Submitted:
16 October 2025
Posted:
22 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Information on the food web structure of fish assemblages is necessary for ecosystem-based fishery management. In this study, we investigated spatial and temporal variations in the trophic structure of fish assemblages in the eastern region of the Yellow Sea. We analyzed the species composition, abundance, and δ13C and δ15N values of fish assemblages and their potential food sources collected at the two sites during the four seasons of 2023. Spatial and temporal differences in the abundance and diversity of fish assemblages were observed between the sites and among the seasons. The isotopic values of fish assemblages with isotopic niche indices differed significantly between sites and seasons. In addition, the isotopic niche indices showed different seasonal patterns between the sites. However, the isotopic distributions and niche indices of fish assemblages showed no clear spatial or seasonal trends. These results suggested that the effect of site-specific variability in environmental factors and community characteristics is linked to different ambient environmental conditions. Overall, this study is important for understanding the ecological role of fishery resources and enhancing ecological-based fishery management in the eastern region of the Yellow Sea under severe anthropogenic effects and climate change.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
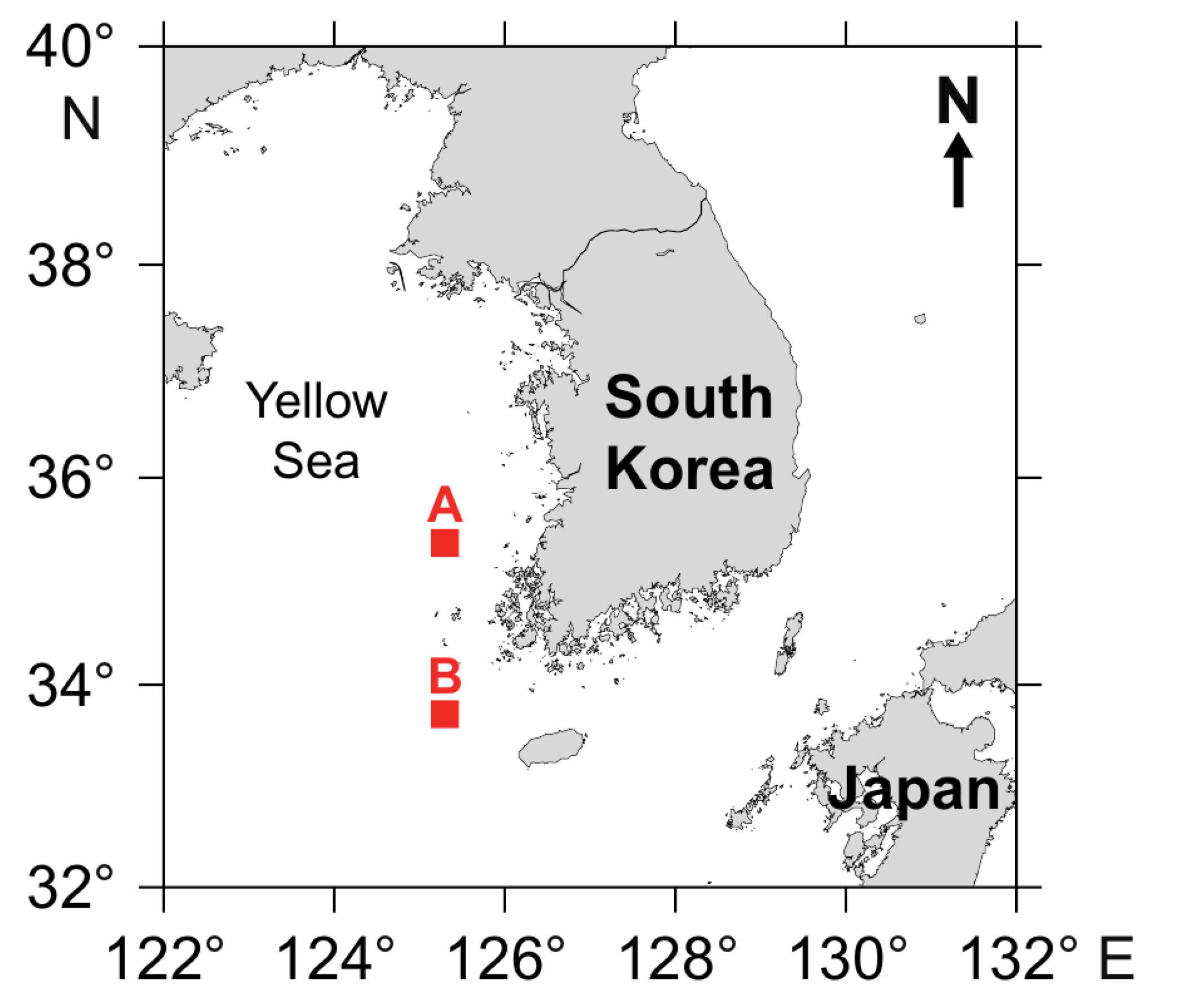
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. Stable Isotope Analyses
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Composition of Fish Assemblages
3.2. Stable Isotope Values of SPOM and Zooplankton
3.3. Stable Isotope Values of Fish Assemblages
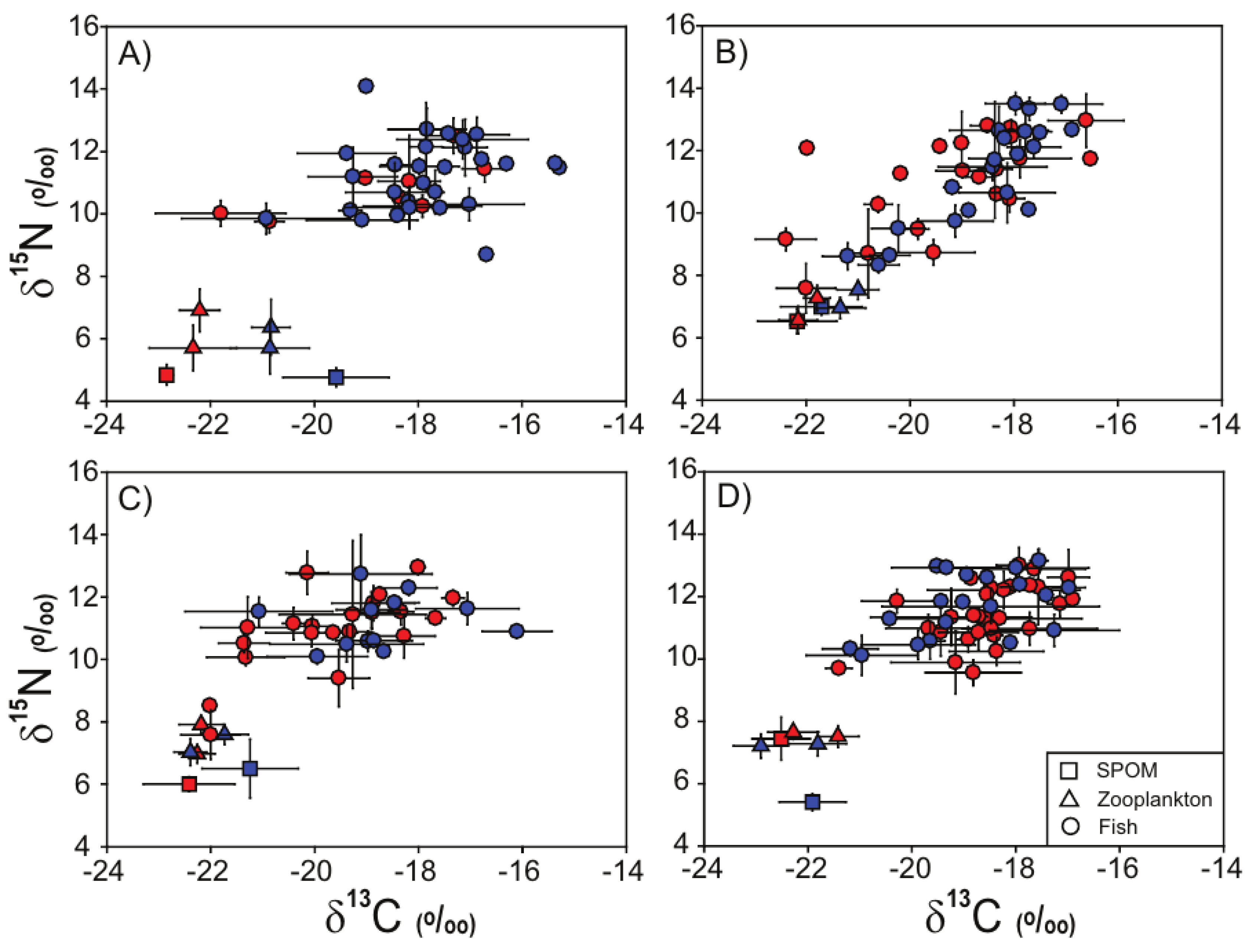
3.4. Trophic Positions and Isotopic Niches of Fish Assemblages
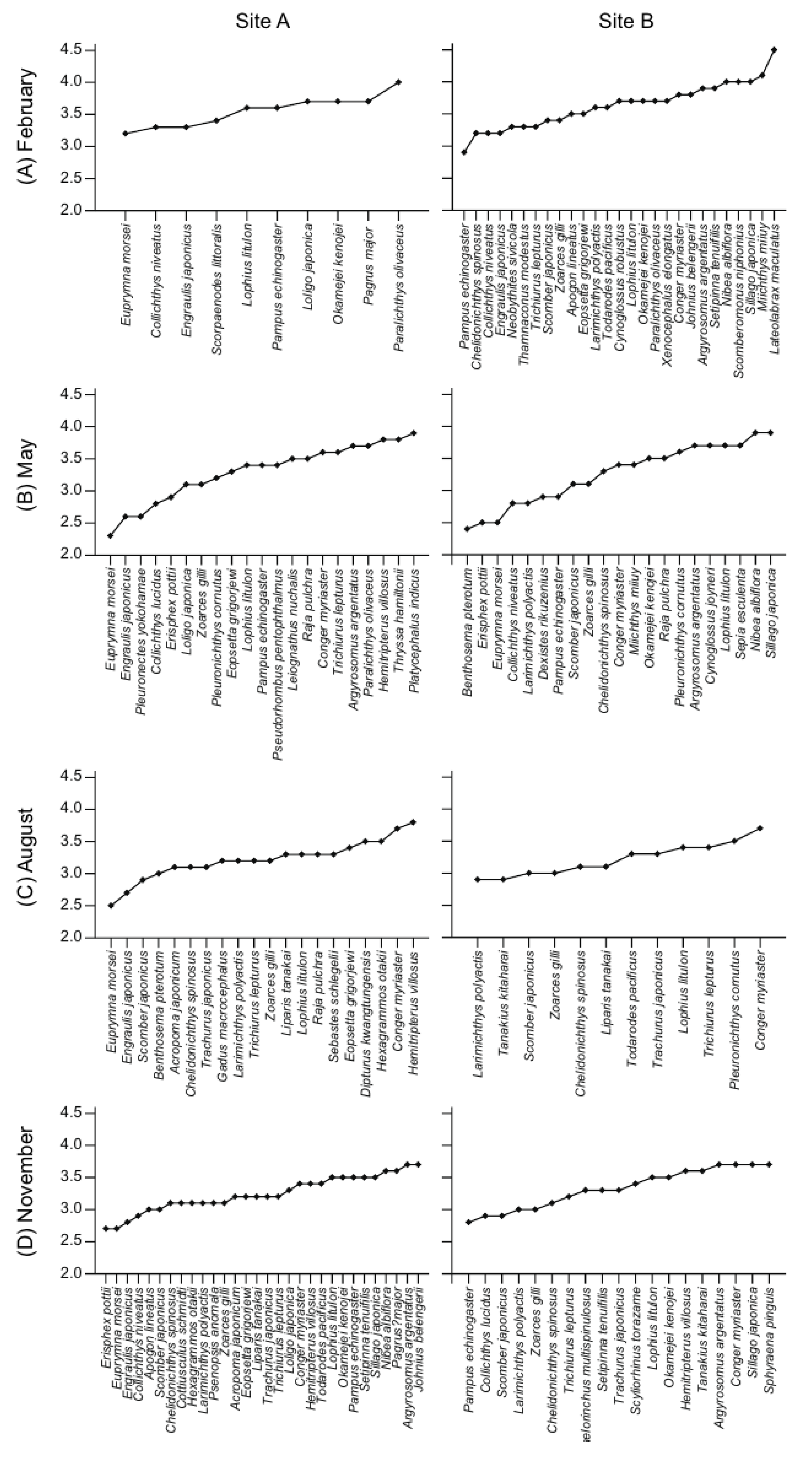
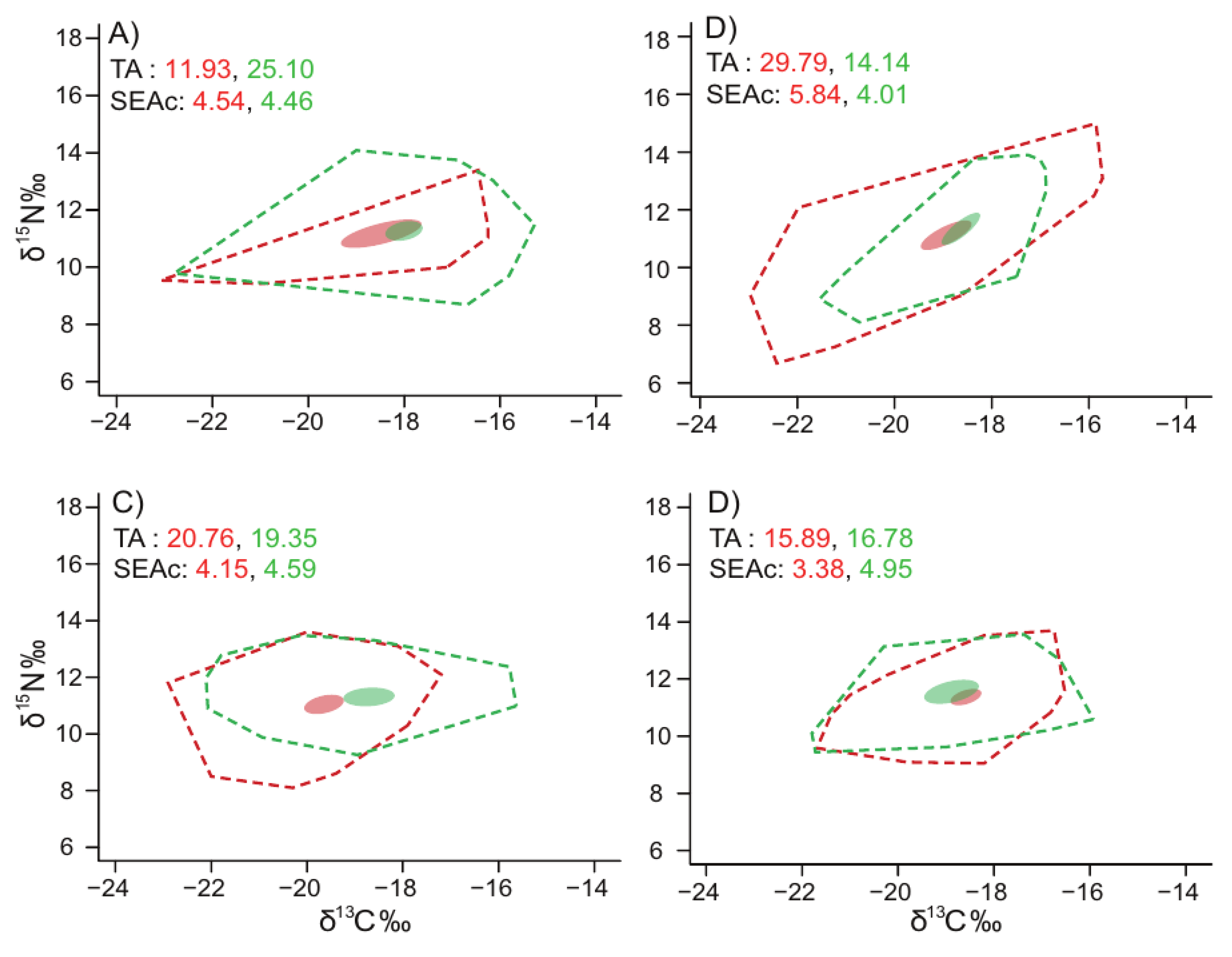
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, J.; Duan, L. The yellow sea. In World Seas: An Environmental Evaluation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 395–413. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, C.R.; Nittrouer, C.A.; Demaster, D.J.; Park, Y.A.; Park, S.C. Macrotidal mudflats of the southwestern Korean coast; a model for interpretation of intertidal deposits. J. Sediment. Res. 1991, 615, 805–824. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, J.H.; Van, S.P.; Choi, B.J.; Chang, Y.S.; Kim, Y.H. The physical processes in the Yellow Sea. Ocean Coast. Manage. 2014, 102, 449–457. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, R.; Tan, H.; Qi, Q. Impacts of and adaptation to inter-decadal marine climate change in coastal China seas. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 3611, 3770–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.K.; Rahman, S.M.; Kang, C.K.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Park, H.J.; Lee, C.I. The influence of climate regime shifts on the marine environment and ecosystems in the East Asian Marginal Seas and their mechanisms. Deep-Sea Res. Part II. 2017, 143, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, C.; Ye, Z.; Sun, P.; Tian, Y. Climate-induced long-term variations in ecosystem structure and atmosphere-ocean-ecosystem processes in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 175, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.; Lee, M.; Jeong, H.J.; Kim, W.J.; Park, J.G.; Yang, J.S. Enhanced benthic nutrient flux during monsoon periods in a coastal lake formed by tideland reclamation. Estuar. Coast. 2009, 32, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, G.H.; Moon, H.B.; Choi, J.H.; Hwang, J.; Kang, C.K. Biomagnification of persistent chlorinated and brominated contaminants in food web components of the Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 731, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.H.; Khim, J.S. The Korean tidal flat of the Yellow Sea: Physical setting, ecosystem and man-agement. Ocean Coast. Manage. 2014, 102, 398–414. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Zhang, C.I.; Kim, J.Y.; Oh, J.H.; Kang, S.; Lee, J.B. Climate variability and its effects on major fisheries in Korea. Ocean Sci. J. 2007, 42, 179–192. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.I.; Lim, J.H.; Kwon, Y.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, D.H.; Seo, Y.I. The current status of west sea fish-eries resources and utilization in the context of fishery management of Korea. Ocean Coast. Man-age. 2014, 102, 493–505. [Google Scholar]
- Cury, P.; Shannon, L.; Shin, Y.J. The functioning of marine ecosystems: a fisheries perspective. Sinclair, M.; Valdimarsson, G. (Eds.), Responsible Fisheries in the Marine Ecosystem, FAO/CAB Internation-al, Rome, Italy/Wallingford, UK. 2003, p. 103.
- Thompson, R.M.; Townsend, C.R. The effect of seasonal variation on the community structure and food-web attributes of two streams: implications for food-web science. Oikos 1999, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, M.R.; Speirs, D.C.; Steele, J.H. Understanding patterns and processes in models of trophic cascades. Ecol. Lett. 2014, 171, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navia, A.F.; Cruz-Escalona, V.H.; Giraldo, A.; Barausse, A. The structure of a marine tropical food web, and its implications for ecosystem-based fisheries management. Ecol. Model. 2016, 328, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, L.M.; Beentjes, M.P.; Wing, S.R. Shifting trophic architecture of marine fisheries in New Zealand: Implications for guiding effective ecosystem-based management. Fish. Fish. 2020, 214, 813–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Fry, B. Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1987, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancinelli, G.; Vizzini, S. Assessing anthropogenic pressures on coastal marine ecosystems using stable CNS isotopes: State of the art, knowledge gaps, and community-scale perspectives. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 156, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boecklen, W.J.; Yarnes, C.T.; Cook, B.A.; James, A.C. On the use of stable isotopes in trophic ecolo-gy. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2011, 421, 411–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.; Sherr, E.B. δ13C measurements as indicators of carbon flow in marine and fresh-water ecosys-tems. Contrib. Mar. Sci. 1984, 27, 13–47. [Google Scholar]
- Vander Zanden, M.J.; Rasmussen, J.B. Variation in δ15N and δ13C trophic fractionation: implications for aquatic food web studies. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 468, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, D.M. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: models, methods, and assump-tions. Ecology 2002, 833, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layman, C.A.; Araujo, M.S.; Boucek, R.; Hammerschlag-Peyer, C.M.; Harrison, E.; Jud, Z.R.; Bearhop, S. Applying stable isotopes to examine food-web structure: an overview of analytical tools. Biol. Rev. 2012, 873, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, S.R.; Bax, N.J. A trophic study of a marine ecosystem off southeastern Australia using stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 593, 514–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Park, T.H.; Lee, C.I.; Kang, C.K. Ontogenetic shifts in diet and trophic position of walleye pollock, Theragra chalcogramma, in the western East Sea Japan Sea revealed by stable isotope and stomach content analyses. Fish. Res. 2018, 204, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 26, Timmerman, C. A.; Giraldo, C.; Cresson, P.; Ernande, B.; Travers-Trolet, M.; Rouquette, M.; Lefebvre, S. Plasticity of trophic interactions in fish assemblages results in temporal stability of benthic-pelagic couplings. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 170, 105412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, D.; Park, T.H.; Lee, C.I.; Jeong, J.M.; Lee, S.J.; Kang, S.; Park, H.J. Trophic ecology of largehead hairtail Trichiurus japonicus in the South Sea of Korea revealed by stable isotope and stomach content analyses. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 910436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, D.M.; Layman, C.A.; Arrington, D.A.; Takimoto, G.; Quattrochi, J.; Montana, C.G. Getting to the fat of the matter: models, methods and assumptions for dealing with lipids in stable isotope anal-yses. Oecologia 2007, 152, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.J. PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER: guide to software and statistical methods. PRIMER-E, Plymouth Marine Laboratory. 2008, 214.
- Layman, C.A.; Arrington, D.A.; Montaña, C.G.; Post, D.M. Can stable isotope ratios provide for community-wide measures of trophic structure? Ecology 2007, 881, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.L.; Inger, R.; Parnell, A.C.; Bearhop, S. Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER–Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R. J. Anim. Ecol. 2011, 803, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.M.; Brose, U.; Dunne, J.A.; Hall, R.O.; Hladyz, S.; Kitching, R.L.; Tylianakis, J.M. Food webs: reconciling the structure and function of biodiversity. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 2712, 689–697. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.H.; Lee, C.I.; Kang, C.K.; Kwak, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, H.J. Seasonal variation in food web structure and fish community composition in the East/Japan Sea. Estuar. Coast. 2020, 43, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Park, T.H.; Kim, D.; Lee, C.I.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, H.J. Spatial and temporal variations in trophic structure of fish assemblages in the Yellow Sea revealed by C and N stable isotopes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 196, 115678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, M.C. The changes in marine environment and biological community in sea areas around an artificial upwelling structure during the summer. Anim. Cells Syst. 2013, 17(5), 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shan, X.; Jin, X.; Johannessen, A.; Yang, T.; Dai, F. Changes in fish diversity and community structure in the central and southern Yellow Sea from 2003 to 2015. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 36, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magill, S.H.; Sayer, M.D.J. Seasonal and interannual variation in fish assemblages of northern tem-perate rocky subtidal habitats. J. Fish Biol. 2002, 615, 1198–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selleslagh, J.; Amara, R. Inter-season and interannual variations in fish and macrocrustacean community structure on an eastern English Channel sandy beach: Influence of environmental factors. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 774, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, F.G.; Teixeira, T.P.; Guedes, A.P.P.; de Azevedo, M.C.C.; Pessanha, A.L.M. Shifts in the abundance and distribution of shallow water fish fauna on the southeastern Brazilian coast: a response to climate change. Hydrobiologia 2018, 814, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, G.L.; Rose, G.A. Seasonal distribution and movements of coastal cod Gadus morhua L. in Placentia Bay, Newfoundland. Fish. Res. 2000, 491, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.G.; De Astarloa, J.D.; Cousseau, M.B.; Figueroa, D.E.; Delpiani, S.M.; Bruno, D.O.; Antoni, M.D. Fish composition in a south-western Atlantic temperate coastal lagoon: spatial–temporal variation and relationships with environmental variables. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K. 2009, 893, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Xu, B.; Tang, Q. Fish assemblage structure in the East China Sea and southern Yellow Sea during autumn and spring. J. Fish Biol. 2003, 625, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, E.H.; Joo, H.W.; Lee, D.W.; Cha, H.K.; Choi, J.H. Community composition and distribution of fish species collected by bottom trawl from the middle of the Yellow Sea in summer 2008-2014. Kor. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 496, 849–855. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, D.; Shi, X.; Zhou, W.; Liu, W.; Zhang, S.; Cao, Y.; Han, Y. Sources and transportation of suspended matter and sediment in the southern Yellow Sea: Evidence from stable carbon isotopes. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.S.; Zhang, Z.N.; Huang, Y. Sublittoral meiofauna with particular reference to nematodes in the southern Yellow Sea, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 713, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.K.; Choy, E.J.; Hur, Y.B.; Myeong, J.I. Isotopic evidence of particle size-dependent food par-titioning in cocultured sea squirt Halocynthia roretzi and Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Aquat. Biol. 2009, 6, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, L.A.; Sharp, J.H.; Fogel, M.L. Stable carbon and nitrogen isotope biogeochemistry in the Delaware estuary. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1988, 335, 1102–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goering, J.; Alexander, V.; Haubenstock, N. Seasonal variability of stable carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios of organisms in a North Pacific Bay. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1990, 303, 239–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Wu, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J.; Gao, L.; Wang, N. Fatty acids and stable isotopes of a marine ecosystem: study on the Japanese anchovy Engraulis japonicus food web in the Yellow Sea. Deep-Sea Res. Part II. 1057. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Ju, S.J.; Kang, J.H.; Shin, K.H. Diet source of Euphausia pacifica revealed using carbon-and nitrogen-stable isotopes in the Yellow Sea Cold Water Mass in summer. J. Oceanogr. 2019, 75, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Park, T.H.; Lee, C.I.; Hwang, K.; Kim, D.N.; Lee, S.J.; Park, H.J. Characterization of trophic structure of fish assemblages in the East and South Seas of Korea based on C and N stable isotope ra-tios. Water 2021, 141, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.N.; Shiao, J.C.; Gong, G.C.; Kao, S.J.; Hsieh, C.H. Stable isotope ratios reveal food source of benthic fish and crustaceans along a gradient of trophic status in the East China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 84, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.K.; Blaber, S.J.; Elliott, M.; Harrison, T.D. Trophic ecology of fishes in estuaries. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2024, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, A.J.; Connolly, R.M. Spatial analysis of stable isotope data to determine primary sources of nutrition for fish. Oecologia. 2003, 136, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, M.D.; Ebert, D.A.; Cailliet, G.M. Stable-isotope analysis of a deep-sea benthic-fish assemblage: evidence of an enriched benthic food web. J. Fish Biol. 2012, 805, 1485–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, G.K.; Kim, C.; Kim, D.; Bibi, R.; Kim, H.; Kang, C.K. Phytoplankton fuel fish food webs in a low-turbidity temperate coastal embayment: A stable isotope approach. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 751551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, D.; Lefebvre, S.; Cachera, M.; Villanueva, M.C.; Ernande, B. Reorganization of a marine trophic network along an inshore–offshore gradient due to stronger pelagic–benthic coupling in coastal are-as. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 130, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa, M.L.; Vacchi, M.; Zunini Sertorio, T. Feeding plasticity of Trematomus newnesi Pisces, Notothe-niidae in Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea, in relation to environmental conditions. Polar Biol. 2000, 23, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Park, T.H.; Lee, C.I.; Jo, J.H.; Choi, C.G.; Kang, S.; Park, H.J. Feeding ecology of common squid Todarodes pacificus in the South Sea of Korea determined through stable isotope and stomach content analyses. Water 2022, 1419, 3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.; Whitfield, A.K.; Potter, I.C.; Blaber, S.J.; Cyrus, D.P.; Nordlie, F.G.; Harrison, T.D. The guild approach to categorizing estuarine fish assemblages: a global review. Fish. Fish. 2007, 83, 241–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerking, S.D. Feeding ecology of fish. Academic Press, San Diego. 2014.
- Leggett, W.C. The ecology of fish migrations. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1977, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatés, A.; Olivar, M.P.; Salat, J.; Palomera, I.; Alemany, F. Physical and biological processes controlling the distribution of fish larvae in the NW Mediterranean. Prog. Oceanogr. 3.
- Abrantes, K.G.; Barnett, A.; Marwick, T.R.; Bouillon, S. Importance of terrestrial subsidies for estuarine food webs in contrasting East African catchments. Ecosphere 2013, 41, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherel, Y.; Hobson, K.A.; Guinet, C.; Vanpe, C. Stable isotopes document seasonal changes in trophic niches and winter foraging individual specialization in diving predators from the Southern Ocean. J. Anim. Ecol. 2007, 764, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.H.; Lee, C.I.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, D.; Park, H.J. Trophic response of fishes to rainfall variability in a temperate estuarine system of Korea: A stable isotope approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 193, 115183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teichert, N.; Lizé, A.; Lepage, M.; Cabral, H.; Trancart, T.; Acou, A.; Carpentier, A. Hy-dro-morphological features and functional structure of fish assemblages mediate species isotopic niches in estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2024, 299, 108686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species Name | February | May | August | November | ||||
| St. A | St. B | St. A | St. B | St. A | St. B | St. A | St. B | |
| Total species number | 11 | 30 | 24 | 23 | 25 | 14 | 36 | 23 |
| Total individuals | 6107 | 13193 | 12855 | 22871 | 8206 | 11766 | 47159 | 3881 |
| Richness (R) | 1.03 | 2.95 | 2.33 | 2.09 | 2.55 | 1.28 | 3.16 | 2.54 |
| Evenness (J) | 0.77 | 0.64 | 0.78 | 0.40 | 0.66 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 0.86 |
| Diversity (H’) | 1.77 | 2.95 | 2.33 | 2.09 | 2.55 | 1.28 | 3.16 | 2.54 |
| St. A | St. B | ||||||||||
| Potential food source | δ13C | δ15N | δ13C | δ15N | |||||||
| n | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | n | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| February | |||||||||||
| SPOM | 4 | −22.8 | 0.1 | 4.8 | 0.3 | 4 | −19.6 | 1.0 | 4.8 | 0.3 | |
| Copepods | 3 | −22.3 | 0.8 | 5.7 | 0.7 | 3 | −20.9 | 0.8 | 5.7 | 0.8 | |
| Euphausiids | 3 | −22.2 | 0.4 | 6.9 | 0.7 | 3 | −20.8 | 0.4 | 6.4 | 0.9 | |
| May | |||||||||||
| SPOM | 5 | −22.2 | 0.8 | 6.5 | 0.4 | 5 | −21.7 | 0.8 | 7.0 | 0.3 | |
| Copepods | 3 | −21.8 | 0.3 | 7.3 | 0.4 | 3 | −21.0 | 0.4 | 7.5 | 0.3 | |
| Euphausiids | 3 | −22.2 | 0.4 | 6.6 | 0.4 | 3 | −21.3 | 0.5 | 7.0 | 0.3 | |
| August | |||||||||||
| SPOM | 5 | −22.4 | 0.9 | 6.0 | 0.2 | 5 | −21.2 | 0.9 | 6.5 | 0.9 | |
| Copepods | 3 | −22.3 | 0.3 | 7.0 | 0.3 | 3 | −22.4 | 0.3 | 7.0 | 0.4 | |
| Euphausiids | 3 | −22.2 | 0.4 | 7.9 | 0.3 | 3 | −21.7 | 0.5 | 7.6 | 0.3 | |
| November | |||||||||||
| SPOM | 5 | −22.5 | 0.6 | 7.4 | 0.7 | 5 | −21.9 | 0.6 | 5.4 | 0.3 | |
| Copepods | 3 | −22.9 | 0.5 | 7.2 | 0.4 | 3 | −21.8 | 0.5 | 7.3 | 0.4 | |
| Euphausiids | 3 | −22.3 | 0.5 | 7.7 | 0.2 | 3 | −21.4 | 0.4 | 7.5 | 0.3 | |
| PERMANOVA test | Season | Site | Interaction | ||||||||
| pseudo-F | p | pseudo-F | p | pseudo-F | p | ||||||
| SPOM | 18.99 | 0.001 | 20.76 | 0.001 | 6.47 | 0.001 | |||||
| Copepods | 9.51 | 0.001 | 4.36 | 0.024 | 0.38 | 0.822 | |||||
| Euphausiids | 5.90 | 0.006 | 9.03 | 0.001 | 0.62 | 0.654 | |||||
| St. A | St. B | |||||||||||||
| δ13C | δ15N | TP | δ13C | δ15N | TP | |||||||||
| n | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| February | 27 | −18.5 | 1.8 | 11.2 | 1.1 | 3.53 | 0.26 | −18.0 | 1.0 | 11.5 | 1.2 | 3.64 | 0.34 | |
| May | 63 | −18.9 | 1.7 | 11..1 | 1.7 | 3.30 | 0.45 | −18.6 | 1.3 | 11.2 | 1.9 | 3.26 | 0.47 | |
| August | 60 | −19.6 | 1.3 | 11.1 | 1.1 | 3.22 | 0.30 | −18.7 | 1.5 | 11.3 | 1.0 | 3.23 | 0.25 | |
| November | 79 | −18.6 | 1.2 | 11.4 | 1.0 | 3.24 | 0.27 | −18.9 | 1.5 | 11.6 | 1.1 | 3.31 | 0.30 | |
| PERMANOVA test | Season | Site | Interaction | |||||||||||
| pseudo-F | p | pseudo-F | p | pseudo-F | p | |||||||||
| 3.73 | 0.007 | 3.64 | 0.047 | 1.43 | 0.226 | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





