Submitted:
08 March 2025
Posted:
10 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
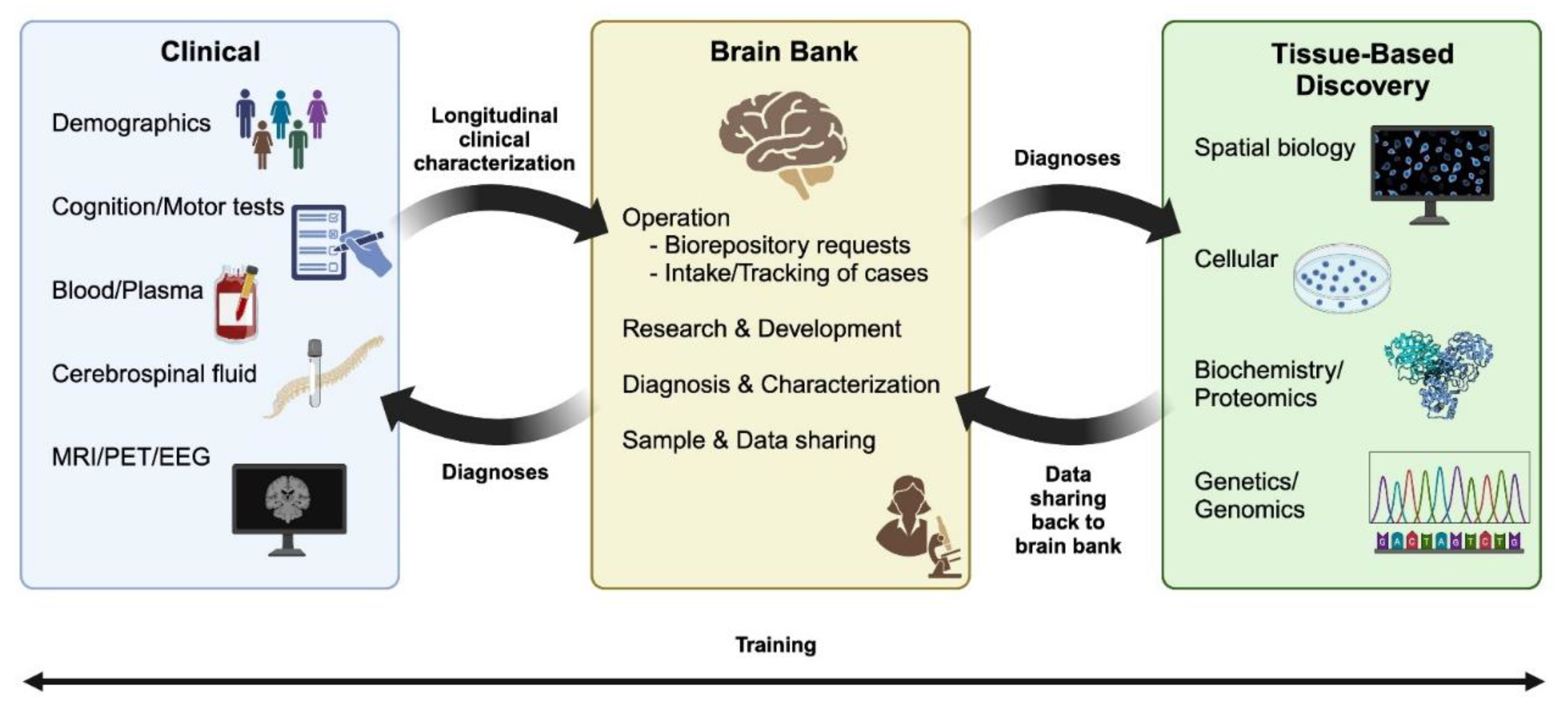
Introduction
Prospective Brain Collections & Increasing Representation for Broader Insights
Building Capacity for Expertise in Neuropathology and Informatics
Innovating Tissue Quality Strategies to Unlock Molecular Insights
Streamlining Digital Slide Sharing and Analysis to Enhance Translational Potential
Building Collaborative Platforms to Accelerate Tissue-Based Discoveries
Harnessing machine learning to revolutionize brain banking
Conclusions
Boxes
| Box 1 | Low autopsy rate for healthy aging and groups with limited representation in scientific research |
| 1.1 Enhanced education on brain donation through outreach |
Recommended solutions:
|
| 1.2 Enhanced efforts to recruit healthy aging and broaden age spectrum of brain donors |
Recommended solutions:
|
| Box 2 | Dearth of neuropathology experts and informaticians with brain banking knowledge |
| 2.1 Neuropathologytraining fellowships for MDs and PhDs |
Recommended solutions:
|
| 2.2 Data science training and integration |
Recommended solutions:
|
| 2.3 NeuroPathopedia - Neuropathology-based encyclopedia |
Recommended solutions:
|
| 2.4 Phenotypic data collection and tissue provision |
Recommended solutions:
|
| Box 3 | Tissue quality innovations needed to maximize molecular discoveries |
| 3.1 Molecular and biochemical diagnostics beyond immunohistochemistry |
Recommended solutions:
|
| 3.2 Enhanced efforts for development of methods to utilize existing brain bank materials |
Recommended solutions:
|
| 3.3 Enhancing procurement areas and autopsy response teams for sample collection |
Recommended solutions:
|
| 3.4 Harmonization in tissue preparation (fixative, freezing), storage, and inventory |
Recommended solutions:
|
| Box 4 | Limited capabilities for digital slide sharing to facilitate harmonization of disease staging and capturing phenotypic heterogeneity |
| 4.1 Neuroanatomic segmentation for digitized slides |
Recommended solutions:
|
| 4.2 Slide sharing/hosting efforts |
Recommended solutions:
|
| 4.3 Neuropathology-centric initiatives |
Recommended solutions:
|
| 4.4 Alliance of worldwide brain banks |
Recommended solutions:
|
| Box 5 | Relative lack of common neuropathologic data models and secure storage platforms |
| 5.1 Data harmonization for common data elements |
Recommended solutions:
|
| 5.2 Sample-level tracking through a universal digital object identifier (DOI) |
Recommended solutions:
|
| 5.3 Codified brain library through an accessible portal |
Recommended solutions:
|
| 5.4 Common Coordinate Framework |
Recommended solutions:
|
| Box 6 | Emerging need for machine learning to optimize brain bank workflow |
| 6.1 Quality control for digitized slides |
Recommended solutions:
|
| 6.2 Convergence of diverse data streams |
Recommended solutions:
|
Acknowledgements
References
- Danner, B.; Gonzalez, A.D.; Corbett, W.C.; Alhneif, M.; Etemadmoghadam, S.; Parker-Garza, J.; and Flanagan, M.E. Brain banking in the United States and Europe: Importance, challenges, and future trends. Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology 2024, 83, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, T.G. Alzheimer's disease and the "Valley Of Death": not enough guidance from human brain tissue? J Alzheimers Dis 2013, 33 Suppl 1, S219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, A.F.; Poloni, T.E.; Medici, V.; Chikhladze, M.; Guaita, A.; and Ceroni, M. From brain collections to modern brain banks: A historical perspective. Alzheimers Dement (N Y) 2019, 5, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, R.; Smith, A.D.; Jobst, K.A.; Refsum, H.; Sutton, L.; and Ueland, P.M. Folate, vitamin B12, and serum total homocysteine levels in confirmed Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 1998, 55, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deary, I.J.; Gow, A.J.; Taylor, M.D.; Corley, J.; Brett, C.; Wilson, V.; Campbell, H.; Whalley, L.J.; Visscher, P.M.; Porteous, D.J.; and Starr, J.M. The Lothian Birth Cohort 1936: a study to examine influences on cognitive ageing from age 11 to age 70 and beyond. BMC Geriatr 2007, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.O.; Geda, Y.E.; Knopman, D.S.; Cha, R.H.; Pankratz, V.S.; Boeve, B.F.; Ivnik, R.J.; Tangalos, E.G.; Petersen, R.C.; and Rocca, W.A. The Mayo Clinic Study of Aging: design and sampling, participation, baseline measures and sample characteristics. Neuroepidemiology 2008, 30, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, M.J.; Lipton, R.B.; Hall, C.B.; Zimmerman, M.E.; Sanders, A.E.; Verghese, J.; Dickson, D.W.; and Derby, C.A. Age-specific and sex-specific prevalence and incidence of mild cognitive impairment, dementia, and Alzheimer dementia in blacks and whites: a report from the Einstein Aging Study. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 2012, 26, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, L.L.; Shah, R.C.; Aggarwal, N.T.; Bennett, D.A.; and Schneider, J.A. The Minority Aging Research Study: ongoing efforts to obtain brain donation in African Americans without dementia. Curr Alzheimer Res 2012, 9, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Sue, L.I.; Serrano, G.; Shill, H.A.; Walker, D.G.; Lue, L.; Roher, A.E.; Dugger, B.N.; Maarouf, C.; et al. Arizona Study of Aging and Neurodegenerative Disorders and Brain and Body Donation Program. Neuropathology 2015, 35, 354–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, E.H.; Paetau, A.; Martiskainen, M.; Lyytikainen, L.P.; Lehtimaki, T.; Karhunen, P.; and Myllykangas, L. Accumulation of Lewy-Related Pathology Starts in Middle Age: The Tampere Sudden Death Study. Ann Neurol 2024, 95, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; and Millar, T. Brain donation procedures in the Sudden Death Brain Bank in Edinburgh. Handb Clin Neurol 2018, 150, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alafuzoff, I.; Arzberger, T.; Al-Sarraj, S.; Bodi, I.; Bogdanovic, N.; Braak, H.; Bugiani, O.; Del-Tredici, K.; Ferrer, I.; Gelpi, E.; et al. Staging of neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer's disease: a study of the BrainNet Europe Consortium. Brain Pathol 2008, 18, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossor, M.N.; Fox, N.C.; Mummery, C.J.; Schott, J.M.; and Warren, J.D. The diagnosis of young-onset dementia. Lancet Neurol 2010, 9, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liesinger, A.M.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Duara, R.; Carter, R.E.; Hanna Al-Shaikh, F.S.; Koga, S.; Hinkle, K.M.; DiLello, S.K.; Johnson, M.F.; Aziz, A.; et al. Sex and age interact to determine clinicopathologic differences in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 2018, 136, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, C.M.; Shah, R.C.; Bennett, D.A.; Wilson, R.S.; and Barnes, L.L. Perceived Impediments to Completed Brain Autopsies Among Diverse Older Adults Who Have Signed a Uniform Anatomical Gift Act for Brain Donation for Clinical Research. Ethn Dis 2020, 30, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, C.M.; Shah, R.C.; Bennett, D.A.; Wilson, R.S.; and Barnes, L.L. The Health Equity Through Aging Research And Discussion (HEARD) Study: A Proposed Two-Phase Sequential Mixed-Methods Research Design To Understand Barriers And Facilitators Of Brain Donation Among Diverse Older Adults. Exp Aging Res 2020, 46, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metter, D.M.; Colgan, T.J.; Leung, S.T.; Timmons, C.F.; and Park, J.Y. Trends in the US and Canadian Pathologist Workforces From 2007 to 2017. JAMA Netw Open 2019, 2, e194337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Kingdom Brain Bank Network (2024). https://ukbbn.brainsfordementiaresearch.org.
- Netherlands Brain Bank (2024). https://www.brainbank.nl.
- Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative (2024). https://www.ppmi-info.org/.
- Rush Alzheimer's Disease Center (2024). https://www.radc.rush.edu.
- National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center (2024). https://naccdata.org/.
- National Institute of Health NeuroBioBank (2024). https://neurobiobank.nih.gov/about/.
- Schmidt, R.E. (2024). https://neuropathologyatlas.wustl.edu/.
- Rademaker, S.H.M.; and Huitinga, I. A new viewpoint: running a nonprofit brain bank as a business. Handb Clin Neurol 2018, 150, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brain & Body Donation Program (2024). https://www.bannerhealth.com/services/research/about-banner-research/research-programs/brain-and-body-donation-program.
- Androvic, P.; Schifferer, M.; Perez Anderson, K.; Cantuti-Castelvetri, L.; Jiang, H.; Ji, H.; Liu, L.; Gouna, G.; Berghoff, S.A.; Besson-Girard, S.; et al. Spatial Transcriptomics-correlated Electron Microscopy maps transcriptional and ultrastructural responses to brain injury. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabitto, M.I.; Travaglini, K.J.; Rachleff, V.M.; Kaplan, E.S.; Long, B.; Ariza, J.; Ding, Y.; Mahoney, J.T.; Dee, N.; Goldy, J.; et al. Integrated multimodal cell atlas of Alzheimer’s disease. bioRxiv 2024, 2023.2005.2008.539485. [CrossRef]
- Maniatis, S.; Petrescu, J.; and Phatnani, H. Spatially resolved transcriptomics and its applications in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2021, 66, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickovic, S.; Lötstedt, B.; Klughammer, J.; Mages, S.; Segerstolpe, Å.; Rozenblatt-Rosen, O.; and Regev, A. SM-Omics is an automated platform for high-throughput spatial multi-omics. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorstad, N.L.; Close, J.; Johansen, N.; Yanny, A.M.; Barkan, E.R.; Travaglini, K.J.; Bertagnolli, D.; Campos, J.; Casper, T.; Crichton, K.; et al. Transcriptomic cytoarchitecture reveals principles of human neocortex organization. Science 2023, 382, eadf6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paryani, F.; Kwon, J.S.; Ng, C.W.; Madden, N.; Ofori, K.; Tang, A.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Mahajan, A.; Davidson, S.M.; et al. Multi-OMIC analysis of Huntington disease reveals a neuroprotective astrocyte state. bioRxiv. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Otero-Garcia, M.; Mahajani, S.U.; Wakhloo, D.; Tang, W.; Xue, Y.-Q.; Morabito, S.; Pan, J.; Oberhauser, J.; Madira, A.E.; Shakouri, T.; et al. Molecular signatures underlying neurofibrillary tangle susceptibility in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 2022, 110, 2929–2948e2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, K.; Li, E.; Eser, R.; Piergies, A.; Sit, R.; Tan, M.; Neff, N.; Li, S.H.; Rodriguez, R.D.; Suemoto, C.K.; et al. Molecular characterization of selectively vulnerable neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Neurosci 2021, 24, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna, M.; Konopka, G.; Liddelow, S.A.; Nowakowski, T.; Awatramani, R.; Bateup, H.S.; Cadwell, C.R.; Caglayan, E.; Chen, J.L.; Gillis, J.; et al. Implementation and validation of single-cell genomics experiments in neuroscience. Nat Neurosci 2024, 27, 2310–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawrylycz, M.J.; Lein, E.S.; Guillozet-Bongaarts, A.L.; Shen, E.H.; Ng, L.; Miller, J.A.; van de Lagemaat, L.N.; Smith, K.A.; Ebbert, A.; Riley, Z.L.; et al. An anatomically comprehensive atlas of the adult human brain transcriptome. Nature 2012, 489, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adameyko, I.; Bakken, T.; Bhaduri, A.; Chhatbar, C.; Filbin, M.G.; Gate, D.; Hochgerner, H.; Kim, C.N.; Krull, J.; La Manno, G.; et al. Applying single-cell and single-nucleus genomics to studies of cellular heterogeneity and cell fate transitions in the nervous system. Nat Neurosci 2024, 27, 2278–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, A.; Sekiya, M.; Beckmann, N.D.; Quan, X.; Schrode, N.; Fernando, M.B.; Yu, A.; Zhu, L.; Cao, J.; et al. Transformative Network Modeling of Multi-omics Data Reveals Detailed Circuits, Key Regulators, and Potential Therapeutics for Alzheimer's Disease. Neuron 2021, 109, 257–272 e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi, S.; Gaiteri, C.; Sullivan, S.E.; White, C.C.; Tasaki, S.; Xu, J.; Taga, M.; Klein, H.U.; Patrick, E.; Komashko, V.; et al. A molecular network of the aging human brain provides insights into the pathology and cognitive decline of Alzheimer's disease. Nat Neurosci 2018, 21, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseling, H.; Mair, W.; Kumar, M.; Schlaffner, C.N.; Tang, S.; Beerepoot, P.; Fatou, B.; Guise, A.J.; Cheng, L.; Takeda, S.; et al. Tau PTM Profiles Identify Patient Heterogeneity and Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell 2020, 183, 1699–1713e1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujardin, S.; Commins, C.; Lathuiliere, A.; Beerepoot, P.; Fernandes, A.R.; Kamath, T.V.; De Los Santos, M.B.; Klickstein, N.; Corjuc, D.L.; Corjuc, B.T.; et al. Tau molecular diversity contributes to clinical heterogeneity in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Med 2020, 26, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, K.P.; Snijders, G.J.L.; Humphrey, J.; Allan, A.; Sneeboer, M.A.M.; Navarro, E.; Schilder, B.M.; Vialle, R.A.; Parks, M.; Missall, R.; et al. Genetic analysis of the human microglial transcriptome across brain regions, aging and disease pathologies. Nat Genet 2022, 54, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jager, P.L.; Ma, Y.; McCabe, C.; Xu, J.; Vardarajan, B.N.; Felsky, D.; Klein, H.U.; White, C.C.; Peters, M.A.; Lodgson, B.; et al. A multi-omic atlas of the human frontal cortex for aging and Alzheimer's disease research. Sci Data 2018, 5, 180142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brase, L.; You, S.F.; D'Oliveira Albanus, R.; Del-Aguila, J.L.; Dai, Y.; Novotny, B.C.; Soriano-Tarraga, C.; Dykstra, T.; Fernandez, M.V.; Budde, J.P.; et al. Single-nucleus RNA-sequencing of autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease and risk variant carriers. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniatis, S.; Aijo, T.; Vickovic, S.; Braine, C.; Kang, K.; Mollbrink, A.; Fagegaltier, D.; Andrusivova, Z.; Saarenpaa, S.; Saiz-Castro, G.; et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of molecular pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 2019, 364, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, M.R.; Dilliott, A.A.; Thomas, R.A.; and Farhan, S.M.K. Transcriptomics of Human Brain Tissue in Parkinson's Disease: a Comparison of Bulk and Single-cell RNA Sequencing. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Allen, M.; Is, O.; Reddy, J.S.; Tutor-New, F.Q.; Castanedes Casey, M.; Carrasquillo, M.M.; Oatman, S.R.; Min, Y.; Asmann, Y.W.; et al. Alzheimer's disease and progressive supranuclear palsy share similar transcriptomic changes in distinct brain regions. J Clin Invest 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, G.S.; Fujita, M.; Yang, H.S.; Taga, M.; Cain, A.; McCabe, C.; Comandante-Lou, N.; White, C.C.; Schmidtner, A.K.; Zeng, L.; et al. Cellular communities reveal trajectories of brain ageing and Alzheimer's disease. Nature 2024, 633, 634–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, A.W.P.; Falcon, B.; He, S.; Murzin, A.G.; Murshudov, G.; Garringer, H.J.; Crowther, R.A.; Ghetti, B.; Goedert, M.; and Scheres, S.H.W. Cryo-EM structures of tau filaments from Alzheimer's disease. Nature 2017, 547, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmer, M.; Close, W.; Funk, L.; Rasmussen, J.; Bsoul, A.; Schierhorn, A.; Schmidt, M.; Sigurdson, C.J.; Jucker, M.; and Fandrich, M. Cryo-EM structure and polymorphism of Abeta amyloid fibrils purified from Alzheimer's brain tissue. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ge, P.; Murray, K.A.; Sheth, P.; Zhang, M.; Nair, G.; Sawaya, M.R.; Shin, W.S.; Boyer, D.R.; Ye, S.; et al. Cryo-EM of full-length alpha-synuclein reveals fibril polymorphs with a common structural kernel. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Boyer, D.R.; Sawaya, M.R.; Ge, P.; and Eisenberg, D.S. Cryo-EM structures of four polymorphic TDP-43 amyloid cores. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2019, 26, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynn, C.; Sawaya, M.R.; Ge, P.; Gallagher-Jones, M.; Short, C.W.; Bowman, R.; Apostol, M.; Zhou, Z.H.; Eisenberg, D.S.; and Rodriguez, J.A. Cryo-EM structure of a human prion fibril with a hydrophobic, protease-resistant core. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2020, 27, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colom-Cadena, M.; Davies, C.; Sirisi, S.; Lee, J.E.; Simzer, E.M.; Tzioras, M.; Querol-Vilaseca, M.; Sanchez-Aced, E.; Chang, Y.Y.; Holt, K.; et al. Synaptic oligomeric tau in Alzheimer's disease - A potential culprit in the spread of tau pathology through the brain. Neuron 2023, 111, 2170–2183 e2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, K.R.; Smith, C.; Wright, A.K.; Serrano-Pozo, A.; Pooler, A.M.; Koffie, R.; Bastin, M.E.; Bak, T.H.; Abrahams, S.; Kopeikina, K.J.; et al. Studying synapses in human brain with array tomography and electron microscopy. Nature protocols 2013, 8, 1366–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouri, N.; Frankenhauser, I.; Peng, Z.; Labuzan, S.A.; Boon, B.D.C.; Moloney, C.M.; Pottier, C.; Wickland, D.P.; Caetano-Anolles, K.; Corriveau-Lecavalier, N.; et al. Clinicopathologic Heterogeneity and Glial Activation Patterns in Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol 2024, 81, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolink, W.M.T.; van Veluw, S.J.; Zwanenburg, J.J.M.; Rozemuller, A.J.M.; van Hecke, W.; Frosch, M.P.; Bacskai, B.J.; Rinkel, G.J.E.; Greenberg, S.M.; and Klijn, C.J.M. Histopathology of Cerebral Microinfarcts and Microbleeds in Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res 2023, 14, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakir, M.N.; and Dugger, B.N. Advances in Deep Neuropathological Phenotyping of Alzheimer Disease: Past, Present, and Future. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2022, 81, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapasi, A.; Poirier, J.; Hedayat, A.; Scherlek, A.; Mondal, S.; Wu, T.; Gibbons, J.; Barnes, L.L.; Bennett, D.A.; Leurgans, S.E.; and Schneider, J.A. High-throughput digital quantification of Alzheimer disease pathology and associated infrastructure in large autopsy studies. Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology 2023, 82, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neltner, J.H.; Abner, E.L.; Schmitt, F.A.; Denison, S.K.; Anderson, S.; Patel, E.; and Nelson, P.T. Digital pathology and image analysis for robust high-throughput quantitative assessment of Alzheimer disease neuropathologic changes. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2012, 71, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalco, R.; Oliveira, L.C.; Lai, Z.; Harvey, D.J.; Abujamil, L.; DeCarli, C.; Jin, L.W.; Chuah, C.N.; and Dugger, B.N. Machine learning quantification of Amyloid-beta deposits in the temporal lobe of 131 brain bank cases. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2024, 12, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rub, U.; de Vos, R.A.; Jansen Steur, E.N.; and Braak, E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; and Braak, E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 1991, 82, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thal, D.R.; Rub, U.; Orantes, M.; and Braak, H. Phases of A beta-deposition in the human brain and its relevance for the development of AD. Neurology 2002, 58, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deramecourt, V.; Slade, J.Y.; Oakley, A.E.; Perry, R.H.; Ince, P.G.; Maurage, C.A.; and Kalaria, R.N. Staging and natural history of cerebrovascular pathology in dementia. Neurology 2012, 78, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, A.C.; Stein, T.D.; Huber, B.R.; Crary, J.F.; Bieniek, K.; Dickson, D.; Alvarez, V.E.; Cherry, J.D.; Farrell, K.; Butler, M.; et al. Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE): criteria for neuropathological diagnosis and relationship to repetitive head impacts. Acta Neuropathol 2023, 145, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettschneider, J.; Del Tredici, K.; Toledo, J.B.; Robinson, J.L.; Irwin, D.J.; Grossman, M.; Suh, E.; Van Deerlin, V.M.; Wood, E.M.; Baek, Y.; et al. Stages of pTDP-43 pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2013, 74, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, M.; Molinari, F.; Ciccarelli, M.; Testi, R.; Taraglio, S.; and Imperiale, D. Quantitative analysis of prion disease using an AI-powered digital pathology framework. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 17759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, N.J.; Bigio, E.H.; Mackenzie, I.R.; Neumann, M.; Lee, V.M.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; White, C.L. ; 3rd, Schneider, J.A.; Grinberg, L.T.; Halliday, G.; et al. Neuropathologic diagnostic and nosologic criteria for frontotemporal lobar degeneration: consensus of the Consortium for Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. Acta Neuropathol 2007, 114, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, I.R.; Neumann, M.; Bigio, E.H.; Cairns, N.J.; Alafuzoff, I.; Kril, J.; Kovacs, G.G.; Ghetti, B.; Halliday, G.; Holm, I.E.; et al. Nomenclature for neuropathologic subtypes of frontotemporal lobar degeneration: consensus recommendations. Acta Neuropathol 2009, 117, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeith, I.G.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Halliday, G.; Taylor, J.P.; Weintraub, D.; Aarsland, D.; Galvin, J.; Attems, J.; Ballard, C.G.; et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Fourth consensus report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology 2017, 89, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, P.T.; Dickson, D.W.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jack, C.R.; Boyle, P.A.; Arfanakis, K.; Rademakers, R.; Alafuzoff, I.; Attems, J.; Brayne, C.; et al. Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy (LATE): consensus working group report. Brain 2019, 142, 1503–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauw, J.J.; Daniel, S.E.; Dickson, D.; Horoupian, D.S.; Jellinger, K.; Lantos, P.L.; McKee, A.; Tabaton, M.; and Litvan, I. Preliminary NINDS neuropathologic criteria for Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome (progressive supranuclear palsy). Neurology 1994, 44, 2015–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roemer, S.F.; Grinberg, L.T.; Crary, J.F.; Seeley, W.W.; McKee, A.C.; Kovacs, G.G.; Beach, T.G.; Duyckaerts, C.; Ferrer, I.A.; Gelpi, E.; et al. Rainwater Charitable Foundation criteria for the neuropathologic diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta neuropathologica 2022, 144, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, I.R.; Neumann, M.; Baborie, A.; Sampathu, D.M.; Du Plessis, D.; Jaros, E.; Perry, R.H.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Mann, D.M.; and Lee, V.M. A harmonized classification system for FTLD-TDP pathology. Acta Neuropathol 2011, 122, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signaevsky, M.; Prastawa, M.; Farrell, K.; Tabish, N.; Baldwin, E.; Han, N.; Iida, M.A.; Koll, J.; Bryce, C.; Purohit, D.; et al. Artificial intelligence in neuropathology: deep learning-based assessment of tauopathy. Laboratory Investigation 2019, 99, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Chuang, K.V.; DeCarli, C.; Jin, L.-W.; Beckett, L.; Keiser, M.J.; and Dugger, B.N. Interpretable classification of Alzheimer’s disease pathologies with a convolutional neural network pipeline. Nature Communications 2019, 10, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiya, H.; Koga, S.; Murakami, A.; Kawazoe, M.; Kim, M.; Martin, N.B.; Uitti, R.J.; Cheshire, W.P.; Wszolek, Z.K.; and Dickson, D.W. Validation Study of the MDS Criteria for the Diagnosis of Multiple System Atrophy in the Mayo Clinic Brain Bank. Neurology 2023, 101, e2460–e2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, S.; Zhou, X.; and Dickson, D.W. Machine learning-based decision tree classifier for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2021, 47, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, S.; Ghayal, N.B.; and Dickson, D.W. Deep Learning-Based Image Classification in Differentiating Tufted Astrocytes, Astrocytic Plaques, and Neuritic Plaques. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2021, 80, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalco, R.; Hamsafar, Y.; White, C.L.; Schneider, J.A.; Reichard, R.R.; Prokop, S.; Perrin, R.J.; Nelson, P.T.; Mooney, S.; Lieberman, A.P.; et al. The status of digital pathology and associated infrastructure within Alzheimer's Disease Centers. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2023, 82, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Digital Slide Archive (2024). https://digitalslidearchive.github.io/digital_slide_archive/.
- Gutman, D.A.; Cobb, J.; Somanna, D.; Park, Y.; Wang, F.; Kurc, T.; Saltz, J.H.; Brat, D.J.; Cooper, L.A.D.; and Kong, J. Cancer Digital Slide Archive: an informatics resource to support integrated in silico analysis of TCGA pathology data. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2013, 20, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mount Sinai Brain Slide (2024). https://www.mountsinaicharcot.org/home.
- Baxi, V.; Edwards, R.; Montalto, M.; and Saha, S. Digital pathology and artificial intelligence in translational medicine and clinical practice. Mod Pathol 2022, 35, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yang, E.; Shen, J.; Gratzinger, D.; Eyerer, F.; Liang, B.; Nirschl, J.; Bingham, D.; Dussaq, A.M.; Kunder, C.; et al. A pathologist-AI collaboration framework for enhancing diagnostic accuracies and efficiencies. Nat Biomed Eng. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.E.; Moloney, C.M.; Kouri, N.; Syrjanen, J.A.; Matchett, B.J.; Rothberg, D.M.; Tranovich, J.F.; Sirmans, T.N.H.; Wiste, H.J.; Boon, B.D.C.; et al. Global neuropathologic severity of Alzheimer's disease and locus coeruleus vulnerability influences plasma phosphorylated tau levels. Mol Neurodegener 2022, 17, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Janelidze, S.; Bateman, R.J.; Smith, R.; Stomrud, E.; Serrano, G.E.; Reiman, E.M.; Palmqvist, S.; Dage, J.L.; Beach, T.G.; and Hansson, O. Soluble P-tau217 reflects amyloid and tau pathology and mediates the association of amyloid with tau. EMBO Mol Med 2021, 13, e14022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.E.; Przybelski, S.A.; Lesnick, T.G.; Liesinger, A.M.; Spychalla, A.; Zhang, B.; Gunter, J.L.; Parisi, J.E.; Boeve, B.F.; Knopman, D.S.; et al. Early Alzheimer's disease neuropathology detected by proton MR spectroscopy. J Neurosci 2014, 34, 16247–16255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna Al-Shaikh, F.S.; Duara, R.; Crook, J.E.; Lesser, E.R.; Schaeverbeke, J.; Hinkle, K.M.; Ross, O.A.; Ertekin-Taner, N.; Pedraza, O.; Dickson, D.W.; et al. Selective Vulnerability of the Nucleus Basalis of Meynert Among Neuropathologic Subtypes of Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol 2020, 77, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arezoumandan, S.; Xie, S.X.; Cousins, K.A.Q.; Mechanic-Hamilton, D.J.; Peterson, C.S.; Huang, C.Y.; Ohm, D.T.; Ittyerah, R.; McMillan, C.T.; Wolk, D.A.; et al. Regional distribution and maturation of tau pathology among phenotypic variants of Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 2022, 144, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.G.; Weiner, M.W.; Thal, L.J.; Petersen, R.C.; Jack, C.; Jagust, W.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Toga, A.W.; and Beckett, L. The Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging initiative. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 2005, 15, 869–877, xi. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Horn, J.D.; and Toga, A.W. Is it time to re-prioritize neuroimaging databases and digital repositories? Neuroimage 2009, 47, 1720–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinov, I.D.; Van Horn, J.D.; Lozev, K.M.; Magsipoc, R.; Petrosyan, P.; Liu, Z.; Mackenzie-Graham, A.; Eggert, P.; Parker, D.S.; and Toga, A.W. Efficient, Distributed and Interactive Neuroimaging Data Analysis Using the LONI Pipeline. Front Neuroinform 2009, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.T.; Knopman, D.S.; Gunter, J.L.; Graff-Radford, J.; Vemuri, P.; Boeve, B.F.; Petersen, R.C.; Weiner, M.W.; Jack, C.R. ; Jr, and Initiative, o. b.o.t.A.s.D.N. Cascading network failure across the Alzheimer’s disease spectrum. Brain 2015, 139, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.; Lowe, V.; Graff-Radford, J.; Botha, H.; Barnard, L.; Wiepert, D.; Murphy, M.C.; Murray, M.; Senjem, M.; Gunter, J.; et al. A computational model of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.C.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Donohue, M.C.; Gamst, A.C.; Harvey, D.J.; Jack, C.R. ; Jr. , Jagust, W.J.; Shaw, L.M.; Toga, A.W.; et al. Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI): clinical characterization. Neurology 2010, 74, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, M.W.; Veitch, D.P.; Miller, M.J.; Aisen, P.S.; Albala, B.; Beckett, L.A.; Green, R.C.; Harvey, D.; Jack, C.R. ; Jr. , Jagust, W.; et al. Increasing participant diversity in AD research: Plans for digital screening, blood testing, and a community-engaged approach in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative 4. Alzheimers Dement 2023, 19, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.E.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Ross, O.A.; Petersen, R.C.; Duara, R.; and Dickson, D.W. Neuropathologically defined subtypes of Alzheimer's disease with distinct clinical characteristics: a retrospective study. Lancet Neurol 2011, 10, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative Image and Data Archive (2024). https://ida.loni.usc.edu/login.jsp.
- Longitudinal Early Onset Alzheimer’s Disease Study (2024). https://leads-study.medicine.iu.edu/.
- Vogel, J.W.; Young, A.L.; Oxtoby, N.P.; Smith, R.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Strandberg, O.T.; La Joie, R.; Aksman, L.M.; Grothe, M.J.; Iturria-Medina, Y.; et al. Four distinct trajectories of tau deposition identified in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Med 2021, 27, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siderowf, A.; Concha-Marambio, L.; Lafontant, D.E.; Farris, C.M.; Ma, Y.; Urenia, P.A.; Nguyen, H.; Alcalay, R.N.; Chahine, L.M.; Foroud, T.; et al. Assessment of heterogeneity among participants in the Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative cohort using alpha-synuclein seed amplification: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Neurol 2023, 22, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, O.; Seibyl, J.; Stomrud, E.; Zetterberg, H.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Bittner, T.; Lifke, V.; Corradini, V.; Eichenlaub, U.; Batrla, R.; et al. CSF biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease concord with amyloid-beta PET and predict clinical progression: A study of fully automated immunoassays in BioFINDER and ADNI cohorts. Alzheimers Dement 2018, 14, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OpenNeuro (2024). https://openneuro.org/.
- Alzheimer's Disease Knowledge Portal (2024). https://adknowledgeportal.synapse.org.
- Global Parkinson's Genetics, P. GP2: The Global Parkinson's Genetics Program. Mov Disord 2021, 36, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.A.; Ballard, S.; Shah, S.; Bianchi, O.; Jones, L.; Koretsky, M.J.; Kuznetsov, N.; Marsan, E.; Jen, B.; Chiang, P.; et al. A new AI-assisted data standard accelerates interoperability in biomedical research. medRxiv. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ding, S.L.; Li, Y.; Royall, J.; Feng, D.; Lesnar, P.; Graddis, N.; Naeemi, M.; Facer, B.; Ho, A.; et al. The Allen Mouse Brain Common Coordinate Framework: A 3D Reference Atlas. Cell 2020, 181, 936–953 e920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markello, R.D.; Hansen, J.Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Bazinet, V.; Shafiei, G.; Suarez, L.E.; Blostein, N.; Seidlitz, J.; Baillet, S.; Satterthwaite, T.D.; et al. neuromaps: structural and functional interpretation of brain maps. Nat Methods 2022, 19, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen Brain Atlas (2024). https://atlas.brain-map.org.
- Ding, S.L.; Royall, J.J.; Sunkin, S.M.; Ng, L.; Facer, B.A.; Lesnar, P.; Guillozet-Bongaarts, A.; McMurray, B.; Szafer, A.; Dolbeare, T.A.; et al. Comprehensive cellular-resolution atlas of the adult human brain. J Comp Neurol 2016, 524, 3127–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizcarra, J.C.; Pearce, T.M.; Dugger, B.N.; Keiser, M.J.; Gearing, M.; Crary, J.F.; Kiely, E.J.; Morris, M.; White, B.; Glass, J.D.; et al. Toward a generalizable machine learning workflow for neurodegenerative disease staging with focus on neurofibrillary tangles. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2023, 11, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, G.A.; Koenigsberg, D.G.; McKenzie, A.T.; Kauffman, J.; Hanson, R.W.; Whitney, K.; Signaevsky, M.; Prastawa, M.; Iida, M.A.; White, C.L. ; 3rd, et al. Artificial intelligence-derived neurofibrillary tangle burden is associated with antemortem cognitive impairment. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2022, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrassia, L.; Boluda, S.; Potier, M.C.; Haik, S.; Jimenez, G.; Kar, A.; Racoceanu, D.; Delatour, B.; and Stimmer, L. Automated deep learning segmentation of neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer disease brain sections using a proprietary software. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2024, 83, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meta (2024). https://ai.meta.com/resources/.
- He, B.; Bukhari, S.; Fox, E.; Abid, A.; Shen, J.; Kawas, C.; Corrada, M.; Montine, T.; and Zou, J. AI-enabled in silico immunohistochemical characterization for Alzheimer's disease. Cell Rep Methods 2022, 2, 100191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; and Hatfield, B. Advancements in computer vision and pathology: Unraveling the potential of artificial intelligence for precision diagnosis and beyond. Adv Cancer Res 2024, 161, 431–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, M.; and Kather, J.N. Deep learning in cancer genomics and histopathology. Genome Med 2024, 16, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Bianchi, F.; Yuksekgonul, M.; Montine, T.J.; and Zou, J. A visual-language foundation model for pathology image analysis using medical Twitter. Nat Med 2023, 29, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuhmann, C.; Beaumont, R.; Vencu, R.; Gordon, C.; Wightman, R.; Cherti, M.; Coombes, T.; Katta, A.; Mullis, C.; Wortsman, M.; et al. LAION-5B: An open large-scale dataset for training next generation image-text models. arXiv:2210.08402. 10.48550/arXiv.2210.08402. [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.Y.; Chen, B.; Williamson, D.F.K.; Chen, R.J.; Liang, I.; Ding, T.; Jaume, G.; Odintsov, I.; Le, L.P.; Gerber, G.; et al. A visual-language foundation model for computational pathology. Nat Med 2024, 30, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velicky, P.; Miguel, E.; Michalska, J.M.; Lyudchik, J.; Wei, D.; Lin, Z.; Watson, J.F.; Troidl, J.; Beyer, J.; Ben-Simon, Y.; et al. Dense 4D nanoscale reconstruction of living brain tissue. Nat Methods 2023, 20, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crist, A.M.; Hinkle, K.M.; Wang, X.; Moloney, C.M.; Matchett, B.J.; Labuzan, S.A.; Frankenhauser, I.; Azu, N.O.; Liesinger, A.M.; Lesser, E.R.; et al. Transcriptomic analysis to identify genes associated with selective hippocampal vulnerability in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutt, J.; Isla, E.; Bertler, A.N.; Bodeker, G.E.; Bracegirdle, T.J.; Cavanagh, R.D.; Comiso, J.C.; Convey, P.; Cummings, V.; De Conto, R.; et al. Cross-disciplinarity in the advance of Antarctic ecosystem research. Mar Genomics 2018, 37, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlett Paredes, A.; Guarena, L.A.; Stickel, A.M.; Schairer, C.E.; and Gonzalez, H.M. To donate, or not to donate, that is the question: Latino insights into brain donation. Alzheimers Dement 2023, 19, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischl, B.; and Dale, A.M. Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000, 97, 11050–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beekly, D.L.; Ramos, E.M.; van Belle, G.; Deitrich, W.; Clark, A.D.; Jacka, M.E.; Kukull, W.A.; and Centers, N.I.-A.s.D. The National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center (NACC) Database: an Alzheimer disease database. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 2004, 18, 270–277. [Google Scholar]
- National Alzheimer's Coordinating Center (2024). https://naccdata.org/adrc-resources/best-practices.
- Fischl, B. FreeSurfer. Neuroimage 2012, 62, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (2024). https://dicom.nema.org/Dicom/DICOMWSI/.
- Moore, J.; Allan, C.; Besson, S.; Burel, J.M.; Diel, E.; Gault, D.; Kozlowski, K.; Lindner, D.; Linkert, M.; Manz, T.; et al. OME-NGFF: a next-generation file format for expanding bioimaging data-access strategies. Nat Methods 2021, 18, 1496–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




