Submitted:
08 September 2025
Posted:
09 September 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval and Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.2.1. Visit 1: Eligibility and Familiarisation
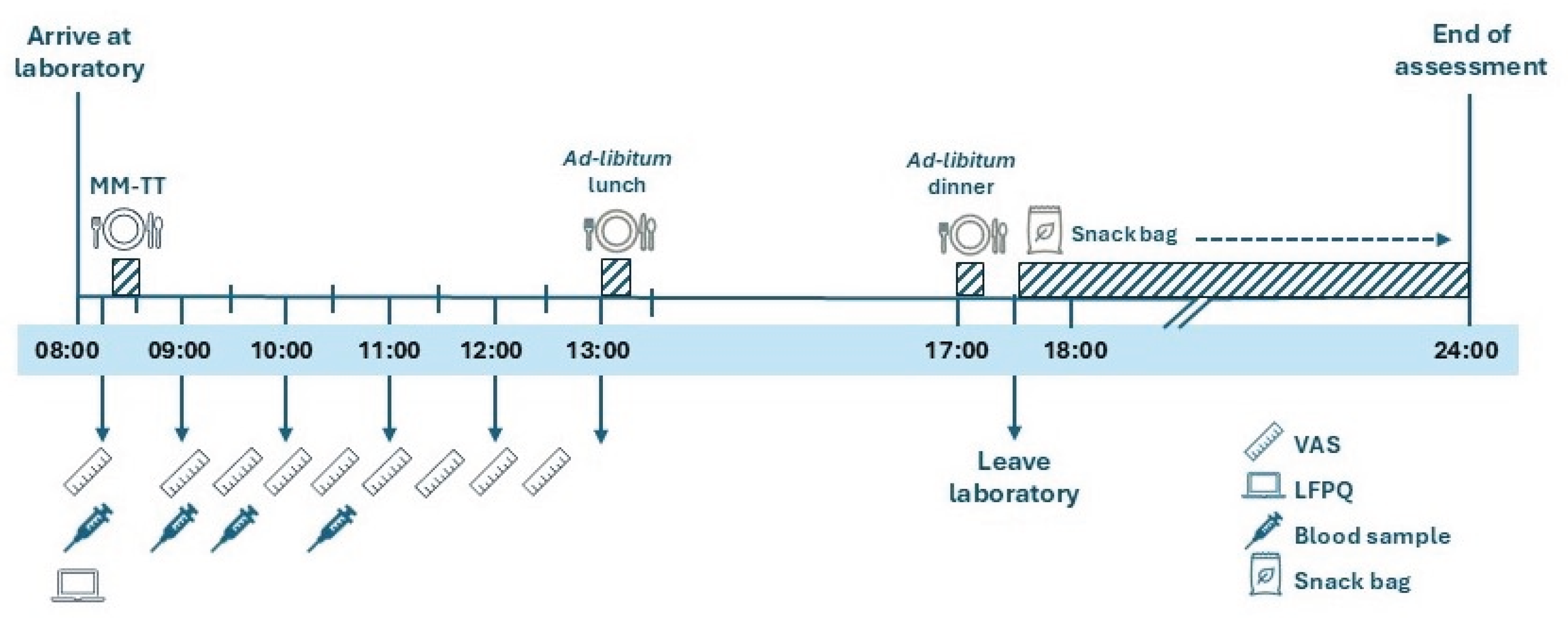
2.2.2. 24-Hour Movement Behaviour Assessment
2.2.3. Free-Living Energy Intake Assessment
2.2.4. Visit 2: Appetite and Energy Intake Assessment
2.2.5. Study Meals
2.2.6. Leeds Food Preference Questionnaire
2.2.7. Blood Sampling and Biochemical Analyses
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
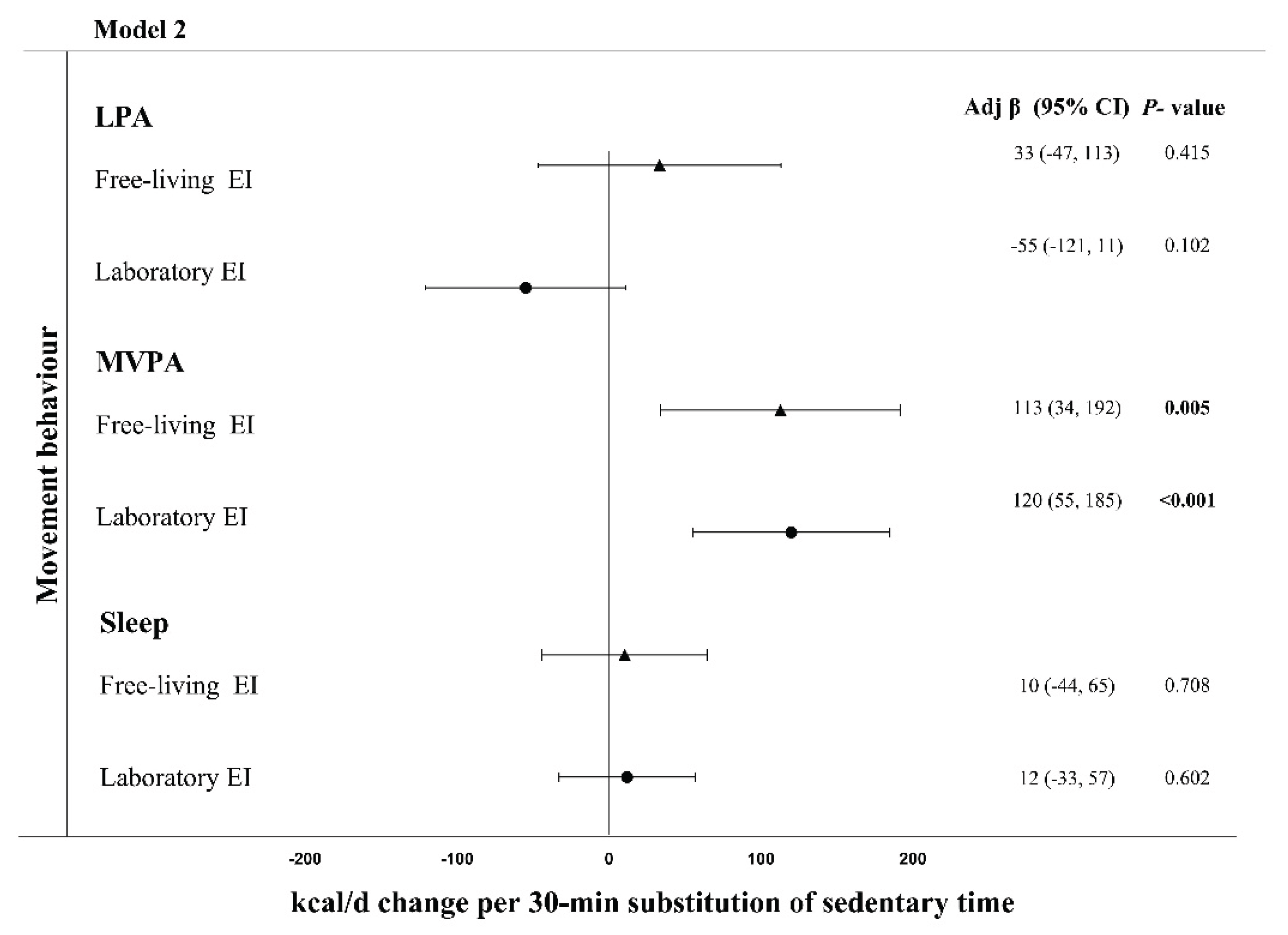
3.2. Energy Intake
3.3. Appetite-Related Hormones
3.4. Perceived Ratings of appetite
3.5. Food Reward, Cravings and Dietary Eating Traits
| LPA | MVPA | Sleep | ||||
| β-coefficient (95% CI) | P-value | β -coefficient (95% CI) | P-value | β -coefficient (95% CI) | P-value | |
| Appetite-related hormones | ||||||
| Fasting leptin (pg·mL−1)* | 0.03 (−0.1, 0.1) | 0.652 | −0.06 (−0.15, 0.03) | 0.111 | −0.06 (−0.12, 0.00) | 0.106 |
| Fasting PYY (pg·mL−1) | 4.6 (−1.8, 11.0) | 0.162 | −0.8 (−7.1, 5.6) | 0.815 | −0.2 (−4.6, 4.1) | 0.916 |
| PYY AUC (2 h, pg·mL−1) | 549.8 (34.8, 1064.9) | 0.036 | −639.3 (−1143.2, −135.3) | 0.013 | 52.7 (−294.5 to 399.8) | 0.766 |
| Fasting acylated ghrelin (pg·mL−1)* | 0.06 (−0.04, 0.14) | 0.234 | 0.10 (0.00, 0.19) | 0.045 | 0.00 (−0.04, 0.06) | 0.648 |
| Acylated ghrelin AUC (2 h, pg·mL−1)* | −0.03 (−0.06, 0.03) | 0.514 | 0.03 (−0.03, 0.09) | 0.566 | −0.03 (−0.06, 0.03) | 0.359 |
| Perceived ratings of appetite | ||||||
| Fasting fullness (mm) | −0.33 (−3.00, 2.33) | 0.809 | 1.00 (−1.65, 3.66) | 0.456 | 0.09 (−1.74, 1.93) | 0.927 |
| Fullness AUC (4 h, mm) | 6.5 (−482.5, 495.4) | 0.979 | −453.8 (−936.9, 29.5) | 0.066 | −286.7 (−618.8 to 45.5) | 0.091 |
| Fasting hunger (mm) | −0.2 (−3.4, 3.0) | 0.915 | 0.8 (−2.4, 4.0) | 0.635 | 0.0 (−2.2, 2.2) | 0.990 |
| Hunger AUC (4 h, mm) | −70.6 (−607.4, 466.3) | 0.797 | 480.8 (−49.1, 1010.7) | 0.075 | 299.3 (−65.5 to 662.0) | 0.108 |
| Fasting PFC (mm) | 0.30 (−1.86, 2.42) | 0.789 | 1.77 (−0.34, 3.85) | 0.101 | 0.53 (−0.93, 1.99) | 0.467 |
| PFC AUC (4 h, mm) | −168.9 (−621.5, 283.8) | 0.464 | 544.6 (93.4, 995.8) | 0.018 | 175.8 (−132.2 to 483.8) | 0.263 |
| Fasting satisfaction (mm) | 1.84 (−1.08, 4.71) | 0.217 | 0.39 (−2.46, 3.24) | 0.785 | 0.72 (−1.23, 2.70) | 0.465 |
| Satisfaction AUC (4 h, mm) | −138.7 (−624.9, 347.7) | 0.576 | −135.2 (−611.9, 341.5) | 0.578 | −192.5 (−521.6 to 136.5) | 0.251 |
| LPA | MVPA | Sleep Duration | ||||
| β -coefficient (95% CI) | P-value | β -coefficient (95% CI) | P-value | β -coefficient (95% CI) | P-value | |
| TEFQ | ||||||
| Cognitive restraint (0-21) | 0.00 (−0.50, 0.51) | 0.957 | −0.03 (−0.50, 0.44) | 0.901 | −0.12 (−0.46, 0.25) | 0.521 |
| Disinhibition (0-16) | −0.15 (−0.45, 0.18) | 0.365 | 0.12 (−0.18, 0.45) | 0.418 | −0.10 (−0.30, 0.15) | 0.476 |
| Hunger (0-14) | 0.16 (−0.25, 0.55) | 0.482 | 0.30 (−0.06, 0.70) | 0.104 | 0.00 (−0.27, 0.25) | 0.967 |
| Total score | −0.03 (−0.72, 0.66) | 0.943 | 0.42 (−0.30, 1.15) | 0.247 | −0.21 (−0.66, 0.25) | 0.397 |
| CoEQ | ||||||
| Craving control (AU) | −3.93 (−12.00, 4.14) | 0.339 | 2.26 (−5.70, 10.22) | 0.577 | 3.27 (−2.22, 8.77) | 0.242 |
| Craving for Sweet (AU) | 2.03 (−7.90, 11.96) | 0.687 | −2.82 (−12.63, 6.98) | 0.575 | 6.18 (−0.60, 13.00) | 0.074 |
| Craving for Savoury (AU) | 2.3 (−7.2, 11.7) | 0.638 | 2.3 (−7.1, 11.6) | 0.630 | −3.4 (−10.0, 3.1) | 0.302 |
| Positive Mood (AU) | 6.3 (−13.5, 26.1) | 0.107 | −6.3 (−22.5, 0.9) | 0.102 | 3.4 (−1.8, 8.7) | 0.201 |
| LFPQ | ||||||
| Fasting fat explicit liking (mm) | −0.5 (−2.0, 1.0) | 0.527 | 0.1 (−1.5, 1.7) | 0.907 | −0.3 (−1.4, 0.8) | 0.618 |
| Fasting fat explicit wanting (mm) | −0.3 (−2.0, 1.4) | 0.754 | 0.6 (−1.2, 2.3) | 0.470 | 0.0 (−1.1, 1.1) | 0.992 |
| Fasting fat implicit wanting (AU) | −1.0 (−4.2, 2.2) | 0.536 | −0.1 (−3.3, 3.0) | 0.930 | −0.3 (−2.5, 1.9) | 0.789 |
| Fasting fat relative preference (AU) | −0.36 (−1.56, 0.84) | 0.538 | −0.18 (−1.42, 1.05) | 0.777 | 0.18 (−0.63, 0.89) | 0.658 |
| Fasting taste explicit liking (mm) | −0.96 (−3.21, 1.30) | 0.401 | −0.75 (−2.94, 1.44) | 0.504 | −0.03 (−1.53, 1.48) | 0.984 |
| Fasting taste explicit wanting (mm) | −1.05 (−3.24, 1.14) | 0.355 | −0.30 (−2.50, 1.89) | 0.777 | 0.45 (−1.02, 1.93) | 0.548 |
| Fasting taste implicit wanting (AU) | 0.57 (−4.09, 5.23) | 0.806 | −3.51 (−8.07, 1.05) | 0.134 | 1.05 (−2.03, 4.14) | 0.512 |
| Fasting taste relative preference (AU) | −0.004 (−6.10, 5.30) | 0.891 | −2.20 (−7.80, 3.40) | 0.442 | 0.60 (−3.20, 4.50) | 0.745 |
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AU | Arbitrary units |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CoEQ | Control of Eating Questionnaire |
| ES | Effect size |
| LFPQ | Leeds Food Preference Questionnaire |
| PFC | Prospective food consumption |
| PYY | Peptide-YY |
| TFEQ | Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire |
| WASO | Wake after sleep onset |
References
- GBD 2021 Adult BMI Collaborators Global, Regional, and National Prevalence of Adult Overweight and Obesity, 1990-2021, with Forecasts to 2050: A Forecasting Study for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2025, 405, 813–838. [CrossRef]
- Johansen, V.B.I.; Petersen, J.; Lund, J.; Mathiesen, C.V.; Fenselau, H.; Clemmensen, C. Brain Control of Energy Homeostasis: Implications for Anti-Obesity Pharmacotherapy. Cell 2025, 188, 4178–4212.
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. New England Journal of Medicine 2022, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Tran, M.T.D.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. New England Journal of Medicine 2021, 384, 989–1002. [CrossRef]
- Wadden, T.A.; Chao, A.M.; Moore, M.; Tronieri, J.S.; Gilden, A.; Amaro, A.; Leonard, S.; Jakicic, J.M. The Role of Lifestyle Modification with Second-Generation Anti-Obesity Medications: Comparisons, Questions, and Clinical Opportunities. Curr Obes Rep 2023, 12, 453–473. [CrossRef]
- Pinkney, J.; Tarrant, M. Time for a New Agenda for Behavioural Treatment of Overweight and Obesity. Clin Obes 2024, 14, e12628. [CrossRef]
- MAYER, J.; ROY, P.; MITRA, K.P. Relation between Caloric Intake, Body Weight, and Physical Work. Am J Clin Nutr 1956, 4, 169–175. [CrossRef]
- Myers, A.; Gibbons, C.; Finlayson, G.; Blundell, J. Associations among Sedentary and Active Behaviours, Body Fat and Appetite Dysregulation: Investigating the Myth of Physical Inactivity and Obesity. Br J Sports Med 2017, 51, 1540–1544. [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, K.; Hopkins, M.; Blundell, J.; Finlayson, G. Does Habitual Physical Activity Increase the Sensitivity of the Appetite Control System? A Systematic Review. Sports Medicine 2016, 46, 1897–1919. [CrossRef]
- Long, S.J.; Hart, K.; Morgan, L.M. The Ability of Habitual Exercise to Influence Appetite and Food Intake in Response to High- and Low-Energy Preloads in Man. British Journal of Nutrition 2002, 87, 517–523. [CrossRef]
- King, N.A.; Caudwell, P.P.; Hopkins, M.; Stubbs, J.R.; Naslund, E.; Blundell, J.E. Dual-Process Action of Exercise on Appetite Control: Increase in Orexigenic Drive but Improvement in Meal-Induced Satiety. Am J Clin Nutr 2009, 90, 921–927. [CrossRef]
- Rosenkilde, M.; Reichkendler, M.H.; Auerbach, P.; Toräng, S.; Gram, A.S.; Ploug, T.; Holst, J.J.; Sjödin, A.; Stallknecht, B. Appetite Regulation in Overweight, Sedentary Men after Different Amounts of Endurance Exercise: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Appl Physiol 2013, 115, 1599–1609. [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.; Kulseng, B.; Rehfeld, J.F.; King, N.A.; Blundell, J.E. Effect of Chronic Exercise on Appetite Control in Overweight and Obese Individuals. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2013, 45, 805–812. [CrossRef]
- Dera, A.M.; Shen, T.; Thackray, A.E.; Hinton, E.C.; King, J.A.; James, L.; Morgan, P.S.; Rush, N.; Miyashita, M.; Batterham, R.L.; et al. The Influence of Physical Activity on Neural Responses to Visual Food Cues in Humans: A Systematic Review of Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2023, 152. [CrossRef]
- Al Khatib, H.K.; Harding, S. V.; Darzi, J.; Pot, G.K. The Effects of Partial Sleep Deprivation on Energy Balance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur J Clin Nutr 2017, 71, 614–624; SUBJMETA=2814,284,459,499,692,700;KWRD=LIFESTYLE+MODIFICATION,NUTRITION,RISK+FACTORS. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Shi, C.; Park, C.G.; Zhao, X.; Reutrakul, S. Effects of Sleep Restriction on Metabolism-Related Parameters in Healthy Adults: A Comprehensive Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sleep Med Rev 2019, 45, 18–30. [CrossRef]
- Chaput, J.P.; McHill, A.W.; Cox, R.C.; Broussard, J.L.; Dutil, C.; da Costa, B.G.G.; Sampasa-Kanyinga, H.; Wright, K.P. The Role of Insufficient Sleep and Circadian Misalignment in Obesity. Nature Reviews Endocrinology 2022 19:2 2022, 19, 82–97. [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, K.; Tasali, E.; Penev, P.; Van Cauter, E. Brief Communication: Sleep Curtailment in Healthy Young Men Is Associated with Decreased Leptin Levels, Elevated Ghrelin Levels, and Increased Hunger and Appetite. Ann Intern Med 2004, 141, 846–850. [CrossRef]
- Thackray, A.E.; Stensel, D.J. The Impact of Acute Exercise on Appetite Control: Current Insights and Future Perspectives. Appetite 2023, 186, 106557. [CrossRef]
- Blundell, J.E.; Beaulieu, K. The Complex Pattern of the Effects of Prolonged Frequent Exercise on Appetite Control, and Implications for Obesity. Appetite 2023, 183, 106482. [CrossRef]
- Biddle, G.J.H.; Henson, J.; Biddle, S.J.H.; Davies, M.J.; Khunti, K.; Rowlands, A. V.; Sutton, S.; Yates, T.; Edwardson, C.L. Modelling the Reallocation of Time Spent Sitting into Physical Activity: Isotemporal Substitution vs. Compositional Isotemporal Substitution. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18, 6210. [CrossRef]
- Covenant, A.; Yates, T.; Rowlands, A. V.; Dempsey, P.C.; Edwardson, C.L.; Hall, A.P.; Davies, M.J.; Henson, J. Replacing Sedentary Time with Sleep and Physical Activity: Associations with Physical Function and Wellbeing in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2024, 217. [CrossRef]
- Nagai, K.; Tamaki, K.; Kusunoki, H.; Wada, Y.; Tsuji, S.; Ito, M.; Sano, K.; Amano, M.; Shimomura, S.; Shinmura, K. Isotemporal Substitution of Sedentary Time with Physical Activity and Its Associations with Frailty Status. Clin Interv Aging 2018, 13, 1831–1836. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Nam, H.K.; Cho, S. Il Association between Accelerometer-Derived Physical Activity and Depression: A Cross-Sectional Study Using Isotemporal Substitution Analysis. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e078199. [CrossRef]
- Declaration of Helsinki World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Participants. JAMA 2024, 333, 71–74. [CrossRef]
- Dalton, M.; Finlayson, G.; Hill, A.; Blundell, J. Preliminary Validation and Principal Components Analysis of the Control of Eating Questionnaire (CoEQ) for the Experience of Food Craving. Eur J Clin Nutr 2015, 69, 1313–1317. [CrossRef]
- Compher, C.; Frankenfield, D.; Keim, N.; Roth-Yousey, L. Best Practice Methods to Apply to Measurement of Resting Metabolic Rate in Adults: A Systematic Review. J Am Diet Assoc 2006, 106, 881–903. [CrossRef]
- Weir, J.B. de V. New Methods for Calculating Metabolic Rate with Special Reference to Protein Metabolism. J Physiol 1949, 109, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- van Hees, V.; Migueles, J.H. GGIR. 2025. [CrossRef]
- Migueles, J.H.; Rowlands, A. V.; Huber, F.; Sabia, S.; Van Hees, V.T. GGIR: A Research Community–Driven Open Source R Package for Generating Physical Activity and Sleep Outcomes From Multi-Day Raw Accelerometer Data. J Meas Phys Behav 2019, 2, 188–196. [CrossRef]
- Van Hees, V.T.; Sabia, S.; Anderson, K.N.; Denton, S.J.; Oliver, J.; Catt, M.; Abell, J.G.; Kivimäki, M.; Trenell, M.I.; Singh-Manoux, A. A Novel, Open Access Method to Assess Sleep Duration Using a Wrist-Worn Accelerometer. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0142533. [CrossRef]
- Covenant, A.; Yates, T.; Rowlands, A. V.; Dempsey, P.C.; Edwardson, C.L.; Hall, A.P.; Davies, M.J.; Henson, J. Replacing Sedentary Time with Sleep and Physical Activity: Associations with Physical Function and Wellbeing in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2024, 217. [CrossRef]
- Van Hees, V.T.; Fang, Z.; Langford, J.; Assah, F.; Mohammad, A.; Da Silva, I.C.M.; Trenell, M.I.; White, T.; Wareham, N.J.; Brage, S. Autocalibration of Accelerometer Data for Free-Living Physical Activity Assessment Using Local Gravity and Temperature: An Evaluation on Four Continents. J Appl Physiol 2014, 117, 738–744. [CrossRef]
- van Hees, V.T.; Sabia, S.; Jones, S.E.; Wood, A.R.; Anderson, K.N.; Kivimäki, M.; Frayling, T.M.; Pack, A.I.; Bucan, M.; Trenell, M.I.; et al. Estimating Sleep Parameters Using an Accelerometer without Sleep Diary. Sci Rep 2018, 8. [CrossRef]
- HILDEBRAND, M.; VAN HEES, V.T.; HANSEN, B.H.; EKELUND, U. Age Group Comparability of Raw Accelerometer Output from Wrist- and Hip-Worn Monitors. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2014, 46, 1816–1824. [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, M.; Hansen, B.H.; van Hees, V.T.; Ekelund, U. Evaluation of Raw Acceleration Sedentary Thresholds in Children and Adults. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2017, 27, 1814–1823. [CrossRef]
- Alruwaili, A.; Nayeemullah, R.; Engin, B.; Malaikah, S.; James, L.; Sanders, J.P.; Thivel, D.; Thackray, A.E.; Stensel, D.J.; King, J.A.; et al. The Association of Cigarette Smoking with Appetite, Appetite-Related Hormones and Food Reward: A Matched-Pair Cohort Study. Appetite 2025, 214, 108194. [CrossRef]
- King, J.A.; Thackray, A.E.; Gibbons, C.; Martins, C.; Broom, D.R.; Stensel, D.J.; Papamargaritis, D.; Arsenyadis, F.; Finlayson, G.; Whelehan, G.; et al. The Mixed-Meal Tolerance Test as an Appetite Assay: Methodological and Practical Considerations. Int J Obes 2025, 1–16;SUBJMETA=163,2743,308,393,575,692;KWRD=OBESITY,TRANSLATIONAL+RESEARCH. [CrossRef]
- Flint, A.; Raben, A.; Blundell, J.E.; Astrup, A. Reproducibility, Power and Validity of Visual Analogue Scales in Assessment of Appetite Sensations in Single Test Meal Studies; 2000; Vol. 24;.
- Oustric, P.; Thivel, D.; Dalton, M.; Beaulieu, K.; Gibbons, C.; Hopkins, M.; Blundell, J.; Finlayson, G. Measuring Food Preference and Reward : Application and Cross-Cultural Adaptation of the Leeds Food Preference Questionnaire in Human Experimental Research. Food Qual Prefer 2020, 80, 103824. [CrossRef]
- Jetté, M.; Sidney, K.; Blümchen, G. Metabolic Equivalents (METS) in Exercise Testing, Exercise Prescription, and Evaluation of Functional Capacity. Clin Cardiol 1990, 13, 555–565. [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, G.; King, N.; Blundell, J. The Role of Implicit Wanting in Relation to Explicit Liking and Wanting for Food: Implications for Appetite Control. Appetite 2008, 50, 120–127. [CrossRef]
- Thackray, A.E.; Willis, S.A.; Clayton, D.J.; Broom, D.R.; Finlayson, G.; Goltz, F.R.; Sargeant, J.A.; Woods, R.M.; Stensel, D.J.; King, J.A. Influence of Short-Term Hyperenergetic, High-Fat Feeding on Appetite, Appetite-Related Hormones, and Food Reward in Healthy Men. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2635. [CrossRef]
- Biddle, G.J.H.; Henson, J.; Biddle, S.J.H.; Davies, M.J.; Khunti, K.; Rowlands, A. V.; Sutton, S.; Yates, T.; Edwardson, C.L. Modelling the Reallocation of Time Spent Sitting into Physical Activity: Isotemporal Substitution vs. Compositional Isotemporal Substitution. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18, 6210. [CrossRef]
- Stuart, E.A. Matching Methods for Causal Inference: A Review and a Look Forward. Stat Sci 2010, 25, 1. [CrossRef]
- Van Walleghen, E.L.; Orr, J.S.; Gentile, C.L.; Davy, K.P.; Davy, B.M. Habitual Physical Activity Differentially Affects Acute and Short-Term Energy Intake Regulation in Young and Older Adults. Int J Obes 2007, 31, 1277–1285. [CrossRef]
- Gregersen, N.T.; Møller, B.K.; Raben, A.; Kristensen, S.T.; Holm, L.; Flint, A.; Astrup, A. Determinants of Appetite Ratings: The Role of Age, Gender, BMI, Physical Activity, Smoking Habits, and Diet/Weight Concern. Food Nutr Res 2011, 55. [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, K.; Hopkins, M.; Long, C.; Blundell, J.; Finlayson, G. High Habitual Physical Activity Improves Acute Energy Compensation in Nonobese Adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2017, 49, 2268–2275. [CrossRef]
- Dorling, J.; Broom, D.R.; Burns, S.F.; Clayton, D.J.; Deighton, K.; James, L.J.; King, J.A.; Miyashita, M.; Thackray, A.E.; Batterham, R.L.; et al. Acute and Chronic Effects of Exercise on Appetite, Energy Intake, and Appetite-Related Hormones: The Modulating Effect of Adiposity, Sex, and Habitual Physical Activity. Nutrients 2018, 10. [CrossRef]
- Lund, M.T.; Taudorf, L.; Hartmann, B.; Helge, J.W.; Holst, J.J.; Dela, F. Meal Induced Gut Hormone Secretion Is Altered in Aerobically Trained Compared to Sedentary Young Healthy Males. Eur J Appl Physiol 2013, 113, 2737–2747. [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Liang, T.; Wang, G.; Li, Z. Ghrelin, A Gastrointestinal Hormone, Regulates Energy Balance and Lipid Metabolism. Biosci Rep 2018, 38. [CrossRef]
- Le Roux, C.W.; Batterham, R.L.; Aylwin, S.J.B.; Patterson, M.; Borg, C.M.; Wynne, K.J.; Kent, A.; Vincent, R.P.; Gardiner, J.; Ghatei, M.A.; et al. Attenuated Peptide YY Release in Obese Subjects Is Associated with Reduced Satiety. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 3–8. [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.M. Leptin and the Endocrine Control of Energy Balance. Nat Metab 2019, 1, 754–764. [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, M.B.E.; Black, A.E. Markers of the Validity of Reported Energy Intake. Journal of Nutrition 2003, 133. [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, G.; King, N.; Blundell, J. The Role of Implicit Wanting in Relation to Explicit Liking and Wanting for Food: Implications for Appetite Control. Appetite 2008, 50, 120–127. [CrossRef]
- Dalton, M.; Finlayson, G.; Hill, A.; Blundell, J. Preliminary Validation and Principal Components Analysis of the Control of Eating Questionnaire (CoEQ) for the Experience of Food Craving. Eur J Clin Nutr 2015, 69, 1313–1317. [CrossRef]
- Stunkard, A.J.; Messick, S. The Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire to Measure Dietary Restraint, Disinhibition and Hunger. J Psychosom Res 1985, 29, 71–83. [CrossRef]
- Oustric, P.; Myers, A.; Gibbons, C.; Buckland, N.; Dalton, M.; Long, C.; Beaulieu, K.; Sophie Hollingworth, S.; Finlayson, G. Are Objectively Measured Free-Living Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour Associated with Control over Eating and Food Preferences in Women? Appetite 2018, 123, 465. [CrossRef]
- Horner, K.M.; Finlayson, G.; Byrne, N.M.; King, N.A. Food Reward in Active Compared to Inactive Men: Roles for Gastric Emptying and Body Fat. Physiol Behav 2016, 160, 43–49. [CrossRef]
- Killgore, W.D.S.; Kipman, M.; Schwab, Z.J.; Tkachenko, O.; Preer, L.; Gogel, H.; Bark, J.S.; Mundy, E.A.; Olson, E.A.; Weber, M. Physical Exercise and Brain Responses to Images of High-Calorie Food. Neuroreport 2013, 24, 962–967. [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; O’Connor, S.G.; Belcher, B.R.; Page, K.A. Effects of Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior on Brain Response to High-Calorie Food Cues in Young Adults. Obesity 2018, 26, 540–546. [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, K.; Oustric, P.; Finlayson, G. The Impact of Physical Activity on Food Reward: Review and Conceptual Synthesis of Evidence from Observational, Acute, and Chronic Exercise Training Studies. Curr Obes Rep 2020, 9, 63–80. [CrossRef]
| Variable | |
| Sex (male) | 70 (58.8%) |
| Ethnicity | |
| White | 53 (44.5%) |
| Indian | 28 (23.5%) |
| Asian | 25 (21.0%) |
| Mixed | 6 (5.0%) |
| Black | 3 (2.5%) |
| Arab | 2 (1.7%) |
| Latino | 2 (1.7%) |
| Age (years) | 24 (9) |
| Body mass (kg) | 70.5 ± 12.8 |
| BMI (kg·m-2) | 23.6 (5.1) |
| Movement behaviours | |
| Sedentary time (min·d-1) | 704 ± 103 |
| LPA (min·d-1) | 194 ± 53 |
| MVPA (min·d-1) | 112 ± 50 |
| Sleep time during sleep period (min·d-1) | 336 ± 76 |
| WASO during sleep period (min·d-1) | 95 ± 49 |
| Total sleep period (min·d-1) | 430 ± 68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





