Submitted:
28 October 2025
Posted:
29 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Test the PINN model in three geometries with increasing complexity.
- (2)
- Evaluate PINN training via the Hessian matrix vs. flow speeds and geometrical complexity.
- (3)
- Nondimensionalize the Navier-Stokes equations to improve training robustness.
- (4)
- Develop an inference module to visualize the PINN results in ANSYS Fluent.
- (5)
- Compare PINN and CFD results of airflows qualitatively and quantitatively.
- (6)
- Compare fidelity between the PINN laminar model and SDF-mixing-length model.
2. Materials and Methods
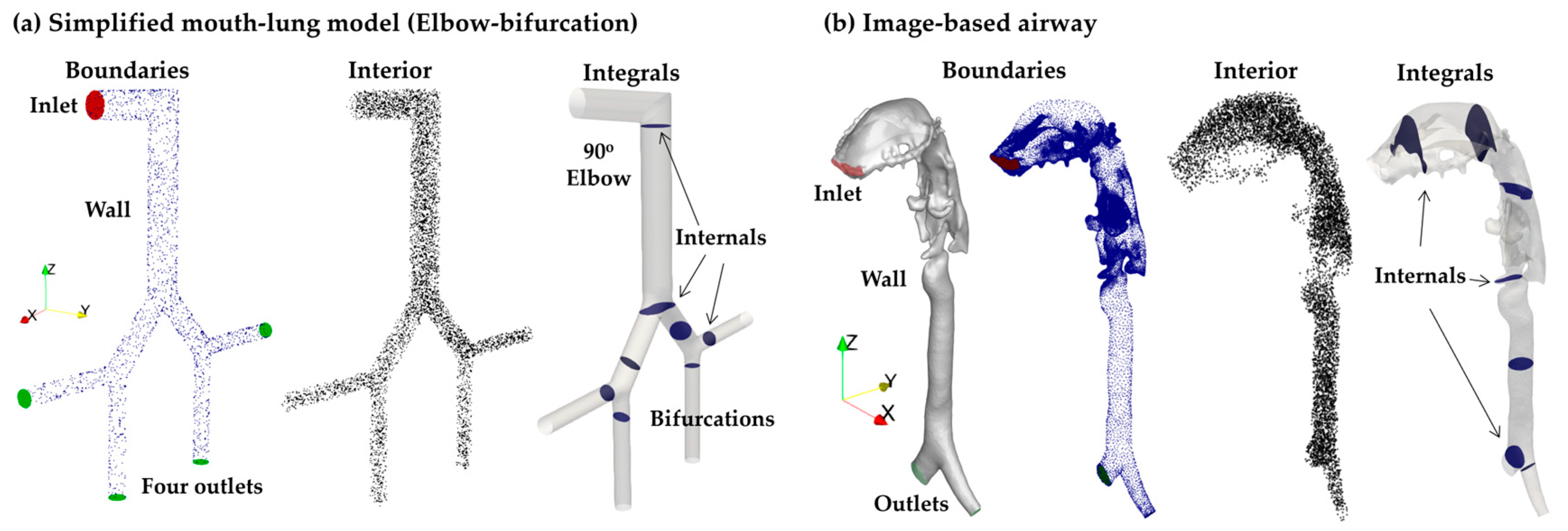
2.1. Testing Geometries
2.2. CFD Numerical Methods
2.3. PINN
2.3.1. Loss Function
2.3.2. Architecture
2.3.3. Nondimensionalization
2.3.4. Hessian Matrix and Control Number
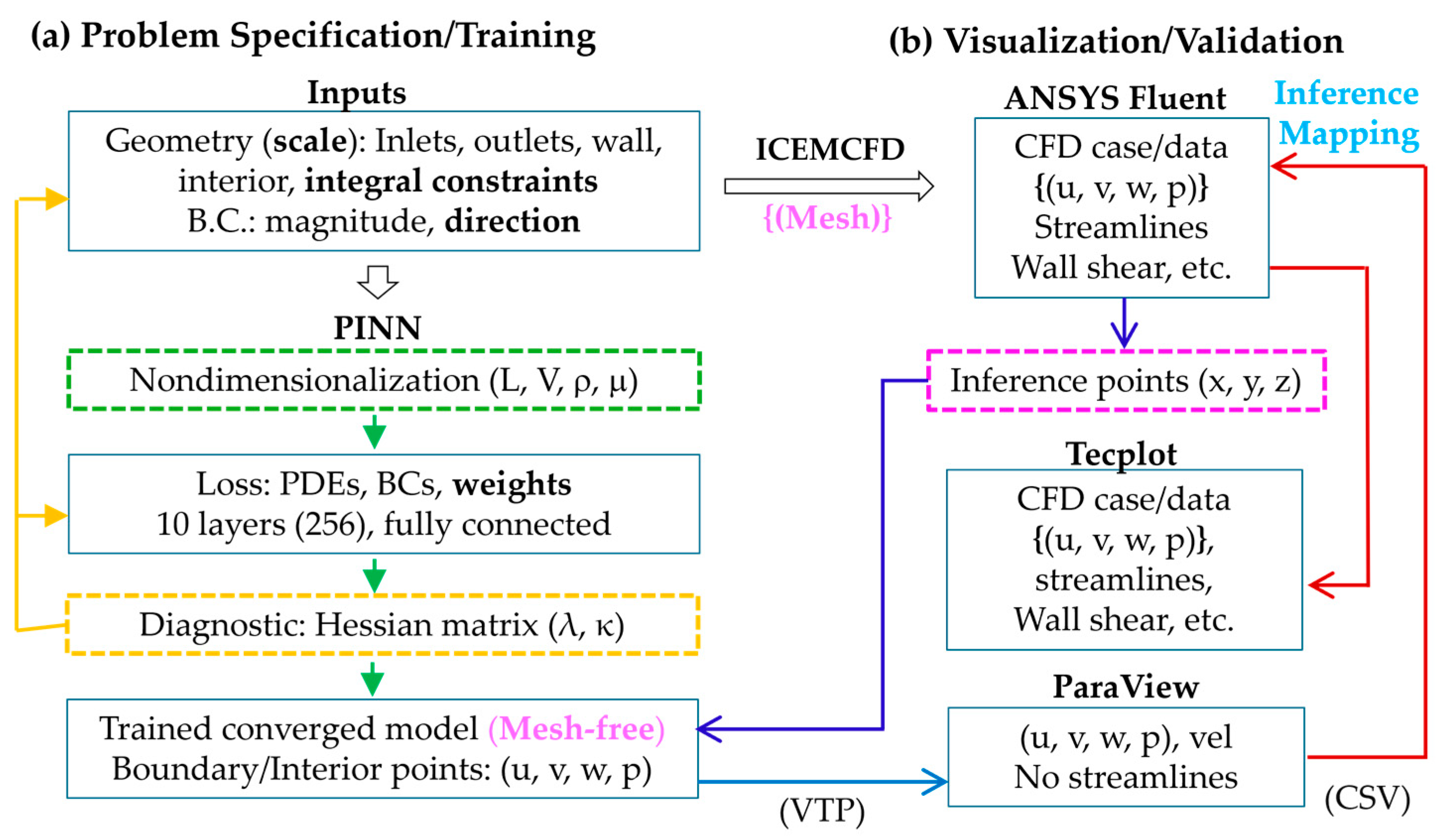
2.4. PINN Training and Visualization
2.4.1. Problem Specification and Training
2.4.2. Fluent-Based Visualization and Validation
2.4.3. PINN Inference Methodology
3. Results
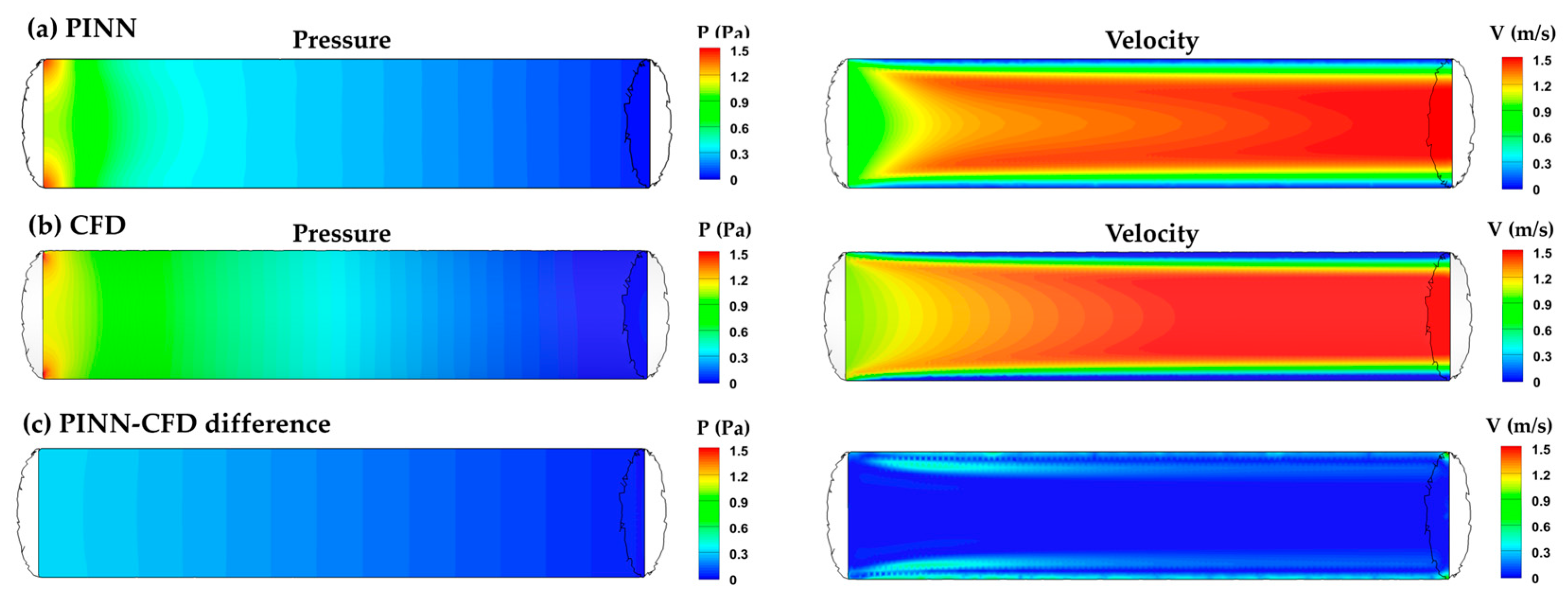
3.1. Duct Flow
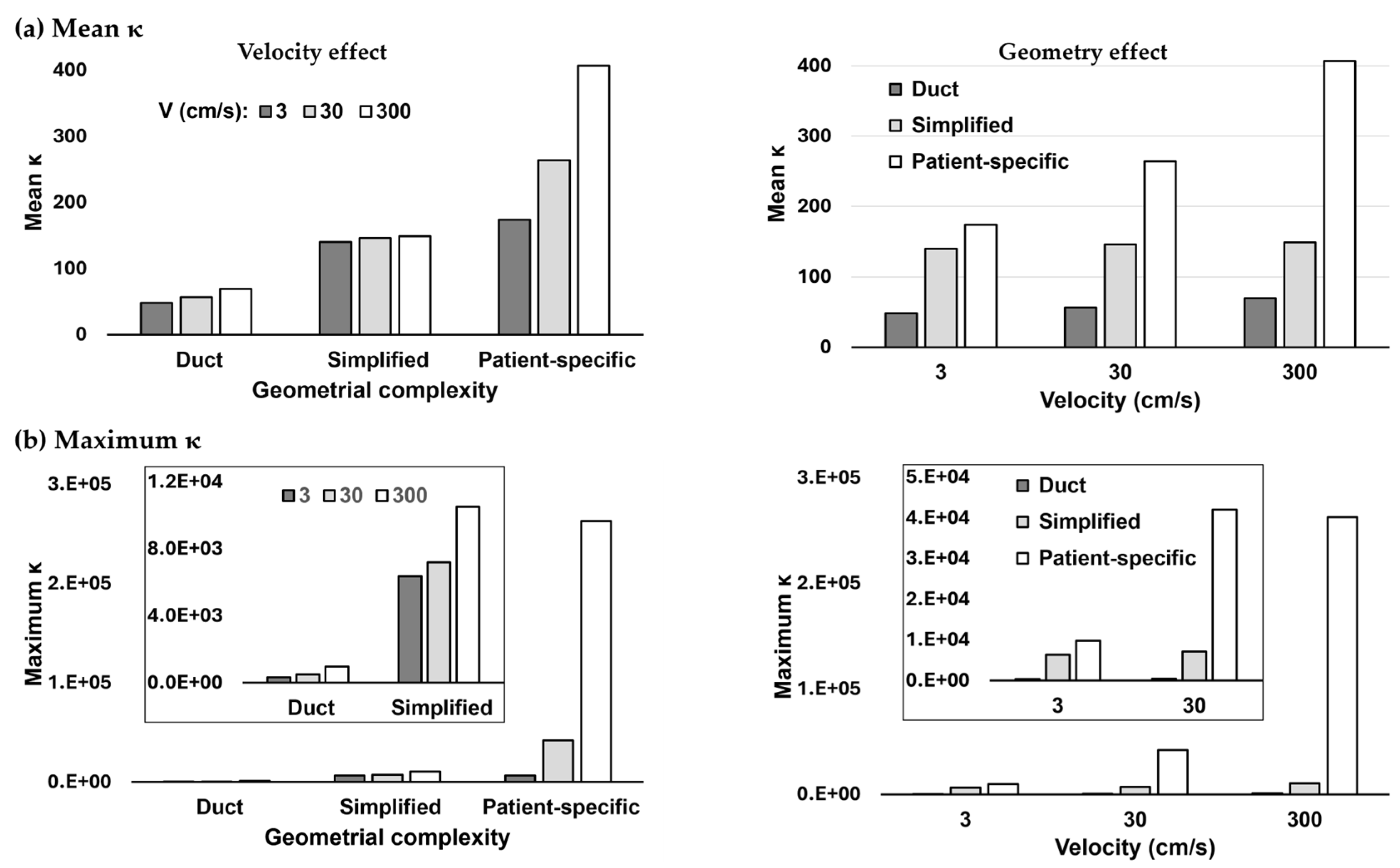
3.2. Hessian Matrix-Based Condition Number κ
3.3. Simplified Mouth-Lung Geometry
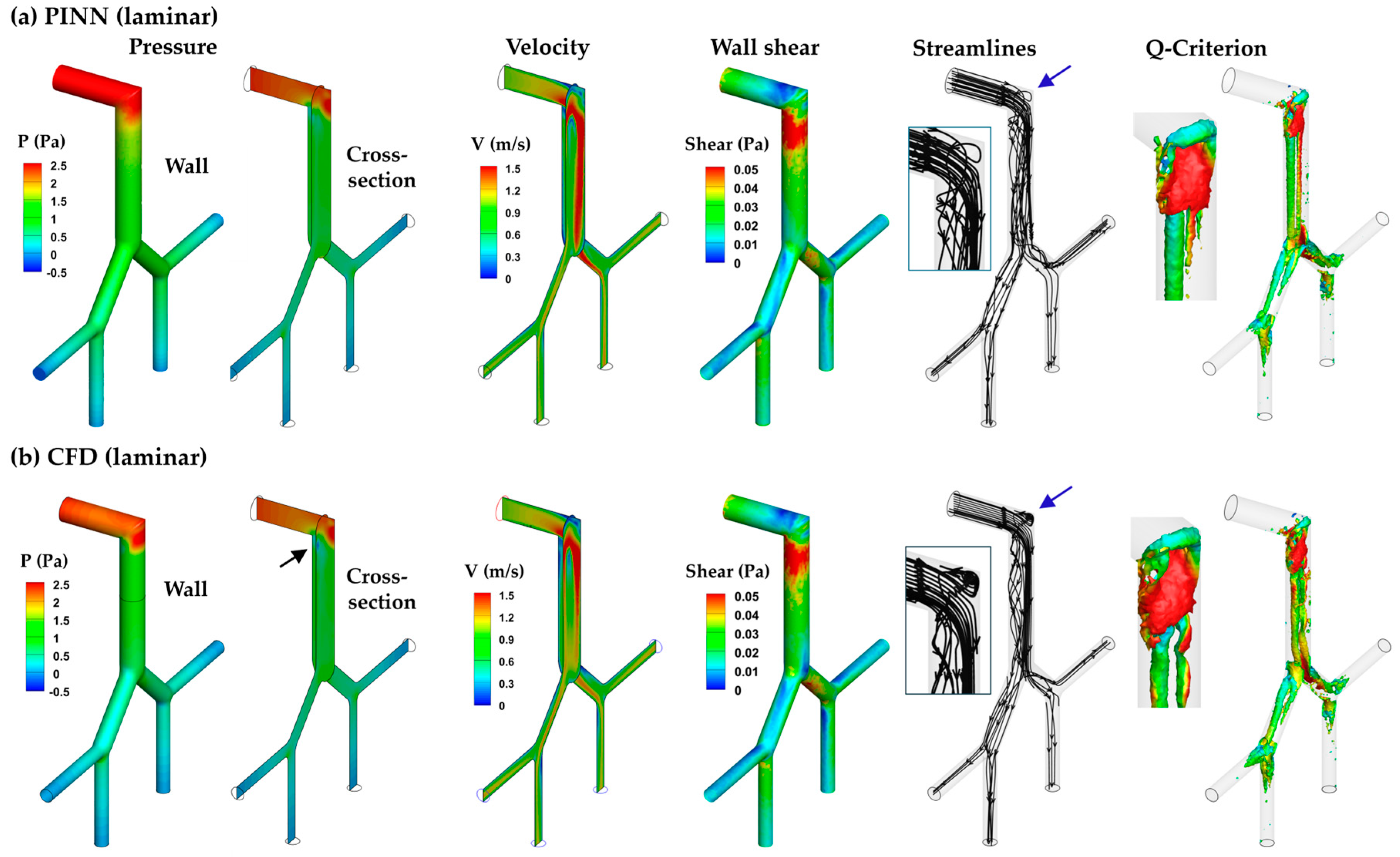
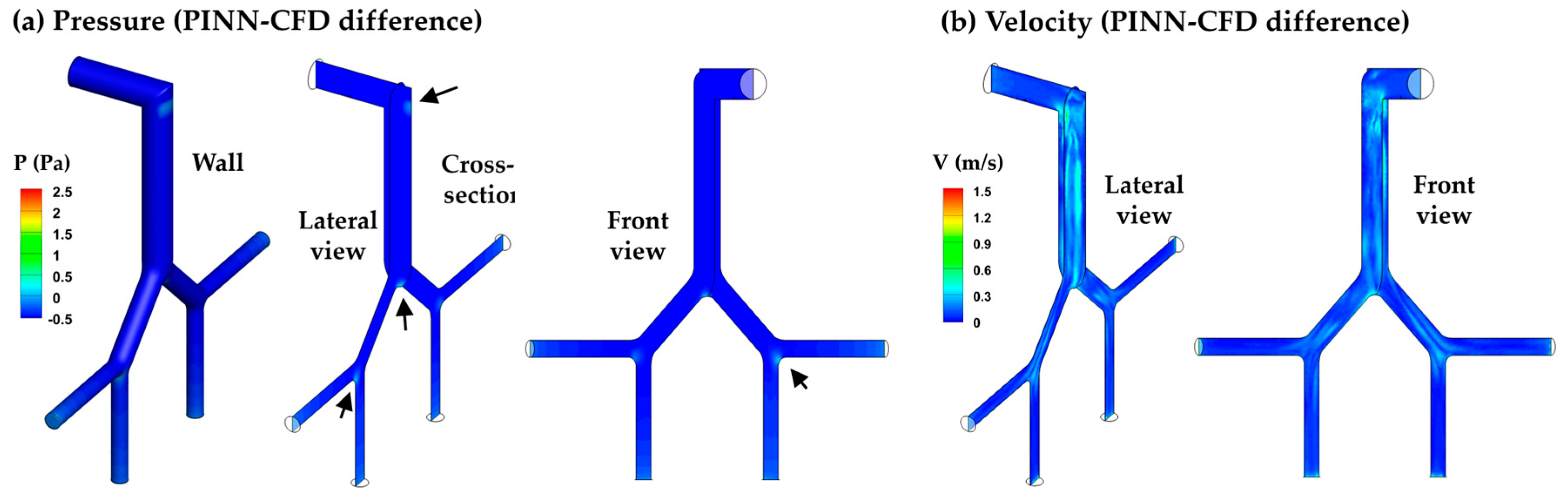
3.3.1. PINN vs. CFD: Laminar Model
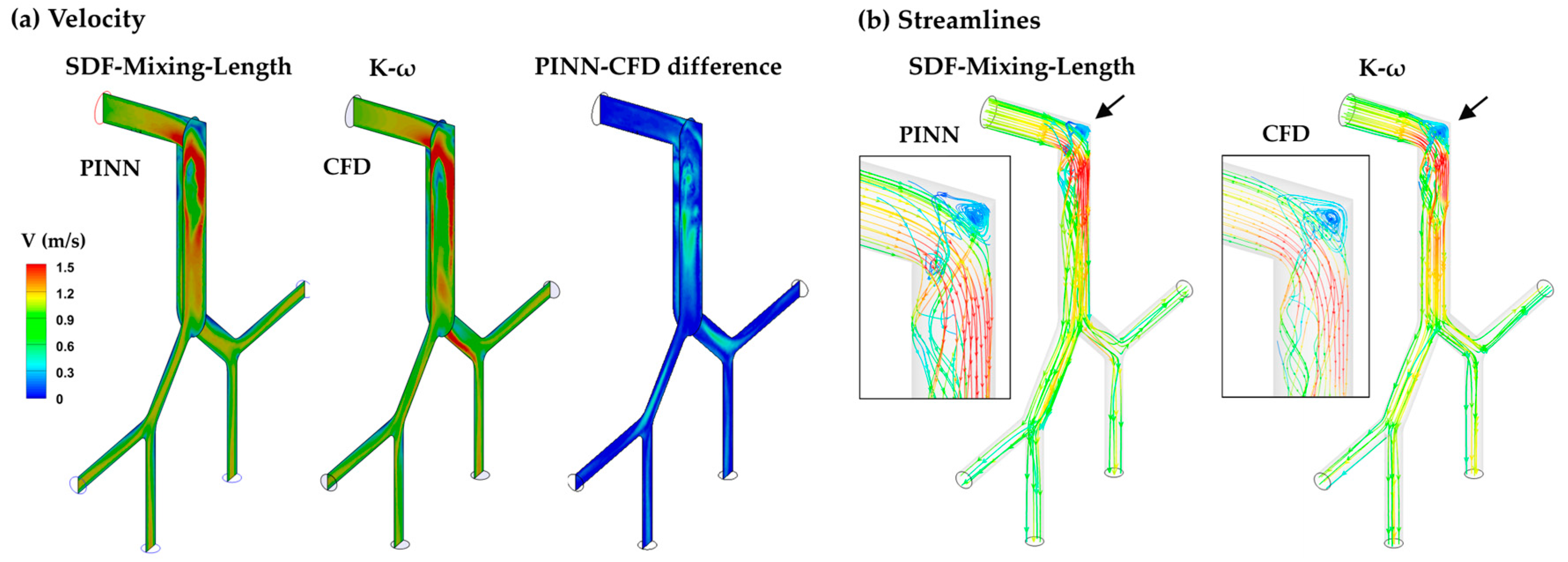
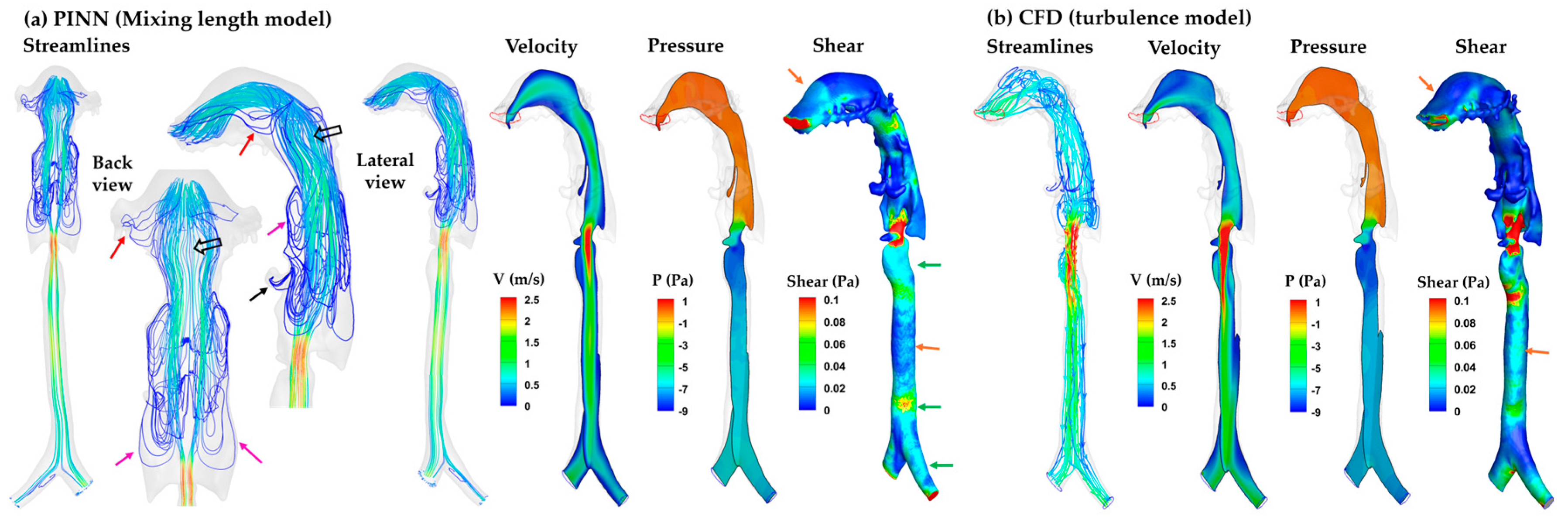
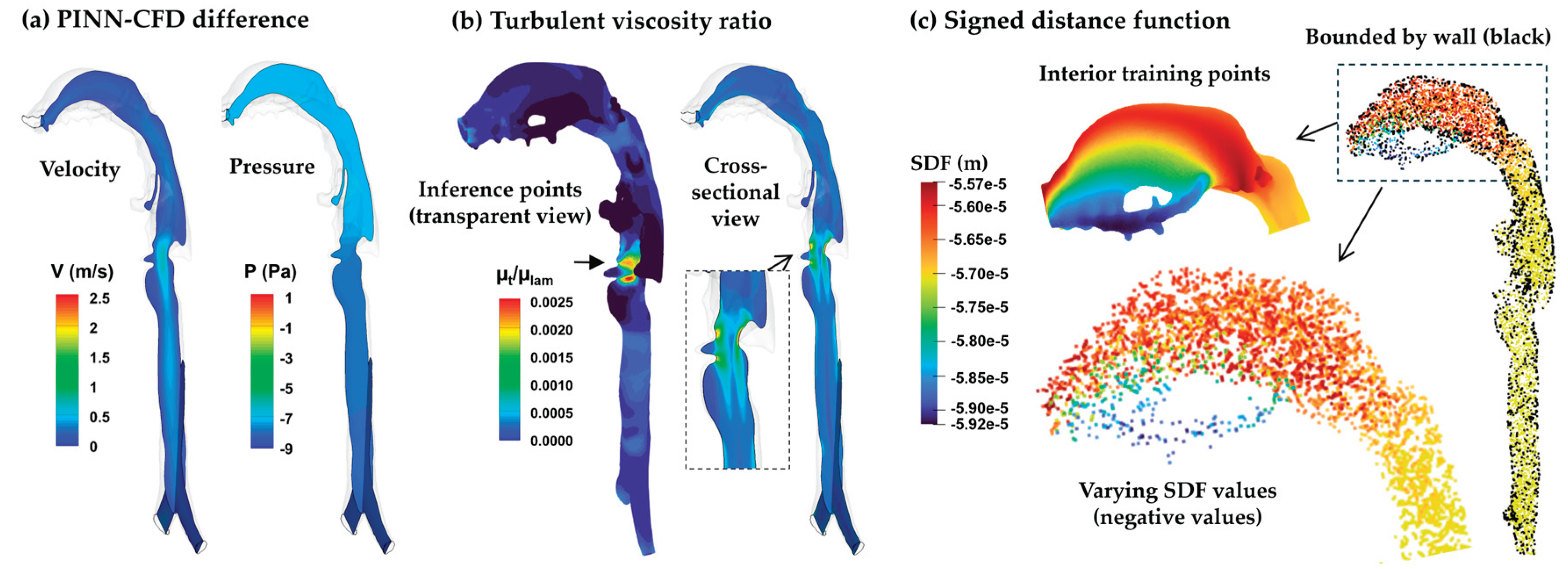
3.3.2. SDF-Mixing-Length PINN vs. CFD Turbulence Model
3.4. Patient-Specific Airway Model
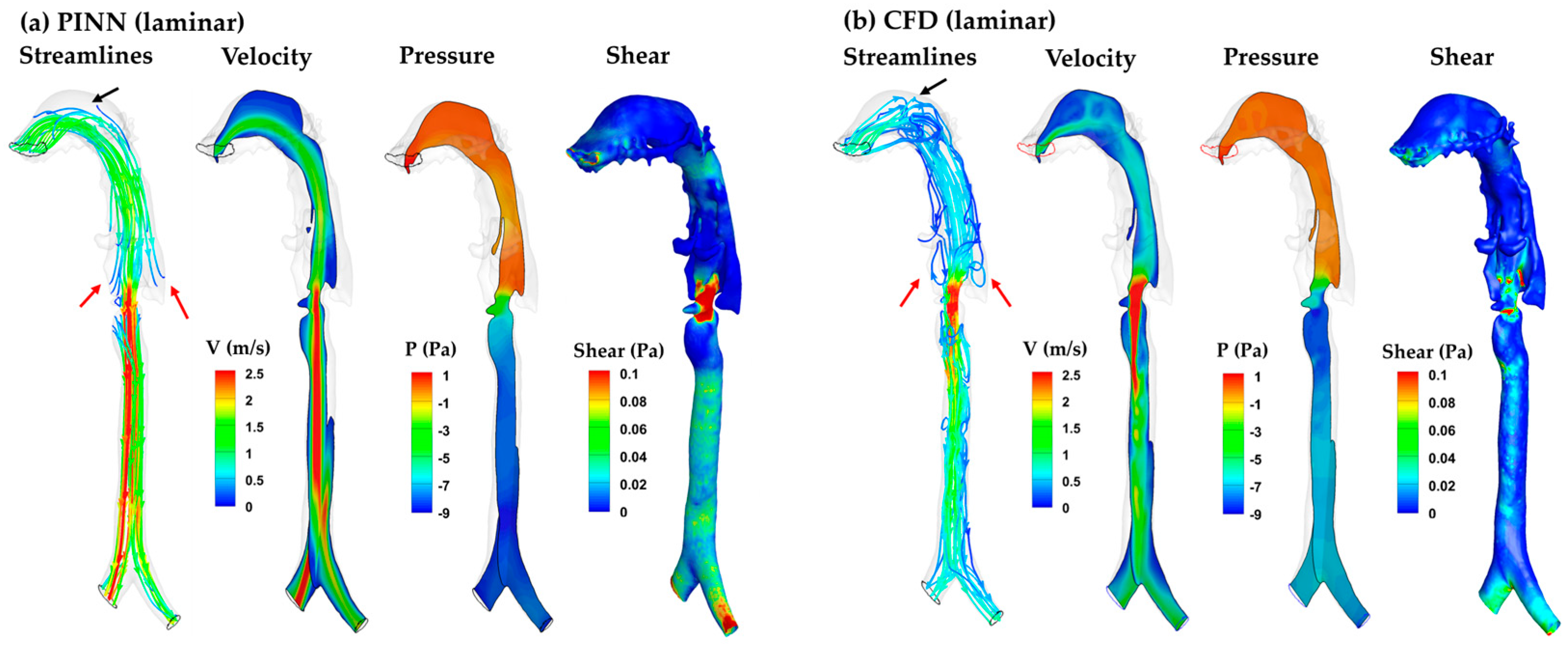
3.4.1. PINN vs. CFD: Laminar Model
3.4.2. SDF-Mixing-Length PINN vs. CFD turbulence Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Novelties Compared to Previous Studies
4.2. Challenges and Best Practices in Implementing and Training PINN
4.2.1. Nondimensional Governing Equations
4.2.2. Flow Constraints and GPU Memory Limitation
4.2.3. Near-Wall Treatment via Signed Distance Function (SDF)
4.3. Implications
4.4. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dawman L, Mukherjee A, Sethi T, Agrawal A, Kabra SK, Lodha R. Role of impulse oscillometry in assessing asthma control in children. Indian Pediatr. 2020;57(2):119-123.
- Xi J, Wang Z, Talaat K, Glide-Hurst C, Dong H. Numerical study of dynamic glottis and tidal breathing on respiratory sounds in a human upper airway model. Sleep Breath. 2018;22(2):463-479.
- Si X, Xi J, Kim J. Effect of laryngopharyngeal anatomy on expiratory airflow and submicrometer particle deposition in human extrathoracic airways. Open J.Fluid Dyn. 2013;3(4):286-301.
- Lancmanová A, Bodnár T. Numerical simulations of human respiratory flows: a review. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025;7(4):242.
- Faizal WM, Ghazali NNN, Khor CY, Badruddin IA, Zainon MZ, Yazid AA, et al. Computational fluid dynamics modelling of human upper airway: A review. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020;196:105627.
- Lauria M, Singhrao K, Stiehl B, Low D, Goldin J, Barjaktarevic I, et al. Automatic triangulated mesh generation of pulmonary airways from segmented lung 3DCTs for computational fluid dynamics. Int. J. Comput. Assit. Radiol. Surg. 2022;17(1):185-197.
- Jing H, Ge H, Wang L, Choi S, Farnoud A, An Z, et al. Investigating unsteady airflow characteristics in the human upper airway based on the clinical inspiration data. Phys. Fluids. 2023;35(10).
- Jing H, Ge H, Wang L, Zhou Q, Chen L, Choi S, et al. Large eddy simulation study of the airflow characteristics in a human whole-lung airway model. Phys. Fluids. 2023;35(7).
- Vara Almirall B, Calmet H, Ang HQ, Inthavong K. Flow behavior in idealized & realistic upper airway geometries. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025;194:110449.
- Jiang F, Hirano T, Liang C, Zhang G, Matsunaga K, Chen X. Multi-scale simulations of pulmonary airflow based on a coupled 3D-1D-0D model. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024;171:108150.
- Dey R, Patni HK, Anand S. Improved aerosol deposition predictions in human upper respiratory tract using coupled mesh phantom-based computational model. Sci. Rep. 2025;15(1):14260.
- Gunatilaka CC, Schuh A, Higano NS, Woods JC, Bates AJ. The effect of airway motion and breathing phase during imaging on CFD simulations of respiratory airflow. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020;127:104099.
- Kim M, Chau N-K, Park S, Nguyen PCH, Baek SS, Choi S. Physics-aware machine learning for computational fluid dynamics surrogate model to estimate ventilation performance. Phys. Fluids. 2025;37(2).
- Gao H, Qian W, Dong J, Liu J. Rapid prediction of indoor airflow field using operator neural network with small dataset. Build. Environ. 2024;251:111175.
- Hao Y, Song F. Fourier neural operator networks for solving reaction–diffusion equations. Fluids. 2024;9(11):258.
- Vinuesa R, Brunton SL. Enhancing computational fluid dynamics with machine learning. Nat. Computat. Sci. 2022;2(6):358-366.
- Raissi M, Perdikaris P, Karniadakis GE. Physics-informed neural networks: A deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2019;378:686-707.
- Raissi M, Yazdani A, Karniadakis GE. Hidden fluid mechanics: Learning velocity and pressure fields from flow visualizations. Science. 2020;367(6481):1026-1030.
- Cai S, Mao Z, Wang Z, Yin M, Karniadakis GE. Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) for fluid mechanics: A review. Acta Mech. Sin. 2022;37(12):1727-1738.
- Arzani A, Wang J-X, D'Souza RM. Uncovering near-wall blood flow from sparse data with physics-informed neural networks. Phys. Fluids. 2021;33(7).
- Zhang X, Mao B, Che Y, Kang J, Luo M, Qiao A, et al. Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) for 4D hemodynamics prediction: An investigation of optimal framework based on vascular morphology. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023;164:107287.
- Alzhanov N, Ng EYK, Zhao Y. Three-dimensional physics-informed neural network simulation in coronary artery trees. Fluids. 2024;9(7):153.
- Kumar AK, Jain S, Jain S, Ritam M, Xia Y, Chandra R. Physics-informed neural entangled-ladder network for inhalation impedance of the respiratory system. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2023;231:107421.
- Jagtap AD, Karniadakis GE. Extended physics-informed neural networks (XPINNs): A generalized space-time domain decomposition based deep learning framework for nonlinear partial differential equations. Commun. Comput. Phys. 2020;28(5):2002-2041.
- McClenny LD, Braga-Neto UM. Self-adaptive physics-informed neural networks. J. Comput. Phys. 2023;474:111722.
- Wang S, Yu X, Perdikaris P. When and why PINNs fail to train: A neural tangent kernel perspective. J. Comput. Phys. 2022;449:110768.
- Gu L, Qin S, Xu L, Chen R. Physics-informed neural networks with domain decomposition for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Phys. Fluids. 2024;36(2).
- Pioch F, Harmening JH, Müller AM, Peitzmann F-J, Schramm D, el Moctar O. Turbulence modeling for physics-informed neural networks: comparison of different RANS models for the backward-facing step Flow. Fluids. 2023;8(2):43.
- Jin X, Cai S, Li H, Karniadakis GE. NSFnets (Navier-Stokes flow nets): Physics-informed neural networks for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2021;426:109951.
- Yu T, Qi Y, Oseledets I, Chen S. Spectral informed neural network: an efficient and low-memory PINN. arXiv. 2024; arXiv:2408.16414.
- Huang Y, Zhang Z, Zhang X. A direct-forcing immersed boundary method for incompressible flows based on physics-informed neural network. Fluids. 2022;7(2):56.
- Karniadakis GE, Kevrekidis IG, Lu L, Perdikaris P, Wang S, L. Y. Physics-informed machine learning. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2021;3(6):422-440.
- Kundu PK, Cohen IM, Dowling DR. Fluid mechanics, 6th ed. ed.; Academic Press: 2015.
- Anderson, JD. Fundamentals of Aeodynamics; McGraw-Hill Education: 2017.
- Krishnapriyan A, Gholami A, Zhe S, Kirby R, Mahoney MW. Characterizing possible failure modes in physics-informed neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021;34:26548-26560.
- Talaat M, Si XA, Xi J. Lower inspiratory breathing depth enhances pulmonary delivery efficiency of ProAir sprays. Pharmaceuticals. 2022;15(6):706.
- Zhou Y, Sun J, Cheng YS. Comparison of deposition in the USP and physical mouth-throat models with solid and liquid particles. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug.Deliv. 2011;24(6):277-284.
- Corley RA, Kabilan S, Kuprat AP, Carson JP, Minard KR, Jacob RE, et al. Comparative computational modeling of airflows and vapor dosimetry in the respiratory tracts of rat, monkey, and human. Toxicol. Sci. 2012;128(2):500-516.
- Xi J, Longest PW, Martonen TB. Effects of the laryngeal jet on nano- and microparticle transport and deposition in an approximate model of the upper tracheobronchial airways. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008;104(6):1761-1777.
- Longest PW, Bass K, Dutta R, Rani V, Thomas ML, El-Achwah A, et al. Use of computational fluid dynamics deposition modeling in respiratory drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019;16(1):7-26.
- He Q, Tartakovsky AM. Physics-informed neural network method for forward and backward advection-dispersion equations. Water Resour. Res. 2021;57(7):e2020WR029479.
- Ma B, Zhou J, Liu Y-S, Han Z. Towards better gradient consistency for neural signed distance functions via level set alignment. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2023; pp. 17724-17734.
- Corporation. N. NVIDIA PhysicsNeMo Sym. Available online: https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/physicsnemo/physicsnemo-sym/user_guide/basics/lid_driven_cavity_flow.html?utm_source (accessed on July 30).
- Buckingham, E. On physically similar systems; illustrations of the use of dimensional equations. Phys. Rev. 1914;135(4):345-376.
- Barenblatt, GI. Scaling, self-similarity, and intermediate asymptotics; Cambridge University Press: 1996.
- Le-Duc T, Lee S, Nguyen-Xuan H, Lee J. A hierarchically normalized physics-informed neural network for solving differential equations: Application for solid mechanics problems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024;133:108400.
- Rasht-Behesht M, Huber C, Shukla K, Karniadakis GE. Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) for wave propagation and full waveform inversions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth. 2022;127(5):e2021JB023120.
- Wang R, Kashinath K, Mustafa M, Albert A, Yu R. Towards physics-informed deep learning for turbulent flow prediction. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, 2020; pp. 1457-1466.
- Xiang Z, Peng W, Liu X, Yao W. Self-adaptive loss balanced physics-informed neural networks. Neurocomputing. 2021;496:11-34.
- Urbán JF, Stefanou P, Pons JA. Unveiling the optimization process of physics informed neural networks: How accurate and competitive can PINNs be? J. Comput. Phys. 2025;523:113656.
- Li S, Feng X. Dynamic weight strategy of physics-informed neural networks for the 2D Navier-Stokes equations. Entropy. 2022;24(9):1254.
- Bottou L, Curtis FE, Nocedal J. Self-adaptive loss balanced physics-informed neural networks. Neurocomputing. 2018;60(2):223-311.
- Duchi J, Hazan E, Singer Y. Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011;12(7):2121-2159.
- Higham, NJ. Accuracy and stability of numerical algorithms; SIAM: 2002.
- Jacot A, Gabriel F, Ged F, Hongler C. Order and chaos: NTK views on DNN normalization, checkerboard and boundary artifacts. arXiv. 2019; arXiv:1907.05715.
- Jacot A, Gabriel F, Hongler C. Neural tangent kernel: Convergence and generalization in neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018;31:8571-8580.
- Wang S, Sankaran S, Perdikaris P. Respecting causality is all you need for training physics-informed neural networks. arXiv. 2022; arXiv:2203.07404.
- Yu T, Kumar S, Gupta A, Levine S, Hausman K, Finn C. Gradient surgery for multi-task learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020;33:5824-5836.
- Gupta V, Koren T, Singer Y. Shampoo: Preconditioned stochastic tensor optimization. arXiv. 2018:1802.09568.
- Ren Z, Zhou S, Liu D, Liu Q. Physics-informed neural networks: A review of methodological evolution, theoretical foundations, and interdisciplinary frontiers toward next-generation scientific computing. Appl. Sci. 2025;15(14):8092.
- Jagtap AD, Kharazmi E, Karniadakis GE. Conservative physics-informed neural networks on discrete domains for conservation laws: Applications to forward and inverse problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2020;365:113028.
- Shukla K, Jagtap AD, Karniadakis GE. Parallel physics-informed neural networks via domain decomposition. J. Comput. Phys.. 2021;447:110683.
- Sukumar N, Srivastava A. Exact imposition of boundary conditions with distance functions in physics-informed deep neural networks. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022;389:114333.
- Xiang Z, Peng W, Zhou W, Yao W. Hybrid finite difference with the physics-informed neural network for solving PDE in complex geometries. arXiv. 2022; arXiv:2202.07926.
- Barschkis, S. Exact and soft boundary conditions in Physics-Informed Neural Networks for the Variable Coefficient Poisson equation. arXiv. 2023; arXiv:2310.02548. [Google Scholar]
- Plankovskyy S, Tsegelnyk Y, Shyshko N, Litvinchev I, Romanova T, Velarde Cantú JM. Review of physics-informed neural networks: Challenges in loss function design and geometric integration. Mathematics. 2025;13(20):3289.
- El Hassan M, Mjalled A, Miron P, Mönnigmann M, Bukharin N. Machine learning in fluid dynamics—physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) using sparse data: A review. Fluids. 2025;10(9):226.
- Martínez-Esteban A, Calvo-Barlés P, Martín-Moreno L, Rodrigom SG. Physics-informed neural networks with dynamical boundary constraints. arXiv. 2025; arXiv:2507.21800.
- Kalajahi AP, Csala H, Naderi F, Mamun Z, Yadav S, Amili O, et al. Input parameterized physics informed neural network for advanced 4d flow MRI processing. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025;150:110600.
- Kang J, Jung EC, Koo HJ, Yang DH, Ha H. Flow-rate constrained physics-informed neural networks for flow field error correction in four-dimensional flow magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 2025.
- Barari K, Si X, Xi J. Impacts of mask wearing and leakages on cyclic respiratory flows and facial thermoregulation. Fluids. 2024;9(1):9.
- Khaled T, Xi J, Baldez P, Hecht A. Radiation dosimetry of inhaled radioactive aerosols: CFPD and MCNP transport simulation of Radionuclides in the lungs. Sci. Rep. 2019;9(1):17450.
- Talaat M, Si X, Tanbour H, Xi J. Numerical studies of nanoparticle transport and deposition in terminal alveolar models with varying complexities. Med One. 2019;4:e190018.
- Si XA, Talaat M, Xi J. Effects of guiding vanes and orifice jet flow of a metered-dose inhaler on drug dosimetry in human respiratory tract. Exp. Comput. Multiph. Flow. 2023;5(3):247-261.
- Talaat M, Si X, Xi J. Evaporation dynamics and dosimetry methods in numerically assessing MDI performance in pulmonary drug delivery. Fluids. 2024;9(12):286.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




