Submitted:
05 November 2025
Posted:
06 November 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methodology
Patients
Data Collection
TARE Procedure
Statistical Analysis
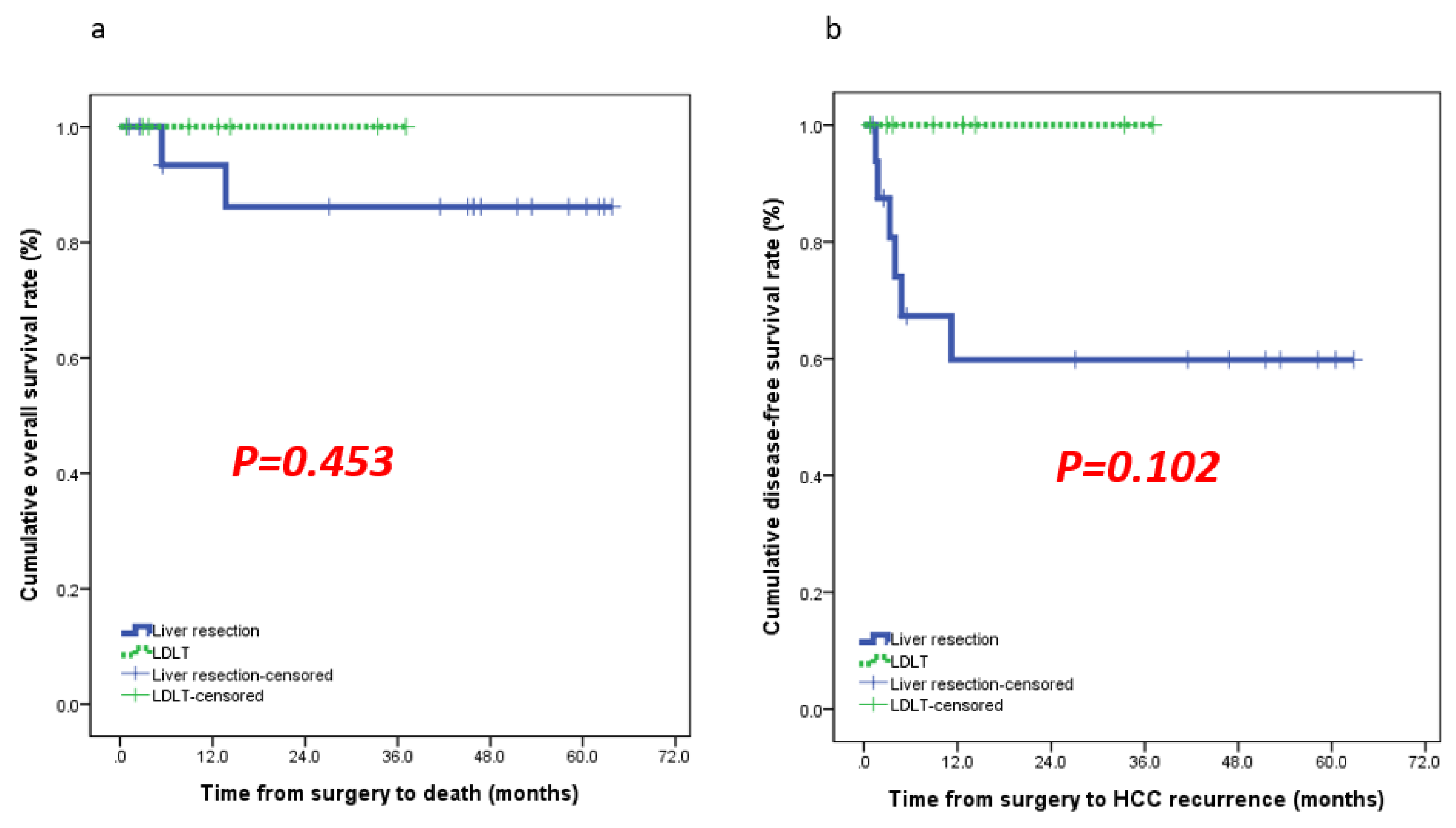
Result
Baseline Characteristics
Pre-Operative Factors
Pathology
TARE
Outcomes
Discussion
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations:
| HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| TARE | Transarterial Radioembolization |
| LDLT | Living Donor Liver Transplantation |
| TACE | Transarterial Chemoembolization |
| RFA | Radiofrequency Ablation |
| FLR | Future Liver Remnant |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists |
| AFP | Alpha-Fetoprotein |
| PIVKA-II | Protein Induced by Vitamin K Absence-II |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| LFT | Liver Function Test |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| DFS | Disease-Free Survival |
| CAP | Controlled Attenuation Parameter |
| HBV | Hepatitis B Virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C Viru |
| EBL | Estimated Blood Loss |
| TTS | TIME TO SURGERY |
| TTR | TIME TO RECURRANCE |
References
- D. Y. Kim and K. H. Han: Epidemiology and surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer. 2012, 1:2-14.
- J. M. Kim, C. H. Kwon, J. W. Joh et al.: Effectiveness of locoregional therapy before living donor liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who meet the Milan criteria. Transplant Proc. 2012, 44:403-8.
- Y. Bekki, A. Mahamid, S. Lewis et al.: Radiological and pathological assessment with EOB-MRI after Y90 radiation lobectomy prior to liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB (Oxford). 2022, 24:2185-2192. [CrossRef]
- V. Lopez-Lopez, K. Miura, C. Kuemmerli et al.: Selecting the Appropriate Downstaging and Bridging Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What Is the Role of Transarterial Radioembolization? A Pooled Analysis. Cancers (Basel). 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- H. Nebelung, T. Wolf, S. Bund et al.: Radioembolization versus portal vein embolization for contralateral liver lobe hypertrophy: effect of cirrhosis. Abdominal Radiology. 2021, 46:4046-4055. [CrossRef]
- H. C. Kim: Radioembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2017, 23:109-114. [CrossRef]
- A. Shehta, J. M. Lee, K. S. Suh et al.: Bridging and downstaging role of trans-arterial radio-embolization for expected small remnant volume before liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2020, 24:421-430. [CrossRef]
- M. Tabone, A. Calvo, N. Russolillo et al.: Downstaging unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma by radioembolization using 90-yttrium resin microspheres: a single center experience. Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. 2019, 11:84-90. [Online]. Available: https://jgo.amegroups.org/article/view/29381.
- T. Baker, P. Tabrizian, I. Zendejas et al.: Conversion to resection post radioembolization in patients with HCC: recommendations from a multidisciplinary working group. HPB. 2022, 24:1007-1018. [CrossRef]
- L. Crocetti, E. Bozzi, P. Scalise et al.: Locoregional Treatments for Bridging and Downstaging HCC to Liver Transplantation. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- F. Y. Yao, L. Ferrell, N. M. Bass et al.: Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: expansion of the tumor size limits does not adversely impact survival. Hepatology. 2001, 33:1394-403. [CrossRef]
- M. Reig, A. Forner, J. Rimola et al.: BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J Hepatol. 2022, 76:681-693. [CrossRef]
- J. Lindemann, J. Yu, and M. M. B. Doyle: New horizons in liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. S Afr J Surg. 2024, 62:8-12.
- V. Mazzaferro, E. Regalia, R. Doci et al.: Liver transplantation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1996, 334:693-9. [CrossRef]
- W. H. She and T. T. Cheung: Bridging and downstaging therapy in patients suffering from hepatocellular carcinoma waiting on the list of liver transplantation. Translational Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2016, 1. [Online]. Available: https://tgh.amegroups.org/article/view/3569.
- K. K. Lee, D. G. Kim, I. S. Moon et al.: Liver transplantation versus liver resection for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2010, 101:47-53. [CrossRef]
- S. Tamura, Y. Sugawara, and N. Kokudo: Living donor liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: the Japanese experience. Oncology. 2011, 81 Suppl 1:111-5. [CrossRef]
- E. Tsochatzis, E. Fatourou, rsquo et al.: Transarterial chemoembolization and bland embolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 2014, 20:3069-3077. [CrossRef]
- M. Ravaioli, G. L. Grazi, G. Ercolani et al.: Partial necrosis on hepatocellular carcinoma nodules facilitates tumor recurrence after liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2004, 78:1780-6. [CrossRef]
- K. Sasaki, L. I. Ruffolo, M. H. Kim et al.: The Current State of Liver Transplantation for Colorectal Liver Metastases in the United States: A Call for Standardized Reporting. Ann Surg Oncol. 2023, 30:2769-2777. [CrossRef]
- S. Tzedakis, A. Sebai, H. Jeddou et al.: Resection Postradioembolization in Patients With Single Large Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ann Surg. 2023, 278:756-762. [CrossRef]
- T. Baker, P. Tabrizian, I. Zendejas et al.: Conversion to resection post radioembolization in patients with HCC: recommendations from a multidisciplinary working group. HPB (Oxford). 2022, 24:1007-1018. [CrossRef]
- X. Wu, A. Kwong, M. Heller et al.: Cost-effectiveness analysis of interventional liver-directed therapies for downstaging of HCC before liver transplant. Liver Transpl. 2024, 30:151-159. [CrossRef]
- H. Bismuth, P. E. Majno, and R. Adam: Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 1999, 19:311-22. [CrossRef]
- T. Shimamura, N. Akamatsu, M. Fujiyoshi et al.: Expanded living-donor liver transplantation criteria for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma based on the Japanese nationwide survey: the 5-5-500 rule - a retrospective study. Transpl Int. 2019, 32:356-368. [CrossRef]
- A. Bharat, D. B. Brown, J. S. Crippin et al.: Pre-liver transplantation locoregional adjuvant therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma as a strategy to improve longterm survival. J Am Coll Surg. 2006, 203:411-20. [CrossRef]
- Y. X. Gao, Q. Q. Ning, P. X. Yang et al.: Recent advances in recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. World J Hepatol. 2023, 15:460-476. [CrossRef]
- W. Abdelhamed and M. El-Kassas: Hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence: Predictors and management. Liver Research. 2023, 7:321-332. [CrossRef]
- Y. Takahashi, Y. Nishimoto, T. Matsuura et al.: Surgical complications after living donor liver transplantation in patients with biliary atresia: a relatively high incidence of portal vein complications. Pediatr Surg Int. 2009, 25:745-51. [CrossRef]
- U. Cillo and L. Carlis, Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery Interplay of Technical and Theoretical Aspects: Interplay of Technical and Theoretical Aspects. 2020.
- E. Giustiniano, F. Nisi, L. Rocchi et al.: Perioperative Management of Complex Hepatectomy for Colorectal Liver Metastases: The Alliance between the Surgeon and the Anesthetist. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- J. Figueras, E. Jaurrieta, C. Valls et al.: Resection or transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients: outcomes based on indicated treatment strategy. J Am Coll Surg. 2000, 190:580-7. [CrossRef]
- Y. Jiang, X. Dong, Y. Zhang et al.: Navigating the complexities: challenges and opportunities in conversion therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Clinical and Experimental Medicine. 2025, 25:169. [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Surgical Resection | LDLT | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n=17) | (n=8) | ||
| Sex (Male) | 16 (94.1%) | 6 (75.0%) | 0.231 |
| Age (Years) | 61 (37-78) | 57 (41-71) | 0.673 |
| BMI (kg/m²) | 25.3 (19.5-32.1) | 22.3 (16.1-29.8) | 0.673 |
| WBC (×10⁹/L) | 5,020 (1,930-13,100) | 5,045 (1,710-13,010) | 1.000 |
| NLR | 0.40 (0.09-1.01) | 0.31 (0.06-0.59) | 0.673 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.5 (9.7-15.9) | 12.1 (6.5-17.0) | 1.000 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.6 (0.2-1.4) | 2.9 (0.3-20.8) | 0.081 |
| AST (U/L) | 27 (15-62) | 33 (18-300) | 0.389 |
| ALT (U/L) | 20 (9-69) | 26 (12-140) | 0.411 |
| INR | 1.01 (0.89-1.12) | 1.16 (0.96-1.45) | 0.010 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.78 (0.61-1.68) | 0.74 (0.50-2.37) | 0.673 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 0.47 (0.09-6.85) | 0.19 (0.03-6.76) | 0.637 |
| Time from TARE to surgery (months) | 8.9 (5.6–34.0) | 10.7 (5.8–29.2) | 0.411 |
| Radiation lobectomy | 5 (29.4%) | 0 (0%) | 0.140 |
| Scheduled surgery | 8 (47.1%) | 2 (25.0%) | 0.402 |
| Initial AFP (ng/mL) | 7.8 (1.3–2,751) | 3.6 (2.4–21.0) | 0.042 |
| Initial PIVKA-II (mAU/mL) | 941 (19–49,984) | 15 (9–189) | 0.002 |
| Preoperative AFP (ng/mL) | 4.3 (2.4–149.3) | 3.7 (1.6–145.0) | 0.234 |
| Preoperative PIVKA-II (mAU/mL) | 40 (14–486) | 50 (18–28,293) | 1.000 |
| ASA 1 2 3 |
0 17(100%) 0 |
1(12.5%) 2(25%) 5(62.5%) |
| Tumour & Pathology Features | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Surgical resection | LDLT | p-value |
| (n=17) | (n=8) | ||
| Maximum tumor size (cm) | 4.2 (1.5–12.5) | 4.5 (1.0–16.2) | 1.000 |
| Tumor number (solitary) | 14 (82.4%) | 2 (25.0%) | 0.012 |
| Tumor grade III | 1 (9.1%) | 0 (0%) | 0.539 |
| Microvascular invasion | 4 (23.5%) | 6 (75.0%) | 0.028 |
| Serosal involvement | 1 (5.9%) | 2 (25.0%) | 0.231 |
| Intrahepatic metastasis | 3 (17.6%) | 6 (75.0%) | 0.010 |
| Tumor necrosis | |||
| Total | 9 (52.9%) | 5 (62.5%) | |
| 5 0–99% | 7 (41.2%) | 1 (12.5%) | 0.171 |
| <50% | 1 (5.9%) | 2 (25.0%) | |
| Follow-up duration(months) | 45.8 (1.1–63.8) | 10.8 (0.8–37.1) | 0.030 |
| Tumor Necrosis (T/N) | Number of Cases (n) | Mean T/N Ratio | Radiation Dose (Gy) | Complications Observed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Near-complete / Complete | 14 | 7.8 | 462 ± 150 | None reported; mild LFT elevation in a few cases, Radiation pneumonia |
| Partial | 8 | 4.9 | 270 ± 120 | Mild abdominal pain in 2 cases, otherwise none |
| Minimal / Poor | 3 | 2.5 | 122 ± 50 | None reported |
| Pt. No | TARE Reason | TARE Side Effects | Procedure | Initial | Pre-op | Y-90 Dose (GBq) | Tumour Radiation Dose (Gy) | TTS | TTR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFP | PIVKA-II | AFP | PIVKA-II | ||||||||
| 1 | AAA | Renal dysfunction, myalgia | TARE | 1.3 | 13235 | 8.1 | 394 | Multiple infusions | N/A | 7.1 | 10.3 |
| 2 | Satellite nodules | none | TARE | 17.3 | 193 | 149.3 | 25 | N/A | N/A | 10.8 | 12.2 |
| 3 | Satellite nodules, small remnant liver volume | LFT elevation, Fever | TARE | 5.5 | 30324 | 4.3 | 20 | Resin-type | N/A | 6.1 | 68.8 |
| 4 | Satellite nodule | none | TACE + TARE | 50.4 | 49984 | 2.6 | 113 | 3.7 | 170 | 8 | 12 |
| 5 | small remnant volume | nausea, vomiting, poor oral intake | Selective TARE | 1.3 | 105 | 2.4 | 32 | 36 | N/A | 6.3 | 66.7 |
| 6 | Satellite nodules, small remnant liver volume, stomach cancer | nausea, vomiting, pain | TARE | 2751 | 941 | 3.8 | 33 | 2.8 | 413.69 | 10.0 | 68.1 |
| 7 | small remnant volume | Generalized abdominal discomfort | TARE + cTACE | 5.5 | 1242 | 6 | 40 | Resin-type | N/A | 5.6 | 58.9 |
| 8 | PVTT, irregular mass, satellite nodules | none | TARE Segmentectomy | 3 | 1357 | 3 | 184 | Glass-type | N/A | 6.7 | 8.5 |
| 9 | Two HCC | none | Selective TARE | 8.6 | 1460 | 6.9 | 31 | 4.62 | 344 _ 120 | 11.5 | 62.9 |
| 10 | Satellite nodule | none | Right Lobar TARE | 16.3 | 709 | 6.8 | 56 | 4.42 | 120 _ 240 | 7.1 | 53.8 |
| 11 | Infiltrative HCC with PVTT | none | TARE | 16.9 | 7231 | 2.5 | 63 | 3 + 10 | 120 _ 240 | 34.0 | 38.8 |
| 12 | Large HCC, satellite nodules | Radiation pneumonia | TARE | 32 | 1141 | 4.1 | 17 | 3.9 | 122 _ 211.9 | 7.4 | 18.6 |
| 13 | small remnant volume | none | Right Lobar TARE | 1121 | 297 | 10.7 | 44 | 2.5 | 269.7 | 8.9 | 50.4 |
| 14 | PCI unstable angina., DM, advanced LC (Plt 69,000) | none | TARE | 6.3 | 706 | 5.3 | 14 | 5 | 216 – 233 | 18.3 | 45.4 |
| 15 | Multiple HCC, irregular margin | none | Right Lobar TARE | 21 | 11 | 145 | 38 | 4 | 354.4 | 10.8 | 23.5 |
| 16 | Multiple HCC | none | TARE Segmentectomy | 3.2 | 12 | 3.6 | 61 | 22 | 250 _ 240 | 29.2 | 66.2 |
| 17 | Multiple HCC | none | TARE Segmentectomy | 2.4 | 12 | 1.9 | 18 | 2.01 | 120 _ 240 | 25.3 | 58.6 |
| 18 | Multiple HCC | none | TARE + cTACE | 5.1 | 18 | 4 | 37 | 5.23 | 420 | 6.0 | 20.2 |
| 19 | Multiple HCC | none | Right Lobar TARE | 2.5 | 162 | 3.8 | 1271 | 5.8 | 164.03 | 15.3 | 18.2 |
| 20 | Multiple HCC | none | Segmental TARE | 7.8 | 69 | 17.9 | 486 | 3.98 | 625 | 14.3 | 16.8 |
| 21 | Multiple HCC | none | Segmental TARE | 3.5 | 19 | 4.1 | 19 | 4.18 | 907 _ 403 | 15.5 | 16.6 |
| 22 | Multiple HCC | none | Right Lobar TARE | 5.1 | 17 | 12.6 | 68 | 5.01 | 462 | 5.8 | 14.7 |
| 23 | Multiple HCC | none | TARE Segmentectomy | 2.2 | 26 | 4.1 | 44 | 3.98 | 603 | 9.0 | 14.5 |
| 24 | Multiple HCC | none | TARE Segmentectomy | 3.9 | 9 | 1.6 | 24 | 7.95 | 618 | 10.6 | 14.3 |
| 25 | Multiple HCC | none | TARE | 3.2 | 189 | 1.6 | 28293 | N/A | N/A | 9.1 | 9.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





