Submitted:
31 August 2025
Posted:
01 September 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Type 2 Diabetes: Diagnosis, Classification, and Risk Factors
2.1. Diabetes Diagnosis
2.2. Classification of Diabetes
2.3. Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
2.4. Characteristics of Type 2 Diabetes
3. Triglycerides
3.1. Fatty Acids
3.1.1. Fatty Acid Structure
3.1.2. Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
3.1.3. Fatty Acid Beta-Oxidation (β-Oxidation)
3.2. Glycerol
3.3. Triglyceride Biosynthesis from Glycerol and Fatty Acid
3.4. Triglyceride Digestion, Absorption, Delivery, and Storage
3.5. Classification of Triglyceride Levels in Humans
- Normal: <150 mg/dL (1.7 mmol/L)
- Borderline high: 150–199 mg/dL (1.8–2.2 mmol/L)
- High: 200–499 mg/dL (2.3–5.6 mmol/L)
- Very high: ≥500 mg/dL (≥5.7 mmol/L)
4. Glucose Metabolism
4.1. Common Glucose Metabolism Pathways
4.2. Conversion of Glucose to Triglycerides
5. Association of High Triglycerides with Diabetes Prevalence, Incidence, and Mortality
5.1. Triglyceride Levels Are Positively Associated with Plasma Glucose Levels
5.2. Association of High Triglycerides with Diabetes Prevalence, Incidence, and Mortality
6. High Carbohydrate Intake Leads to Ectopic Triglyceride Deposition
7. Ectopic Triglyceride Deposition Induces Insulin Resistance
7.1. Insulin Signaling in Regulating Circulating Glucose
- Akt phosphorylates and inactivates glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3), resulting in activation of glycogen synthase and increased glycogen synthesis [141].
- Akt phosphorylates tuberous sclerosis complex 2 (TSC2) and proline-rich Akt substrate of 40 kDa (PRAS40), leading to activation of mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) [145,146]. mTORC1 promotes cleavage and nuclear translocation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP), which upregulates lipogenic gene expression [147,148].
- Akt phosphorylates TBC1D4/AS160 (TBC1 domain family member 1/Akt substrate of 160 kDa), a Rab GTPase-activating protein, promoting GLUT4 vesicle trafficking to the membrane. In the absence of insulin, AS160 inhibits GLUT4 movement; upon insulin stimulation, AS160 is phosphorylated and inactivated, allowing vesicle translocation and fusion with the membrane [153].
- The activated insulin receptor binds APS (adapter protein with PH and SH2 domains), which recruits a complex containing c-CBL and c-CBL-associated protein. This leads to c-CBL phosphorylation and activation [158,159]. Activated c-CBL recruits CRK, which activates TC10 (RhoQ), a small GTPase. TC10 interacts with the exocyst tethering complex, enabling docking of GLUT4 vesicles at the cell surface [158,160].
7.2. Insulin Resistance
7.3. Ectopic Triglyceride Deposition Induces Insulin Resistance
8. Ectopic Triglyceride Deposition Induces Hyperinsulinemia
8.1. Insulin Secretion Signaling Pathway
8.2. Acute Increase in Triglycerides and Fatty Acids Potentiate Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion
8.3. Ectopic Triglyceride Deposition Promotes Adaptive β-Cell Proliferation as a Response to Insulin Resistance
8.4. Ectopic Triglyceride Deposition Leads to Hyperinsulinemia
9. Ectopic Triglyceride Deposition Impairs β-Cell Function over Time
9.1. Chronic Exposure to Fatty Acids Impairs GSIS
9.2. Inhibition of Fatty Acids on GSIS Is Reversible
9.3. Chronic Ectopic Triglyceride Deposition in β-Cells Inhibits Glucose-Induced Increase in Insulin Gene Expression
9.4. High Triglycerides Cause Pancreatitis
10. Long-Term Ectopic Triglyceride Deposition in the Liver Enhances Gluconeogenesis
10.1. Glucoseogenesis from Triglycerides
10.2. Long-Term Ectopic Triglyceride Deposition in the Liver Enhances Gluconeogenesis
11. Severe and Long-Term Ectopic Triglyceride Deposition Induces β-Cell Apoptosis
11.1. Ceramide Formation and β-Cell Apoptosis
11.2. Fatty Acid-Induced ER Stress and Apoptosis
11.3. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
11.4. Apoptosis and Type 2 Diabetes Progression
12. Examples of Reducing Ectopic Triglyceride Deposition in Type 2 Diabetes Remission
12.1. Reversal of Type 2 Diabetes by Bariatric Surgery
12.2. Reversal of Type 2 Diabetes by Dietary Energy Restriction
13. Lowering Triglycerides by Fibrates, But Not Omega-3 Fatty Acids or Niacin, Decreases Insulin Resistance and Protects Against Type 2 Diabetes
14. Ectopic Triglyceride Deposition and Cardiometabolic Diseases
15. Conclusion
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hudish, L. I.; Reusch, J. E.; Sussel, L. , β Cell dysfunction during progression of metabolic syndrome to type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Invest. 2019, 129, 4001–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDF Diabetes Atlas 11th Edition Committee, IDF Diabetes Atlas 11th Edition. Available from https://diabetesatlas.org/media/uploads/sites/3/2025/04/IDF_Atlas_11th_Edition_2025.pdf. 2025.
- GBD 2021 Diabetes Collaborators, Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2023, 402, 203–234. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization, Diabetes. Available at https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes. Accessed on 18 October 2024.
- Wang, Y.; Magliano, D. J. , Special Issue: “New Trends in Diabetes, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Diseases—2nd Edition”. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Magliano, D. J. , Special Issue: “New Trends in Diabetes, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Diseases”. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, E. D.; Lin, J.; Mahoney, T.; Ume, N.; Yang, G.; Gabbay, R. A.; ElSayed, N. A.; Bannuru, R. R. , Economic Costs of Diabetes in the U.S. in 2022. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F. B.; Manson, J. E.; Stampfer, M. J.; Colditz, G.; Liu, S.; Solomon, C. G.; Willett, W. C. , Diet, lifestyle, and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 790–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomilehto, J.; Lindström, J.; Eriksson, J. G.; Valle, T. T.; Hämäläinen, H.; Ilanne-Parikka, P.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Laakso, M.; Louheranta, A.; Rastas, M.; Salminen, V.; Uusitupa, M. , Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1343–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowler, W. C.; Barrett-Connor, E.; Fowler, S. E.; Hamman, R. F.; Lachin, J. M.; Walker, E. A.; Nathan, D. M. , Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 393–403. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. , Higher fasting triglyceride predicts higher risks of diabetes mortality in US adults. Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Ma, S.; Qian, T.; Sun, H.; Xu, Q.; Hou, X.; Hu, W.; Zhang, G.; Jelinic, M.; Habenicht, A. J.; Song, D.; Yang, G. , Normal Triglycerides Are Positively Associated with Plasma Glucose and Risk for Type 2 Diabetes in Chinese Adults. Preprints 2024, 2024011501. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, N.-Q. , Non-Fasting Plasma Triglycerides Are Positively Associated with Diabetes Mortality in a Representative US Adult Population. Targets 2024, 2, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirosh, A.; Shai, I.; Bitzur, R.; Kochba, I.; Tekes-Manova, D.; Israeli, E.; Shochat, T.; Rudich, A. , Changes in triglyceride levels over time and risk of type 2 diabetes in young men. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 2032–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Magliano, D. J.; Charchar, F. J.; Sobey, C. G.; Drummond, G. R.; Golledge, J. , Fasting triglycerides are positively associated with cardiovascular mortality risk in people with diabetes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 826–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Oishi, A.; Han, S. I.; Kumagai, K.; Ohno, H.; Mizunoe, Y.; Iwasaki, H.; Sekiya, M.; Matsuzaka, T.; Shimano, H. , The Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor α (PPARα) Agonist Pemafibrate Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenenbaum, A.; Motro, M.; Fisman, E. Z.; Schwammenthal, E.; Adler, Y.; Goldenberg, I.; Leor, J.; Boyko, V.; Mandelzweig, L.; Behar, S. , Peroxisome Proliferator–Activated Receptor Ligand Bezafibrate for Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Patients With Coronary Artery Disease. Circulation 2004, 109, 2197–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The ACCORD Study Group, Effects of Combination Lipid Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. New England Journal of Medicine 2010, 362, 1563–1574. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keech, A. C.; Mitchell, P.; Summanen, P. A.; O’Day, J.; Davis, T. M.; Moffitt, M. S.; Taskinen, M. R.; Simes, R. J.; Tse, D.; Williamson, E.; Merrifield, A.; Laatikainen, L. T.; d’Emden, M. C.; Crimet, D. C.; O’Connell, R. L.; Colman, P. G. , Effect of fenofibrate on the need for laser treatment for diabetic retinopathy (FIELD study): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2007, 370, 1687–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruckert, E.; Baccara-Dinet, M.; Eschwege, E. , Low HDL-cholesterol is common in European Type 2 diabetic patients receiving treatment for dyslipidaemia: data from a pan-European survey. Diabet. Med. 2007, 24, 388–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Philip, S.; Granowitz, C.; Toth, P. P.; Wong, N. D. , Residual hypertriglyceridemia and estimated atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk by statin use in US adults with diabetes: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2014. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 2307–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera Echegoyen, F. X.; Szeto, A.; Mendez, A. J.; Garg, R.; Goldberg, R. B. , The nature and characteristics of hypertriglyceridemia in a large cohort with type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complications 2023, 37, 108387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElSayed, N. A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V. R.; Bannuru, R. R.; Brown, F. M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B. S.; Hilliard, M. E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E. L.; Kahan, S.; Khunti, K.; Leon, J.; Lyons, S. K.; Perry, M. L.; Prahalad, P.; Pratley, R. E.; Seley, J. J.; Stanton, R. C.; Gabbay, R. A.; on behalf of the American Diabetes, A., 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, (Suppl 1), S19–s40.
- The Royal Australian College of General Practitioners, General practice management of type 2 diabetes: 2016–18. East Melbourne, Vic: RACGP, 2016. Available from https://www.diabetesaustralia.com.au/wp-content/uploads/General-Practice-Management-of-Type-2-Diabetes-2016-18.pdf.
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Y. , Late non-fasting plasma glucose predicts cardiovascular mortality independent of hemoglobin A1c. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association, 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, (Supplement 1), S15–S33.
- Cowie, C. C.; Rust, K. F.; Byrd-Holt, D. D.; Gregg, E. W.; Ford, E. S.; Geiss, L. S.; Bainbridge, K. E.; Fradkin, J. E., Prevalence of diabetes and high risk for diabetes using A1C criteria in the U.S. population in 1988-2006. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 562–8.
- Bergman, M.; Manco, M.; Satman, I.; Chan, J.; Schmidt, M. I.; Sesti, G.; Vanessa Fiorentino, T.; Abdul-Ghani, M.; Jagannathan, R.; Kumar Thyparambil Aravindakshan, P.; Gabriel, R.; Mohan, V.; Buysschaert, M.; Bennakhi, A.; Pascal Kengne, A.; Dorcely, B.; Nilsson, P. M.; Tuomi, T.; Battelino, T.; Hussain, A.; Ceriello, A.; Tuomilehto, J. , International Diabetes Federation Position Statement on the 1-hour post-load plasma glucose for the diagnosis of intermediate hyperglycaemia and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 209, 111589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, R.; Buysschaert, M.; Medina, J. L.; Katz, K.; Musleh, S.; Dorcely, B.; Bergman, M. , The 1-h post-load plasma glucose as a novel biomarker for diagnosing dysglycemia. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Aberson, C. L.; Charchar, F. J.; Ceriello, A. , Postprandial Plasma Glucose between 4 and 7.9 h May Be a Potential Diagnostic Marker for Diabetes. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Yang, G., The 2-Hour Plasma Glucose Levels During OGTT, Conducted in the Postprandial Period Between 4 and 7.9 Hours, Are Associated With the Diagnosis of Diabetes, Diabetes Mortality, and Cardiovascular Mortality. Preprints 2024, 2024070510. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Habenicht, A.J. R.; Golledge, J.; Giovannucci, E. L.; Ceriello, A. , Postprandial Plasma Glucose With a Fasting Time of 4–7.9 h Is Positively Associated With Cancer Mortality in US Adults. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2024, 40, e70008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y. Postprandial Plasma Glucose Measured from Blood Taken between, 4.; 79 h Is Positively Associated with Mortality from Hypertension Cardiovascular Disease, J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2024, 11, 53.
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee, 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, (Supplement_1), S20-S42.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Diabetes Risk Factors. Available at https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/risk-factors/index.html. Accessed on 18 June 2025.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, Type 2 diabetes: prevention in people at high risk. Available at https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ph38. Accessed on 17 June 2025. 17 June.
- Fletcher, B.; Gulanick, M. ; Lamendola C, Risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus, J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2002, 16, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healthdirct, Type 2 diabetes. Available at https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/type-2-diabetes Accessed on 19 June 2025.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes. Available at https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/risk-factors-type-2-diabetes. Accessed on 12 June 2025.
- Wang, Y. Tree nut consumption is associated with higher sex hormone-binding globulin levels in premenopausal US women. Nutr. Res. 2021, 93, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Y. Tree nut consumption is associated with a lower risk of hyperestrogenism in men. Nutr. Res. 2022, 98, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Witting, P. K.; Charchar, F. J.; Sobey, C. G.; Drummond, G. R.; Golledge, J. , Dietary fatty acids and mortality risk from heart disease in US adults: an analysis based on NHANES. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Stage 1 hypertension risk of cardiovascular disease mortality in United States adults with or without diabetes. J. Hypertens. 2022, 40, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Qian, T.; Sun, H.; Xu, Q.; Hou, X.; Hu, W.; Zhang, G.; Song, D.; Fang, Y.; Magliano, D. J.; Witting, P. K.; Golledge, J.; Yang, G. , Hypouricemia is a risk factor for diabetes in Chinese adults. Obesity Medicine 2022, 31, 100405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Qian, T.; Sun, H.; Xu, Q.; Hou, X.; Hu, W.; Zhang, G.; Fang, Y.; Song, D.; Chai, Z.; Magliano, D. J.; Golledge, J.; Wang, Y. , Both low and high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol are risk factors for diabetes diagnosis in Chinese adults. Diabetes Epidemiology and Management 2022, 6, 100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Ma, S.; Qian, T.; Sun, H.; Xu, Q.; Hou, X.; Hu, W.; Zhang, G.; Fang, Y.; Yang, G. , Higher triglyceride is a risk factor for diabetes in adults with normal triglyceride in Chinese adults. Research Square 2022. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. , Definition, prevalence, and risk factors of low sex hormone-binding globulin in US adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2021, 106, e3946–e3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis-Herrera, C.; Triplitt, C.; Cersosimo, E.; DeFronzo, R. A., Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. In Endotext, Feingold, K. R.; Anawalt, B.; Boyce, A.; Chrousos, G.; de Herder, W. W.; Dhatariya, K.; Dungan, K.; Hershman, J. M.; Hofland, J.; Kalra, S.; Kaltsas, G.; Koch, C.; Kopp, P.; Korbonits, M.; Kovacs, C. S.; Kuohung, W.; Laferrère, B.; Levy, M.; McGee, E. A.; McLachlan, R.; Morley, J. E.; New, M.; Purnell, J.; Sahay, R.; Singer, F.; Sperling, M. A.; Stratakis, C. A.; Trence, D. L.; Wilson, D. P., Eds. MDText: South Dartmouth: 2021.
- Taylor, R. Type 2 diabetes: etiology and reversibility. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 1047–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyer, C.; Bogardus, C.; Mott, D. M.; Pratley, R. E. , The natural history of insulin secretory dysfunction and insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Invest. 1999, 104, 787–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Vrablik, M. , Homeostasis Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance Mediates the Positive Association of Triglycerides with Diabetes. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Y. , Postabsorptive homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance is a reliable biomarker for cardiovascular disease mortality and all-cause mortality. Diabetes Epidemiology and Management 2021, 6, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Mantovani, A. ; Targher G, Hypertension diabetes atherosclerosis NASH: Cause or consequence?, J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pories, W. J.; MacDonald, K. G., Jr.; Morgan, E. J.; Sinha, M. K.; Dohm, G. L.; Swanson, M. S.; Barakat, H. A.; Khazanie, P. G.; Leggett-Frazier, N.; Long, S. D. , Surgical treatment of obesity and its effect on diabetes: 10-y follow-up. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, (2 Suppl), 582s–585s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S. E. , The relative contributions of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction to the pathophysiology of Type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A. E.; Janson, J.; Bonner-Weir, S.; Ritzel, R.; Rizza, R. A.; Butler, P. C. , β-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003, 52, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, S. C.; Austin, E.; Assouline-Thomas, B. a.; Kapeluto, J.; Blaichman, J.; Moosavi, M.; Petropavlovskaia, M.; Rosenberg, L. , β-Cell Mass Dynamics and Islet Cell Plasticity in Human Type 2 Diabetes. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1462–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, R. C.; Cull, C. A.; Stratton, I. M.; Manley, S. E.; Kohner, E. M.; Matthews, D. R.; Haw., N.; Levy, J. C.; Holman, R. R., U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study 16: Overview of 6 Years’ Therapy of Type II Diabetes: A Progressive Disease. Diabetes 1995, 44, 1249 - 1258.
- Lim, E. L.; Hollingsworth, K. G.; Aribisala, B. S.; Chen, M. J.; Mathers, J. C.; Taylor, R. , Reversal of type 2 diabetes: normalisation of beta cell function in association with decreased pancreas and liver triacylglycerol. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 2506–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victoria State Government, Diabetes and insulin. Available at https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/diabetes-and-insulin Accessed on 26 June 2025. 26 June.
- Andersen, I. R.; Søndergaard, E.; Sørensen, L. P.; Nellemann, B.; Gormsen, L. C.; Jensen, M. D.; Nielsen, S. , Increased VLDL-TG Fatty Acid Storage in Skeletal Muscle in Men With Type 2 Diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2017, 102, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, M.; Roden, M. , Molecular mechanisms of lipid-induced insulin resistance in muscle, liver and vasculature. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2005, 7, 621–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levelt, E.; Pavlides, M.; Banerjee, R.; Mahmod, M.; Kelly, C.; Sellwood, J.; Ariga, R.; Thomas, S.; Francis, J.; Rodgers, C.; Clarke, W.; Sabharwal, N.; Antoniades, C.; Schneider, J.; Robson, M.; Clarke, K.; Karamitsos, T.; Rider, O. ; Neubauer S, Ectopic Visceral Fat Deposition in Lean Obese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes, J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaborit, B.; Abdesselam, I.; Kober, F.; Jacquier, A.; Ronsin, O.; Emungania, O.; Lesavre, N.; Alessi, M. C.; Martin, J. C.; Bernard, M.; Dutour, A. , Ectopic fat storage in the pancreas using 1H-MRS: importance of diabetic status and modulation with bariatric surgery-induced weight loss. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2015, 39, 480–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, M. P.; Lamon-Fava, S.; Fielding, R. A. , Skeletal muscle lipid deposition and insulin resistance: effect of dietary fatty acids and exercise. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2007, 85, 662–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, G. I. , Ectopic fat in insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and cardiometabolic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1131–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, P.; Weiskirchen, R. , Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance. Current Tissue Microenvironment Reports 2024, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, G.; Murru, E.; Banni, S.; Manca, C. , Palmitic Acid: Physiological Role, Metabolism and Nutritional Implications. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murru, E.; Manca, C.; Carta, G.; Banni, S. , Impact of Dietary Palmitic Acid on Lipid Metabolism. Frontiers in Nutrition 2022, 9, 861664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, S.; Bermudez, B.; Montserrat-de la Paz, S.; Jaramillo, S.; Varela, L. M.; Ortega-Gomez, A.; Abia, R.; Muriana, F. J. G. , Membrane composition and dynamics: A target of bioactive virgin olive oil constituents. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 1638–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, M. A.; Gad, M. Z. , Omega-9 fatty acids: potential roles in inflammation and cancer management. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2022, 20, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotronen, A.; Seppänen-Laakso, T.; Westerbacka, J.; Kiviluoto, T.; Arola, J.; Ruskeepää, A.-L.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Orešič, M. , Comparison of Lipid and Fatty Acid Composition of the Liver, Subcutaneous and Intra-abdominal Adipose Tissue, and Serum. Obesity 2010, 18, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, J.; Garg, M.; Bilgin, A.; Grant, R. , Relationship between central and peripheral fatty acids in humans. Lipids Health Dis. 2013, 12, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, A.; Nälsén, C.; Tengblad, S.; Vessby, B. , Fatty acid composition of skeletal muscle reflects dietary fat composition in humans123. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2002, 76, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y. P.; Grill, V. E. , Long-term exposure of rat pancreatic islets to fatty acids inhibits glucose-induced insulin secretion and biosynthesis through a glucose fatty acid cycle. J. Clin. Invest. 1994, 93, 870–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremlich, S.; Bonny, C.; Waeber, G. ; Thorens B, Fatty acids decrease IDX-1 expression in rat pancreatic islets reduce GLUT2, glucokinase insulin somatostatin levels, J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 30261–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maedler, K.; Spinas, G. A.; Dyntar, D.; Moritz, W.; Kaiser, N.; Donath, M. Y. , Distinct effects of saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids on beta-cell turnover and function. Diabetes 2001, 50, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D. L.; Cox, M. M., Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. Eight Edition. In New York: Worth Publishing: 2021.
- Paiva, P.; Medina, F. E.; Viegas, M.; Ferreira, P.; Neves, R. P. P.; Sousa, J. P. M.; Ramos, M. J.; Fernandes, P. A. , Animal Fatty Acid Synthase: A Chemical Nanofactory. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 9502–9553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumanov, S.; Bulusu, V.; Kamphorst, J. , Analysis of Fatty Acid Metabolism Using Stable Isotope Tracers and Mass Spectrometry. Methods Enzymol. 2015, 561. [Google Scholar]
- Talley, J. T.; Mohiuddin, S. S., Biochemistry, fatty acid oxidation. In StatPearls [Internet], StatPearls Publishing: 2023.
- Alves-Bezerra, M.; Cohen, D. E. , Triglyceride Metabolism in the Liver. Compr Physiol 2017, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, C. R.; Hoy, A. J.; Turner, N.; Watt, M. J.; Allen, T. L.; Carpenter, K.; Cooney, G. J.; Febbraio, M. A.; Kraegen, E. W. , Overexpression of carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1 in skeletal muscle is sufficient to enhance fatty acid oxidation and improve high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 2009, 58, 550–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, F. B.; Constantin-Teodosiu, D.; Greenhaff, P. L. , New insights concerning the role of carnitine in the regulation of fuel metabolism in skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 2007, (Pt 2) Pt 2, 431–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.; Narayan, K.M. V.; Chan, J. C. N.; Jha, P.; Shah, B. R. , Pathophysiology, phenotypes and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Indian and Chinese populations. Nature Reviews Endocrinology 2022, 18, 413–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampe, M. A.; Burlingame, A. L.; Whitney, J.; Williams, M. L.; Brown, B. E.; Roitman, E.; Elias, P. M. , Human stratum corneum lipids: characterization and regional variations. J. Lipid Res. 1983, 24, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T. T.; Liu, X. T.; Chen, Q. X.; Shi, Y. , Lipase Inhibitors for Obesity: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birari, R. B.; Bhutani, K. K. , Pancreatic lipase inhibitors from natural sources: unexplored potential. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lengsfeld, H.; Beaumier-Gallon, G.; Chahinian, H.; De Caro, A.; Verger, R.; Laugier, R.; Carrière, F., Physiology of gastrointestinal lipolysis and therapeutical use of lipases and digestive lipase inhibitors. Lipases and phospholipases in drug development: from biochemistry to molecular pharmacology 2004, 195-229.
- Carriere, F.; Barrowman, J. A.; Verger, R.; Laugier, R. , Secretion and contribution to lipolysis of gastric and pancreatic lipases during a test meal in humans. Gastroenterology 1993, 105, 876–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrière, F.; Renou, C.; Ransac, S.; Lopez, V.; De Caro, J.; Ferrato, F.; De Caro, A.; Fleury, A.; Sanwald-Ducray, P.; Lengsfeld, H.; Beglinger, C.; Hadvary, P.; Verger, R. ; Laugier R, Inhibition of gastrointestinal lipolysis by Orlistat during digestion of test meals in healthy volunteers Am, J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2001, 281, G16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basque, J. R.; Ménard, D. , Establishment of culture systems of human gastric epithelium for the study of pepsinogen and gastric lipase synthesis and secretion. Microsc Res Tech 2000, 48, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloulou, A.; Carrière, F. , Gastric lipase: an extremophilic interfacial enzyme with medical applications. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 2008, 65, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrière, F.; Grandval, P.; Renou, C.; Palomba, A.; Priéri, F.; Giallo, J.; Henniges, F.; Sander-Struckmeier, S.; Laugier, R. , Quantitative study of digestive enzyme secretion and gastrointestinal lipolysis in chronic pancreatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 3, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, B. V.; Mattes, R. D. , Lingual lipase activity in the orosensory detection of fat by humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2014, 306, R879–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamosh, M. , Lingual and gastric lipases. Nutrition 1990, 6, 421–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lowe, M. E. , The triglyceride lipases of the pancreas. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, N. , Interaction Parameters for the Formation of Mixed Micelles and Partitioning of Solutes in Them: A Review. AppliedChem 2024, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, N. ; Lindenbaum S, Kinetics thermodynamics of the formation of mixed micelles of egg phosphatidylcholine bile salts, J. Lipid Res. 1984, 25, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, J. R.; Irvine, S. A.; Ramji, D. P. , Lipoprotein lipase: structure, function, regulation, and role in disease. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 2002, 80, 753–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, K. H.; Neher, S. B. , Structure of dimeric lipoprotein lipase reveals a pore adjacent to the active site. Nature Communications 2023, 14, 2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.; Stone, N. J.; Ballantyne, C.; Bittner, V.; Criqui, M. H.; Ginsberg, H. N.; Goldberg, A. C.; Howard, W. J.; Jacobson, M. S.; Kris-Etherton, P. M.; Lennie, T. A.; Levi, M.; Mazzone, T.; Pennathur, S. , Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011, 123, 2292–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althaher, A. R. , An Overview of Hormone-Sensitive Lipase (HSL). ScientificWorldJournal 2022, 2022, 1964684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, R.; Goulet, N.; Mauger, J. F.; Imbeault, P. , Physiological Responses to Hypoxia on Triglyceride Levels. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 730935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, A.; Arranz-Martínez, E.; López-Uriarte, B.; Rivera-Teijido, M.; Palacios-Martínez, D.; Dávila-Blázquez, G. M.; Rosillo-González, A.; González-Posada Delgado, J. A.; Mariño-Suárez, J. E.; Revilla-Pascual, E.; Quintana-Gómez, J. L.; Íscar-Valenzuela, I.; Alonso-Roca, R.; Javierre-Miranda, A. P.; Escrivá-Ferrairó, R. A.; Tello-Meco, I.; Ibarra-Sánchez, A. M.; Gutiérrez Sánchez, M. I.; Iglesias Quintana, J. R.; Hernández-Beltrán, M. I.; Pérez Fernández, M.; Barrios-Rueda, E.; Pérez Muñoz, R.; Prieto Marcos, M.; Delgado Rodríguez, S.; Pleite Raposo, R.; Rodríguez-Cabanillas, R.; Morales-Chico, M. R.; Fernández-Pacheco Vila, D.; Remón-Pérez, B.; Del Villar Redondo, M. J.; Reguillo-Díaz, J.; Aguilera Reija, P.; Rodríguez Rodríguez, A. O.; Gómez-Fernández, O.; Antón-Sanz, M. D. C.; Sánchez-Calso, A.; Doria-Carlin, N. A.; Frías-Vargas, M. J., Prevalence of hypertriglyceridemia in adults and related cardiometabolic factors. SIMETAP-HTG study. Clin Investig Arterioscler 2020, 32, 242-255.
- Pejic, R. N.; Lee, D. T. , Hypertriglyceridemia. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2006, 19, 310–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, O. A.; Mohiuddin, S. S. , Biochemistry, Oxidative Phosphorylation. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553192. 2023.
- Softic, S.; Gupta, M. K.; Wang, G. X.; Fujisaka, S.; O’Neill, B. T.; Rao, T. N.; Willoughby, J.; Harbison, C.; Fitzgerald, K.; Ilkayeva, O.; Newgard, C. B.; Cohen, D. E.; Kahn, C. R. , Divergent effects of glucose and fructose on hepatic lipogenesis and insulin signaling. J. Clin. Invest. 2017, 127, 4059–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.; Blanco, G. , Chapter 15 - Lipid Metabolism. In Med. Biochem., Blanco, A.; Blanco, G., Eds. Academic Press: 2017; pp 325-365.
- Patra, K. C.; Hay, N. , The pentose phosphate pathway and cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 347–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mawali, A.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Jayapal, S. K.; Morsi, M.; Pinto, A. D.; Al-Shekaili, W.; Al-Kharusi, H.; Al-Balushi, Z.; Idikula, J. , Prevalence and risk factors of diabetes in a large community-based study in the Sultanate of Oman: STEPS survey 2017. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrutia, I.; Martín-Nieto, A.; Martínez, R.; Casanovas-Marsal, J. O.; Aguayo, A.; Del Olmo, J.; Arana, E.; Fernandez-Rubio, E.; Castaño, L.; Gaztambide, S. , Incidence of diabetes mellitus and associated risk factors in the adult population of the Basque country, Spain. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesini, G.; Brizi, M.; Bianchi, G.; Tomassetti, S.; Bugianesi, E.; Lenzi, M.; McCullough, A. J.; Natale, S.; Forlani, G.; Melchionda, N. , Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Feature of the Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1844–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkanawati, R. Y.; Sumiwi, S. A.; Levita, J. , Impact of Lipids on Insulin Resistance: Insights from Human and Animal Studies. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2024, 18, 3337–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C. Y.; Huang, J. F.; Hsieh, M. Y.; Lee, L. P.; Hou, N. J.; Yu, M. L.; Chuang, W. L. , Links between triglyceride levels, hepatitis C virus infection and diabetes. Gut 2007, 56, 1167–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, R. B., Jr.; Hamman, R. F.; Karter, A. J.; Mykkanen, L.; Wagenknecht, L. E.; Haffner, S. M. , Cardiovascular disease risk factors predict the development of type 2 diabetes: the insulin resistance atherosclerosis study. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2234–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P. W.; Meigs, J. B.; Sullivan, L.; Fox, C. S.; Nathan, D. M.; D’Agostino, R. B., Sr. , Prediction of incident diabetes mellitus in middle-aged adults: the Framingham Offspring Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1068–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, F.; Song, J.; Cao, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, K.; Feng, S. ; Li W-D, Triglyceride is an independent predictor of type 2 diabetes among middle-aged older adults: a prospective study with 8-year follow-ups in two cohorts, J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, K.; Sugawara, A.; Heianza, Y.; Sairenchi, T.; Irie, F.; Iso, H.; Doi, M.; Shimano, H.; Watanabe, H.; Sone, H.; Ota, H. , Utility of the triglyceride level for predicting incident diabetes mellitus according to the fasting status and body mass index category: the Ibaraki Prefectural Health Study. J Atheroscler Thromb 2014, 21, 1152–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimentidis, Y. C.; Chougule, A.; Arora, A.; Frazier-Wood, A. C.; Hsu, C. H. , Triglyceride-Increasing Alleles Associated with Protection against Type-2 Diabetes. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshara, A.; Cohen, E.; Goldberg, E.; Lilos, P.; Garty, M. ; Krause I, Triglyceride levels risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a longitudinal large study, J. Investig. Med. 2016, 64, 383–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y. , Higher Non-fasting Triglyceride also Predicts Higher Risks of Diabetes Mortality. Research Square 2022. [CrossRef]
- Briaud, I.; Harmon, J. S.; Kelpe, C. L.; Segu, V. B.; Poitout, V. , Lipotoxicity of the pancreatic beta-cell is associated with glucose-dependent esterification of fatty acids into neutral lipids. Diabetes 2001, 50, 315–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witters, L. A.; Watts, T. D.; Daniels, D. L.; Evans, J. L. , Insulin stimulates the dephosphorylation and activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1988, 85, 5473–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witters, L. A.; Kemp, B. E. , Insulin activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase accompanied by inhibition of the 5’-AMP-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 2864–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurr, M. , Lipid metabolism in man. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1988, 47, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dif, N.; Euthine, V.; Gonnet, E.; Laville, M.; Vidal, H. ; Lefai E, Insulin activates human sterol-regulatory-element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) promoter through SREmotifs Biochem, J. 2006, 400, 179-88.
- Postic, C.; Dentin, R.; Denechaud, P. D.; Girard, J. , ChREBP, a transcriptional regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2007, 27, 179–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, H.; Takenoshita, M.; Sakurai, M.; Bruick, R. K.; Henzel, W. J.; Shillinglaw, W.; Arnot, D.; Uyeda, K. , A glucose-responsive transcription factor that regulates carbohydrate metabolism in the liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2001, 98, 9116–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentin, R.; Pégorier, J. P.; Benhamed, F.; Foufelle, F.; Ferré, P.; Fauveau, V.; Magnuson, M. A.; Girard, J.; Postic, C. , Hepatic glucokinase is required for the synergistic action of ChREBP and SREBP-1c on glycolytic and lipogenic gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 20314–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liimatta, M.; Towle, H. C.; Clarke, S.; Jump, D. B. , Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids interfere with the insulin/glucose activation of L-type pyruvate kinase gene transcription. Mol. Endocrinol. 1994, 8, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda, K.; Repa, J. J. , Carbohydrate response element binding protein, ChREBP, a transcription factor coupling hepatic glucose utilization and lipid synthesis. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 107–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poungvarin, N.; Lee, J. K.; Yechoor, V. K.; Li, M. V.; Assavapokee, T.; Suksaranjit, P.; Thepsongwajja, J. J.; Saha, P. K.; Oka, K.; Chan, L. , Carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP) plays a pivotal role in beta cell glucotoxicity. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 1783–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, K.; Takao, K.; Yabe, D. , ChREBP-Mediated Regulation of Lipid Metabolism: Involvement of the Gut Microbiota, Liver, and Adipose Tissue. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 587189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Prieto, P.; Postic C, Carbohydrate Sensing Through the Transcription Factor, C.h.R.E.B.P. Frontiers in Genetics 2019, 10, 472.
- Demir, S.; Nawroth, P. P.; Herzig, S.; Ekim Üstünel, B. , Emerging Targets in Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Complications. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2021, 8, e2100275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, T. M.; Haider, N.; Kahn, C. R. , Defining the underlying defect in insulin action in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez Báez, A.; Ayala, G.; Pedroza-Saavedra, A.; González-Sánchez, H. M.; Chihu Amparan, L. , Phosphorylation Codes in IRS-1 and IRS-2 Are Associated with the Activation/Inhibition of Insulin Canonical Signaling Pathways. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 634–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.K. C.; Dao, X. D.; Nguyen, D. V.; Luu, D. H.; Bui, T. M. H.; Le, T. H.; Nguyen, H. T.; Le, T. N.; Hosaka, T.; Nguyen, T. T. T. , Insulin signaling and its application. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2023, 14, 1226655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, A.; Komander, D.; van Aalten, D.M. F.; Alessi, D. R. , PDK1, the master regulator of AGC kinase signal transduction. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 15, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, D.A. E.; Alessi, D. R.; Cohen, P.; Andjelkovich, M.; Hemmings, B. A. , Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature 1995, 378, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Chen, J.; Yuan Z, Post-translational regulation of, F. O.X.O. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 2012, 44, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Pocai, A.; Rossetti, L.; DePinho, R. A.; Accili, D. , Impaired Regulation of Hepatic Glucose Production in Mice Lacking the Forkhead Transcription Factor Foxo1 in Liver. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakae, J.; Barr, V.; Accili D, Differential regulation of gene expression by insulin IGF-1 receptors correlates with phosphorylation of a single amino acid residue in the forkhead transcription factor, F.K.H.R. The EMBO Journal 2000, 19, 989-996-996.
- Sancak, Y.; Thoreen, C. C.; Peterson, T. R.; Lindquist, R. A.; Kang, S. A.; Spooner, E.; Carr, S. A.; Sabatini, D. M. , PRAS40 Is an Insulin-Regulated Inhibitor of the mTORC1 Protein Kinase. Mol. Cell 2007, 25, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tee, A. R.; Fingar, D. C.; Manning, B. D.; Kwiatkowski, D. J.; Cantley, L. C.; Blenis, J. , Tuberous sclerosis complex-1 and -2 gene products function together to inhibit mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-mediated downstream signaling. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2002, 99, 13571–13576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Li, X.; Ding, Y.; Liu, X.; Diggle, K.; Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D. A. , SREBP Regulation of Lipid Metabolism in Liver Disease, and Therapeutic Strategies. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D. M. , An emerging role of mTOR in lipid biosynthesis. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, R1046–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, N. J.; Govers, R.; James, D. E. , Regulated transport of the glucose transporter GLUT4. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2002, 3, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slot, J. W.; Geuze, H. J.; Gigengack, S.; Lienhard, G. E.; James, D. E. , Immuno-localization of the insulin regulatable glucose transporter in brown adipose tissue of the rat. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 113, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.; Millar, C. A.; Lyttle, C. T.; Meerloo, T.; Marsh, B. J.; Gould, G. W.; James, D. E. , Effects of insulin on intracellular GLUT4 vesicles in adipocytes: evidence for a secretory mode of regulation. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 3427–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, L. J.; James, D. E. , Insulin-regulated sorting of glucose transporters in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, (2 Pt 1) Pt 1, E383–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S. X.; Ng, Y.; Burchfield, J. G.; Ramm, G.; Lambright, D. G.; Stöckli, J.; James, D. E. , The Rab GTPase-activating protein TBC1D4/AS160 contains an atypical phosphotyrosine-binding domain that interacts with plasma membrane phospholipids to facilitate GLUT4 trafficking in adipocytes. Mol Cell Biol 2012, 32, 4946–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hook, S. C.; Chadt, A.; Heesom, K. J.; Kishida, S.; Al-Hasani, H.; Tavaré, J. M.; Thomas, E. C. , TBC1D1 interacting proteins, VPS13A and VPS13C, regulate GLUT4 homeostasis in C2C12 myotubes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, H.; Kanzaki, M. , Regulatory mode shift of Tbc1d1 is required for acquisition of insulin-responsive GLUT4-trafficking activity. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 809–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenti, M.; Frittoli, E.; Ponzanelli, I.; Falck, J. R.; Brachmann, S. M.; Di Fiore, P. P.; Scita, G. , Phosphoinositide 3-kinase activates Rac by entering in a complex with Eps8, Abi1, and Sos-1. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, T. T.; Jensen, T. E.; Sylow, L.; Richter, E. A.; Klip, A. , Rac1 signalling towards GLUT4/glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 1546–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leto, D.; Saltiel, A. R. , Regulation of glucose transport by insulin: traffic control of GLUT4. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2012, 13, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kimura, A.; Baumann, C. A.; Saltiel, A. R. , APS facilitates c-Cbl tyrosine phosphorylation and GLUT4 translocation in response to insulin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Cell Biol 2002, 22, 3599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, S.-H.; Baumann, C. A.; Kanzaki, M.; Thurmond, D. C.; Watson, R. T.; Neudauer, C. L.; Macara, I. G.; Pessin, J. E.; Saltiel, A. R. , Insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation requires the CAP-dependent activation of TC10. Nature 2001, 410, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulman, G. I.; Rothman, D. L.; Jue, T.; Stein, P.; DeFronzo, R. A.; Shulman, R. G. , Quantitation of muscle glycogen synthesis in normal subjects and subjects with non-insulin-dependent diabetes by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 223–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R. A. , Lilly lecture 1987. The triumvirate: beta-cell, muscle, liver. A collusion responsible for NIDDM. Diabetes.
- Brüning, J. C.; Michael, M. D.; Winnay, J. N.; Hayashi, T.; Hörsch, D.; Accili, D.; Goodyear, L. J.; Kahn, C. R. , A Muscle-Specific Insulin Receptor Knockout Exhibits Features of the Metabolic Syndrome of NIDDM without Altering Glucose Tolerance. Mol. Cell 1998, 2, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüher, M.; Michael, M. D.; Peroni, O. D.; Ueki, K.; Carter, N.; Kahn, B. B.; Kahn, C. R. , Adipose tissue selective insulin receptor knockout protects against obesity and obesity-related glucose intolerance. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauro, D.; Kido, Y.; Castle, A. L.; Zarnowski, M. J.; Hayashi, H.; Ebina, Y.; Accili, D. , Impaired glucose tolerance in mice with a targeted impairment of insulin action in muscle and adipose tissue. Nat. Genet. 1998, 20, 294–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Liew, C. W.; Hu, J.; Hinault, C.; Michael, M. D.; Krtzfeldt, J.; Yin, C.; Holzenberger, M.; Stoffel, M.; Kulkarni, R. N. , Insulin receptors in beta-cells are critical for islet compensatory growth response to insulin resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 8977–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, R. N.; Brüning, J. C.; Winnay, J. N.; Postic, C.; Magnuson, M. A.; Kahn, C. R. , Tissue-specific knockout of the insulin receptor in pancreatic beta cells creates an insulin secretory defect similar to that in type 2 diabetes. Cell 1999, 96, 329–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, O. P.; Dahl, D. B.; Brechtel, K.; Machann, J.; Haap, M.; Maier, T.; Loviscach, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Claussen, C. D.; Schick, F.; Häring, H. U.; Jacob, S. , Effects of intravenous and dietary lipid challenge on intramyocellular lipid content and the relation with insulin sensitivity in humans. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2579–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepaniak, L. S.; Babcock, E. E.; Schick, F.; Dobbins, R. L.; Garg, A.; Burns, D. K.; McGarry, J. D.; Stein, D. T. , Measurement of intracellular triglyceride stores by H spectroscopy: validation in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, E977–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesch, C.; Slotboom, J.; Hoppeler, H.; Kreis, R. , In vivo determination of intra-myocellular lipids in human muscle by means of localized 1H-MR-spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997, 37, 484–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, K.; Daa Schroeder, H.; Alford, F. P.; Beck-Nielsen, H. , Morphometric documentation of abnormal intramyocellular fat storage and reduced glycogen in obese patients with Type II diabetes. Diabetologia 2001, 44, 824–33. [Google Scholar]
- Packard, C. J.; Boren, J.; Taskinen, M. R. , Causes and Consequences of Hypertriglyceridemia. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2020, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumenthal, S. A. , Stimulation of gluconeogenesis by palmitic acid in rat hepatocytes: evidence that this effect can be dissociated from the provision of reducing equivalents. Metabolism 1983, 32, 971–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiébaud, D.; DeFronzo, R. A.; Jacot, E.; Golay, A.; Acheson, K.; Maeder, E.; Jéquier, E.; Felber, J. P. , Effect of long chain triglyceride infusion on glucose metabolism in man. Metabolism 1982, 31, 1128–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivri, D.; Akdevelioğlu, Y. , Effect of Fatty Acids on Glucose Metabolism and Type 2 Diabetes. Nutr. Rev. 2025, 83, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E.; Barrett, E. J.; Bevilacqua, S.; DeFronzo, R. A. , Effect of fatty acids on glucose production and utilization in man. J. Clin. Invest. 1983, 72, 1737–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, A. J.; Brandon, A. E.; Turner, N.; Watt, M. J.; Bruce, C. R.; Cooney, G. J.; Kraegen, E. W. , Lipid and insulin infusion-induced skeletal muscle insulin resistance is likely due to metabolic feedback and not changes in IRS-1, Akt, or AS160 phosphorylation. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Høeg, L. D.; Sjøberg, K. A.; Jeppesen, J.; Jensen, T. E.; Frøsig, C.; Birk, J. B.; Bisiani, B.; Hiscock, N.; Pilegaard, H.; Wojtaszewski, J. F. P.; Richter, E. A.; Kiens, B. , Lipid-Induced Insulin Resistance Affects Women Less Than Men and Is Not Accompanied by Inflammation or Impaired Proximal Insulin Signaling. Diabetes 2010, 60, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaepfer, I. R.; Glodé, L. M.; Hitz, C. A.; Pac, C. T.; Boyle, K. E.; Maroni, P.; Deep, G.; Agarwal, R.; Lucia, S. M.; Cramer, S. D.; Serkova, N. J.; Eckel, R. H. , Inhibition of Lipid Oxidation Increases Glucose Metabolism and Enhances 2-Deoxy-2-[18F]Fluoro-d-Glucose Uptake in Prostate Cancer Mouse Xenografts. Molecular Imaging and Biology 2015, 17, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, N. D.; Cooney, G. J.; Camilleri, S.; Chisholm, D. J.; Kraegen, E. W. , Mechanisms of liver and muscle insulin resistance induced by chronic high-fat feeding. Diabetes 1997, 46, 1768–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, M. E.; Marcucci, M. J.; Cline, G. W.; Bell, K.; Barucci, N.; Lee, D.; Goodyear, L. J.; Kraegen, E. W.; White, M. F.; Shulman, G. I. , Free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance is associated with activation of protein kinase C theta and alterations in the insulin signaling cascade. Diabetes 1999, 48, 1270–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalkley, S. M.; Hettiarachchi, M.; Chisholm, D. J.; Kraegen, E. W. , Five-hour fatty acid elevation increases muscle lipids and impairs glycogen synthesis in the rat. Metabolism 1998, 47, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, C. B.; Storgaard, H.; Holst, J. J.; Dela, F.; Madsbad, S.; Vaag, A. A. , Insulin secretion and cellular glucose metabolism after prolonged low-grade intralipid infusion in young men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003, 88, 2775–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phielix, E.; Begovatz, P.; Gancheva, S.; Bierwagen, A.; Kornips, E.; Schaart, G.; Hesselink, M.K. C.; Schrauwen, P.; Roden, M. , Athletes feature greater rates of muscle glucose transport and glycogen synthesis during lipid infusion. JCI insight 2019, 4, e127928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flatt, J. P. , Conversion of carbohydrate to fat in adipose tissue: an energy-yielding and, therefore, self-limiting process. J. Lipid Res. 1970, 11, 131–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, M.; King, G. L. , Protein kinase C activation and its pharmacological inhibition in vascular disease. Vasc. Med. 2000, 5, 173–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz-Peiffer, C.; Browne, C. L.; Oakes, N. D.; Watkinson, A.; Chisholm, D. J.; Kraegen, E. W.; Biden, T. J. , Alterations in the expression and cellular localization of protein kinase C isozymes epsilon and theta are associated with insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of the high-fat-fed rat. Diabetes 1997, 46, 169–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Chen, Y.; Cline, G. W.; Zhang, D.; Zong, H.; Wang, Y.; Bergeron, R.; Kim, J. K.; Cushman, S. W.; Cooney, G. J.; Atcheson, B.; White, M. F.; Kraegen, E. W.; Shulman, G. I. , Mechanism by which fatty acids inhibit insulin activation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1)-associated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 50230–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Soos, T. J.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; DeGennaro, M.; Sun, X.; Littman, D. R.; Birnbaum, M. J.; Polakiewicz, R. D. , Protein Kinase C θ Inhibits Insulin Signaling by Phosphorylating IRS1 at Ser1101*. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45304–45307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresner, A.; Laurent, D.; Marcucci, M.; Griffin, M. E.; Dufour, S.; Cline, G. W.; Slezak, L. A.; Andersen, D. K.; Hundal, R. S.; Rothman, D. L.; Petersen, K. F.; Shulman, G. I. , Effects of free fatty acids on glucose transport and IRS-1–associated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity. J. Clin. Invest. 1999, 103, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfort, R.; Mandarino, L.; Kashyap, S.; Wirfel, K.; Pratipanawatr, T.; Berria, R.; DeFronzo, R. A.; Cusi, K. , Dose-Response Effect of Elevated Plasma Free Fatty Acid on Insulin Signaling. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roden, M.; Price, T. B.; Perseghin, G.; Petersen, K. F.; Rothman, D. L.; Cline, G. W.; Shulman, G. I. , Mechanism of free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance in humans. J. Clin. Invest. 1996, 97, 2859–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, M.; Krssak, M.; Nowotny, P.; Weghuber, D.; Gruber, S.; Mlynarik, V.; Bischof, M.; Stingl, H.; Fürnsinn, C.; Waldhäusl, W.; Roden, M. , Free fatty acids inhibit the glucose-stimulated increase of intramuscular glucose-6-phosphate concentration in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001, 86, 2153–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevilacqua, S.; Bonadonna, R.; Buzzigoli, G.; Boni, C.; Ciociaro, D.; Maccari, F.; Giorico, M. A.; Ferrannini, E. , Acute elevation of free fatty acid levels leads to hepatic insulin resistance in obese subjects. Metabolism 1987, 36, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golay, A.; Swislocki, A. L.; Chen, Y. D.; Reaven, G. M. , Relationships between plasma-free fatty acid concentration, endogenous glucose production, and fasting hyperglycemia in normal and non-insulin-dependent diabetic individuals. Metabolism 1987, 36, 692–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogardus, C.; Lillioja, S.; Howard, B. V.; Reaven, G.; Mott, D. , Relationships between insulin secretion, insulin action, and fasting plasma glucose concentration in nondiabetic and noninsulin-dependent diabetic subjects. J. Clin. Invest. 1984, 74, 1238–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, P. E.; Joseph, J. W.; Rorsman, P., Glucose-sensing mechanisms in pancreatic β-cells. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2005, 360, 2211-2225.
- Deepa Maheshvare, M.; Raha, S.; König, M.; Pal, D. , A pathway model of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in the pancreatic β-cell. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2023, 14, 1185656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelin Klemen, M.; Dolenšek, J.; Slak Rupnik, M.; Stožer, A. , The triggering pathway to insulin secretion: Functional similarities and differences between the human and the mouse β cells and their translational relevance. Islets 2017, 9, 109–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Bryan, L.; Bryan, J.; Nakazaki, M. , Of mice and men: K(ATP) channels and insulin secretion. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 2001, 56, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes, Insulin secretion - Homo sapiens (human). Availabe at https://www.kegg.jp/pathway/hsa04911. Access on 6 July 2025.
- Schalch, D. S.; Kipnis, D. M. , Abnormalities in carbohydrate tolerance associated with elevated plasma nonesterified fatty acids. J. Clin. Invest. 1965, 44, 2010–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelkonen, R.; Miettinen, T. A.; Taskinen, M. R.; Nikkilä, E. A. , Effect of acute elevation of plasma glycerol, triglyceride and FFA levels on glucose utilization and plasma insulin. Diabetes 1968, 17, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnotte, C.; Gilon, P.; Nenquin, M.; Henquin, J.-C. , Mechanisms of the Stimulation of Insulin Release by Saturated Fatty Acids: A Study of Palmitate Effects in Mouse β-cells. Diabetes 1994, 43, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasse, E. O.; Ooms, H. A. , Role of plasma free fatty acids in the control of insulin secretion in man. Diabetologia 1973, 9, 145–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpentier, A.; Mittelman, S. D.; Lamarche, B.; Bergman, R. N.; Giacca, A.; Lewis, G. F. , Acute enhancement of insulin secretion by FFA in humans is lost with prolonged FFA elevation. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, E1055–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, C. P.; Tadayyon, M.; Andrews, J. L.; Benson, W. G.; Chambers, J. K.; Eilert, M. M.; Ellis, C.; Elshourbagy, N. A.; Goetz, A. S.; Minnick, D. T.; Murdock, P. R.; Sauls, H. R., Jr.; Shabon, U.; Spinage, L. D.; Strum, J. C.; Szekeres, P. G.; Tan, K. B.; Way, J. M.; Ignar, D. M.; Wilson, S.; Muir, A. I. , The orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR40 is activated by medium and long chain fatty acids. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11303–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, Y.; Kawamata, Y.; Harada, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Fujii, R.; Fukusumi, S.; Ogi, K.; Hosoya, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Uejima, H.; Tanaka, H.; Maruyama, M.; Satoh, R.; Okubo, S.; Kizawa, H.; Komatsu, H.; Matsumura, F.; Noguchi, Y.; Shinohara, T.; Hinuma, S.; Fujisawa, Y.; Fujino, M. , Free fatty acids regulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells through GPR40. Nature 2003, 422, 173–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Gilbert, E. R.; Liu, D. , Regulation of insulin synthesis and secretion and pancreatic Beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2013, 9, 25–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentki, M.; Matschinsky, F. M. , Ca2+, cAMP, and phospholipid-derived messengers in coupling mechanisms of insulin secretion. Physiol. Rev. 1987, 67, 1185–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz-Peiffer, C.; Biden, T. J. , Protein kinase C function in muscle, liver, and beta-cells and its therapeutic implications for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1774–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trexler, A. J.; Taraska, J. W. , Regulation of insulin exocytosis by calcium-dependent protein kinase C in beta cells. Cell Calcium 2017, 67, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozem, M.; Nenquin, M.; Henquin, J. C. , The ionic, electrical, and secretory effects of protein kinase C activation in mouse pancreatic B-cells: studies with a phorbol ester. Endocrinology 1987, 121, 1025–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamateris, R. E.; Sharma, R. B.; Hollern, D. A.; Alonso, L. C. , Adaptive β-cell proliferation increases early in high-fat feeding in mice, concurrent with metabolic changes, with induction of islet cyclin D2 expression. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 305, E149–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vara, E.; Fernández-Martín, O.; García, C.; Tamarit-Rodríguez, J. , Palmitate dependence of insulin secretion, “de novo” phospholipid synthesis and 45Ca2+-turnover in glucose stimulated rat islets. Diabetologia 1988, 31, 687–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terauchi, Y.; Takamoto, I.; Kubota, N.; Matsui, J.; Suzuki, R.; Komeda, K.; Hara, A.; Toyoda, Y.; Miwa, I.; Aizawa, S.; Tsutsumi, S.; Tsubamoto, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Eto, K.; Nakamura, A.; Noda, M.; Tobe, K.; Aburatani, H.; Nagai, R. ; Kadowaki T, Glucokinase IRS-2 are required for compensatory beta cell hyperplasia in response to high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance, J. Clin. Invest. 2007, 117, 246–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folli, F.; Okada, T.; Perego, C.; Gunton, J.; Liew, C. W.; Akiyama, M.; D’Amico, A.; La Rosa, S.; Placidi, C.; Lupi, R.; Marchetti, P.; Sesti, G.; Hellerstein, M.; Perego, L.; Kulkarni, R. N. , Altered Insulin Receptor Signalling and β-Cell Cycle Dynamics in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. PLoS One 2011, 6, e28050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golson, M. L.; Misfeldt, A. A.; Kopsombut, U. G.; Petersen, C. P.; Gannon, M. , High Fat Diet Regulation of β-Cell Proliferation and β-Cell Mass. Open Endocrinol. J. 2010, 4, 66–77. [Google Scholar]
- Takamoto, I.; Terauchi, Y.; Kubota, N.; Ohsugi, M.; Ueki, K.; Kadowaki, T. , Crucial role of insulin receptor substrate-2 in compensatory beta-cell hyperplasia in response to high fat diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2008, 10 Suppl 4, 147–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirakawa, J. , Signaling pathways that regulate adaptive β-cell proliferation for the treatment of diabetes. Journal of Diabetes Investigation 2023, 14, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, J.; Fernandez, M.; Takatani, T.; El Ouaamari, A.; Jungtrakoon, P.; Okawa, E. R.; Zhang, W.; Yi, P.; Doria, A.; Kulkarni, R. N. , Insulin Signaling Regulates the FoxM1/PLK1/CENP-A Pathway to Promote Adaptive Pancreatic β Cell Proliferation. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 868–882.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glauser, D. A.; Schlegel, W. , The FoxO/Bcl-6/cyclin D2 pathway mediates metabolic and growth factor stimulation of proliferation in Min6 pancreatic β-cells. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2009, 29, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. S.; Hossain, K. S.; Das, S.; Kundu, S.; Adegoke, E. O.; Rahman, M. A.; Hannan, M. A.; Uddin, M. J.; Pang, M. G. , Role of Insulin in Health and Disease: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, W. , How Western Diet And Lifestyle Drive The Pandemic Of Obesity And Civilization Diseases. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentki, M.; Vischer, S.; Glennon, M. C.; Regazzi, R.; Deeney, J. T.; Corkey, B. E. , Malonyl-CoA and long chain acyl-CoA esters as metabolic coupling factors in nutrient-induced insulin secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 5802–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitout, V.; Robertson, R. P. , Minireview: Secondary β-Cell Failure in Type 2 Diabetes—A Convergence of Glucotoxicity and Lipotoxicity. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosokawa, H.; Corkey, B. E.; Leahy, J. L. , Beta-cell hypersensitivity to glucose following 24-h exposure of rat islets to fatty acids. Diabetologia 1997, 40, 392–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, T. M.; Goh, T.; Tchipashvili, V.; Sandhu, H.; Gupta, N.; Lewis, G. F.; Giacca, A. , Prolonged elevation of plasma free fatty acids desensitizes the insulin secretory response to glucose in vivo in rats. Diabetes 1999, 48, 524–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGarry, J. D.; Dobbins, R. L. , Fatty acids, lipotoxicity and insulin secretion. Diabetologia 1999, 42, 128–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boden, G.; Chen, X.; Rosner, J.; Barton, M. , Effects of a 48-h fat infusion on insulin secretion and glucose utilization. Diabetes 1995, 44, 1239–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAKO,, Y. ; GRILL,, V. E., A 48-hour Lipid Infusion in the Rat Time-Dependently Inhibits Glucose-Induced Insulin Secretion and B Cell Oxidation Through a Process Likely Coupled to Fatty Acid Oxidation*. Endocrinology 1990, 127, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y. P.; Grill, V. , Long term exposure to fatty acids and ketones inhibits B-cell functions in human pancreatic islets of Langerhans. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 1995, 80, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar]
- Ritz-Laser, B.; Meda, P.; Constant, I.; Klages, N.; Charollais, A.; Morales, A.; Magnan, C.; Ktorza, A.; Philippe, J. , Glucose-induced preproinsulin gene expression is inhibited by the free fatty acid palmitate. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 4005–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, H.; Kaneto, H.; Weir, G. C.; Bonner-Weir, S. , PDX-1 protein containing its own antennapedia-like protein transduction domain can transduce pancreatic duct and islet cells. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1732–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S. M.; Stone, N. J.; Bailey, A. L.; Beam, C.; Birtcher, K. K.; Blumenthal, R. S.; Braun, L. T.; Ferranti, S. d.; Faiella-Tommasino, J.; Forman, D. E.; Goldberg, R.; Heidenreich, P. A.; Hlatky, M. A.; Jones, D. W.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; Lopez-Pajares, N.; Ndumele, C. E.; Orringer, C. E.; Peralta, C. A.; Saseen, J. J.; Smith, S. C.; Sperling, L.; Virani, S. S.; Yeboah, J. , 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2019, 139, e1082–e1143. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Jeon, S.; Lee, M.; Yoon, M. , Fenofibrate alleviates insulin resistance by reducing tissue inflammation in obese ovariectomized mice. Nutr. Diabetes 2023, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansen, T. B.; Wirtz, K. W. , The peroxisome in oxidative stress. IUBMB Life 2001, 51, 223–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrmann, W.; Elsner, M.; Lenzen, S. , Role of metabolically generated reactive oxygen species for lipotoxicity in pancreatic β-cells. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2010, 12 Suppl 2, 149–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wang, J. G.; Liu, R. Q.; Shi, Q.; Wang, W. X. , Association between intra-pancreatic fat deposition and diseases of the exocrine pancreas: A narrative review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2025, 31, 101180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Wang, Y.; Wondisford, F. E. , Differential Metabolism of Glycerol Based on Oral versus Intravenous Administration in Humans. Metabolites 2022, 12, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A. M.; Wondisford, F. E. , Tracking the carbons supplying gluconeogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 14419–14429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basicmedical Key, Gluconeogenesis and Maintenance of Blood Glucose Levels. Available from https://basicmedicalkey.com/gluconeogenesis-and-maintenance-of-blood-glucose-levels/. Accessed on 30 June 2025.
- Droppelmann, C. A.; Sáez, D. E.; Asenjo, J. L.; Yáñez, A. J.; García-Rocha, M.; Concha, II; Grez, M.; Guinovart, J. J.; Slebe, J. C., A new level of regulation in gluconeogenesis: metabolic state modulates the intracellular localization of aldolase B and its interaction with liver fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Biochem. J. 2015, 472, 225-37.
- Montell, E.; Lerı́n, C.; Newgard, C. B.; Gómez-Foix, A. M. , Effects of Modulation of Glycerol Kinase Expression on Lipid and Carbohydrate Metabolism in Human Muscle Cells*. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 2682–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melkonian, E. A.; Asuka, E.; Schury, M. P. , Physiology, Gluconeogenesis. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL): 2025.
- Weinman, E. O.; Strisower, E. H.; Chaikoff, I. L. , Conversion of fatty acids to carbohydrate; application of isotopes to this problem and role of the Krebs cycle as a synthetic pathway. Physiol. Rev. 1957, 37, 252–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrebaek, B.; Bremer, J.; Davis, E. J.; Davis-Van Thienen, W.; Singh, B. , The effect of glucagon on the carbon flux from palmitate into glucose, lactate and ketone bodies, studied with isolated hepatocytes. Int. J. Biochem. 1984, 16, 841–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaleta, C.; de Figueiredo, L. F.; Werner, S.; Guthke, R.; Ristow, M.; Schuster, S. , In silico evidence for gluconeogenesis from fatty acids in humans. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannun, Y. A.; Obeid, L. M. , Many Ceramides. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 27855–27862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, H.-J.; Shin, W.-R.; Sekhon, S. S.; Woo, S. M.; Kim, Y.-C.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H. , Codon optimization of the synthetic 3-ketosphinganine reductase (3KSR) protein for enhancing sphingolipid biosynthetic enzyme expression. Molecular & Cellular Toxicology 2021, 17, 453–464. [Google Scholar]
- Shimabukuro, M.; Higa, M.; Zhou, Y. T.; Wang, M. Y.; Newgard, C. B.; Unger, R. H. , Lipoapoptosis in beta-cells of obese prediabetic fa/fa rats. Role of serine palmitoyltransferase overexpression. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 32487–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabionet, M.; Gorgas, K.; Sandhoff, R. , Ceramide synthesis in the epidermis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costes, S.; Bertrand, G.; Ravier, M. A., Mechanisms of Beta-Cell Apoptosis in Type 2 Diabetes-Prone Situations and Potential Protection by GLP-1-Based Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, (10).
- Lee, J.-H.; Mellado-Gil, J. M.; Bahn, Y. J.; Pathy, S. M.; Zhang, Y. E.; Rane, S. G. , Protection from β-cell apoptosis by inhibition of TGF-β/Smad3 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, J.; Bermudez, V.; Palmar, J.; Martínez, M. S.; Olivar, L. C.; Nava, M.; Tomey, D.; Rojas, M.; Salazar, J.; Garicano, C.; Velasco, M. , Pancreatic Beta Cell Death: Novel Potential Mechanisms in Diabetes Therapy. J Diabetes Res 2018, 2018, 9601801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutter, G. A. , Insulin Secretion: Fatty Acid Signalling via Serpentine Receptors. Curr. Biol. 2003, 13, R403–R405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, D. A.; Hekerman, P.; Ladrière, L.; Bazarra-Castro, A.; Ortis, F.; Wakeham, M. C.; Moore, F.; Rasschaert, J.; Cardozo, A. K.; Bellomo, E.; Overbergh, L.; Mathieu, C.; Lupi, R.; Hai, T.; Herchuelz, A.; Marchetti, P.; Rutter, G. A.; Eizirik, D. c. L.; Cnop, M. , Initiation and execution of lipotoxic ER stress in pancreatic β-cells. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 2308–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urano, F.; Wang, X.; Bertolotti, A.; Zhang, Y.; Chung, P.; Harding, H. P.; Ron, D. , Coupling of stress in the ER to activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase IRE1. Science 2000, 287, 664–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, E.; Higa, A.; Schuster-Klein, C.; Bernard, C.; Sulpice, T.; Guardiola, B.; Chevet, E.; Alquier, T. , Deletion of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) protects pancreatic beta-cells from stress-induced death but not from glucose homeostasis alterations under pro-inflammatory conditions. PLoS One 2014, 9, e112714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirot, P.; Ortis, F.; Cnop, M.; Ma, Y.; Hendershot, L. M.; Eizirik, D. L.; Cardozo, A. K. , Transcriptional regulation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress gene chop in pancreatic insulin-producing cells. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1069–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwiazda, K. S.; Yang, T.-L. B.; Lin, Y.; Johnson, J. D., Effects of palmitate on ER and cytosolic Ca2+ homeostasis in β-cells. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism 2009, 296, E690-E701.
- Hu, H.; Tian, M.; Ding, C.; Yu, S. , The C/EBP Homologous Protein (CHOP) Transcription Factor Functions in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis and Microbial Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilon, P.; Chae, H.-Y.; Rutter, G. A.; Ravier, M. A. , Calcium signaling in pancreatic β-cells in health and in Type 2 diabetes. Cell Calcium 2014, 56, 340–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, T.; Mahadevan, J.; Kanekura, K.; Hara, M.; Lu, S.; Urano, F. , Calcium efflux from the endoplasmic reticulum leads to β-cell death. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 758–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J. D.; Han, Z.; Otani, K.; Ye, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Horikawa, Y.; Misler, S.; Bell, G. I.; Polonsky, K. S. , RyR2 and Calpain-10 Delineate a Novel Apoptosis Pathway in Pancreatic Islets. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 24794–24802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Ji, Q. , Free Fatty Acid Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis of β-cells by Ca2+/Calpain-2 Pathways. PLoS One 2013, 8, e59921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, A.; Fukasawa, T. , The role of calcium-calpain pathway in hyperthermia. Frontiers in Molecular Medicine 2022, 2, 1005258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C. J.; Gurlo, T.; Haataja, L.; Costes, S.; Daval, M.; Ryazantsev, S.; Wu, X.; Butler, A. E.; Butler, P. C. , Calcium-activated calpain-2 is a mediator of beta cell dysfunction and apoptosis in type 2 diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 339–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; Jain, S. K. , Oxidative stress and apoptosis. Pathophysiology 2000, 7, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haanen, C.; Vermes, I. , Apoptosis and inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 1995, 4, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Anesi, J. C.; Panicker, I. S.; Cook, D.; Bista, P.; Fang, Y.; Oqueli, E. , Neuroimmune Interactions and Their Role in Immune Cell Trafficking in Cardiovascular Diseases and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Golledge, J. , Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and sympathetic nerve activity in neurovascular and metabolic systems. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2013, 10, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Anesi, J.; Maier, M. C.; Myers, M. A.; Oqueli, E.; Sobey, C. G.; Drummond, G. R.; Denton, K. M. , Sympathetic Nervous System and Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzen, S. , Oxidative stress: the vulnerable beta-cell. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36 Pt 3, 343–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiedge, M.; Lortz, S.; Drinkgern, J.; Lenzen, S. , Relation between antioxidant enzyme gene expression and antioxidative defense status of insulin-producing cells. Diabetes 1997, 46, 1733–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenzen, S.; Drinkgern, J.; Tiedge, M. , Low antioxidant enzyme gene expression in pancreatic islets compared with various other mouse tissues. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 463–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, R. J.; Waterham, H. R. , Biochemistry of mammalian peroxisomes revisited. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006, 75, 295–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsner, M.; Gehrmann, W.; Lenzen, S. , Peroxisome-generated hydrogen peroxide as important mediator of lipotoxicity in insulin-producing cells. Diabetes 2011, 60, 200–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pick, A.; Clark, J.; Kubstrup, C.; Levisetti, M.; Pugh, W.; Bonner-Weir, S.; Polonsky, K. S. , Role of apoptosis in failure of beta-cell mass compensation for insulin resistance and beta-cell defects in the male Zucker diabetic fatty rat. Diabetes 1998, 47, 358–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, O.; Mints, G.; Hussain, M. A. , Beta-cell apoptosis in the pathogenesis of human type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Endocrinol 2003, 149, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.; Wells, C. A.; Buley, I. D.; Cruickshank, J. K.; Vanhegan, R. I.; Matthews, D. R.; Cooper, G. J.; Holman, R. R.; Turner, R. C. , Islet amyloid, increased A-cells, reduced B-cells and exocrine fibrosis: quantitative changes in the pancreas in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. 1988, 9, 151–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sakuraba, H.; Mizukami, H.; Yagihashi, N.; Wada, R.; Hanyu, C.; Yagihashi, S. , Reduced beta-cell mass and expression of oxidative stress-related DNA damage in the islet of Japanese Type II diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2002, 45, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahier, J.; Guiot, Y.; Goebbels, R. M.; Sempoux, C.; Henquin, J. C. , Pancreatic beta-cell mass in European subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2008, 10 Suppl 4, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, B. G.; Collier, S. A.; Gupta, N., Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass. In StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing.
- Copyright © 2025, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island (FL), 2025.
- Eid, I.; Birch, D. W.; Sharma, A. M.; Sherman, V.; Karmali, S. , Complications associated with adjustable gastric banding for morbid obesity: a surgeon’s guides. Can. J. Surg. 2011, 54, 61–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeras, K.; Sankararaman, S.; Lopez, P. P., Sleeve Gastrectomy. In StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing.
- Copyright © 2025, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island (FL), 2025.
- Hess, D. S.; Hess, D. W. , Biliopancreatic diversion with a duodenal switch. Obes. Surg. 1998, 8, 267–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebran, S. G.; Knighton, B.; Ngaage, L. M.; Rose, J. A.; Grant, M. P.; Liang, F.; Nam, A. J.; Kavic, S. M.; Kligman, M. D.; Rasko, Y. M. , Insurance Coverage Criteria for Bariatric Surgery: A Survey of Policies. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, D.; Johal, G. S., Bariatric Surgery Cardiac Outcomes. In StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing.
- Copyright © 2025, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island (FL), 2025.
- Sjöström, L.; Lindroos, A. K.; Peltonen, M.; Torgerson, J.; Bouchard, C.; Carlsson, B.; Dahlgren, S.; Larsson, B.; Narbro, K.; Sjöström, C. D.; Sullivan, M.; Wedel, H. , Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2683–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, J. B.; O’Brien, P. E.; Playfair, J.; Chapman, L.; Schachter, L. M.; Skinner, S.; Proietto, J.; Bailey, M.; Anderson, M. , Adjustable gastric banding and conventional therapy for type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2008, 299, 316–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courcoulas, A. P.; Patti, M. E.; Hu, B.; Arterburn, D. E.; Simonson, D. C.; Gourash, W. F.; Jakicic, J. M.; Vernon, A. H.; Beck, G. J.; Schauer, P. R.; Kashyap, S. R.; Aminian, A.; Cummings, D. E.; Kirwan, J. P. , Long-Term Outcomes of Medical Management vs Bariatric Surgery in Type 2 Diabetes. JAMA 2024, 331, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirwan, J. P.; Courcoulas, A. P.; Cummings, D. E.; Goldfine, A. B.; Kashyap, S. R.; Simonson, D. C.; Arterburn, D. E.; Gourash, W. F.; Vernon, A. H.; Jakicic, J. M.; Patti, M. E.; Wolski, K.; Schauer, P. R. , Diabetes Remission in the Alliance of Randomized Trials of Medicine Versus Metabolic Surgery in Type 2 Diabetes (ARMMS-T2D). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genua, I.; Ramos, A.; Caimari, F.; Balagué,, C.; Sánchez-Quesada, J. L.; Pérez, A.; Miñambres, I., Effects of Bariatric Surgery on HDL Cholesterol. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 1793-1798. 2020, 30, 1793–1798.
- Heffron, S. P.; Lin, B. X.; Parikh, M.; Scolaro, B.; Adelman, S. J.; Collins, H. L.; Berger, J. S.; Fisher, E. A. , Changes in High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Efflux Capacity After Bariatric Surgery Are Procedure Dependent. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, Y.; Ohta, M.; Hirashita, T.; Masuda, T.; Inomata, M.; Kitano, S. , Effects of sleeve gastrectomy on lipid metabolism in an obese diabetic rat model. Obes. Surg. 2013, 23, 1947–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminian, A.; Nissen, S. E. , Success (but Unfinished) Story of Metabolic Surgery. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1175–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminian, A.; Brethauer, S. A.; Kirwan, J. P.; Kashyap, S. R.; Burguera, B.; Schauer, P. R. , How safe is metabolic/diabetes surgery? Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2015, 17, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomp, A. , Safety of bariatric surgery. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2014, 2, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virani, S. S.; Morris, P. B.; Agarwala, A.; Ballantyne, C. M.; Birtcher, K. K.; Kris-Etherton, P. M.; Ladden-Stirling, A. B.; Miller, M.; Orringer, C. E.; Stone, N. J. , 2021 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on the Management of ASCVD Risk Reduction in Patients With Persistent Hypertriglyceridemia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 960–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K. R., Triglyceride Lowering Drugs. In Endotext, Feingold, K. R.; Ahmed, S. F.; Anawalt, B.; Blackman, M. R.; Boyce, A.; Chrousos, G.; Corpas, E.; de Herder, W. W.; Dhatariya, K.; Dungan, K.; Hofland, J.; Kalra, S.; Kaltsas, G.; Kapoor, N.; Koch, C.; Kopp, P.; Korbonits, M.; Kovacs, C. S.; Kuohung, W.; Laferrère, B.; Levy, M.; McGee, E. A.; McLachlan, R.; Muzumdar, R.; Purnell, J.; Rey, R.; Sahay, R.; Shah, A. S.; Singer, F.; Sperling, M. A.; Stratakis, C. A.; Trence, D. L.; Wilson, D. P., Eds. MDText.com, Inc.
- Copyright © 2000-2025, MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth (MA), 2000.
- Wang, Y. , Omega-3 Fatty Acids Effect on Major Cardiovascular Events in Patients at High Cardiovascular Risk. JAMA 2021, 325, 1333–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, K.; Fan, C.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, H.; Jiao, H.; Meng, Q.; Deckelbaum, R. J. , Omega-3 fatty acid containing diets decrease plasma triglyceride concentrations in mice by reducing endogenous triglyceride synthesis and enhancing the blood clearance of triglyceride-rich particles. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 424–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganji, S. H.; Tavintharan, S.; Zhu, D.; Xing, Y.; Kamanna, V. S.; Kashyap, M. L. , Niacin noncompetitively inhibits DGAT2 but not DGAT1 activity in HepG2 cells. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 1835–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliewer, S. A.; Sundseth, S. S.; Jones, S. A.; Brown, P. J.; Wisely, G. B.; Koble, C. S.; Devchand, P.; Wahli, W.; Willson, T. M.; Lenhard, J. M.; Lehmann, J. M. , Fatty acids and eicosanoids regulate gene expression through direct interactions with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha and gamma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1997, 94, 4318–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulick, T.; Cresci, S.; Caira, T.; Moore, D. D.; Kelly, D. P. , The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor regulates mitochondrial fatty acid oxidative enzyme gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1994, 91, 11012–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dentin, R.; Benhamed, F.; Pégorier, J. P.; Foufelle, F.; Viollet, B.; Vaulont, S.; Girard, J.; Postic, C. , Polyunsaturated fatty acids suppress glycolytic and lipogenic genes through the inhibition of ChREBP nuclear protein translocation. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 2843–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamanna, V. S.; Kashyap, M. L. , Mechanism of action of niacin. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, (8a), 20b–26b. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganji, S. H.; Kamanna, V. S.; Kashyap, M. L. , Niacin and cholesterol: role in cardiovascular disease (review). J. Nutr. Biochem. 2003, 14, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F. Y.; Kamanna, V. S.; Kashyap, M. L. , Niacin accelerates intracellular ApoB degradation by inhibiting triacylglycerol synthesis in human hepatoblastoma (HepG2) cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 1051–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T. J.; Brainard, J.; Song, F.; Wang, X.; Abdelhamid, A.; Hooper, L. , Omega-3, omega-6, and total dietary polyunsaturated fat for prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldie, C.; Taylor, A. J.; Nguyen, P.; McCoy, C.; Zhao, X.-Q.; Preiss, D. , Niacin therapy and the risk of new-onset diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Heart 2016, 102, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera Lopez, E.; Ballard, B. D.; Jan, A. , Cardiovascular Disease. StatPearls.
- Copyright © 2025, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island (FL), 2025.
- Vaduganathan, M.; Mensah, G. A.; Turco, J. V.; Fuster, V.; Roth, G. A. , The Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk: A Compass for Future Health. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 2361–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judkins, C. P.; Wang, Y.; Jelinic, M.; Bobik, A.; Vinh, A.; Sobey, C. G.; Drummond, G. R. , Association of constipation with increased risk of hypertension and cardiovascular events in elderly Australian patients. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, T.; Sun, H.; Xu, Q.; Hou, X.; Hu, W.; Zhang, G.; Drummond, G. R.; Sobey, C. G.; Charchar, F. J.; Golledge, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G. , Hyperuricemia is independently associated with hypertension in men under 60 years in a general Chinese population. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2021, 35, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackman, K. A.; Brait, V. H.; Wang, Y.; Maghzal, G. J.; Ball, H. J.; McKenzie, G.; De Silva, T. M.; Stocker, R.; Sobey, C. G. , Vascular expression, activity and function of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-1 following cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion in mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2011, 383, 471–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eroglu, T.; Capone, F.; Schiattarella, G. G. , The evolving landscape of cardiometabolic diseases. eBioMedicine 2024, 109, 105447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabani, M.; Shapiro, M. D.; Toth, P. P. , The Role of Triglyceride-rich Lipoproteins and Their Remnants in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Eur Cardiol 2023, 18, e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsberg, H. N.; Packard, C. J.; Chapman, M. J.; Borén, J.; Aguilar-Salinas, C. A.; Averna, M.; Ference, B. A.; Gaudet, D.; Hegele, R. A.; Kersten, S.; Lewis, G. F.; Lichtenstein, A. H.; Moulin, P.; Nordestgaard, B. G.; Remaley, A. T.; Staels, B.; Stroes, E. S. G.; Taskinen, M. R.; Tokgözoğlu, L. S.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Stock, J. K.; Catapano, A. L. , Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and their remnants: metabolic insights, role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, and emerging therapeutic strategies-a consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 4791–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Nguyen, D. T.; Anesi, J.; Alramahi, A.; Witting, P. K.; Chai, Z.; Khan, A. W.; Kelly, J.; Denton, K. M.; Golledge, J. , Moxonidine Increases Uptake of Oxidised Low-Density Lipoprotein in Cultured Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells and Inhibits Atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xie, Q.; Pan, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Peng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, S.; Tong, N. , Type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults: pathogenesis, prevention and therapy. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2024, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briaud, I.; Kelpe, C. L.; Johnson, L. M.; Tran, P. O.; Poitout, V. , Differential effects of hyperlipidemia on insulin secretion in islets of langerhans from hyperglycemic versus normoglycemic rats. Diabetes 2002, 51, 662–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Accili, D. , Reversing pancreatic β-cell dedifferentiation in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensellam, M.; Jonas, J.-C.; Laybutt, D. R. , Mechanisms of β-cell dedifferentiation in diabetes: recent findings and future research directions. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 236, R109–R143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, D.; Feng, X.; Lei, S.; Zhang, H.; Hu, W.; Yang, S.; Yu, X. ; Su Z, Pancreatic β-cell failure clinical implications therapeutic strategies in type 2 diabetes Chin Med, J. (Engl.) 2024, 137, 791–805. [Google Scholar]
- Wajchenberg, B. L. , beta-cell failure in diabetes and preservation by clinical treatment. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 187–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facilitating Positive Health Behaviors and Well-being to Improve Health Outcomes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, (Suppl 1), S77-s110.
- Reynolds, A.; Mitri, J., Dietary advice for individuals with diabetes. Endotext [Internet].South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc. 2024, Available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279012/.
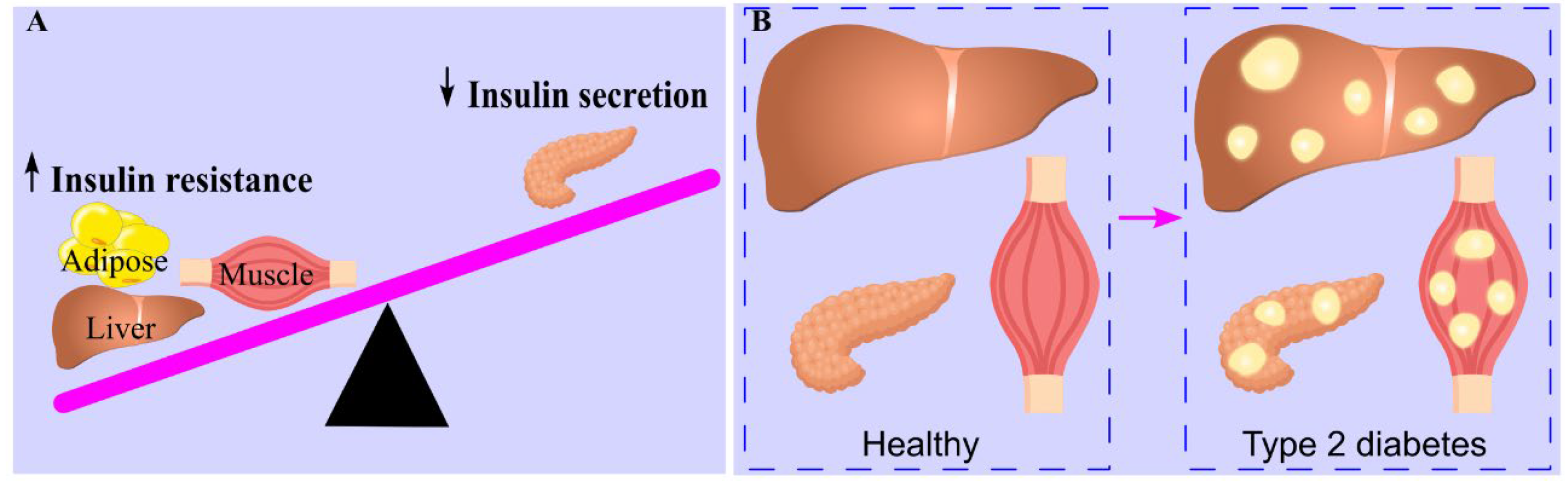
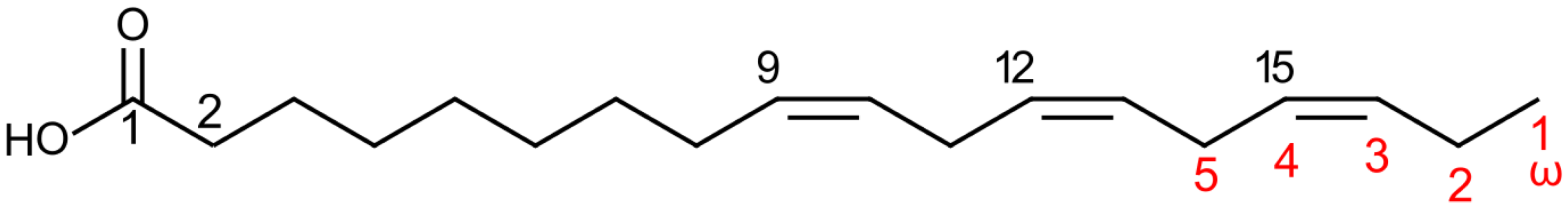
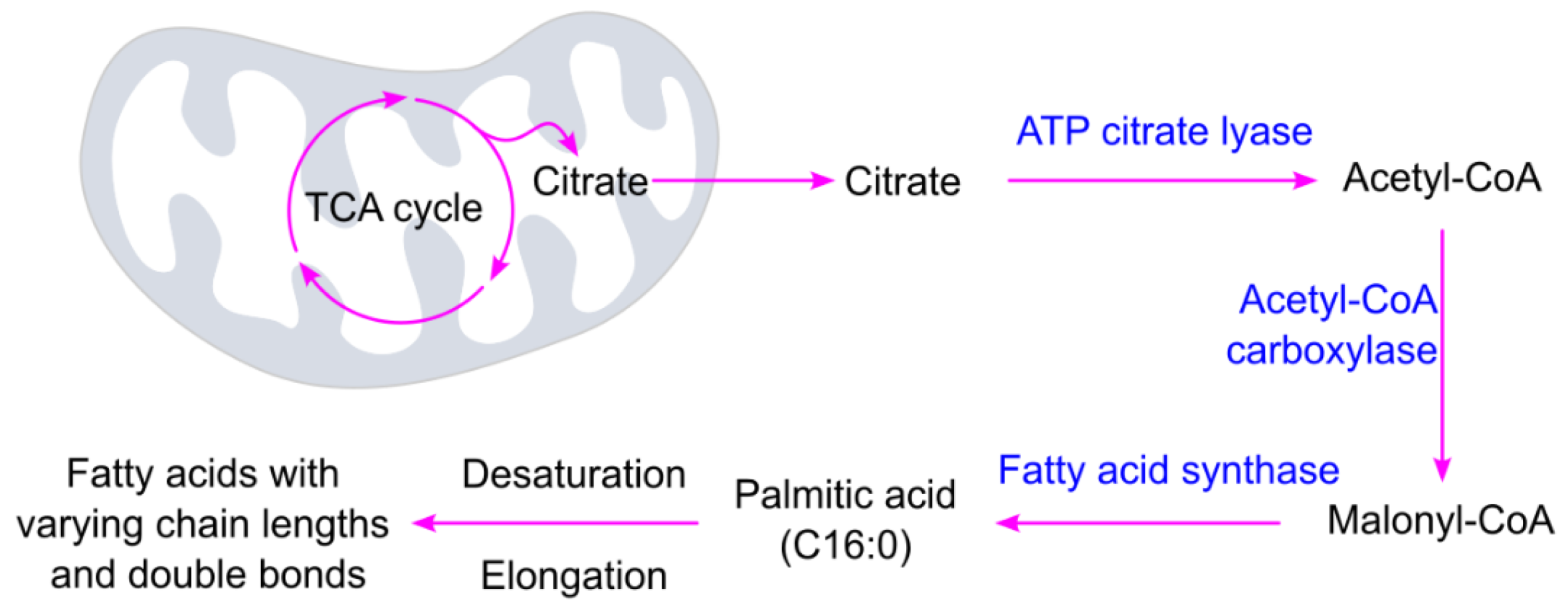
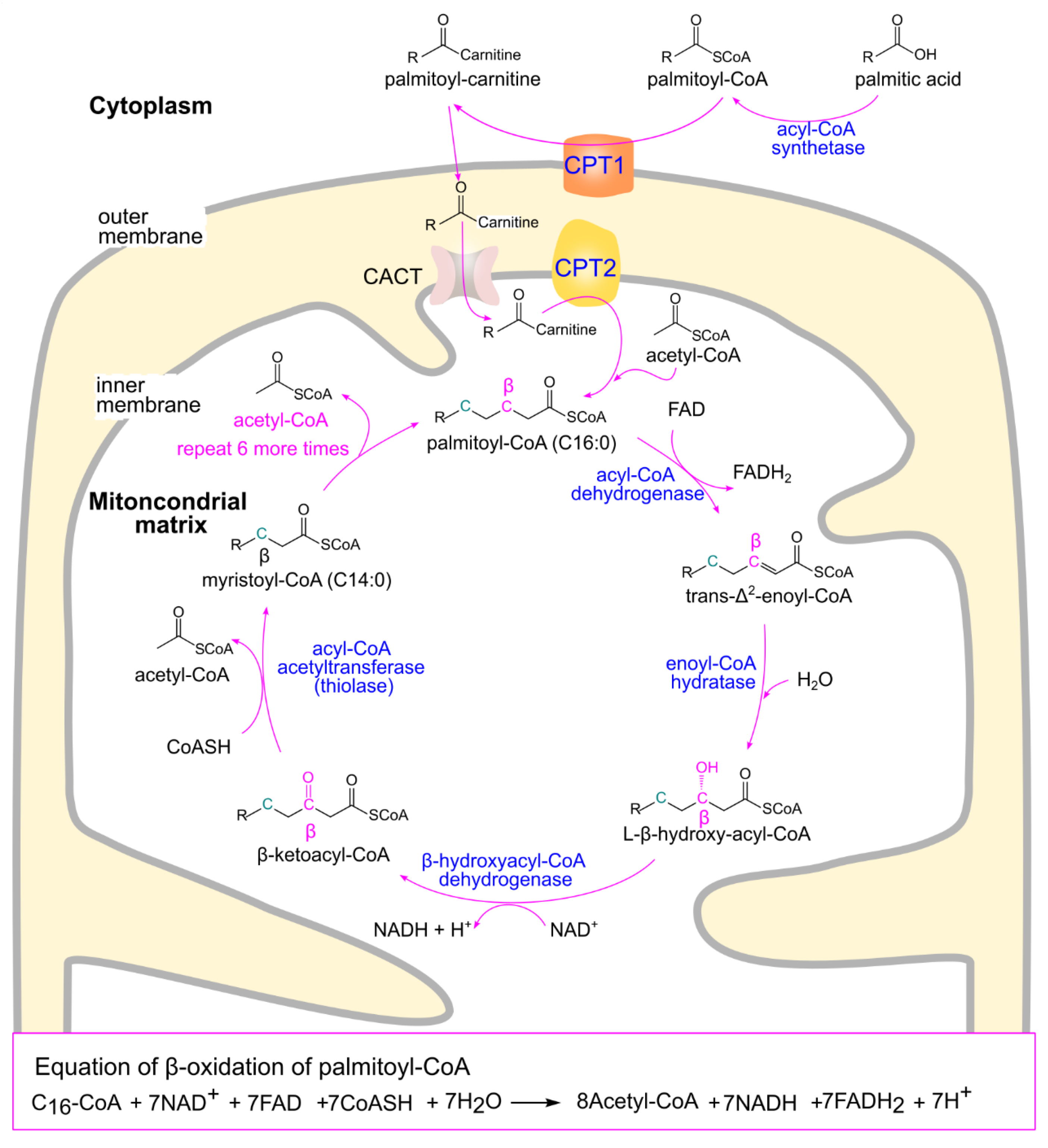
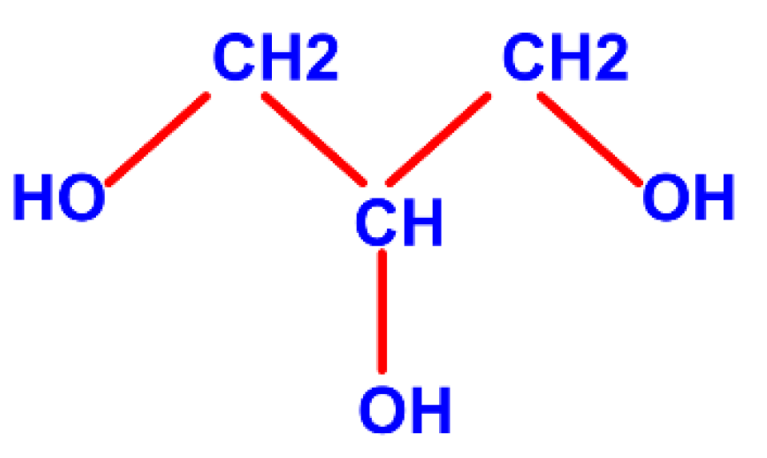
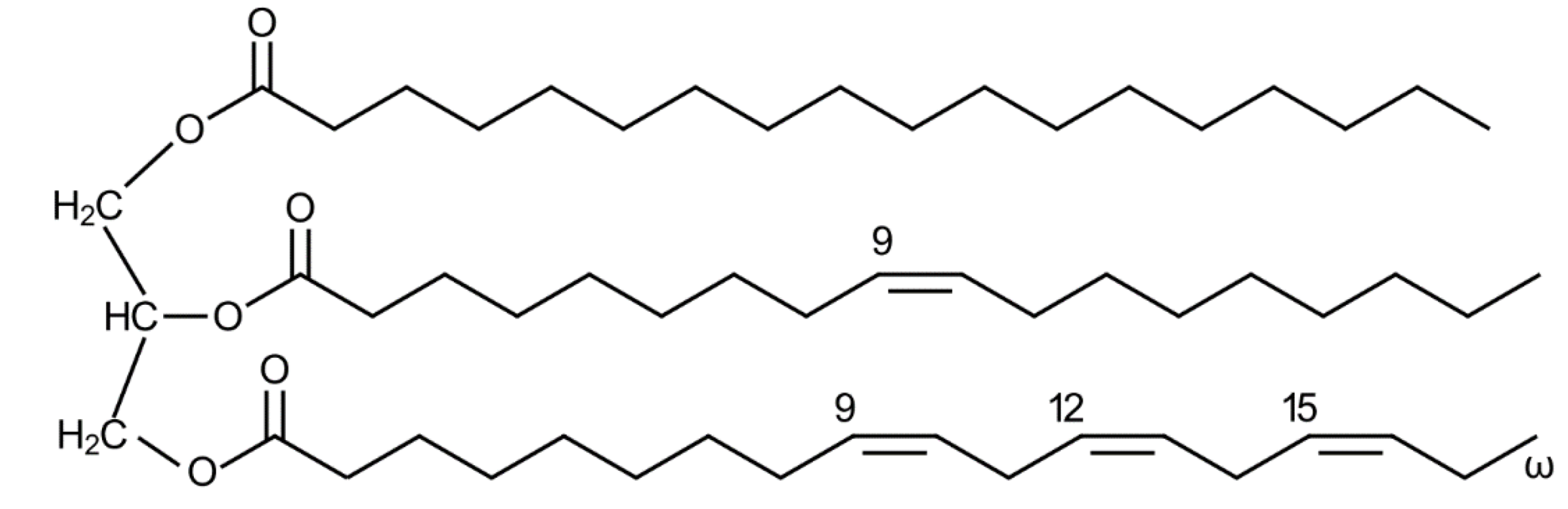
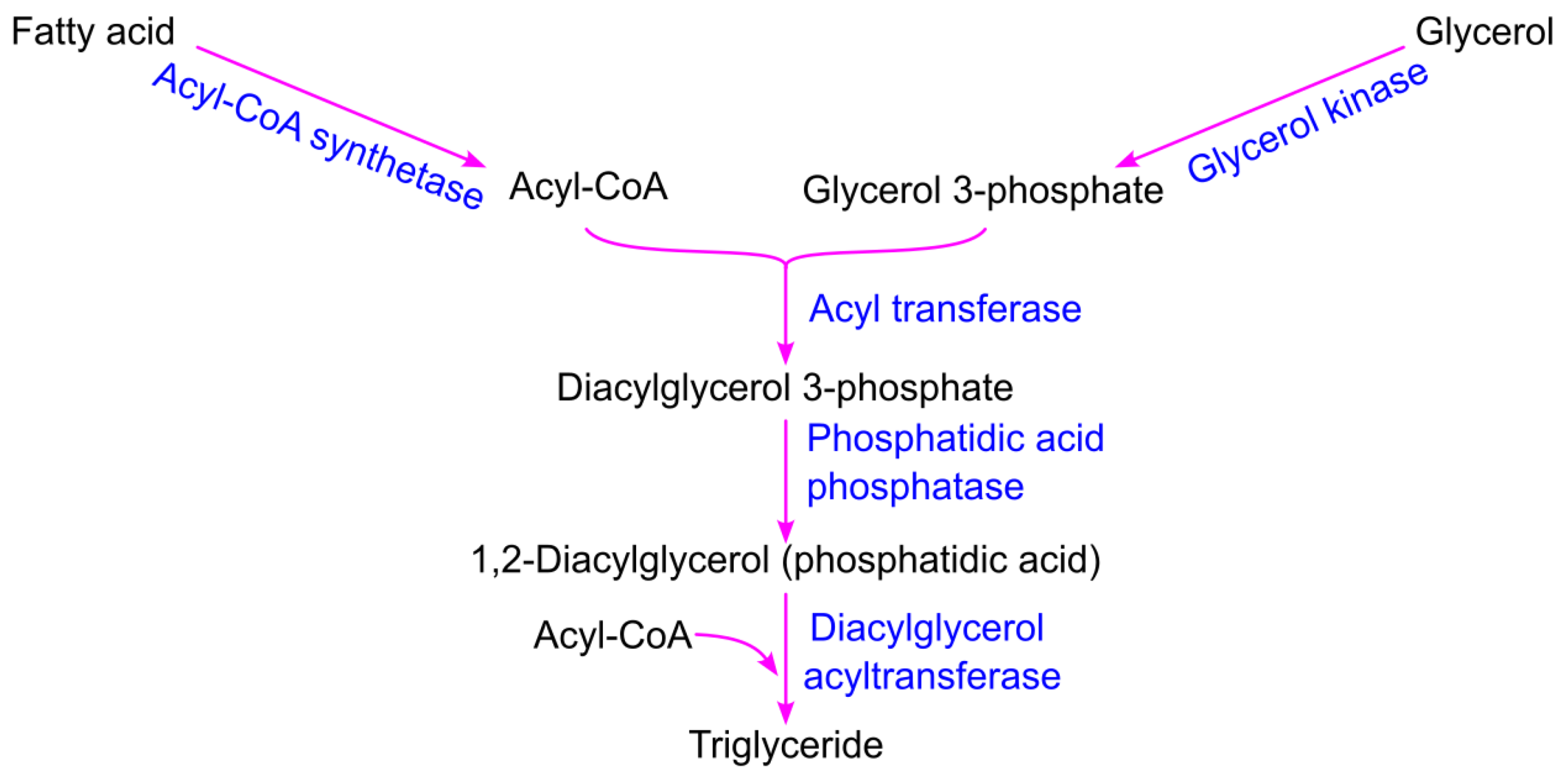
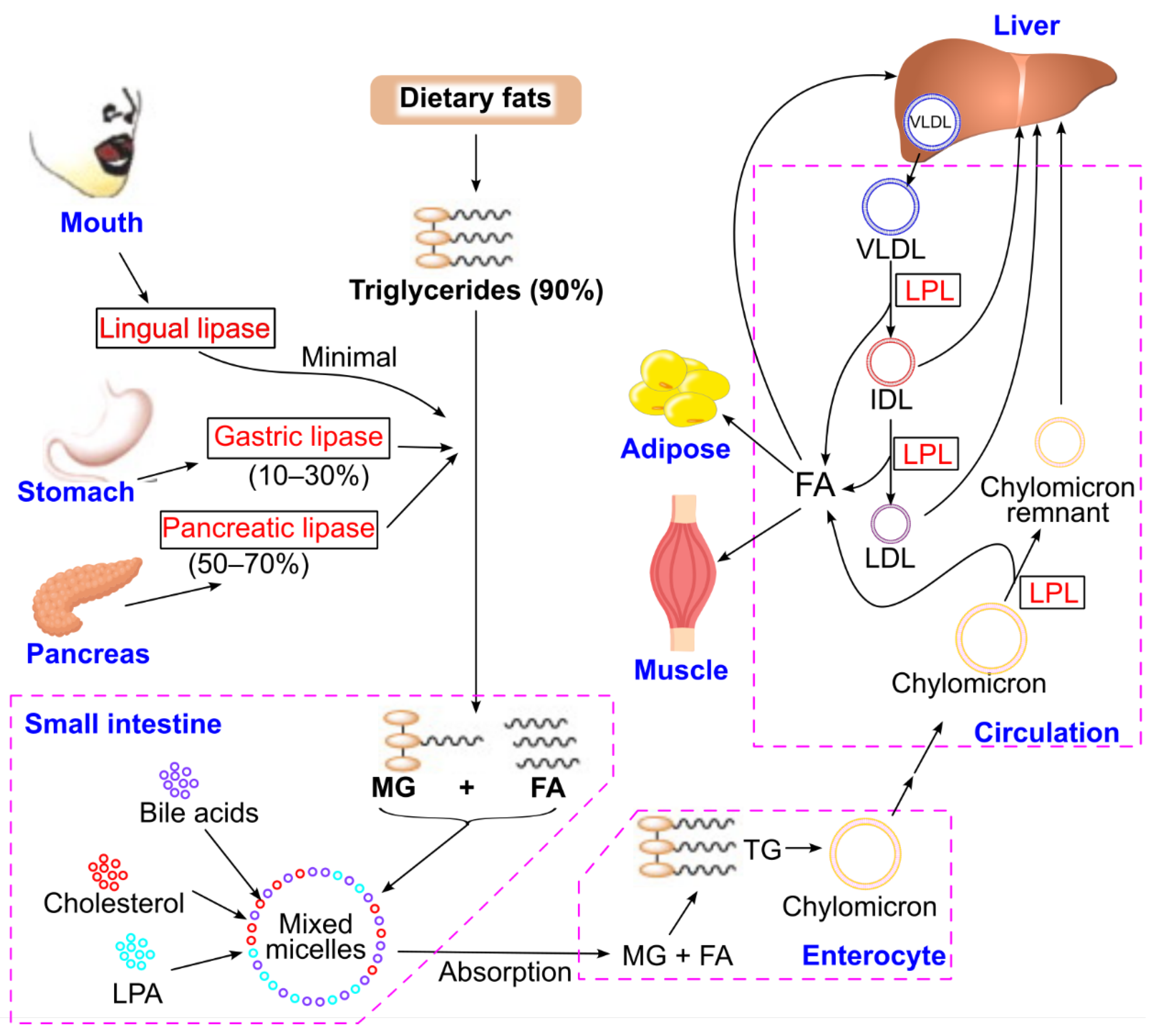
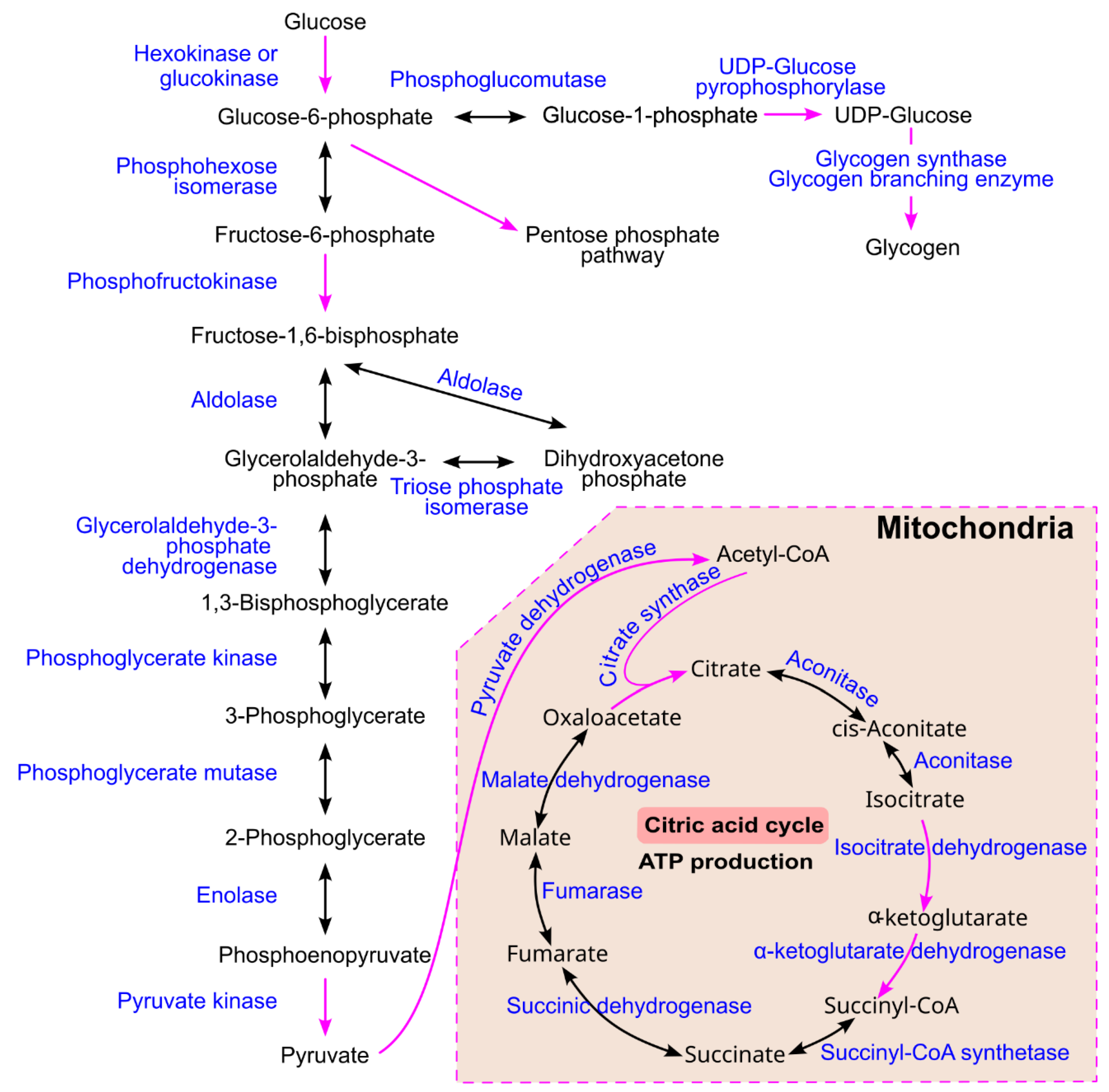
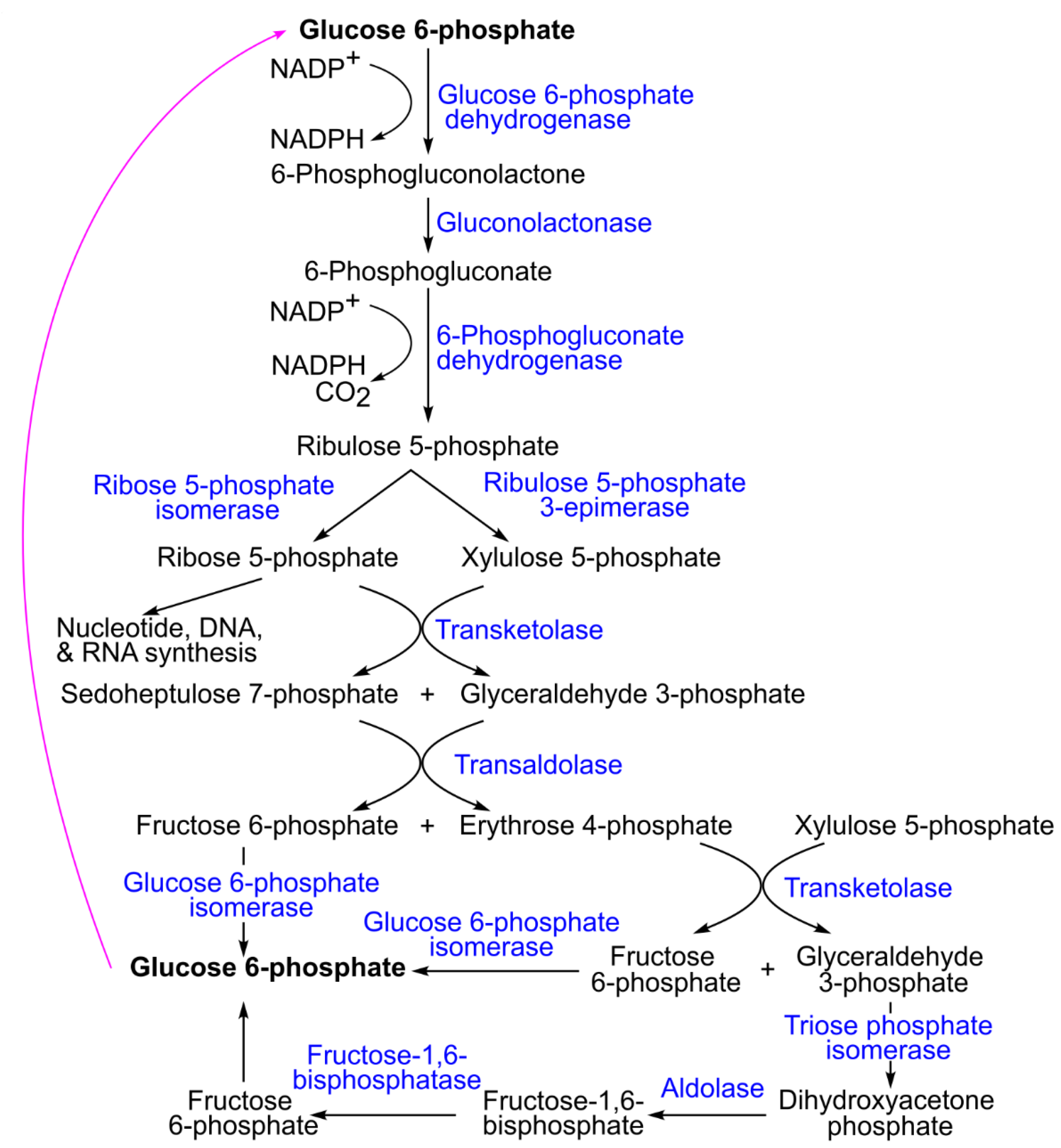
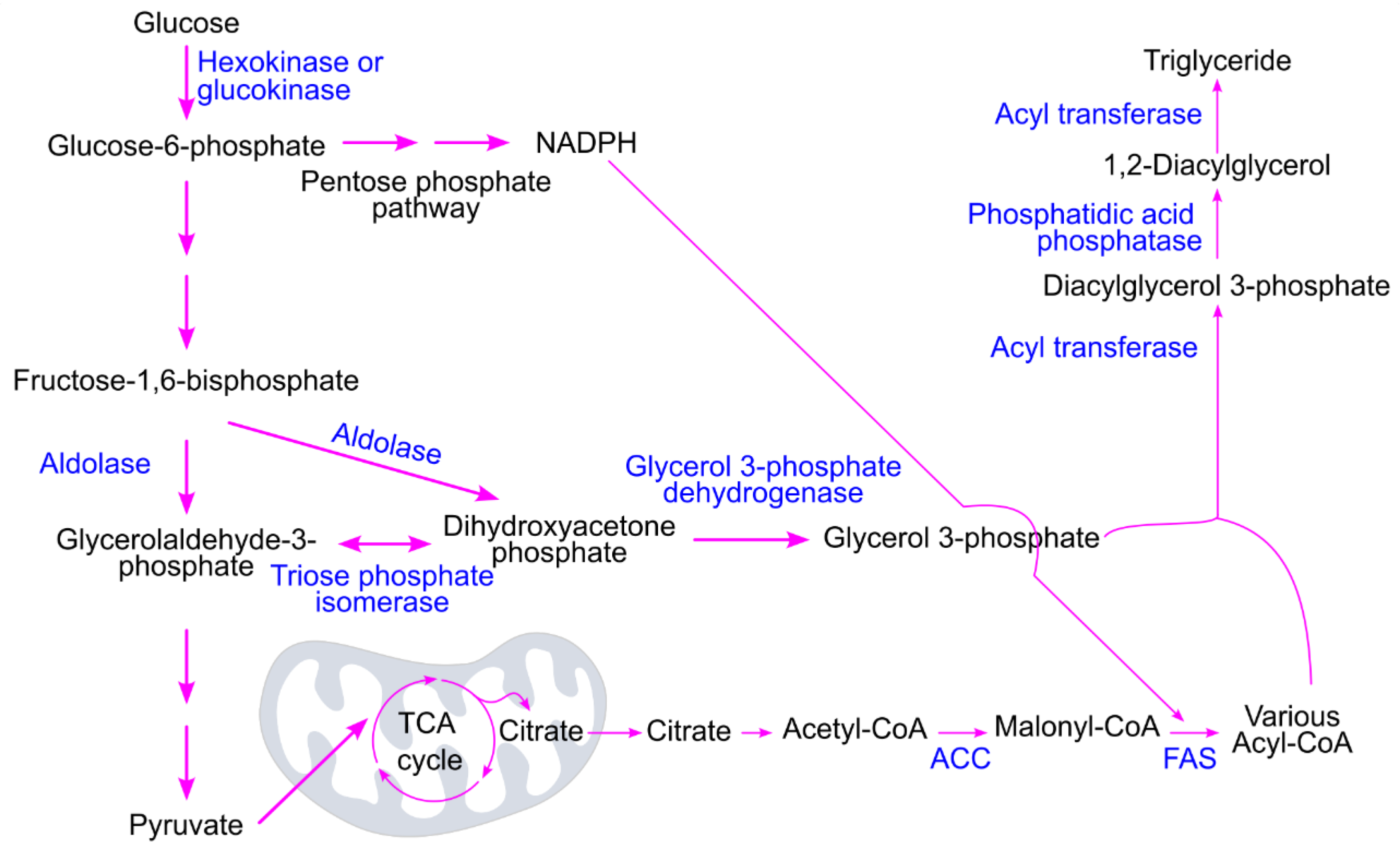
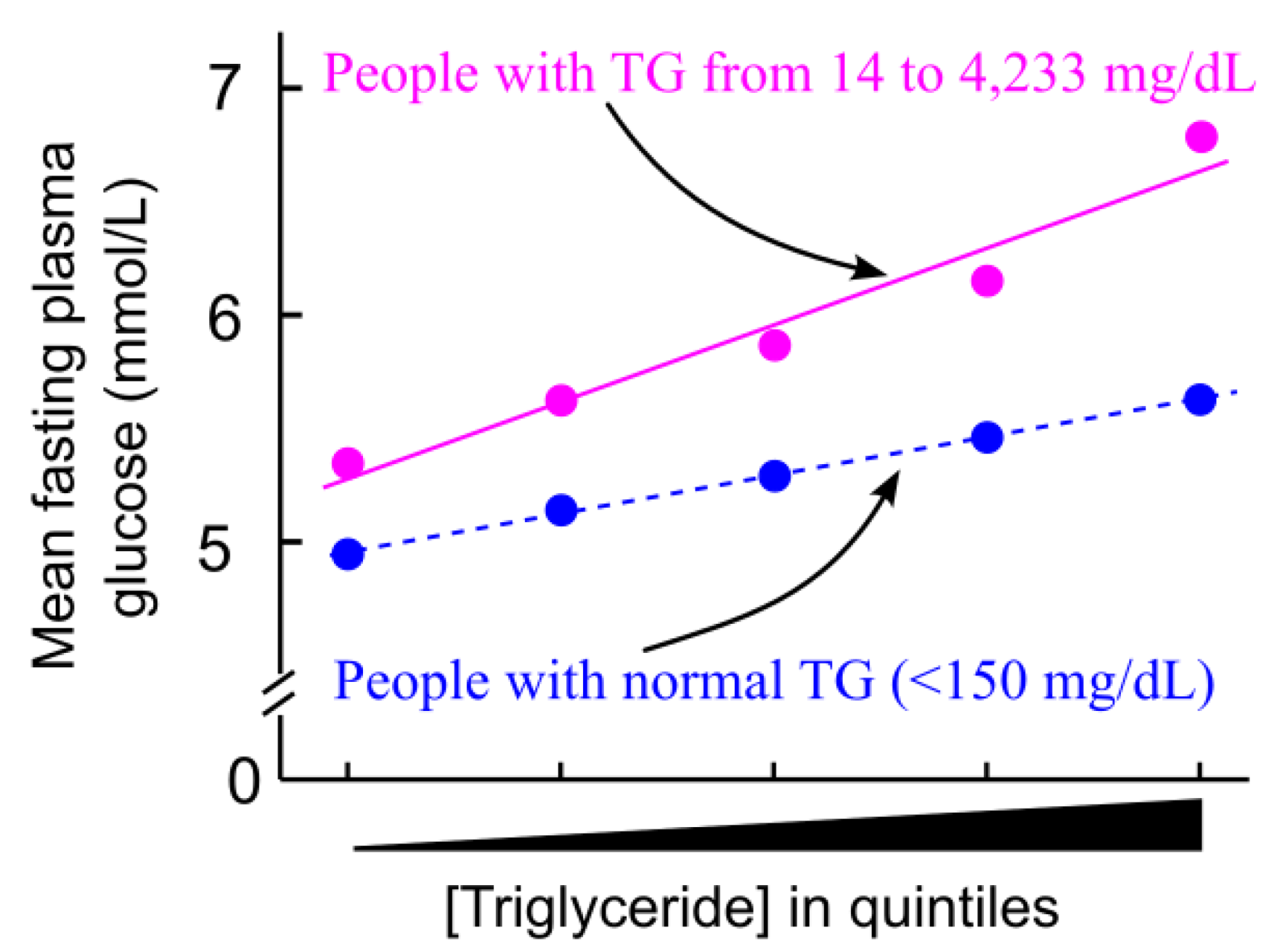
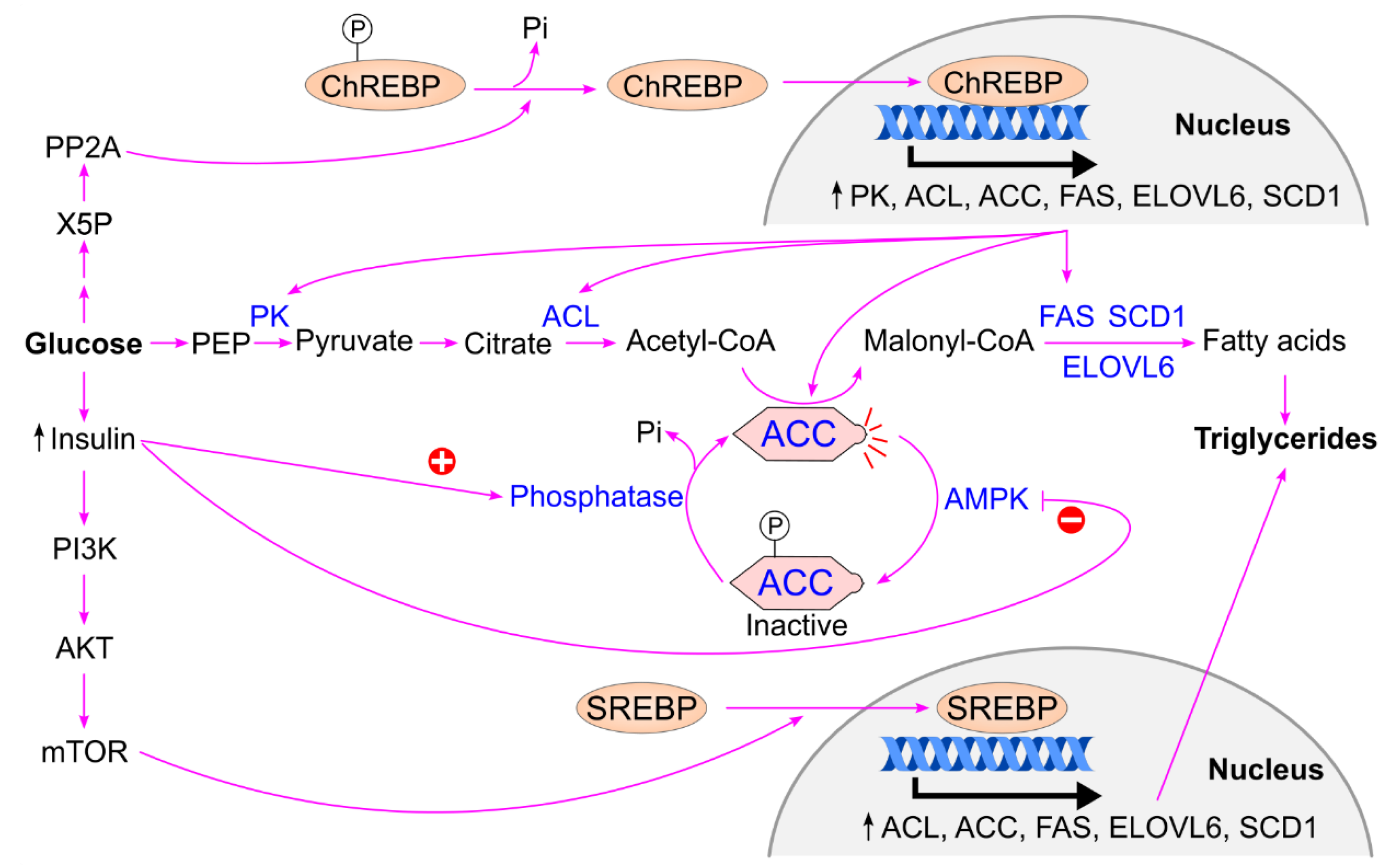
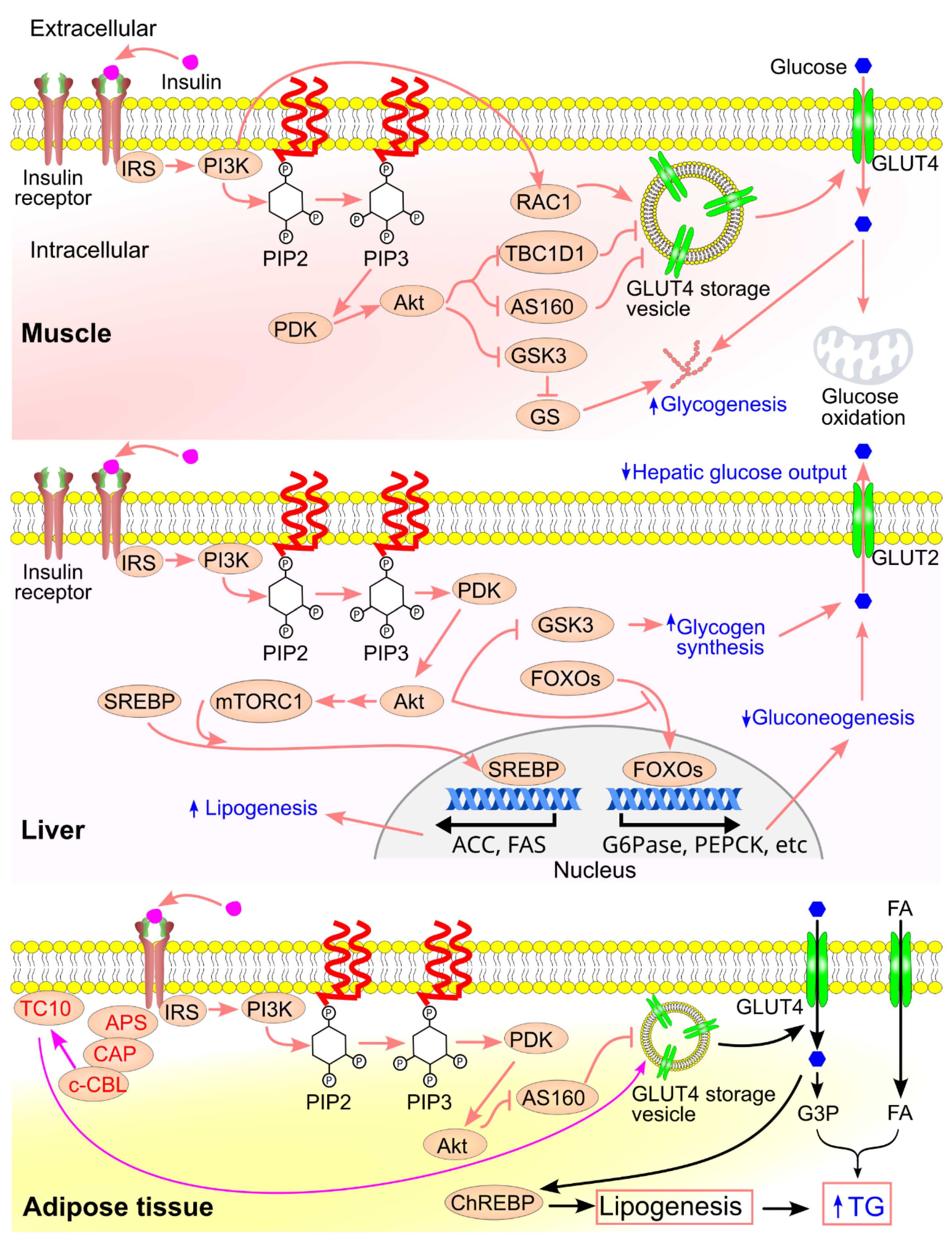
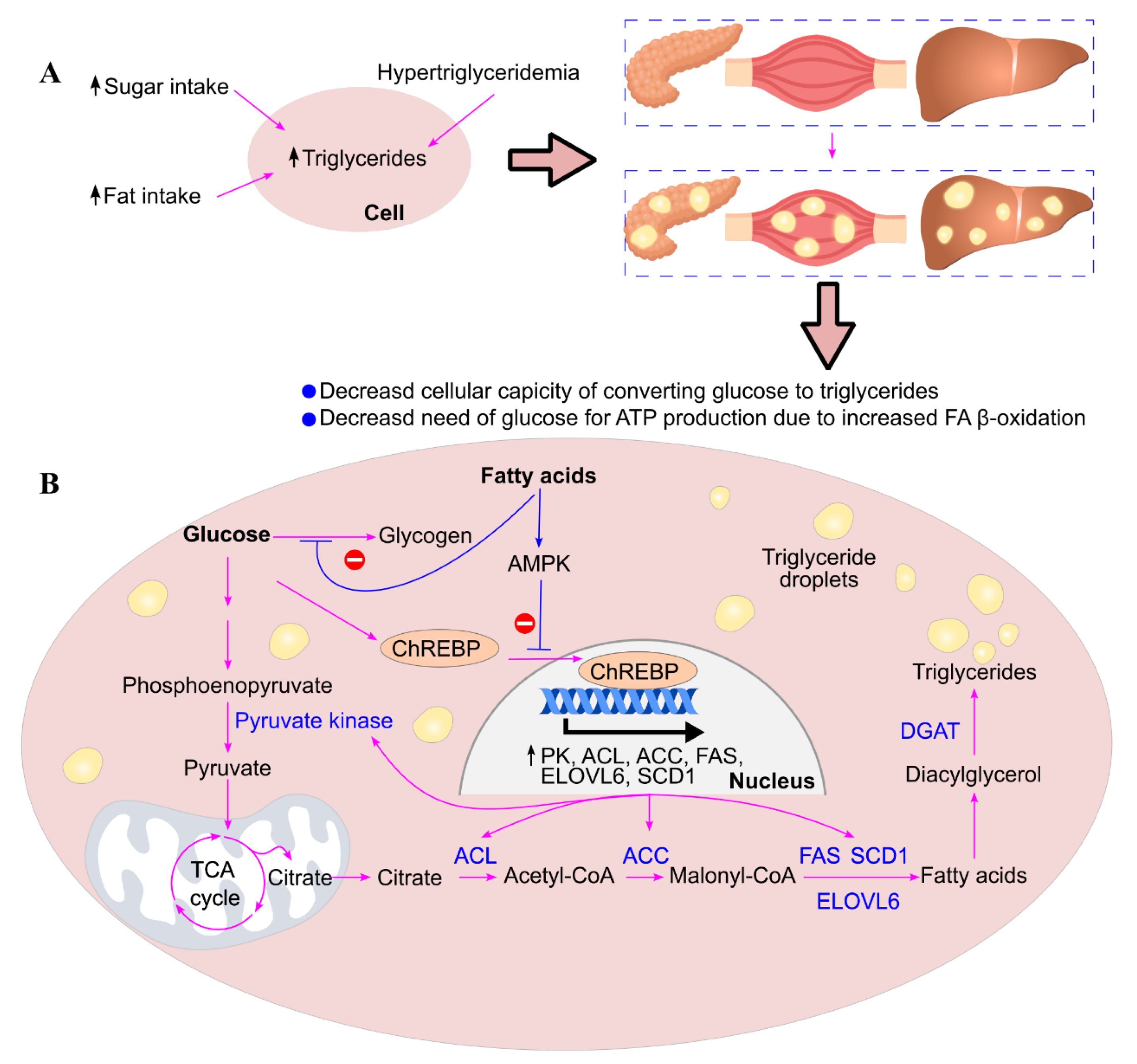
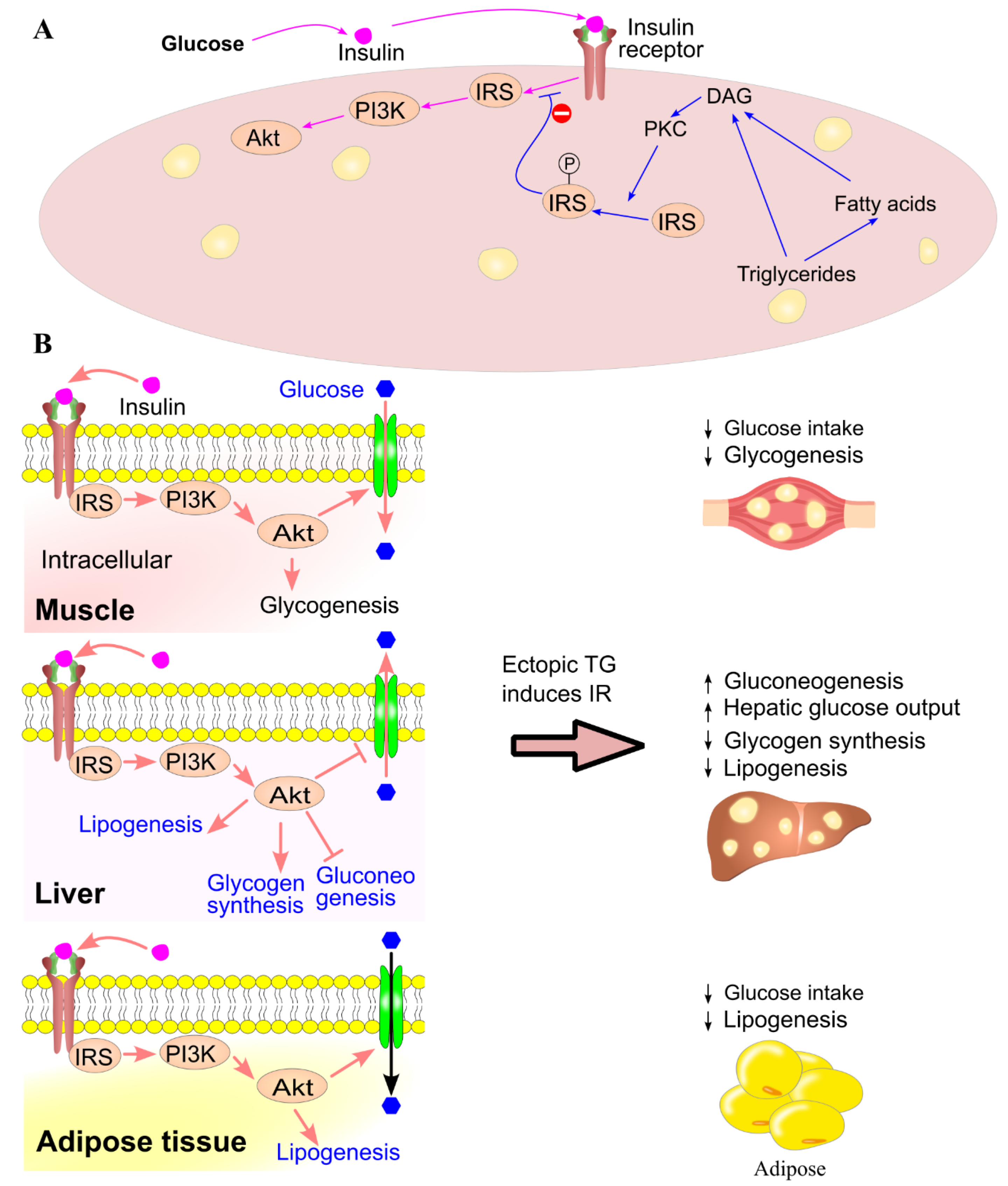
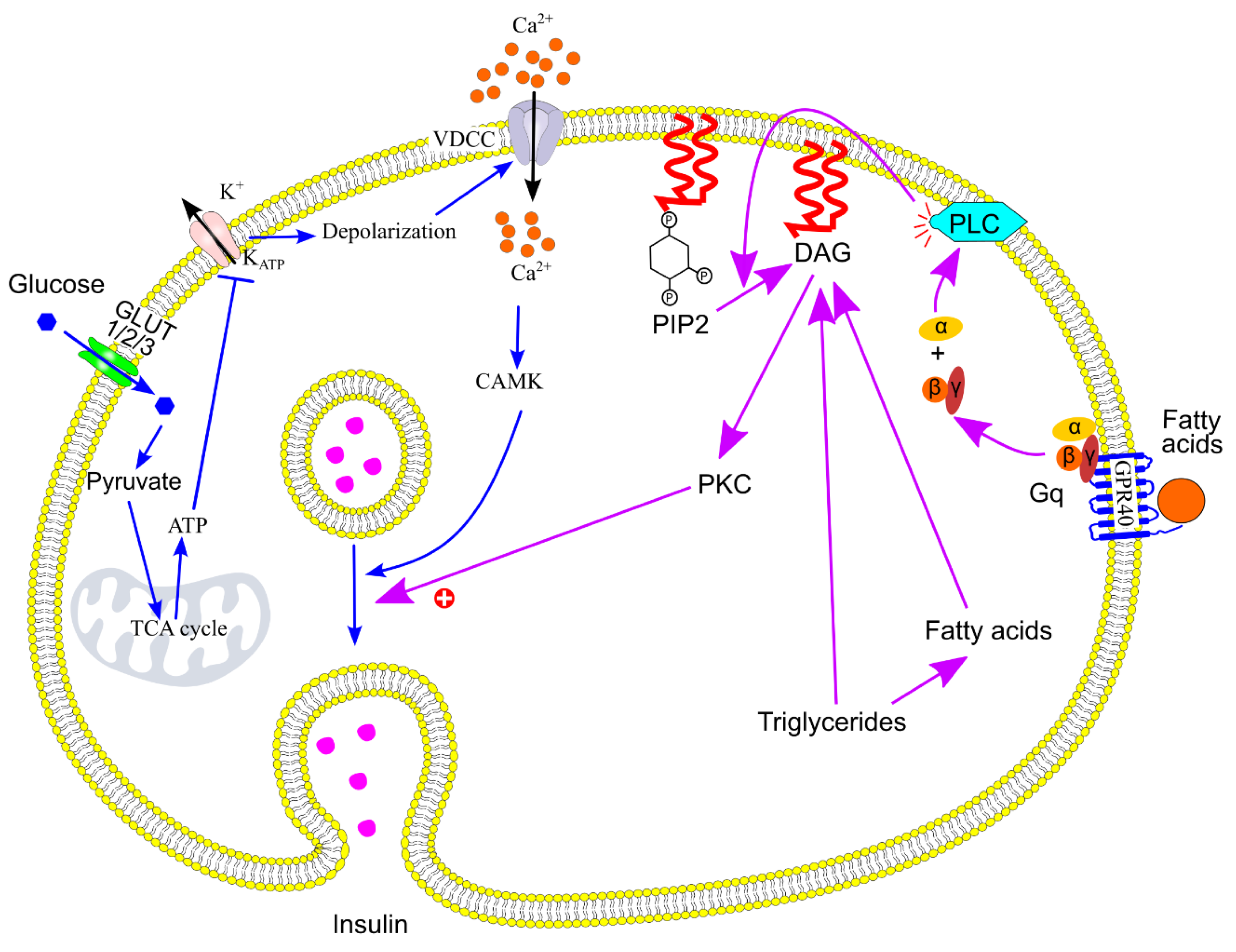
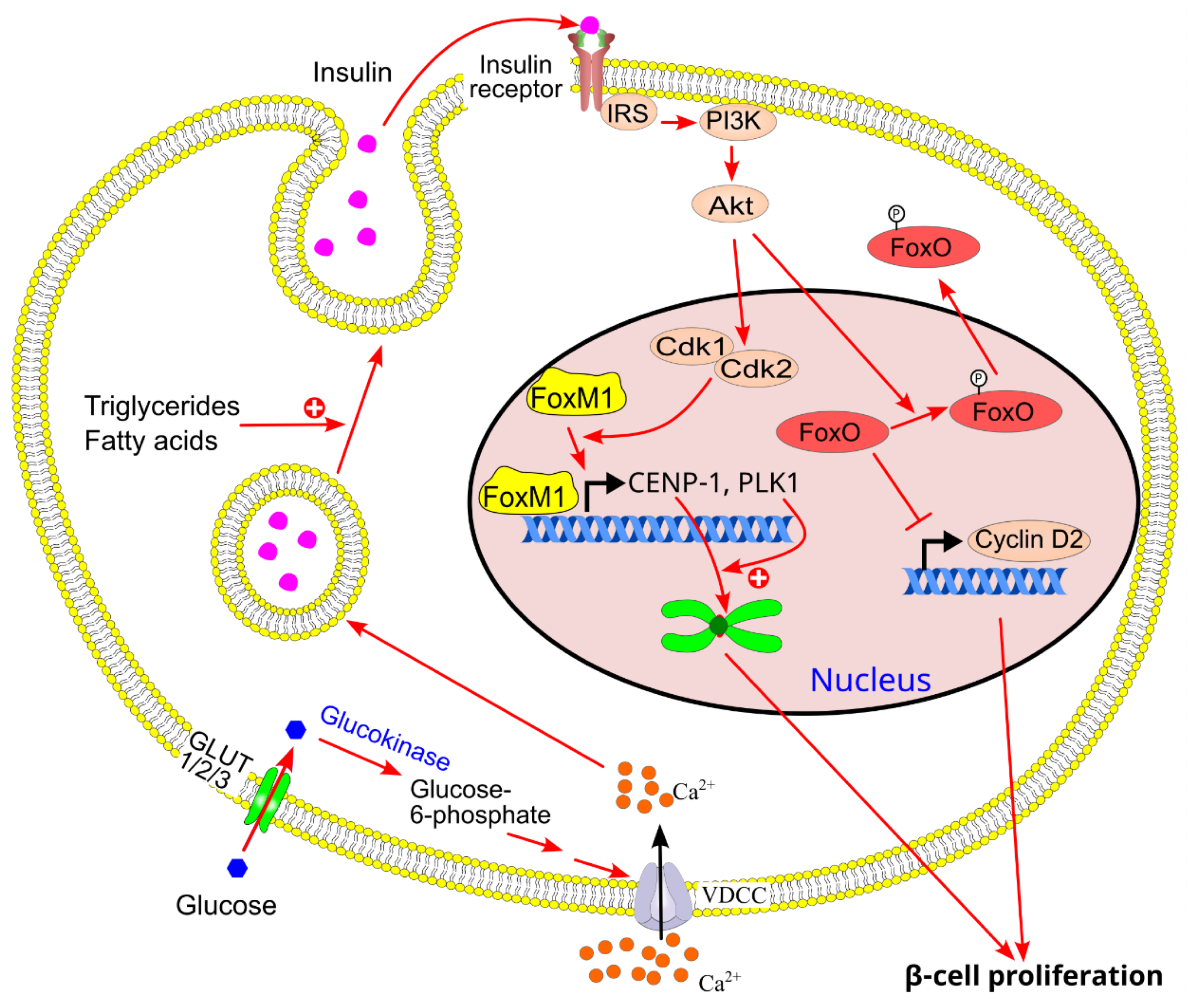
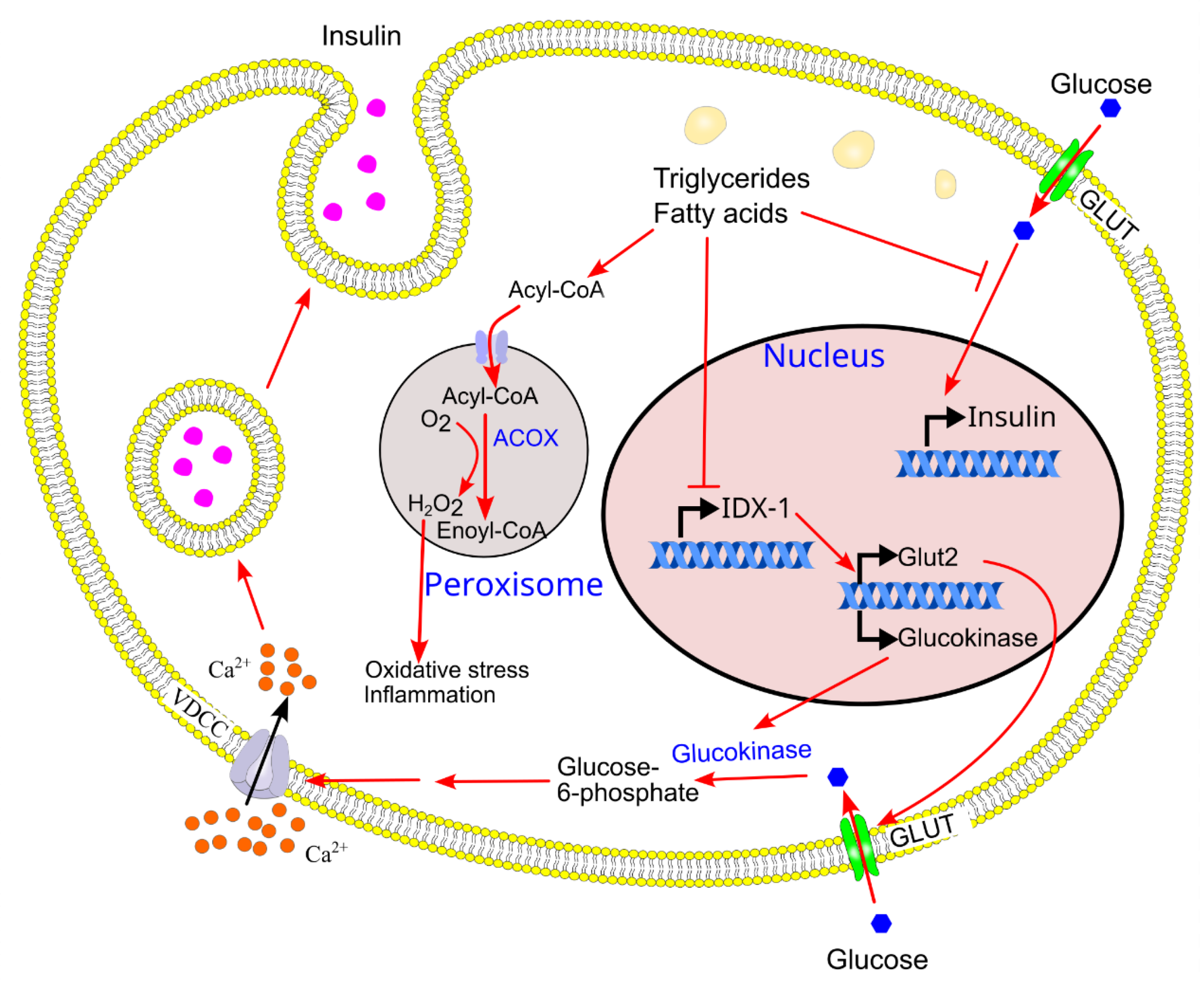
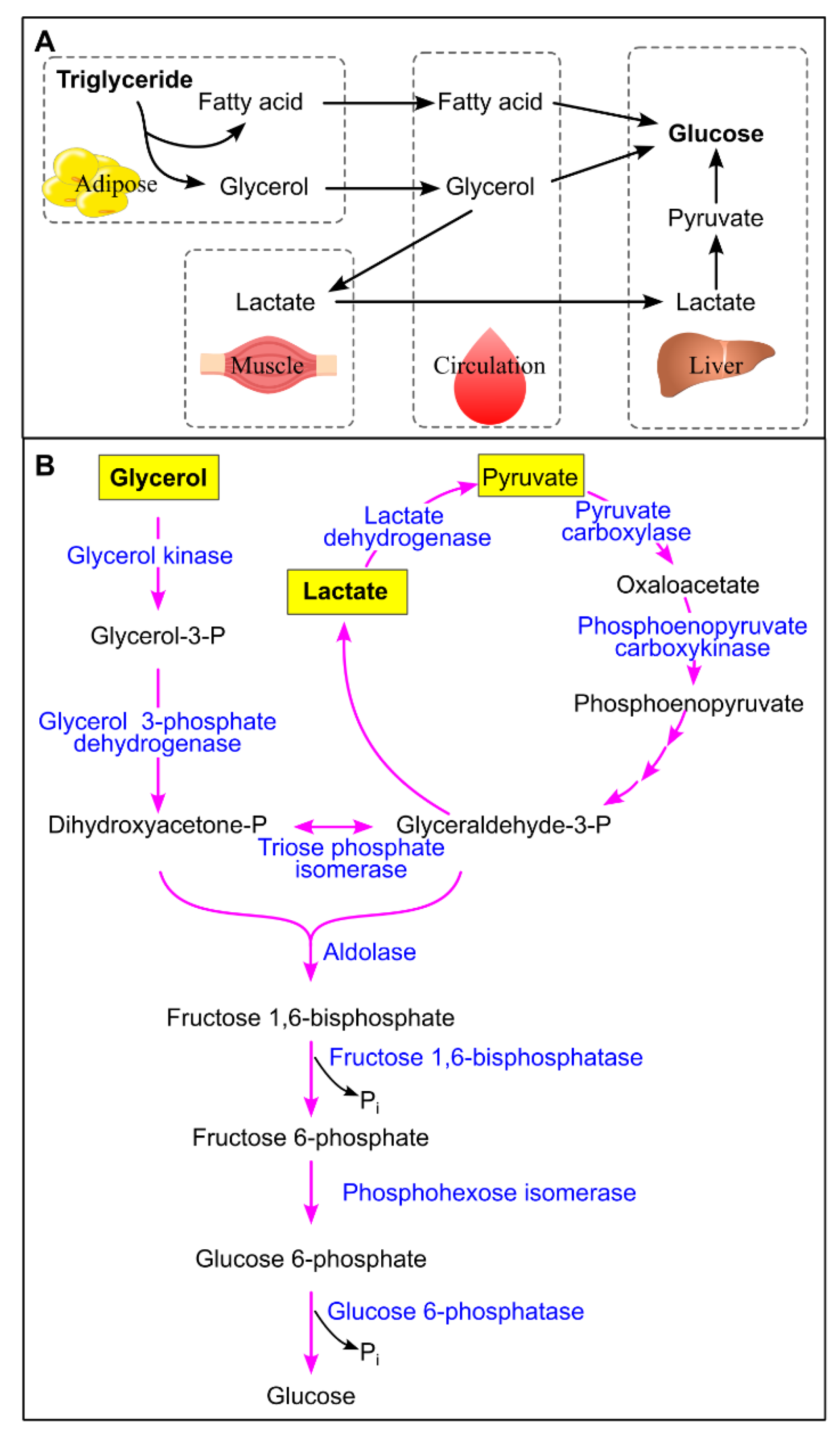
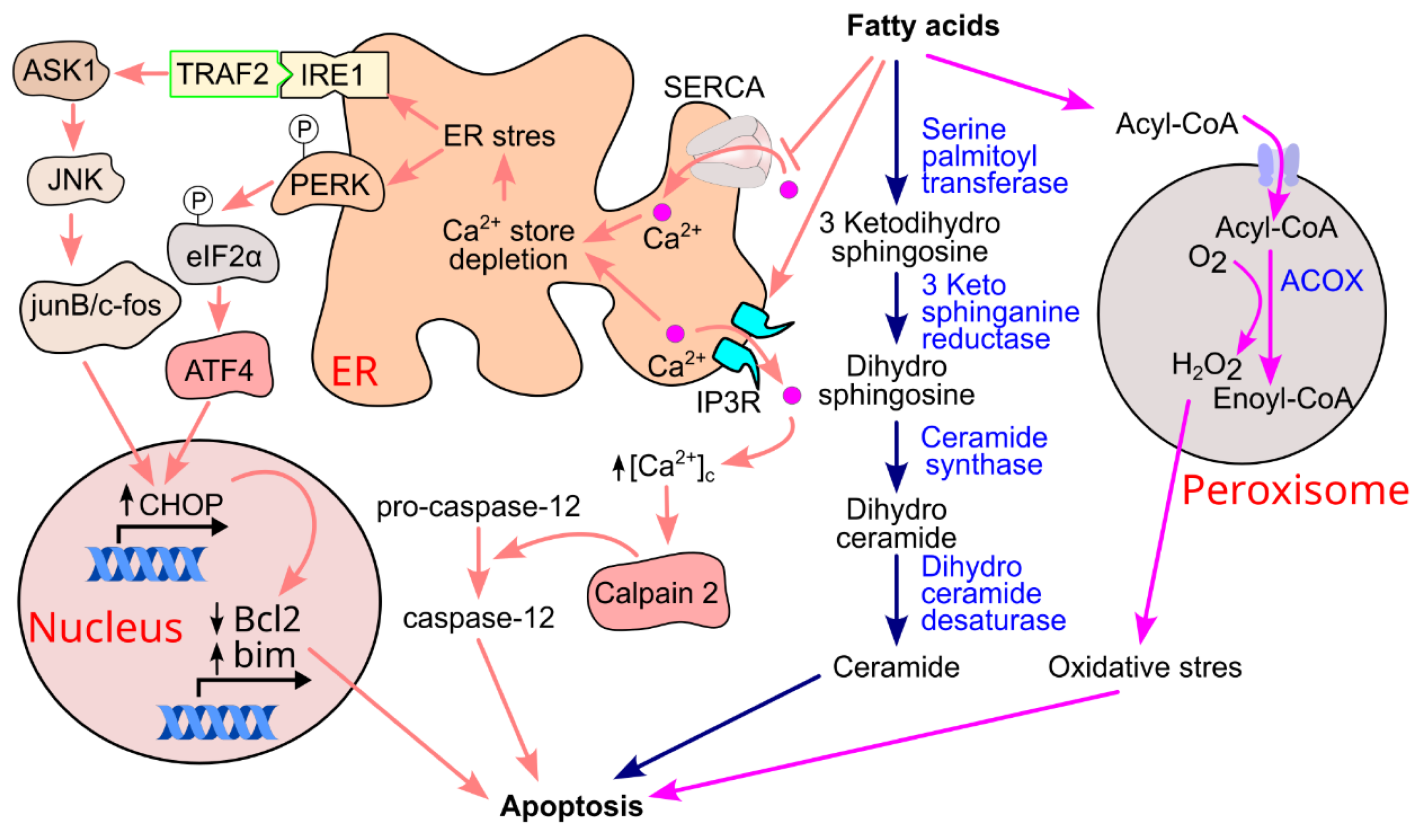
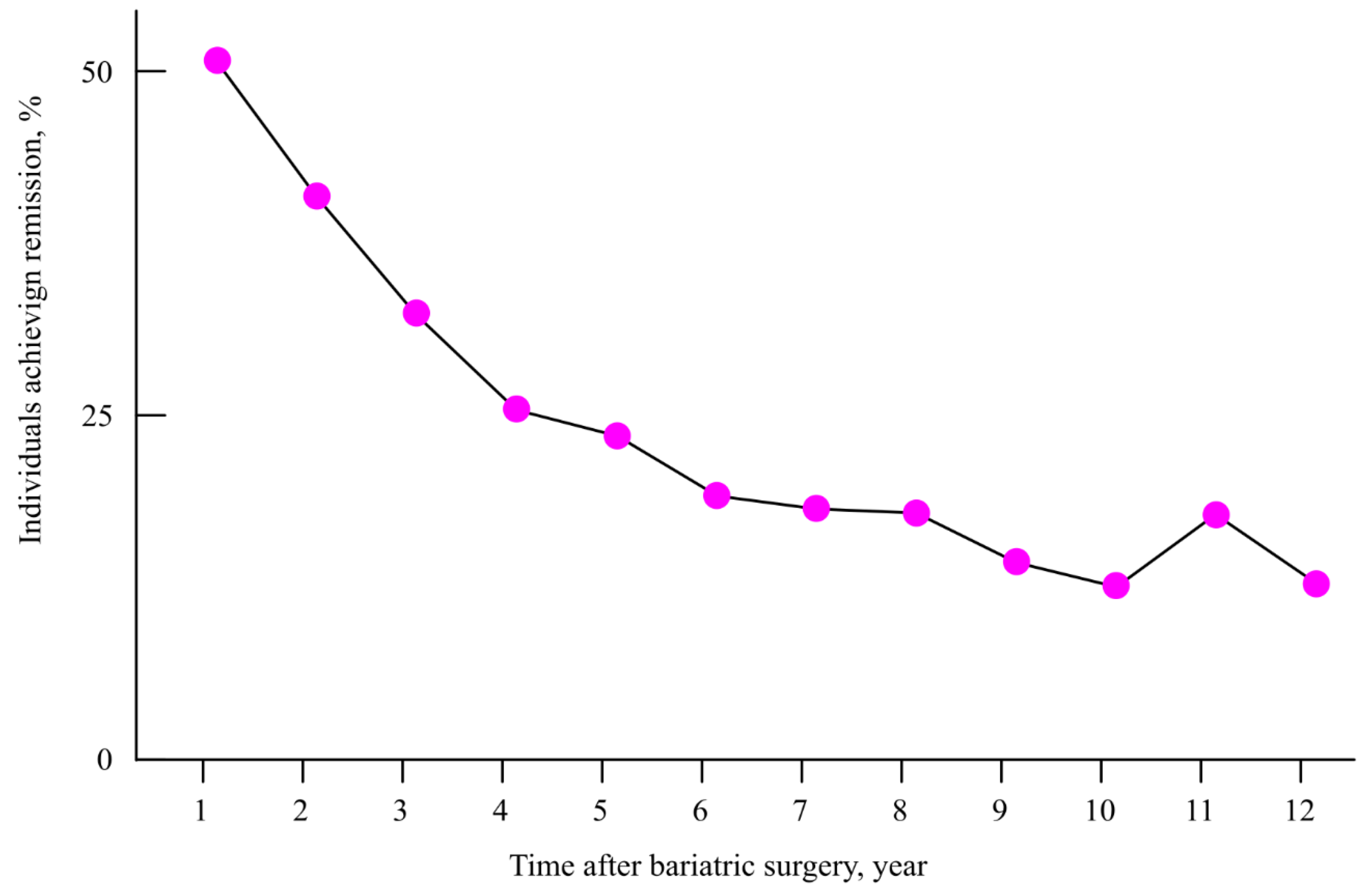
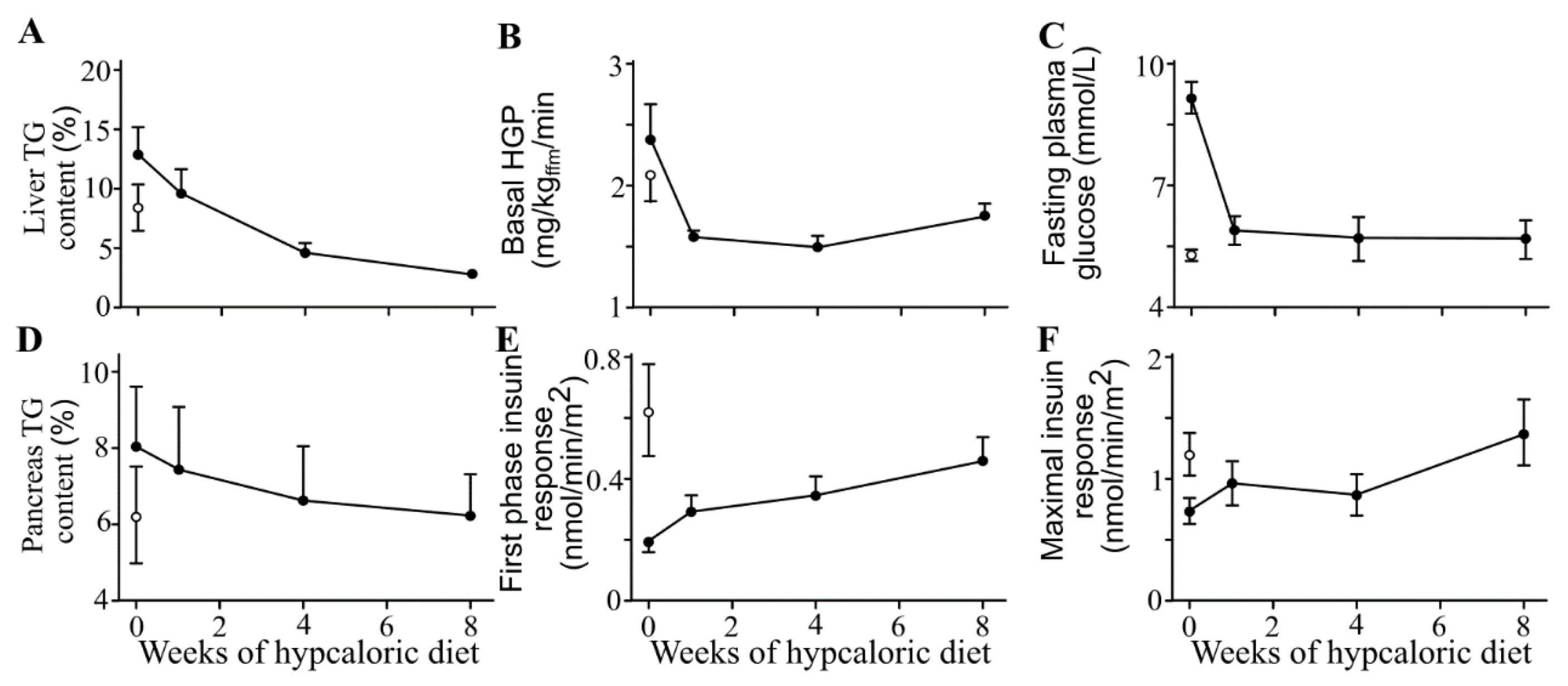
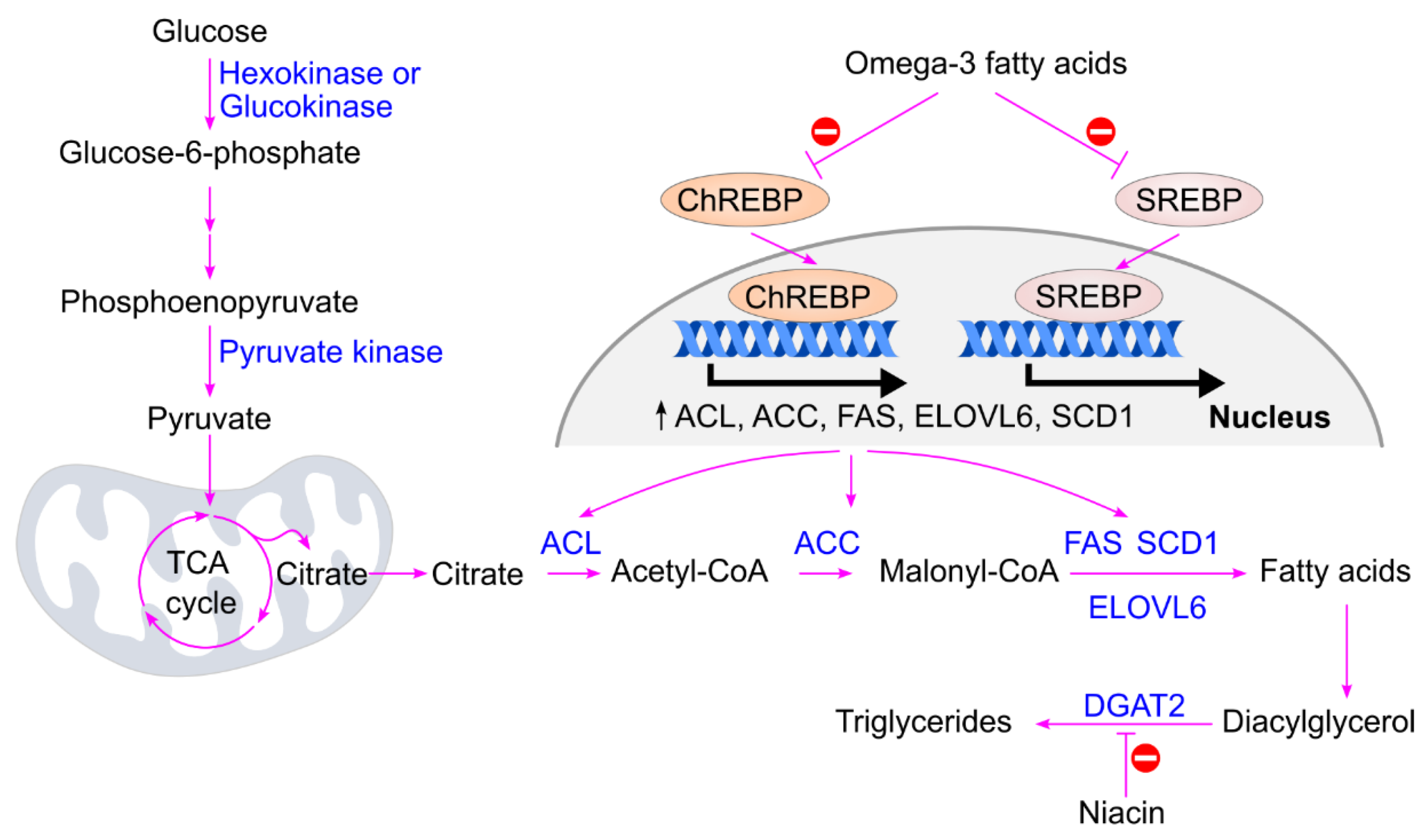
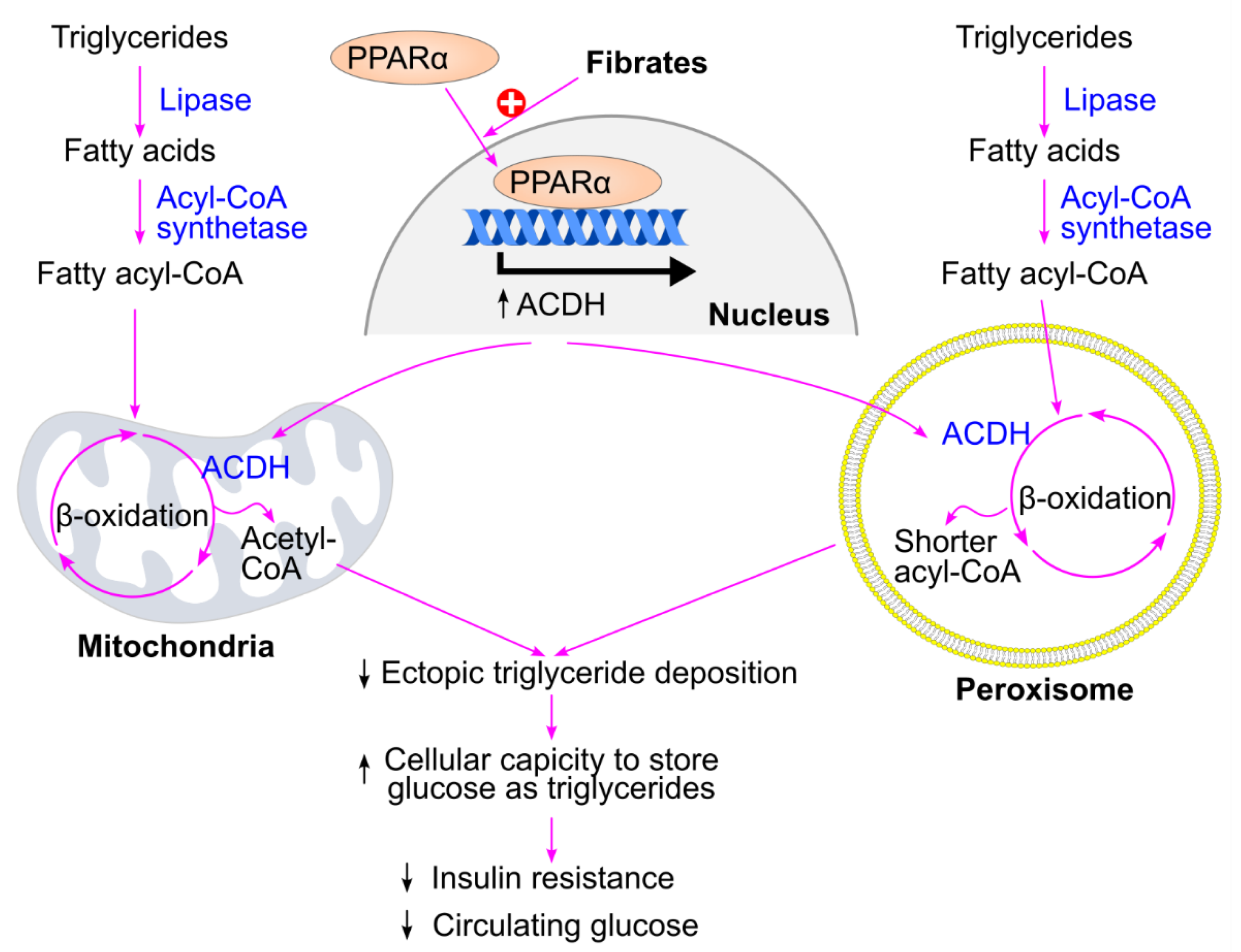
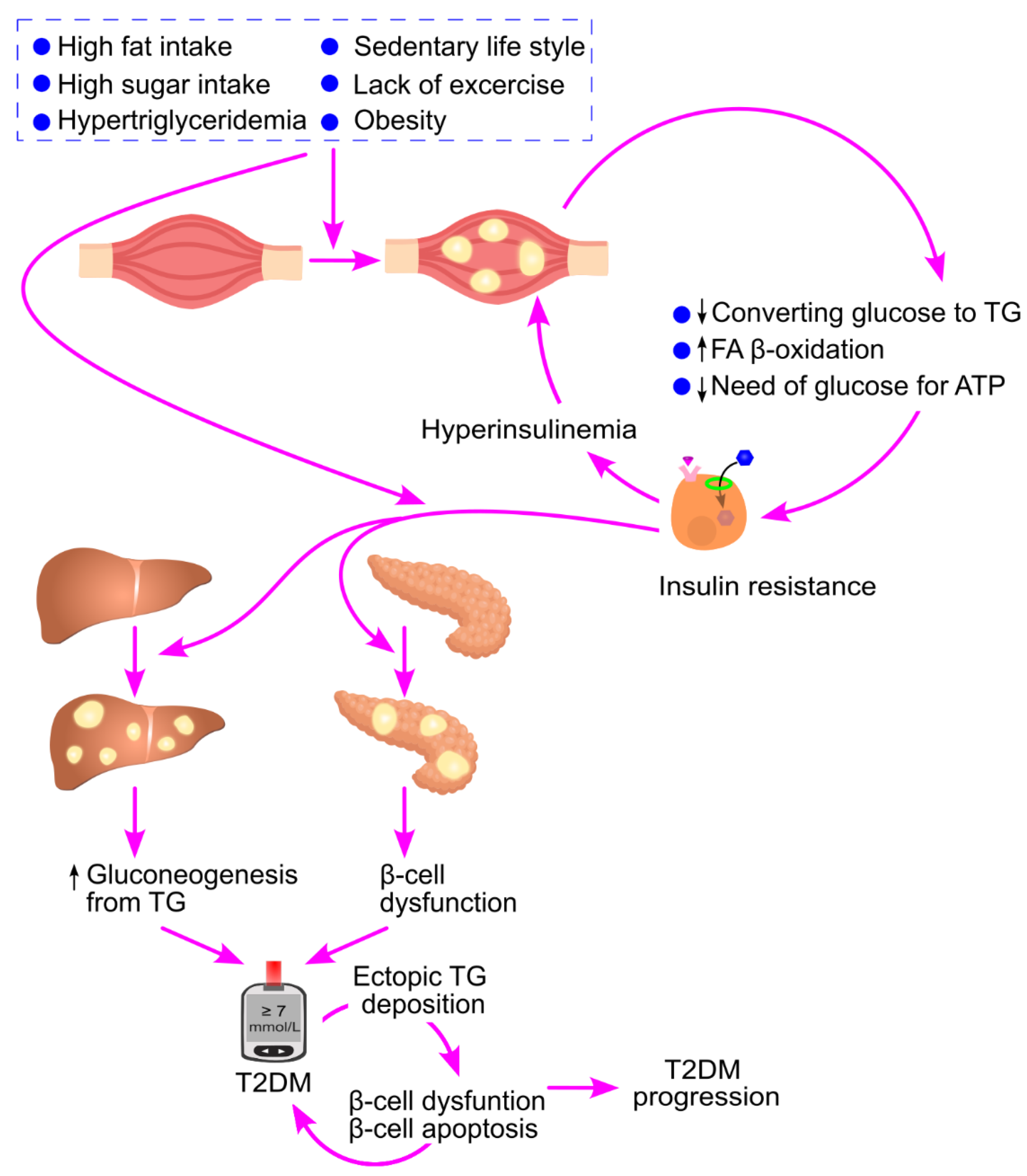
| Name | Carbon skeleton | Structure |
| Saturated fatty acids | ||
| Butyric acid | 4:0 | CH3(CH2)2COOH |
| Valeric acid | 5:0 | CH3(CH2)3COOH |
| Lauric acid | 12:0 | CH3(CH2)10COOH |
| Myristic aid | 14:0 | CH3(CH2)12COOH |
| Palmitic acid | 16:0 | CH3(CH2)14COOH |
| Stearic acid | 18:0 | CH3(CH2)16COOH |
| Arachidic acid | 20:0 | CH3(CH2)18COOH |
| Lignoceric acid | 24:0 | CH3(CH2)22COOH |
| Unsaturated fatty acids | ||
| Palmitoleic acid | 16:1 (∆9) | CH3(CH2)5CH=CH(CH2)7COOH |
| Oleic acid | 18:1 (∆9) | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH |
| Linoleic acid | 18:2 (∆9,12) | CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH |
| α-Linolenic acid | 18:3 (∆9,12,15) | CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH |
| Arachidonic acid | 20:4 (∆5,8,11,14) | CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)3COOH |
| EPA | 20:5 (∆5,8,11,14,17) | CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH (CH2)3COOH |
| DHA | 22:6 (∆4,7,10,13,16,19) | CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH CH2CH=CH(CH2)2COOH |
| Study: Author, year | Triglyceride change in the surgery group |
Triglyceride change in the control group |
P value | Reference |
| Sjöström et al., 2004 | -16.3 mg/dL | 2.2 mg/dL | <0.001 | [290] |
| Dixon et al., 2008 | -71.7 mg/dL | 2.1mg/dL | 0.02 | [291] |
| Courcoulas et al., 2024 | -19.0% | 2.3% | 0.002 | [292] |
| Kirwan et al., 2022 | -48 mg/dL | -10 mg/dL | 0.004 | [293] |
| Heffron, et al., 2018 | -13 mg/dL | N/A | N/A | [295] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





