Submitted:
04 November 2025
Posted:
04 November 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
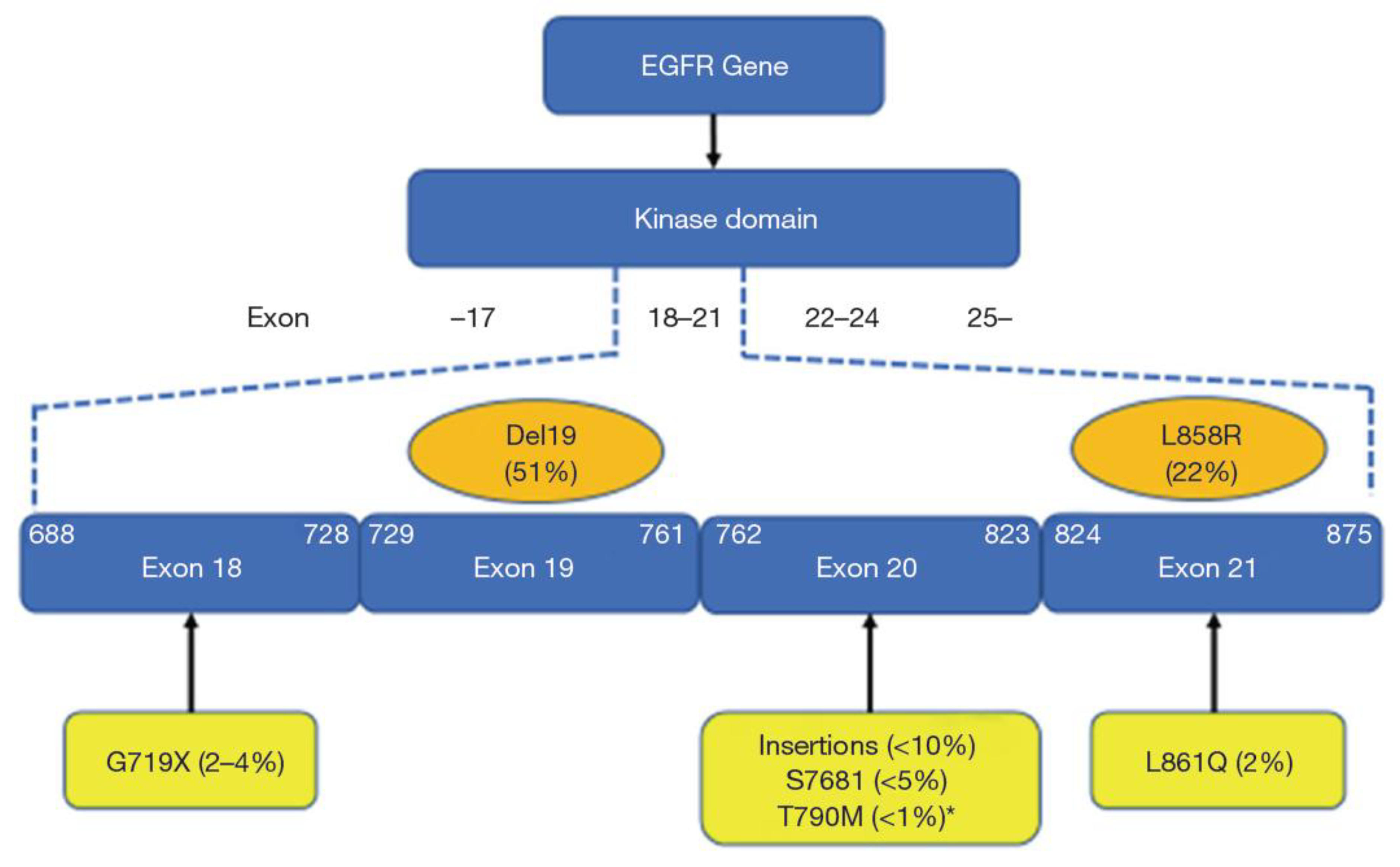
1. Introduction
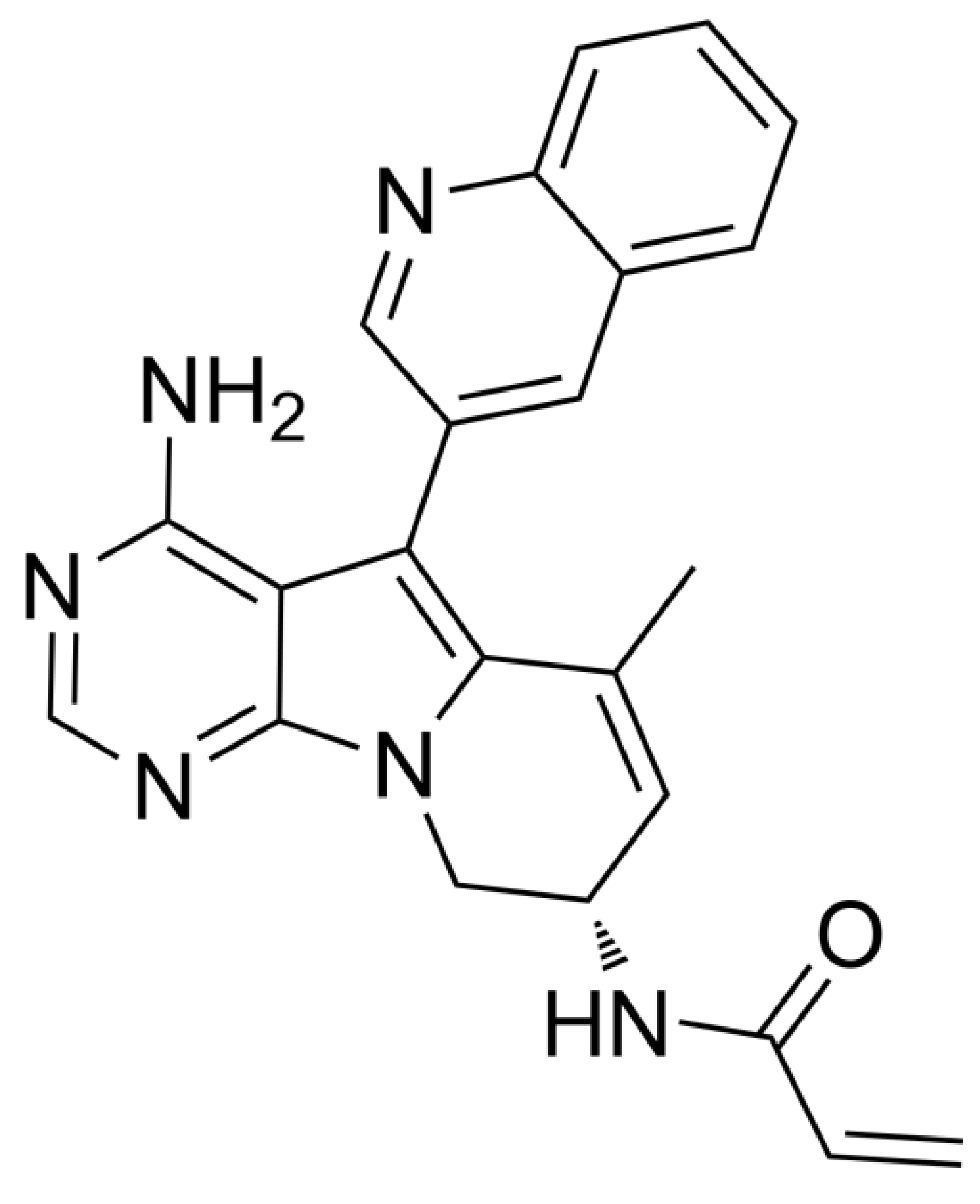
2. Zipalertinib—Preclinical Data
3. Zipalertinib—Clinical Development Status
3.1. REZILIENT 1 Trial
3.2. REZILIENT 2 Trial
3.3. REZILIENT 3 Trial
3.4. REZILIENT 4 Trial
4. Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin 58: 71-96 (2008).
- Shi Y, Au JS, Thongprasert S, et al. A prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J Thorac Oncol 9: 154-162 (2014).
- Fujimoto, N. Subtype of EGFR exon 19 deletion mutations. Trans Lung Cancer Res 13: 195-198 (2024).
- Grant MJ, Aredo JV, Starrett JH, et al. Efficacy of osimertinib in patients with lung cancer positive for uncommon EGFR exon 19 deletion mutations. Clin Cancer Res 29: 2123-2130 (2023).
- Cho BC, Lu S, Felip E, et al. Amivantamab plus lazertinib in previously untreated EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med 319: 1486-1498 (2024).
- Yang JCH, Lu S, Haya H, et al. Overall survival with amivantamab-lazertinib in EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med 2025. [CrossRef]
- Bevestvina CM, Waters D, Morrison L, et al. Impact of next-generation sequencing vs polymerase chain reaction testing on payer costs and clinical outcomes throughout the treatment journeys of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. J Manag Care Spec Pharm 12: 1467-1478 (2024).
- Borgeoud M, Parikh K, Banna GL, et al. Unveiling the landscape of uncommon EGFR mutations in NSCLC – a systematic review. J Thorac Oncol 7: 973-983 (2024).
- Miura S, Tanaka H, Misumi T, et al. Pragmatic randomized study of afatinib versus chemotherapy for patients with non-small cell lung cancer with uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor mutations: ACHILLES/TORG1834. J Clin Oncol 43: 2049-2058 (2025).
- Garzon-Ibanez M, Reyes R, Molina-Vila MA et al. Landscape and clinical implications of EGFR exon 20 insertions in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin Trans Oncol 9: 3559-3569 (2025).
- Lavdovskaia ED, Iyevleva AG, Sokolenko AP, et al. EGFR T790M mutation in TKI-naïve clinical samples: frequency, tissue mosaicism, predictive value and awareness on artifacts. Oncol Res Treat 41: 634-642 (2018).
- Dempke WCM, Fenchel K. Targeting C797S mutations and beyond in non-small cell lung cancer - a mini-review. Transl Cancer Res 13: 6540-6549 (2024).
- Wu JY, Yu CJ, Chang YC, et al. Effectiveness of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on “uncommon” epidermal growth factor receptor mutations of unknown clinical significance in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 17: 3812-3821 (2011).
- Seo D, Lim JH. Targeted therapies for EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation in non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2024. [CrossRef]
- Zhou C, Tang KJ, Cho BC, et al. Amivantamab plus chemotherapy in NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertions. N Engl J Med 389: 2039-2051 (2023).
- Park K, Haura EB, Leighl NB, et al. Amivantamab in EGFR exon 20 insertion-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer progressing on platinum chemotherapy: initial results from the CHRYSALIS phase I study. J Clin Oncol 39: 3391-3401 (2021).
- Yang JCH, Wang M, Doucet L, et al. Phase II dose-randomized study of sunvozertinib in platinum-pretreated non-small cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 insertions (WU-KONG1B). J Clin Oncol 2025. [CrossRef]
- Udagawa H, Hasako S, Ohashi A, et al. TAS6417/CLN-081 is a pan-mutation-selective EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor with a broad spectrum of preclinical activity against clinically relevant EGFR mutations. Mol Cancer Res 11: 2233-2243 (2019).
- Zwierenga F, Zhang L, Mecr J, et al. The prediction of treatment outcome in NSCLC patients harboring an EGFR exon 20 mutation using molecular modeling. Lung Cancer 197: 107973 (2024).
- Friedlaender A, Subbiah V, Russo A, et al. EGFR and HER2 exon 20 insertions in solid tumours: from biology to treatment. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 19: 51–69 (2022).
- Viteri S, Minchom A, Bazhenova L, et al. Frequency, underdiagnosis, and heterogeneity of epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 insertion mutations using real-world genomic datasets. Mol Oncol 17:230–237 (2023).
- Aggerwal C, Liu SV. Zipalertinib in EGFR exon 20-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer: drug development in a rare but crowded setting. J Clin Oncol 41: 4200-4203 (2023).
- Sentana-Lledo D, Academia E, Viray H, et al. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations and ERBB2 mutations in lung cancer: a narrative review on approved targeted therapies from oral kinase inhibitors to antibody-drug conjugates. Transl Lung Cancer Res 12: 1590-1610 (2023).
- Jänne PA, Wang BC, Cho BC, et al. First-line mobocertinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion-positive metastatic non-small cell lung cancer in the phase III EXCLAIM-2 trial. J Clin Oncol 43: 1553-1563 (2025).
- Deeks ED. Furmonertinib: first approval. Drugs 81: 1775-1780 (2021).
- O’Connor M, Lucas M, Romashko D, et al. BDTX-1536, a CNS penetrant, irreversible inhibitor potently inhibits the family of allosteric oncogenic EGFR mutants expressed in GBM and demonstrates efficacy in patient-derived xenograft models. Cancer Res 81: abstr LB140 (2021).
- Pagliarini RA, Henderson JA, Milgram BC, et al. STX-721, a covalent EGFR/HER2 exon 20 inhibitor, utilizes exon 20–mutant dynamic protein states and achieves unique mutant selectivity across human cancer models. Clin Cancer Res 31: 3002-3018 (2025).
- Piotrowska Z, Passaro A, Nguyen D, et al. Zipalertinib in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 insertions-positive non-small cell lung cancer previously treated with platinum-based chemotherapy with or without amivantamab. J Clin Oncol 43: 2387-2397 (2025).
- https://investors.cullinantherapeutics.com/news-releases/news-release-details/fda-grants-breakthrough-therapy-designation-cullinan-oncologys.
- Yu HA, Ohashi K, Ariyasu R, et al. Activity of zipalertinib against active central nervous system (CNS) metastases in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring EGFR exon20ins (ex20ins)/other uncommon mutations. ESMO Congress 2025, abstract 1847MO.
- Jänne P, Ramalingam S, Yang J, et al. Mobocertinib (TAK-788) in EGFR exon 20 insertion (ex20ins)+ metastatic non–small cell lung cancer (mNSCLC): treatment (tx) beyond progressive disease (PD) in platinum-pretreated patients (pts) with and without intracranial PD. J Clin Oncol 40 (suppl 16): 9099 (2022).
- Le X, Yu Y, Zhao Y, et al. FURTHER: A global, randomized study of firmonertinib at two dose levels in TKI-naive, advanced NSCLC with EGFR PACC mutations. J Thorac Oncol 19: S5-6 (2024).
- Udagawa H, Hayashi H, Yamaguchi M, et al. Phase 2 interim results of zipalertinib in patients with NSCLC harboring non-exon 20 insertion EGFR mutations. WCLC 2025, abstract MA08.04.
- Haymach JV, Hu HA, Besse B, et al. REZILIENT3: randomized phase III study of first-line zipalertinib plus chemotherapy in patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion-mutated NSCLC. Future Oncol 5: 549-556 (2025).
- Dempke WCM, Edvardsen K, Lu S, et al. Brain Metastases in NSCLC – are TKIs changing the treatment strategy? Anticancer Res 35: 5745-5757 (2015).
- Park GH, Park S, Kim H, et al. Prospective investigation of biomarker and resistance mechanisms using longitudinal cell-free NGS in non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertion treated with amivantamab. Eur J Cancer 226: 115631 (2025).
- Bazhenova L, Minchom A, Viteri S, et al. Comparative clinical outcomes for patients with advanced NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations and common EGFR mutations. Lung Cancer 162: 154-161 (2021).
- Wu W, Yu S, Huang J, et al. Molecular heterogeneity and treatment outcome of EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in Chinese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: insights from a large-scale real-world study. BMC Cancer 24: 1010-1022 (2024).
- Han B, Zhou C, Zheng W, et al. FAVOUR: a phase 1b study of furmonertinib, an oral, brain penetrant, selective EGFR inhibitor, in patients with advanced NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertions. J Thorac Oncol 18: S49 (2023).
- Yang JCH, Wang M, Chin CH, et al. Sunvozertinib as first-line treatment in NSCLC patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. Ann Oncol 34: S765 (2023).
| Compound | Targets | Comments (References) |
|---|---|---|
| Poziotinib | Exon 20 insertions, HER-2/neu |
Approved denied by FDA [23] |
| Mobocertinib | Exon 20 insertions, L858R, del18, L861R | FDA approval voluntarily withdrawn (no PFS benefit in the EXCLAIM-2 phase III trial) [24] |
| Sunvozertinib | Exon 20 insertions, L858R, del19, T790M, G719A, L861Q | Second-line: Approval by FDA, phase III ongoing in first-line |
| Firmonertinib | Exon 20 insertions, L858R, del19, T790M, G719X, S768I, L861Q | Approval in China [25], phase II/III trials ongoing |
|
Silevertinib (formerly BDTX-1535) |
Active against almost all common and uncommon mutations; weaker activity against exon 20 insertions | Phase II ongoing [26] |
| STX-721 | Exon 20 insertions, L858R, del19, HER2 A775_G776insYVMA (exon 20) | STX-721 demonstrated exon 20 insertion potency and selectivity relative to wild-type (WT) EGFR that surpassed all other tested clinical-phase benchmark EGFR inhibitors suggesting that STX-721 may be less prone to WT EGFR–driven adverse events that have limited the efficacy of other exon 20 insertion inhibitors. Phase II ongoing [27] |
| Zipalertinib | Most EGFR mutation (except C797S), exon 20 insertions | Phase III ongoing |
| Amivantamab | EGFR amplifications, L858R, del19, T790M, G796S, exon 20 insertions, c-MET (monoclonal antibody) |
Approved by FDA and EMA |
| Trial Name | Design (NCT number) | Status |
|---|---|---|
| REZILIENT 1 | Phase I/II open-label trial in NSCLC patients harbouring exon20ins previously being treated with platinum-based chemotherapy (with or without exon20ins-targeted therapies) PEs: ORR and DoR (NCT04036682) |
Recruitment completed. N = 244 [28] |
| REZILIENT 2 | Multicentre cohort trial (phase IIB): Cohort A: prior exon20ins treatment Cohort B: first-line exon20ins treatment Cohort C: active brain metastases (exon20ins, uncommon mutations) Cohort D: uncommon mutations (NCT05967689) |
Recruitment ongoing (N = 224 in all cohorts; cohorts A and B closed) |
| REZILIENT 3 | Randomized phase III trial in advanced or metastatic first-line NSCLC patients harbouring exon20ins: platinum/pemetrexed chemotherapy and zipalertinib (4 cycles) followed by zipalertinib plus pemetrexed versus platinum/pemetrexed followed by pemetrexed plus placebo maintenance therapy. PE: mPFS (NCT05973773) |
Recruitment ongoing (N = 266 planned) |
| REZILIENT 4 | Adjuvant randomized phase III trial in NSCLC patients (stage IB-IIIA) harbouring exon 20ins and/or uncommon mutations: Platinum-based chemotherapy and zipalertinib (after tumour resection, 4 cycles) followed by zipalertinib monotherapy versus platinum-based chemotherapy (after tumour resection, 4 cycles) followed by placebo. PE: DFS after 3 years. (NCT07128199) |
Recruiting ongoing (N = 360 planned) |
| Drug | N | TL | Mutations | Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mobocertinib | 40 | second-line (after platinum) |
Exon20ins | ORR 18% mPFS: 3.7 months |
Jänne et al. 2024 [31] |
| Firmonertinib | 13 | first-line | PACC mutations | ORR (240 mg): 46.2% | Le et al. 2024 [32] |
| Sunvozertinib | 21 | second-line (after platinum) |
Exon20ins | ORR: 52.4% | Yang et al. 2025 [17] |
| Zipalertinib | 16 | no limit (range: 1-12) |
Exon20ins, uncommon mutations |
ORR: 31.3% iDCR: 68.8% DoR: 8.1 months |
Yu et al. 2025 [30] |
| Drug | Study | Design | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Firmonertinib | FAVOUR (NCT04858958): completed (China only) |
Phase Ib Part A: 1L (240 mg, N = 30), Part B: 2L (240 vs. 160 mg, N = 49) |
ORR 1L: 78.6% ORR 2L (240 mg): 46.2% ORR 2L (160 mg): 38.5% |
Han et al. 2023 [39] |
| Firmonertinib | FURVENT (NCT05607550): ongoing (mainly USA and China) |
Phase III (1L) Firmonertinib vs. platinum-based chemotherapy (N = 398), PE: mPFS, SE: mOS |
Study is active, but not recruiting patients, primary completion expected Q3/2025 | www.clincialtrials.gov |
| Sunvozertinib | WU-KONG 1B (NCT03974022): completed (mainly China and EU) |
Phase II (2L) 200 mg (part A) vs. 300 mg (part B) |
ORR 46% (2L) ORR 41.7% in amivantamab-pretreated patients FDA approval |
Yang et al. 2025 [17] |
| Sunvozertinib | WU-KONG 15* (part of WU-KONG 1) (NCT05559645): completed (China only) |
Phase II (1L and 2L) N = 28 in 1L (of note: only 1 site in China recruited patients) |
ORR 73.1% (1L) | Yang et al. 2023 [40] |
| Sunvozertinib | WU-KONG 28 (NCT05668988): ongoing (mainly China and EU) |
Phase III (1L) Sunvozertinib vs. platinum-based chemotherapy (N = 320) PE: mPFS, SE: mOS |
Study is recruiting patients, completion expected Q1/2026 | www.clincialtrials.gov |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




