1. Introduction
In the Medical Industry, Reading Disability (Dyslexia) identification is a major problem to detect, because there are multiple reasons which causes this reading disability to the people.
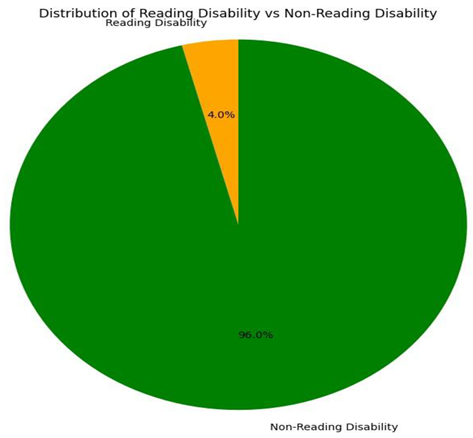
The reading disability leads to lack of reading words, color co-ordination complexity, mismatching and assumptions of words. Dyslexia are also associated with the human eyes (vision power), majority of the people with low vision power are affected mainly and majority of the school Students from the age group of 5-12 are affected by reading disability, which can lead to lack of interest in studies and unhealthy lifestyle among the people.
In this digital era with the help of Machine Learning, predicting the accuracy of Dyslexia in the people has become possible. Identifying the causes and symptoms which lead to dyslexia helps medical professionals and people to predict and provide the necessary medications and treatments in the earlier stage and helps them to lead a better life.
Various algorithms are used in machine learning to fetch accuracy to predict the person affected by reading disability. Data are collected in different forms like structured, unstructured and semi structured data, these data can be used for training and testing the data. To process, analyze, preprocess and get the output from the collected data and there are different types of algorithms applied to these data, while using these algorithms there are time complexity and space complexity involved, which involves the time and memory that is taken by the algorithm to produce the result in a faster way and store the result.
There is various research under process to get a higher accuracy by reducing the time and space complexity with the various algorithms. But there is still a lack of best results among the different algorithms and data, there are new algorithms which are under development to provide the results faster.
By opting and placing various Machine Learning algorithms to the different types of data, the highest accuracy can be achieved for prediction. To store the data which is collected will be stored in the cloud to reduce the physical storage space and to maximize the availability of the resources so that the resources can be accessed anywhere at any time.
2. Literature Review
There is much research that is conducted, and various results have been obtained by different research patterns. The varying results include the time and space complexity of prediction the Dyslexia. The research papers are got from various research and journal portals such as Scopus Index, ResearchGate, Academia and Google Scholar.
The research methodologies conducted by various research practitioners include major machine learning algorithms Decision Tree, KNN, SVM, Random Forest and logistic regression, which are used for getting better output. The first step is collecting data from various resources for testing the data, then the actual data is gathered from the medical industry, Google Forms and from various other resources to compare with the testing data to get the better results with less time and space complexity.
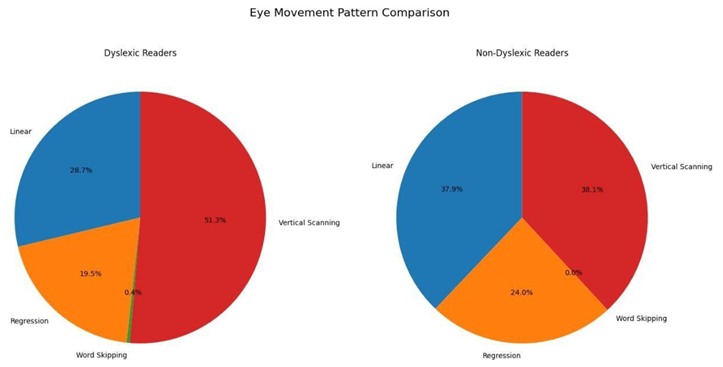
Eye co-ordination data is used to analyze the speed of the people’s view toward the words and pictures of various formats. The patterns which they can identify easier and the difficult patterns which take a long time for analyzing the data. Both sides angles of the eyes (left and right) are included in the study for getting better results.
While collecting the data, noisy data was also present, so the data has been cleaned and preprocessed into a particular format for the next steps. There was mostly positive data that was also presented with less accuracy for dyslexia.
The algorithms are implemented using Python with different development environments by analyzing the CSV files and responses from the people to predict the Dyslexia levels. There are algorithms which have performed well by providing the best accuracy rates with lower time and space complexity and vice versa.
3. Methodology
The data is collected from a variety of resources for testing the Pattern of Eye movements, reading speed, writing speed, word recognition, image recognition and speech recognition data are utilized for getting better accuracy. Developed the Python code using multiple built-in libraries which includes a variety of algorithms to analysis and produce better output from the data.
Scikit-learn is a popular machine learning library used for performing the analysis and prediction from testing and training data. The Scikit-learn provides a simple and efficient API for data processing, evaluation and choosing the right model. NumPy is a foundational library which is built using the C language, the library supports multi-dimensional arrays also for the larger datasets the library ensures high performance. The NumPy library is a dependency for the libraries like SciPy and Pandas. Pandas library used for reading the data from CSV files better for cleaning, filtering and aggregation tools. The Pandas library is better for preprocessing exploratory data analysis. Matplotlib Library used for plotting and visualization of the results and better understanding of the results, the Matplotlib library is used to integrate with the NumPy, Pandas and with Jupyter notebooks for the interactive workflows.
KNN algorithm – KNN algorithm also known as a Lazy learning algorithm is used for performing the classification and regression tasks, it is a simple and supervised learning algorithm. The algorithm works well with the class-based dataset where values are pre-defined and KNN algorithm does not work well with the large datasets because the algorithm works on a points-based method.
Decision Tree algorithm – The Tree like structured and a supervised learning algorithm where the input is split into multiple nodes and each of the leaf nodes represents the result, the decision tree algorithm produces good results for the large datasets but, not used for the small datasets due to the splits and threshold values.
Random Forest algorithm – A supervised learning algorithm used for performing the classification and regression task, developed by combining multiple Decision Tree Algorithms for providing the faster results, the algorithm uses bagging technique, the algorithm can be used for categorial and numerical data, the limitation of random forest algorithm is as the number of trees grows the complexity also increases.
XGBoost Classifier algorithm – The fast and efficient algorithm provides better performance for the tabular data. The sequential trees are created where the tree corrects the error of the previous trees. The algorithm is used variety of Machine Learning areas, it implements the loss function using the gradient descent.
Gradient Boosting Classifier algorithm – The base model for the XGBoost algorithm, builds the decision tree, implements the boosting framework loss function using the gradient descent. This algorithm is very effective for the structured data and involves complexity for hyperparameter tuning.
RNN algorithm – A artificial neural network algorithm used in the natural language processing, speech and time series tasks, implements memory functions for retaining the previous outputs but, struggles with the vanishing and exploding gradients.
CNN algorithm – The CNN algorithm is a artificial neural network algorithm that implements different layers for minimizing the dimensions and capturing the important layers, widely used in the natural language processing and computer vision tasks.
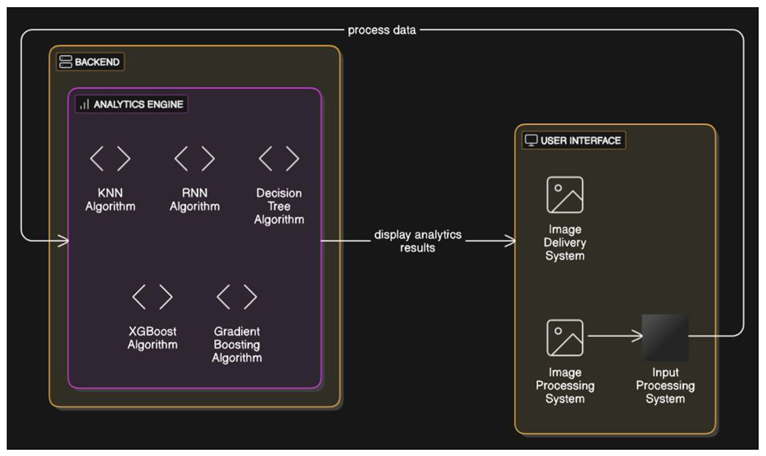
Frontend Technologies – The user interactivity for the websites are widely built using the HTML [for the skeleton structure], CSS [used for styling the webpages] and JavaScript [it is used for the functionality and navigation purposes within the webpage].
IV. Results and Discussion
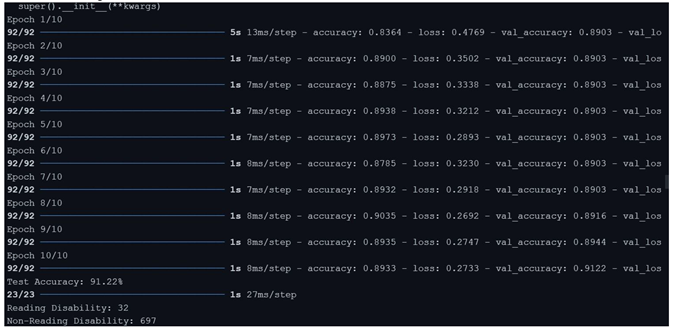
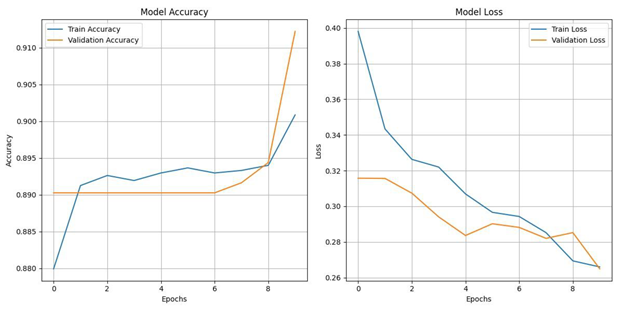
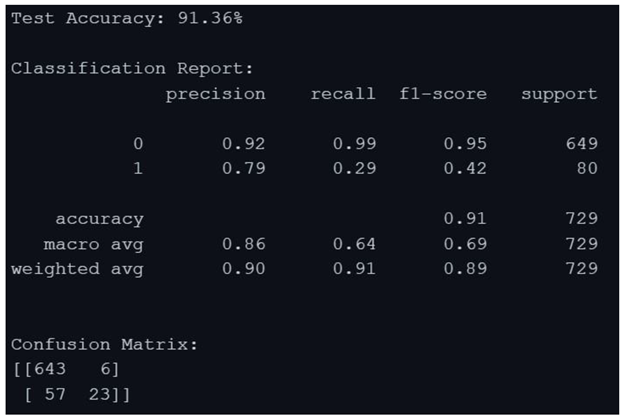
By applying various machine learning algorithms to the data, which was collected from various resources, the results vary depending on the time, speed, space and memory complexities.
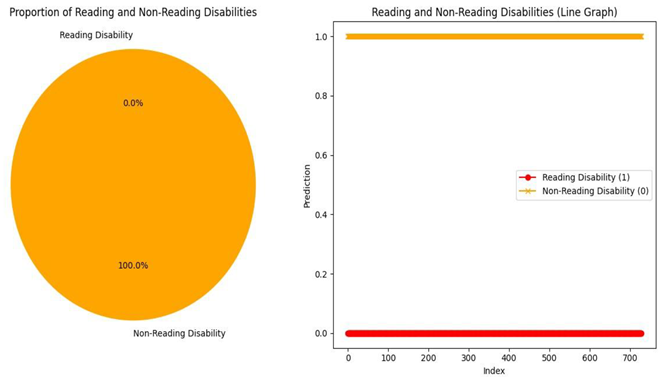
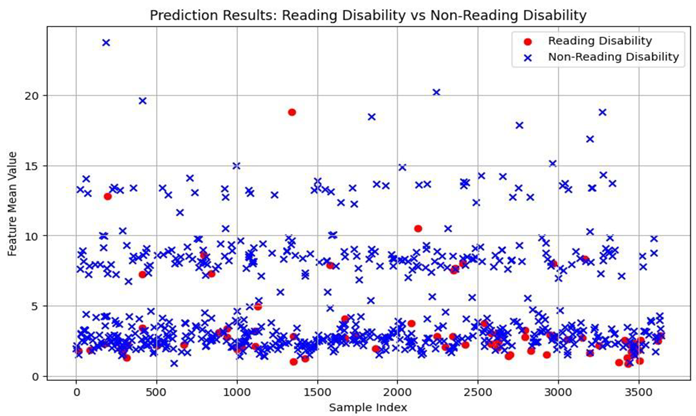
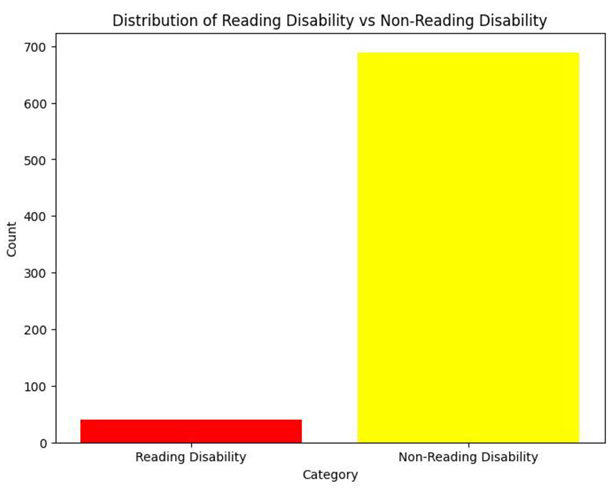
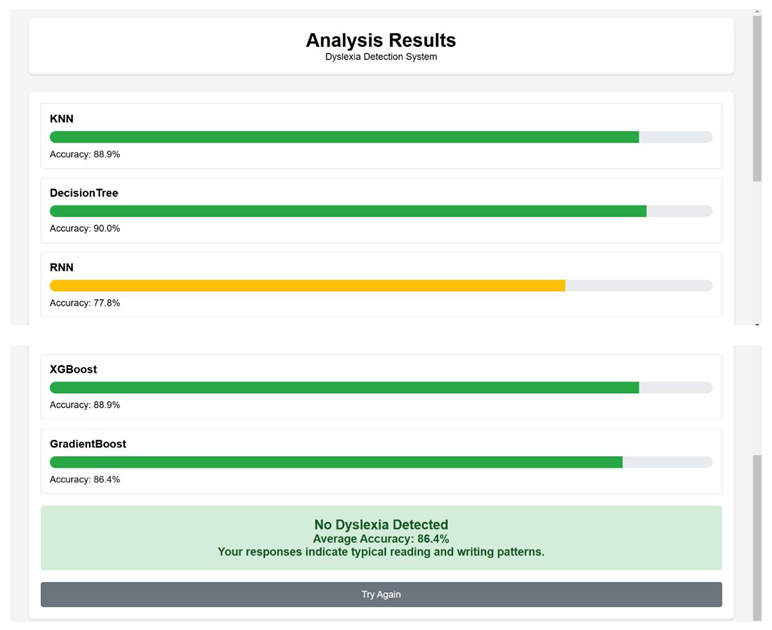
The following pictures represents the results of processed data.
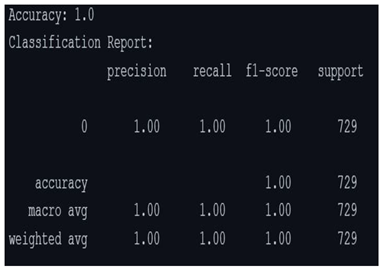
KNN algorithm
Decision Tree algorithm
RNN algorithm
XG Boost Classifier algorithm
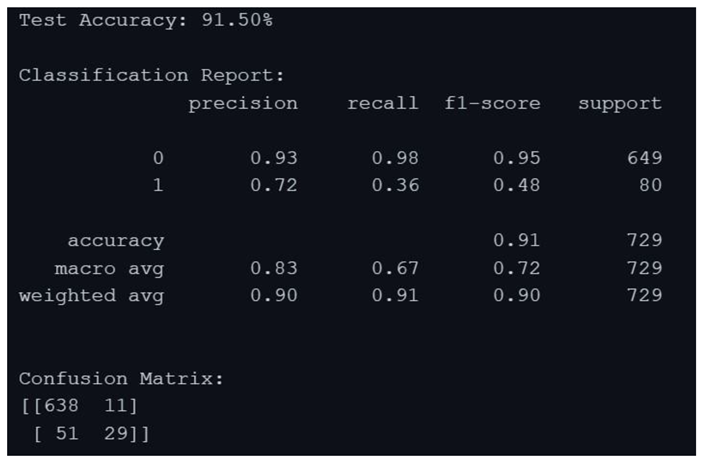
Gradient Boosting Classifier algorithm
CNN algorithm
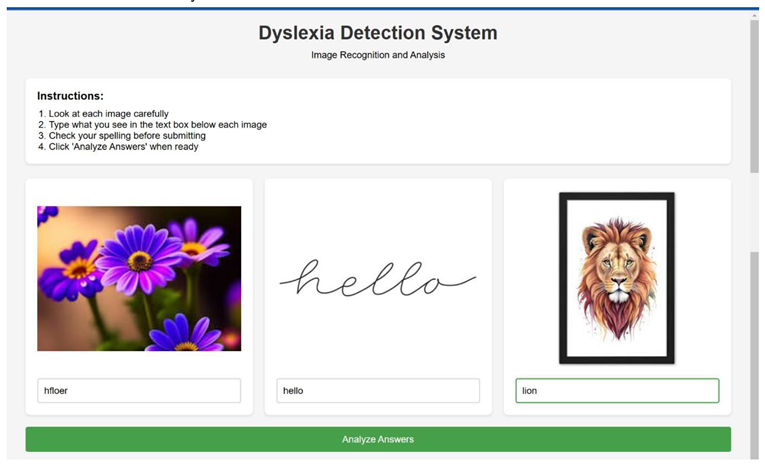
Real Time Data analysis website
By analysing the above results, the Gradient Boosting Classifier algorithm produced the result of 91.50% and XGBoost Classifier algorithm produced a result of 91.36% the two algorithms work well with the data, due to the overfitting of the data to KNN algorithm the result produced was 100%, but there were some misses in the data. CNN algorithm has been implemented on the eye co-ordination data, the algorithm helped in finding the eye patterns of Dyslexia affected people and non-dyslexia affected people. There were epochs and space complexities present in the algorithms which made the result processing slower compared to Gradient Boosting Classifier algorithm and XGBoost Classifier algorithm.
While implementing the algorithms on the website which takes inputs from the real user and produces the results, the KNN and XGBoost Classifier algorithm performance were good compared to other algorithms. The eye co-ordination for the real-time analysis has not been implemented.
In the future enhancements the real-time website will be developed with the advanced features to help the medical practitioners to get the results faster from the people.
5. Conclusion
Dyslexia a common problem with a variety of sub-domains present, by implementing the Machine Learning with low latency and high accuracy the data can be processed faster by the medical professionals to predict the symptoms of the Dyslexia affected people by adapting variety of testing strategies. By implementing the GradientBoostingClassifier and XGBoostClassifier the latency and accuracy has been attained more than 91% with a very less latency level. The testing method used in the algorithm clearly defines the variety of results got using the various algorithms by taking the user input in the real-time, in the future ahead the accuracy will be improved to more than 95% to provide a better result with low latency will be developed to identify the people affected with Dyslexia so that medication and training will be provided to defend against dyslexia.
References
- PREDICTION OF DYSLEXIA USING MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHMS M. Mahalakshmi1, Dr.K.Merriliance2 Department of Computer Applications, Sarah Tucker College, Thirunelveli-7.
- Dyslexia Prediction using Machine Learning Isaac Punith Kumar1 Vidya Vikas Institute of Engineering & Technology, Mysore Hemanth Kumar B N2 Vidya Vikas Institute of Engineering & Technology, Mysore.
- Dyslexia Prediction Pallavi Akhade1, Prof Sana Shaikh2, Aditi Ghaitade3, Tanuja Mukane4, Dipti Patil5 1,2,3,4,5Department of Information Technology/G. S. Moze College of Engineering/Savitribai Phule Pune University/India.
- PROJECT ON DYSLEXIA PREDICTION USING MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHMS Abhishek M*1, Hemanth Kumar BN*2 *1,2Department Of MCA, VVIET, Mysore, Karnataka, India.
- Dyslexia Detection: Using Decision Tree Algorithm Rishi Jain, Pranav Patel, Tanaya Jadhav, Kimaya Joshi, Ishita Jasuja Department of Information Technology (IT) Vishwakarma Institute of Technology, Pune, 411037, Maharashtra, India.
- Dyslexia Prediction Using Machine Learning Algorithms – A Review G. Vanitha1, M. Kasthuri2.
- 1Research Scholar, Bishop Heber College (Autonomous), Tiruchirappalli- 620017.
- 2Assistant professor, Department of Computer Science, Bishop Heber College (Autonomous).
- Tiruchirappalli-620017, Affiliated to Bharathidasan University.
- Predicting Dyslexia with Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Review of Feature Selection, Algorithms, and Evaluation Metrics Velmurugan S[0000−0003−1956−3674] Department of Electrical Engineering, Indian Institute of technology Madras Chennai, India.
- Integrating oversampling and ensemble-based machine learning techniques for an imbalanced dataset in dyslexia screening tests Shahriar Kaisara,∗, Abdullahi Chowdhuryb a Department of Information Systems and Business Analytics, RMIT University, Australia b Faculty of Engineering, Computer and Mathematical Sciences, University of Adelaide, Australia.
- An ensemble features aware machine learning model for detection and staging of dyslexia Sailaja Mulakaluri1,2 , Girisha Gowdra Shivappa2 1Department of Computer Science, St. Francis De Sales College, Bengaluru, India 2Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Dayananda Sagar University, Bengaluru, India.
- A machine learning approach for dyslexia detection using Turkish audio records TUĞBERK TAŞ MUHAMMED ABDULLAH BÜLBÜL ABAS HAŞİMOĞLU YAVUZ MERAL YASİN ÇALIŞKAN GUNAY BUDAGOVA, and MÜCAHİD KUTLU.
- An Effective Feature Selection and Classification Technique based on Ensemble Learning for Dyslexia Detection Tabassum Gull Jan1(corresponding author), Sajad Mohammad Khan2 1 PhD Scholar, Department of Computer Science, University of Kashmir, Srinagar (J&K) 2 Senior Scientist, Department of Computer Science, University of Kashmir, Srinagar (J&K).
- Fast Algorithm for Dyslexia Detection Boris Nerusil1, Jaroslav Polec1 and Juraj Skunda1 1 Institute of Multimedia ICT, Slovak University of Technology in Bratislava, Slovakia.
- An Efficient Machine Learning Model for Prediction of Dyslexia from Eye Fixation Events A. Jothi Prabha1*, R. Bhargavi2 and B. Harish3.
- Machine learning and deep learning performance in classifying dyslexic children’s electroencephalogram during writing Ahmad Zuber Ahmad Zainuddin1,2,3,4, Wahidah Mansor1,2,3, Khuan Yoot Lee2,3, Zulkifli Mahmoodin4 1Microwave Research Institute, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah Alam, Malaysia 2School of Electrical Engineering, College of Engineering, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah Alam, Malaysia 3Computational Intelligence Detection RG, Health and Wellness ReNEU, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah Alam, Malaysia 4Medical Engineering Technology Section, Universiti Kuala Lumpur British Malaysian Institute, Malaysia.
- A Study on different Classification Models for predicting Dyslexia Vani Chakraborty Department of Computer Science[PG], Kristu Jayanti College.
- Optimized k-nearest neighbours classifier based prediction of epileptic seizures Himayavardhini Jagath Prasad1, Roji Marjorie S.2 1Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Saveetha School of Engineering, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences (SIMATS), Chennai, India 2Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, SRM Institute of Science and Technology (SRMIST), Kattankulathur, Chennai, India.
- Medical Health Big Data Classification Based on KNN Classification Algorithm Wenchao Xing 1, Yilin Bei2* 1.School of Primary education;JiNing University; Qufu Shandong; 273100; China 2. School of Information Science and Technology; TaiShan University; Taian Shandong;271000; China.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).