Submitted:
12 October 2025
Posted:
13 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
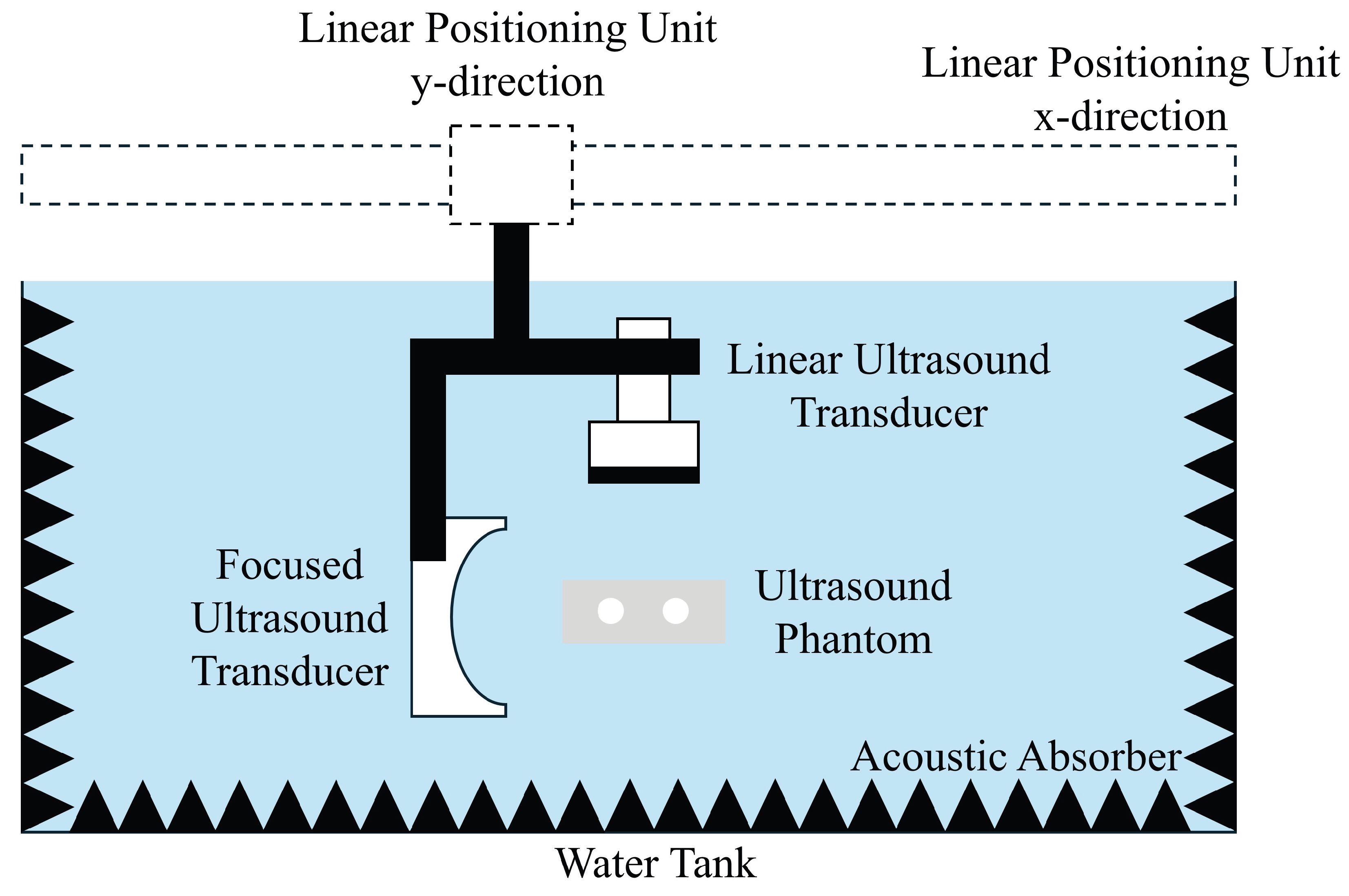
2. Materials and Methods
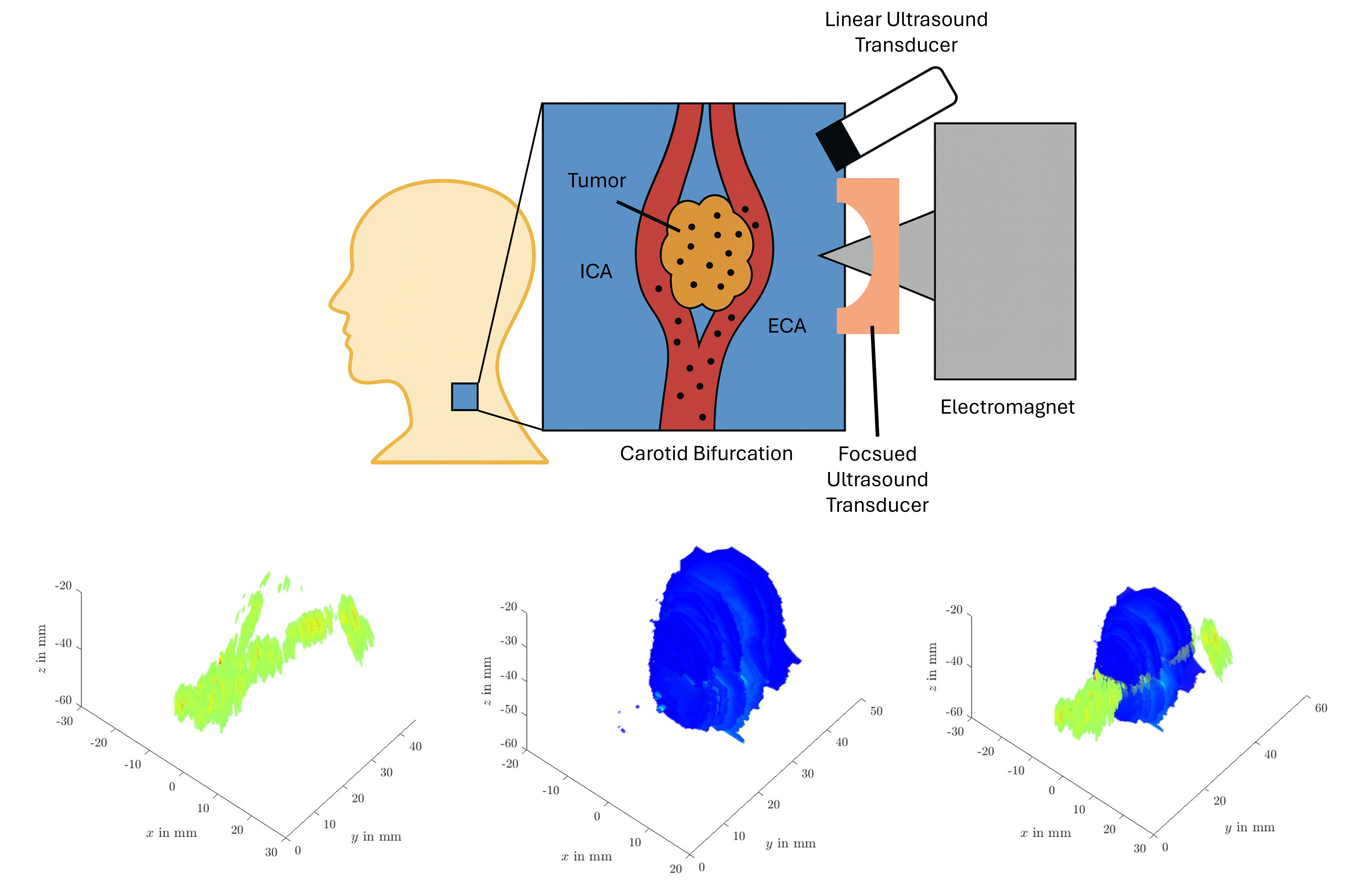
2.1. Ultrasound Phantom Fabrication
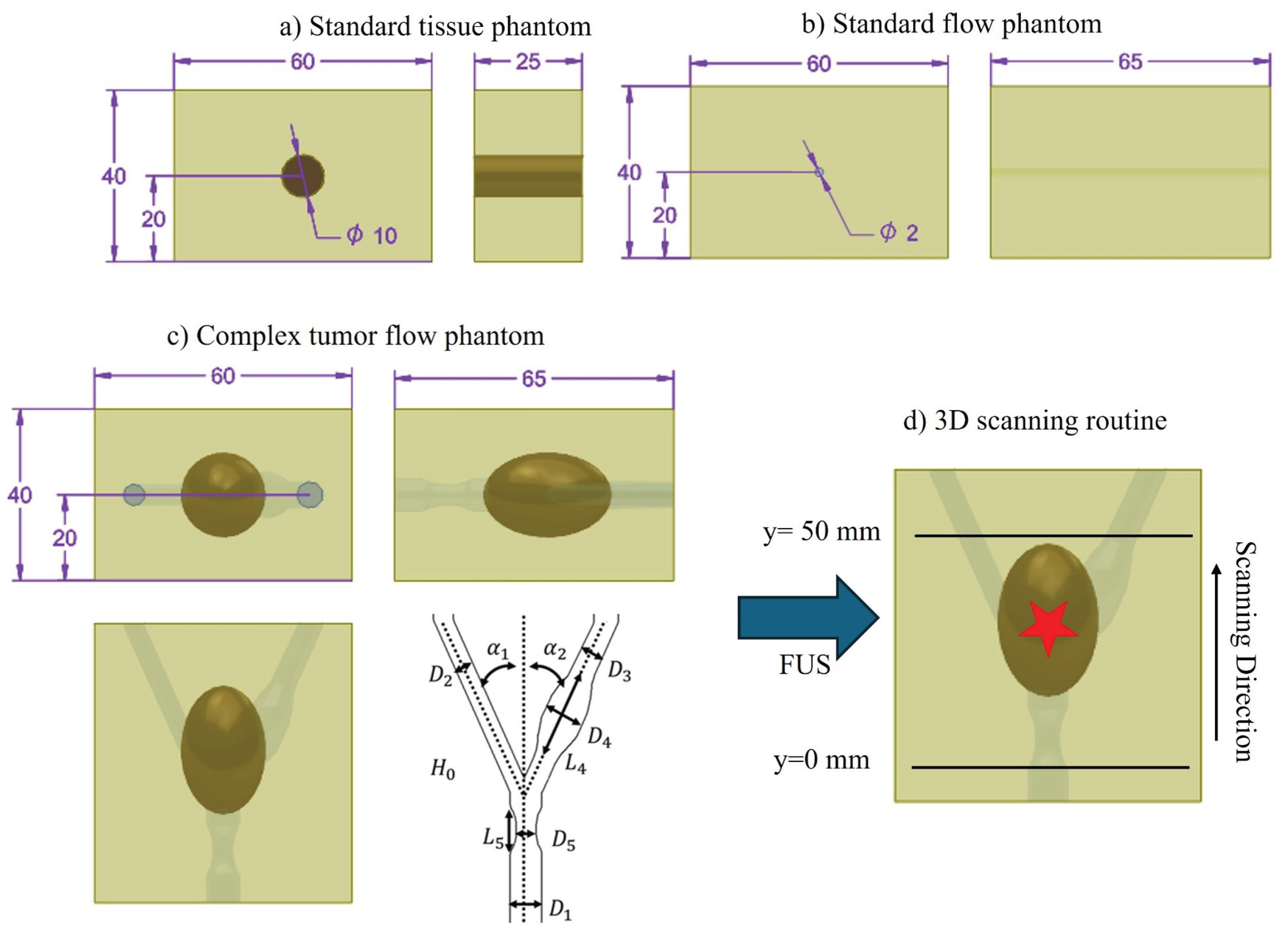
2.1.1. Standard Tissue Phantom
2.1.2. Standard Flow Phantom
2.1.3. Complex Flow Tumor Phantom
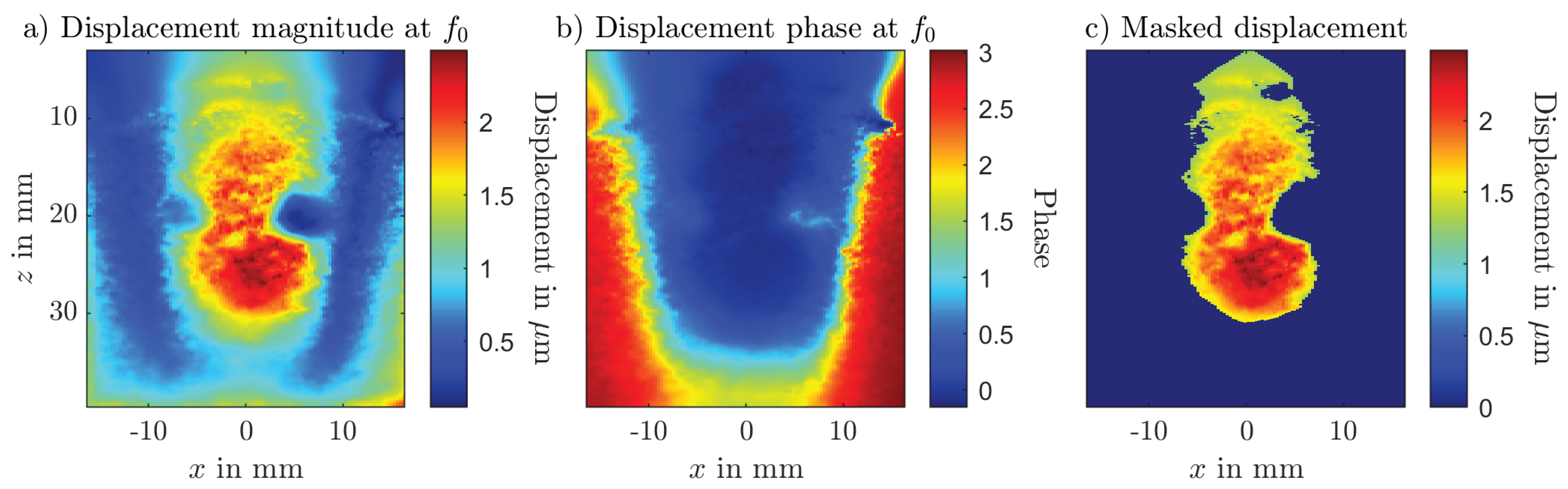
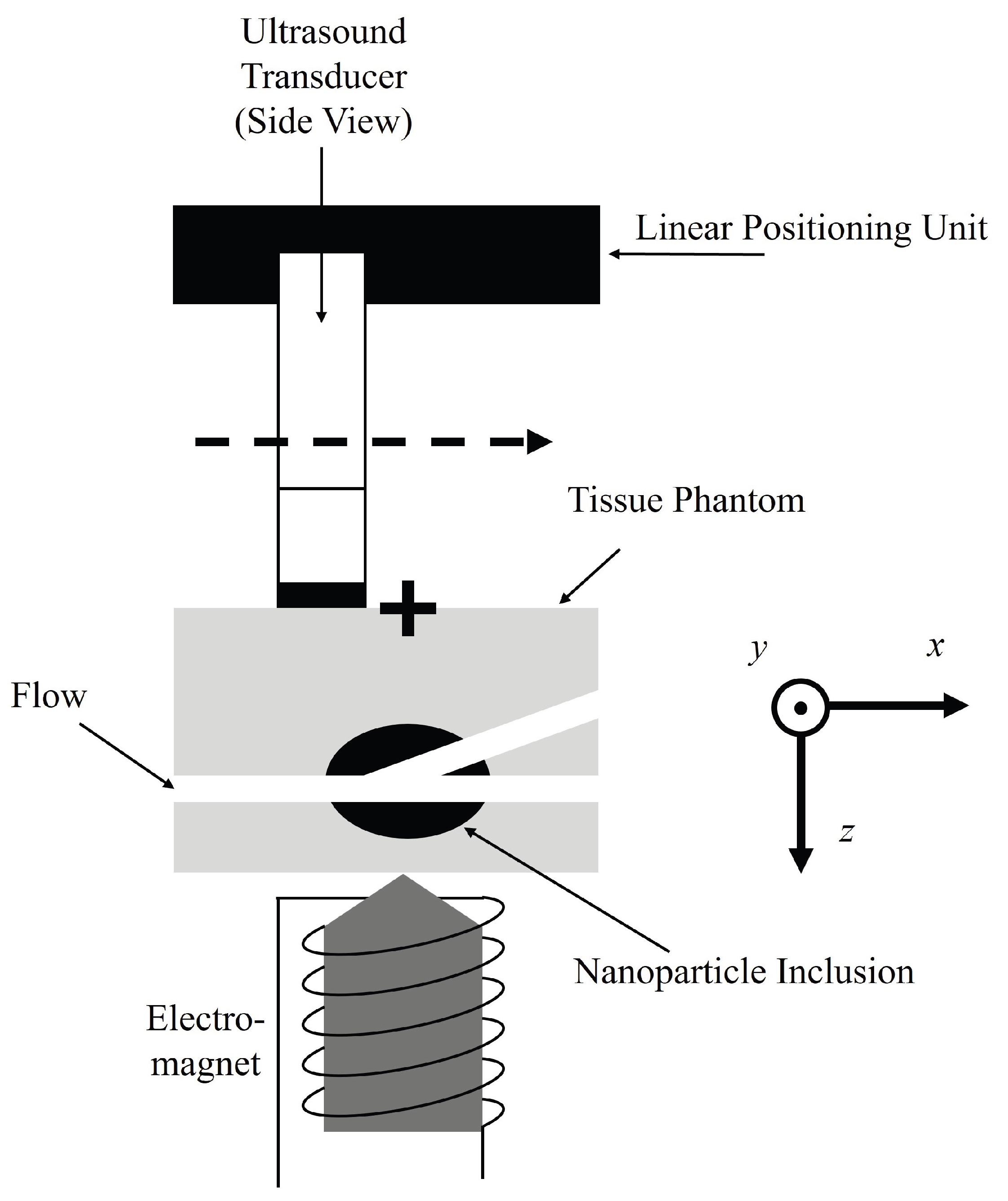
2.2. Magnetomotive Ultrasound
2.3. Passive Cavitation Mapping
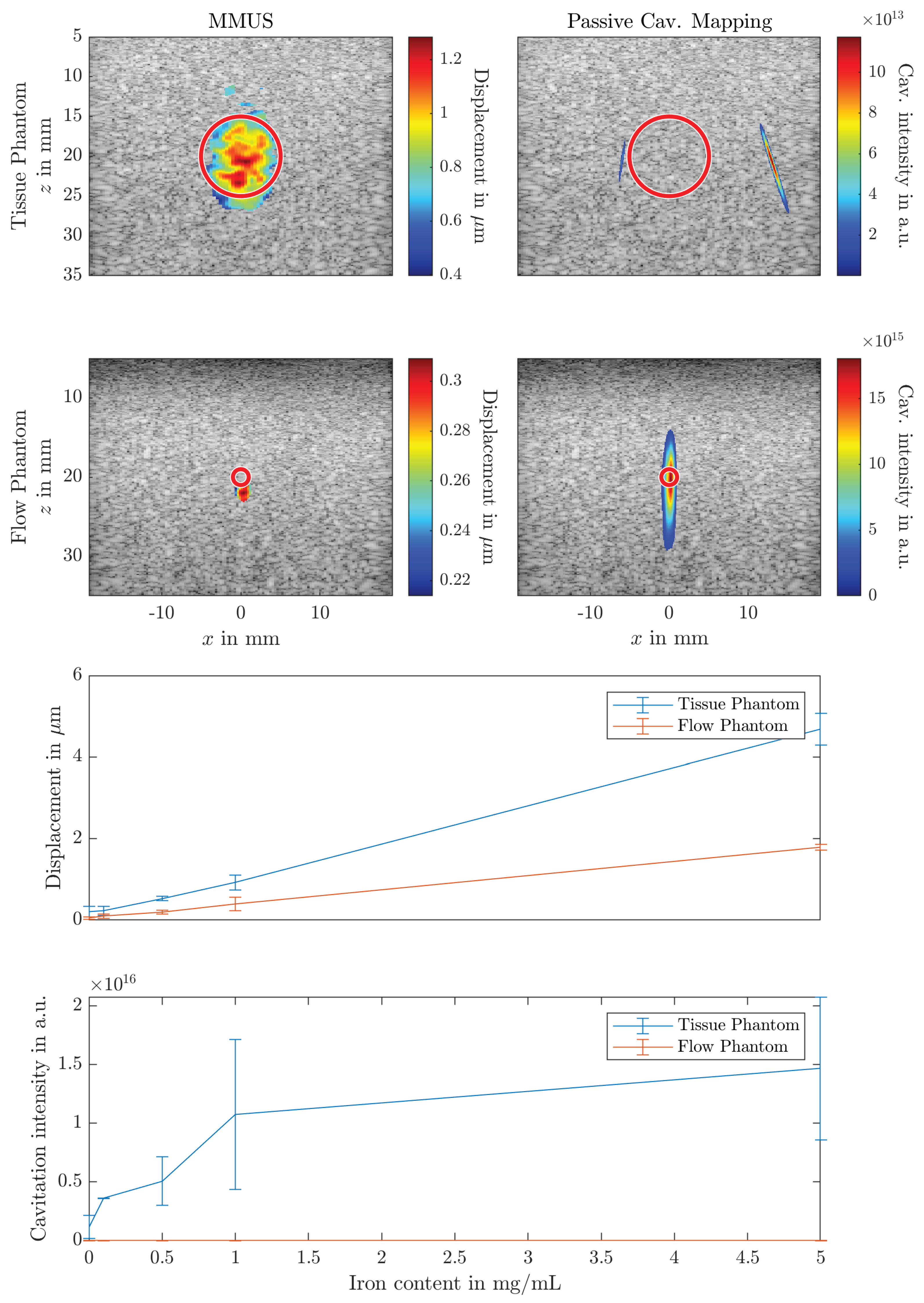
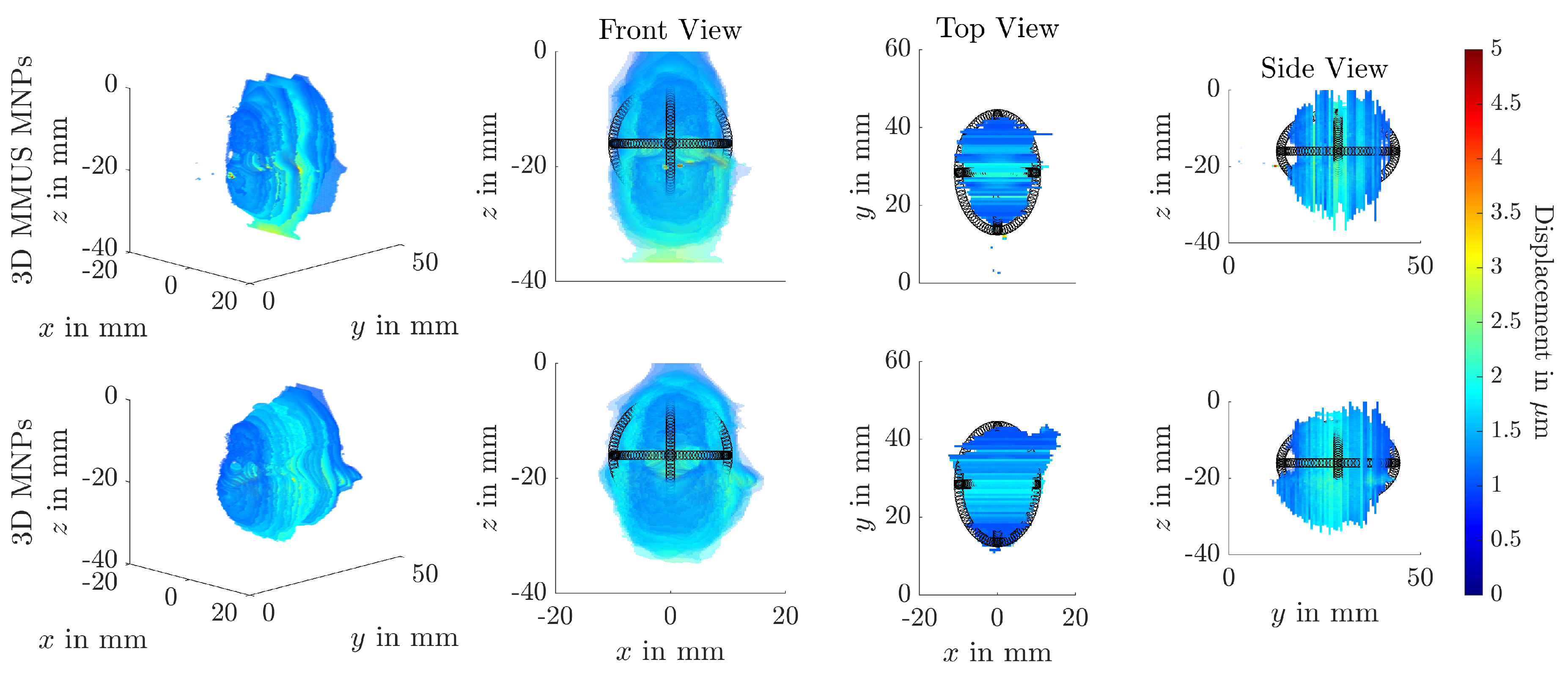
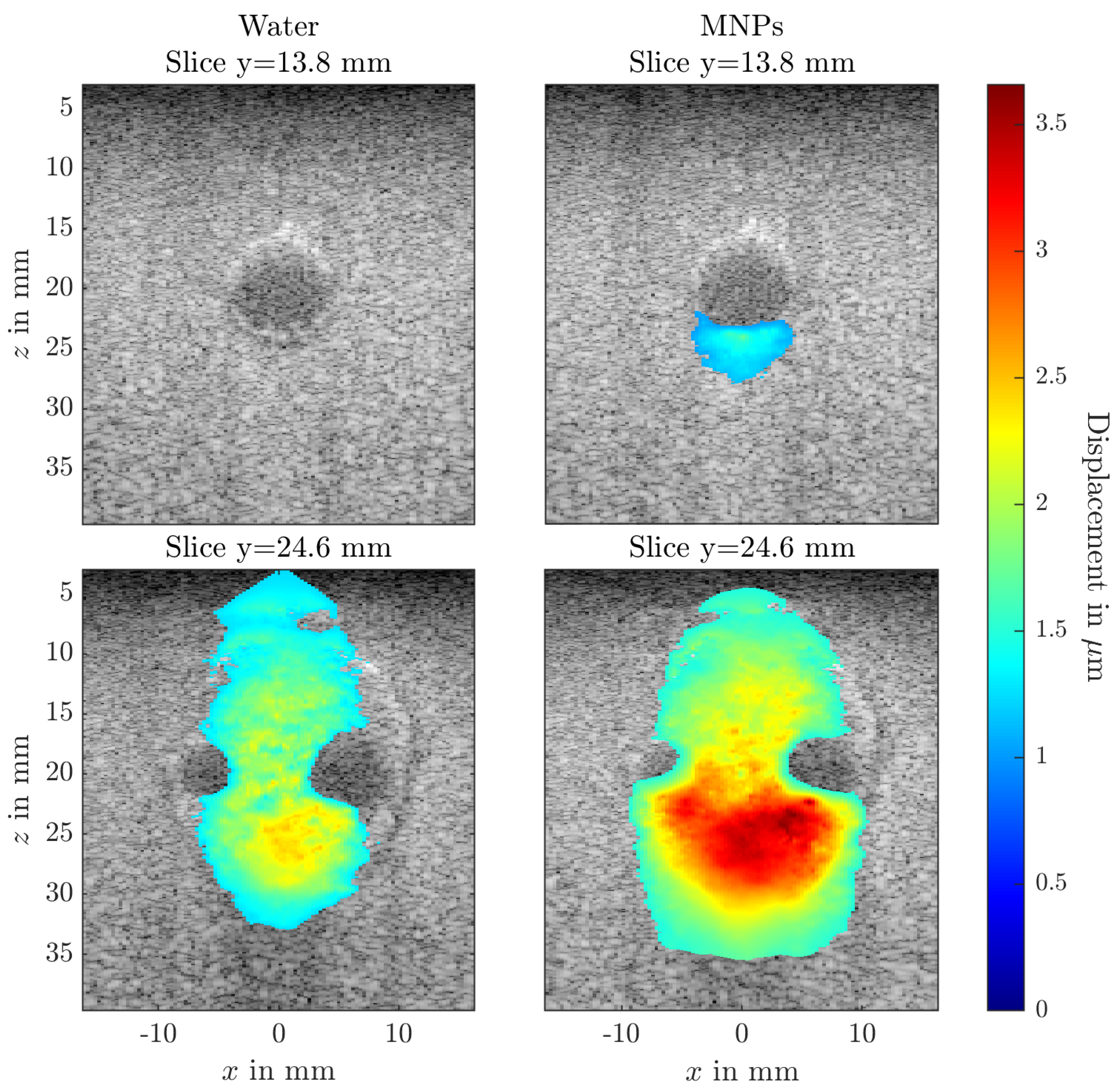
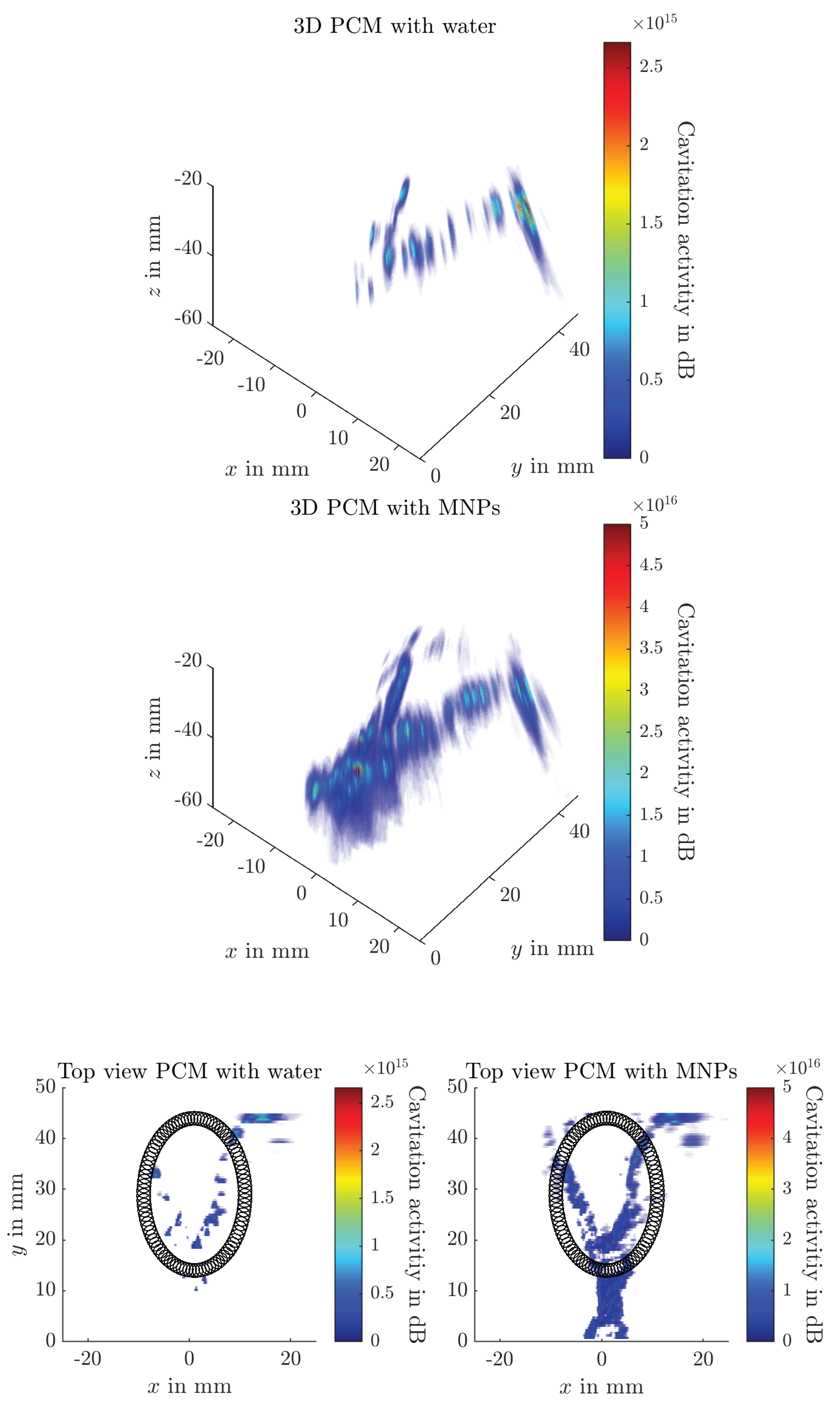
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Ultrasound Phantom Fabrication
4.2. Magnetomotive Ultrasound
4.3. Passive Cavitation Mapping
4.4. Advantages, Limitations and Challenges of the Dual Modality Approach
4.5. Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABS | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene |
| ACM | Active Cavitation Mapping |
| DAS | Delay and Sum Beamformer |
| DFT | Discrete Fourier Transform |
| DMAS | Delay Multiply and Sum |
| DMAS3 | Third order Delay Multiply and Sum |
| EPR | Enhanced Permeability and Retention |
| FTC | Freeze-Thaw Cycle |
| FUS | Focused Ultrasound |
| GLUE | Global Ultrasound Strain Elastography |
| HIPS | High-Impact Polystyrene |
| LA-SPIONs | Lauric Acid Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles |
| MDT | Magnetic Drug Targeting |
| MH | Magnetic Hyperthermia |
| MMUS | Magnetomotive Ultrasound |
| MPI | Magnetic Particle Imaging |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| PCM | Passive Cavitation Mapping |
| PVA | Polyvinyl Alcohol |
| RF | Radiofrequency |
| SPIONs | Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles |
| TEA | Time Exposure Acoustics |
| TMMs | Tissue-Mimicking Materials |
References
- Gaidai, O.; Cao, Y.; Loginov, S. Global Cardiovascular Diseases Death Rate Prediction. Current problems in cardiology 2023, 48, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. International journal of cancer 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghebati-Maleki, A.; Dolati, S.; Ahmadi, M.; Baghbanzhadeh, A.; Asadi, M.; Fotouhi, A.; Yousefi, M.; Aghebati-Maleki, L. Nanoparticles and cancer therapy: Perspectives for application of nanoparticles in the treatment of cancers. Journal of cellular physiology 2020, 235, 1962–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, C.Y.X.; Ho, J.; Demaria, S.; Ferrari, M.; Grattoni, A. Emerging technologies for local cancer treatment. Advanced therapeutics 2020, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavas, S.; Quazi, S.; Karpiński, T.M. Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: Current Progress and Challenges. Nanoscale research letters 2021, 16, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, H.; Ye, Y.; Lei, Y.; Islam, R.; Tan, S.; Tong, R.; Miao, Y.B.; Cai, L. Smart nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Signal transduction and targeted therapy 2023, 8, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, F.; Carnell, L.R.; Löffler, L.; Boosz, P.; Schaft, N.; Dörrie, J.; Stein, R.; Lenz, M.; Spiecker, E.; Huber, C.M.; et al. Loading of CAR-T cells with magnetic nanoparticles for controlled targeting suppresses inflammatory cytokine release and switches tumor cell death mechanism. MedComm 2025, 6, e70039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, V.R.; Revi, N.; Murugappan, S.; Singh, S.P.; Rengan, A.K. Enhanced permeability and retention effect: A key facilitator for solid tumor targeting by nanoparticles. Photodiagnosis and photodynamic therapy 2022, 39, 102915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyane, D.; Raval, N.; Maheshwari, R.; Tambe, V.; Kalia, K.; Tekade, R.K. Employment of enhanced permeability and retention effect (EPR): Nanoparticle-based precision tools for targeting of therapeutic and diagnostic agent in cancer. Materials science & engineering. C, Materials for biological applications 2019, 98, 1252–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metselaar, J.M.; Lammers, T. Challenges in nanomedicine clinical translation. Drug delivery and translational research 2020, 10, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, X.; Lin, X.; Koo, S.; Yaremenko, A.V.; Qin, D.; Kong, N.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Tao, W. Cancer nanomedicine toward clinical translation: Obstacles, opportunities, and future prospects. Med (New York, N.Y.) 2023, 4, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rümenapp, C.; Gleich, B.; Haase, A. Magnetic nanoparticles in magnetic resonance imaging and diagnostics. Pharmaceutical research 2012, 29, 1165–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.M.; Pavan, T.Z.; Ullmann, I.; Heim, C.; Rupitsch, S.J.; Vossiek, M.; Alexiou, C.; Ermert, H.; Lyer, S. A Review on Ultrasound-based Methods to Image the Distribution of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Biomedical Applications. Ultrasound in medicine & biology 2025, 51, 210–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alphandéry, E. Nanomaterials as Ultrasound Theragnostic Tools for Heart Disease Treatment/Diagnosis. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, X.Y.; Sena-Torralba, A.; Álvarez-Diduk, R.; Muthoosamy, K.; Merkoçi, A. Nanomaterials for Nanotheranostics: Tuning Their Properties According to Disease Needs. ACS nano 2020, 14, 2585–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinoi, P.; Chen, Y.T.; Vittur, V.; Marquez, M.D.; Lee, T.R. Bimetallic Nanoparticles: Enhanced Magnetic and Optical Properties for Emerging Biological Applications. Applied Sciences 2018, 8, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materón, E.M.; Miyazaki, C.M.; Carr, O.; Joshi, N.; Picciani, P.H.; Dalmaschio, C.J.; Davis, F.; Shimizu, F.M. Magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical applications: A review. Applied Surface Science Advances 2021, 6, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lübbe, A.S.; Alexiou, C.; Bergemann, C. Clinical applications of magnetic drug targeting. The Journal of surgical research 2001, 95, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agiotis, L.; Theodorakos, I.; Samothrakitis, S.; Papazoglou, S.; Zergioti, I.; Raptis, Y.S. Magnetic manipulation of superparamagnetic nanoparticles in a microfluidic system for drug delivery applications. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 2016, 401, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, R.; Lyer, S.; Dürr, S.; Struffert, T.; Engelhorn, T.; Schwarz, M.; Eckert, E.; Göen, T.; Vasylyev, S.; Peukert, W.; et al. Efficient drug-delivery using magnetic nanoparticles–biodistribution and therapeutic effects in tumour bearing rabbits. Nanomedicine : nanotechnology, biology, and medicine 2013, 9, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, A.; Sahu, N.K. Review on magnetic nanoparticle-mediated hyperthermia for cancer therapy. Journal of Nanoparticle Research 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, E.; Oda, T.; Kayano, T.; Sato, S.; Minagawa, M.; Yanagihara, H.; Kishimoto, M.; Mitsumata, C.; Hashimoto, S.; Yamada, K.; et al. Ferromagnetic nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia and thermoablation therapy. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics 2010, 43, 474011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, M.; Berti, D.; Baglioni, P. Nanostructures for magnetically triggered release of drugs and biomolecules. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science 2013, 18, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Song, J.; Chen, X. Ultrasound-Activated Theranostic Materials and Their Bioapplications. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English) 2025, 64, e202422278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Fan, C.H.; Yeh, C.K. Ultrasound-activated nanomaterials for sonodynamic cancer theranostics. Drug discovery today 2022, 27, 1590–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.; George, B.; Rupitsch, S.J.; Ermert, H.; Ullmann, I.; Vossiek, M.; Lyer, S. Ultrasound-Mediated Cavitation of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Applications. Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering 2022, 8, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.M.; Hageroth, L.; Meyer, C.; Ermert, H.; Ullmann, I.; Vossiek, M.; Lyer, S. Ultrasound-Induced Stable and Inertial Cavitation of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Applications. Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering 2024, 10, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalmayer, A.S.; Fink, L.; Fischer, G. Experimental and Simulative Characterization of a Hybrid Magnetic Array for Steering Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles in Drug Targeting. IEEE transactions on bio-medical engineering 2025, 72, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, E.Y.; Bishop, M.; Zheng, B.; Ferguson, R.M.; Khandhar, A.P.; Kemp, S.J.; Krishnan, K.M.; Goodwill, P.W.; Conolly, S.M. Magnetic Particle Imaging: A Novel in Vivo Imaging Platform for Cancer Detection. Nano letters 2017, 17, 1648–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.; Feldman, M.D.; Kim, J.; Condit, C.; Emelianov, S.; Milner, T.E. Detection of magnetic nanoparticles in tissue using magneto-motive ultrasound. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 4183–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöstrand, S.; Evertsson, M.; Jansson, T. Magnetomotive Ultrasound Imaging Systems: Basic Principles and First Applications. Ultrasound in medicine & biology 2020, 46, 2636–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M.; Rupitsch, S.J.; Ermert, H.; Lyer, S. In Vivo Study on Magnetomotive Ultrasound Imaging in the Framework of Nanoparticle based Magnetic Drug Targeting. Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering 2020, 6, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M.; Rupitsch, S.J.; Lyer, S.; Ermert, H. Quantitative Determination of Local Density of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Used for Drug Targeting Employing Inverse Magnetomotive Ultrasound. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control 2021, 68, 2482–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neppiras, E.A. Acoustic cavitation. Physics Reports 1980, 61, 159–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Fan, C.H.; Ting, C.Y.; Yeh, C.K. Combining microbubbles and ultrasound for drug delivery to brain tumors: current progress and overview. Theranostics 2014, 4, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, J.; Tian, Z.; Huang, T.J. Sonoporation: Past, Present, and Future. Advanced materials technologies 2022, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDannold, N.; Vykhodtseva, N.; Hynynen, K. Targeted disruption of the blood-brain barrier with focused ultrasound: association with cavitation activity. Physics in medicine and biology 2006, 51, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzzi, G.; Sinibaldi, G.; Silvani, G.; Ruocco, G.; Casciola, C.M. Perspectives on cavitation enhanced endothelial layer permeability. Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces 2018, 168, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husseini, G.A.; La Diaz de Rosa, M.A.; Richardson, E.S.; Christensen, D.A.; Pitt, W.G. The role of cavitation in acoustically activated drug delivery. Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society 2005, 107, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stride, E.; Coussios, C. Nucleation, mapping and control of cavitation for drug delivery. Nature Reviews Physics 2019, 1, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezy, S.; Shi, X.; Martin, R.W.; Chi, E.; Nelson, P.I.; Bailey, M.R.; Crum, L.A. Real-time visualization of high-intensity focused ultrasound treatment using ultrasound imaging. Ultrasound in medicine & biology 2001, 27, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Khokhlova, T.D.; Sapozhnikov, O.A.; O’Donnell, M.; Hwang, J.H. A new active cavitation mapping technique for pulsed HIFU applications–bubble Doppler. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control 2014, 61, 1698–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgaonkar, V.A.; Datta, S.; Holland, C.K.; Mast, T.D. Passive cavitation imaging with ultrasound arrays. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 2009, 126, 3071–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyöngy, M.; Coussios, C.C. Passive cavitation mapping for localization and tracking of bubble dynamics. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 2010, 128, EL175–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyöngy, M.; Coussios, C.C. Passive spatial mapping of inertial cavitation during HIFU exposure. IEEE transactions on bio-medical engineering 2010, 57, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, C.R.; Ritchie, R.W.; Gyöngy, M.; Collin, J.R.T.; Leslie, T.; Coussios, C.C. Spatiotemporal monitoring of high-intensity focused ultrasound therapy with passive acoustic mapping. Radiology 2012, 262, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, H.S.; Rivaz, H. Global Time-Delay Estimation in Ultrasound Elastography. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control 2017, 64, 1625–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culjat, M.O.; Goldenberg, D.; Tewari, P.; Singh, R.S. A review of tissue substitutes for ultrasound imaging. Ultrasound in medicine & biology 2010, 36, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, B.E.; Oldenburg, A.L. Elastometry of clot phantoms via magnetomotive ultrasound-based resonant acoustic spectroscopy. Physics in medicine and biology 2022, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar Mazon Valadez, E.; Henrique Uliana, J.; Tiburcio Vicente, T.; Adilton Oliveira Carneiro, A.; Zeferino Pavan, T. Fully-Automated Theranostic System Integrating Magnetomotive Ultrasound and Magnetic Hyperthermia. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2025, 74, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collazos-Burbano, D.A.; Freire, J.E.; Sanches, A.F.; Zufelato, N.; Uliana, J.H.; Brassesco, M.S.; Carneiro, A.A.O.; Pavan, T.Z. Beyond Axial Symmetry: Tracking Vectorial Motion Enhances Nanoparticles Mapping With Magnetomotive Ultrasound. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 62704–62716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, A.; Reniaud, J.; Santesson, M.; Persson, L.; Jansson, T. Design of a Phantom Mimicking Rectal Lymph Nodes for Magnetomotive Ultrasound. Ultrasound in medicine & biology 2025, 51, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evertsson, M.; Cinthio, M.; Fredriksson, S.; Olsson, F.; Persson, H.; Jansson, T. Frequency- and phase-sensitive magnetomotive ultrasound imaging of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control 2013, 60, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, C.; Saleem, T.; Rupitsch, S.J.; Huber, C.M.; Lyer, S.; Ermert, H.; Ullmann, I. D1 4 - Modelling and Construction of Complex Shaped Polyvinyl Alcohol based Ultrasound Phantoms for Inverse Magnetomotive Ultrasound Imaging. In Proceedings of the Vorträge. AMA Service GmbH, Von-Münchhausen-Str. 49, 31515 Wunstorf. 2024; pp. 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.M.; Heim, C.; Li, J.; Ermert, H.; Rupitsch, S.J.; Ullmann, I.; Lyer, S. Magnetomotive Displacement of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Different Tissue Phantoms. Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering 2024, 10, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromageau, J.; Gennisson, J.L.; Schmitt, C.; Maurice, R.L.; Mongrain, R.; Cloutier, G. Estimation of polyvinyl alcohol cryogel mechanical properties with four ultrasound elastography methods and comparison with gold standard testings. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control 2007, 54, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.M.; Heim, C.; Ermert, H.; Rupitsch, S.J.; Ullmann, I.; Lyer, S. Wall-less Flow Phantoms with 3D printed Soluble Filament for Ultrasonic Experiments. Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering 2023, 9, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.M.; Heim, C.; Ermert, H.; Rupitsch, S.J.; Ullmann, I.; Vossiek, M.; Lyer, S. Ultrasound Phantom of a Carotid Bifurcation Tumor Using Multiple 3D Printed Soluble Filaments. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI). IEEE; 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.M.; Lahmadi, W.; Alballa, A.; Heim, C.; Rupitsch, S.J.; Ermert, H.; Ullmann, I.; Lyer, S. Water-soluble filament in multifilament approach for ultrasound phantom fabrication. Transactions on Additive Manufacturing Meets Medicine 2024, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallidi, S.; Wang, B.; Mehrmohammadi, M.; Qu, M.; Chen, Y.S.; Joshi, P.; Kim, S.; Homan, K.A.; Karpiouk, A.B.; Smalling, R.W.; et al. Ultrasound-based imaging of nanoparticles: From molecular and cellular imaging to therapy guidance. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium. IEEE; 2009; pp. 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersepke, T.; Kranemann, T.C.; Schmitz, G. On the Performance of Time Domain Displacement Estimators for Magnetomotive Ultrasound Imaging. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control 2019, 66, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, M.; Ermert, H.; Alexiou, C.; Lyer, S. C2 2 - Detection of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Local Chemotherapeutic Treatment Employing Coded Magnetomotive Ultrasound. In Proceedings of the Proceedings Sensor 2017. AMA Service GmbH, Von-Münchhausen-Str. 49, 31515 Wunstorf. Germany; 2017; pp. 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, M.; Ermert, H.; Lyer, S.; Alexiou, C. Sonographic detection of magnetic nanoparticles for Magnetic Drug Targeting using coded magnetic fields. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS). IEEE; 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivaz, H.; Boctor, E.M.; Choti, M.A.; Hager, G.D. Real-time regularized ultrasound elastography. IEEE transactions on medical imaging 2011, 30, 928–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coviello, C.; Kozick, R.; Choi, J.; Gyöngy, M.; Jensen, C.; Smith, P.P.; Coussios, C.C. Passive acoustic mapping utilizing optimal beamforming in ultrasound therapy monitoring. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 2015, 137, 2573–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Li, R.; Yu, X.; Wang, D.; Wan, M. Delay multiply and sum beamforming method applied to enhance linear-array passive acoustic mapping of ultrasound cavitation. Medical physics 2019, 46, 4441–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.M.; Dorsch, N.; Ermert, H.; Vossiek, M.; Ullmann, I.; Lyer, S. Passive cavitation mapping for biomedical applications using higher order delay multiply and sum beamformer with linear complexity. Ultrasonics 2025, 153, 107653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Liu, K.; Pouliopoulos, A.N.; Ji, R.; Konofagou, E.E. Real-Time Passive Acoustic Mapping With Enhanced Spatial Resolution in Neuronavigation-Guided Focused Ultrasound for Blood-Brain Barrier Opening. IEEE transactions on bio-medical engineering 2023, 70, 2874–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haworth, K.J.; Mast, T.D.; Radhakrishnan, K.; Burgess, M.T.; Kopechek, J.A.; Huang, S.L.; McPherson, D.D.; Holland, C.K. Passive imaging with pulsed ultrasound insonations. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 2012, 132, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.C.; Wang, R.; Lin, H.J.; Liu, Y.L.; Chen, C.P.; Chang, Y.L.; Pei, S.C. Explorable Tone Mapping Operators.
- George, B.; Rupitsch, S.J. Assessing Ultrasound Safety: A Method for Correlating Stimulus Parameters with MI and TI. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 2025; 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, H.S.; Honarvar, M.; Salcudean, T.; Rohling, R. 3D Global Time-Delay Estimation for Shear-Wave Absolute Vibro-Elastography of the Placenta. Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Annual International Conference 2020, 2020, 2079–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




