Submitted:
21 October 2025
Posted:
21 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
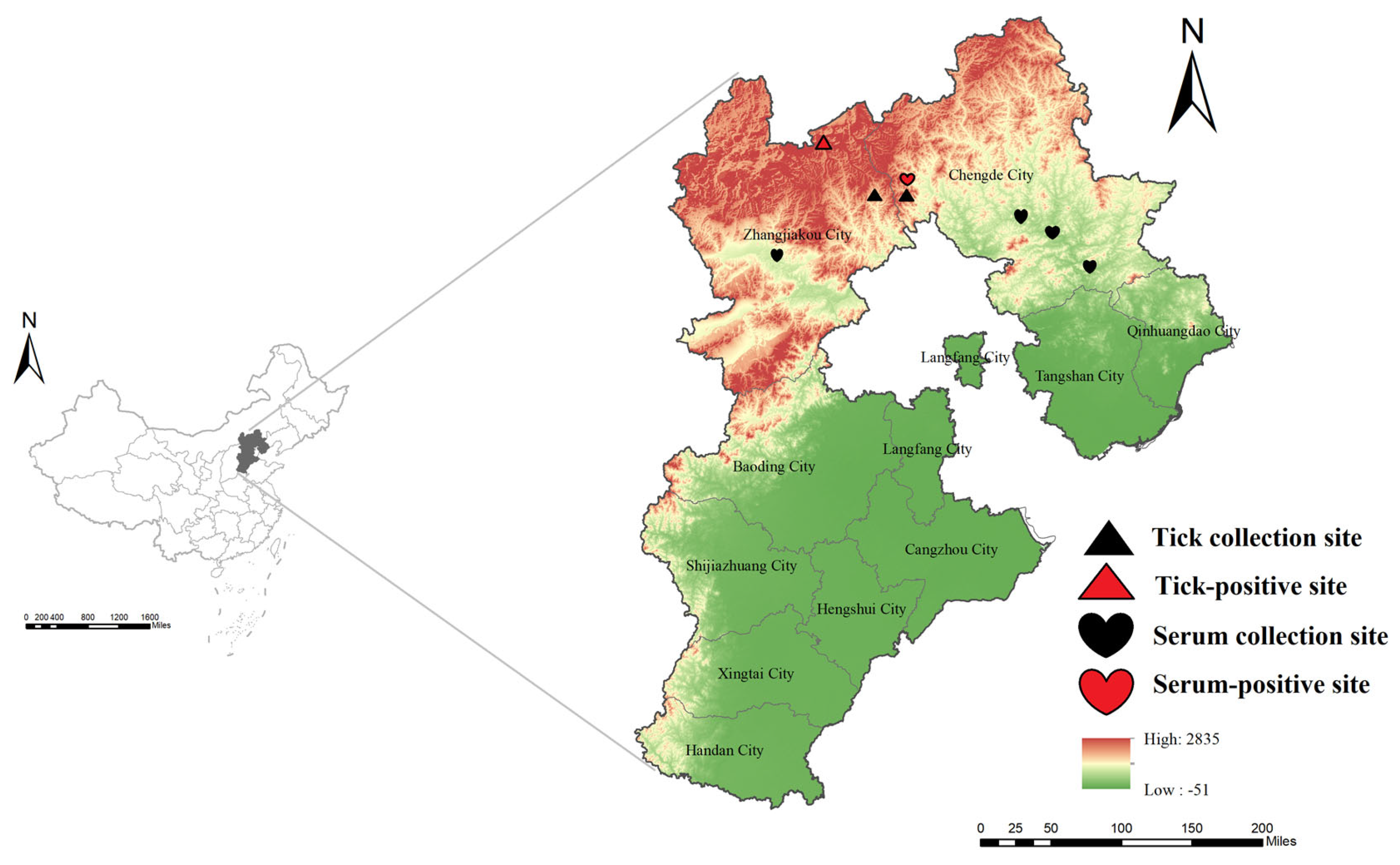
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Detection of SFTSV
2.3. Virus Isolation and Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.4. Phylogenetic and Evolutionary Analysis
2.5. Reassortment and Recombination
2.6. Phylogenetic Analyses by BEAST
3. Results
3.1. Detection of SFTSV RNA in Patients and Ticks
3.2. Genomic Characteristics of SFTSV Isolates
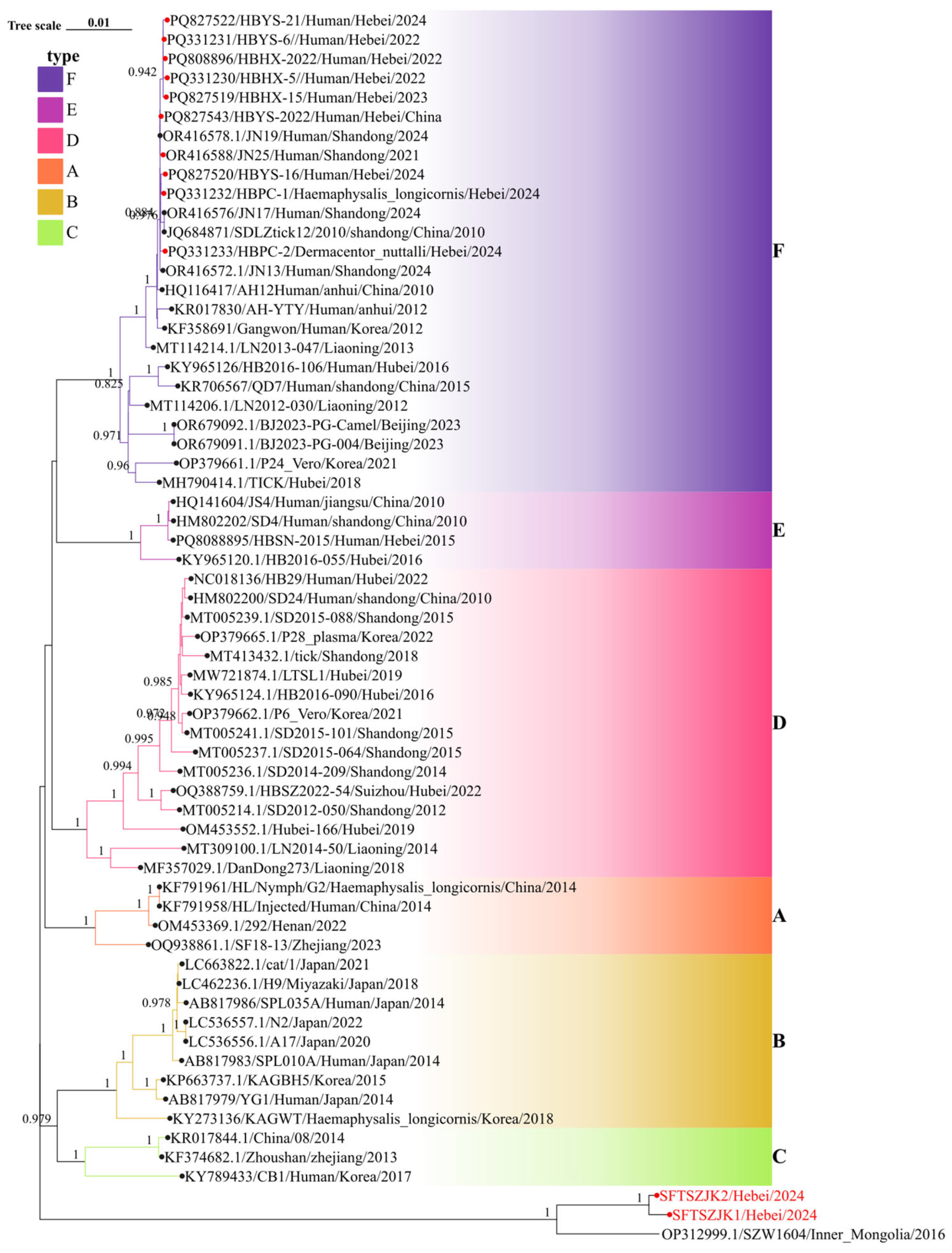
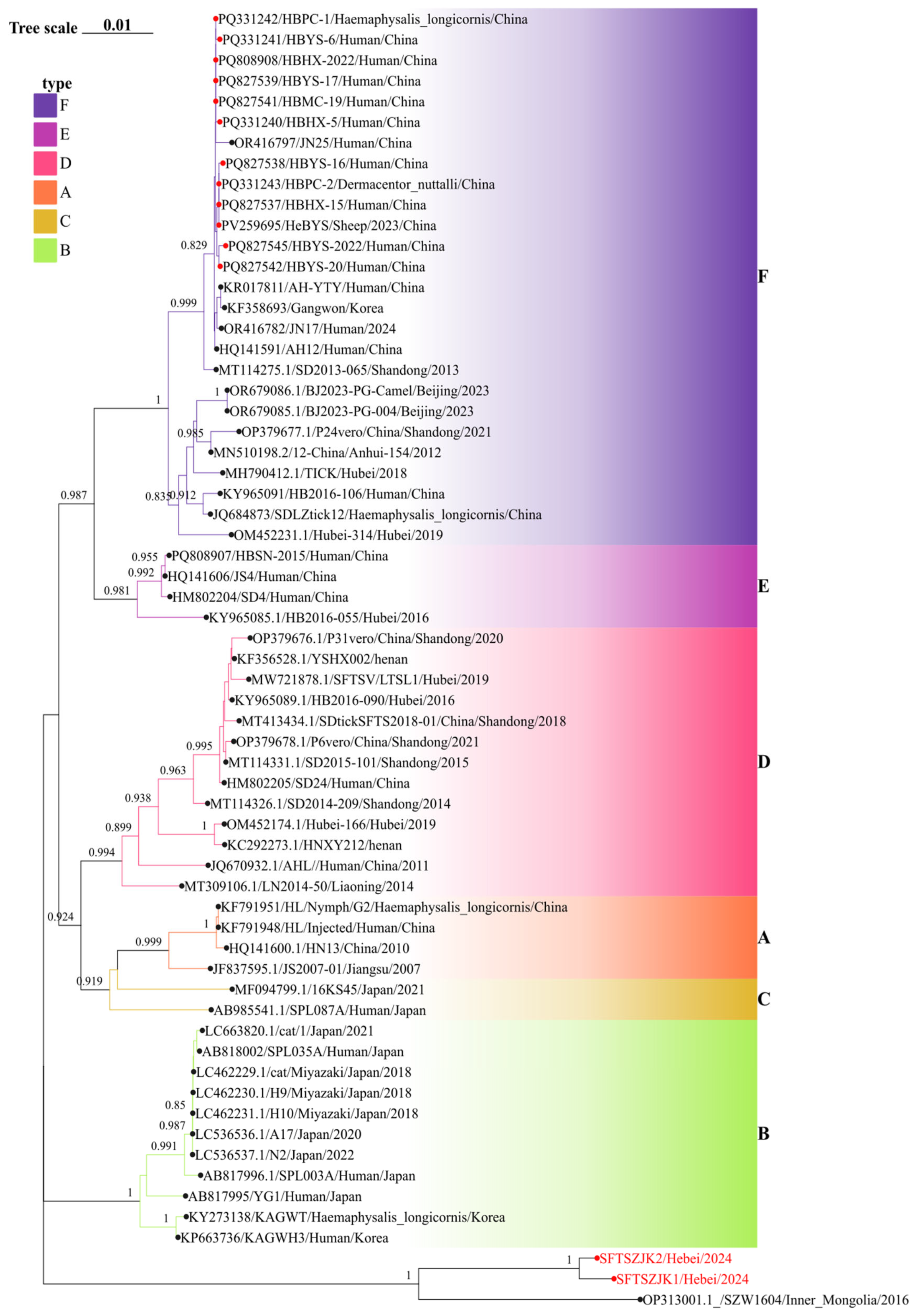
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of SFTSV
3.4. Recombination Analysis
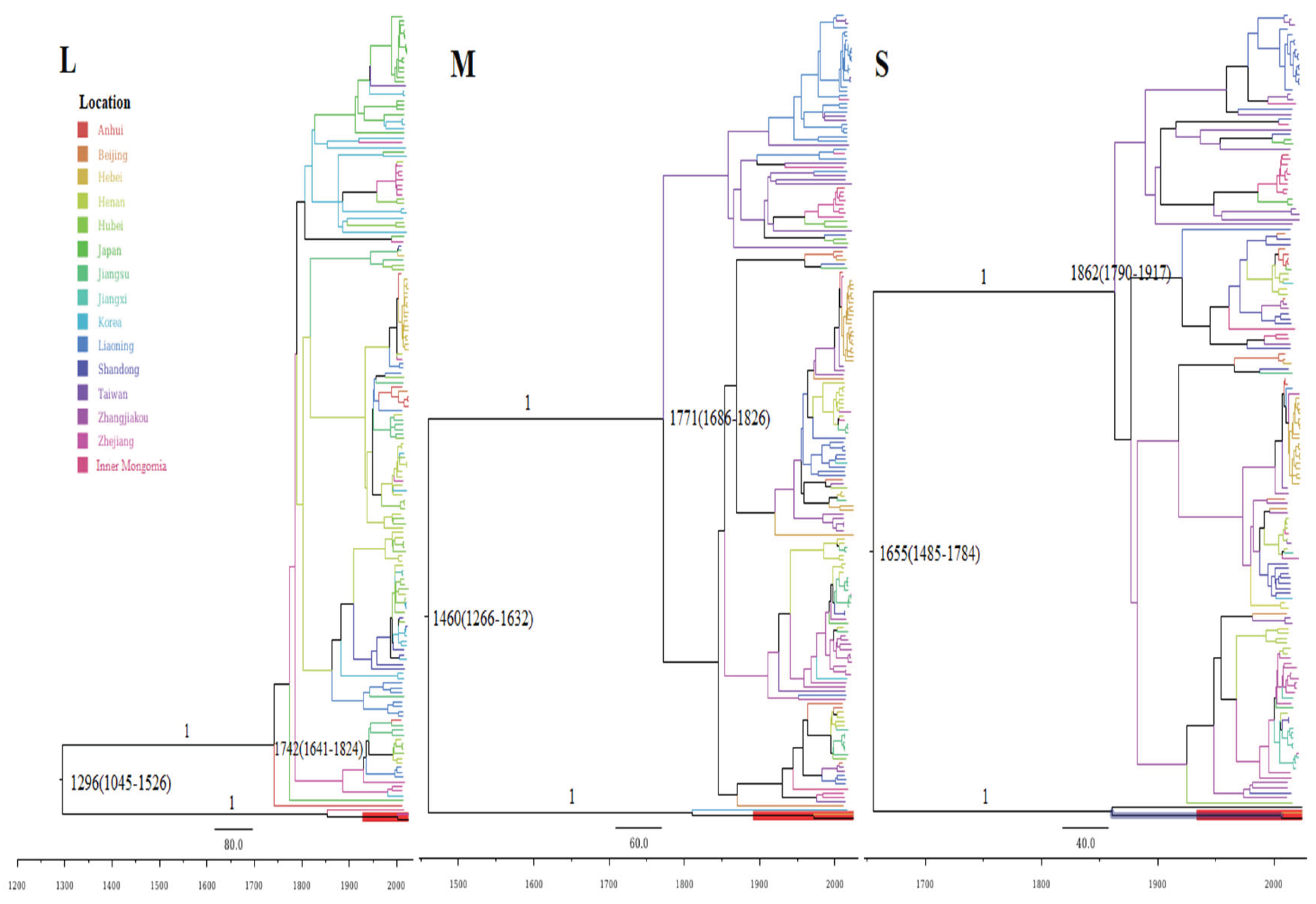
3.5. Evolutionary History and Divergence Time Estimation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, X.J. ; Liang, M.F. ; Zhang, S. Y. ; Liu, Y. ; Li, J. D. ; Sun, Y. L. ; Zhang, L. ; Zhang, Q. F. ; Popov, V. L. ; Li, C.; et al. Fever with Thrombocytopenia Associated with a Novel Bunyavirus in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1523–1532. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Kamthania, M. A new emerging pandemic of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS). VirusDisease 2021, 32, 220–227. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Tian, T.; Li, A.; Du, S.; Wang, S.; Li, D.; Huang, X.; Li, J. Epidemiological characteristics of human-to-human transmission of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China from 1996 to 2023. PLOS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2025, 19, e0013283. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, J.; Li, A.; Wang, S.; Li, D. Epidemiological Characteristics of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome from 2010 to 2019 in Mainland China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2021, 18, 3092. [CrossRef]
- KIM K H, YI J, KIM G, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, South Korea, 2012 [J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2013, 19(11): 1892-4.
- Takahashi, T.; Maeda, K.; Suzuki, T.; Ishido, A.; Shigeoka, T.; Tominaga, T.; Kamei, T.; Honda, M.; Ninomiya, D.; Sakai, T.; et al. The First Identification and Retrospective Study of Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in Japan. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 816–827. [CrossRef]
- TRAN X C, YUN Y, VAN AN L, et al. Endemic Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome, Vietnam [J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2019, 25(5): 1029-31.
- Tian, B.; Qu, D.; Sasaki, A.; Chen, J.; Deng, B. Acute pancreatitis in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 1631–1636. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Guo, B.; Yan, H.; Wu, A.L.; Yao, W.W.; Chen, K.; Pan, J.H.; Li, Z.X.; Mao, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.J. Patient with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection and central nervous system disturbance in Dongyang, Zhejiang Province, China, 2017. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Hu, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Mei, L.; Walker, D.H.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.-J. Person-to-Person Transmission of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 156–160. [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-W.; Kim, D.; Yun, N.; Kim, D.-M. Clinical Update of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Viruses 2021, 13, 1213. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hu, K.; Zou, J.; Xiao, J. A cluster of cases of human-to-human transmission caused by severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, e206–e208. [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Shi, J.; Su, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Tang, S.; Liu, H.; et al. A Cluster of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Infections of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Caused by Person-to-Person Transmission. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 396–402. [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, L.; Geng, M.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Han, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Han, X.; et al. Identification of Endemic Region for Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in an Alluvial Plain of Hebei Province, China. Viruses 2025, 17, 854. [CrossRef]
- MIFANG L A L L W W L Y H X L C L D L J W S L D L. Molecular evolution and genetic diversity analysis of SFTS virus based on next-generation sequencing [J]. Biosafety and Health, 2021, 2021,3(2).
- Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; He, B.; Wang, S.; Wei, F.; Tu, C.; Liu, Q. The first molecular evidence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in ticks in Jilin, Northeastern China. Ticks Tick-borne Dis. 2016, 7, 1280–1283. [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; He, Y.; Chen, F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Yang, S.; Qian, K.; Zhan, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus was found in Northern Jiangxi Province, China. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1500146. [CrossRef]
- Thawng, C.N.; Smith, G.B. Transcriptome software results show significant variation among different commercial pipelines. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549, https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096.
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [CrossRef]
- WEI Y, CAI Y, HAN X, et al. Genetic diversity and molecular evolution of Seoul virus in Hebei province, China [J]. Infection, Genetics and Evolution : Journal of Molecular Epidemiology and Evolutionary Genetics In Infectious Diseases, 2023, 114: 105503. [CrossRef]
- Samson, S.; Lord, É.; Makarenkov, V. SimPlot++: a Python application for representing sequence similarity and detecting recombination. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 3118–3120. [CrossRef]
- Posada, D. jModelTest: Phylogenetic Model Averaging. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1253–1256. [CrossRef]
- Hill, V.; Baele, G. Bayesian Estimation of Past Population Dynamics in BEAST 1.10 Using the Skygrid Coalescent Model. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 2620–2628. [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Stephan, K.E. Markov chain Monte Carlo methods for hierarchical clustering of dynamic causal models. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 2973–2989. [CrossRef]
- Sheng, R.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Y.; Wen, H. Molecular evolution and geographic migration of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in Asia. PLOS Pathog. 2025, 21, e1012970. [CrossRef]
- Chevenet, F.; Fargette, D.; Bastide, P.; Vitré, T.; Guindon, S. EvoLaps 2: Advanced phylogeographic visualization. Virus Evol. 2023, 10, vead078. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-W.; Zhao, L.; Luo, L.-M.; Liu, M.-M.; Sun, Y.; Su, X.; Yu, X.-J. Molecular Evolution and Spatial Transmission of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus Based on Complete Genome Sequences. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0151677–e0151677. [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, X.; Li, Y. Metatranscriptomics Reveals the Diversity of the Tick Virome in Northwest China. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0111522. [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Sun, J.; Yao, M.; Sun, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, C.; Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Nie, X.; He, L.; et al. Isolation and Identification of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus from Farmed Mink in Shandong, China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2024, 2024, 9604673. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, L.; Ojcius, D.M.; Lou, X.; Wang, C.; Feng, C.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in Rural Regions of Zhejiang, China. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e111127–e111127. [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Wang, Q.; Fu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, X. Molecular identification of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome viruses from tick and bitten patient in Southeast China. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, S.; Shi, J.; Su, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, M.; Hu, Z.; Peng, C.; Zheng, X.; et al. Isolation, characterization, and phylogenic analysis of three new severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus strains derived from Hubei Province, China. Virol. Sin. 2017, 32, 89–96. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Man, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, X. Phylogeographic analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus from Zhoushan Islands, China: implication for transmission across the ocean. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19563–19563. [CrossRef]
- LAM T T-Y, LIU W, BOWDEN T A, et al. Evolutionary and molecular analysis of the emergent severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus [J]. Epidemics, 2013, 5(1).
- Oh, S.-S.; Chae, J.-B.; Kang, J.-G.; Kim, H.-C.; Chong, S.-T.; Shin, J.-H.; Hur, M.-S.; Suh, J.-H.; Oh, M.-D.; Jeong, S.-M.; et al. Detection of Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus from Wild Animals and Ixodidae Ticks in the Republic of Korea. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2016, 16, 408–414. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, L.; Du, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, H.; Su, J.; Tang, X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. The Evolutionary History and Spatiotemporal Dynamics of the Fever, Thrombocytopenia and Leukocytopenia Syndrome Virus (FTLSV) in China. PLOS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3237–e3237. [CrossRef]
- FREIRE C C M, IAMARINO A, SOUMARé P O L, et al. Reassortment and distinct evolutionary dynamics of Rift Valley Fever virus genomic segments [J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 11353.
- Park, J.-Y.; Sivasankar, C.; Kirthika, P.; Prabhu, D.; Lee, J.H. Non-Structural Protein-W61 as a Novel Target in Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus (SFTSV): An In-Vitro and In-Silico Study on Protein-Protein Interactions with Nucleoprotein and Viral Replication. Viruses 2023, 15, 1963. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Man, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, X. Phylogeographic analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus from Zhoushan Islands, China: implication for transmission across the ocean. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19563–19563. [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Guan, X.; Liu, L.; Zhan, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, G.; Xiong, J.; Tan, L.; Xu, J.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Natural Transmission Model for Severe Fever With Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Bunyavirus in Villages of Hubei Province, China. Medicine 2016, 95, e2533–e2533. [CrossRef]
| SFTSV strain | Source | GenBank accession No. (L/M/S) |
Sequence similarity(%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L segment | M segment | S segment | |||||||
| Nt | RDRP | Nt | GP | Nt | NSs | NP | |||
| SFTSZJK1/Hebei/2024 | Haemaphysalis verticalis | PX226566/ PX226564/ PX226562 |
88.53 | 97.36 | 87.44 | 94.13 | 89.20 | 91.47 | 96.36 |
| SFTSZJK2/Hebei/2024 | Haemaphysalis verticalis | PX226567/ PX226565/ PX226563 |
88.24 | 97.41 | 87.38 | 94.04 | 89.55 | 91.47 | 96.36 |
| Gene | L | M |
|---|---|---|
| Recombinant Sequence(s) | SFTSZJK1/Hebei/2024 | SFTSZJK2/Hebei/2024 |
| Beginning | 66 | 1607 |
| Ending | 6322 | 1730 |
| RDPRCS | 0.446 | 0.436 |
| RDP | 8.39×10−6 | 4.02×10−4 |
| GENECONV | NS | NS |
| Bootscan | NS | NS |
| Maxchi | NS | 1.42×10−4 |
| Chimaera | NS | NS |
| SiSscan | NS | NS |
| 3Seq | 5.50×10−4 | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





