Submitted:
12 September 2025
Posted:
15 September 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design and Scope
2.2. Literature Search Strategy
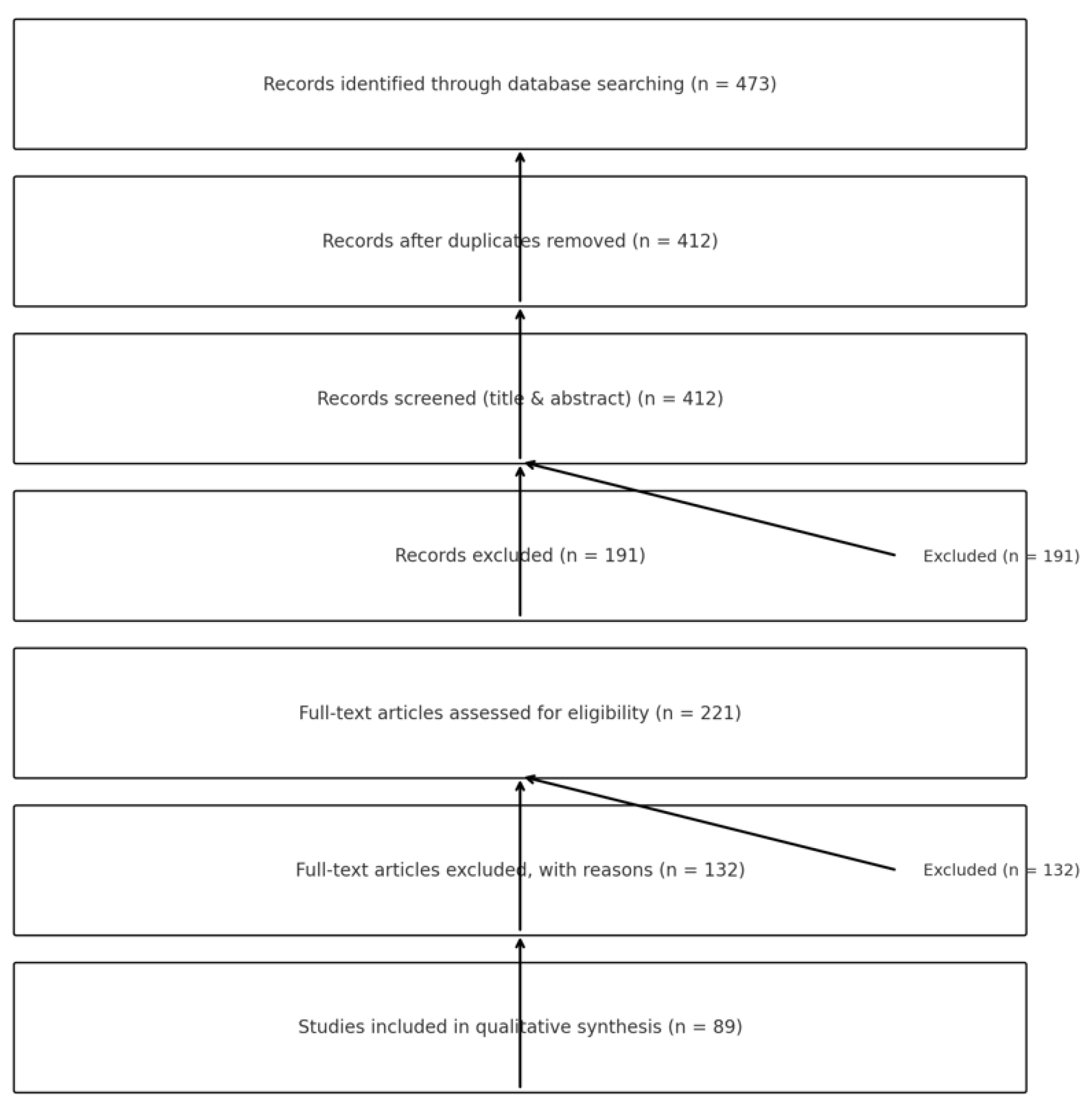
2.3. Eligibility, Inclusion Strategy, and Thematic Synthesis
- Peer-reviewed journal articles published between January 2019 and August 2025.
- Studies written in English and indexed in international databases (e.g., Scopus, WoS, IEEE Xplore).
- Articles presenting empirical results, simulation-based validations, experimental frameworks, or case studies related to intelligent energy management in building environments.
- Research incorporating at least one of the following components: IoT-based monitoring systems, machine learning algorithms, predictive control strategies, occupancy-based automation, fault detection systems, or smart grid integration within BEMS.
- Papers focusing on energy efficiency outcomes, performance metrics, or system architecture innovations applicable to residential, commercial, or institutional buildings.
- Non-peer-reviewed publications such as white papers, editorials, and conference abstracts.
- Studies focusing solely on industrial or manufacturing process control without relevance to building energy management.
- Theoretical or conceptual articles lacking implementation, performance evaluation, or reproducible models.
- Redundant or duplicate studies, literature reviews without new contributions, and articles failing to meet quality benchmarks for data transparency or methodological clarity.
- Application domains (e.g., residential retrofits, smart campuses, office complexes).
- Technological enablers (e.g., types of IoT sensors, cloud vs. edge computing, specific AI algorithms like SVM, DRL, MAS).
- Functional objectives (e.g., HVAC control, lighting automation, predictive maintenance, anomaly detection).
- Performance metrics (e.g., kWh saved, CO₂ emissions reduced, Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), response latency).
- System architecture (e.g., digital twin-enhanced BEMS, grid-interactive systems, hybrid cloud-edge deployments).
- Identified barriers (e.g., interoperability, cybersecurity, cost, scalability).
2.4. Analytical Framework, Reproducibility Ethics, and Transparency Standards
- Python 3.11 was used to develop a modular data analysis pipeline. Key libraries included:
- ○
- pandas for data tabulation and matrix transformation,
- ○
- scikit-learn for regression-based performance evaluations and outlier detection,
- ○
- matplotlib and seaborn for data visualization (e.g., heatmaps, scatter plots, bar graphs),
- ○
- NumPy for statistical operations and correlation matrices.
- Benchmarking of energy efficiency performance was conducted by normalizing reported values against standard Building Management Systems (BMS) and static control baselines.
- Cross-validation of classification and regression results was applied where applicable, based on metrics such as MAPE, RMSE, R², and F1-scores.
- Grammar refinement and sentence structure improvement,
- Reference formatting and citation consistency,
- Syntactic harmonization across bibliographic metadata.
- Annotated Jupyter Notebooks (.ipynb),
- CSV-formatted bibliographic metadata,
- NVivo project files (.nvp) containing thematic codes,
- Co-occurrence network files compatible with VOSviewer (.net, .map).
3. Results
3.1. Functional Distribution and Performance of Intelligent BEMS Technologies
3.1.1. Quantitative Performance Indicators
3.2. Interpretation and Cross-Reference with Prior Studies
- Low adoption of digital twin technologies, as shown in [14,77,82], is attributed to the complexity of implementation and high infrastructural cost. Nonetheless, their integration with generative design and real-time feedback mechanisms positions them as a transformative element for future BEMS evolution.
4. Discussion
4.1. Alignment and Divergence with Existing Literature
4.2. Practical Implications and Systemic Impact
4.3. Methodological Observations and Gaps
4.4. Future Research Directions
- Explainable AI (XAI) in BEMS: Future studies should prioritize transparency in decision-making processes to foster greater acceptance among end-users and regulators.
4.5. Broader Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, S.F.A.; Iqbal, M.; Aziz, Z.; Rana, T.A.; Khalid, A.; Cheah, Y.-N.; Arif, M. The Role of Machine Learning and the Internet of Things in Smart Buildings for Energy Efficiency. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, T., Amir Malik, A., Haq, I., Rozeela, I., Ullah, I., Khan, M. A. Adhikari, D., Othman, M.T.B., Hamam, H. The role of ML, AI, and 5G technology in smart energy and buildings. Electronics 2022, 11, 3960. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Chavez, S.A.; Eltamaly, A.M.; Garces, H.O.; Rojas, A.J.; Kim, Y.-C. Toward an Intelligent Campus: IoT Platform for Remote Monitoring and Control of Smart Buildings. Sensors 2022, 22, 045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Shahzad, M.; Abbas, F.; Muqeet, H.A.; Hussain, M.M.; Bin, L. Optimal Energy Management System of IoT-Enabled Large Building Considering Electric Vehicle Scheduling, Distributed Resources, and Demand Response Schemes. Sensors 2022, 22, 7448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-L.; Park, K.-J.; Son, S.-Y. Occupancy-Based Energy Consumption Estimation Improvement through Deep Learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Husseini, F.; Noura, H.N.; Salman, O.; Chahine, K. Machine Learning in Smart Buildings: A Review of Methods, Challenges, and Future Trends. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, S.; Guarascio, M.; Guerrieri, A.; Mungari, S. A Deep Anomaly Detection System for IoT-Based Smart Buildings. Sensors 2023, 23, 9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknia, S.; Ghiai, M. Simulation-Based Prediction of Office Buildings Energy Performance Under RCP Scenarios Across All U.S. Climate Zones. Architecture 2025, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.H.; Asar, A.U.; Ullah, N.; Albogamy, F.R.; Rafique, M.K. Modeling and Optimization of Smart Building Energy Management System Considering Both Electrical and Thermal Load. Energies 2022, 15, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyyamozhi, M.; Murugesan, B.; Rajamanickam, N.; Shorfuzzaman, M.; Aboelmagd, Y. IoT—A Promising Solution to Energy Management in Smart Buildings: A Systematic Review, Applications, Barriers, and Future Scope. Buildings 2024, 14, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Chen, L. Sustainable Air-Conditioning Systems Enabled by Artificial Intelligence: Research Status, Enterprise Patent Analysis, and Future Prospects. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, N. A.; Dahlan, N. Y. Optimum energy management strategy with enhanced time of use tariff for campus building using particle swarm optimization. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 2022, 28(2), 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Tsai, F.-P. Air Conditioning Energy Saving from Cloud-Based Artificial Intelligence: Case Study of a Split-Type Air Conditioner. Energies 2020, 13, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J. Multi-dimensional model and interactive simulation of intelligent construction based on digital twins. Scientific Reports 2025, 15, 32189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliero, M.S.; Asif, M.; Ghani, I.; Pasha, M.F.; Jeong, S.R. Systematic Review Analysis on Smart Building: Challenges and Opportunities. Sustainability 2022, 14(5), 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, M.Y.L.; Teo, E.A.L.; Shah, K.W.; Kumar, V.; Hussein, G.F. Evaluating the Roadmap of 5G Technology Implementation for Smart Building and Facilities Management in Singapore. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M. A.; Chavez, S. A.; Eltamaly, A. M.; Garces, H. O.; Rojas, A. J.; Kim, Y.-C. Toward an intelligent campus: IoT platform for remote monitoring and control of smart buildings. Sensors 2022, 22, 9045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, A.; Starace, G. Advanced and Complex Energy Systems Monitoring and Control: A Review on Available Technologies and Their Application Criteria. Sensors 2022, 22, 4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starace, G.; Tiwari, A.; Colangelo, G.; Massaro, A. Advanced Data Systems for Energy Consumption Optimization and Air Quality Control in Smart Public Buildings Using a Versatile Open Source Approach. Electronics 2022, 11, 3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozadowicz, A. A Hybrid Approach in Design of Building Energy Management System with Smart Readiness Indicator and Building as a Service Concept. Energies 2022, 15, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, T.; Irfan, H.M.; Haq, I.; Ullah, I.; Ashraf, M.; Shloul, T.A.; Ghadi, Y.Y.; Imran; Elkamchouchi, D.H. Analysis of Challenges and Solutions of IoT in Smart Grids Using AI and Machine Learning Techniques: A Review. Electronics 2023, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, P.; Prabu, A.V.; Loganathan, S.; Routray, S.; Ghosh, U.; AL-Numay, M. Analyzing and Managing Various Energy-Related Environmental Factors for Providing Personalized IoT Services for Smart Buildings in Smart Environment. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitan, N.C.; Ungurean, I.; Roman, C.; Francu, C. An Optimizing Heat Consumption System Based on BMS. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H. A Review of Data-Driven Building Energy Prediction. Buildings 2023, 13, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, K.M.; Hossain, M.; Alduais, N.A.M.; Al-Duais, H.S.; Omrany, H.; Ghaffarianhoseini, A. A Review of Using IoT for Energy Efficient Buildings and Cities: A Built Environment Perspective. Energies 2022, 15, 5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, J.; Kadir, A.F.A.; Hanafi, A.N.; Shareef, H.; Khatib, T.; Baharin, K.A.; Sulaima, M.F. A Review on Optimal Energy Management in Commercial Buildings. Energies 2023, 16, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraliyage, H.; Dahanayake, S.; De Silva, D.; Mills, N.; Rathnayaka, P.; Nguyen, S.; Alahakoon, D.; Jennings, A. A Robust Artificial Intelligence Approach with Explainability for Measurement and Verification of Energy Efficient Infrastructure for Net Zero Carbon Emissions. Sensors 2022, 22, 9503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayla, A.; Swierczewska, K.S.; Kaya, M.; Karaca, B.; Arayici, Y.; Ayözen, Y.E.; Tokdemir, O.B. Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Based Occupant-Centric Heating Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Control System for Multi-Zone Commercial Buildings. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, A.; Ramallo González, A.P.; Jaglan, G.; Fensel, A. A Semantically Data-Driven Classification Framework for Energy Consumption in Buildings. Energies 2022, 15, 3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgoshaei, P.; Heidarinejad, M.; Austin, M.A. A Semantic Approach for Building System Operations: Knowledge Representation and Reasoning. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, J.; Blank, T. A Systematic Literature Review on Data-Driven Residential and Industrial Energy Management Systems. Energies 2023, 16, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, N.; Barreto, R.; Gomes, L.; Faria, P.; Vale, Z. A Trustworthy Building Energy Management System to Enable Direct IoT Devices’ Participation in Demand Response Programs. Electronics 2022, 11, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agharazi, H.; Prica, M.D.; Loparo, K.A. A Two-Level Model Predictive Control-Based Approach for Building Energy Management including Photovoltaics, Energy Storage, Solar Forecasting and Building Loads. Energies 2022, 15, 3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Woo, D.-O.; Jang, J.; Junghans, L.; Leigh, S.-B. Collection and Utilization of Indoor Environmental Quality Information Using Affordable Image Sensing Technology. Energies 2022, 15, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piira, K.; Kantorovitch, J.; Kannari, L.; Piippo, J.; Vu Hoang, N. Decision Support Tool to Enable Real-Time Data-Driven Building Energy Retrofitting Design. Energies 2022, 15, 5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntafalias, A.; Tsakanikas, S.; Skarvelis-Kazakos, S.; Papadopoulos, P.; Skarmeta-Gómez, A.F.; González-Vidal, A.; Tomat, V.; Ramallo-González, A.P.; Marin-Perez, R.; Vlachou, M.C. Design and Implementation of an Interoperable Architecture for Integrating Building Legacy Systems into Scalable Energy Management Systems. Smart Cities 2022, 5, 1421–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yoon, Y.; Lee, J.; Mago, P.J.; Lee, K.; Cho, H. Design and Implementation of Smart Buildings: A Review of Current Research Trend. Energies 2022, 15, 4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlik, B. Energy Centers in a Smart City as a Platform for the Application of Artificial Intelligence and the Internet of Things. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althaus, P.; Redder, F.; Ubachukwu, E.; Mork, M.; Xhonneux, A.; Müller, D. Enhancing Building Monitoring and Control for District Energy Systems: Technology Selection and Installation within the Living Lab Energy Campus. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualandri, F.; Kuzior, A. Home Energy Management Systems Adoption Scenarios: The Case of Italy. Energies 2023, 16, 4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkas, C.; Dimara, A.; Michailidis, I.; Krinidis, S.; Marin-Perez, R.; Martínez García, A.I.; Skarmeta, A.; Kitsikoudis, K.; Kosmatopoulos, E.; Anagnostopoulos, C.-N.; et al. Integration and Verification of PLUG-N-HARVEST ICT Platform for Intelligent Management of Buildings. Energies 2022, 15, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadri, H.; Yitmen, I.; Tagliabue, L.C.; Westphal, F.; Tezel, A.; Taheri, A.; Sibenik, G. Integration of Blockchain and Digital Twins in the Smart Built Environment Adopting Disruptive Technologie-A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-C.; Dwijendra, N.K.A.; Sayed, B.T.; Alvarez, J.R.N.; Al-Bahrani, M.; Alviz-Meza, A.; Cárdenas-Escrocia, Y. Internet of Things Energy Consumption Optimization in Buildings: A Step toward Sustainability. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, J.A.; Monteiro, V.; Afonso, J.L. Internet of Things Systems and Applications for Smart Buildings. Energies 2023, 16, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, V.; Bruno, G.; Aliev, K.; Piantanida, P.; Corneli, A.; Antonelli, D. Machine Learning Framework for the Sustainable Maintenance of Building Facilities. Sustainability 2022, 14, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.H.; Asar, A.U.; Ullah, N.; Albogamy, F.R.; Rafique, M.K. Modeling and Optimization of Smart Building Energy Management System Considering Both Electrical and Thermal Load. Energies 2022, 15, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Shahzad, M.; Abbas, F.; Muqeet, H.A.; Hussain, M.M.; Bin, L. Optimal Energy Management System of IoT-Enabled Large Building Considering Electric Vehicle Scheduling, Distributed Resources, and Demand Response Schemes. Sensors 2022, 22, 7448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves-Silva, R.; Camarinha-Matos, L.M. Simulation-Based Decision Support System for Energy Efficiency in Buildings Retrofitting. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliero, M.S.; Asif, M.; Ghani, I.; Pasha, M.F.; Jeong, S.R. Systematic Review Analysis on Smart Building: Challenges and Opportunities. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.F.A.; Iqbal, M.; Aziz, Z.; Rana, T.A.; Khalid, A.; Cheah, Y.-N.; Arif, M. The Role of Machine Learning and the Internet of Things in Smart Buildings for Energy Efficiency. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apanavičienė, R.; Shahrabani, M.M.N. Key Factors Affecting Smart Building Integration into Smart City: Technological Aspects. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 1832–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcher, E.J.; Abraham, Y.S. Lifecycle Applications of Building Information Modeling for Transportation Infrastructure Projects. Buildings 2023, 13, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliero, M.S.; Pasha, M.F.; Toosi, Adel N. T.; Ghani, I. The COVID-19 impact on air condition usage: a shift towards residential energy saving. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 85727–85741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Molina, A.; Alamaniotis, M. Enhancing Historic Building Performance with the Use of Fuzzy Inference System to Control the Electric Cooling System. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Al-Turjman, F.; Nayyar, A. IoT-based green city architecture using secured and sustainable android services, Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2020, 20, 101091. [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, K.; Lee, S.; Jeon, G.; EBDS: An energy-efficient big data-based secure framework using Internet of Things for green environment, Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2020, 20, 101129. [CrossRef]
- Talebi, A.; Hatami, A. Online fuzzy control of HVAC systems considering demand response and users’ comfort. Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning, and Policy, 2020, 15, 403–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.; Kim, J. H.; An, K.; Mesicek, L.; Marreiros, G.; Pan, S. B.; Kim, P., Smart home energy strategy based on human behaviour patterns for transformative computing. Information Processing & Management 2020, 57(5), 102256, ISSN 0306-4573. [CrossRef]
- de Castro Tomé, M.; J. Nardelli, P.H.; Hussain, H.M.; Wahid, S.; Narayanan, A. A Cyber-Physical Residential Energy Management System via Virtualized Packets. Energies 2020, 13, 699. [CrossRef]
- Chamandoust, H.; Derakhshan, G.; Hakimi, S.M.; Bahramara, S. Tri-objective scheduling of residential smart electrical distribution grids with optimal joint of responsive loads with renewable energy sources. Journal of Energy Storage 2020, 27, 101112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, P.; TarunKumar, M.; Vittal, K.P. An IoT based Intelligent Smart Energy Management System with accurate forecasting and load strategy for renewable generation. Measurement 2020, 152, 107187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedolhosseini, A.; Masoumi, N.; Modarressi, M.; Karimian, N. Daylight adaptive smart indoor lighting control method using artificial neural networks. Journal of Building Engineering 2020, 29, 101141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paukstadt, U.; Becker, J. Uncovering the business value of the internet of things in the energy domain – a review of smart energy business models. Electronic Markets 2021, 31, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakirullin, R. S. A Smart Window for Angular Selective Filtering of Direct Solar Radiation. ASME. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2020, 142(1): 011001. [CrossRef]
- Samadi, A.; Saidi, H.; Latify, M.A.; Mahdavi, M. Home energy management system based on task classification and the resident’s requirements, International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 2020, 118, 105815. [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Hussain, I.; Singh, M. Exploiting Grasshopper and Cuckoo Search Bio-Inspired Optimization Algorithms for Industrial Energy Management System: Smart Industries. Electronics 2020, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, D.; Badarla, V. Occupancy detection systems for indoor environments: A survey of approaches and methods. Indoor and Built Environment. 2019, 29(8), 1053–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. A review of studies applying machine learning models to predict occupancy and window-opening behaviours in smart buildings, Energy and Buildings 2020, 223, 110159. [CrossRef]
- Simsek, Y.; Santika, W. G.; Anisuzzaman, M.; Urmee, T.; Bahri, P.A.; Escobar, R. An analysis of additional energy requirement to meet the sustainable development goals, Journal of Cleaner Production 2020, 272, 122646. [CrossRef]
- Mukilan, P.; Balasubramanian, M.; Rajamanickam, N.; Shorfuzzaman, M.; Aboelmagd, Y. IoT—A Promising Solution to Energy Management in Smart Buildings: A Systematic Review, Applications, Barriers, and Future Scope. Buildings 2024, 14, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taboada-Orozco, A.; Yetongnon, K.; Nicolle, C. Smart Buildings: A Comprehensive Systematic Literature Review on Data-Driven Building Management Systems. Sensors 2024, 24, 4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, D.M.T.E.; Motuzienė, V.; Džiugaitė-Tumėnienė, R. AI-Driven Innovations in Building Energy Management Systems: A Review of Potential Applications and Energy Savings. Energies 2024, 17, 4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, A.; Daneshvar, M.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A. Energy Intelligence: A Systematic Review of Artificial Intelligence for Energy Management. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.K.; Sahoo, S.K.; Yanine, F.F. A comprehensive review of smart energy management systems for photovoltaic power generation utilizing the internet of things. Unconventional Resources, 2025, 7, 100197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, M.; Barik, D.; Othman, N.A. Seepana Praveenkumar, Kapura Tudu. Investigating the performance of AI-driven smart building systems through advanced deep learning model analysis. Energy Reports 2025, 13, 5885–5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasmant, H.; Bossoufi, B.; Alaoui, C.; Siano, P. A review of machine learning and IoT-based energy management systems for AC microgrids. Computers and Electrical Engineering 2025, 127(Part A), 110563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Kim, J.; Yoon, S. DT-BEMS: Digital twin-enabled building energy management system for information fusion and energy efficiency. Energy 2025, 326, 136162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, R.; Huang, Q.; Zalhaf, A.S.; Bamisile, O.; Li, J.; Mansour, D.-E.A.; Lin, X.; Yehia, D.M. Energy Management in Residential Microgrid Based on Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring and Internet of Things. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 1907–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Ahmed, I.; Mihet-Popa, L. Development and testing of an IoT platform with smart algorithms for building energy management systems. Energy and Buildings 2025, 344, 115970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Misnan, M.S.; Halim, N.H.F.A. A Systematic Literature Review on Energy Efficiency Analysis of Building Energy Management. Buildings 2024, 14, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roka, R.; Figueiredo, A.; Vieira, A.; Cardoso, C. A Systematic Review of Sensitivity Analysis in Building Energy Modeling: Key Factors Influencing Building Thermal Energy Performance. Energies 2025, 18, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palley, B.; Poças Martins, J.; Bernardo, H.; Rossetti, R. Integrating Machine Learning and Digital Twins for Enhanced Smart Building Operation and Energy Management: A Systematic Review. Urban Sci. 2025, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amangeldy, B.; Tasmurzayev, N.; Imankulov, T.; Baigarayeva, Z.; Izmailov, N.; Riza, T.; Abdukarimov, A.; Mukazhan, M.; Zhumagulov, B. AI-Powered Building Ecosystems: A Narrative Mapping Review on the Integration of Digital Twins and LLMs for Proactive Comfort, IEQ, and Energy Management. Sensors 2025, 25, 5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Lu, S.; Zhou, S.; Tian, Z.; Kim, M.K.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. A Systematic Review of Building Energy Consumption Prediction: From Perspectives of Load Classification, Data-Driven Frameworks, and Future Directions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Strbac, G. Novel Artificial Intelligence Applications in Energy: A Systematic Review. Energies 2025, 18, 3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, B.N.; Ma, Z.G. Impact of EU Laws on the Adoption of AI and IoT in Advanced Building Energy Management Systems: A Review of Regulatory Barriers, Technological Challenges, and Economic Opportunities. Buildings 2025, 15, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojek, I.; Mikołajewski, D.; Mroziński, A.; Macko, M.; Bednarek, T.; Tyburek, K. Internet of Things Applications for Energy Management in Buildings Using Artificial Intelligence - A Case Study. Energies 2025, 18, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad Alotaibi, B.; Ibrahim Shema, A.; Umar Ibrahim, A.; Awad Abuhussain, M.; Abdulmalik, H.; Aminu Dodo, Y.; Atakara, C. Assimilation of 3D printing, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) for the construction of eco-friendly intelligent homes: An explorative review. Heliyon 2024, 10(17): e36846. [CrossRef]
- Shahrabani, M.M.N.; Apanaviciene, R. An AI-Based Evaluation Framework for Smart Building Integration into Smart City. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
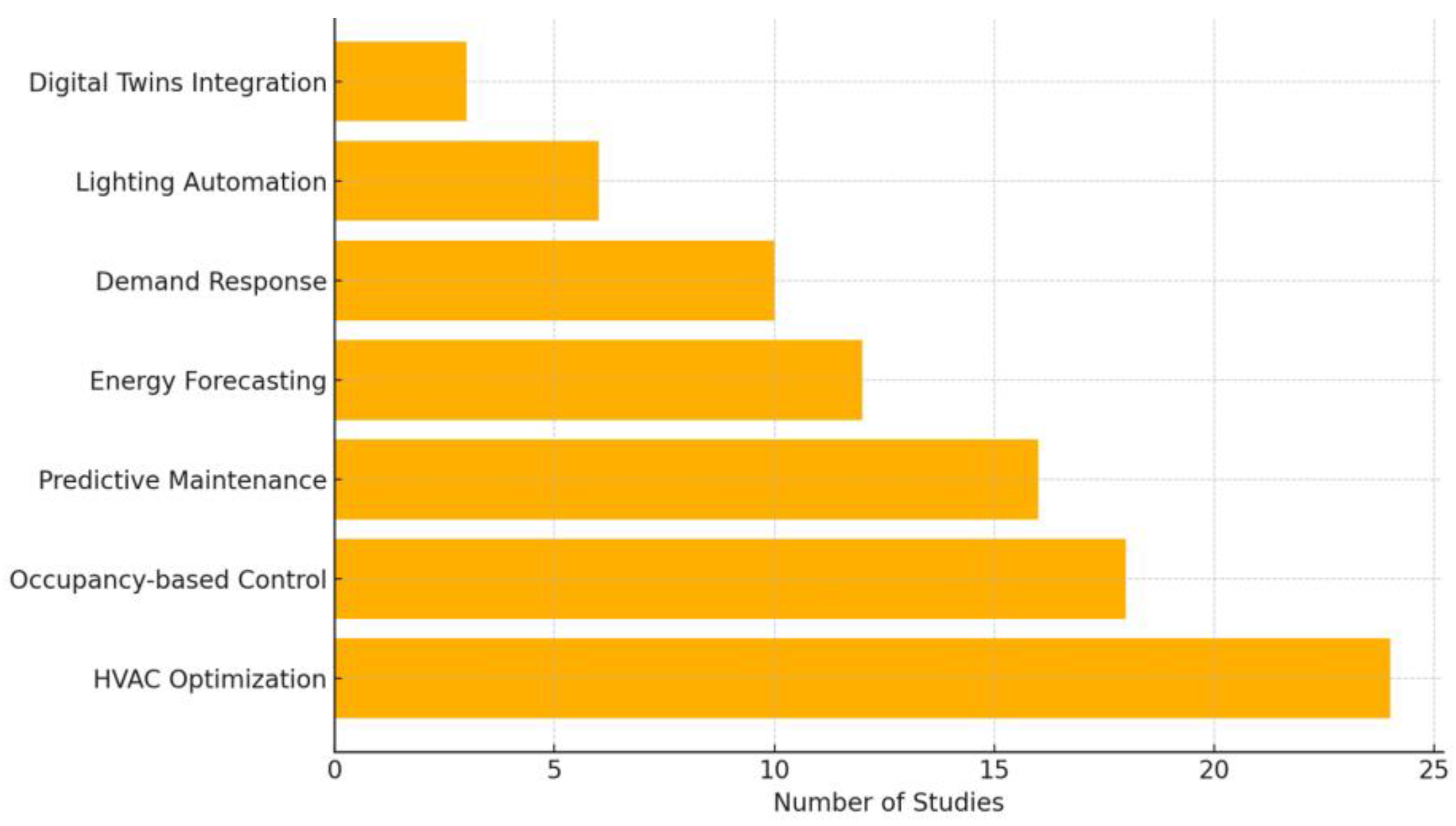
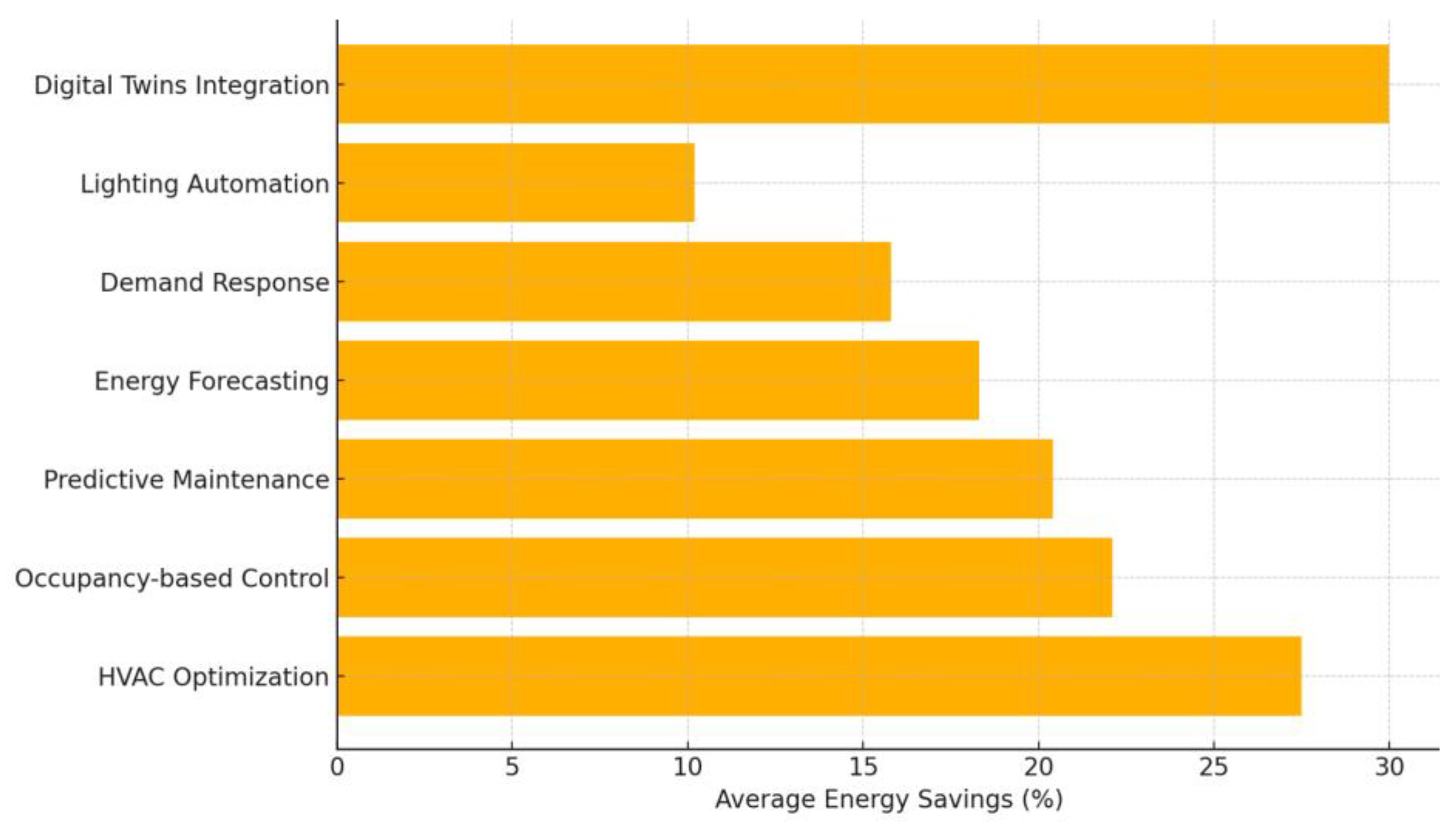
| Application Category | Number of Studies | Average Energy Savings (%) |
| HVAC Optimization | 24 | 27.5 |
| Occupancy-based Control | 18 | 22.1 |
| Predictive Maintenance | 16 | 20.4 |
| Energy Forecasting | 12 | 18.3 |
| Demand Response | 10 | 15.8 |
| Lighting Automation | 6 | 10.2 |
| Digital Twins Integration | 3 | 30.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





