Submitted:
26 October 2025
Posted:
28 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
This paper presents a finite element analysis of the electrostatic field in gas ionization chambers used for beam diagnostics in laser-accelerated proton therapy systems. With the advent of laser-driven proton accelerators, such as the CLAPA-II project, there is a growing need for precise beam monitoring systems capable of handling high peak currents and large energy dispersion. Gas ionization chambers are widely employed for this purpose due to their reliability and accuracy. Using ANSYS software, this study establishes a detailed electrostatic finite element model of a multi-electrode ionization chamber. Key steps include model simplification, gas region definition, regional meshing, and solver selection. The analysis demonstrates the convergence of the electrostatic field solution and validates the model’s accuracy. The proposed modeling approach not only enhances computational efficiency but also facilitates interoperability with other simulation platforms such as Garfield++. This work provides a reliable foundation for optimizing ionization chamber design and improving beam diagnostic precision in advanced proton therapy applications.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
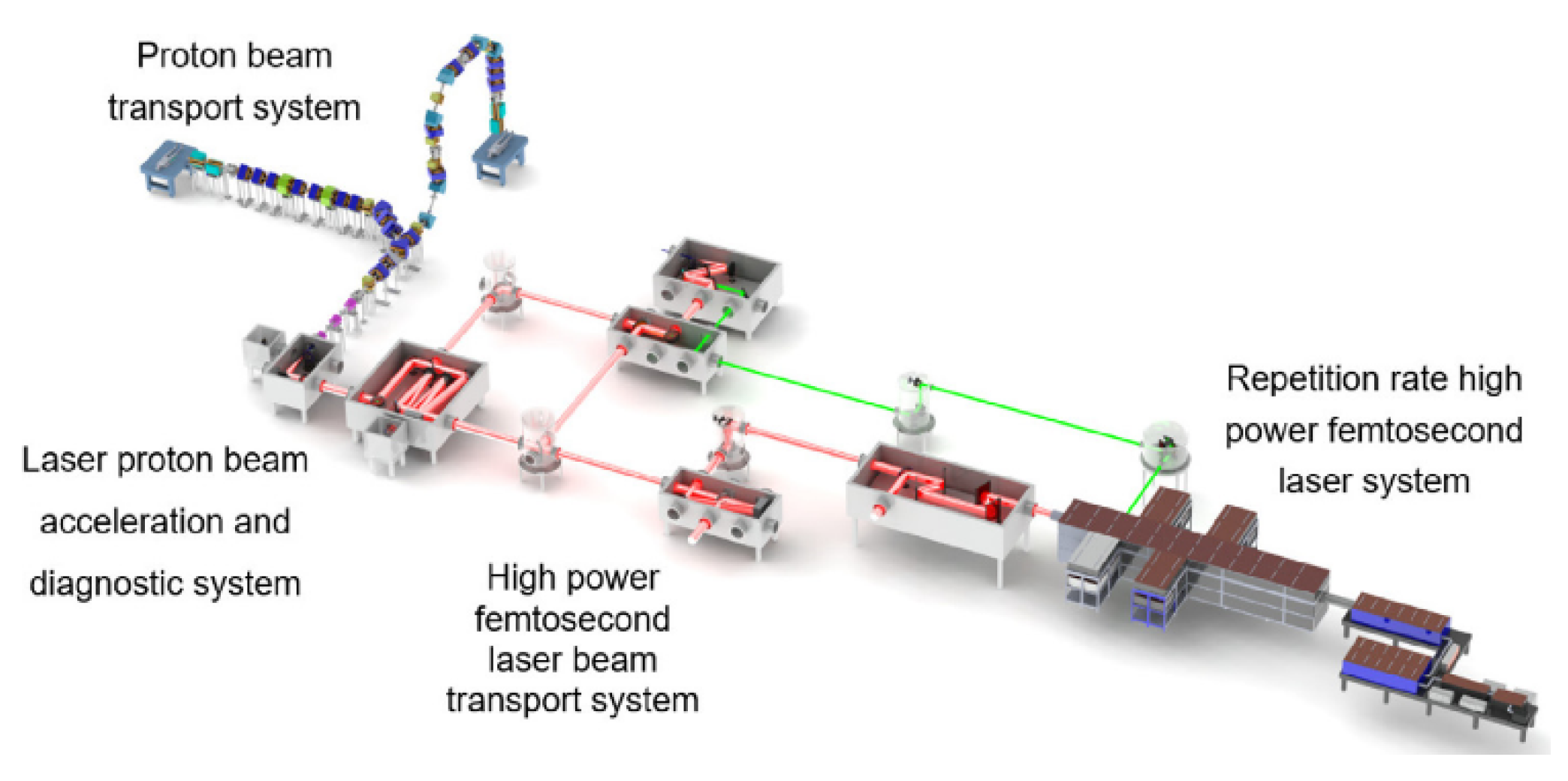
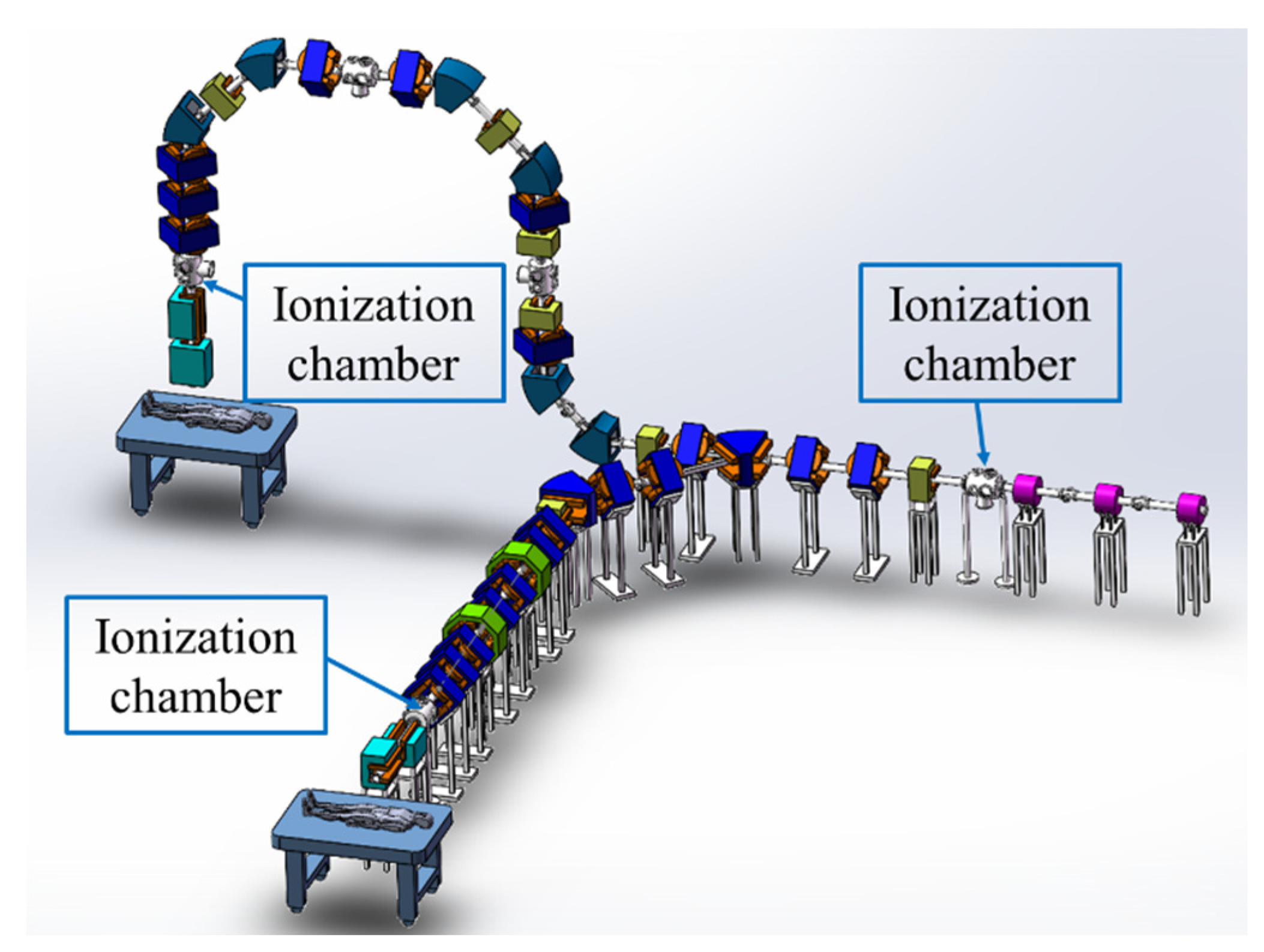
2. Principle and Technical Background
2.1. Gas Ionization Chamber Working Principle
2.2. Introduction to the ANSYS Platform and the Research Significance
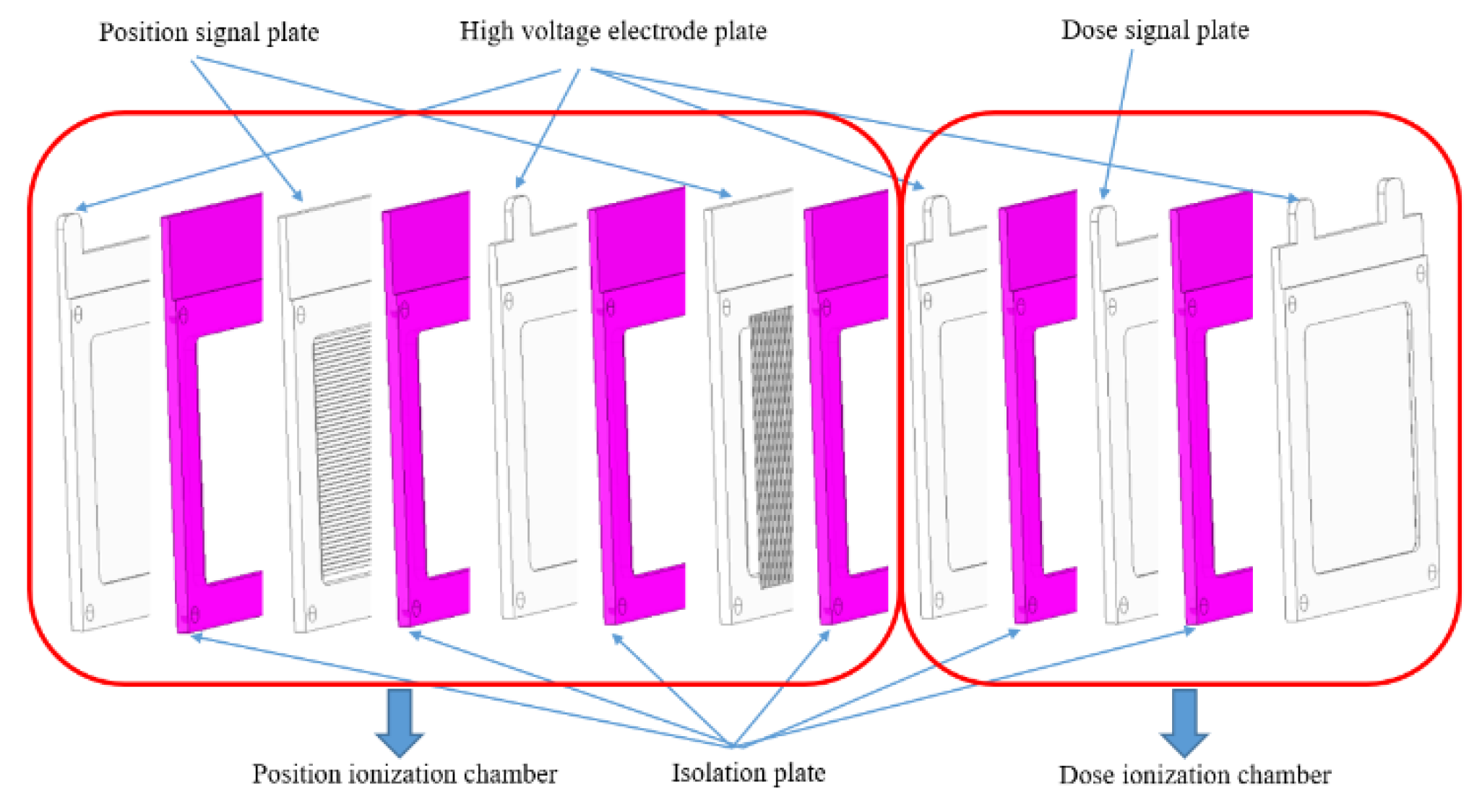
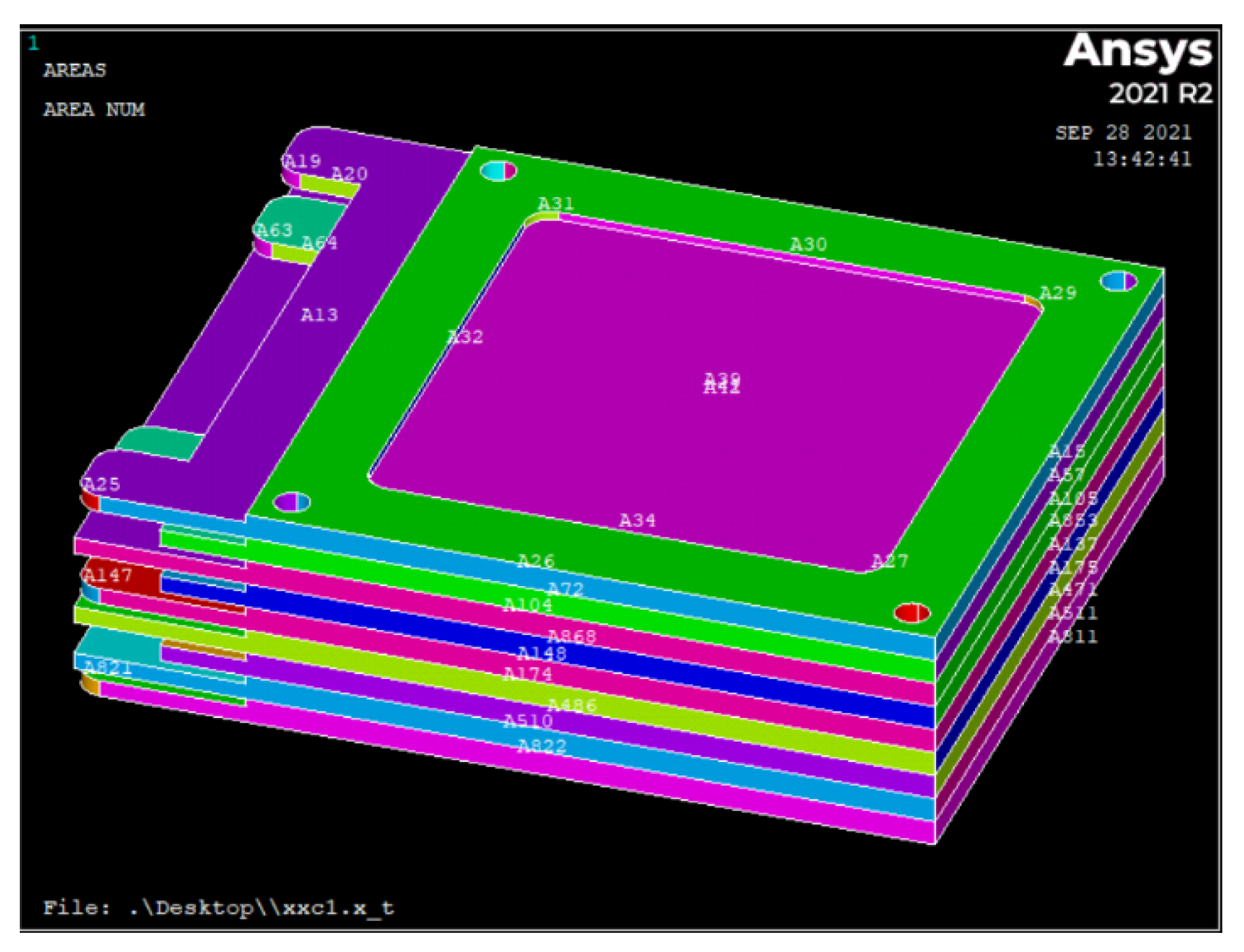
3. Ansys Modeling of Gas Ionization Chamber
3.1. Technical Scheme and Approach
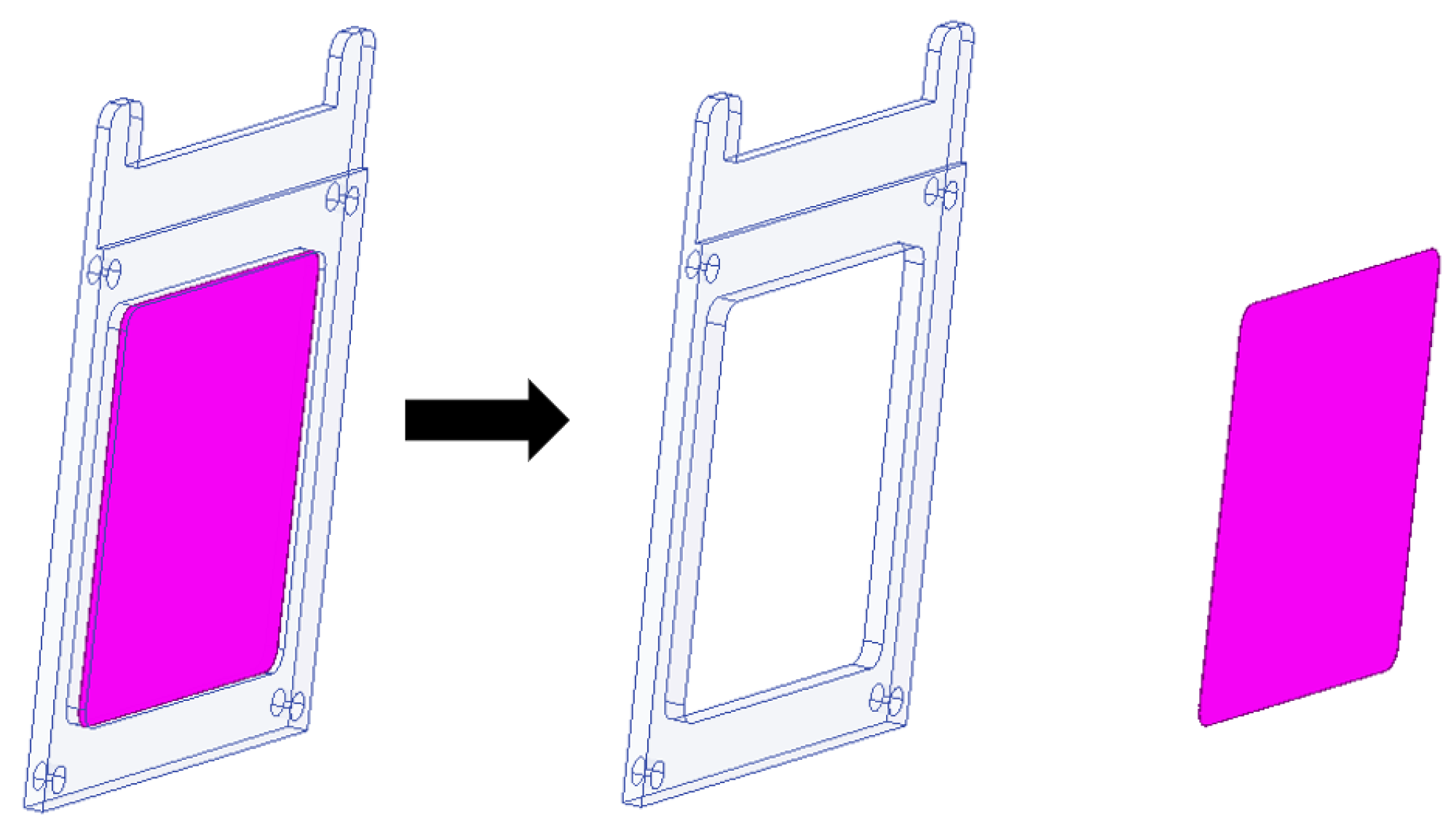
3.2. Advantages and Innovations
4. ANSYS Modeling Process and Steps for the Gas Ionization Chamber
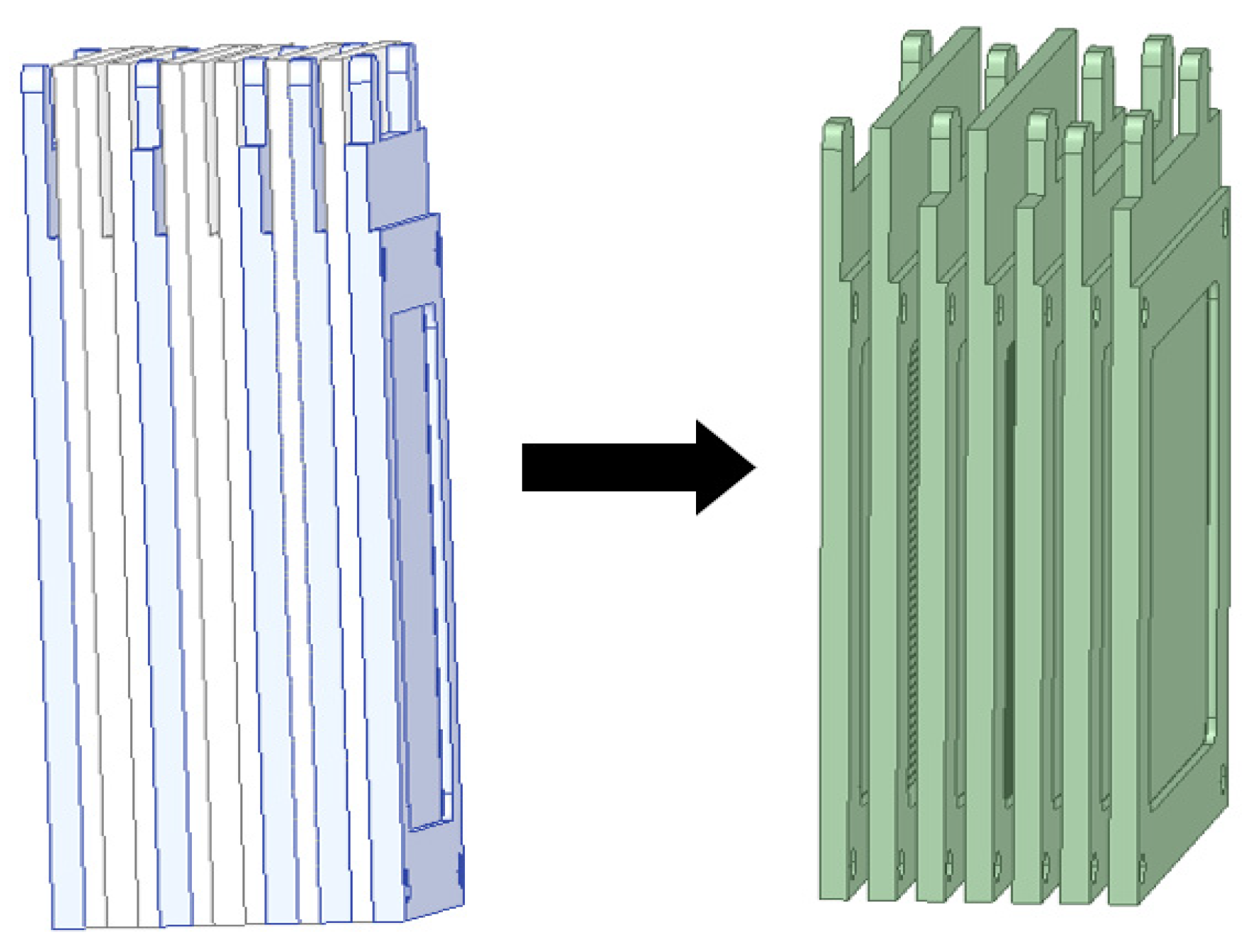
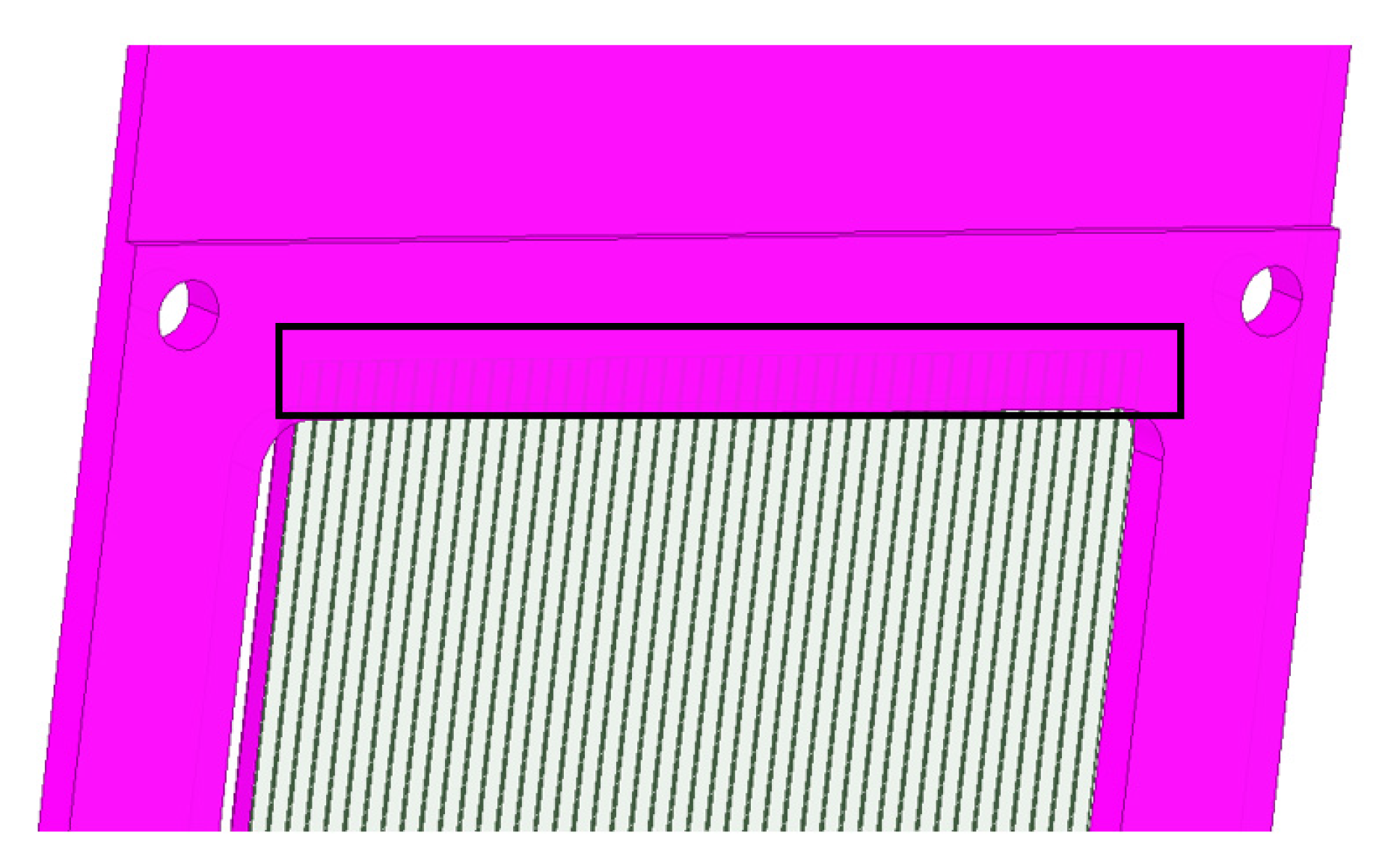
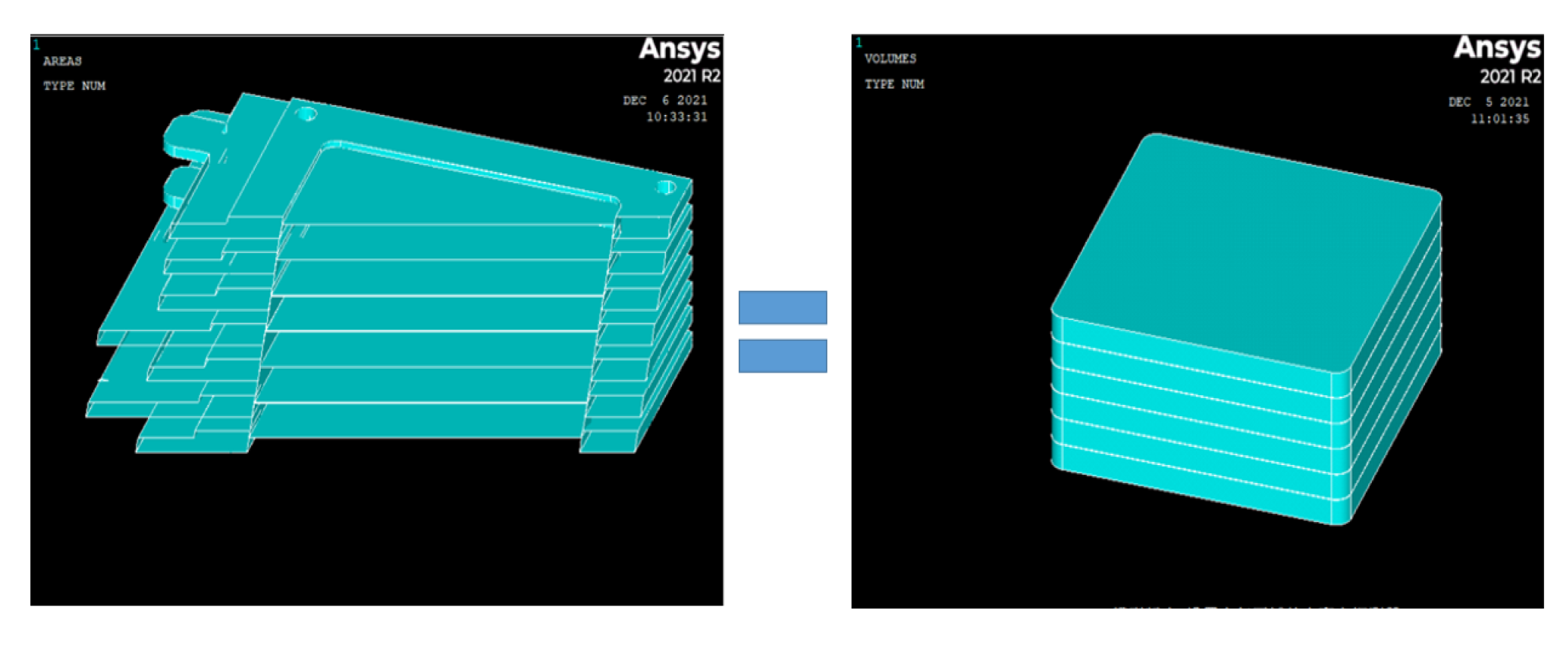
4.1. Experimental and Modeling Steps
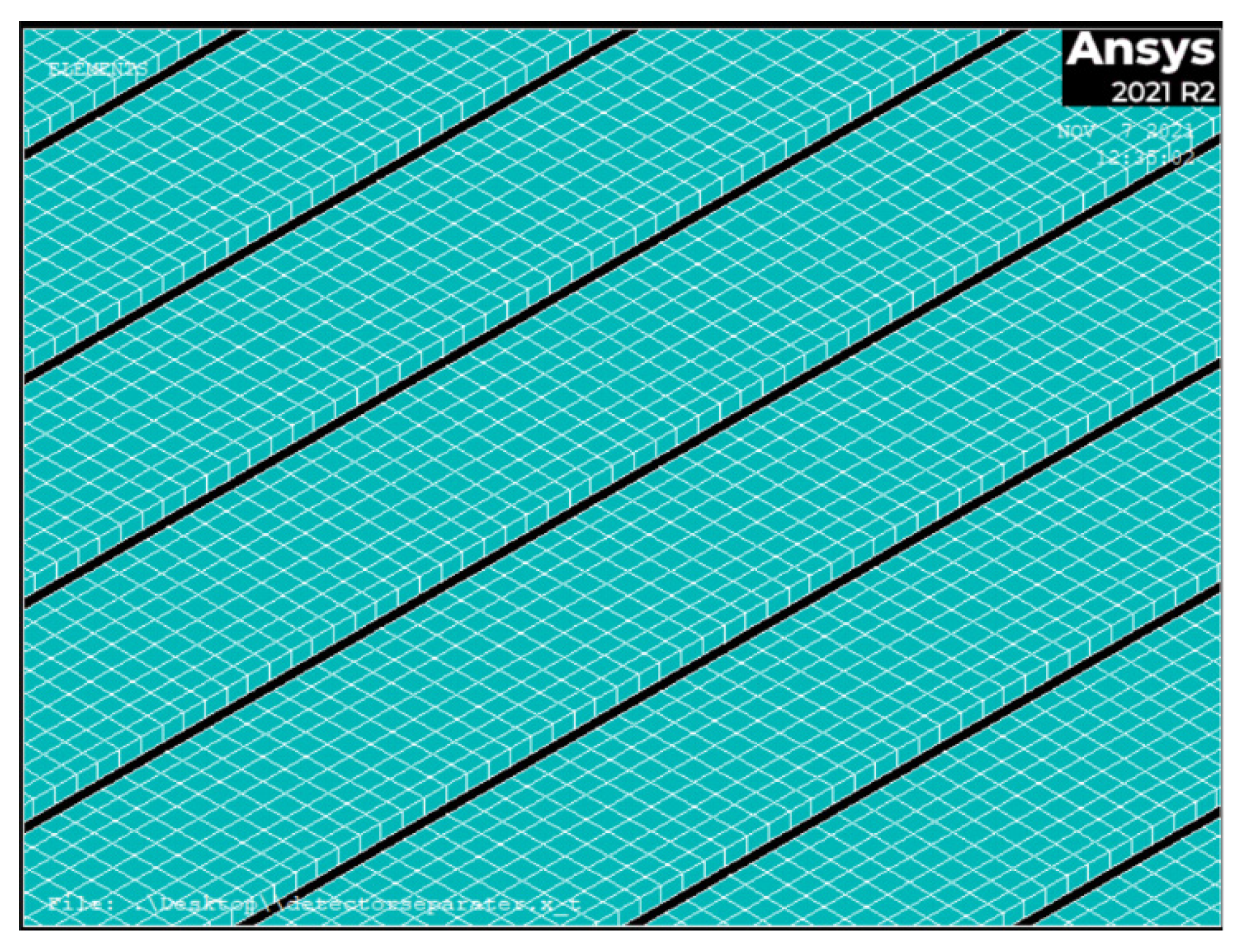
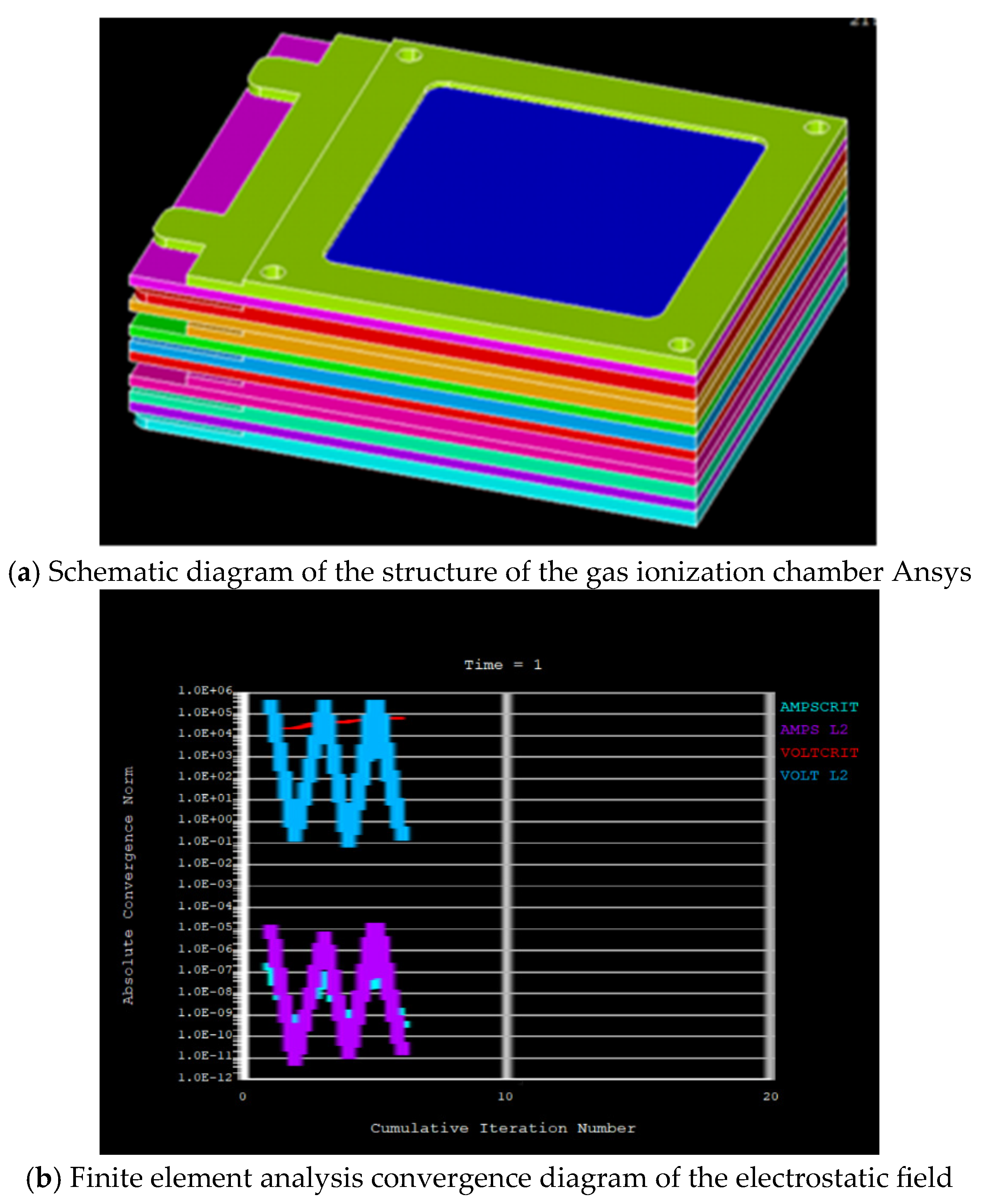
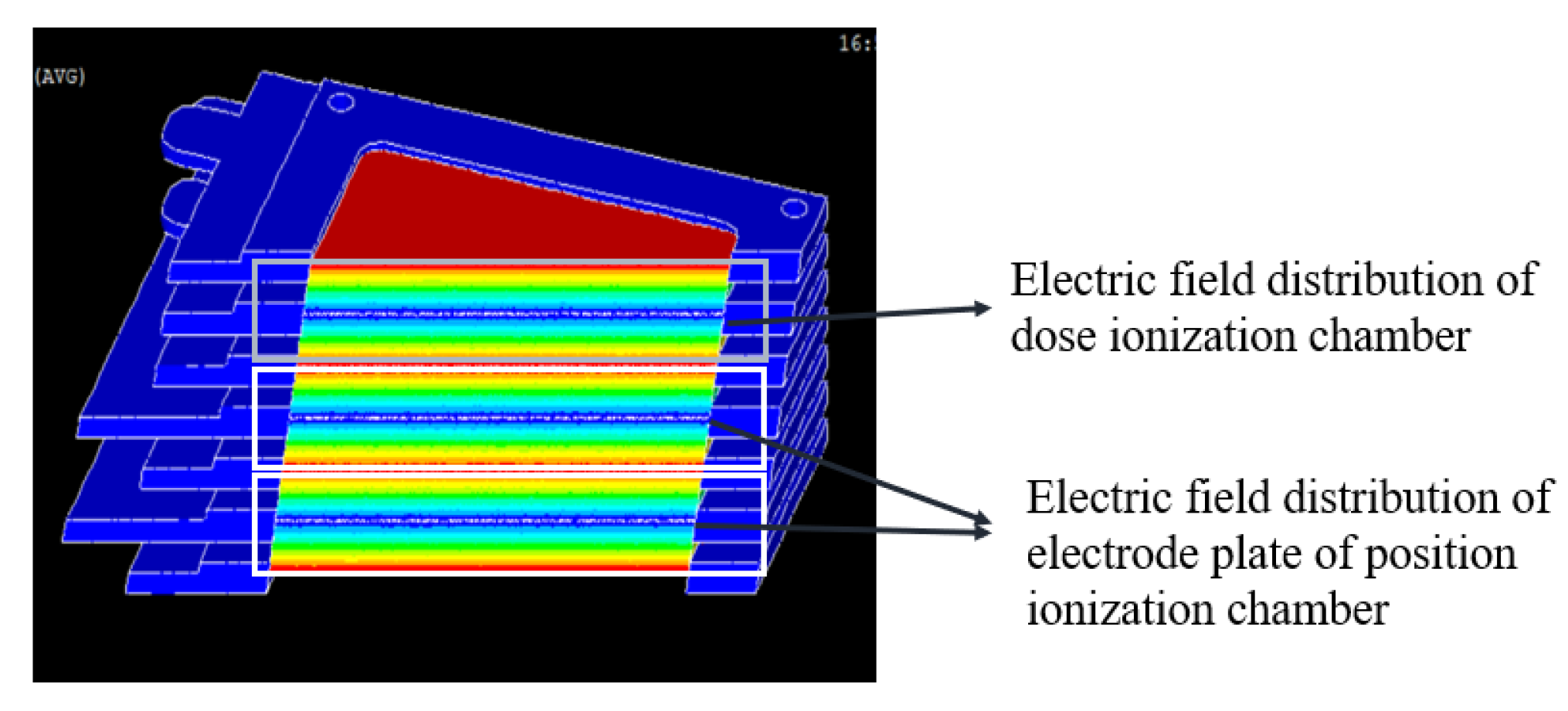
4.2. finite Element Analysis Results of Gas Ionization Chamber
5. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ZHENG Rongshou, SUN Kexin, ZHANG Siwei, et al. Analysis of the prevalence of malignant tumors in China in 2015 [J]. Chinese Journal of Oncology, 2019, 41(1): 19-28(in Chinese).
- Bray F I, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2018, 68(6): 394-424.
- Liu Shiyao. Status and development of proton therapy equipment[J]. Basic Medicine and Clinical, 2005, 25(2): 123-127(in Chinese).
- P. Mulser, D. Bauer, H. Ruhl, Collisionless laser-energy conversion by anharmonic resonance, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 (2008) 225002. [CrossRef]
- T. Ziegler, D. Albach, C. Bernert, S. Bock, F.-E. Brack, T.E. Cowan, N.P. Dover, M. Garten, L. Gaus, R. Gebhardt, I. Goethel, et al., Proton beam quality enhancement by spectral phase control of a PW-class laser system, Sci. Rep. 11 (2021) 7338. [CrossRef]
- Z.-C. Yan, W. Nörtershäuser, G.W.F. Drake, High precision atomic theory for Li and Be+: QED shifts and isotope shifts, Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 (2008) 243002. [CrossRef]
- H.Y. Wang, C. Lin, Z.M. Sheng, B. Liu, S. Zhao, Z.Y. Guo, Y.R. Lu, X.T. He, J.E. Chen, X.Q. Yan, Laser shaping of a relativistic intense, short Gaussian pulse by a plasma lens, Phys. Rev. Lett. 107 (2011) 265002. [CrossRef]
- A.A. Morris, Applications of 10 MeV photons and 100 MeV protons in radiotherapy, 2020, http://dx.doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.2006.13117, arXiv preprint.
- F. Kroll, F.-E. Brack, C. Bernert, S. Bock, E. Bodenstein, K. Brüchner, T.E. Cowan,L. Gaus, R. Gebhardt, U. Helbig, L. Karsch, T. Kluge, et al., Tumour irradiation in mice with a laser-accelerated proton beam, Nat. Phys. 18 (2022) 316–322. [CrossRef]
- U. Masood, M. Bussmann, T.E. Cowan, W. Enghardt, L. Karsch, F. Kroll, U. Schramm, J. Pawelke, A compact solution for ion beam therapy with laser accelerated protons, Appl. Phys. B 117 (1) (2014) 41–52. [CrossRef]
- U. Masood, T.E. Cowan, W. Enghardt, K.M. Hofmann, J. Pawelke, A light-weight compact proton gantry design with a novel dose delivery system for broad-energetic laser-accelerated beams, Phys. Med. Biol. 62 (13) (2017) 5531–5555. [CrossRef]
- F.H. Lindner, D. Haffa, J.H. Bin, F. Englbrecht, Y. Gao, J. Gebhard, J. Hartmann,P.Hilz, C. Kreuzer, S. Lehrack, et al., Towards swift ion bunch acceleration by high-power laser pulses at the centre for advanced laser applications (CALA), Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 402 (2017) 354–357, http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.nimb.2017.02.088, Proceedings of the 7th International Conference Channeling 2016: Charged and Neutral Particles Channeling Phenomena.
- T.F. Rösch, Z. Szabó, D. Haffa, J.H. Bin, S. Brunner, F.S. Englbrecht, A.A. Friedl, Y.Gao, J. Hartmann, P. Hilz, C. Kreuzer, F.H. Lindner, et al., A feasibility study of zebrafish embryo irradiation with laser-accelerated protons, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 91 (6) (2020) 063303. [CrossRef]
- G.A.P. Cirrone, M. Carpinelli, G. Cuttone, S. Gammino, S. Bijan Jia, G. Korn,M.Maggiore, L. Manti, D. Margarone, J. Prokupek, et al., ELIMED, future hadrontherapy applications of laser-accelerated beams, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 730 (2013) 174–177, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2013.05. 051, Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Materials Detectors and Devices.
- F. Romano, F. Schillaci, G.A.P. Cirrone, G. Cuttone, V. Scuderi, L. Allegra, A. Amato, A. Amico, G. Candiano, G. De Luca, et al., The ELIMED transport and dosimetry beamline for laser-driven ion beams, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 829 (2016) 153–158, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2016.01.064, 2nd European Advanced Accelerator Concepts Workshop - EAAC 2015.
- G. Aymar, T. Becker, S. Boogert, M. Borghesi, R. Bingham, C. Brenner, P.N. Burrows, O.C. Ettlinger, T. Dascalu, S. Gibson, T. Greenshaw, et al., LhARA: The laser-hybrid accelerator for radiobiological applications, Front. Phys. 8 (2020) 567738. [CrossRef]
- GSI Helmholtz, ATHENA — Accelerator technology Helmholtz infrastructure, 2022, project website (accessed on 22 April 2022). URL https://www.athena-helmholtz.de.
- K.D. Wang, K. Zhu, M.J. Easton, Y.J. Li, C. Lin, X.Q. Yan, Achromatic beamline design for a laser-driven proton therapy accelerator, Phys. Rev. Accelerators Beams 23 (2020) 111302. [CrossRef]
- Denker, D. Cordini, J. Heufelder, H. Homeyer, H. Kluge, I. Simiantonakis, R. Stark, A. Weber, Ion accelerator applications in medicine and cultural heritage, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A580 (1) (2007) 457–461, http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.nima.2007.05.320, Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Radiation Physics.
- K.D. Wang, K. Zhu, Matthew J. Easton, Y.J. Li, K. Wang a, X.C. Xie, H.Y. Lan,S.X. Cai, H. Wang, H.L. Ge, T.R. Zhu, J. Li a, C.J. Zhang, X.Y. Zhao, C. Lin,X.Q. Yan, Beam distribution homogenization design for laser-driven proton therapy.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




