1. Introduction
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), a high-performance polyester valued for its excellent mechanical properties, chemical stability, and processability, finds extensive global application. Consequently, the accumulation of PET waste poses a significant environmental challenge. Within the global context of “carbon neutrality” and the “circular economy,” efficient recycling and resource utilization of post-consumer PET have garnered widespread attention. While physical recycling via melt-processing and pelletization allows for PET re-use, the resulting material often suffers from degraded properties due to chain scission and impurity introduction. In contrast, chemical recycling, which operates at the molecular level, offers a pathway to higher-value products [
1,
2,
3].
Chemical degradation of PET primarily proceeds through glycolysis, hydrolysis, or ammonolysis [
4,
5,
6]. Among these, glycolysis, which depolymerizes the polyester into high-purity monomers via transesterification, is particularly prominent. This process typically employs ethylene glycol, methanol and iso-octanol as solvents, generating bis(2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate (BHET), dimethyl terephthalate (DMT), or dioctyl terephthalate (DOTP), respectively. BHET is the precursor for PET, sharing an identical molecular structure. Compared to the limitations of DMT, which requires multi-step purification including hydrolysis, and DOTP, which is hindered for direct polycondensation due to terminal group sterics, the ethylene glycol route has emerged as a research focus for green recycling technologies due to its superior atom economy and product re-polymerizability [
7,
8,
9].
Recent research on PET glycolysis catalysts has concentrated on performance and stability. Non-metallic catalysts, such as functionalized ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents, are notable for the environmental friendliness [
10,
11]. The mechanism primarily relies on hydrogen-bond activation or synergistic acid-base effects to cleave the ester bond. However, these systems often exhibit low intrinsic activity, necessitating prolonged reaction times and frequently requiring intensification by external fields like microwave or ultraviolet irradiation. In comparison, transition metal catalysts demonstrate higher efficiency by leveraging the d-orbital electrons of the metal center to coordinate strongly with the PET ester group, polarizing the carbonyl electron cloud and thereby activating the ester moiety. Liu et al. reported that when zinc acetate/1,3-dimethylurea (Zn(OAc)₂/DMU) used for the PET glycolysis, Zn²⁺ coordinates with the ester bonds, and the DMU cation stabilizes the intermediates through electrostatic interaction, thus forming a synergistic reaction pathway [
12]. Similarly, in the Urea/ZnCl₂ system, Zn²⁺ coordination combines with the hydrogen-bonding network from urea to lower the reaction activation energy [
13]. Our prior studies using Zn(OAc)₂/ChCl for PET degradation confirmed that the metal center coordinates with the ester group, facilitating a five-membered ring transition state that accelerates ester bond cleavage [
14,
15].
The performance of transition metal catalysts is highly dependent on ligand design and selection. Cyclic (alkyl)(amino)carbenes (CAACs), highly reactive intermediates with two non-bonding electrons, exhibit strong nucleophilicity (higher HOMO, stronger σ-donor) and electrophilicity (lower LUMO, stronger π-acceptor) [
16,
17]. Their exceptional ability to stabilize highly reactive species and metal centers, enabling the activation of strong bonds and small molecules, ranks them among the most powerful organic ligands in catalysis [
18,
19]. Our previous work successfully applied CAACs-metal complexes in diverse catalytic reactions, revealing synergistic electronic effects between the CAACs ligand and the metal center that effectively promote C=O bond activation or hydrogen transfer processes [
20,
21,
22]. In this study, the CAAC-Cu catalyst was successfully prepared starting from 2,6-diisopropylaniline, with copper(I) chloride serving as the metal center. Various reaction parameters, including catalyst loading and temperature were optimized, and a plausible reaction mechanism was proposed. Experimental results demonstrated that the CAAC-Cu catalyst exhibits excellent activity for PET glycolysis, and indicated that the reaction follows a first-order reaction kinetics. In addition, the catalysts can be conveniently recycled alongside the reaction solvent for repeated use.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of CAAC-Cu Complex
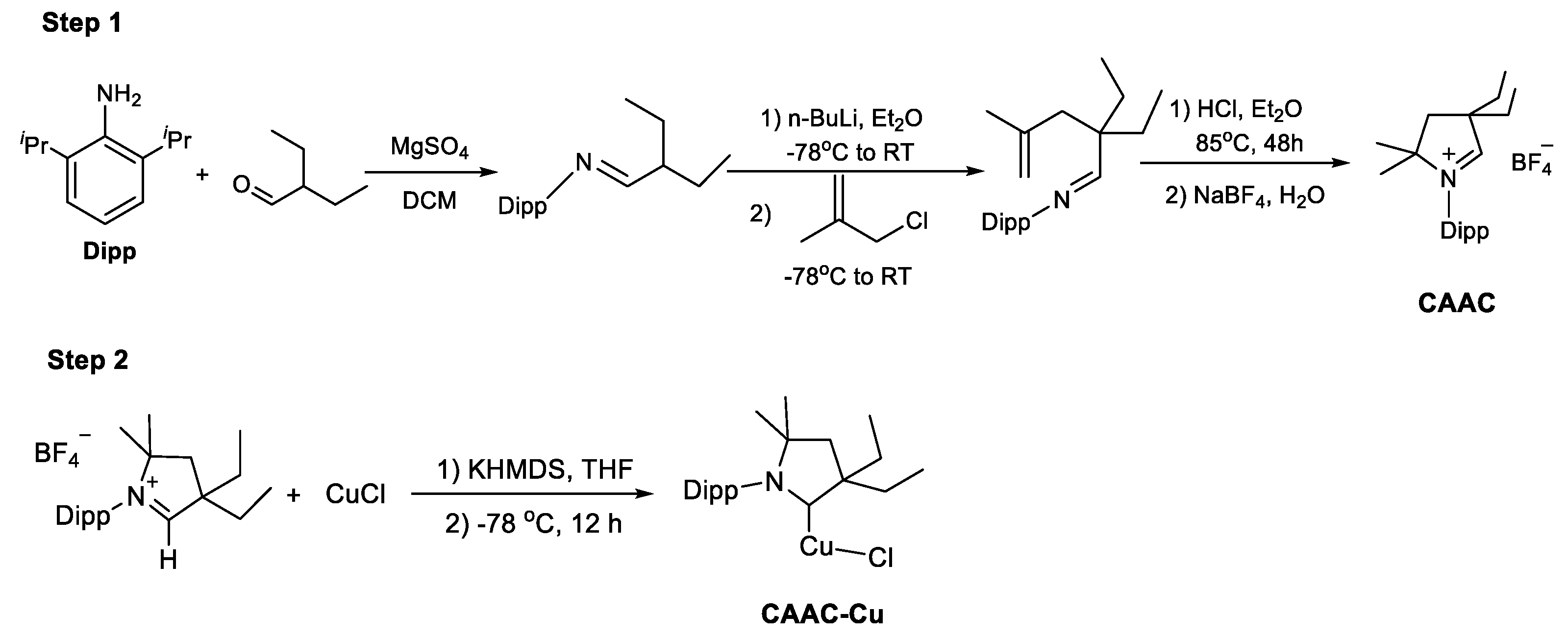
Firstly, the CAAC ligand was prepared following
Scheme 1, and the ligand can be purified using diethyl ether, which was obtained as white solids after vacuum drying. Subsequently, the CAAC-Cu complex was synthesized as white solids following previously reported protocols [
23]. The results indicated that in the ¹H NMR spectrum of the CAAC-Cu complex, the original signal at δ 9.7 ppm of ligand disappeared, while a distinct carbene carbon appeared at δ 249.5 ppm in the ¹³C NMR spectrum, confirming the successful preparation of the catalyst. More detailed information can be found in the ESI.
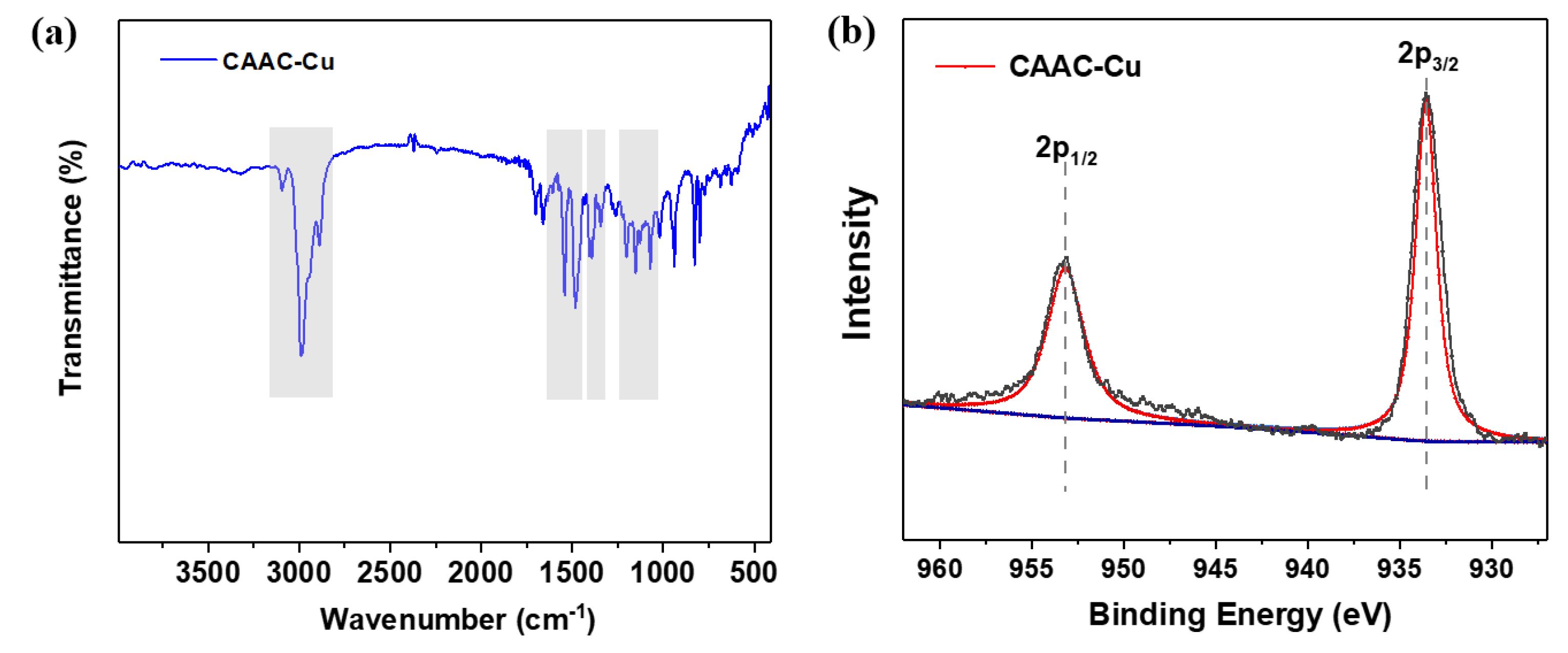
Figure 1a displayed the FT-IR results for the CAAC-Cu catalyst, the peaks at 3095 cm⁻¹, 2980 cm⁻¹, and 2887 cm⁻¹ are attributed to C-H stretching vibrations of -CH, -CH
2 or -CH
3. Peaks at 1540 cm⁻¹ and 1485 cm⁻¹ correspond to aromatic ring C-C skeletal vibrations; the 1344 cm⁻¹ peak to aromatic ring C-N vibration, and the 1400 cm⁻¹ peak to heterocyclic N-C vibration, and the frequency is mainly affected by electronic and steric effects of adjacent groups. Peaks at 1202 cm⁻¹, 1152 cm⁻¹, and 1070 cm⁻¹ are ascribed to side-chain C-C skeletal vibrations. In addition, XPS surface analysis of Cu(I) for the CAAC-Cu complex was presented in
Figure 1b. The binding energy (BE) of surface charges was calibrated using the C 1s peak of carbon at 284.5 eV. It can be seen that the sample exhibits a Cu 2p₃/₂ peak at 932.9 eV and a Cu 2p₁/₂ peak at 952.8 eV, both of which are characteristic of Cu(I) compounds, as verified by comparison with standard spectral data [
24,
25]. Notably, no characteristic satellite peaks of Cu(II) (~942 eV or ~962 eV) were detected, which confirms the stability of the Cu(I) valence state in the complex. Collectively, these results further demonstrate the structural integrity of the carbene moiety during synthesis and the successful coordination of the metal active center.
2.2. General Procedure for the PET Glycolysis
In each PET degradation experiment, EG was used as the reaction medium with CAAC-Cu complex as the catalyst. All degradation reactions were carried out in a 250 mL double-necked round-bottom glass reactor equipped with a magnetic stirrer, thermometer, and reflux condenser to ensure stable and controllable reaction conditions.
The experiments were performed under atmospheric pressure, with key parameters such as reaction time, temperature, and catalyst dosage systematically optimized to explore the optimal reaction conditions. Upon completion of the reaction, the system was cooled to 100 °C and subjected to hot filtration to separate unreacted PET. After the filtrate was completely cooled, a secondary filtration was performed, and the resulting filter residue was BHET. At this point, CAAC-Cu complex remained in the excess EG and could be directly reused for cyclic reactions. The aforementioned filter residue was dissolved in an appropriate amount of hot water, and after cooling and crystallization, high-purity BHET products were obtained as white needle-like crystals.
The separation yield of BHET was calculated, and its structure was analyzed using relevant characterization methods. The conversion rate of PET, selectivity and yield of BHET were calculated according to the following equation Equations (1)–(3):
where W
0 represents the initial weight of PET and W
1 represents the weight of undegraded PET. n
BHET represents the number of moles of BHET, n
units represents the number of moles of the degraded PET units, S
BHET represents the selectivity of BHET and C
PET represents the conversion of BHET.
2.3. CAAC-Cu Performance in PET Glycolysis
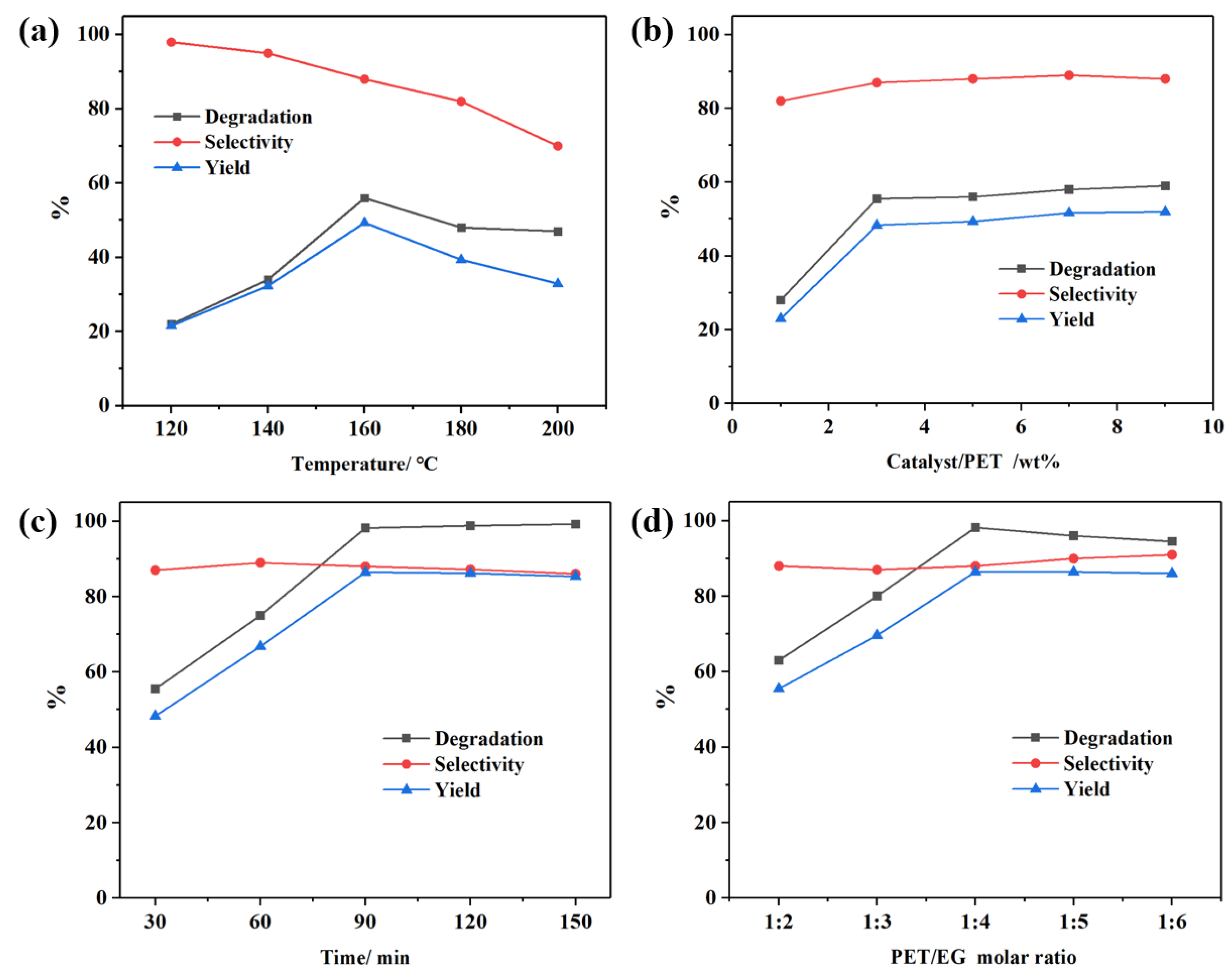
The influence of reaction temperature on PET glycolysis was investigated under specific conditions (5 g PET, 30 min, PET:EG molar ratio of 1:4) using a 5 wt% CAAC-Cu complex as catalyst, with results presented in
Figure 2a. At 120 °C, the PET glycolysis rate was minimal, achieving a BHET yield of 22.3%, while the selectivity toward BHET was relatively higher at this low temperature; as the temperature increased from 120 °C to 160 °C, both the PET glycolysis rate and Y
BHET increased, though this was accompanied by a concurrent decrease in S
BHET. Optimal PET C
PET and Y
BHET were obtained at 160 °C, reaching 56.2% and 49.3% respectively. Further temperature elevation did not significantly improve C
PET, because the CAAC-Cu complex undergoes slight decomposition when the temperature exceeds 150 °C from the TGA analysis (
Figure S7), which leads to a decrease in its catalytic activity. In addition, excessively high temperature enhanced side reactions instead, leading to reduced Y
BHET and S
BHET. Hence, the subsequent experiments were conducted at 160 °C.
Then, to explore the impact of catalyst dosage on PET glycolysis, experiments were carried out under the conditions: 5 g PET, 30 min, 160 °C, and a PET:EG molar ratio of 1:4, with results depicted in
Figure 2b. It was observed that at a catalyst loading of 3 wt%, the degradation rate approached its maximum within C
PET and Y
BHET reaching 55.8% and 48.7% respectively. Further increasing the catalyst amount did not alter the degradation rate. This confirms that the CAAC-Cu complex still exhibits good catalytic activity even at relatively low concentrations.
The influence of reaction time on PET glycolysis was examined under the conditions of 5 g PET, 3 wt% catalyst, a PET:EG molar ratio of 1:4, and 160 °C, with results presented in
Figure 2c. With the extension of the reaction time, the conversion of PET increased significantly until it approached nearly 100%. The S
BHET and Y
BHET reached the maximum 87.8% and 86.4% when the reaction time was 90 min. Beyond 90 min, a slight decline in S
BHET and Y
BHET was observed, attributed to the equilibrium established between BHET, dimers, and oligomers in the PET glycolysis reaction [
26].
Finally, the influence of the reactant ratio was investigated under the previously optimized reaction conditions (5 g PET, 3 wt% catalyst, 90 min reaction time, 160 °C), with the results presented in
Figure 2d. The experimental data showed that when the dosage of EG was relatively low, the reaction efficiency was low, which attributed to the fact that PET degradation is a heterogeneous reaction. So, increasing the concentration of substrates can effectively accelerate the reaction rate. When the molar ratio of EG to PET reached 4:1, all performance indicators achieved optimal values. However, a further increase in EG dosage led to a slight decline in reaction performance, possibly due to the reduced concentration of reactants and the increased occurrence of side reactions. Therefore, the optimal PET:EG molar ratio was determined to be 1:4.
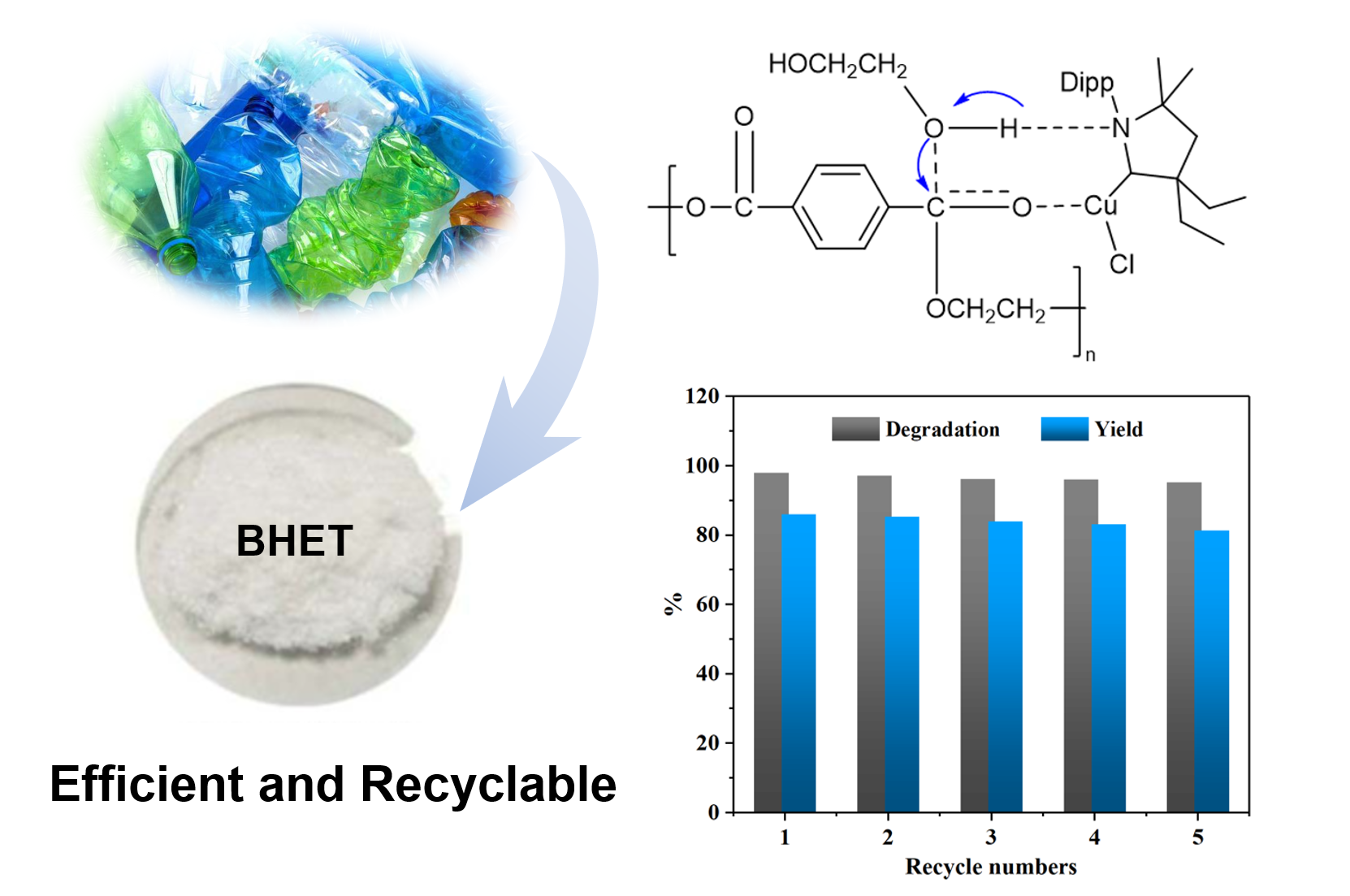
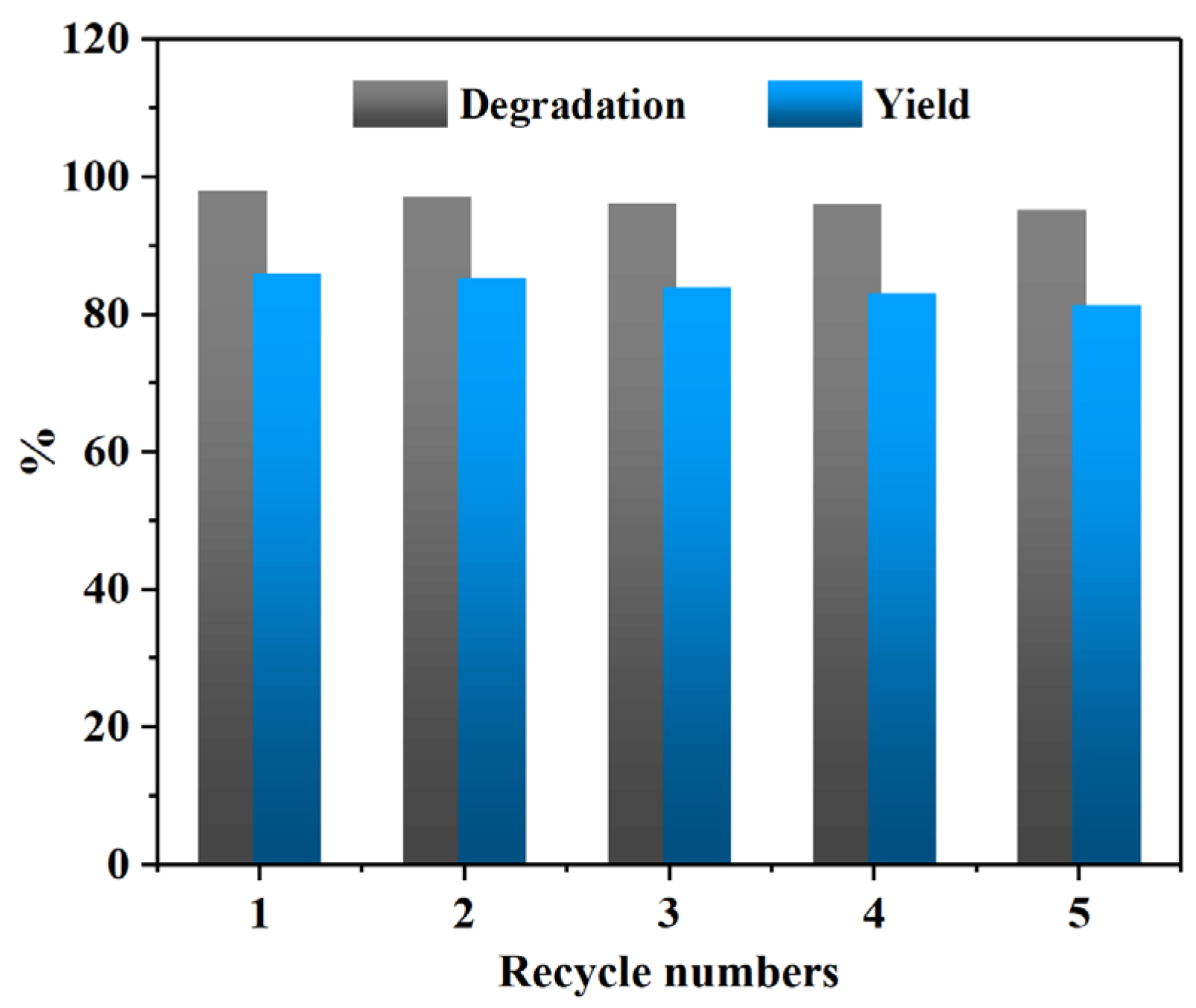
By comparing the above results, it can be observed that the reaction conditions exert a significant influence on the PET glycolysis reaction. Considering the cost of practical application comprehensively, the optimal reaction conditions for PET glycolysis using the CAAC-Cu catalyst are as follows: 160 °C, 90 min, catalyst dosage of 3 wt%, and a PET:EG molar ratio of 1:4. The PET conversion, BHET selectivity and yield reached 98.2%, 88.1%, and 86.5%, respectively. In addition, the reusability of the CAAC-Cu was also investigated. After each experiment, the catalyst was recovered together with the excess EG, and only the consumed EG needed to be supplemented, which is very convenient. As shown in
Figure 3, after multiple recovery cycles, the catalytic activity remains good, with the PET degradation rate and BHET yield maintained above 95% and 80%, respectively.
2.4. Kinetic of PET Glycolysis Catalyzed by CAAC-Cu
In the field of polymer depolymerization kinetics, there is an ongoing discussion that the reaction order is typically regarded as first-order [
27,
28]. Accordingly, for the glycolysis of PET catalyzed by CAAC-Cu, the reaction was initially assumed to follow first-order kinetic equations:
Here, k denotes the reaction rate constant, while C
PET represents the concentration of PET at time t.
Here, x refers to the conversion of PET. Subsequently, Equation (4) can be rearranged to give:
Equation (6) was integrated over time to provide:
The activation energy (Ea) can be derived from the Arrhenius equation using the determined rate constant. Here, A denotes the pre-exponential factor, R is the gas constant with a value of 8.314 J K⁻¹ mol⁻¹, and T represents the temperature in Kelvin.
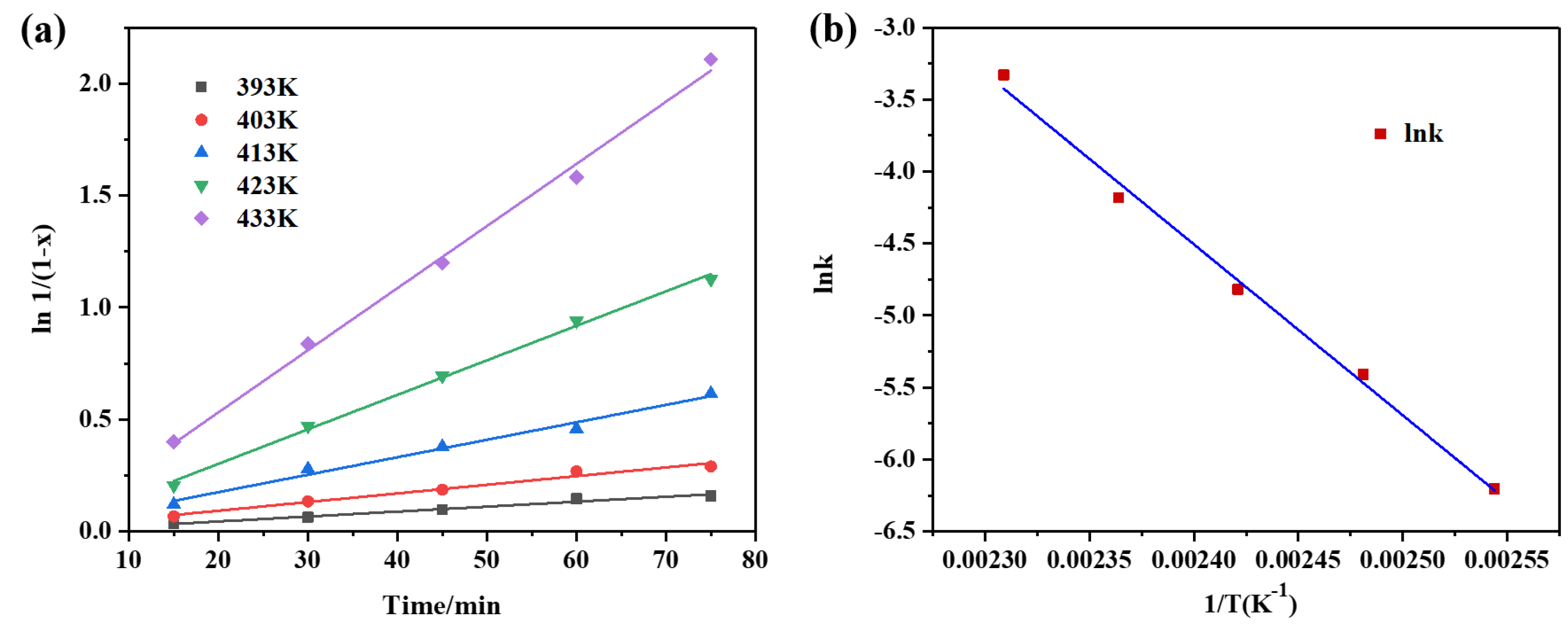
Figure 4.
(a) Effect of temperature on the rate of PET glycolysis, reaction conditions: 3 wt% catalyst, PET:EG =1:4 molar ratio. (b) Arrhenius plots of the rate constant of PET glycolysis.
Figure 4.
(a) Effect of temperature on the rate of PET glycolysis, reaction conditions: 3 wt% catalyst, PET:EG =1:4 molar ratio. (b) Arrhenius plots of the rate constant of PET glycolysis.
The effect of reaction temperature on the degradation rate of PET in the presence of CAAC-Cu was shown in Figure. 4a. This indicated that the reaction conversion rate is proportional to the reaction time at different temperatures, and the process follows a first-order kinetic reaction. The activation energy of this reaction, calculated from the slope of the Arrhenius plot in Figure. 4b, is 98.7 kJ·mol⁻¹. Furthermore, with the increase in temperature, the reaction rate constant increases rapidly, which demonstrates that temperature exerts a significant influence on PET degradation, and this result is consistent with previous experiments.
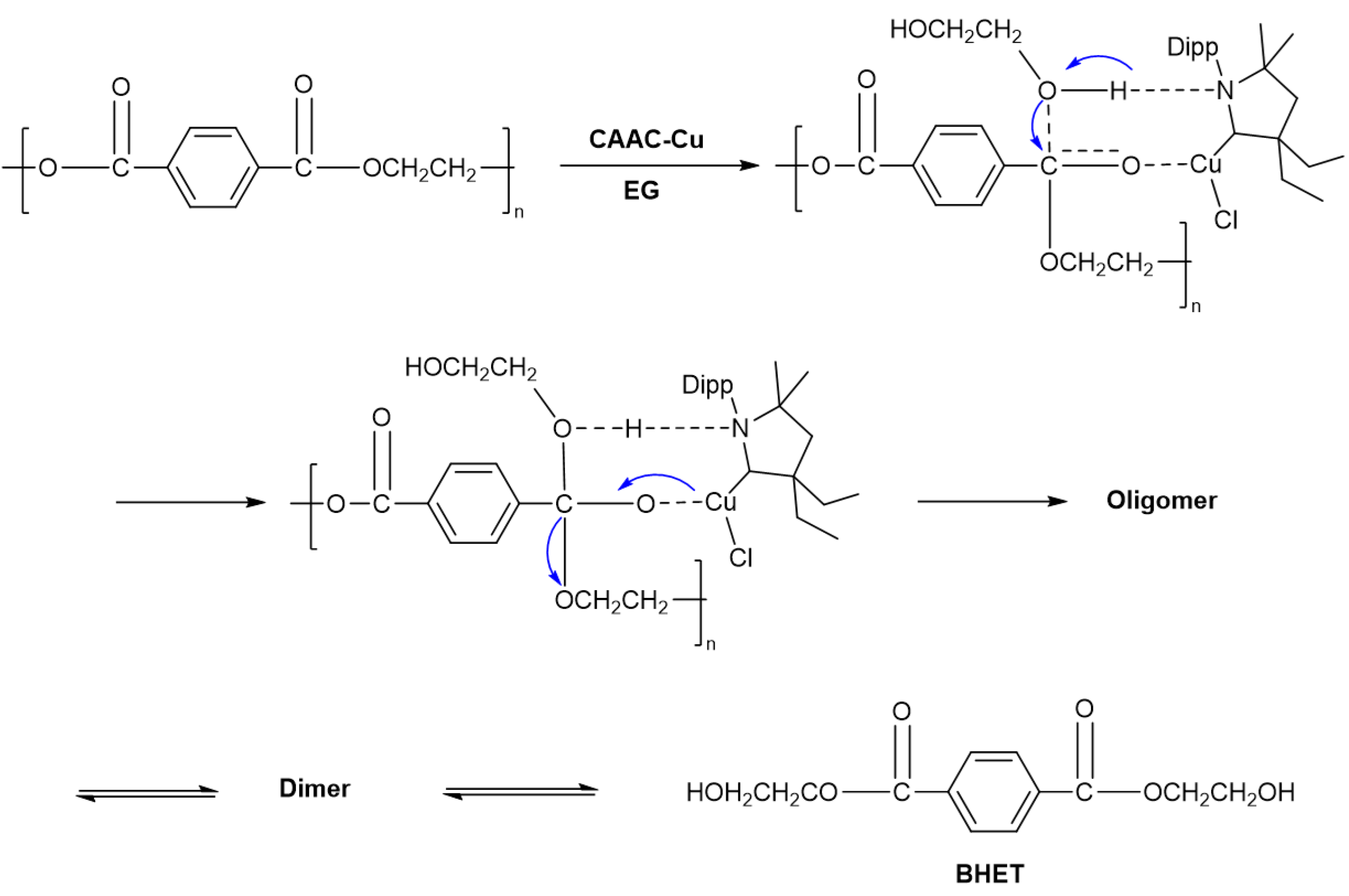
2.5. Proposed Mechanism of PET Glycolysis
In the process of PET glycolysis or other transesterification reactions, transition metals are generally regarded as Lewis acid catalysts, with the capability to attack the carbonyl oxygen attached to the ester group [
29,
30]. In this study, Cu⁺ interacts with the carbonyl group on PET, leading to the formation of a carbon cation and this reaction pathway adheres to the acid-catalyzed mechanism. Moreover, the hydrogen bonding interaction between amino carbene and EG exerted a critical effect in PET glycolysis, and this specific process is consistent with the base-catalyzed mechanism. Under the action of such synergistic catalysis, the long polymeric chains of PET undergo rapid cleavage. The potential mechanism underlying the degradation of PET catalyzed by CAAC-Cu was presented in
Scheme 2.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
PET pellets (2×2×2.5 mm) were purchased from Sinopec Yizheng Chemical Fibre Co. Ltd. After being ground in a crusher, these PET pellets were sieved through a screen to collect powders with a particle size of 60–80 mesh, which were then used for the degradation experiment. Ethylene glycol (EG), 2,6-Diisopropylaniline (Dipp), copper(I) chloride, n-Butyllithium, Tetrahydrofuran (THF), ethyl acetate and potassium bis (trimethylsilyl) amide (KHMDS), et al. were purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. and Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. All reagents were used as received without further treatment.
3.2. Characterization of Catalysts and Products
The prepared CAAC-Cu catalyst and the PET glycolysis products were characterized. 1H and 13C spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance 400 spectrometer (Landkreis Karlsruhe, Baden-Württemberg, Germany). NMR multiplicities are abbreviated as follows: s = singlet, d = doublet, t = triplet, q = quartet, m = multiplet, br = broad signal. Fourier transform-infrared (FT-IR) spectra were obtained with a Nicolet 380 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) spectrometer, using KBr as the blank. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) scans were obtained using the DSC-1 STARe system by heating from 25 °C to 180 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C min−1 in an atmosphere of nitrogen with a flow rate of 10 mL min−1 (Mettler Toledo, Zurich, Switzerland). Mass spectroscopy (MS) measurements were performed on a Thermo Finnigan Q-TOF spectrometer. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis was performed by PHI 5000 Versa Probe (ULVAC-PHI, Kanagawa, Japan). Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES) Avio 200 (PerkinElmer, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). HPLC analysis of the main product was under the condition of a column temperature of 25 °C, detector temperature of 40 °C, solvent water/methanol ratio (6:4), and flow rate of 0.3 mL/min. The analysis is performed with an ACQUITY HPLC (Waters, Milford, Massachusetts, USA) which was equipped with a refractive index detector and BET C18 column. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was performed using DTG-60H under a nitrogen atmosphere by heating the sample from 25 °C to 600 °C at the rate of 5 °C min-1 (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan).
4. Conclusions
In summary, the cyclic(alkyl)(amino)carbene copper (CAAC-Cu) complex catalyst was successfully prepared and applied for the first time in the glycolysis of PET, realizing efficient degradation and high-value conversion of PET. Multiple characterizations have confirmed the successful coordination between the CAAC ligand and CuCl as well as the stable existence of the metal active center. The optimal parameters were determined as a reaction temperature of 160 °C, reaction time of 90 min, catalyst dosage of 3 wt%, and a PET: EG molar ratio of 1:4, under which the PET conversion rate reached 98.2%, the selectivity for BHET was 88.1%, and the yield was 86.5%. In addition, experimental results showed the reaction followed a first-order kinetic with an activation energy of 98.7 kJ·mol⁻¹. The CAAC-Cu catalyst could be recovered with the filtrate and maintained high catalytic activity after multiple reaction cycles. A plausible reaction mechanism has been inferred as the copper ions attack the ester groups on PET to form carbocations (acid-catalyzed pathway), while the amino carbene formed hydrogen bonds with EG to assist ester bond cleavage (base-catalyzed pathway). In conclusion, the CAAC-Cu catalyst provided a novel strategy for PET chemical recycling and holding great significance for the industrialization of closed-loop PET recycling, mitigation of plastic pollution, and achievement of “carbon neutrality”.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: Preprints.org, Figure S1. 1H NMR spectrum of CAAC; Figure S2. 13C NMR spectrum of CAAC; Figure S3. 1H NMR spectrum of CAAC-Cu; Figure S4. 13C NMR spectrum of CAAC-Cu; Figure S5. 1H NMR spectrum of the main product; Figure S6. XPS spectrum of CAAC-Cu was calibrated using the C 1s peak of carbon at 284.5 eV; Figure S7. TGA curves of CAAC-Cu; Figure S8. DSC curves of main product; Table S1. Elemental analysis results of the main product.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Z. and Y.W.; Methodology, L.Z., M.L. and H.H.; Validation, Y.W.; Formal analysis, J.H., Y.W., and L.Z.; Investigation, I.P. and N.F.; Writing—original draft, L.Z.; Writing—review & editing, L.Z. and M.L.; Supervision, I.P. and N.F.; Project administration, L.Z. and H.H.; Funding acquisition, L.Z. and J.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Natural Science Foundation of Yangzhou (YZ2023171); Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (23KJD150014, 24KJB530023); Lv Yang Jin Feng Plan Project of Yangzhou.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Lingling Peng for providing the testing conditions of ICP data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cao, J.; Liang, H.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, X.; Elimelech, M.; Lu, X. Depolymerization mechanisms and closed-loop assessment in polyester waste recycling. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Lele, A.D.; Zhao, X.; Li, S.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Cui, M.; Guo, M.; Brozena, A.H.; Lin, Y.; Li, T.; Xu, L.; Qi, A.; Kevrekidis, I.G.; Mei, J.; Pan, X.; Liu, D.; Ju, Y.; Hu, L. Depolymerization of plastics by means of electrified spatiotemporal heating. Nature. 2023, 616, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, P.E. Renewable fuels and chemical recycling of plastics via hydrothermal liquefaction. Acc. Chem. Res. 2024, 57, 3386–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedsoltan, H. A focused review on recycling and hydrolysis techniques of polyethylene terephthalate. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2023, 63, 2651–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Tang, J.-T.; Li, X.; Nie, X.-S.; Ye, B. Valorization of polyester plastics and biomass into amines through a dual zirconium catalysis. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 3089–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopperi, H.; Mamidi, V.; Suresh, G.; Mohan, S.V. Tandem chemical hydrolysis and bioelectrochemical upcycling of waste polyethylene terephthalate (PET) for sustainable biobutanol and ethanol production ensuring plastics circularity. Green Chem. 2025, 27, 2359–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, X. Mechanistic investigation on hydrolysis, alcoholysis, and ammonolysis of polyethylene terephthalate initiated by participation of calcium ions. Process Saf. Environ. 2025, 194, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yao, X.; Ding, R.; Bao, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, D.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Xin, J.; Lu, X. Directional glycolysis of waste PET using deep eutectic solvents for preparation of aromatic-based polyurethane elastomers. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 9802–9813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Qin, E.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. PET glycolysis to bhet efficiently catalyzed by stable and recyclable Pd-Cu/γ-Al2O3. Molecules. 2024, 29, 4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, X.; Yao, H.; Zhou, Q.; Xin, J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S. Degradation of poly(ethylene terephthalate) catalyzed by metal-free choline-based ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 3122–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, G.-S.; Al Mamunur Rashid, M.; Ha, J.-M.; Yoo, C.-J.; Jeon, B.-H.; Jeong, K.; Kim, K.H. Enhancing polyethylene terephthalate conversion through efficient microwave-assisted deep eutectic solvent-catalyzed glycolysis. Chemosphere. 2024, 349, 140781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Fu, W.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, S. Lewis acid–base synergistic catalysis for polyethylene terephthalate degradation by 1,3-dimethylurea/Zn(OAc)2 deep eutectic solvent. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 7, 3292–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yao, X.; Geng, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S. Deep eutectic solvents as highly active catalysts for the fast and mild glycolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate)(PET). Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2473–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lu, X.; Ju, Z.; Liu, B.; Yao, H.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, S. Alcoholysis of polyethylene terephthalate to produce dioctyl terephthalate using choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents as efficient catalysts. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Z.; Zhou, L.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Yao, X.; Cheng, S.; Chen, G.; Ge, C. Mechanistic insight into the roles of anions and cations in the degradation of poly(ethylene terephthalate) catalyzed by ionic liquids. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 2021, 23, 18659–18668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.; Jung, E.; Yang, Y.; Noh, J.; Song, H.; Kim, H.; Kang, H.; Choe, S.; Choi, T.-L.; Lee, E. Air and thermally stable cyclic (alkyl)(amino)carbene ruthenium complexes for efficient ring expansion metathesis polymerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 2571–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, B.M.P.; Faas, M.R.; West, D.; Suvinen, R.A.; Tuononen, H.M.; Roesler, R. An isolable, chelating bis cyclic (alkyl)(amino)carbene stabilizes a strongly bent, dicoordinate Ni(0) complex. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, C.; Sharma, A.; Das, B.; Yadav, R.; Kundu, S. Cyclic (alkenyl)(amino)carbene (SMe CAenAC): Introducing a member to the cyclic (alkyl)(amino)carbenes family featuring a narrow energy gap. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 6905–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jang, M.; Kang, H.; Choe, S.; Lee, E.; Choi, T.-L. Synthesis of linear and cyclic poly(allenamer)s by powerful cyclic-alkyl-amino-carbene (CAAC) ruthenium catalysts and facile post-modification. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Peng, L.; Ji, J.; Ma, W.; Hu, J.; Wu, Y.; Geng, J.; Hu, X. Cyclic (alkyl)(amino)carbene-copper supported on SBA-15 as an efficient and recyclable catalyst for CO2 hydrogenation to formate. J. CO2. Util. 2022, 58, 101910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, D.; Hu, J.; Wu, Y.; Geng, J.; Hu, X. Thermal dehydrogenation and hydrolysis of BH3NH3 catalyzed by cyclic (alkyl)(amino)carbene iridium complexes under mild conditions. Organometallics. 2021, 40, 2643–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yao, C.; Ma, W.; Hu, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, X. CO2 hydrogenation to formate catalyzed by highly stable and recyclable carbene-iridium under mild condition. J. CO2. Util. 2021, 54, 101769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, B.L.; Fulton, J.L.; Linehan, J.C.; Balasubramanian, M.; Lercher, J.A.; Bullock, R.M. Operando XAFs studies on Rh(CAAC)-catalyzed arene hydrogenation. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 4106–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hensen, E.J. Highly efficient and robust Au/MgCuCr2O4 catalyst for gas-phase oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 14032–14035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Rioux, R.M. Highly stereoselective anti-markovnikov hydrothiolation of alkynes and electron-deficient alkenes by a supported Cu-NHC complex. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 3916–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somayeh, M.; Bouldo, M.G.; Mojtaba, E. Controlled glycolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate) to oligomers under microwave irradiation using antimony(III) oxide. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 6574–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabagh, A.M.; Yehia, F.Z.; Eissa, A.M.F.; Moustafa, M.E.; Eshaq, G.; Rabie, A.M.; ElMetwally, A.E. Cu- and Zn-acetate-containing ionic liquids as catalysts for the glycolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 110, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Fonseca, R.; Duque-Ingunza, I.; de Rivas, B.; Flores-Giraldo, L.; Gutiérrez-Ortiz, J.I. Kinetics of catalytic glycolysis of PET wastes with sodium carbonate. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyet Thi Ho, L.; Minh Ngo, D.; Cho, J.; Jung, H.M. Enhanced catalytic glycolysis conditions for chemical recycling of glycol-modified poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 155, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, M.; Bai, X. The glycolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate) waste: Lewis acidic ionic liquids as high efficient catalysts. Polymers. 2013, 5, 1258–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).