Submitted:
28 August 2025
Posted:
29 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Computational Breast Cancer Data Analysis
2.2. Patient Tissue Samples
2.3. Isolation of RNA from Tissue Samples
2.4. Gene Expression Analysis
2.5. Prognostic Analysis
2.6. Exploring the Function of TNFRSR12A
2.7. Tumor Microenvironment Immune Cell Profiling
2.8. Single-Cell Data Analysis
2.9. Drug Sensitivity Analyses
2.10. Molecular Docking Simulation of TNFRSF12A and Docetaxe
2.11. The Culture of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Lines
2.12. Cell Transfection
2.13. Real-Time Fluorescent Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.14. In Vitro T-Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
2.15. Tube Formation Assay
2.16. CCK-8 Cytotoxicity Assay
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
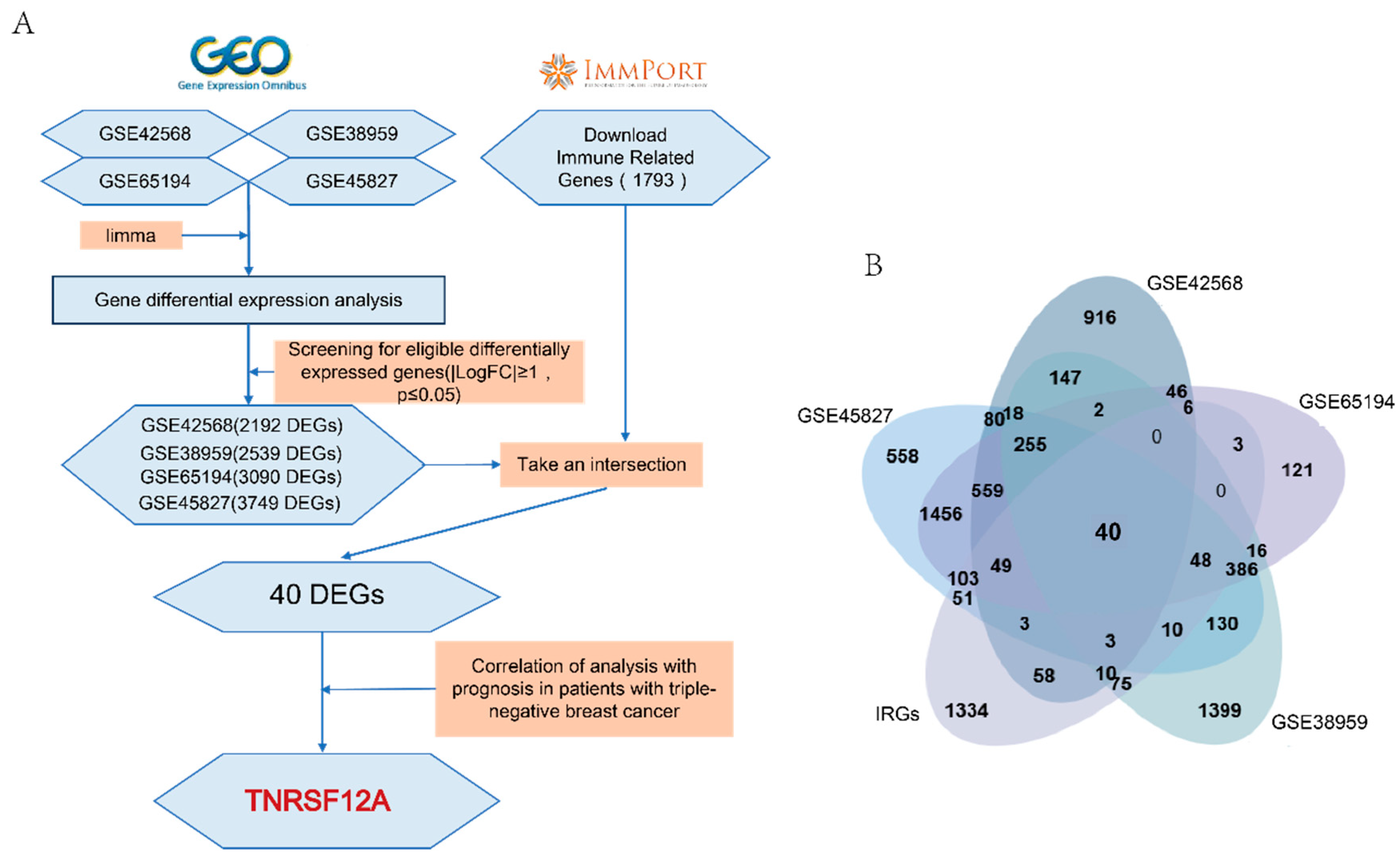
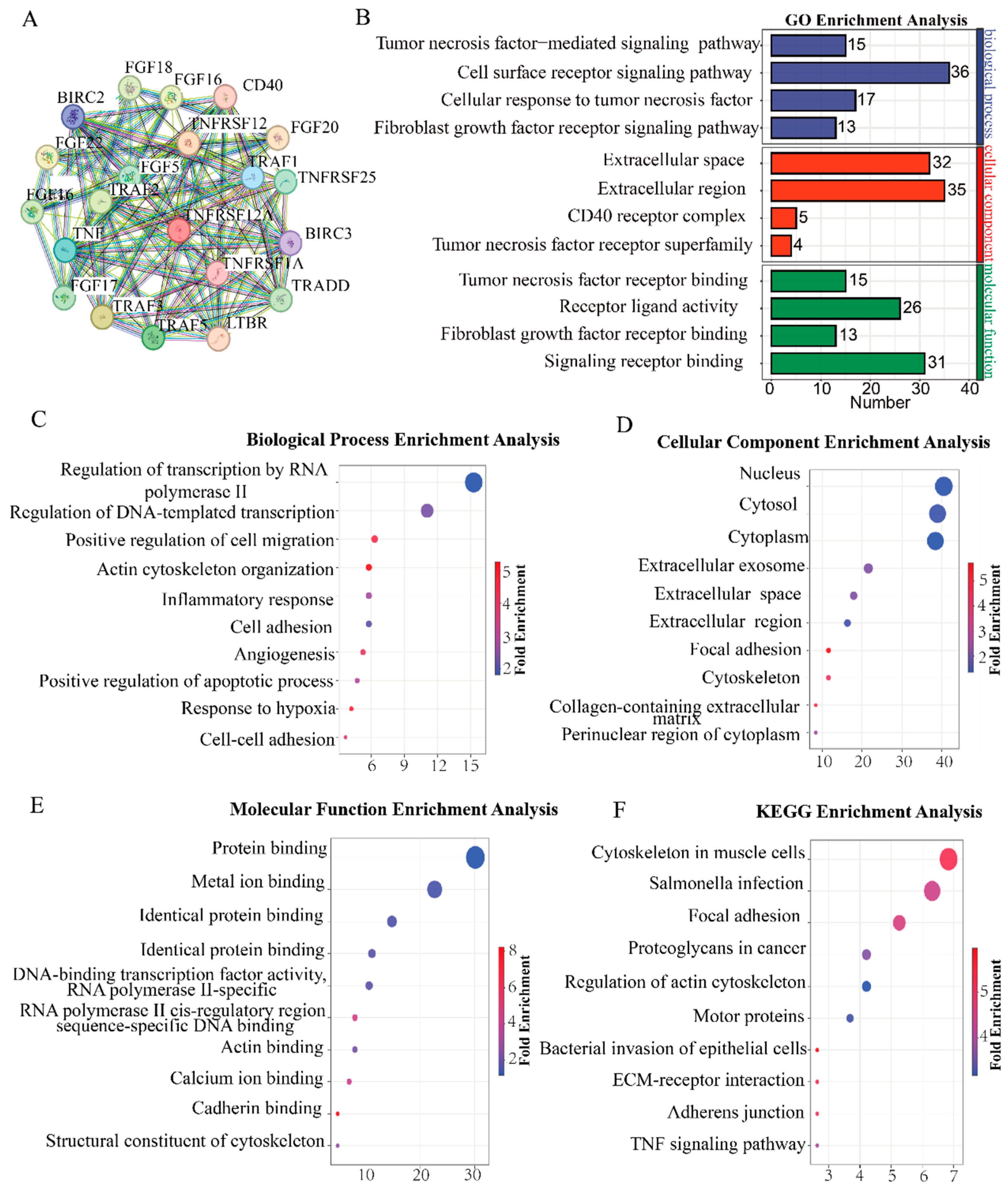
3.1. Identify TNFRSF12A for Subsequent Studies Based on Bioinformatics Analysis
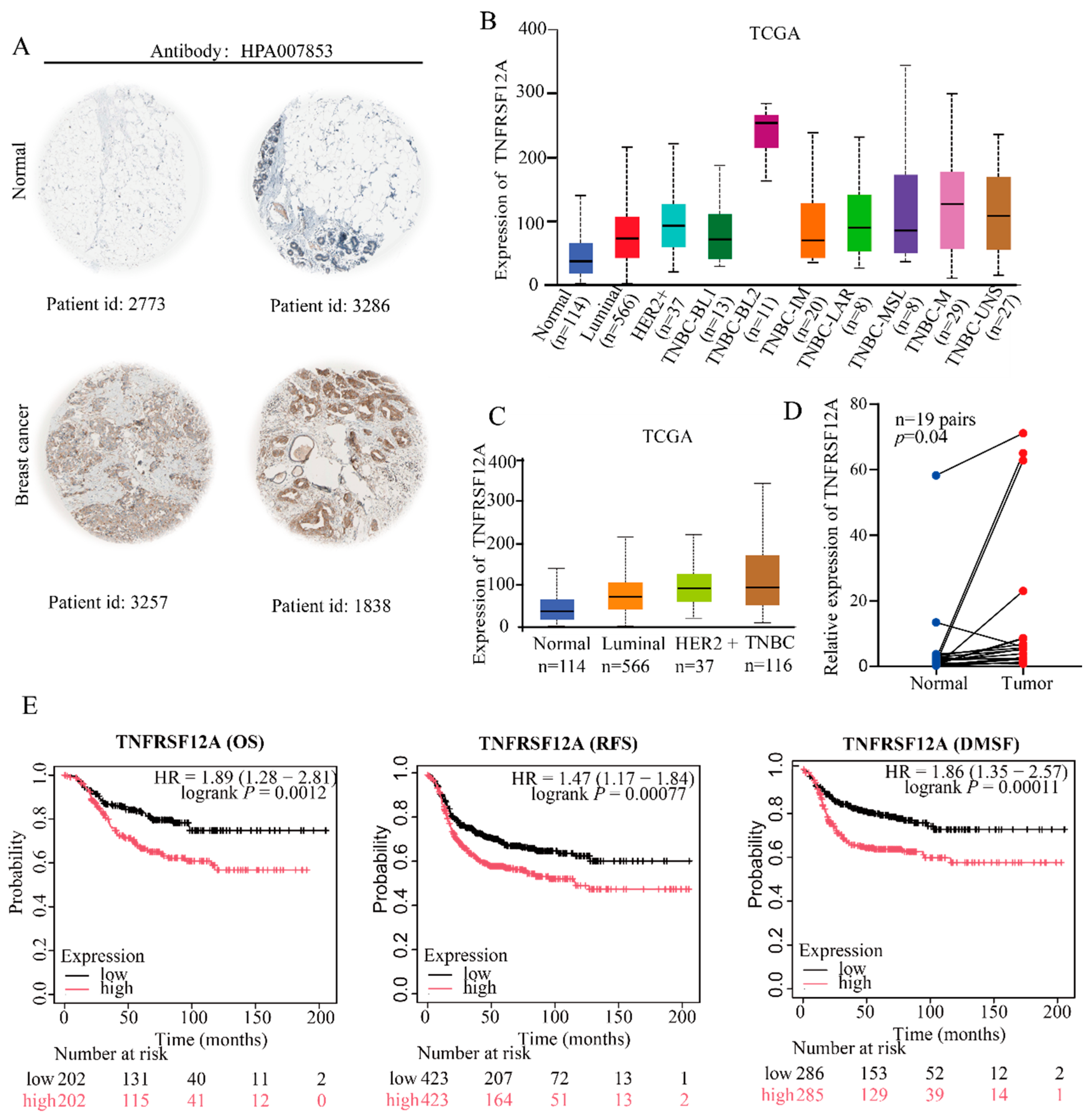
3.2. Clinical Validation Confirms Marked TNFRSF12A Upregulation in TNBC Correlating Significantly with Adverse Patient Outcomes
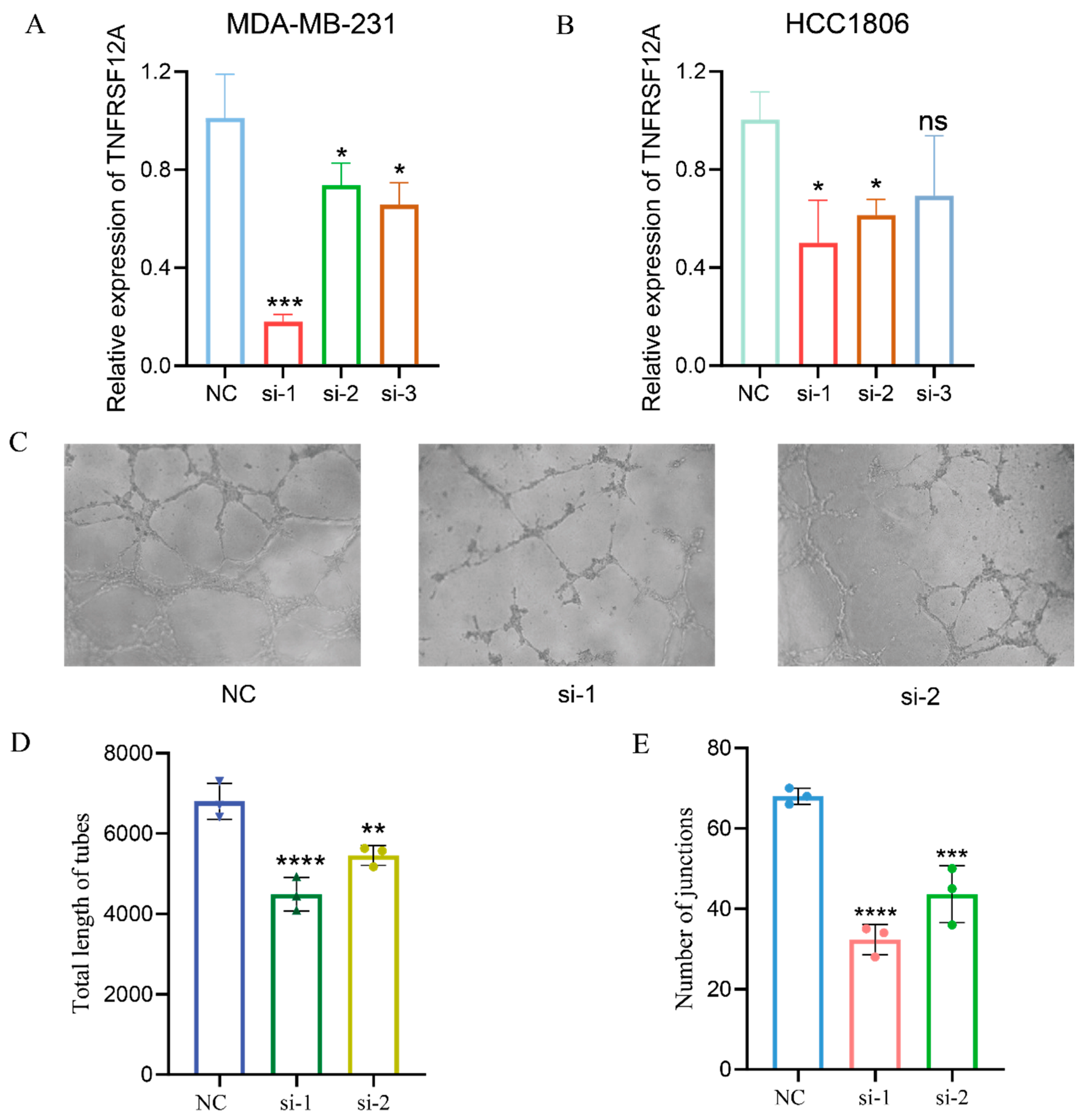
3.3. TNFRSF12A Promotes Angiogenesis in TNBC
3.4. TNFRSF12A Knockdown Attenuates Angiogenic Capacity
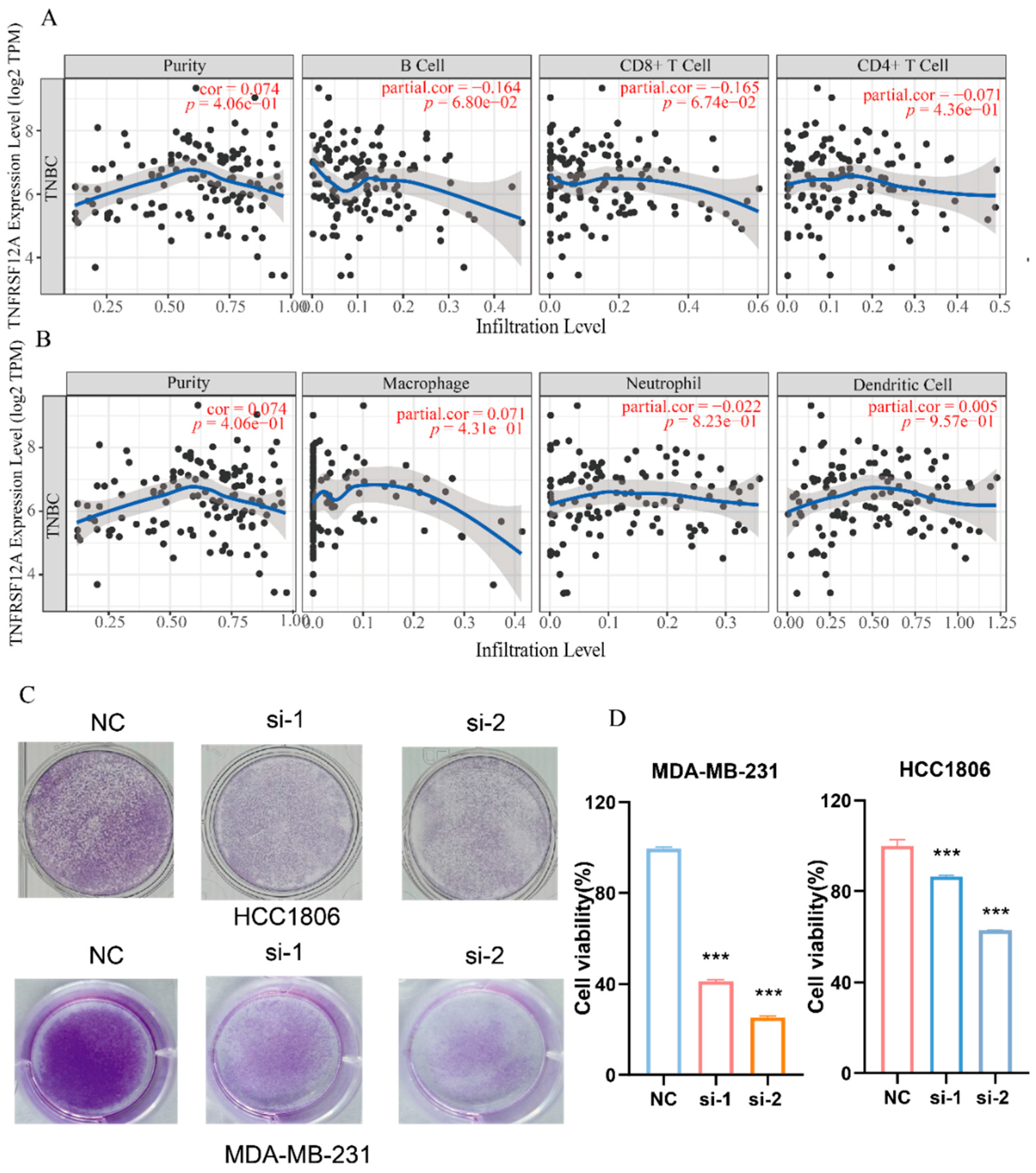
3.5. TNFRSF12A Exerts an Inhibitory Impact on Anti-Tumor Immunity by Hindering Immune Cell Infiltration into Tumors and Suppressing T-Cell Cytotoxic Activity
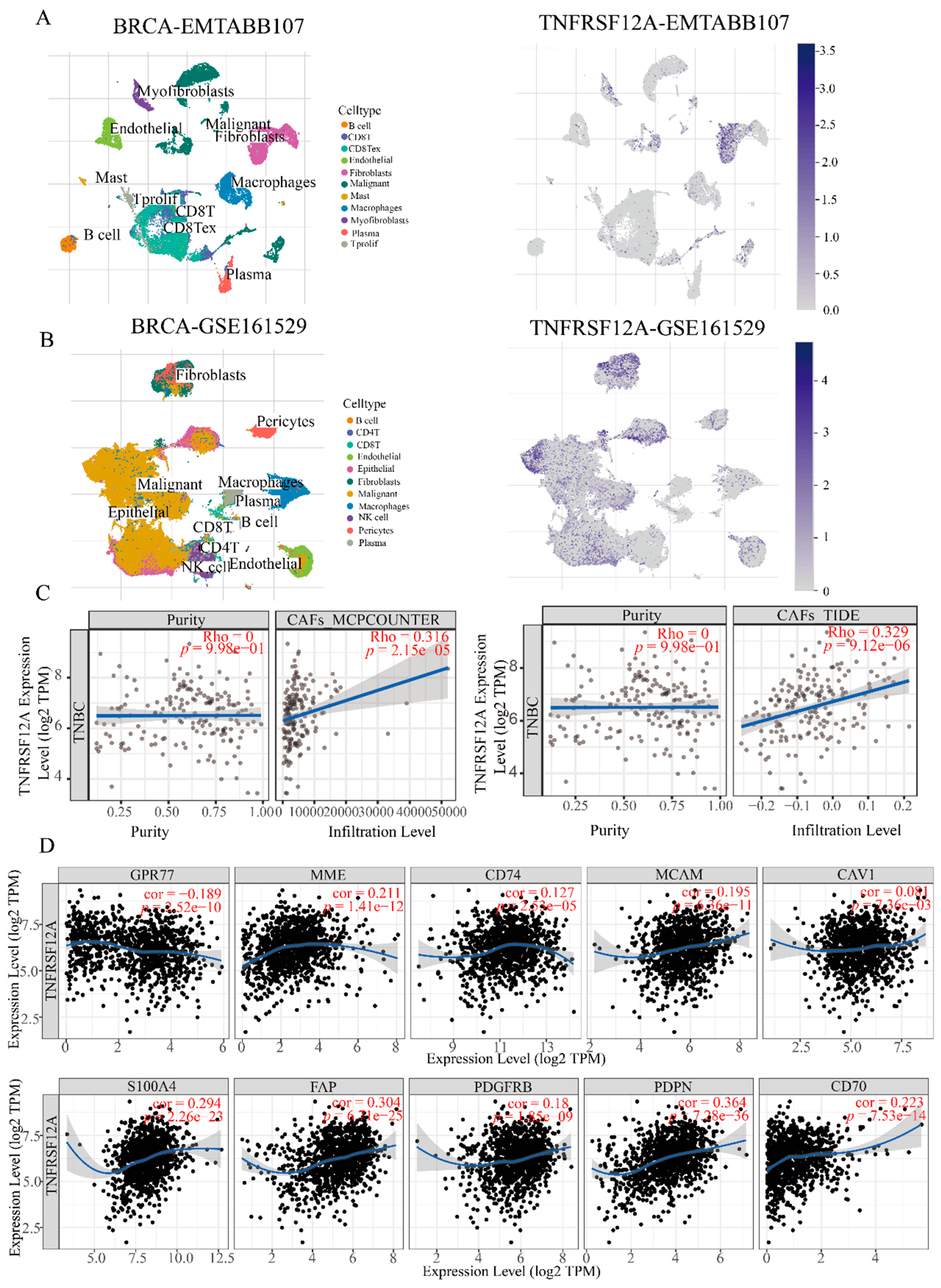
3.6. CAF-Specific TNFRSF12A Elevation Correlates with Increased Stromal Abundance
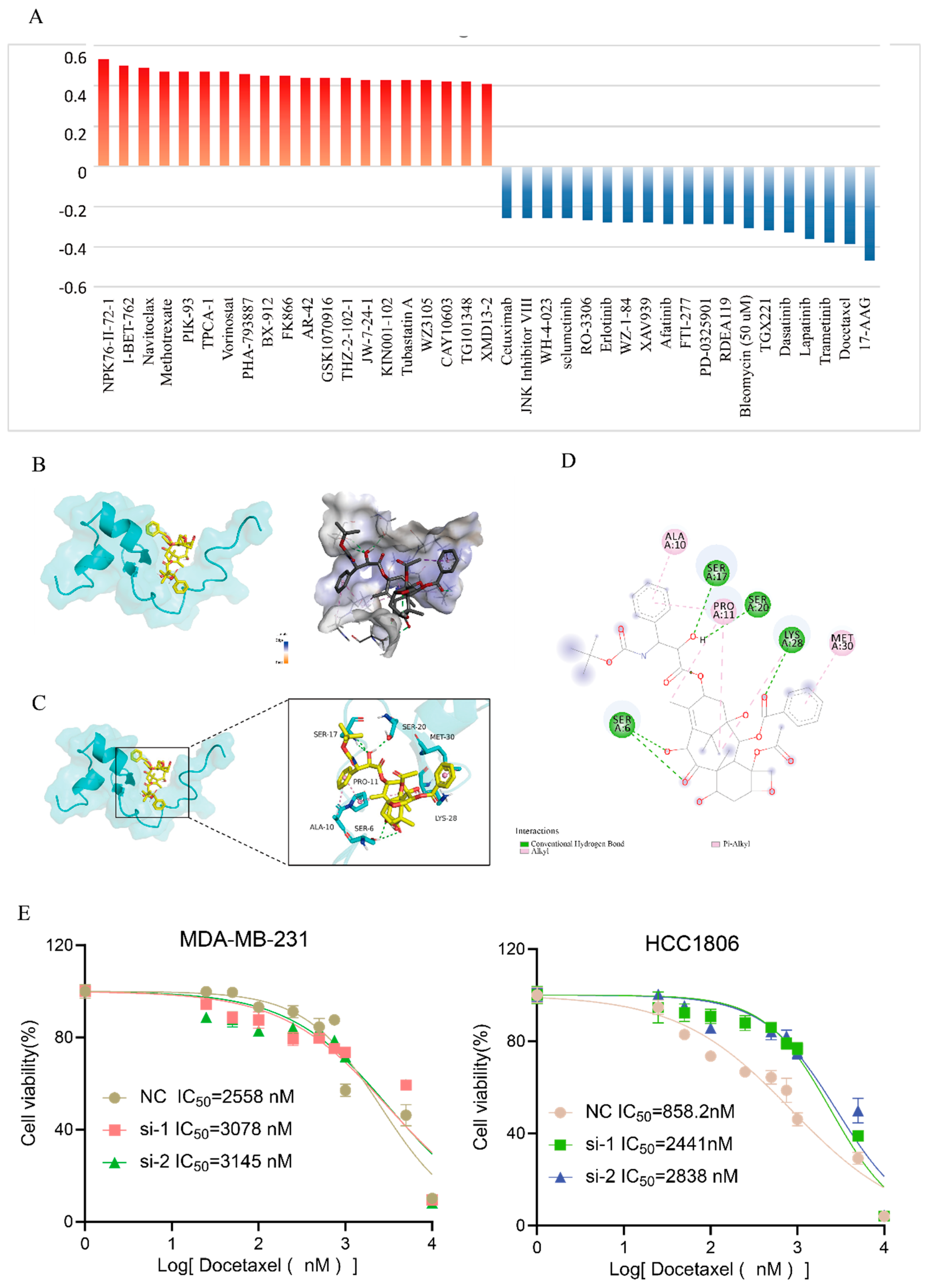
3.7. Elevated TNFRSF12A Expression Promotes Sensitivity to Docetaxel Treatment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviations | Full name |
| TNBC | Triple-negative breast cancer |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
| OS | Overall survival |
| RFS | Recurrence-Free Survival |
| DMFS | Distant Metastasis Free Survival |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| CAFs | Cancer-associated fibroblasts |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| HUVECs | Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| PPI | Protein-Protein Interaction Networks |
| BP | Biological process |
| MF | Molecular function |
| CC | Cellular component |
| FGF | Fibroblast growth factor |
| FGFR | Fibroblast growth factor receptor |
| Cor | correlation coefficient |
References
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024; 74: 229-63. [CrossRef]
- Tong L, Yu X, Wang S, Chen L, Wu Y. Research Progress on Molecular Subtyping and Modern Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2023; 15: 647-58. [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Castro AC, Lin NU, Polyak K. Insights into Molecular Classifications of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Improving Patient Selection for Treatment. Cancer Discov. 2019; 9: 176-98. [CrossRef]
- Obidiro O, Battogtokh G, Akala EO. Triple Negative Breast Cancer Treatment Options and Limitations: Future Outlook. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15. [CrossRef]
- Xiong N, Wu H, Yu Z. Advancements and challenges in triple-negative breast cancer: a comprehensive review of therapeutic and diagnostic strategies. Front Oncol. 2024; 14: 1405491. [CrossRef]
- Zagami P, Carey LA. Triple negative breast cancer: Pitfalls and progress. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2022; 8: 95. [CrossRef]
- Rong L, Li N, Zhang Z. Emerging therapies for glioblastoma: current state and future directions. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022; 41: 142. [CrossRef]
- Keenan TE, Tolaney SM. Role of Immunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2020; 18: 479-89. [CrossRef]
- Marra A, Viale G, Curigliano G. Recent advances in triple negative breast cancer: the immunotherapy era. BMC Med. 2019; 17: 90. [CrossRef]
- Lan J, Chen L, Li Z, Liu L, Zeng R, He Y, et al. Multifunctional Biomimetic Liposomes with Improved Tumor-Targeting for TNBC Treatment by Combination of Chemotherapy, Antiangiogenesis and Immunotherapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024; 13: e2400046. [CrossRef]
- Baldominos P, Barbera-Mourelle A, Barreiro O, Huang Y, Wight A, Cho JW, et al. Quiescent cancer cells resist T cell attack by forming an immunosuppressive niche. Cell. 2022; 185: 1694-708.e19. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz BI, Lowman XH, Yang Y, Fan Q, Wang T, Wu H, et al. Alpha-Ketoglutarate Regulates Tnfrsf12a/Fn14 Expression via Histone Modification and Prevents Cancer-Induced Cachexia. Genes (Basel). 2023; 14. [CrossRef]
- Xu RD, Feng F, Yu XS, Liu ZD, Lao LF. miR-149-5p inhibits cell growth by regulating TWEAK/Fn14/PI3K/AKT pathway and predicts favorable survival in human osteosarcoma. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2018; 32: 2058738418786656. [CrossRef]
- Xu Q, Fan G, Shao S. Role of TNFRSF12A in cell proliferation, apoptosis, and proinflammatory cytokine expression by regulating the MAPK and NF-κB pathways in thyroid cancer cells. Cytokine. 2025; 186: 156841. [CrossRef]
- Liu T, Pu J, Theil S, Liu Y, Jiang L, Liu H, et al. Potential role of TNFRSF12A in linking glioblastoma and alzheimer’s disease via shared tumour suppressor pathways. Sci Rep. 2025; 15: 21535. [CrossRef]
- Wang C, Zhao Y, Chen Y, Shi Y, Yang Z, Wu W, et al. The Oncogenic Role of TNFRSF12A in Colorectal Cancer and Pan-Cancer Bioinformatics Analysis. Cancer Res Treat. 2025; 57: 212-28. [CrossRef]
- Wu ZH, Niu X, Wu GH, Cheng Q. Decreased expression of TNFRSF12A in thyroid gland cancer predicts poor prognosis: A study based on TCGA data. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020; 99: e21882. [CrossRef]
- Guo L, Chen Q, Xu M, Huang J, Ye H. Communication between alveolar macrophages and fibroblasts via the TNFSF12-TNFRSF12A pathway promotes pulmonary fibrosis in severe COVID-19 patients. J Transl Med. 2024; 22: 698. [CrossRef]
- Svobodová B, Löfdahl A, Nybom A, Wigén J, Hirdman G, Olm F, et al. Overlapping Systemic Proteins in COVID-19 and Lung Fibrosis Associated with Tissue Remodeling and Inflammation. Biomedicines. 2024; 12. [CrossRef]
- Brown SA, Richards CM, Hanscom HN, Feng SL, Winkles JA. The Fn14 cytoplasmic tail binds tumour-necrosis-factor-receptor-associated factors 1, 2, 3 and 5 and mediates nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Biochem J. 2003; 371: 395-403. [CrossRef]
- Yin J, Liu YN, Tillman H, Barrett B, Hewitt S, Ylaya K, et al. AR-regulated TWEAK-FN14 pathway promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis. Cancer Res. 2014; 74: 4306-17. [CrossRef]
- Cheng E, Whitsett TG, Tran NL, Winkles JA. The TWEAK Receptor Fn14 Is an Src-Inducible Protein and a Positive Regulator of Src-Driven Cell Invasion. Mol Cancer Res. 2015; 13: 575-83. [CrossRef]
- Hu G, Liang L, Liu Y, Liu J, Tan X, Xu M, et al. TWEAK/Fn14 Interaction Confers Aggressive Properties to Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J Invest Dermatol. 2019; 139: 796-806. [CrossRef]
- Dwyer BJ, Jarman EJ, Gogoi-Tiwari J, Ferreira-Gonzalez S, Boulter L, Guest RV, et al. TWEAK/Fn14 signalling promotes cholangiocarcinoma niche formation and progression. J Hepatol. 2021; 74: 860-72. [CrossRef]
- Li G, Zhang Z, Cai L, Tang X, Huang J, Yu L, et al. Fn14-targeted BiTE and CAR-T cells demonstrate potent preclinical activity against glioblastoma. Oncoimmunology. 2021; 10: 1983306. [CrossRef]
- Zhu C, Zhang L, Liu Z, Li C, Bai Y. TWEAK/Fn14 interaction induces proliferation and migration in human airway smooth muscle cells via activating the NF-κB pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2018; 119: 3528-36. [CrossRef]
- Liu JY, Jiang L, He T, Liu JJ, Fan JY, Xu XH, et al. NETO2 promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells via activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB/Snail axis and predicts outcome of the patients. Cell Death Dis. 2019; 10: 162. [CrossRef]
- Morales-Guadarrama G, Méndez-Pérez EA, García-Quiroz J, Avila E, Ibarra-Sánchez MJ, Esparza-López J, et al. The Inhibition of the FGFR/PI3K/Akt Axis by AZD4547 Disrupts the Proangiogenic Microenvironment and Vasculogenic Mimicry Arising from the Interplay between Endothelial and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24. [CrossRef]
- Wu Y, Yi Z, Li J, Wei Y, Feng R, Liu J, et al. FGFR blockade boosts T cell infiltration into triple-negative breast cancer by regulating cancer-associated fibroblasts. Theranostics. 2022; 12: 4564-80. [CrossRef]
- Lv B, Wang Y, Ma D, Cheng W, Liu J, Yong T, et al. Immunotherapy: Reshape the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2022; 13: 844142. [CrossRef]
- Dunn GP, Bruce AT, Ikeda H, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. Cancer immunoediting: from immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat Immunol. 2002; 3: 991-8. [CrossRef]
- Roerden M, Spranger S. Cancer immune evasion, immunoediting and intratumour heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2025; 25: 353-69. [CrossRef]
- Xia L, Jiang L, Chen Y, Zhang G, Chen L. ThPOK transcriptionally inactivates TNFRSF12A to increase the proliferation of T cells with the involvement of the NF-kB pathway. Cytokine. 2021; 148: 155658. [CrossRef]
- Xiao Y, Yu D. Tumor microenvironment as a therapeutic target in cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 2021; 221: 107753. [CrossRef]
- Mottini C, Auciello FR, Manni I, Pilarsky C, Caputo D, Caracciolo G, et al. The cross-talk between the macro and micro-environment in precursor lesions of pancreatic cancer leads to new and promising circulating biomarkers. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024; 43: 198. [CrossRef]
- Lee J, Hyeon DY, Hwang D. Single-cell multiomics: technologies and data analysis methods. Exp Mol Med. 2020; 52: 1428-42. [CrossRef]
- Raaijmakers K, Adema GJ, Bussink J, Ansems M. Cancer-associated fibroblasts, tumor and radiotherapy: interactions in the tumor micro-environment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024; 43: 323. [CrossRef]
- Mori N, Jin J, Krishnamachary B, Mironchik Y, Wildes F, Vesuna F, et al. Functional roles of FAP-α in metabolism, migration and invasion of human cancer cells. Front Oncol. 2023; 13: 1068405. [CrossRef]
- Zhang L, Wang K, Zhang J, Qian X, Zhang X, Wang Y, et al. PDGFR-β/Cav1-induced autophagy via mTOR/FIP200/ATG13 activation in cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes the malignant progression of breast cancer. J Transl Med. 2025; 23: 784. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Geng YH, Yang H, Yang H, Zhou YT, Zhang HQ, et al. Extracellular ATP drives breast cancer cell migration and metastasis via S100A4 production by cancer cells and fibroblasts. Cancer Lett. 2018; 430: 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Qu S, Wu J, Bao Q, Yao B, Duan R, Chen X, et al. Osterix promotes the migration and angiogenesis of breast cancer by upregulation of S100A4 expression. J Cell Mol Med. 2019; 23: 1116-27. [CrossRef]
- Liao M, Liao J, Qu J, Shi P, Cheng Y, Pan Q, et al. Hepatic TNFRSF12A promotes bile acid-induced hepatocyte pyroptosis through NFκB/Caspase-1/GSDMD signaling in cholestasis. Cell Death Discov. 2023; 9: 26. [CrossRef]
- Wang T, Ma S, Qi X, Tang X, Cui D, Wang Z, et al. Knockdown of the differentially expressed gene TNFRSF12A inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2017; 15: 1172-8. [CrossRef]
- Shindo K, Aishima S, Ohuchida K, Fujiwara K, Fujino M, Mizuuchi Y, et al. Podoplanin expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts enhances tumor progression of invasive ductal carcinoma of the pancreas. Mol Cancer. 2013; 12: 168. [CrossRef]
- Feng C, Yu A, Wang Z, Wang K, Chen J, Wu Y, et al. A novel PDPN antagonist peptide CY12-RP2 inhibits melanoma growth via Wnt/β-catenin and modulates the immune cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024; 43: 9. [CrossRef]
| siRNA name | Sequence |
| siRNA-1 | 5’-AGAGAGAAGTTCACCACC -3’ |
| SiRNA-2 | 5’- CACTCATCATTCATTCATC-3’ |
| Gene name | Forward | Reverse |
| TNFRSF12A | GACCTGGACAAGTGCAT | GGTGGTGAACTTCTCTCTC |
| U6 | CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA | AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT |
| β-actin | CTCTTCCAGCCTTCCTTCCT | AGCACTGTGTTGGCGTACAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





