorganism-Functional Materials. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2023, 30, 90500–90521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, K.; Banerjee, M. Structural Dynamics of Nonenveloped Virus Disassembly Intermediates. J Virol 2019, 93, e01115-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, V.; Charatzidou, A.; Oliver, D.M.; Weidmann, M.; Matallana-Surget, S.; Quilliam, R.S. Binding, Recovery, and Infectiousness of Enveloped and Non-Enveloped Viruses Associated with Plastic Pollution in Surface Water. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiCaprio, E.; Culbertson, D.; Li, J. Evidence of the Internalization of Animal Caliciviruses via the Roots of Growing Strawberry Plants and Dissemination to the Fruit. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2727–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.R.; Adam, V.; Rizvi, T.F.; Zhang, B.; Ahamad, F.; Jośko, I.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, M.; Mao, C. Nanoparticle-Plant Interactions: Two-Way Traffic. Small 2019, 15, e1901794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.S. Virus Entry: Molecular Mechanisms and Biomedical Applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernaudat, F.; Frelet-Barrand, A.; Pochon, N.; Dementin, S.; Hivin, P.; Boutigny, S.; Rioux, J.-B.; Salvi, D.; Seigneurin-Berny, D.; Richaud, P.; et al. Heterologous Expression of Membrane Proteins: Choosing the Appropriate Host. PLoS One 2011, 6, e29191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulshreshtha, A.; Sharma, S.; Padilla, C.S.; Mandadi, K.K. Plant-Based Expression Platforms to Produce High-Value Metabolites and Proteins. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1043478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baulcombe, D. RNA Silencing in Plants. Biochem. (Lond.) 2015, 37, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorel, M.; Mooney, B.; De Marchi, R.; Graciet, E. Ubiquitin/Proteasome System in Plant Pathogen Responses. In Annual Plant Reviews online; Roberts, J.A., Ed.; Wiley, 2019; pp. 65–116. ISBN 978-1-119-31299-4.
- Huang, X.; Chen, S.; Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, G. Friend or Enemy: A Dual Role of Autophagy in Plant Virus Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zure, D.; Sung, M.-H.; Rahim, A.; Kuo, H.-W. In Silico Assessment of Chemical Disinfectants on Surface Proteins Unveiled Dissimilarity in Antiviral Efficacy and Suitability towards Pathogenic Viruses. IJMS 2024, 25, 6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachmadi, A.T.; Kitajima, M.; Pepper, I.L.; Gerba, C.P. Enteric and Indicator Virus Removal by Surface Flow Wetlands. Science of The Total Environment 2016, 542, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandros, S.I.; Akratos, C.S. Removal of Pathogenic Bacteria in Constructed Wetlands: Mechanisms and Efficiency. In Phytoremediation; Ansari, A.A., Gill, S.S., Gill, R., Lanza, G.R., Newman, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2016; pp. 327–346. ISBN 978-3-319-41810-0. [Google Scholar]
- Plaza-Garrido, A.; Limaico, M.; Villamar-Ayala, C.A. Influence of Wastewater Treatment Technologies on Virus Removal under a Bibliometric-Statistical Analysis. Journal of Water Process Engineering 2022, 47, 102642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Khalid, S.; Abbas, G.; Shahid, N.; Nadeem, M.; Sabir, M.; Aslam, M.; Dumat, C. Heavy Metal Stress and Crop Productivity. In Crop Production and Global Environmental Issues; Hakeem, K.R., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2015; pp. 1–25. ISBN 978-3-319-23161-7. [Google Scholar]
- Vangronsveld, J.; Herzig, R.; Weyens, N.; Boulet, J.; Adriaensen, K.; Ruttens, A.; Thewys, T.; Vassilev, A.; Meers, E.; Nehnevajova, E.; et al. Phytoremediation of Contaminated Soils and Groundwater: Lessons from the Field. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2009 16:7 2009, 16, 765–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataki, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Vairale, M.G.; Dwivedi, S.K.; Gupta, D.K. Constructed Wetland, an Eco-Technology for Wastewater Treatment: A Review on Types of Wastewater Treated and Components of the Technology (Macrophyte, Biolfilm and Substrate). 2021, 283, 111986–111986. [CrossRef]
- Armanious, A.; Aeppli, M.; Jacak, R.; Refardt, D.; Sigstam, T.; Kohn, T.; Sander, M. Viruses at Solid-Water Interfaces: A Systematic Assessment of Interactions Driving Adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanenko, A.; Peter, H.; Meibom, J.; Borchardt, M.A.; Kohn, T. Diversity of Lake Bacteria Promotes Human Echovirus Inactivation. Appl Environ Microbiol 2025, 91, e02366-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zure, D.; David Kuo, H.-W.; Drizo, A. Insights of Phytoremediation Mechanisms for Viruses Based on In-Vitro, in-Vivo and in-Silico Assessments of Selected Herbal Plants. Chemosphere 2024, 351, 141101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Fu, G.; Liu, K.; Adnan, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.; Jiang, F.; Wang, M. Chemical Speciation and Transformation of Heavy Metals in Soil and Groundwater: Implications for Ecotoxicology and Remediation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 119858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrey, J.; Von Gunten, U.; Kohn, T. Differences in Viral Disinfection Mechanisms as Revealed by Quantitative Transfection of Echovirus 11 Genomes. Appl Environ Microbiol 2019, 85, e00961-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Huang, X.; Li, M.; Lu, Z.; Ling, X. Advances in Soil Amendments for Remediation of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soils: Mechanisms, Impact, and Future Prospects. Toxics 2024, 12, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firquet, S.; Beaujard, S.; Lobert, P.-E.; Sané, F.; Caloone, D.; Izard, D.; Hober, D. Survival of Enveloped and Non-Enveloped Viruses on Inanimate Surfaces. Microbes and environments 2015, 30, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldan-Hernandez, L.; Boehm, A.B. Adsorption of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV), Rhinovirus, SARS-CoV-2, and F+ Bacteriophage MS2 RNA onto Wastewater Solids from Raw Wastewater 2023.
- Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Lu, X.; He, M.; Jan Meijer, E.; Wang, R. Surface Complexation of Heavy Metal Cations on Clay Edges: Insights from First Principles Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Ni(II). Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 2017, 203, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulos, S.; Smeets, P. Quantifying the Log Reduction of Pathogenic Microorganisms by Constructed Wetlands: A Review. In Proceedings of the The 4th International Electronic Conference on Water Sciences, MDPI, November 12 2019; p. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Shingare, R.P.; Thawale, P.R.; Raghunathan, K.; Mishra, A.; Kumar, S. Constructed Wetland for Wastewater Reuse: Role and Efficiency in Removing Enteric Pathogens. Journal of Environmental Management 2019, 246, 444–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldan-Hernandez, L.; Van Oost, C.; Boehm, A.B. Solid-Liquid Partitioning of Dengue, West Nile, Zika, Hepatitis A, Influenza A, and SARS-CoV-2 Viruses in Wastewater from across the United States 2024.
- Schück, M.; Greger, M. Screening the Capacity of 34 Wetland Plant Species to Remove Heavy Metals from Water. IJERPH 2020, 17, 4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urase, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Ohgaki, S. Effect of Pore Structure of Membranes and Module Configuration on Virus Retention. Journal of Membrane Science 1996, 115, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.K.; Agrawal, C.; Blunden, G. Rutin: A Potential Antiviral for Repurposing as a SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (Mpro ) Inhibitor. Natural Product Communications 2021, 16, 1934578X21991723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargallo-Garriga, A.; Preece, C.; Sardans, J.; Oravec, M.; Urban, O.; Peñuelas, J. Root Exudate Metabolomes Change under Drought and Show Limited Capacity for Recovery. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Hao, T.; Chen, W.; Li, C.; Pang, S.; Fu, C.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, C.; Ghorbanpour, M.; Miao, S. Reprogrammed Plant Metabolism During Viral Infections: Mechanisms, Pathways and Implications. Molecular Plant Pathology 2025, 26, e70066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhao, M.; Yang, N.; Feng, L.; Wang, L.; Jiang, C.; Jiang, M.; Guo, J.; Li, T. Regulated the Electrokinetic Application of Different Plant Growth Stages and Parameters Enhance the Economic Extraction of Soil Heavy Metals. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1557261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras-Socias, P.; Tomasino, M.P.; Fernandes, J.P.; De Menezes, A.B.; Fernández, B.; Collins, G.; Alves, M.J.; Castro, R.; Gomes, C.R.; Almeida, C.M.R.; et al. Removal of Metals and Emergent Contaminants from Liquid Digestates in Constructed Wetlands for Agricultural Reuse. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1388895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargos, C.H.M.; Yang, L.; Jackson, J.C.; Tanganini, I.C.; Francisco, K.R.; Ceccato-Antonini, S.R.; Rezende, C.A.; Faria, A.F. Lignin and Nanolignin: Next-Generation Sustainable Materials for Water Treatment. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2025, 8, 2632–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Luo, S.; Yu, B.; Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. A Comparative Analysis for the Development and Recovery Processes of Different Types of Clogging in Lab-Scale Vertical Flow Constructed Wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2018, 25, 24073–24083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Ren, J.; Ling, T.; Wei, B.; Wang, G. Chemical Speciation and Phytoavailability of Cr, Ni, Zn and Cu in Loess Amended with Attapulgite-Stabilized Sewage Sludge. Environmental Pollutants and Bioavailability 2019, 31, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Luca, G.A.; Hadad, H.R.; Mufarrege, M.M.; Maine, M.A.; Sánchez, G.C. Improvement of Cr Phytoremediation by Pistia Stratiotes in Presence of Nutrients. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2014, 16, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhir, B. Effective Control of Waterborne Pathogens by Aquatic Plants. In Waterborne Pathogens; Elsevier, 2020; pp. 339–361. ISBN 978-0-12-818783-8.
- Nguyen Vo Chau, N.; Huynh Van, T.; Nguyen Cong, T.; Kim, L.; Pham, D.V. Water Lettuce ( Pistia Stratiotes L.) Increases Biogas Effluent Pollutant Removal Efficacy and Proves a Positive Substrate for Renewable Energy Production. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharrer, M.J.; Summerfelt, S.T. Ozonation Followed by Ultraviolet Irradiation Provides Effective Bacteria Inactivation in a Freshwater Recirculating System. Aquacultural Engineering 2007, 37, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R.S. Ferrates: Greener Oxidants with Multimodal Action in Water Treatment Technologies. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, P.; Venieri, D.; Mantzavinos, D. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water and Wastewater Viral Disinfection. A Systematic Review. Food Environ. Virol. 2021, 13, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoquart, C.; Servais, P.; Bérubé, P.R.; Barbeau, B. Hybrid Membrane Processes Using Activated Carbon Treatment for Drinking Water: A Review. Journal of Membrane Science 2012, 411–412, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiegler, A.N.; Cecchetti, A.R.; Scholes, R.C.; Sedlak, D.L. Persistent Trace Organic Contaminants Are Transformed Rapidly under Sulfate- and Fe(III)-Reducing Conditions in a Nature-Based Subsurface Water Treatment System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 16616–16627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uggetti, E.; Hughes-Riley, T.; Morris, R.H.; Newton, M.I.; Trabi, C.L.; Hawes, P.; Puigagut, J.; García, J. Intermittent Aeration to Improve Wastewater Treatment Efficiency in Pilot-Scale Constructed Wetland. Science of The Total Environment 2016, 559, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, A.J.; Constantino, C.; Dotro, G.; Cartmell, E.; Campo, P. Fate and Removal of Metals in Municipal Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2018, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.E.; Bin Halmi, M.I.E.; Bin Abd Samad, M.Y.; Uddin, M.K.; Mahmud, K.; Abd Shukor, M.Y.; Sheikh Abdullah, S.R.; Shamsuzzaman, S.M. Design, Operation and Optimization of Constructed Wetland for Removal of Pollutant. 2020, 17, 8339–8339. [CrossRef]
- Dykes, C.; Pearson, J.; Bending, G.; Abolfathi, S. Impact of Seasonal Climate Variability on Constructed Wetland Treatment Efficiency. J. Water Proc.engineering 2025, 72, 107350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ju, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Xie, X.; Dai, C.; et al. Exopolysaccharide-Producing Bacteria Enhanced Pb Immobilization and Influenced the Microbiome Composition in Rhizosphere Soil of Pakchoi (Brassica Chinensis L.). Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1117312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vojnovic, S.; Aleksic, I.; Ilic-Tomic, T.; Stevanovic, M.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J. Bacillus and Streptomyces Spp. as Hosts for Production of Industrially Relevant Enzymes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2024, 108, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Parihar, P.; Singh, R.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Heavy Metal Tolerance in Plants: Role of Transcriptomics, Proteomics, Metabolomics, and Ionomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Jing, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Huang, Z.; Sun, B.; Li, P.; Li, H.; Zhang, C. The Great Game between Plants and Viruses: A Focus on Protein Homeostasis. IJMS 2023, 24, 12582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Hao, T.; Chen, W.; Li, C.; Pang, S.; Fu, C.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, C.; Ghorbanpour, M.; Miao, S. Reprogrammed Plant Metabolism during Viral Infections: Mechanisms, Pathways and Implications. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2025, 26, e70066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.K.; Agrawal, C.; Blunden, G. Rutin: A Potential Antiviral for Repurposing as a SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease (Mpro) Inhibitor. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2021, 16, 1934578X2199172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Tian, L.; Zhou, P.; Babakhani, P.; Gregory, J.; Graham, N.; Elimelech, M.; Yu, W. Nanonet Trapping for Effective Removal of Nanoplastics by Iron Coagulation. Nat Commun 2025, 16, 5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ju, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Xie, X.; Dai, C.; et al. Exopolysaccharide-Producing Bacteria Enhanced Pb Immobilization and Influenced the Microbiome Composition in Rhizosphere Soil of Pakchoi (Brassica Chinensis L.). Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1117312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, M.; Gupta, A.K.; Ghosal, P.S.; Majumder, A. A Review on Performance of Constructed Wetlands in Tropical and Cold Climate: Insights of Mechanism, Role of Influencing Factors, and System Modification in Low Temperature. 2021, 755, 142540–142540. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mancuso, G.; Petrotto, L.; Lavrnić, S.; Dong, Z.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, J.; Toscano, A. AI-Driven Solutions in Wastewater Treatment and Agricultural Reuse Systems: A Comprehensive Review. J. Environ. Manage. 2025, 393, 127008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanneru, C.T.; Chellam, S. Mechanisms of Virus Control during Iron Electrocoagulation – Microfiltration of Surface Water. Water Research 2012, 46, 2111–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Narayanan, J.; Sen, A.; Chellam, S. Virus Removal and Inactivation Mechanisms during Iron Electrocoagulation: Capsid and Genome Damages and Electro-Fenton Reactions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, acs.est.0c04438. [CrossRef]
- Bicudo, B.; Medema, G.; van Halem, D. Inactivation of Escherichia Coli and Somatic Coliphage ΦX174 by Oxidation of Electrochemically Produced Fe2+. J. Water Proc.engineering 2022, 47, 102683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Man, Y.; Ruan, W.; Tam, N.F.; Tao, R.; Yin, L.; Yang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Tai, Y. The Effect of Rhizosphere and the Plant Species on the Degradation of Sulfonamides in Model Constructed Wetlands Treating Synthetic Domestic Wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hdidou, M.; Necibi, M.C.; Labille, J.; El Hajjaji, S.; Dhiba, D.; Chehbouni, A.; Roche, N. Potential Use of Constructed Wetland Systems for Rural Sanitation and Wastewater Reuse in Agriculture in the Moroccan Context. Energies 2021, 15, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xie, H.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Liu, C.; Zhao, C.; Li, H. Effect of Plant Harvesting on the Performance of Constructed Wetlands during Winter: Radial Oxygen Loss and Microbial Characteristics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2015, 22, 7476–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourredine, Y.; Naima, A.; Dalila, H.; Habib, S.; Karim, S.; Zohra, F.-L. Changes of Peroxidase Activities under Cold Stress in Annuals Populations of Medicago. Mol. Plant Breed. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, P.; Dotro, G.; Nivala, J.; García, J. Clogging in Subsurface-Flow Treatment Wetlands: Occurrence and Contributing Factors. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, H. Functions of Macrophytes in Constructed Wetlands. Water Sci. Technol. 1994, 29, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaib, K.H.; Bhunia, P. Dynamics of Clogging in Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2022, 26, 03121004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, L.-C.; Ng, L.-T.; Cheng, P.-W.; Chiang, W.; Lin, C.-C. Antiviral Activities of Extracts and Selected Pure Constituents of Ocimum Basilicum. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology 2005, 32, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Taheri, E.; Ehrampoush, M.H.; Nasiri, S.; Jalali, F.; Soltani, R.; Fatehizadeh, A. Efficiency of Constructed Wetland Vegetated with Cyperus Alternifolius Applied for Municipal Wastewater Treatment. J. Environ. Public Health 2013, 2013, 815962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cangioli, L.; Salobehaj, M.; Del Duca, S.; Fagorzi, C.; Berardi, C.; Coppini, E.; Fibbi, D.; Fani, R.; Vassallo, A. Effect of Wastewater on the Composition of Bacterial Microbiota of Phragmites Australis Used in Constructed Wetlands for Phytodepuration. Plants 2022, 11, 3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, V.; Vergani, L.; Rashed, A.A.; El Saadi, A.; Sabatino, R.; Di Cesare, A.; Crotti, E.; Mapelli, F.; Borin, S. Plant Species Influences the Composition of Root System Microbiome and Its Antibiotic Resistance Profile in a Constructed Wetland Receiving Primary Treated Wastewater. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1436122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-L.; Yen, H.-R.; Chang, Y.-S.; Lin, Y.-P.; Huang, S.-H.; Lin, C.-W. Antiviral Action of Tryptanthrin Isolated from Strobilanthes Cusia Leaf against Human Coronavirus NL63. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantanam, A.; Mana, N.; Semkum, P.; Lueangaramkul, V.; Phecharat, N.; Lekcharoensuk, P.; Theerawatanasirikul, S. Dual Effects of Ipecac Alkaloids with Potent Antiviral Activity against Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus as Replicase Inhibitors and Direct Virucides. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2024, 12, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Goyal, D. Analyzing Remediation Potential of Wastewater through Wetland Plants: A Review. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2014, 33, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochi, L.Y.; Freitas, P.L.; Maranho, L.T.; Juneau, P.; Gomes, M.P. Aquatic Macrophytes in Constructed Wetlands: A Fight against Water Pollution. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranho, L.T.; Gomes, M.P. Morphophysiological Adaptations of Aquatic Macrophytes in Wetland-Based Sewage Treatment Systems: Strategies for Resilience and Efficiency under Environmental Stress. Plants 2024, 13, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markland, S.M.; Bais, H.; Kniel, K.E. Human Norovirus and Its Surrogates Induce Plant Immune Response in Arabidopsis Thaliana and Lactuca Sativa. Foodborne Pathogens and Disease 2017, 14, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esseili, M.A.; Meulia, T.; Saif, L.J.; Wang, Q. Tissue Distribution and Visualization of Internalized Human Norovirus in Leafy Greens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muerdter, C.P.; LeFevre, G.H.; Cwiertny, D.; Just, C.; Lehmler, H.-J.; Schnoor, J. Vegetation-Facilitated Removal Kinetics and Transformation of Organic Biocides. Doctor of Philosophy, University of Iowa: Iowa City, IA, United States, 2021.
- Li, J.; Zheng, L.; Ye, C.; Ni, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, H. Evaluation of an Intermittent-Aeration Constructed Wetland for Removing Residual Organics and Nutrients from Secondary Effluent: Performance and Microbial Analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 329, 124897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, H.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Song, F.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. Recent Advances in Constructed Wetlands Methane Reduction: Mechanisms and Methods. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1106332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.; Singh, S.V.; Savio, N.; Bhutto, J.K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Yadav, K.K.; Sharma, R.; Nandipamu, T.M.K.; Sarkar, B. Biochar Application in Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment: A Critical Review. J. Water Proc.engineering 2025, 69, 106713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; An, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Din, K.; Qin, C.; Li, K.; Cui, M.; et al. Virus Disinfection from Environmental Water Sources Using Living Engineered Biofilm Materials. Advanced Science 2020, 7, 1903558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndjomgoue-Yossa, A.C.; Nanseu-Njiki, C.P.; Ngameni, E. Effect of pH on Escherichia Coli Removal by Electrocoagulation and Elimination Kinetics after Treatment. J. Chem. 2022, 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Shokrani, H.; Shokrani, A.; Jabbour, K.; Abida, O.; Mousavi Khadem, S.S.; Habibzadeh, S.; Sonawane, S.H.; Saeb, M.R.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; et al. Recent Advances in Aqueous Virus Removal Technologies. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, J. Seasonal Effects of Constructed Wetlands on Water Quality Characteristics in Jinshan Lake: A Gate Dam Lake (Zhenjiang City, China). Biology (Basel) 2024, 13, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Feng, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Deng, P. Removal of Nutrients from Septic Effluent with Re-Circulated Hybrid Tidal Flow Constructed Wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 46, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Feng, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Deng, P. Removal of Nutrients from Septic Effluent with Re-Circulated Hybrid Tidal Flow Constructed Wetland. Ecological Engineering 2012, 46, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cangioli, L.; Salobehaj, M.; Del Duca, S.; Fagorzi, C.; Berardi, C.; Coppini, E.; Fibbi, D.; Fani, R.; Vassallo, A. Effect of Wastewater on the Composition of Bacterial Microbiota of Phragmites Australis Used in Constructed Wetlands for Phytodepuration. Plants 2022, 11, 3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Abbas, Z.; Rizwan, M.; Zaheer, I.; Yavaş, İ.; Ünay, A.; Abdel-DAIM, M.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Kalderis, D. Application of Floating Aquatic Plants in Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals Polluted Water: A Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhilkina, T.; Gerasimova, I.; Babich, T.; Kanapatskiy, T.; Sokolova, D.; Kadnikov, V.; Kamionskaya, A. Evaluation of the Phytoremediation Potential of Aquatic Plants and Associated Microorganisms for the Cleaning of Aquatic Ecosystems from Oil Products. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Dai, Y.; Wang, F.; Liang, W. Seasonal Variation of Microbial Community for the Treatment of Tail Water in Constructed Wetland. Water Science and Technology 2017, 75, 2434–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.Y.; Weaver, R.W. Ultraviolet Disinfection of Effluent from Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands. Environmental Technology 2003, 24, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arden, S.; Anderson, M.; Blue, J.; Ma, X. (Cissy); Jahne, M.; Garland, J. Towards the Definition of Treatment Wetland Pathogen Log Reduction Credits. Science of The Total Environment 2024, 957, 177613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruthi, R.; Shivashankara, G.P. Effect of HRT and Seasons on the Performance of Pilot-Scale Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetland to Treat Rural Wastewater. Water Practice and Technology 2022, 17, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GARCÍA, J.; ROUSSEAU, D.P.L.; MORATÓ, J.; LESAGE, E.L.S.; MATAMOROS, V.; BAYONA, J.M. Contaminant Removal Processes in Subsurface-Flow Constructed Wetlands: A Review. 2010, 40, 561–661. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Bai, Y.; Qu, J. The Phragmites Root-Inhabiting Microbiome: A Critical Review on Its Composition and Environmental Application. Engineering 2022, 9, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foladori, P.; Ruaben, J.; Ortigara, A.R.C.; Andreottola, G. Batch Feed and Intermittent Recirculation to Increase Removed Loads in a Vertical Subsurface Flow Filter. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 70, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirdashtzadeh, M.; Chua, L.H.C.; Brau, L. Microbial Communities and Nitrogen Transformation in Constructed Wetlands Treating Stormwater Runoff. Front. Water 2022, 3, 751830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Zhang, S.; Liang, R.; Shen, J. Effects of Root Exudates on Denitrifier Gene Abundance, Community Structure and Activity in a Micro-Polluted Constructed Wetland. Science of The Total Environment 2017, 598, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, W.; Xia, A.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Ni, L.; Jin, F. Carbon Starvation Induces the Expression of PprB-Regulated Genes in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol 2019, 85, e01705-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Y. Advances in AHLs-Mediated Quorum Sensing System in Wastewater Biological Nitrogen Removal: Mechanism, Function, and Application. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 1927–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, N.; Saeed, M.; Zafarullah, S.; Hyder, S.; Rizvi, Z.F.; Gondal, A.S.; Jamil, N.; Iqbal, R.; Ali, B.; Ercisli, S.; et al. Multifaceted Impacts of Plant-Beneficial Pseudomonas Spp. In Managing Various Plant Diseases and Crop Yield Improvement. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 22296–22315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, R.; Li, M.; Guo, X.; Lu, S.; Li, M.; Wu, H. Intensified Performance and Mechanism of Nitrogen Removal in Constructed Wetland Incorporating Algal Pond for Treating Low Carbon Nitrogen Ratio Wastewater. Bioresource Technology 2025, 429, 132488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Z.; Fan, W.; Dong, X. Inducers of Plant Systemic Acquired Resistance Regulate NPR1 Function through Redox Changes. Cell 2003, 113, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Ding, P.; Wang, D.; Cheng, Y.T.; He, J.; Gao, M.; Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Control of Salicylic Acid Synthesis and Systemic Acquired Resistance by Two Members of a Plant-Specific Family of Transcription Factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2010, 107, 18220–18225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine, M.B.; Xiao, X.; Kachroo, P.; Kachroo, A. Signaling Mechanisms Underlying Systemic Acquired Resistance to Microbial Pathogens. Plant Science 2019, 279, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Q.; Mou, Z. Redox Signaling and Oxidative Stress in Systemic Acquired Resistance. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 75, 4535–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, N.N.; Chua, L.H.C.; Mustaffa, Z.; Das, S.; Takaijudin, H. A Review Study on the Association between Hydraulic Performance and Treatment Effectiveness in Free Surface Flow Constructed Wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 203, 107258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Xiang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y. Enzyme Treatment Improves the Performance of Laboratory-Scale Vertical Flow Constructed Wetland. Bioresource Technology 2018, 268, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhofstad, M.J.J.M.; Poelen, M.D.M.; Van Kempen, M.M.L.; Bakker, E.S.; Smolders, A.J.P. Finding the Harvesting Frequency to Maximize Nutrient Removal in a Constructed Wetland Dominated by Submerged Aquatic Plants. Ecological Engineering 2017, 106, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Singh, H.O.; Raja, S.K.; Dixit, S. Constructed Wetland for Improved Wastewater Management and Increased Water Use Efficiency in Resource Scarce SAT Villages: A Case Study from Kothapally Village, in India. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2021, 23, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernes, P.J.; Miller, R.L.; Dyda, R.Y.; Bergamaschi, B.A. Vegetation vs. Anoxic Controls on Degradation of Plant Litter in a Restored Wetland. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, F.; Cheng, L. Effects of Multi-Plant Harvesting on Nitrogen Removal and Recovery in Constructed Wetlands. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.-Y.; Song, Z.-X.; Ding, Y.-L.; You, S.-H.; He, S. Correlation of substrate structure and hydraulic characteristics in subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2014, 35, 592–596. [Google Scholar]
- Pedescoll, A.; Corzo, A.; Alvarez, E.; García, J.; Puigagut, J. The Effect of Primary Treatment and Flow Regime on Clogging Development in Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands: An Experimental Evaluation. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3579–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivala, J.; Headley, T.; Wallace, S.; Bernhard, K.; Brix, H.; Van Afferden, M.; Müller, R.A. Comparative Analysis of Constructed Wetlands: The Design and Construction of the Ecotechnology Research Facility in Langenreichenbach, Germany. Ecological Engineering 2013, 61, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakizimana, J.N.; Gourich, B.; Chafi, M.; Stiriba, Y.; Vial, C.; Drogui, P.; Naja, J. Electrocoagulation Process in Water Treatment: A Review of Electrocoagulation Modeling Approaches. Desalination 2017, 404, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Jothikumar, N.; Sen, A.; Murphy, J.L.; Chellam, S. Removal and Inactivation of an Enveloped Virus Surrogate by Iron Conventional Coagulation and Electrocoagulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 2674–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicudo, B.; van der Werff, B.-J.; Medema, G.; van Halem, D. Disinfection during Iron Electrocoagulation: Differentiating between Inactivation and Floc Entrapment for Escherichia Coli and Somatic Coliphage ØX174. ACS ES T Water 2022, 2, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Pasco, E.V.; Xagoraraki, I.; Tarabara, V.V. Virus Removal and Inactivation in a Hybrid Microfiltration–UV Process with a Photocatalytic Membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 149, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques dos Santos, M.; Li, C.; Jemain, M.H.; Yuen, J.W.; Snyder, S.A. Removal of Human Coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43) in Simulated Drinking Water Treatment Processes. ACS ES T Water 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barocsi, A.; Csintalan, Z.; Kocsanyi, L.; Dushenkov, S.; Kuperberg, J.M.; Kucharski, R.; Richter, P.I. Optimizing Phytoremediation of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soil by Exploiting Plants’ Stress Adaptation. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2003, 5, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, S.; Ali Wani, O.; Lone, J.K.; Manhas, S.; Kour, N.; Alam, P.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, P. Reactive Oxygen Species in Plants: From Source to Sink. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Dai, Y.; Wang, F.; Liang, W. Seasonal Variation of Microbial Community for the Treatment of Tail Water in Constructed Wetland. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 2434–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.J.; Farrell, M.; Huang, J.; Reynolds, C.; Rupasinghe, M.; Mosley, L.M. Long-Term Water Quality Response to Increased Hydraulic Loadings in a Field-Scale Free Water Surface Constructed Wetland Treating Domestic Effluent. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 311, 114858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.-Y.; Han, Y.-C.; Easa, S.M.; Chu, P.-P.; Wang, Y.-L.; Zhou, X.-Y. New Solution to Build Constructed Wetland in Cold Climatic Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abir Ahsan, T.M.; Rahman, M.S.; Ahamed, M.S. Geothermal Energy Application for Greenhouse Microclimate Management: A Review. Geothermics 2025, 127, 103209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Alamin, Md.; Tsuji, S.; Hara-Yamamura, H.; Hata, A.; Zhao, B.; Ihara, M.; Honda, R. Removal Performance of SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater Treatment by Membrane Bioreactor, Anaerobic-Anoxic-Oxic, and Conventional Activated Sludge Processes. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 851, 158310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, M.F.; Verbyla, M.E.; Vassalle, L.; Rosa-Machado, A.T.; Zhao, F.; Gaunin, A.; Mota, C.R. Reduction and Partitioning of Viral and Bacterial Indicators in a UASB Reactor Followed by High Rate Algal Ponds Treating Domestic Sewage. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 144309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbyla, M.E.; Mihelcic, J.R. A Review of Virus Removal in Wastewater Treatment Pond Systems. Water Research 2015, 71, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arden, S.; Ma, X. Constructed Wetlands for Greywater Recycle and Reuse: A Review. Science of the Total Environment 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Liang, S.; Fan, J.; Lu, S.; Wu, H. Optimizations on Supply and Distribution of Dissolved Oxygen in Constructed Wetlands: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sossalla, N.A.; Nivala, J.; Escher, B.I.; Reemtsma, T.; Schlichting, R.; Van Afferden, M.; Müller, R.A. Resilience of Micropollutant and Biological Effect Removal in an Aerated Horizontal Flow Treatment Wetland. Water 2020, 12, 3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.K.; Balasubramanian, R. Constructed Wetlands for Reclamation and Reuse of Wastewater and Urban Stormwater: A Review. Frontiers in Environmental Science 2022, 10, 836289–836289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augsburger, N.; Rachmadi, A.T.; Zaouri, N.; Lee, Y.; Hong, P.-Y. Recent Update on UV Disinfection to Fulfill the Disinfection Credit Value for Enteric Viruses in Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 16283–16298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Han, J.-L.; Zheng, C.; Zheng, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wang, A. Why the Disinfection Efficiency of Ultraviolet Radiation May Become Unsatisfactory at Low Suspended Solid Concentrations: The Mechanism of Extracellular Polymeric Substances Secretion Induced by Different Particles. Water Research 2025, 274, 123122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaizeh, H.; Linden, K.G.; Barstow, C.; Kalbouneh, S.; Tellawi, A.; Albalawneh, A.; Gerchman, Y. Constructed Wetlands Combined with UV Disinfection Systems for Removal of Enteric Pathogens and Wastewater Contaminants. Water Science and Technology 2013, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Rijnaarts, H.; Langenhoff, A. Mesocosm Constructed Wetlands to Remove Micropollutants from Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent: Effect of Matrices and Pre-Treatments. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirer, G.S.; Silva, T.N.; Jackson, C.T.; Thomas, J.B.; W Ehrhardt, D.; Rhee, S.Y.; Mortimer, J.C.; Landry, M.P. Nanotechnology to Advance CRISPR-Cas Genetic Engineering of Plants. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zafar, N.; Ali, Q.; Manghwar, H.; Wang, G.; Yu, L.; Ding, X.; Ding, F.; Hong, N.; Wang, G.; et al. CRISPR/Cas Genome Editing Technologies for Plant Improvement against Biotic and Abiotic Stresses: Advances, Limitations, and Future Perspectives. Cells 2022, 11, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Yadav, V.K.; Chundawat, R.S.; Soltane, R.; Awwad, N.S.; Ibrahium, H.A.; Yadav, K.K.; Vicas, S.I. Enhancing Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacterial Activities through Consortium Exposure: A Review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1099999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragland, C.J.; Shih, K.Y.; Dinneny, J.R. Choreographing Root Architecture and Rhizosphere Interactions through Synthetic Biology. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskett, T.L.; Tkacz, A.; Poole, P.S. Engineering Rhizobacteria for Sustainable Agriculture. ISME J. 2021, 15, 949–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemla, Y.; Sweeney, C.J.; Wozniak, C.A.; Voigt, C.A. Design and Regulation of Engineered Bacteria for Environmental Release. Nat. Microbiol. 2025, 10, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lea-Smith, D.J.; Hassard, F.; Coulon, F.; Partridge, N.; Horsfall, L.; Parker, K.D.J.; Smith, R.D.J.; McCarthy, R.R.; McKew, B.; Gutierrez, T.; et al. Engineering Biology Applications for Environmental Solutions: Potential and Challenges. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouki, J.; Fattah, G.; Kherraf, S.; Abrouki, Y.; Azrour, M.; Hajjaji, S.E. Artificial Intelligence System for Intelligent Monitoring and Management of Water Treatment Plants. In Emerging Real-World Applications of Internet of Things; CRC Press: Boca Raton, 2022; pp. 69–87. ISBN 978-1-003-30420-3. [Google Scholar]
- Reymond, P.; Chandragiri, R.; Ulrich, L. Governance Arrangements for the Scaling Up of Small-Scale Wastewater Treatment and Reuse Systems – Lessons From India. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Baserba, M.; Sedlak, D.L.; Molinos-Senante, M.; Barnosell, I.; Schraa, O.; Rosso, D.; Verdaguer, M.; Poch, M. Using Water and Wastewater Decentralization to Enhance the Resilience and Sustainability of Cities. Nat. Water 2024, 2, 953–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. Surface-Flow Constructed Treatment Wetlands for Pollutant Removal: Applications and Perspectives. Wetlands (Wilmington) 2011, 31, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasse, C.; Wenk, J.; Jasper, J.T.; Ternes, T.A.; Sedlak, D.L. Co-Occurrence of Photochemical and Microbiological Transformation Processes in Open-Water Unit Process Wetlands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14136–14145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, T.; Barya, M.; Dutta, J.; Mukherjee, P.; Thakur, A.; Swamy, S.; Anderson, J. Integrated Phytobial Remediation of Dissolved Pollutants from Domestic Wastewater through Constructed Wetlands: An Interactive Macrophyte-Microbe-Based Green and Low-Cost Decontamination Technology with Prospective Resource Recovery. Water 2023, 15, 3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Sauba, K.; Fattah, K.P.; Smith, J.R. Designing Constructed Wetlands for Reclamation of Pretreated Wastewater and Stormwater. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 2017, 16, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Wang, T.; Liao, J.; Shi, W.; Huang, Z.; Miao, H.; Wu, P.; Ruan, W. Operational Performances and Enzymatic Activities for Eutrophic Water Treatment by Vertical-Flow and Horizontal-Flow Constructed Wetlands. Water (Basel) 2020, 12, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino-Solís, M.; Villegas, E.; De Anda, J.; López-López, A. The Effect of the Hydraulic Retention Time on the Performance of an Ecological Wastewater Treatment System: An Anaerobic Filter with a Constructed Wetland. Water (Basel) 2015, 7, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, D.Q.; Dong, J.W.; Tan, S.K. Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment in Cold Climate — A Review. Journal of Environmental Sciences 2017, 57, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Chauhan, M.; Kumar Sharma, P.; Kumari, M.; Mitra, D.; Joshi, S. Microbiological Dimensions and Functions in Constructed Wetlands: A Review. Current Research in Microbial Sciences 2024, 7, 100311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barca, C.; Troesch, S.; Meyer, D.; Drissen, P.; Andrès, Y.; Chazarenc, F. Steel Slag Filters to Upgrade Phosphorus Removal in Constructed Wetlands: Two Years of Field Experiments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zou, Y.; Yu, X.; Ding, S.; Yan, J.; Min, Y. Vegetated Steel Slag Substrate Constructed Wetlands Can Achieve High Efficiency Simultaneous Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 947783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Wang, T.; Liao, J.; Shi, W.; Huang, Z.; Miao, H.; Wu, P.; Ruan, W. Operational Performances and Enzymatic Activities for Eutrophic Water Treatment by Vertical-Flow and Horizontal-Flow Constructed Wetlands. Water 2020, 12, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdoğan, İ.; Cevher-Keskin, B.; Bilir, Ö.; Hong, Y.; Tör, M. Recent Developments in CRISPR/Cas9 Genome-Editing Technology Related to Plant Disease Resistance and Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Biology (Basel) 2023, 12, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Bai, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yang, S.; Ren, N. Virtual Sample Generation Empowers Machine Learning-Based Effluent Prediction in Constructed Wetlands. J. Environ. Manage. 2023, 346, 118961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aman, R.; Mahas, A.; Marsic, T.; Hassan, N.; Mahfouz, M.M. Efficient, Rapid, and Sensitive Detection of Plant RNA Viruses with One-Pot RT-RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a Assay. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 610872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Saltepe, B.; Yu, L.; Wang, B. Programming Living Sensors for Environment, Health and Biomanufacturing. Microbial Biotechnology 2021, 14, 2334–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncker, K.E.; Holmes, Z.A.; You, L. Engineered Microbial Consortia: Strategies and Applications. Microb. Cell Fact. 2021, 20, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Huang, Y.-H. The Effect of Key Physiological Features on Roots Oxygen Release of Five Wetland Vegetations. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2023, 21, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licata, M.; Gennaro, M.C.; Tuttolomondo, T.; Leto, C.; La Bella, S. Research Focusing on Plant Performance in Constructed Wetlands and Agronomic Application of Treated Wastewater - A Set of Experimental Studies in Sicily (Italy). PLoS One 2019, 14, e0219445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Emergent Plants Used in Free Water Surface Constructed Wetlands: A Review. 2013, 61, 582–592. [CrossRef]
- Suquet, J.; Godo-Pla, L.; Valentí, M.; Verdaguer, M.; Martin, M.J.; Poch, M.; Monclús, H. Development of an Environmental Decision Support System for Enhanced Coagulation in Drinking Water Production. Water 2020, 12, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agaton, C.B.; Guila, P.M.C. Success Factors and Challenges: Implications of Real Options Valuation of Constructed Wetlands as Nature-Based Solutions for Wastewater Treatment. Resources 2024, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgoglione, A.; Torretta, V. Sustainable Management and Successful Application of Constructed Wetlands: A Critical Review. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.; He, B.; Fu, Y.; Kou, S.; Gao, J. Optimized Design of Modular Constructed Wetland for Treating Rural Black–Odorous Water. Water (Basel) 2024, 16, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, J.; Han, R.; Luo, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; He, B. Modular Constructed Wetlands for Treatment of Rural Domestic Wastewater: Laboratory Performance and Field Application. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, E.K.; Stoddart, A.K.; Gagnon, G.A. Adsorption of SARS-CoV-2 onto Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) in Wastewater: Implications for Improvements in Passive Sampling. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zhu, D.; Yao, Z.; Zhu, D.Z. Virus-Prokaryote Interactions Assist Pollutant Removal in Constructed Wetlands. Bioresource Technology 2025, 416, 131791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, J.; Domingues, E.; Frasson, D.; Martins, R.C.; Matos, A.M. Virus Removal from Real Wastewater as an Environmental Management Approach. Molecules 2024, 29, 5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waly, M.M.; Ahmed, T.; Abunada, Z.; Mickovski, S.B.; Thomson, C. Constructed Wetland for Sustainable and Low-Cost Wastewater Treatment: Review Article. Land 2022, 11, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Ramírez, L.E.; Zamora-Castro, S.A.; Sandoval-Herazo, L.C.; Herrera-May, A.L.; Salgado-Estrada, R.; De La Cruz-Dessavre, D.A. Technological Innovations in the Application of Constructed Wetlands: A Review. Processes (Basel) 2023, 11, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, R.; Li, B.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Hao, R. Study on the Optimization of Hydrodynamic Characteristics and Pollutant Removal Efficiency in Integrated Vertical Flow Constructed Wetlands. Sci Rep 2025, 15, 6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.; Queloz, P.; Brovelli, A.; Margot, J.; Barry, D.A. Enhancement of Micropollutant Degradation at the Outlet of Small Wastewater Treatment Plants. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, S.; Zluwa, I.; Österreicher, D. The “PV Rooftop Garden”: Providing Recreational Green Roofs and Renewable Energy as a Multifunctional System within One Surface Area. Applied Sciences 2020, 10, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, L.M.; Larsen, T.A. Towards a Performance-Based Approach for Multifunctional Green Roofs: An Interdisciplinary Review. Build. Environ. 2021, 188, 107489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uludag-Demirer, S.; Olson, N.; Ives, R.; Nshimyimana, J.P.; Rusinek, C.A.; Rose, J.B.; Liao, W. Techno-Economic Analysis of Electrocoagulation on Water Reclamation and Bacterial/Viral Indicator Reductions of a High-Strength Organic Wastewater—Anaerobic Digestion Effluent. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens, A.; Folch, M.; Salgot, M. Design and Performance of an Innovative Hybrid Constructed Wetland for Sustainable Pig Slurry Treatment in Small Farms. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 8, 577186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, Z.; Li, F.; Fan, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Hu, H. Effect of Oxygen Supply Strategy on Nitrogen Removal of Biochar-Based Vertical Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetland: Intermittent Aeration and Tidal Flow. Chemosphere 2019, 223, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, M.; Yaseen, A.; Refai, L.; El-Qanni, A. Conceptual Feasibility of a Portable Containerized and Decentralized Wastewater Treatment System for Rural Regions: A Case Study in Palestine. An-Najah University Journal for Research - A 2024, 38, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabay, G.; DeCastro, J.; Altay, A.; Smith, K.; Lu, H.-W.; Capossela, A.M.; Moarefian, M.; Aran, K.; Dincer, C. Emerging Biosensing Technologies for the Diagnostics of Viral Infectious Diseases. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2201085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Tian, F.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, J.; Luo, Z.; Yang, M.; Yi, C. Virus Detection: From State-of-the-Art Laboratories to Smartphone-Based Point-of-Care Testing. Advanced Science 2022, 9, 2105904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Fang, X.; Gao, Y.; Yu, K.; Gao, X. Research Progress on the Application of RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a in the Rapid Visual Detection of Pathogenic Microorganisms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1640938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, J.-R.S.; Tulipan, J.U.; Banawa, A.; Umali, K.D.C.; Villanueva, J.A.L. Advancements and Challenges in Decentralized Wastewater Treatment: A Comprehensive Review. Desalination and Water Treatment 2024, 320, 100830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A.K.; Salama, R.S.; Mostafa, M.M.M. Natural-Based Coagulants/Flocculants as Sustainable Market-Valued Products for Industrial Wastewater Treatment: A Review of Recent Developments. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 19335–19355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proano-Pena, G.; Carrano, A.L.; Blersch, D.M. Analysis of Very-High Surface Area 3D-Printed Media in a Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor for Wastewater Treatment. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy Barman, S.; Gavit, P.; Chowdhury, S.; Chatterjee, K.; Nain, A. 3D-Printed Materials for Wastewater Treatment. JACS Au 2023, 3, 2930–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, I.; Fulk, E.M.; Kalvapalle, P.; Silberg, J.J.; Masiello, C.A.; Stadler, L.B. Translating New Synthetic Biology Advances for Biosensing into the Earth and Environmental Sciences. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 618373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ostaku, J.; Aras, E.; Safak Seker, U.O. Combating Infectious Diseases with Synthetic Biology. ACS Synth. Biol. 2022, 11, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wölle, J.; Steinmetz, H.; Hansen, J.; Einsfeld, K.; Ebert, A. An Intelligent Visualisation and Decision Support System for Decentralised Wastewater Treatment Plants. Water Science and Technology 2007, 56, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternak, G.; Greenman, J.; Ieropoulos, I. Self-Powered, Autonomous Biological Oxygen Demand Biosensor for Online Water Quality Monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 244, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLamore, E.S.; Datta, S.P.A. A Connected World: System-Level Support through Biosensors. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. (Palo Alto Calif.) 2023, 16, 285–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.Y.A.; Siggins, A.; Healy, M.G.; Ó hUallacháin, D.; Fenton, O.; Tuohy, P. A Novel Hybrid Coagulation-Constructed Wetland System for the Treatment of Dairy Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crovella, T.; Paiano, A.; Falciglia, P.P.; Lagioia, G.; Ingrao, C. Wastewater Recovery for Sustainable Agricultural Systems in the Circular Economy - A Systematic Literature Review of Life Cycle Assessments. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, A.; Beretsou, V.G.; Iakovides, I.C.; Karaolia, P.; Michael, C.; Benmarhnia, T.; Chefetz, B.; Donner, E.; Gawlik, B.M.; Lee, Y.; et al. Sustainable Wastewater Reuse for Agriculture. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 504–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Guerra, E.; Castillo-Valenzuela, J.; Gude, V.G. Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment. Water Environ. Res. 2018, 90, 1537–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, U.; Nandimandalam, H.; Martinez-Guerra, E.; Gude, V.G. Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruyer, N.; Dorais, M.; Zagury, G.J.; Alsanius, B.W. Removal of Plant Pathogens from Recycled Greenhouse Wastewater Using Constructed Wetlands. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 117, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, B.A.; Mahoney, L.E.; Yao, S. Field Evaluation of a Novel UV Water Disinfection System for Use in Underserved Rural Communities. Water Environment Research 2019, 91, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarasu, P.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Moore, M.D. Research Progress in Viral Inactivation Utilizing Human Norovirus Surrogates. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.B.; Tiwari, A.K.; Srivastava, N.; Ahmad, I.; Abohashrh, M.; Gupta, V.K. Biomass Valorization of Eichhornia Crassipes Root Using Thermogravimetric Analysis. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Huo, Y.; Fu, M.-L.; Sun, W.; Yuan, B. Inactivation and Genome Damage of Rotavirus and a Human Norovirus Surrogate by Monochloramine Treatment and Sequential Application with UV. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, M.; Monis, P.T.; King, B.J. The Efficacy of Current Treatment Processes to Remove, Inactivate, or Reduce Environmental Bloom-Forming Escherichia Coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0085624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Gao, S.-H.; Li, J.; Su, Y.; Huang, F.; Liang, B.; Fan, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, A. Emerging Technologies for the Control of Biological Contaminants in Water Treatment: A Critical Review. Engineering (Beijing) 2025, 48, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Shokrani, H.; Shokrani, A.; Jabbour, K.; Abida, O.; Mousavi Khadem, S.S.; Habibzadeh, S.; Sonawane, S.H.; Saeb, M.R.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; et al. Recent Advances in Aqueous Virus Removal Technologies. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Majumder, A.; Ghosal, P.S. Introduction to Modular Wastewater Treatment System and Its Significance. In Modular Treatment Approach for Drinking Water and Wastewater; Elsevier, 2022; pp. 81–106. ISBN 978-0-323-85421-4.
- Wen, X.; Meng, F.; Li, S. Analyzing the Effect of Public Private Partnership Mode on Sewage Treatment in China. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, A.-V.; Simon-Várhelyi, M.; Mihály, N.-B.; Cristea, V.-M. Data Driven Detection of Different Dissolved Oxygen Sensor Faults for Improving Operation of the WWTP Control System. Processes (Basel) 2021, 9, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntalaperas, D.; Christophoridis, C.; Angelidis, I.; Iossifidis, D.; Touloupi, M.-F.; Vergeti, D.; Politi, E. Intelligent Tools to Monitor, Control and Predict Wastewater Reclamation and Reuse. Sensors (Basel) 2022, 22, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynaert, E.; Nagappa, D.; Sigrist, J.A.; Morgenroth, E. Ensuring Microbial Water Quality for On-Site Water Reuse: Importance of Online Sensors for Reliable Operation. Water Research X 2024, 22, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D, N.S.; C, M.; R. Kshirsagar, P.; Tirth, V.; Islam, S.; Qaiyum, S.; B, S.; Al Duhayyim, M.; Waji, Y.A. IOT Based Smart Wastewater Treatment Model for Industry 4.0 Using Artificial Intelligence. Scientific Programming 2022, 2022, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.R.; Singh, P.K. Reuse-Focused Selection of Appropriate Technologies for Municipal Wastewater Treatment: A Multi-Criteria Approach. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 12505–12522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eseoglu, G.; Yapsakli, K.; Tozan, H.; Vayvay, O. A Novel Fuzzy Framework for Technology Selection of Sustainable Wastewater Treatment Plants Based on TODIM Methodology in Developing Urban Areas. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagklis, D.P.; Bampos, G. Tertiary Wastewater Treatment Technologies: A Review of Technical, Economic, and Life Cycle Aspects. Processes 2022, 10, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottinghaus, A.G.; Ferreiro, A.; Fishbein, S.R.S.; Dantas, G.; Moon, T.S. Genetically Stable CRISPR-Based Kill Switches for Engineered Microbes. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, D.; Kaushik, A.; Kumar, R.; Arya, A.; Santoyo, G.; Singh, V.K.; Kashyap, N.; Solanki, M.K.; Kumari, M.; Bhardwaj, N.; et al. Improving Plant Performance through Microbiome Manipulation: The Potential Role of Current Bioengineering Approaches. Bacteria 2025, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puyol, D.; Batstone, D.J.; Hülsen, T.; Astals, S.; Peces, M.; Krömer, J.O. Resource Recovery from Wastewater by Biological Technologies: Opportunities, Challenges, and Prospects. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.; Shah, K.J.; Lin, Y.-I.; Sun, Y.; Pan, S.-Y. Advances in Circular Bioeconomy Technologies: From Agricultural Wastewater to Value-Added Resources. Environments 2021, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Agarwal, S.; Agarwal Malik, R.; Kumar, G.; Pal, D.B.; Mandal, M.; Sarkar, A.; Bantun, F.; Haque, S.; Singh, P.; et al. Recent Advances in Microbial Engineering Approaches for Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Bioengineered 2023, 14, 2184518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Serrano, M.J.; Lakho, F.H.; Van Hulle, S.W.H.; Batlles-delaFuente, A. Life Cycle Cost Assessment and Economic Analysis of a Decentralized Wastewater Treatment to Achieve Water Sustainability within the Framework of Circular Economy. Oecon. Copernic. 2023, 14, 103–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, A.; Arora, P.; Prajapati, S.K. Occurrence, Fates and Potential Treatment Approaches for Removal of Viruses from Wastewater: A Review with Emphasis on SARS-CoV-2. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousazadeh, M.; Kabdaşlı, I.; Khademi, S.; Sandoval, M.A.; Moussavi, S.P.; Malekdar, F.; Gilhotra, V.; Hashemi, M.; Dehghani, M.H. A Critical Review on the Existing Wastewater Treatment Methods in the COVID-19 Era: What Is the Potential of Advanced Oxidation Processes in Combatting Viral Especially SARS-CoV-2? Journal of Water Process Engineering 2022, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleotu, C.; Matei, L.; Dragu, L.D.; Necula, L.G.; Pitica, I.M.; Chivu-Economescu, M.; Diaconu, C.C. Viruses in Wastewater-A Concern for Public Health and the Environment. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidweiler, D.; Peter, H.; Pramateftaki, P.; De Anna, P.; Battin, T.J. Unraveling the Biophysical Underpinnings to the Success of Multispecies Biofilms in Porous Environments. The ISME Journal 2019, 13, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Tabasi, Z.A.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.H.; Zhao, Y. Recent Advances in Functional Materials for Wastewater Treatment: From Materials to Technological Innovations. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samari-Kermani, M.; De Vries, E.T.; Schijven, J.F.; Raoof, A. A Closer Look at the Role of Biofilms in Water Filtration: Bridging Microscopic Insights with System Performance. Journal of Water Process Engineering 2024, 67, 106104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checconi, P.; De Angelis, M.; Marcocci, M.E.; Fraternale, A.; Magnani, M.; Palamara, A.T.; Nencioni, L. Redox-Modulating Agents in the Treatment of Viral Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunatha, L.; Rajashekara, H.; Uppala, L.S.; Ambika, D.S.; Patil, B.; Shankarappa, K.S.; Nath, V.S.; Kavitha, T.R.; Mishra, A.K. Mechanisms of Microbial Plant Protection and Control of Plant Viruses. Plants 2022, 11, 3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Perdrial, J.; Abbott, B.W.; Bernal, S.; Dupas, R.; Godsey, S.E.; Harpold, A.; Rizzo, D.; Underwood, K.; Adler, T.; et al. Temperature Controls Production but Hydrology Regulates Export of Dissolved Organic Carbon at the Catchment Scale. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 945–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baetge, N.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Fox, J.; Halsey, K.H.; Mojica, K.D.A.; Novoa, A.; Stephens, B.M.; Carlson, C.A. The Seasonal Flux and Fate of Dissolved Organic Carbon through Bacterioplankton in the Western North Atlantic. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 669883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berggren, M.; Guillemette, F.; Bieroza, M.; Buffam, I.; Deininger, A.; Hawkes, J.A.; Kothawala, D.N.; LaBrie, R.; Lapierre, J.-F.; Murphy, K.R.; et al. Unified Understanding of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Controls of Dissolved Organic Carbon Reactivity in Aquatic Ecosystems. Ecology 2022, 103, e3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xagoraraki, I.; Yin, Z.; Svambayev, Z. Fate of Viruses in Water Systems. J. Environ. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, A.M.; Adam, M.R.; Mohamad Kamal, S.N.E.A.; Jaafar, J.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ismail, A.F.; Aziz, F.; Yusof, N.; Bilad, M.R.; Mohamud, R.; et al. A Review of the Potential of Conventional and Advanced Membrane Technology in the Removal of Pathogens from Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asheghmoalla, M.; Mehrvar, M. Integrated and Hybrid Processes for the Treatment of Actual Wastewaters Containing Micropollutants: A Review on Recent Advances. Processes (Basel) 2024, 12, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Han, Q.; Ju, K.; Wei, D.; Sun, Y.; Wan, Q. Effects of Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT)and Packing Height on the Performanceof Homemade Ceramsite-Soil Constructed Wetlandfor Rural Domestic Wastewater Treatment. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 4845–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, C.K.; Morvannou, A.; Petitjean, A.; Nivala, J.; Molle, P. Hydraulic Characterization of a Hybrid Aerated Vertical and Horizontal Treatment Wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 206, 107301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulshreshtha, N.M.; Kumar, A.; Bisht, G.; Pasha, S.; Kumar, R. Usefulness of Organic Acid Produced by Exiguobacterium Sp. 12/1 on Neutralization of Alkaline Wastewater. ScientificWorldJournal 2012, 2012, 345101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monje, V.; Nobel, P.; Junicke, H.; Kjellberg, K.; Gernaey, K.V.; Flores-Alsina, X. Assessment of Alkaline Stabilization Processes in Industrial Waste Streams Using a Model-Based Approach. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 293, 112806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, I.N.; Ahammed, M.M. Granular Media Filtration for On-Site Treatment of Greywater: A Review. Water Science and Technology 2022, 86, 992–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Upadhyay, S.; Rani, A.; Sharma, P.K.; Rawat, J.M.; Rawat, B.; Prashant; Bhattacharya, P. Assessment of Pathogen Removal Efficiency of Vertical Flow Constructed Wetland Treating Septage. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 18703. [CrossRef]
- Rimoldi, S.G.; Stefani, F.; Gigantiello, A.; Polesello, S.; Comandatore, F.; Mileto, D.; Maresca, M.; Longobardi, C.; Mancon, A.; Romeri, F.; et al. Presence and Infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 Virus in Wastewaters and Rivers. Science of The Total Environment 2020, 744, 140911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Compte, A.; González, S.; Arnaldos, M.; Berlendis, S.; Courtois, S.; Loret, J.F.; Schlosser, O.; Yáñez, A.M.; Soria-Soria, E.; Fittipaldi, M.; et al. Elimination of SARS-CoV-2 along Wastewater and Sludge Treatment Processes. Water Research 2021, 202, 117435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamin, M.; Tsuji, S.; Hata, A.; Hara-Yamamura, H.; Honda, R. Selection of Surrogate Viruses for Process Control in Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Cashman, S.; Gaglione, A.; Mosley, J.; Weiss, L.; Ma, X.C.; Cashdollar, J.; Garland, J. Holistic Analysis of Urban Water Systems in the Greater Cincinnati Region: (1) Life Cycle Assessment and Cost Implications. Water Research X 2019, 2, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitby, G.E.; Lawal, O.; Ropic, P.; Shima, S.; Ferran, B.; Dussert, B. Uniform Protocol for Wastewater UV Validation Applications. Water Practice and Technology 2013, 8, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, S.; Lay, M.; Glasgow, G.; Tanner, C.; Craggs, R.; Northcott, G. Nature Based Solutions for Removal of Steroid Estrogens in Wastewater. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1437795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muoghalu, C.C.; Owusu, P.A.; Lebu, S.; Nakagiri, A.; Semiyaga, S.; Iorhemen, O.T.; Manga, M. Biochar as a Novel Technology for Treatment of Onsite Domestic Wastewater: A Critical Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama Aziz, K.H.; Fatah, N.M.; Muhammad, K.T. Advancements in Application of Modified Biochar as a Green and Low-Cost Adsorbent for Wastewater Remediation from Organic Dyes. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2024, 11, 232033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, L.; Yan, Z.; Xu, J.; Feng, L.; He, N.; Guo, M.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; et al. Recent Advances of CRISPR-Based Genome Editing for Enhancing Staple Crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1478398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, I.; Frantová, N.; Zouhar, J. A Sword or a Buffet: Plant Endomembrane System in Viral Infections. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1226498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Hu, T.; Wang, Y.; Lozano-Durán, R.; Yang, X.; Zhou, X. Two Viral Proteins Translated from One Open Reading Frame Target Different Layers of Plant Defense. Plant Commun. 2024, 5, 100788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Takaki, Y.; Yoshida-Takashima, Y.; Hiraoka, S.; Kurosawa, K.; Nunoura, T.; Takai, K. A Sequential One-Pot Approach for Rapid and Convenient Characterization of Putative Restriction-Modification Systems. mSystems 2023, 8, e00817-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, S.A.; Diggans, J.; Densmore, D.; Dai, J.; Knight, T.; Leproust, E.; Boeke, J.D.; Wheeler, N.; Cai, Y. Safety by Design: Biosafety and Biosecurity in the Age of Synthetic Genomics. iScience 2023, 26, 106165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.R.; Danciu, M.; Davenport, P.W.; Lakin, M.R.; Chappell, J.; Frow, E.K. A Bumpy Road Ahead for Genetic Biocontainment. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Wu, Y.; Sørensen, S.J.; Zhang, M.; Dai, K.; Gao, C.; Qu, C.; Huang, Q.; Cai, P. The Mitigation of Spatial Constraint in Porous Environments Enhances Biofilm Phylogenetic and Functional Diversity. Microbiome 2025, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckerstorfer, M.F.; Dolezel, M.; Engelhard, M.; Giovannelli, V.; Grabowski, M.; Heissenberger, A.; Lener, M.; Reichenbecher, W.; Simon, S.; Staiano, G.; et al. Recommendations for the Assessment of Potential Environmental Effects of Genome-Editing Applications in Plants in the EU. Plants 2023, 12, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, N.; Smith, A.; Smith, P.; Key, I.; Chausson, A.; Girardin, C.; House, J.; Srivastava, S.; Turner, B. Getting the Message Right on Nature-based Solutions to Climate Change. Global Change Biology 2021, 27, 1518–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, J.; Pereira, A.; Jefferies, L.; Kemp, A.H.; Isham, A. Nature-Based Interventions for Individual, Collective and Planetary Wellbeing: A Protocol for a Scoping Review. PLoS One 2025, 20, e0314591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, D.; Ward, S.; Sweetapple, C.; Astaraie-Imani, M.; Diao, K.; Farmani, R.; Fu, G. Reliable, Resilient and Sustainable Water Management: The Safe & SuRe Approach. Global Chall. 2017, 1, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerullis, M.; Pieruschka, R.; Fahrner, S.; Hartl, L.; Schurr, U.; Heckelei, T. From Genes to Policy: Mission-Oriented Governance of Plant-Breeding Research and Technologies. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1235175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyam, S.; Patra, S. Innovations and Challenges in Adsorption-Based Wastewater Remediation: A Comprehensive Review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wu, X.; Gong, B.; Lü, G.; Li, J.; Gao, H. Review of the Mechanisms by Which Transcription Factors and Exogenous Substances Regulate ROS Metabolism under Abiotic Stress. Antioxidants (Basel) 2022, 11, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, G.; Gangola, S.; Bhatt, P.; Rafatullah, M. Editorial: Potential of the Plant Rhizomicrobiome for Bioremediation of Contaminants in Agroecosystems. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1397360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Dong, C.; Sreeprasad, T.S.; Xia, Z. Biomimetic Self-Cleaning Surfaces: Synthesis, Mechanism and Applications. J. R. Soc. Interface. 2016, 13, 20160300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumanath, S.; Pillai, R.; Borg, M.K. Contaminant Removal from Nature’s Self-Cleaning Surfaces. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 4234–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, M. Prediction of River Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Based on Multi-Source Data and Various Machine Learning Coupling Models. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0319256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.S.; Martins, G.; Oliveira, P.; Fernandes, B.; Ferreira, E.C.; Alves, M.M.; Lopes, F.; Pereira, M.A.; Novais, P. A Review of Computational Modeling in Wastewater Treatment Processes. ACS ES T Water 2024, 4, 784–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClary-Gutierrez, J.S.; Aanderud, Z.T.; Al-Faliti, M.; Duvallet, C.; Gonzalez, R.; Guzman, J.; Holm, R.H.; Jahne, M.A.; Kantor, R.S.; Katsivelis, P.; et al. Standardizing Data Reporting in the Research Community to Enhance the Utility of Open Data for SARS-CoV-2 Wastewater Surveillance. Environ. Sci. (Camb.) 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, E.; Tian, C.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, C.; Tian, L. Current Studies of the Effects of Drought Stress on Root Exudates and Rhizosphere Microbiomes of Crop Plant Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, G.; Ahmed, Z.; Eldin, S.M.; Ali, B.; Bawazeer, S.; Usman, M.; Iqbal, R.; Neupane, D.; Ullah, A.; Khan, A.; et al. Biochar-Soil-Plant Interactions: A Cross Talk for Sustainable Agriculture under Changing Climate. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1059449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepal, J.; Ahmad, W.; Munsif, F.; Khan, A.; Zou, Z. Advances and Prospects of Biochar in Improving Soil Fertility, Biochemical Quality, and Environmental Applications. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes Méndez, D.; Pérez-Sánchez, M.; Sánchez-Romero, F.J.; Coronado-Hernández, O.E. Assessment of the Effectiveness of Green Infrastructure Interventions to Enhance the Ecosystem Services in Developing Countries. Urban Sci. 2025, 9, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
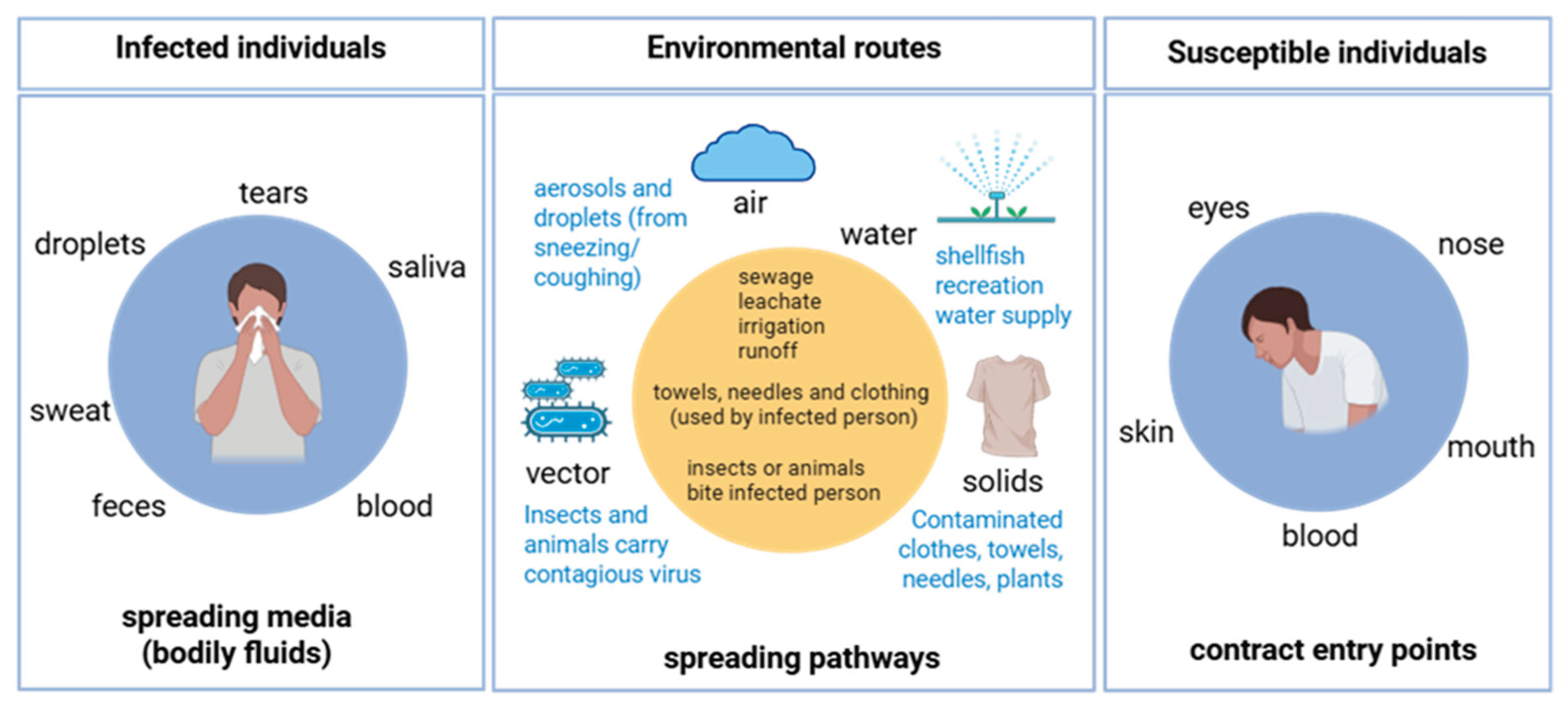
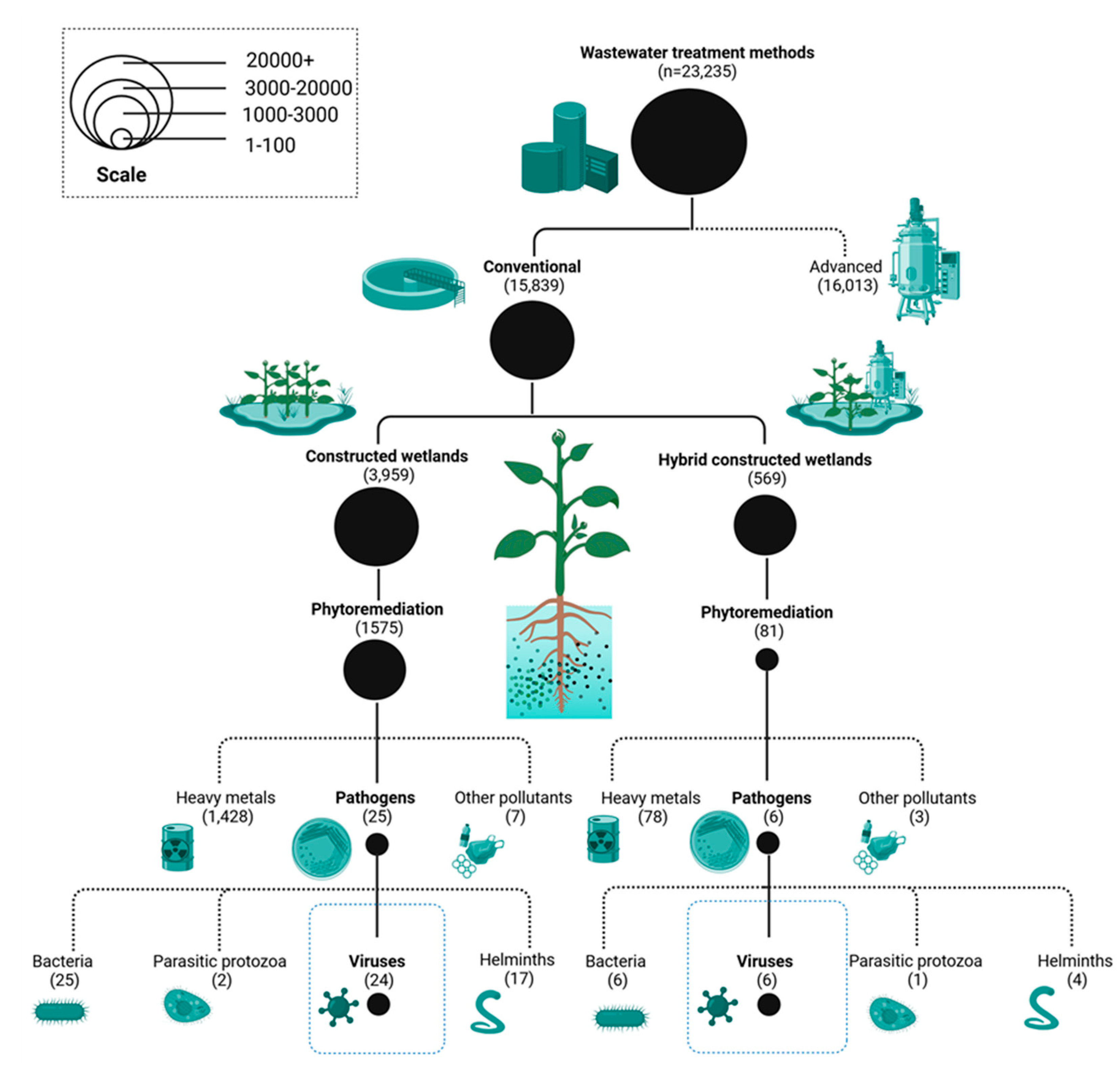
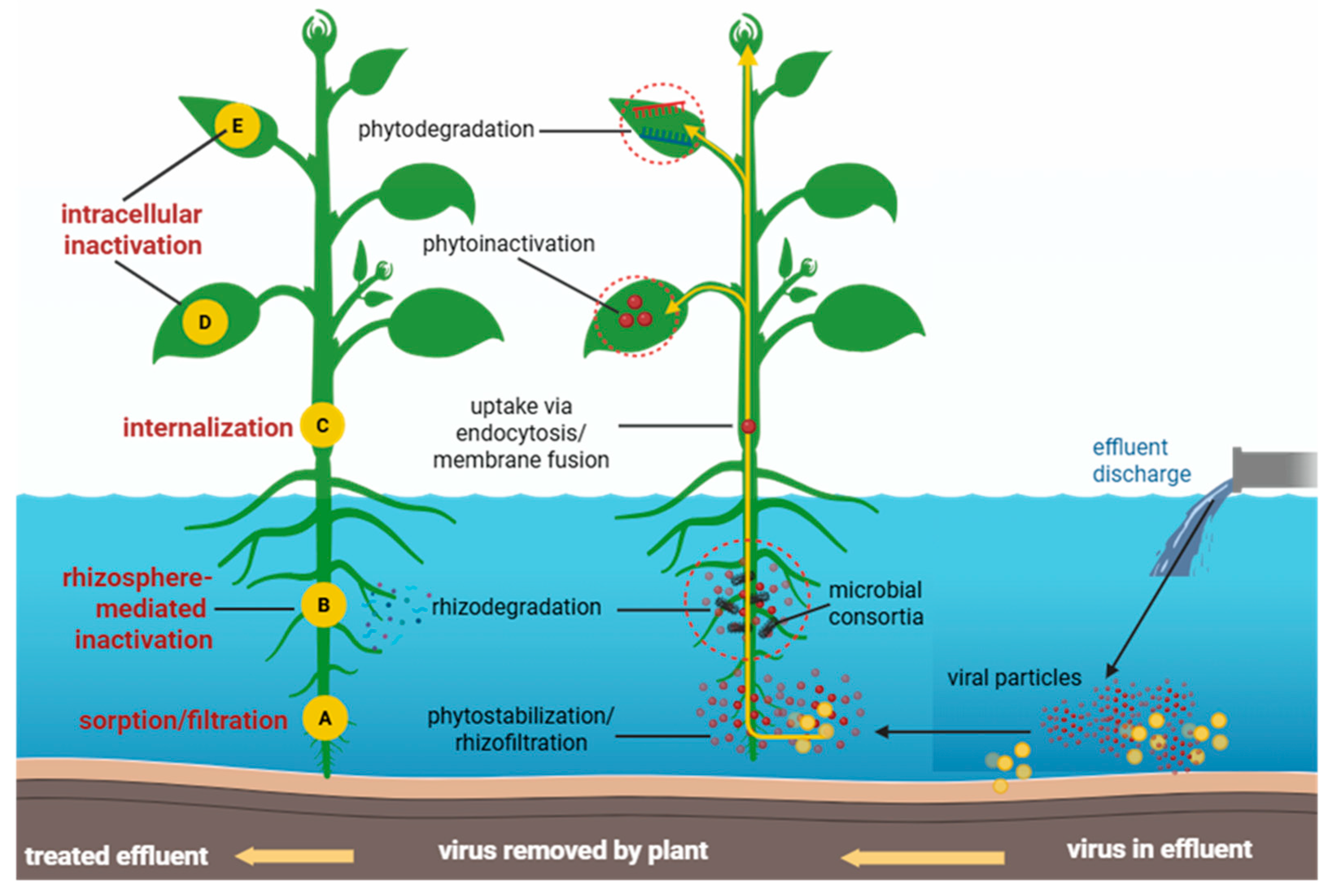
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





