Submitted:
30 October 2025
Posted:
31 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
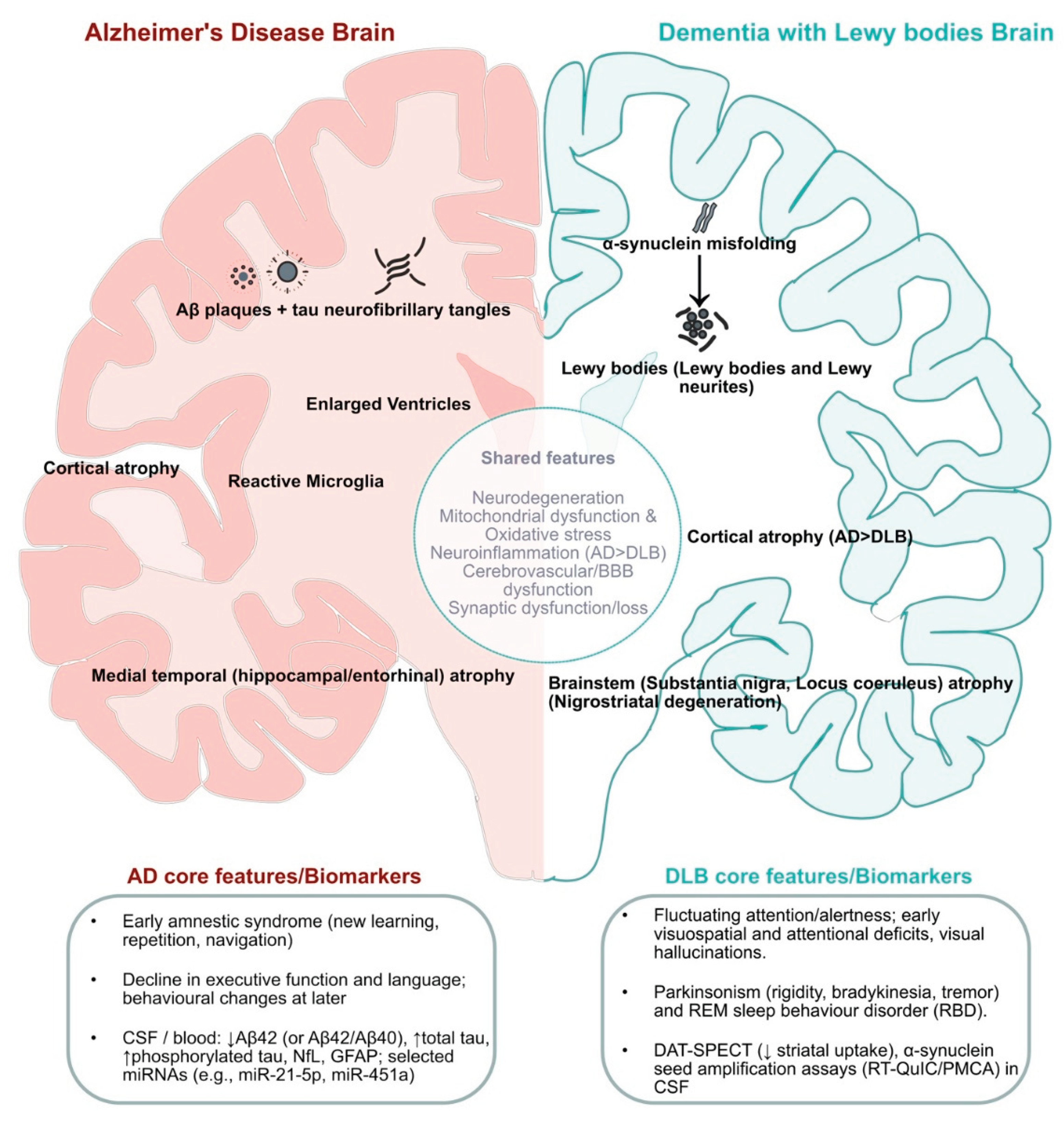
2. Clinical and Neuropathological Overlap Between AD and DLB
2.1. Clinical Features of AD
2.2. Clinical Features of DLB
2.3. Neuropathological Features of AD
2.4. Neuropathological Features of DLB
3. Shared and Divergent Molecular Pathways
3.1. From Etiology to Genetics: AD Versus DLB
3.2. Pathogenic Frameworks: Aβ/Tau/Cholinergic Hypotheses in AD and α-Syn Pathology in DLB
3.3. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in AD Versus DLB
3.4. Neuroinflammation and Cerebrovascular/Endothelial Dysfunction in AD and DLB
3.5. Emerging Pathways from Multi-Omics of AD and DLB
4. Emerging Next-Generation Biomarkers
5. Conclusions and Therapeutic Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Hippius, H.; Neundörfer, G. The Discovery of Alzheimer’s Disease. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience 2003, 5, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakor, V.S.; Tyagi, A.; Lee Jr., J. M.; Coffman, F.; Mittal, R. Alois Alzheimer (1864-1915): The Father of Modern Dementia Research and the Discovery of Alzheimer’s Disease. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.D.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.B.; Young, L.D. History of Alzheimer’s Disease. Dement Neurocognitive Disord 2016, 15, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciurea, V.A.; Covache-Busuioc, R.-A.; Mohan, A.G.; Costin, H.P.; Voicu, V. Alzheimer’s Disease: 120 Years of Research and Progress. JMedLife 2023, 16, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia Prevention, Intervention, and Care: 2020 Report of the Lancet Commission. The Lancet 2020, 396, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaopeng, Z.; Jing, Y.; Xia, L.; Xingsheng, W.; Juan, D.; Yan, L.; Baoshan, L. Global Burden of Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias in Adults Aged 65 Years and Older, 1991–2021: Population-Based Study. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1585711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.-S.; Li, D.-J.; Yang, F.-C.; Tseng, P.-T.; Carvalho, A.F.; Stubbs, B.; Thompson, T.; Mueller, C.; Shin, J.I.; Radua, J.; et al. Mortality Rates in Alzheimer’s Disease and Non-Alzheimer’s Dementias: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. The Lancet Healthy Longevity 2021, 2, e479–e488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J.; Dickerson, B.C.; Frost, C.; Jiskoot, L.C.; Wolk, D.; Van Der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s Disease First Symptoms Are Age Dependent: Evidence from the NACC Dataset. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2015, 11, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förstl, H.; Kurz, A. Clinical Features of Alzheimer’s Disease.
- Zvěřová, M. Clinical Aspects of Alzheimer’s Disease. Clinical Biochemistry 2019, 72, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo-Lopez, J.A.; Yachnis, A.T.; Prokop, S. Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics 2022, 19, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, K.M. Entorhinal Cortex Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Trends in Neurosciences 2023, 46, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacikowski, P.; Kalender, G.; Ciliberti, D.; Fried, I. Human Hippocampal and Entorhinal Neurons Encode the Temporal Structure of Experience. Nature 2024, 635, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzi, R.E.; Bertram, L. Twenty Years of the Alzheimer’s Disease Amyloid Hypothesis: A Genetic Perspective. Cell 2005, 120, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenner, G.G.; Wong, C.W. Alzheimer’s Disease: Initial Report of the Purification and Characterization of a Novel Cerebrovascular Amyloid Protein. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 1984, 120, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K.; Tung, Y.-C.; Wisniewski, H.M. Alzheimer Paired Helical Filaments: Immunochemical Identification of Polypeptides. Acta Neuropathol 1984, 62, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K.; Tung, Y.C.; Quinlan, M.; Wisniewski, H.M.; Binder, L.I. Abnormal Phosphorylation of the Microtubule-Associated Protein Tau (Tau) in Alzheimer Cytoskeletal Pathology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1986, 83, 4913–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capouch, S.D.; Farlow, M.R.; Brosch, J.R. A Review of Dementia with Lewy Bodies’ Impact, Diagnostic Criteria and Treatment. Neurol Ther 2018, 7, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedert, M.; Jakes, R.; Spillantini, M.G. The Synucleinopathies: Twenty Years On. Journal of Parkinson’s Disease 2017, 7, S51–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Outeiro, T.F.; Koss, D.J.; Erskine, D.; Walker, L.; Kurzawa-Akanbi, M.; Burn, D.; Donaghy, P.; Morris, C.; Taylor, J.-P.; Thomas, A.; et al. Dementia with Lewy Bodies: An Update and Outlook. Mol Neurodegeneration 2019, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Hasegawa, M.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Filamentous Inclusions of Lewy Bodies from Parkinson’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1998, 95, 6469–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Neuropathological Spectrum of Synucleinopathies. Mov Disord. 2003, 18, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellinger, K.A.; Lantos, P.L. Papp–Lantos Inclusions and the Pathogenesis of Multiple System Atrophy: An Update. Acta Neuropathol 2010, 119, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Heterogeneity of Multiple System Atrophy: An Update. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, J.E.; Chrisphonte, S.; Cohen, I.; Greenfield, K.K.; Kleiman, M.J.; Moore, C.; Riccio, M.L.; Rosenfeld, A.; Shkolnik, N.; Walker, M.; et al. Characterization of Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB) and Mild Cognitive Impairment Using the Lewy Body Dementia Module (LBD-MOD). Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2021, 17, 1675–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vann Jones, S.A.; O’Brien, J.T. The Prevalence and Incidence of Dementia with Lewy Bodies: A Systematic Review of Population and Clinical Studies. Psychol. Med. 2014, 44, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakisaka, Y.; Furuta, A.; Tanizaki, Y.; Kiyohara, Y.; Iida, M.; Iwaki, T. Age-Associated Prevalence and Risk Factors of Lewy Body Pathology in a General Population: The Hisayama Study. Acta Neuropathologica 2003, 106, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnavel, A.; Dino, F.R.; Jiang, C.; Azmy, S.; Wyman-Chick, K.A.; Bayram, E. Risk Factors and Predictors for Lewy Body Dementia: A Systematic Review. npj Dement. 2025, 1, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Katta, M.R.; Abhishek, S.; Sridhar, R.; Valisekka, S.S.; Hameed, M.; Kaur, J.; Walia, N. Recent Advances in Lewy Body Dementia: A Comprehensive Review. Disease-a-Month 2023, 69, 101441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trétiakoff, K.N. Contribution à L’étude De L’anatomie Pathologique Du Locus Niger De Soemmering Avec Quelques Deductions Relatives A La Pathogenie Des Troubles Du Tonus Musculaire Et De La Maladie De Parkinson. Paris: Universtié de Paris. 1919.
- Okazaki, H.; Lipkin, L.E.; Aronson, S.M. Diffuse Intracytoplasmic Ganglionic Inclusions (Lewy Type) Associated with Progressive Dementia and Quadriparesis in Flexion. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1961, 20, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, K.; Iseki, E. Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Current Opinion in Neurology 1996, 9, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, K. Lewy Bodies in Cerebral Cortex. Report of Three Cases. Acta Neuropathol 1978, 42, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeith, I.G.; Galasko, D.; Kosaka, K.; Perry, E.K.; Dickson, D.W.; Hansen, L.A.; Salmon, D.P.; Lowe, J.; Mirra, S.S.; Byrne, E.J.; et al. Consensus Guidelines for the Clinical and Pathologic Diagnosis of Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB): Report of the Consortium on DLB International Workshop. Neurology 1996, 47, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.; Ballard, C.; Corbett, A.; Aarsland, D. Historical Landmarks in Dementia with Lewy Bodies. The Lancet Neurology 2017, 16, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Lewy Bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, G.; Laczó, J.; Hort, J.; Minihane, A.-M.; Hornberger, M. Spatial Navigation Deficits — Overlooked Cognitive Marker for Preclinical Alzheimer Disease? Nat Rev Neurol 2018, 14, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopman, D.S.; Amieva, H.; Petersen, R.C.; Chételat, G.; Holtzman, D.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Nixon, R.A.; Jones, D.T. Alzheimer Disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.; Drachman, D.; Folstein, M.; Katzman, R.; Price, D.; Stadlan, E.M. Clinical Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Report of the NINCDS—ADRDA Work Group under the Auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 1984, 939–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The Diagnosis of Dementia Due to Alzheimer’s Disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association Workgroups on Diagnostic Guidelines for Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R.; Andrews, J.S.; Beach, T.G.; Buracchio, T.; Dunn, B.; Graf, A.; Hansson, O.; Ho, C.; Jagust, W.; McDade, E.; et al. Revised Criteria for Diagnosis and Staging of Alzheimer’s Disease: Alzheimer’s Association Workgroup. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2024, 20, 5143–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a Biological Definition of Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porsteinsson, A.P.; Isaacson, R.S.; Knox, S.; Sabbagh, M.N.; Rubino, I. Diagnosis of Early Alzheimer’s Disease: Clinical Practice in 2021. The Journal of Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease 2021, 8, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaghy, P.C.; McKeith, I.G. The Clinical Characteristics of Dementia with Lewy Bodies and a Consideration of Prodromal Diagnosis. Alz Res Therapy 2014, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Komatsu, J.; Nakamura, K.; Sakai, K.; Samuraki-Yokohama, M.; Nakajima, K.; Yoshita, M. Diagnostic Criteria for Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Updates and Future Directions. JMD 2020, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capouch, S.D.; Farlow, M.R.; Brosch, J.R. A Review of Dementia with Lewy Bodies’ Impact, Diagnostic Criteria and Treatment. Neurol Ther 2018, 7, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeith, I.G.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Halliday, G.; Taylor, J.-P.; Weintraub, D.; Aarsland, D.; Galvin, J.; Attems, J.; Ballard, C.G.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Fourth Consensus Report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2017, 89, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencze, J.; Seo, W.; Hye, A.; Aarsland, D.; Hortobágyi, T. Dementia with Lewy Bodies – a Clinicopathological Update. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, T.G.; Serrano, G.E.; Zhang, N.; Driver-Dunckley, E.D.; Sue, L.I.; Shill, H.A.; Mehta, S.H.; Belden, C.; Tremblay, C.; Choudhury, P.; et al. Clinicopathological Heterogeneity of Lewy Body Diseases: The Profound Influence of Comorbid Alzheimer’s Disease 2024.
- McKeith, I.G.; Dickson, D.W.; Lowe, J.; Emre, M.; O’Brien, J.T.; Feldman, H.; Cummings, J.; Duda, J.E.; Lippa, C.; Perry, E.K.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Third Report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2005, 65, 1863–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laczó, M.; Svacova, Z.; Lerch, O.; Martinkovic, L.; Krejci, M.; Nedelska, Z.; Horakova, H.; Matoska, V.; Vyhnalek, M.; Hort, J.; et al. Spatial Navigation Deficits in Early Alzheimer’s Disease: The Role of Biomarkers and APOE Genotype. J Neurol 2025, 272, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, R.; Wong, G.; Huang, X. Lewy Body Dementia: Exploring Biomarkers and Pathogenic Interactions of Amyloid β, Tau, and α-Synuclein. Mol Neurodegeneration 2025, 20, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongve, A.; Soennesyn, H.; Skogseth, R.; Oesterhus, R.; Hortobágyi, T.; Ballard, C.; Auestad, B.H.; Aarsland, D. Cognitive Decline in Dementia with Lewy Bodies: A 5-Year Prospective Cohort Study. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, S.S.; Saeed, U.; Ramirez, J.; Herrmann, N.; Stuss, D.T.; Black, S.E.; Masellis, M. Effects of White Matter Hyperintensities, Neuropsychiatric Symptoms, and Cognition on Activities of Daily Living: Differences between Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Alz & Dem Diag Ass & Dis Mo 2022, 14, e12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The Neuropathological Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurodegeneration 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perl, D.P. Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mount Sinai J Medicine 2010, 77, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickerson, B.C.; Bakkour, A.; Salat, D.H.; Feczko, E.; Pacheco, J.; Greve, D.N.; Grodstein, F.; Wright, C.I.; Blacker, D.; Rosas, H.D.; et al. The Cortical Signature of Alzheimer’s Disease: Regionally Specific Cortical Thinning Relates to Symptom Severity in Very Mild to Mild AD Dementia and Is Detectable in Asymptomatic Amyloid-Positive Individuals. Cerebral Cortex 2009, 19, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriagada, P.V.; Growdon, J.H.; Hedley-Whyte, E.T.; Hyman, B.T. Neurofibrillary Tangles but Not Senile Plaques Parallel Duration and Severiti of Azheimer’s Disease.
- Browne, D.F.; Smirnov, D.S.; Coughlin, D.G.; Peng, I.; Standke, H.G.; Kim, Y.; Pizzo, D.P.; Unapanta, A.; Andreasson, T.; Hiniker, A.; et al. Early Alzheimer’s Disease with Frequent Neuritic Plaques Harbors Neocortical Tau Seeds Distinct from Primary Age-Related Tauopathy. Nat Commun 2025, 16, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-Z.; Xia, Y.-Y.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K. Abnormal Hyperphosphorylation of Tau: Sites, Regulation, and Molecular Mechanism of Neurofibrillary Degeneration. JAD 2012, 33, S123–S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuropathological Stageing of Alzheimer-Related Changes. Acta Neuropathol 1991, 82, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Alafuzoff, I.; Arzberger, T.; Kretzschmar, H.; Del Tredici, K. Staging of Alzheimer Disease-Associated Neurofibrillary Pathology Using Paraffin Sections and Immunocytochemistry. Acta Neuropathol 2006, 112, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-D.; Lu, J.-Y.; Li, H.-Q.; Yang, Y.-X.; Jiang, J.-H.; Cui, M.; Zuo, C.-T.; Tan, L.; Dong, Q.; Yu, J.-T.; et al. Staging Tau Pathology with Tau PET in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Longitudinal Study. Transl Psychiatry 2021, 11, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thal, D.R.; Rüb, U.; Orantes, M.; Braak, H. Phases of Aβ-Deposition in the Human Brain and Its Relevance for the Development of AD. Neurology 2002, 58, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montine, T.J.; Phelps, C.H.; Beach, T.G.; Bigio, E.H.; Cairns, N.J.; Dickson, D.W.; Duyckaerts, C.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; Mirra, S.S.; et al. National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association Guidelines for the Neuropathologic Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Practical Approach. Acta Neuropathol 2012, 123, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outeiro, T.F.; Koss, D.J.; Erskine, D.; Walker, L.; Kurzawa-Akanbi, M.; Burn, D.; Donaghy, P.; Morris, C.; Taylor, J.-P.; Thomas, A.; et al. Dementia with Lewy Bodies: An Update and Outlook. Mol Neurodegeneration 2019, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencze, J.; Szarka, M.; Bencs, V.; Szabó, R.N.; Smajda, M.; Aarsland, D.; Hortobágyi, T. Neuropathological Characterization of Lemur Tyrosine Kinase 2 (LMTK2) in Alzheimer’s Disease and Neocortical Lewy Body Disease. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 17222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelska, Z.; Ferman, T.J.; Boeve, B.F.; Przybelski, S.A.; Lesnick, T.G.; Murray, M.E.; Gunter, J.L.; Senjem, M.L.; Vemuri, P.; Smith, G.E.; et al. Pattern of Brain Atrophy Rates in Autopsy-Confirmed Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Neurobiology of Aging 2015, 36, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, L.; Fumagalli, G.G.; Barkhof, F.; Scheltens, P.; O’Brien, J.T.; Bouwman, F.; Burton, E.J.; Rohrer, J.D.; Fox, N.C.; Ridgway, G.R.; et al. MRI Visual Rating Scales in the Diagnosis of Dementia: Evaluation in 184 Post-Mortem Confirmed Cases. Brain 2016, 139, 1211–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attems, J.; Toledo, J.B.; Walker, L.; Gelpi, E.; Gentleman, S.; Halliday, G.; Hortobagyi, T.; Jellinger, K.; Kovacs, G.G.; Lee, E.B.; et al. Neuropathological Consensus Criteria for the Evaluation of Lewy Pathology in Post-Mortem Brains: A Multi-Centre Study. Acta Neuropathol 2021, 141, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, T.; Uchihara, T.; Takahashi, A.; Nakamura, A.; Orimo, S.; Mizusawa, H. Three-Layered Structure Shared Between Lewy Bodies and Lewy Neurites—Three-Dimensional Reconstruction of Triple-Labeled Sections. Brain Pathology 2008, 18, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, S.; Sekiya, H.; Kondru, N.; Ross, O.A.; Dickson, D.W. Neuropathology and Molecular Diagnosis of Synucleinopathies. Mol Neurodegeneration 2021, 16, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, J.; Holmes, C.; Dorey, R.B.; Tommasino, E.; Casal, Y.R.; Williams, D.M.; Dupuy, C.; Nicoll, J.A.R.; Boche, D. Neuroinflammation in Dementia with Lewy Bodies: A Human Post-Mortem Study. Transl Psychiatry 2020, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, E.J.; Karas, G.; Paling, S.M.; Barber, R.; Williams, E.D.; Ballard, C.G.; McKeith, I.G.; Scheltens, P.; Barkhof, F.; O’Brien, J.T. Patterns of Cerebral Atrophy in Dementia with Lewy Bodies Using Voxel-Based Morphometry. NeuroImage 2002, 17, 618–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, E.J.; Barber, R.; Mukaetova-Ladinska, E.B.; Robson, J.; Perry, R.H.; Jaros, E.; Kalaria, R.N.; O’Brien, J.T. Medial Temporal Lobe Atrophy on MRI Differentiates Alzheimer’s Disease from Dementia with Lewy Bodies and Vascular Cognitive Impairment: A Prospective Study with Pathological Verification of Diagnosis. Brain 2009, 132, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, D.G.; Hurtig, H.I.; Irwin, D.J. Pathological Influences on Clinical Heterogeneity in Lewy Body Diseases. Movement Disorders 2020, 35, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhr, S. Making Time for Brain Health: Recognising Temporal Inequity in Dementia Risk Reduction.
- Yegambaram, M.; Manivannan, B.; Beach, T.; Halden, R. Role of Environmental Contaminants in the Etiology of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review. CAR 2015, 12, 116–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin-Chan, M.; Navarro-Yepes, J.; Quintanilla-Vega, B. Environmental Pollutants as Risk Factors for Neurodegenerative Disorders: Alzheimer and Parkinson Diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giridharan, V.V.; Masud, F.; Petronilho, F.; Dal-Pizzol, F.; Barichello, T. Infection-Induced Systemic Inflammation Is a Potential Driver of Alzheimer’s Disease Progression. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzi, R.E. The Genetics of Alzheimer Disease. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine 2012, 2, a006296–a006296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellenguez, C.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Lambert, J.-C. Genetics of Alzheimer’s Disease: Where We Are, and Where We Are Going. Current Opinion in Neurobiology 2020, 61, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellenguez, C.; Küçükali, F.; Jansen, I.E.; Kleineidam, L.; Moreno-Grau, S.; Amin, N.; Naj, A.C.; Campos-Martin, R.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Andrade, V.; et al. New Insights into the Genetic Etiology of Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias. Nat Genet 2022, 54, 412–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korologou-Linden, R.; Bhatta, L.; Brumpton, B.M.; Howe, L.D.; Millard, L.A.C.; Kolaric, K.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Williams, D.M.; Smith, G.D.; Anderson, E.L.; et al. The Causes and Consequences of Alzheimer’s Disease: Phenome-Wide Evidence from Mendelian Randomization. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Bp, K.; C R, S.; Saikumar, N.V.; Philip, P.; Narayanan, M. Alzheimer’s Disease Rewires Gene Coexpression Networks Coupling Different Brain Regions. npj Syst Biol Appl 2024, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellenguez, C.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Lambert, J.-C. Genetics of Alzheimer’s Disease: Where We Are, and Where We Are Going. Current Opinion in Neurobiology 2020, 61, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamatham, P.T.; Shukla, R.; Khatri, D.K.; Vora, L.K. Pathogenesis, Diagnostics, and Therapeutics for Alzheimer’s Disease: Breaking the Memory Barrier. Ageing Research Reviews 2024, 101, 102481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Härtig, W.; Bauer, A.; Brauer, K.; Grosche, J.; Hortobágyi, T.; Penke, B.; Schliebs, R.; Harkany, T. Functional Recovery of Cholinergic Basal Forebrain Neurons under Disease Conditions: Old Problems, New Solutions? Reviews in the Neurosciences 2002, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Dementia with Lewy Bodies and Parkinson’s Disease-Dementia: Current Concepts and Controversies. J Neural Transm 2018, 125, 615–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agin, A.; Blanc, F.; Bousiges, O.; Villette, C.; Philippi, N.; Demuynck, C.; Martin-Hunyadi, C.; Cretin, B.; Lang, S.; Zumsteg, J.; et al. Environmental Exposure to Phthalates and Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Contribution of Metabolomics. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2020, 91, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Xu, Y. Environmental Risk Factors Provoke New Thinking for Prevention and Treatment of Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, R.; Sabir, M.S.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Saez-Atienzar, S.; Reynolds, R.H.; Gustavsson, E.; Walton, R.L.; Ahmed, S.; Viollet, C.; Ding, J.; et al. Genome Sequencing Analysis Identifies New Loci Associated with Lewy Body Dementia and Provides Insights into Its Genetic Architecture. Nat Genet 2021, 53, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaivola, K.; Shah, Z.; Chia, R. ; International LBD Genomics Consortium; Black, S. E.; Gan-Or, Z.; Keith, J.; Masellis, M.; Rogaeva, E.; Brice, A.; et al. Genetic Evaluation of Dementia with Lewy Bodies Implicates Distinct Disease Subgroups. Brain 2022, 145, 1757–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalls, M.A.; Blauwendraat, C.; Vallerga, C.L.; Heilbron, K.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Chang, D.; Tan, M.; Kia, D.A.; Noyce, A.J.; Xue, A.; et al. Identification of Novel Risk Loci, Causal Insights, and Heritable Risk for Parkinson’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Studies. The Lancet Neurology 2019, 18, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talyansky, S.; Le Guen, Y.; Kasireddy, N.; Belloy, M.E.; Greicius, M.D. APOE-Ε4 and BIN1 Increase Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology but Not Specifically of Lewy Body Pathology. acta neuropathol commun 2023, 11, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, R.; Ross, O.A.; Kun-Rodrigues, C.; Hernandez, D.G.; Orme, T.; Eicher, J.D.; Shepherd, C.E.; Parkkinen, L.; Darwent, L.; Heckman, M.G.; et al. Investigating the Genetic Architecture of Dementia with Lewy Bodies: A Two-Stage Genome-Wide Association Study. The Lancet Neurology 2018, 17, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.A.; Higgins, G.A. Alzheimer’s Disease: The Amyloid Cascade Hypothesis. Science 1992, 256, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The Amyloid Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease at 25 Years. EMBO Mol Med 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-Q.; Mobley, W.C. Exploring the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer Disease in Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons: Converging Insights From Alternative Hypotheses. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Luehmann, M.; Spires-Jones, T.L.; Prada, C.; Garcia-Alloza, M.; De Calignon, A.; Rozkalne, A.; Koenigsknecht-Talboo, J.; Holtzman, D.M.; Bacskai, B.J.; Hyman, B.T. Rapid Appearance and Local Toxicity of Amyloid-β Plaques in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Nature 2008, 451, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Cheung, T.T.; Cai, X.-D.; Odaka, A.; Otvos, L.; Eckman, C.; Golde, T.E.; Younkin, S.G. An Increased Percentage of Long Amyloid β Protein Secreted by Familial Amyloid β Protein Precursor (βApp717 ) Mutants. Science 1994, 264, 1336–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.P.; LeVine, H. Alzheimer’s Disease and the Amyloid-β Peptide. JAD 2010, 19, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-Q.; Mobley, W.C. Exploring the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer Disease in Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons: Converging Insights From Alternative Hypotheses. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, P.T.; Palmer, A.M.; Snape, M.; Wilcock, G.K. The Cholinergic Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review of Progress. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry 1999, 66, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Mesulam, M.-M.; Cuello, A.C.; Khachaturian, A.S.; Vergallo, A.; Farlow, M.R.; Snyder, P.J.; Giacobini, E.; Khachaturian, Z.S. Revisiting the Cholinergic Hypothesis in Alzheimer’s Disease: Emerging Evidence from Translational and Clinical Research. The Journal of Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease 2019, 6, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, J.; Lucas, J.J.; Pérez, M.; Hernández, F. Role of Tau Protein in Both Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Physiological Reviews 2004, 84, 361–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.D.C.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K. Alzheimer’s Disease Hyperphosphorylated Tau Sequesters Normal Tau into Tangles of Filaments and Disassembles Microtubules. Nat Med 1996, 2, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moloney, C.M.; Lowe, V.J.; Murray, M.E. Visualization of Neurofibrillary Tangle Maturity in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Clinicopathologic Perspective for Biomarker Research. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2021, 17, 1554–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguzzi, A.; Lakkaraju, A.K.K. Cell Biology of Prions and Prionoids: A Status Report. Trends in Cell Biology 2016, 26, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, B.; Stancu, I.-C.; Buist, A.; Bird, M.; Wang, P.; Vanoosthuyse, A.; Van Kolen, K.; Verheyen, A.; Kienlen-Campard, P.; Octave, J.-N.; et al. Heterotypic Seeding of Tau Fibrillization by Pre-Aggregated Abeta Provides Potent Seeds for Prion-like Seeding and Propagation of Tau-Pathology in Vivo. Acta Neuropathol 2016, 131, 549–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, G.S. Amyloid-β and Tau: The Trigger and Bullet in Alzheimer Disease Pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol 2014, 71, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, B.; Stancu, I.-C.; Buist, A.; Bird, M.; Wang, P.; Vanoosthuyse, A.; Van Kolen, K.; Verheyen, A.; Kienlen-Campard, P.; Octave, J.-N.; et al. Heterotypic Seeding of Tau Fibrillization by Pre-Aggregated Abeta Provides Potent Seeds for Prion-like Seeding and Propagation of Tau-Pathology in Vivo. Acta Neuropathol 2016, 131, 549–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAleese, K.E.; Walker, L.; Erskine, D.; Thomas, A.J.; McKeith, I.G.; Attems, J. TDP-43 Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease, Dementia with Lewy Bodies and Ageing. Brain Pathology 2017, 27, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, C.; Soga, T.; Okano, H.J.; Parhar, I. α-Synuclein-Mediated Neurodegeneration in Dementia with Lewy Bodies: The Pathobiology of a Paradox. Cell Biosci 2021, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, S.; De Cecco, E.; Aguzzi, A. The Hidden Cell-to-Cell Trail of α-Synuclein Aggregates. Journal of Molecular Biology 2022, 167930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, J.I.; Lee, J.; Monteiro, O.; Woerman, A.L.; Lazar, A.A.; Condello, C.; Paras, N.A.; Prusiner, S.B. Different α-Synuclein Prion Strains Cause Dementia with Lewy Bodies and Multiple System Atrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2022, 119, e2113489119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Perren, A.; Gelders, G.; Fenyi, A.; Bousset, L.; Brito, F.; Peelaerts, W.; Van Den Haute, C.; Gentleman, S.; Melki, R.; Baekelandt, V. The Structural Differences between Patient-Derived α-Synuclein Strains Dictate Characteristics of Parkinson’s Disease, Multiple System Atrophy and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Acta Neuropathol 2020, 139, 977–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative Stress: A Key Modulator in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuner, K.; Schütt, T.; Kurz, C.; Eckert, S.H.; Schiller, C.; Occhipinti, A.; Mai, S.; Jendrach, M.; Eckert, G.P.; Kruse, S.E.; et al. Mitochondrion-Derived Reactive Oxygen Species Lead to Enhanced Amyloid Beta Formation. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 2012, 16, 1421–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, R.H. The Alzheimer’s Disease Mitochondrial Cascade Hypothesis: A Current Overview. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2023, 92, 751–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.J.; Sagara, Y.; Arroyo, A.; Rockenstein, E.; Sisk, A.; Mallory, M.; Wong, J.; Takenouchi, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Masliah, E. α-Synuclein Promotes Mitochondrial Deficit and Oxidative Stress. The American Journal of Pathology 2000, 157, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billingsley, K.J.; Barbosa, I.A.; Bandrés-Ciga, S.; Quinn, J.P.; Bubb, V.J.; Deshpande, C.; Botia, J.A.; Reynolds, R.H.; Zhang, D.; Simpson, M.A.; et al. Mitochondria Function Associated Genes Contribute to Parkinson’s Disease Risk and Later Age at Onset. npj Parkinsons Dis. 2019, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spano, M. The Possible Involvement of Mitochondrial Dysfunctions in Lewy Body Dementia: A Systematic Review. Functional Neurology 2015. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Dai, X.; Zhang, C.; Duan, Z.; Zhou, G.; Wang, J. Investigating the Causal Relationships between Mitochondrial Proteins and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2025, 105, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millot, P.; Pujol, C.; Paquet, C.; Mouton-Liger, F. Impaired Mitochondrial Dynamics in the Blood of Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease and Lewy Body Dementia. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2023, 19, e075795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; Khoury, J.E.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease. The Lancet Neurology 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-Y.; Tan, M.-S.; Yu, J.-T.; Tan, L. Role of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Released from Microglia in Alzheimer’s Disease. Ann Transl Med 2015; 3(10): 136 2015, Ann Transl Med 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Griciuc, A.; Patel, S.; Federico, A.N.; Choi, S.H.; Innes, B.J.; Oram, M.K.; Cereghetti, G.; McGinty, D.; Anselmo, A.; Sadreyev, R.I.; et al. TREM2 Acts Downstream of CD33 in Modulating Microglial Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuron 2019, 103, 820–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Van Der Flier, W.M.; Jessen, F.; Hoozemanns, J.; Thal, D.R.; Boche, D.; Brosseron, F.; Teunissen, C.; Zetterberg, H.; Jacobs, A.H.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer Disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2025, 25, 321–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plantone, D.; Pardini, M.; Righi, D.; Manco, C.; Colombo, B.M.; De Stefano, N. The Role of TNF-α in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Narrative Review. Cells 2023, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, T.J.; Murray, T.E.; Noyovitz, B.; Narayana, K.; Gray, T.E.; Le, J.; He, J.; Simtchouk, S.; Gibon, J.; Alcorn, J.; et al. Cardiolipin Released by Microglia Can Act on Neighboring Glial Cells to Facilitate the Uptake of Amyloid-β (1–42). Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience 2023, 124, 103804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellinger, K.A.; Attems, J. Prevalence and Impact of Vascular and Alzheimer Pathologies in Lewy Body Disease. Acta Neuropathol 2008, 115, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Alzheimer Disease and Cerebrovascular Pathology: An Update. Journal of Neural Transmission 2002, 109, 813–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attems, J.; Jellinger, K.A. Only Cerebral Capillary Amyloid Angiopathy Correlates with Alzheimer Pathology? A Pilot Study. Acta Neuropathologica 2004, 107, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeev, V.; Fann, D.Y.; Dinh, Q.N.; Kim, H.A.; De Silva, T.M.; Lai, M.K.P.; Chen, C.L.-H.; Drummond, G.R.; Sobey, C.G.; Arumugam, T.V. Pathophysiology of Blood Brain Barrier Dysfunction during Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion in Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Theranostics 2022, 12, 1639–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenaro, E.; Piacentino, G.; Constantin, G. The Blood-Brain Barrier in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiology of Disease 2017, 107, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelario-Jalil, E.; Dijkhuizen, R.M.; Magnus, T. Neuroinflammation, Stroke, Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction, and Imaging Modalities. Stroke 2022, 53, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, T.Y.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, X. Peripheral and Central Neuroimmune Mechanisms in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis. Mol Neurodegeneration 2025, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cechetto, D.F.; Hachinski, V.; Whitehead, S.N. Vascular Risk Factors and Alzheimer’s Disease. Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics 2008, 8, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surendranathan, A.; Rowe, J.B.; O’Brien, J.T. Neuroinflammation in Lewy Body Dementia. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 2015, 21, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, A.P.; Bidkhori, G.; Shoaie, S.; Clarke, E.; Morrin, H.; Hye, A.; Williams, G.; Ballard, C.; Francis, P.; Aarsland, D. Postmortem Cortical Transcriptomics of Lewy Body Dementia Reveal Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Lack of Neuroinflammation. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2020, 28, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Prevalence of Vascular Lesions in Dementia with Lewy Bodies. A Postmortem Study. J Neural Transm 2003, 110, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.C.B.; Carter, E.K.; Dammer, E.B.; Duong, D.M.; Gerasimov, E.S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Betarbet, R.; Ping, L.; Yin, L.; et al. Large-Scale Deep Multi-Layer Analysis of Alzheimer’s Disease Brain Reveals Strong Proteomic Disease-Related Changes Not Observed at the RNA Level. Nat Neurosci 2022, 25, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathys, H.; Davila-Velderrain, J.; Peng, Z.; Gao, F.; Mohammadi, S.; Young, J.Z.; Menon, M.; He, L.; Abdurrob, F.; Jiang, X.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Nature 2019, 570, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knörnschild, F.; Zhang, E.J.; Ghosh Biswas, R.; Kobus, M.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.X.; Rao, A.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; et al. Correlations of Blood and Brain NMR Metabolomics with Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Models. Transl Psychiatry 2025, 15, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Tsuneyoshi, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Aoshima, K.; Tsugawa, H. ; the Alzheimer’s Disease Metabolomics Consortium; Weiner, M. ; Aisen, P.; Petersen, R.; et al. Multiomics Analysis to Explore Blood Metabolite Biomarkers in an Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative Cohort. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greally, S.; Kumar, M.; Schlaffner, C.; Van Der Heijden, H.; Lawton, E.S.; Biswas, D.; Berretta, S.; Steen, H.; Steen, J.A. Dementia with Lewy Bodies Patients with High Tau Levels Display Unique Proteome Profiles. Mol Neurodegeneration 2024, 19, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goralski, T.M.; Meyerdirk, L.; Breton, L.; Brasseur, L.; Kurgat, K.; DeWeerd, D.; Turner, L.; Becker, K.; Adams, M.; Newhouse, D.J.; et al. Spatial Transcriptomics Reveals Molecular Dysfunction Associated with Cortical Lewy Pathology. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Donaghy, P.C.; Roberts, G.; Chouliaras, L.; O’Brien, J.T.; Thomas, A.J.; Heslegrave, A.J.; Zetterberg, H.; McGuinness, B.; Passmore, A.P.; et al. Plasma Metabolites Distinguish Dementia with Lewy Bodies from Alzheimer’s Disease: A Cross-Sectional Metabolomic Analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 15, 1326780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canal-Garcia, A.; Branca, R.M.; Francis, P.T.; Ballard, C.; Winblad, B.; Lehtiö, J.; Nilsson, P.; Aarsland, D.; Pereira, J.B.; Bereczki, E. Proteomic Signatures of Alzheimer’s Disease and Lewy Body Dementias: A Comparative Analysis. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2025, 21, e14375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shantaraman, A.; Dammer, E.B.; Ugochukwu, O.; Duong, D.M.; Yin, L.; Carter, E.K.; Gearing, M.; Chen-Plotkin, A.; Lee, E.B.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; et al. Network Proteomics of the Lewy Body Dementia Brain Reveals Presynaptic Signatures Distinct from Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurodegeneration 2024, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habbal, S.; Mian, M.; Imam, M.; Tahiri, J.; Amor, A.; Reddy, P.H. Harnessing Artificial Intelligence for Transforming Dementia Care: Innovations in Early Detection and Treatment. Brain Organoid and Systems Neuroscience Journal 2025, 3, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, T.R.; Brookes, K.J.; Sharma, R.; Moemeni, A.; Rajkumar, A.P. Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Genomics, Transcriptomics, and Its Future with Data Science. Cells 2024, 13, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, P.; Guo, Y.; Yu, J. Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease: Emerging Trends and Clinical Implications. Chinese Medical Journal 2025, 138, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Criteria for the Neuropathological Diagnosis of Dementing Disorders: Routes out of the Swamp? Acta Neuropathol 2009, 117, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGettigan, S.; Nolan, Y.; Ghosh, S.; O’Mahony, D. The Emerging Role of Blood Biomarkers in Diagnosis and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur Geriatr Med 2023, 14, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, G.; Valletta, M.; Rizzuto, D.; Xia, X.; Qiu, C.; Orsini, N.; Dale, M.; Andersson, S.; Fredolini, C.; Winblad, B.; et al. Blood-Based Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease and Incident Dementia in the Community. Nat Med 2025, 31, 2027–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afrin, M.R.; Upadhyaya, P.G.; Hashim, A.; Bhattacharya, K.; Chanu, N.R.; Das, D.; Khanal, P.; Deka, S. Advanced Biomarkers: Beyond Amyloid and Tau: Emerging Non-Traditional Biomarkers for Alzheimer`s Diagnosis and Progression. Ageing Research Reviews 2025, 108, 102736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutrot, A.; Schmidt, S.; Coutrot, L.; Pittman, J.; Hong, L.; Wiener, J.M.; Hölscher, C.; Dalton, R.C.; Hornberger, M.; Spiers, H.J. Virtual Navigation Tested on a Mobile App Is Predictive of Real-World Wayfinding Navigation Performance. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, N.; Bouter, C.; Müller, S.J.; Van Riesen, C.; Khadhraoui, E.; Ernst, M.; Riedel, C.H.; Wiltfang, J.; Lange, C. New Insights into Potential Biomarkers in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment Occurring in the Prodromal Stage of Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Brain Sciences 2023, 13, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, S.K. Updates in Fluid, Tissue, and Imaging Biomarkers for Dementia with Lewy Bodies and Implications for Biologically Based Disease Definitions. Curr Treat Options Neurol 2024, 26, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashuel, H.A.; Surmeier, D.J.; Simuni, T.; Merchant, K.; Caughey, B.; Soto, C.; Fares, M.-B.; Heym, R.G.; Melki, R. Alpha-Synuclein Seed Amplification Assays: Data Sharing, Standardization Needed for Clinical Use. Science AdvAnceS 2025. [CrossRef]
- Bsoul, R.; McWilliam, O.H.; Waldemar, G.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Simonsen, A.H.; Von Buchwald, C.; Bech, M.; Pinborg, C.H.; Pedersen, C.K.; Baungaard, S.O.; et al. Accurate Detection of Pathologic α-Synuclein in CSF, Skin, Olfactory Mucosa, and Urine with a Uniform Seeding Amplification Assay. acta neuropathol commun 2025, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjaelland, N.S.; Gramkow, M.H.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Frederiksen, K.S. Digital Biomarkers for the Assessment of Non-Cognitive Symptoms in Patients with Dementia with Lewy Bodies: A Systematic Review. JAD 2024, 100, 431–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Campo, M.; Vermunt, L.; Peeters, C.F.W.; Sieben, A.; Hok-A-Hin, Y.S.; Lleó, A.; Alcolea, D.; Van Nee, M.; Engelborghs, S.; Van Alphen, J.L.; et al. CSF Proteome Profiling Reveals Biomarkers to Discriminate Dementia with Lewy Bodies from Alzheimer´s Disease. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellinger, K.A. Comorbid Pathologies and Their Impact on Dementia with Lewy Bodies—Current View. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevigny, J.; Chiao, P.; Bussière, T.; Weinreb, P.H.; Williams, L.; Maier, M.; Dunstan, R.; Salloway, S.; Chen, T.; Ling, Y.; et al. The Antibody Aducanumab Reduces Aβ Plaques in Alzheimer’s Disease. Nature 2016, 537, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neupane, S.; Nikolić, L.; Maraio, L.; Goiran, T.; Karpilovsky, N.; Sellitto, S.; Bouris, V.; Yin, J.-A.; Melki, R.; Fon, E.A.; et al. Large-Scale Bidirectional Arrayed Genetic Screens Identify OXR1 and EMC4 as Modifiers of α-Synuclein Aggregation. bioRxiv 2025. [CrossRef]
- Neupane, S.; Khadka, J.; Rayamajhi, S.; Pandey, A.S. Binding Modes of Potential Anti-Prion Phytochemicals to PrPC Structures in Silico. Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine 2023, 14, 100750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacesa, M.; Nickel, L.; Schellhaas, C.; Schmidt, J.; Pyatova, E.; Kissling, L.; Barendse, P.; Choudhury, J.; Kapoor, S.; Alcaraz-Serna, A.; et al. One-Shot Design of Functional Protein Binders with BindCraft. Nature 2025, 646, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



