Submitted:
07 October 2025
Posted:
08 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Evaluation of Hypoxia-Resistant and Susceptible CNDH Lines
2.2. Genetic Mapping of Hypoxia-Responsive QTLs
2.3. Selection and Relative Expression of Candidate Genes Regulated Against Hypoxia
2.4. Phylogenetic, Sequence Homology, and Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis of Selected Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Experimental Design
4.2. Construction of a Genetic Map and Analysis of QTLs Following Hypoxia
4.3. Annotation of Candidate Genes Related to Hypoxia
4.4. Relative Gene Expression
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gautam, P.; Lal, B.; Raja, R.; Tripathi, R.; Shahid, M.; Baig, M.; Puree, C.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, A., Effect of simulated flash flooding on rice and its recovery after flooding with nutrient management strategies. Ecological Engineering 2015, 77, 250-256. [CrossRef]
- Fukao, T.; Barrera-Figueroa, B. E.; Juntawong, P.; Peña-Castro, J. M., Submergence and waterlogging stress in plants: a review highlighting research opportunities and understudied aspects. Frontiers in Plant Science 2019, 10, 340. [CrossRef]
- Giuntoli, B.; Licausi, F.; van Veen, H.; Perata, P., Functional balancing of the hypoxia regulators RAP2. 12 and HRA1 takes place in vivo in Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Frontiers in plant science 2017, 8, 591. [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Sharma, G.; Dambire, C.; Marquez, J.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; Proaño, K.; Holdsworth, M. J., An oxygen-sensing mechanism for angiosperm adaptation to altitude. Nature 2022, 606, (7914), 565-569. [CrossRef]
- Bailey-Serres, J.; Voesenek, L., Flooding stress: acclimations and genetic diversity. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, (1), 313-339. [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Miura, K.; Asano, K.; Yamamoto, E.; Mori, H.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M.; Ashikari, M., A major QTL confers rapid internode elongation in response to water rise in deepwater rice. Breeding Science 2007, 57, (4), 305-314. [CrossRef]
- Kende, H.; Van Der Knaap, E.; Cho, H.-T., Deepwater rice: a model plant to study stem elongation. Plant physiology 1998, 118, (4), 1105-1110. [CrossRef]
- Métraux, J.-P.; Kende, H., The role of ethylene in the growth response of submerged deep water rice. Plant Physiology 1983, 72, (2), 441-446. [CrossRef]
- Hamamura, K., Floating rice. Science of the Rice Plant 1993, 1, 66-70.
- Zaidi, P. H.; Rashid, Z.; Vinayan, M. T.; Almeida, G. D.; Phagna, R. K.; Babu, R., QTL mapping of agronomic waterlogging tolerance using recombinant inbred lines derived from tropical maize (Zea mays L) germplasm. PLoS One 2015, 10, (4), e0124350. [CrossRef]
- Loreti, E.; Poggi, A.; Novi, G.; Alpi, A.; Perata, P., A genome-wide analysis of the effects of sucrose on gene expression in Arabidopsis seedlings under anoxia. Plant Physiology 2005, 137, (3), 1130-1138. [CrossRef]
- Lasanthi-Kudahettige, R.; Magneschi, L.; Loreti, E.; Gonzali, S.; Licausi, F.; Novi, G.; Beretta, O.; Vitulli, F.; Alpi, A.; Perata, P., Transcript profiling of the anoxic rice coleoptile. Plant physiology 2007, 144, (1), 218-231. [CrossRef]
- Mustroph, A.; Lee, S. C.; Oosumi, T.; Zanetti, M. E.; Yang, H.; Ma, K.; Yaghoubi-Masihi, A.; Fukao, T.; Bailey-Serres, J., Cross-kingdom comparison of transcriptomic adjustments to low-oxygen stress highlights conserved and plant-specific responses. Plant Physiology 2010, 152, (3), 1484-1500. [CrossRef]
- Narsai, R.; Rocha, M.; Geigenberger, P.; Whelan, J.; van Dongen, J. T., Comparative analysis between plant species of transcriptional and metabolic responses to hypoxia. New Phytologist 2011, 190, (2). [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Jingdong, L.; Du, Y.; Khatoon, R.; Wagan, S. A.; Nisar, S. K., Flood disaster in Pakistan and its impact on agriculture growth (a review). Environ Dev Econ 2016, 6, (23), 39-42.
- Olesen, J. E.; Trnka, M.; Kersebaum, K. C.; Skjelvåg, A. O.; Seguin, B.; Peltonen-Sainio, P.; Rossi, F.; Kozyra, J.; Micale, F., Impacts and adaptation of European crop production systems to climate change. European journal of agronomy 2011, 34, (2), 96-112. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, B.; Wu, Q.; Min, Q.; Zeng, R.; Xie, Z.; Huang, J., OsMADS23 phosphorylated by SAPK9 confers drought and salt tolerance by regulating ABA biosynthesis in rice. PLoS Genetics 2021, 17, (8), e1009699. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Chen, F.; Meng, Y.; Chandrasekaran, U.; Luo, X.; Yang, W.; Shu, K., Plant waterlogging/flooding stress responses: From seed germination to maturation. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2020, 148, 228-236. [CrossRef]
- Khan, I. U.; Ali, A.; Khan, H. A.; Baek, D.; Park, J.; Lim, C. J.; Zareen, S.; Jan, M.; Lee, S. Y.; Pardo, J. M., PWR/HDA9/ABI4 complex epigenetically regulates ABA dependent drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Frontiers in Plant Science 2020, 11, 623. [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, U.; Luo, X.; Zhou, W.; Shu, K., Multifaceted signaling networks mediated by abscisic acid insensitive 4. Plant Communications 2020, 1, (3). [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-K., Abiotic stress signaling and responses in plants. Cell 2016, 167, (2), 313-324. [CrossRef]
- Iida, S.; Ikeda, M.; Amano, M.; Sakayama, H.; Kadono, Y.; Kosuge, K., Loss of heterophylly in aquatic plants: not ABA-mediated stress but exogenous ABA treatment induces stomatal leaves in Potamogeton perfoliatus. Journal of plant research 2016, 129, 853-862: Correction in Journal of plant research 2017, 130, 1097.
- He, F.; Wang, H. L.; Li, H. G.; Su, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Feng, C. H.; Yin, W.; Xia, X., Pe CHYR 1, a ubiquitin E3 ligase from Populus euphratica, enhances drought tolerance via ABA-induced stomatal closure by ROS production in Populus. Plant Biotechnology Journal 2018, 16, (8), 1514-1528. [CrossRef]
- Dawood, T.; Yang, X.; Visser, E. J.; Te Beek, T. A.; Kensche, P. R.; Cristescu, S. M.; Lee, S.; Floková, K.; Nguyen, D.; Mariani, C., A co-opted hormonal cascade activates dormant adventitious root primordia upon flooding in Solanum dulcamara. Plant Physiology 2016, 170, (4), 2351-2364. [CrossRef]
- De Ollas, C.; González-Guzmán, M.; Pitarch, Z.; Matus, J. T.; Candela, H.; Rambla, J. L.; Granell, A.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; Arbona, V., Identification of ABA-mediated genetic and metabolic responses to soil flooding in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L. Mill). Frontiers in Plant Science 2021, 12, 613059. [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S.; Han, C.; Nanjo, Y.; Altaf-Un-Nahar, M.; Wang, K.; He, D.; Yang, P., Label-free quantitative proteomic analysis of abscisic acid effect in early-stage soybean under flooding. Journal of Proteome Research 2013, 12, (11), 4769-4784. [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Nishimura, M.; Hajika, M.; Komatsu, S., Quantitative proteomics reveals the flooding-tolerance mechanism in mutant and abscisic acid-treated soybean. Journal of Proteome Research 2016, 15, (6), 2008-2025. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sakata, K.; Komatsu, S., An integrated approach of proteomics and computational genetic modification effectiveness analysis to uncover the mechanisms of flood tolerance in soybeans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2018, 19, (5), 1301. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Yao, Q.; Guo, X.; Nguyen, V.; Li, F.; Chen, G., A tomato MADS-box protein, SlCMB1, regulates ethylene biosynthesis and carotenoid accumulation during fruit ripening. Scientific reports 2018, 8, (1), 3413. [CrossRef]
- Steffens, B.; Wang, J.; Sauter, M., Interactions between ethylene, gibberellin and abscisic acid regulate emergence and growth rate of adventitious roots in deepwater rice. Planta 2006, 223, 604-612. [CrossRef]
- Vidoz, M. L.; Loreti, E.; Mensuali, A.; Alpi, A.; Perata, P., Hormonal interplay during adventitious root formation in flooded tomato plants. The Plant Journal 2010, 63, (4), 551-562. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Jansen, M. J.; Zhang, Q.; Sergeeva, L.; Ligterink, W.; Mariani, C.; Rieu, I.; Visser, E. J., A disturbed auxin signaling affects adventitious root outgrowth in Solanum dulcamara under complete submergence. Journal of plant physiology 2018, 224, 11-18. [CrossRef]
- Voesenek, L.; Benschop, J.; Bou, J.; Cox, M.; Groeneveld, H.; Millenaar, F.; Vreeburg, R.; Peeters, A., Interactions between plant hormones regulate submergence-induced shoot elongation in the flooding-tolerant dicot Rumex palustris. Annals of Botany 2003, 91, (2), 205-211. [CrossRef]
- Rajhi, I.; Yamauchi, T.; Takahashi, H.; Nishiuchi, S.; Shiono, K.; Watanabe, R.; Mliki, A.; Nagamura, Y.; Tsutsumi, N.; Nishizawa, N. K., Identification of genes expressed in maize root cortical cells during lysigenous aerenchyma formation using laser microdissection and microarray analyses. New Phytologist 2011, 190, (2), 351-368. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-N.; Tuan, P. A.; Mukherjee, S.; Son, S.; Ayele, B. T., Hormonal regulation in adventitious roots and during their emergence under waterlogged conditions in wheat. Journal of Experimental Botany 2018, 69, (16), 4065-4082. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Chandrasekaran, U.; Luo, X.; Zheng, C.; Shu, K., ABA biosynthesis and signaling cascades under hypoxia stress. Frontiers in Plant Science 2021, 12, 661228. [CrossRef]
- Saika, H.; Okamoto, M.; Miyoshi, K.; Kushiro, T.; Shinoda, S.; Jikumaru, Y.; Fujimoto, M.; Arikawa, T.; Takahashi, H.; Ando, M., Ethylene promotes submergence-induced expression of OsABA8ox1, a gene that encodes ABA 8′-hydroxylase in rice. Plant and Cell Physiology 2007, 48, (2), 287-298. [CrossRef]
- Fukao, T.; Bailey-Serres, J., Submergence tolerance conferred by Sub1A is mediated by SLR1 and SLRL1 restriction of gibberellin responses in rice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2008, 105, (43), 16814-16819. [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Liang, H.; Hu, Z., Silencing of the MADS-box gene SlMADS83 enhances adventitious root formation in tomato plants. Journal of plant growth regulation 2020, 39, 941-953. [CrossRef]
- Fornara, F.; Parenicová, L.; Falasca, G.; Pelucchi, N.; Masiero, S.; Ciannamea, S.; Lopez-Dee, Z.; Altamura, M. M.; Colombo, L.; Kater, M. M., Functional characterization of OsMADS18, a member of the AP1/SQUA subfamily of MADS box genes. Plant Physiology 2004, 135, (4), 2207-2219.
- Park, J.-R.; Yang, W.-T.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, K.-M. J. I. J. o. M. S., Identification of a novel gene, osbht, in response to high temperature tolerance at booting stage in rice. 2020, 21, (16), 5862. [CrossRef]
- Asif, S.; Kim, E.-G.; Jang, Y.-H.; Jan, R.; Kim, N.; Asaf, S.; Farooq, M.; Kim, K.-M., Identification of the OsCML4 Gene in Rice Related to Salt Stress Using QTL Analysis. Plants 2022, 11, (19), 2467. [CrossRef]
- Sarra, E.; Jihène, J.; Samira, S.-A., Physiological responses of Medicago truncatula growth under prolonged hypoxia stress. African Journal of Agricultural Research 2015, 10, (31), 3073-3079. [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Jan, R.; Park, J.-R.; Asif, S.; Zhao, D.-D.; Kim, E.-G.; Jang, Y.-H.; Eom, G.-H.; Lee, G.-S.; Kim, K.-M. J. I. J. o. M. S., QTL mapping and candidate gene analysis for seed germination response to low temperature in Rice. 2022, 23, (13), 7379. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.-D.; Jang, Y.-H.; Kim, E.-G.; Park, J.-R.; Jan, R.; Asaf, S.; Asif, S.; Farooq, M.; Chung, H.; Kang, D.-J., Identification of a Major Locus for Lodging Resistance to Typhoons Using QTL Analysis in Rice. Plants 2023, 12, (3), 449. [CrossRef]
- McCough, S. R.; Doerge, R. W., QTL mapping in rice. Trends in Genetics 1995, 11, (12), 482-487. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.-D.; Jang, Y.-H.; Farooq, M.; Park, J.-R.; Kim, E.-G.; Du, X.-X.; Jan, R.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, S. I.; Lee, G.-S., Identification of a major QTL and validation of related genes for tiller angle in rice based on QTL analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, (9), 5192. [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, W., Aeration in higher plants. In Advances in botanical research, Elsevier: 1980; Vol. 7, pp 225-332.
- Colmer, T., Long-distance transport of gases in plants: a perspective on internal aeration and radial oxygen loss from roots. Plant, Cell & Environment 2003, 26, (1), 17-36. [CrossRef]
- Colmer, T.; Pedersen, O., Oxygen dynamics in submerged rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytologist 2008, 178, (2), 326-334. [CrossRef]
- Colmer, T. D.; Pedersen, O., Underwater photosynthesis and respiration in leaves of submerged wetland plants: gas films improve CO2 and O2 exchange. New Phytologist 2008, 177, (4), 918-926. [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, O.; Rich, S. M.; Colmer, T. D., Surviving floods: leaf gas films improve O2 and CO2 exchange, root aeration, and growth of completely submerged rice. The Plant Journal 2009, 58, (1), 147-156. [CrossRef]
- Raskin, I.; Kende, H., How does deep water rice solve its aeration problem. Plant Physiology 1983, 72, (2), 447-454. [CrossRef]
- Bailey-Serres, J.; Fukao, T.; Ronald, P.; Ismail, A.; Heuer, S.; Mackill, D., Submergence tolerant rice: SUB1’s journey from landrace to modern cultivar. Rice 2010, 3, 138-147. [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M. B.; Ram, P. C., Physiological and molecular basis of susceptibility and tolerance of rice plants to complete submergence. Annals of botany 2003, 91, (2), 227-241. [CrossRef]
- Colmer, T.; Voesenek, L., Flooding tolerance: suites of plant traits in variable environments. Functional Plant Biology 2009, 36, (8), 665-681. [CrossRef]
- Colmer, T.; Bloom, A., A comparison of NH4+ and NO3–net fluxes along roots of rice and maize. Plant, Cell & Environment 1998, 21, (2), 240-246.
- Jackson, M.; Armstrong, W., Formation of aerenchyma and the processes of plant ventilation in relation to soil flooding and submergence. Plant Biology 1999, 1, (03), 274-287.
- Alvarez-Buylla, E. R.; Liljegren, S. J.; Pelaz, S.; Gold, S. E.; Burgeff, C.; Ditta, G. S.; Vergara-Silva, F.; Yanofsky, M. F., MADS-box gene evolution beyond flowers: expression in pollen, endosperm, guard cells, roots and trichomes. The Plant Journal 2000, 24, (4), 457-466. [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Theißen, G., The major clades of MADS-box genes and their role in the development and evolution of flowering plants. Molecular phylogenetics and evolution 2003, 29, (3), 464-489.
- Nam, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; An, G.; Ma, H.; Nei, M., Type I MADS-box genes have experienced faster birth-and-death evolution than type II MADS-box genes in angiosperms. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2004, 101, (7), 1910-1915. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Woo, Y.-M.; Ryu, S.-I.; Shin, Y.-D.; Kim, W. T.; Park, K. Y.; Lee, I.-J.; An, G., Further characterization of a rice AGL12 group MADS-box gene, OsMADS26. Plant physiology 2008, 147, (1), 156-168. [CrossRef]
- Ugalde, J. M., Every breath you don’t take, I’ll be helping you: Ethylene promotes hypoxia tolerance. In Oxford University Press: 2022.
- Hartman, S.; Liu, Z.; Van Veen, H.; Vicente, J.; Reinen, E.; Martopawiro, S.; Zhang, H.; Van Dongen, N.; Bosman, F.; Bassel, G. W., Ethylene-mediated nitric oxide depletion pre-adapts plants to hypoxia stress. Nature Communications 2019, 10, (1), 4020. [CrossRef]
- Loreti, E.; Perata, P., ERFVII transcription factors and their role in the adaptation to hypoxia in Arabidopsis and crops. Frontiers in Genetics 2023, 14, 1213839. [CrossRef]
- Loreti, E.; Valeri, M. C.; Novi, G.; Perata, P., Gene regulation and survival under hypoxia requires starch availability and metabolism. Plant Physiology 2018, 176, (2), 1286-1298. [CrossRef]
- Locke, A. M.; Barding Jr, G. A.; Sathnur, S.; Larive, C. K.; Bailey-Serres, J., Rice SUB1A constrains remodelling of the transcriptome and metabolome during submergence to facilitate post-submergence recovery. Plant, cell & environment 2018, 41, (4), 721-736. [CrossRef]
- Bui, L. T.; Giuntoli, B.; Kosmacz, M.; Parlanti, S.; Licausi, F., Constitutively expressed ERF-VII transcription factors redundantly activate the core anaerobic response in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Science 2015, 236, 37-43. [CrossRef]
- Papdi, C.; Pérez-Salamó, I.; Joseph, M. P.; Giuntoli, B.; Bögre, L.; Koncz, C.; Szabados, L., The low oxygen, oxidative and osmotic stress responses synergistically act through the ethylene response factor VII genes RAP 2.12, RAP 2.2 and RAP 2.3. The Plant Journal 2015, 82, (5), 772-784. [CrossRef]
- Gasch, P.; Fundinger, M.; Müller, J. T.; Lee, T.; Bailey-Serres, J.; Mustroph, A., Redundant ERF-VII transcription factors bind to an evolutionarily conserved cis-motif to regulate hypoxia-responsive gene expression in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell 2016, 28, (1), 160-180. [CrossRef]
- Mustroph, A.; Zanetti, M. E.; Jang, C. J.; Holtan, H. E.; Repetti, P. P.; Galbraith, D. W.; Girke, T.; Bailey-Serres, J., Profiling translatomes of discrete cell populations resolves altered cellular priorities during hypoxia in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2009, 106, (44), 18843-18848. [CrossRef]
- Perata, P.; Alpi, A., Plant responses to anaerobiosis. Plant science 1993, 93, (1-2), 1-17.
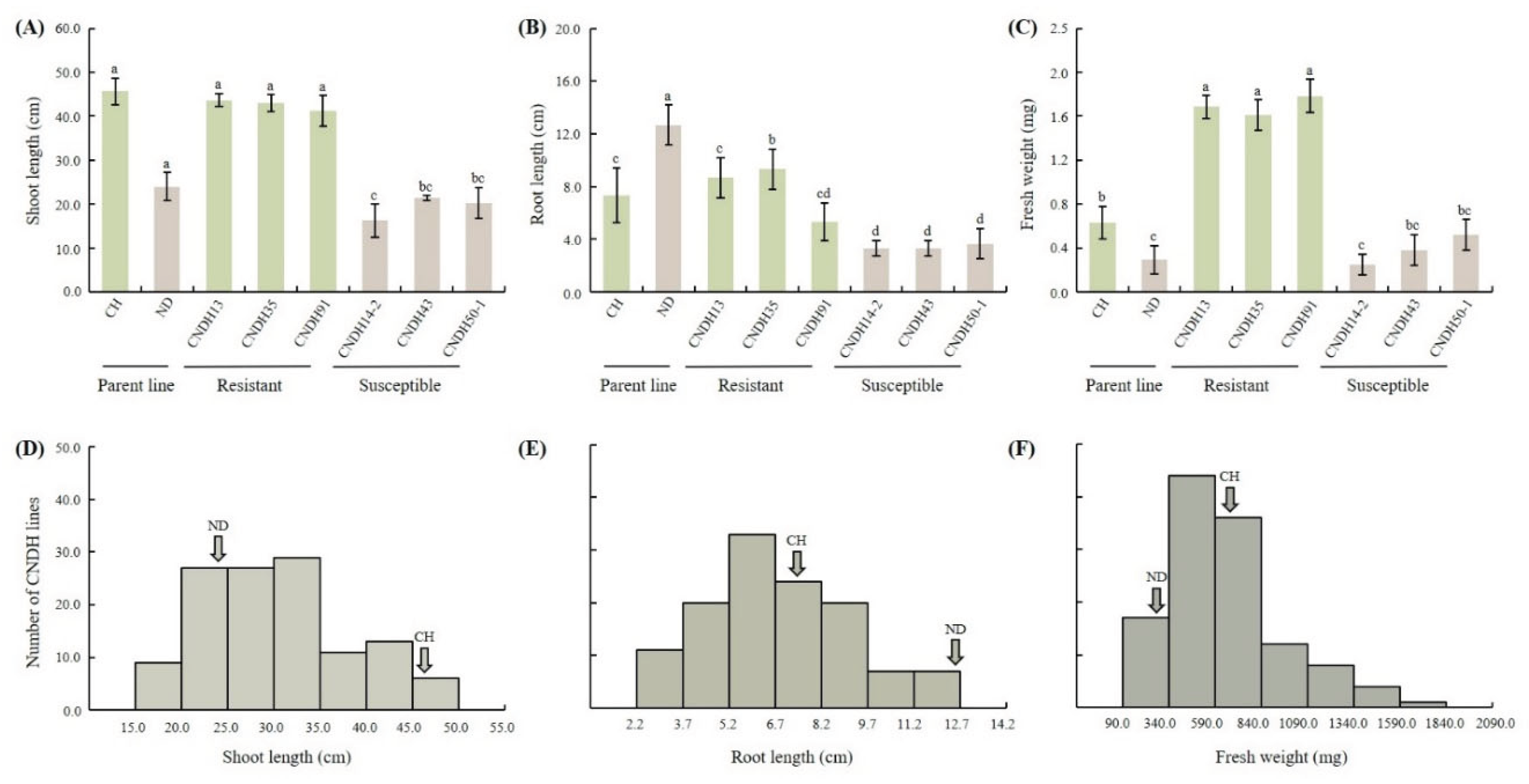
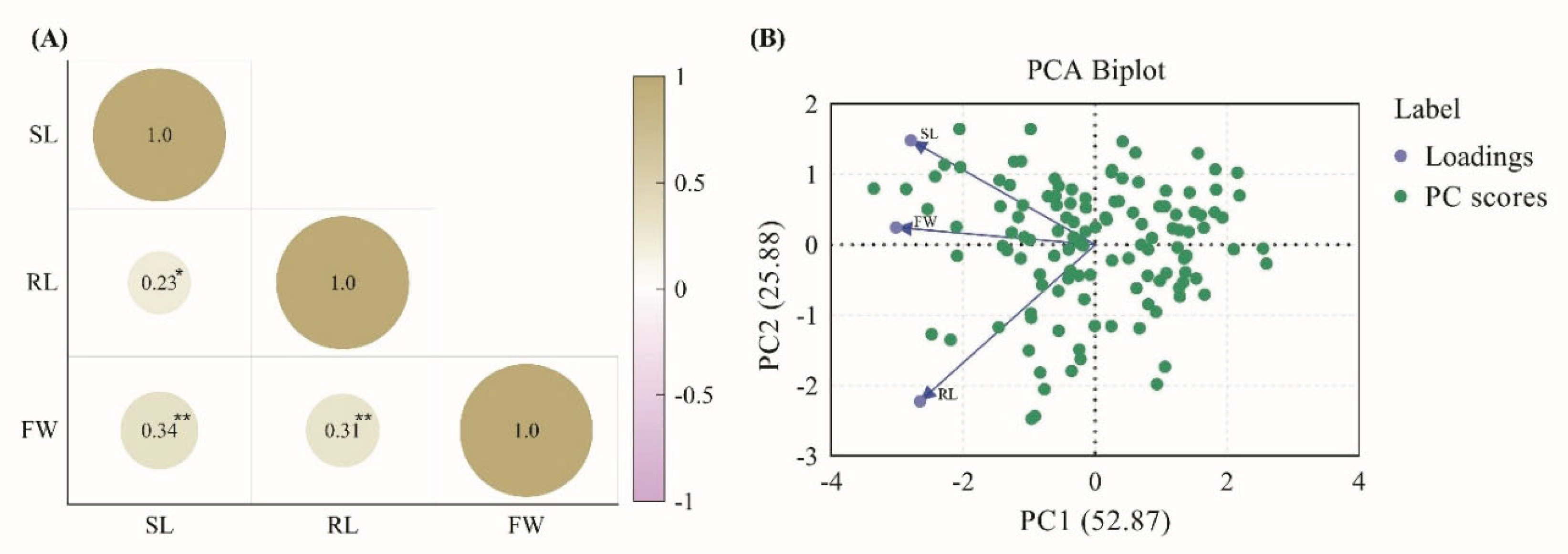
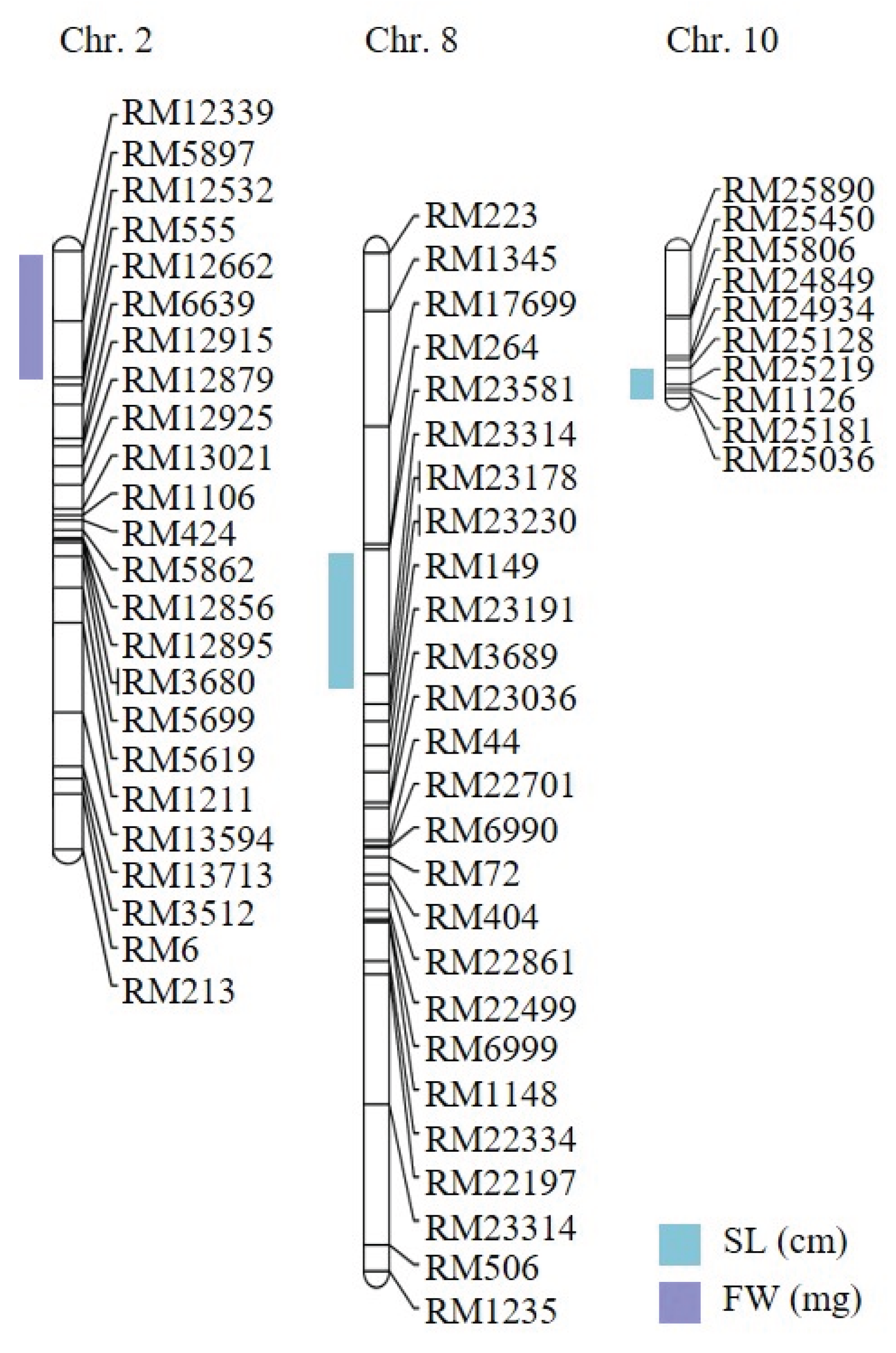
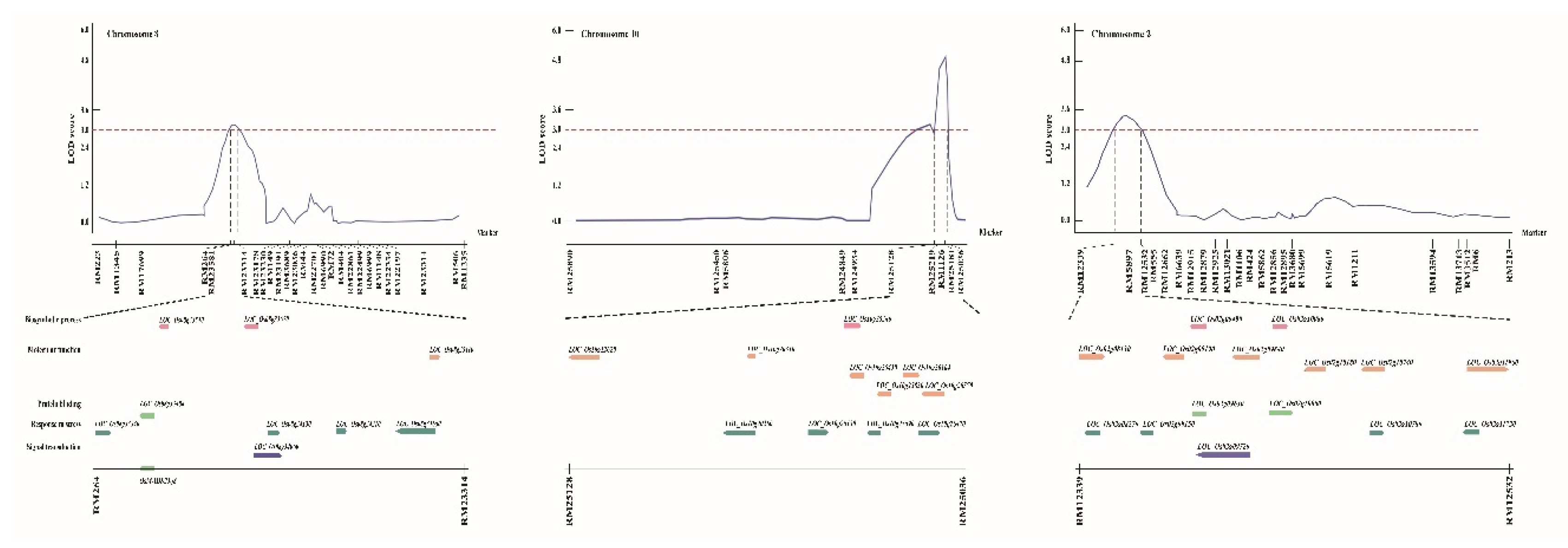
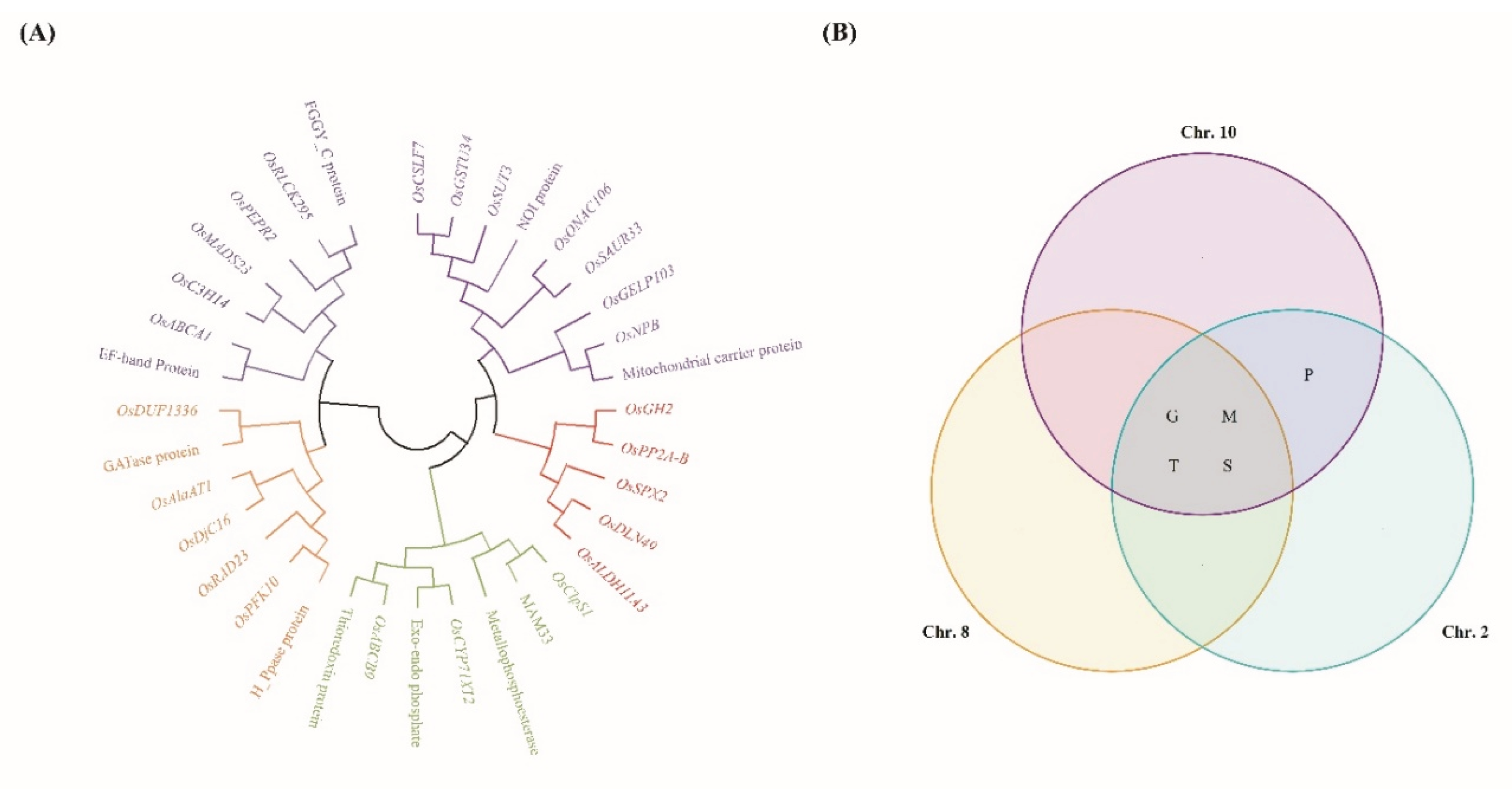
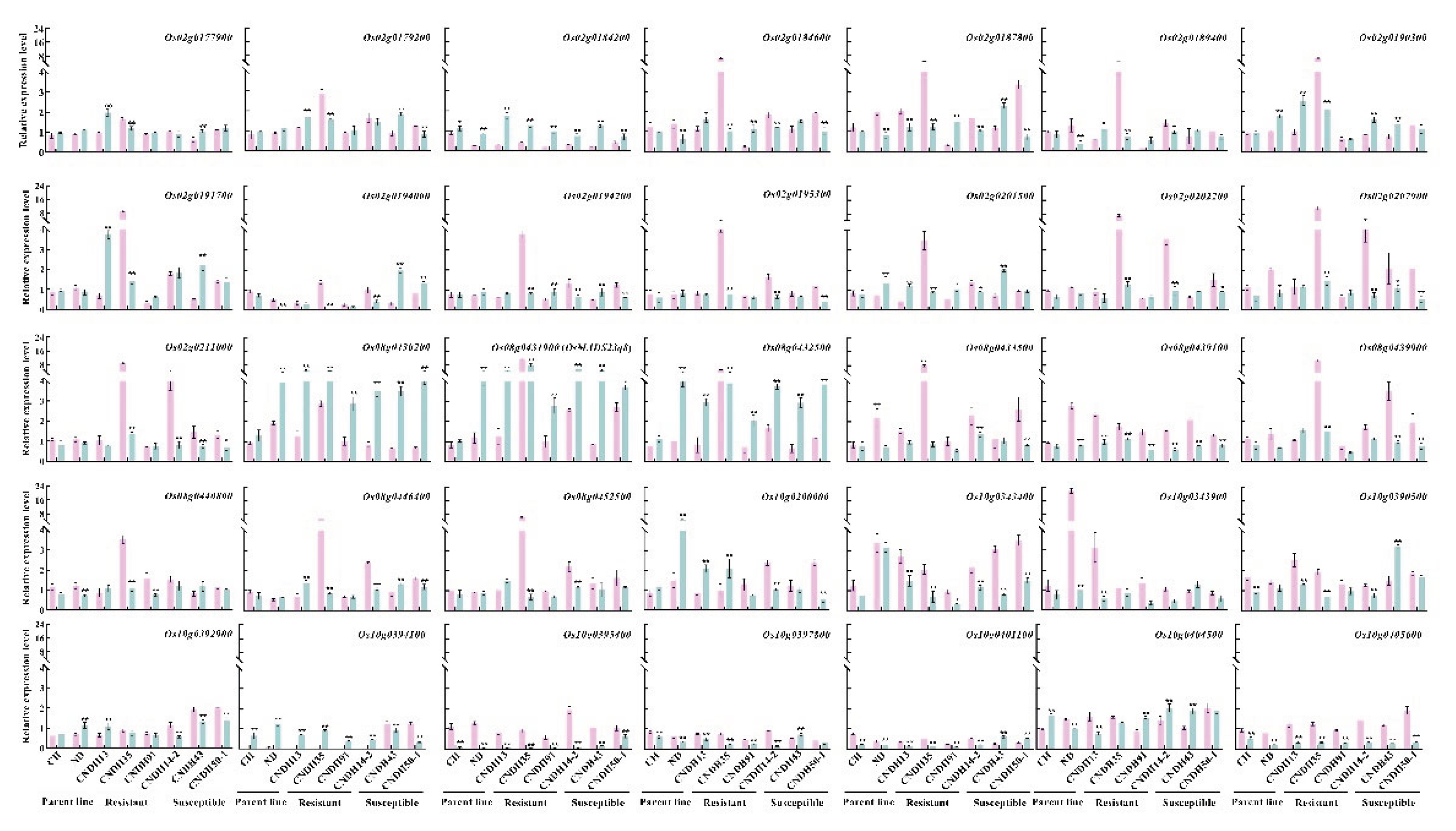
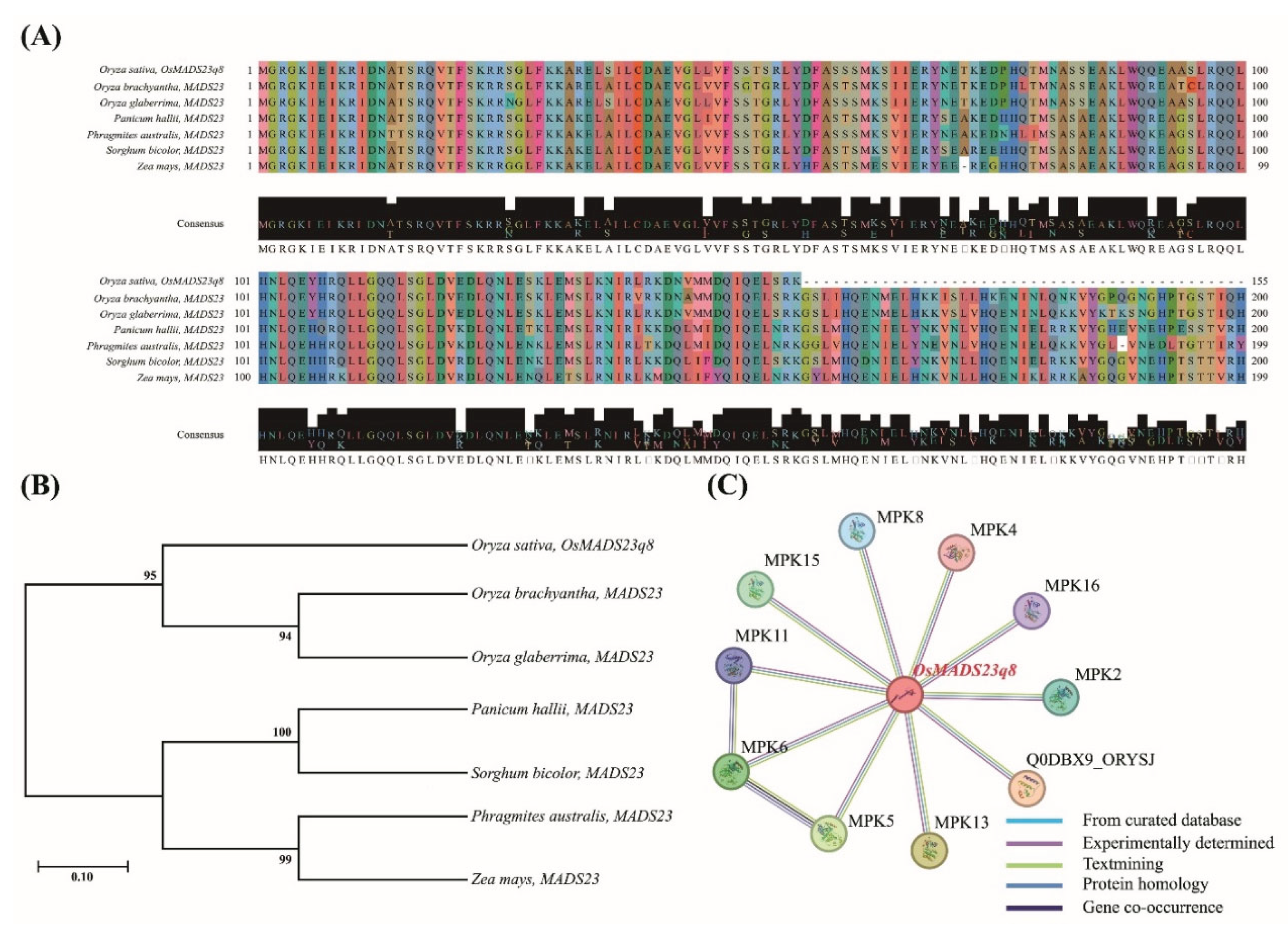
| Traits | QTLs | Chr | Interval markersz | LOD | Additive effecty | R2x | Increasing effectsw |
| Shoot length (cm) | qSL-8 | 8 | RM264–RM23314 | 3.02 | 4.24 | 0.34 | Cheong cheong |
| qSL-10 | 10 | RM25128–RM25036 | 5.03 | 6.39 | 0.28 | Cheong cheong |
|
| Fresh weight (mg) | qFW-2 | 2 | RM12339–RM12532 | 3.60 | -0.12 | 0.28 | Nagdong |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





