Submitted:
22 August 2025
Posted:
27 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
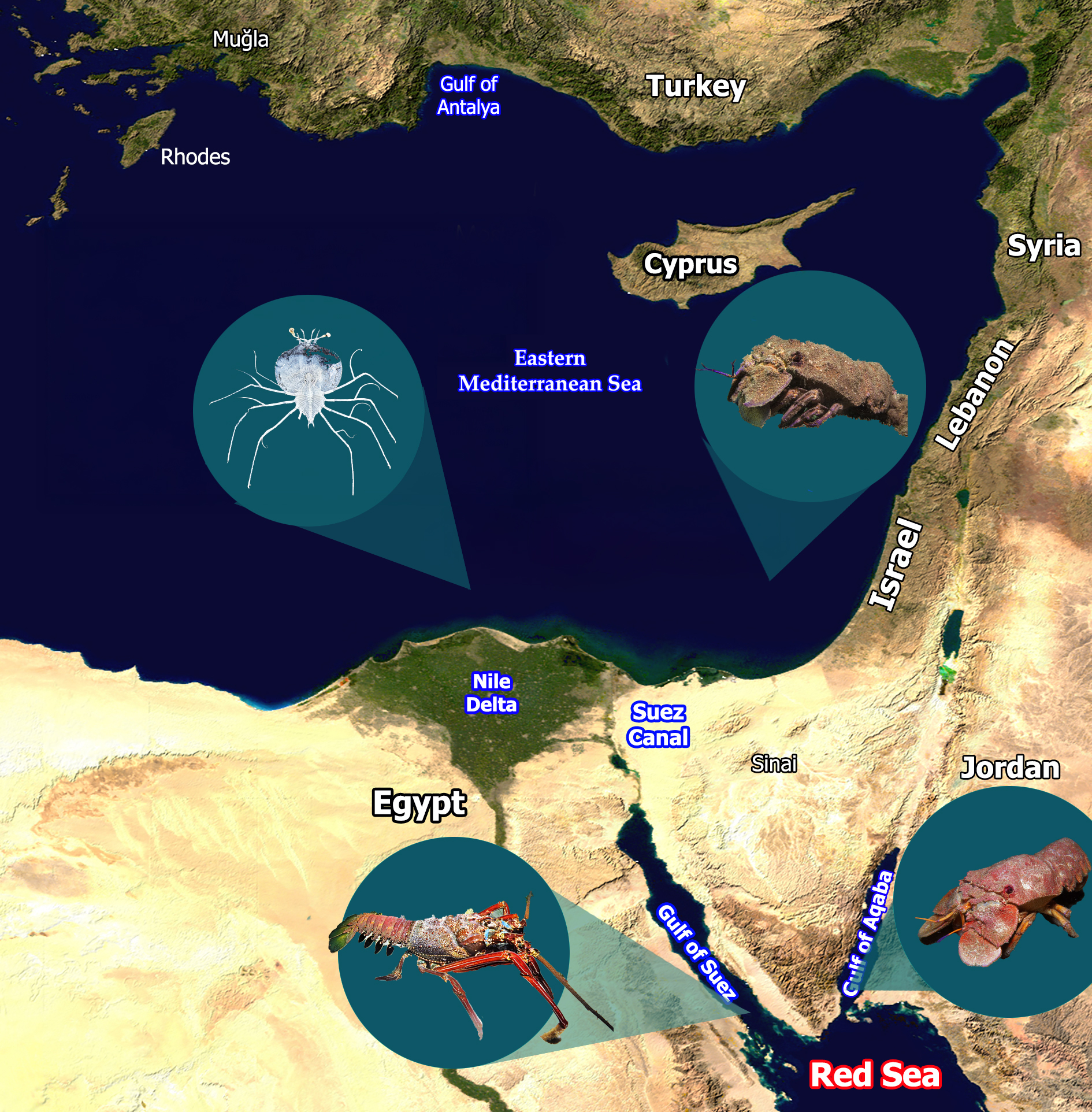
2. Lobsters from the Southeastern Mediterranean Coast
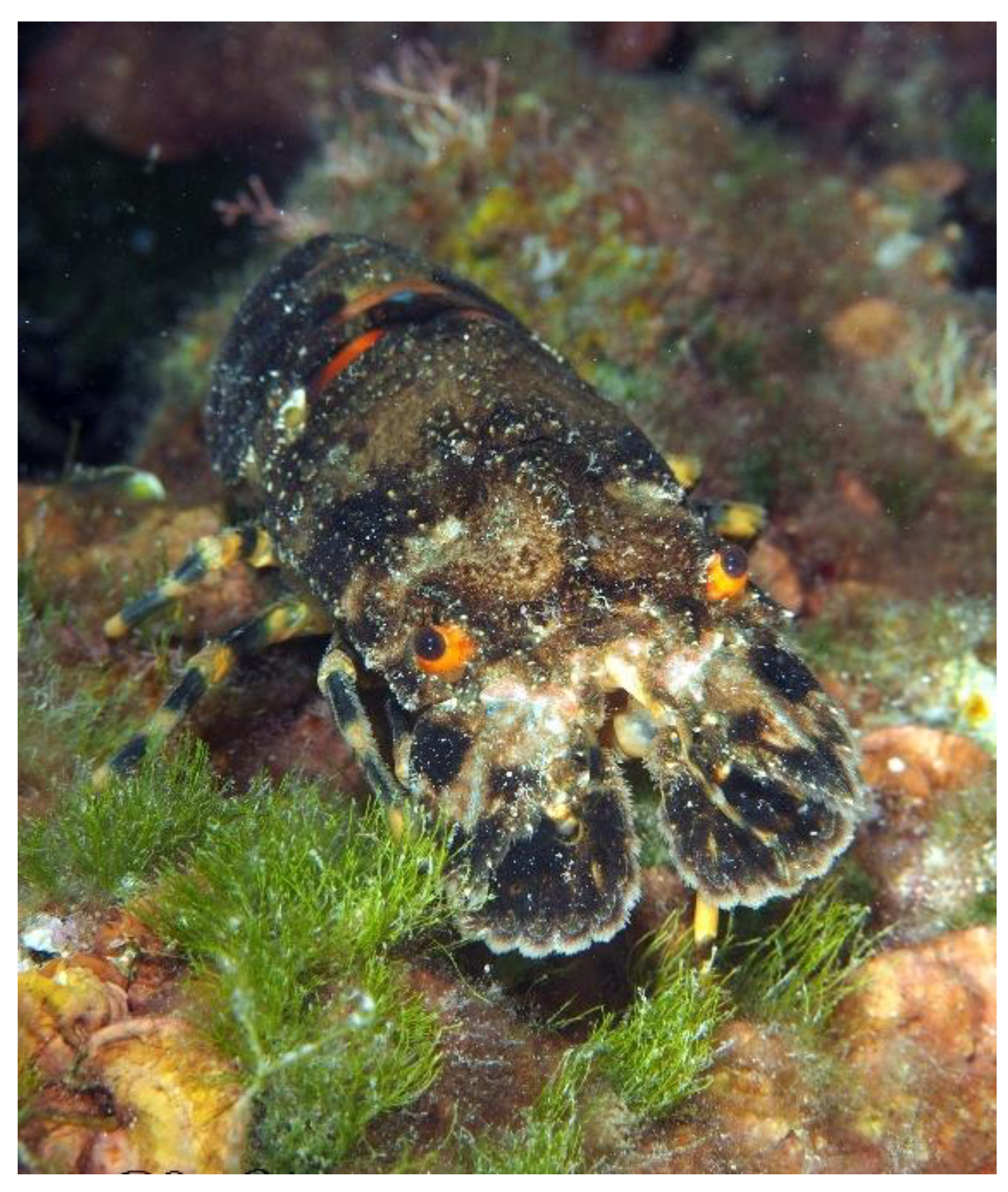
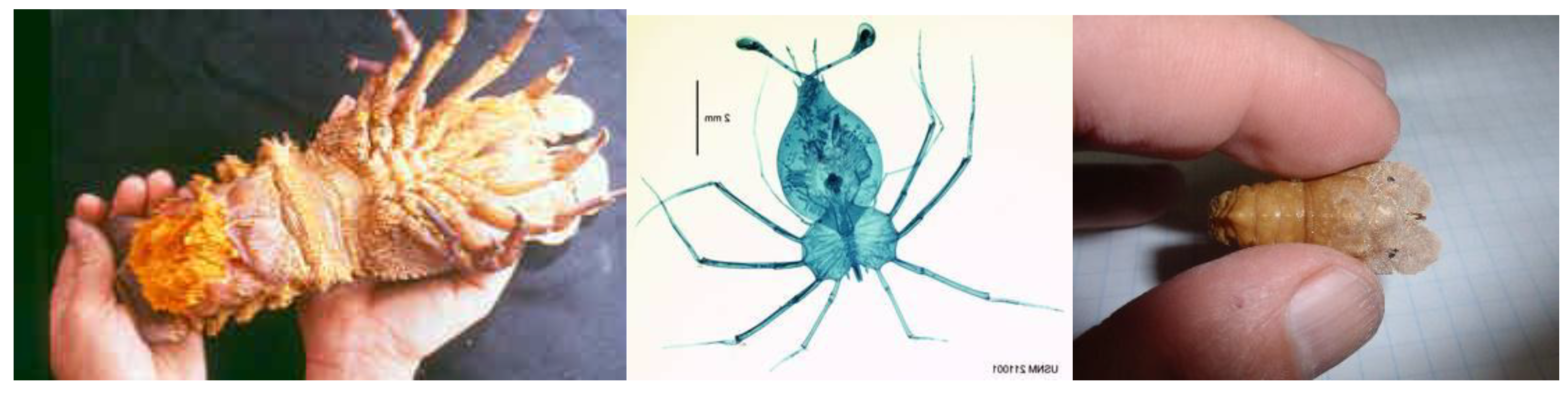
2.1. The Mediterranean Slipper Lobster
2.1.1. Reproduction and Development
2.1.2. Food and Predators
2.1.3. Sensory Modalities
2.1.4. Environmental Impacts, Threats and Conservation
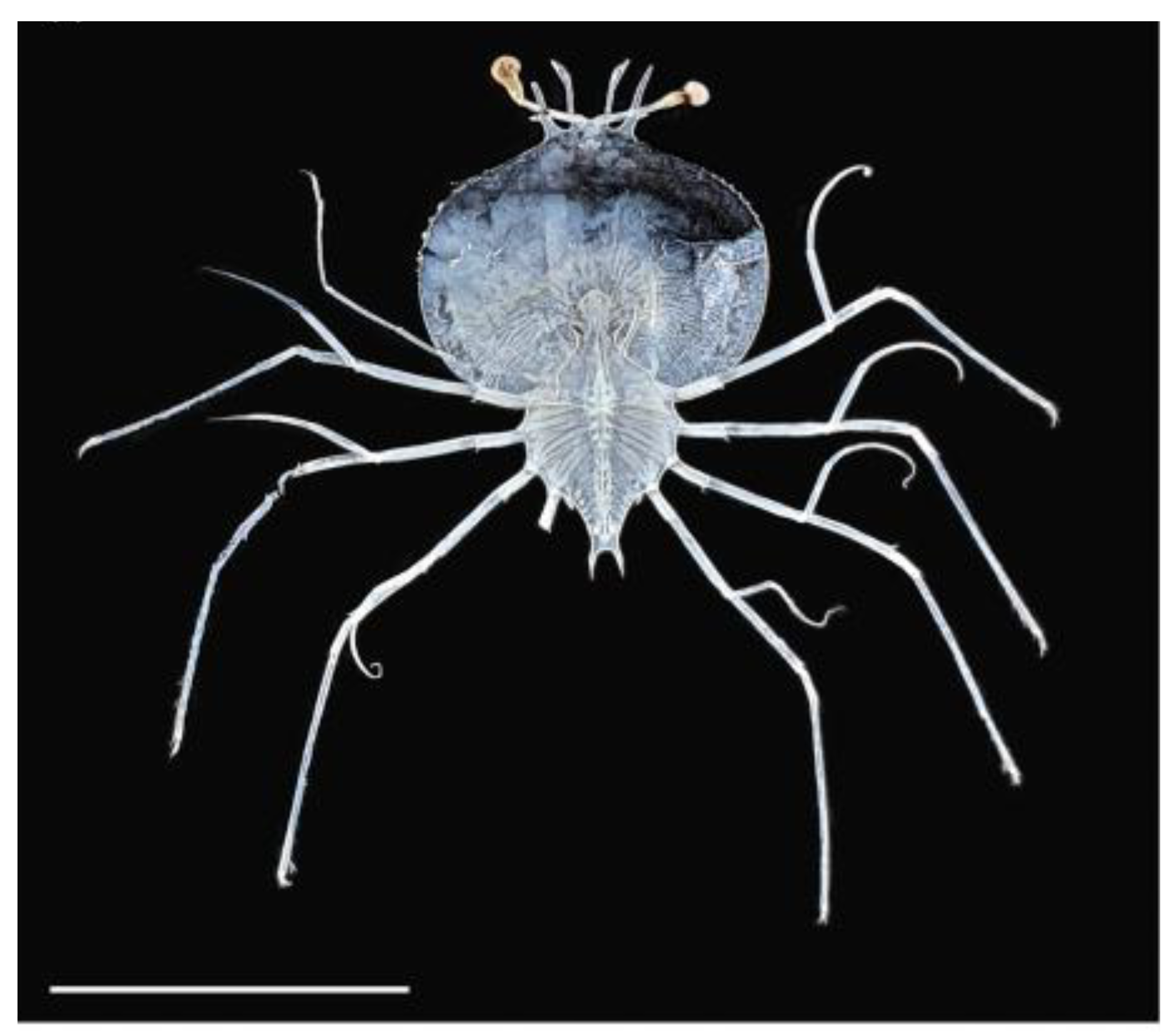
2.2. Locust Lobsters
2.2.1. The Small European Locust Lobster
2.2.2. The Pygmy Locust Lobster
2.3. Occasional Species on the Mediterranean Coast
3. Lobsters from the Northern Red Sea
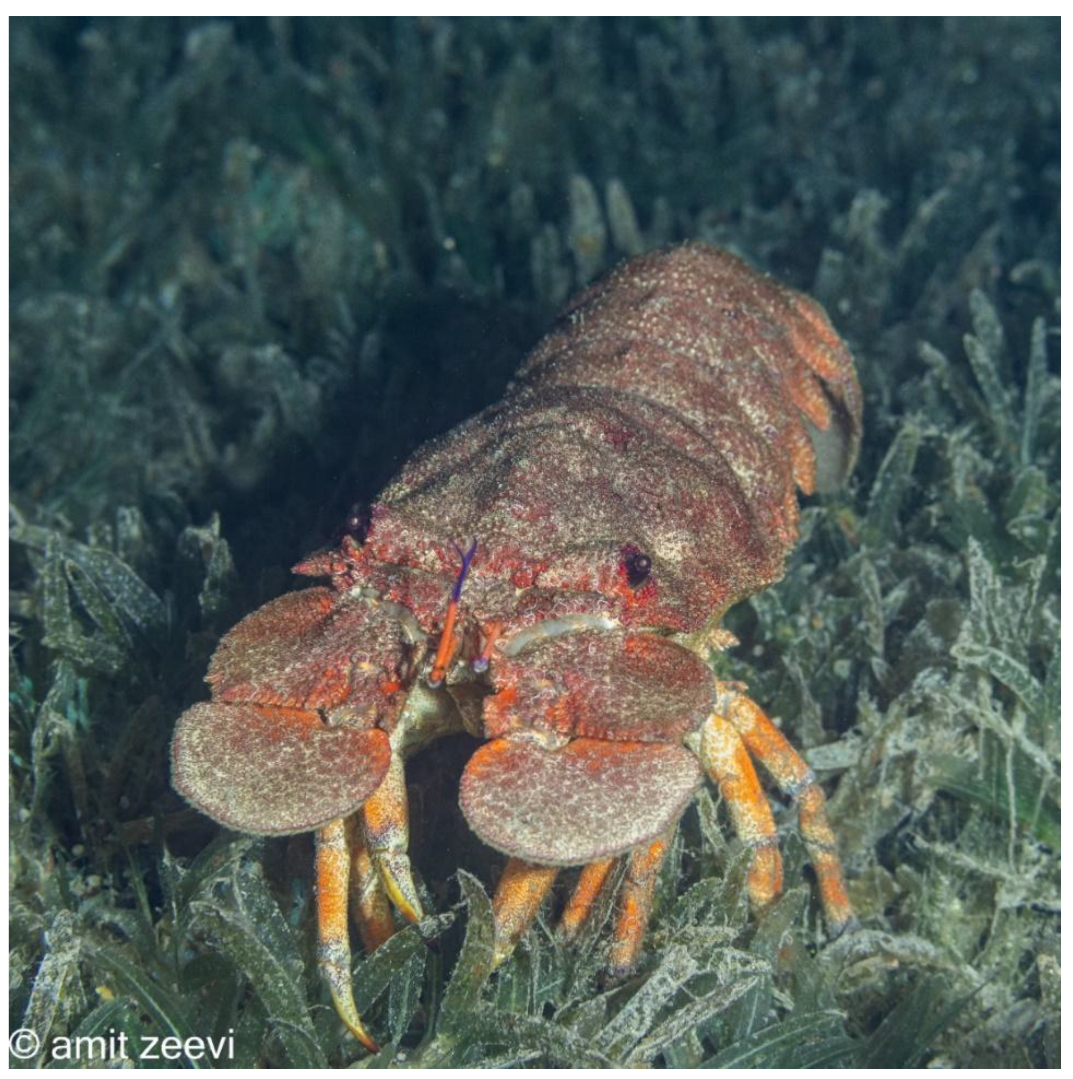
3.1. Clamkiller Slipper Lobster
3.1.1. Food
3.1.2. Reproduction
3.1.3. Threats, Environmental Impacts and Conservation
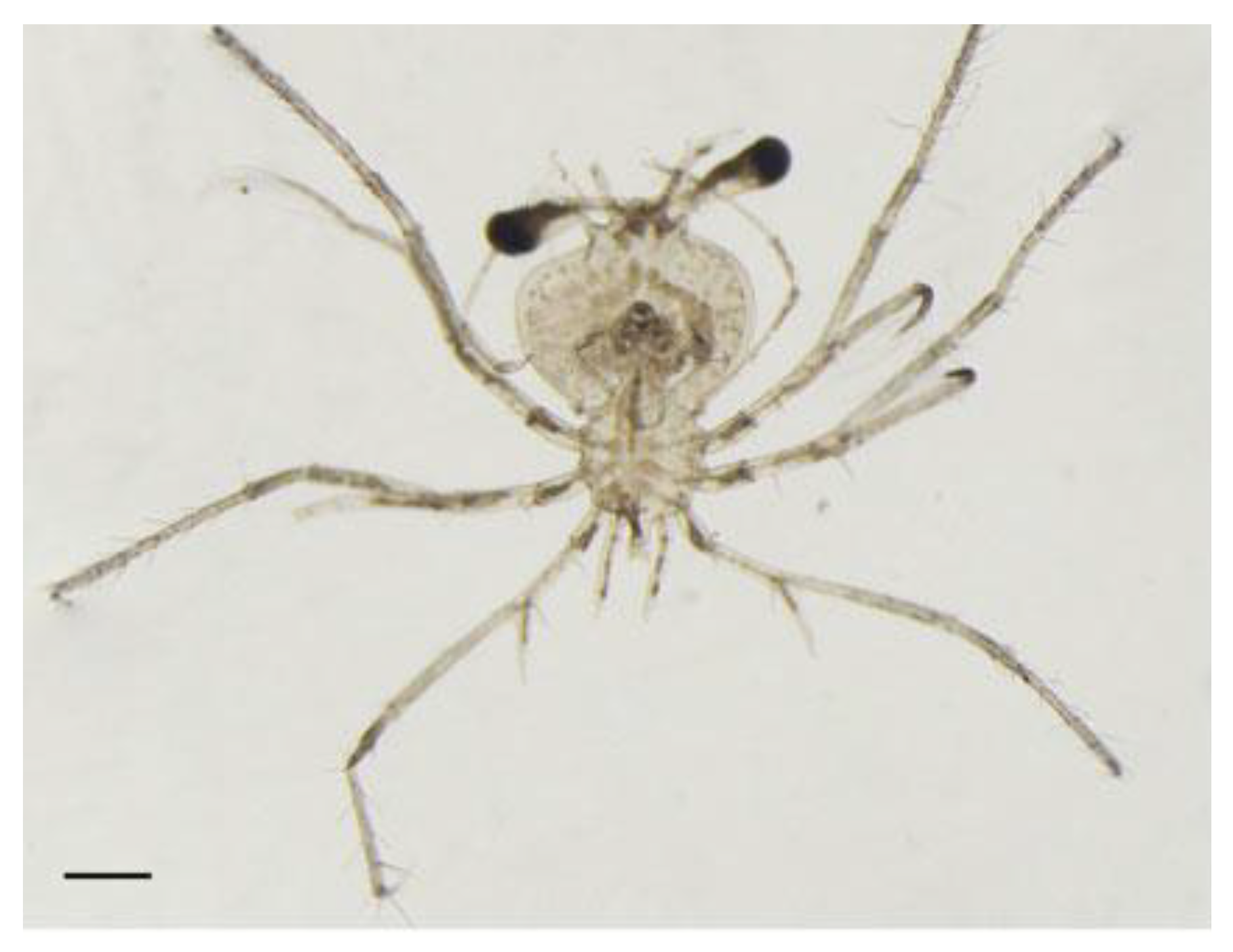
3.2. The Lewinsohn Locust Slipper Lobster
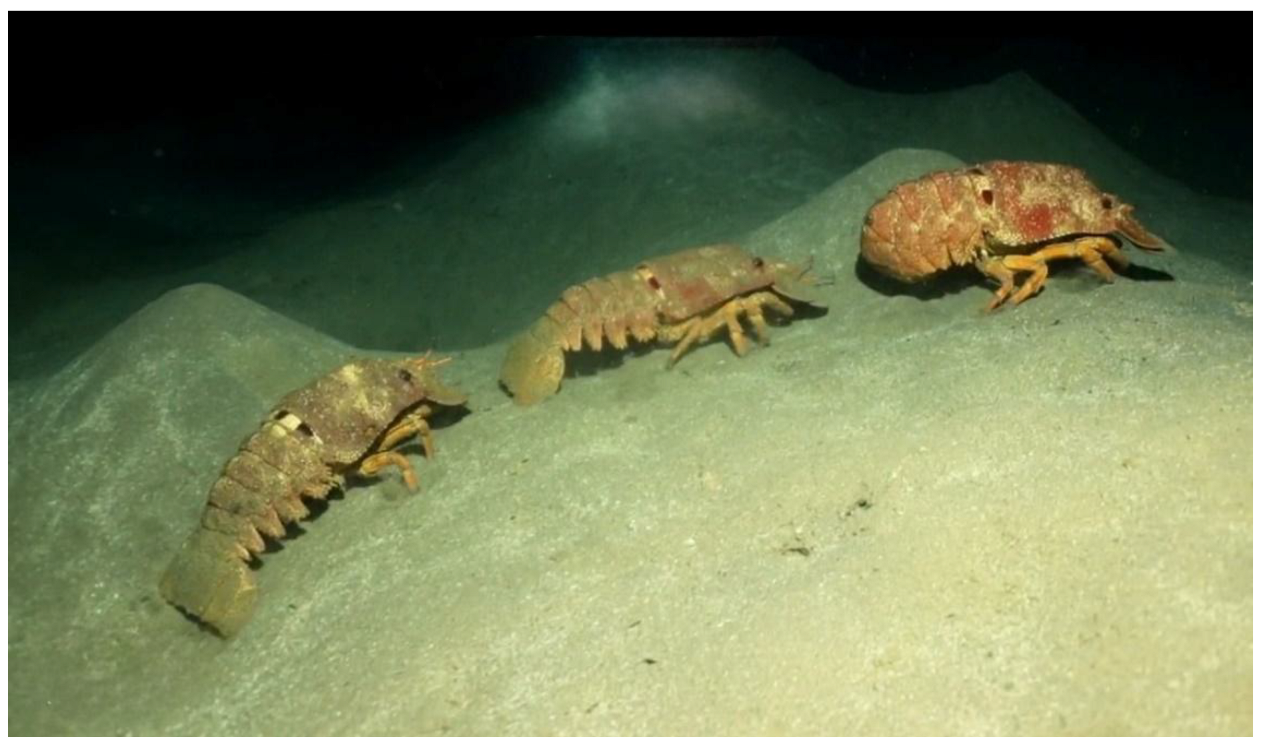
3.3. Evidence of a New Species of Pygmy Slipper Lobster in Eilat the Gulf of Aqaba—Biarctus sordidus
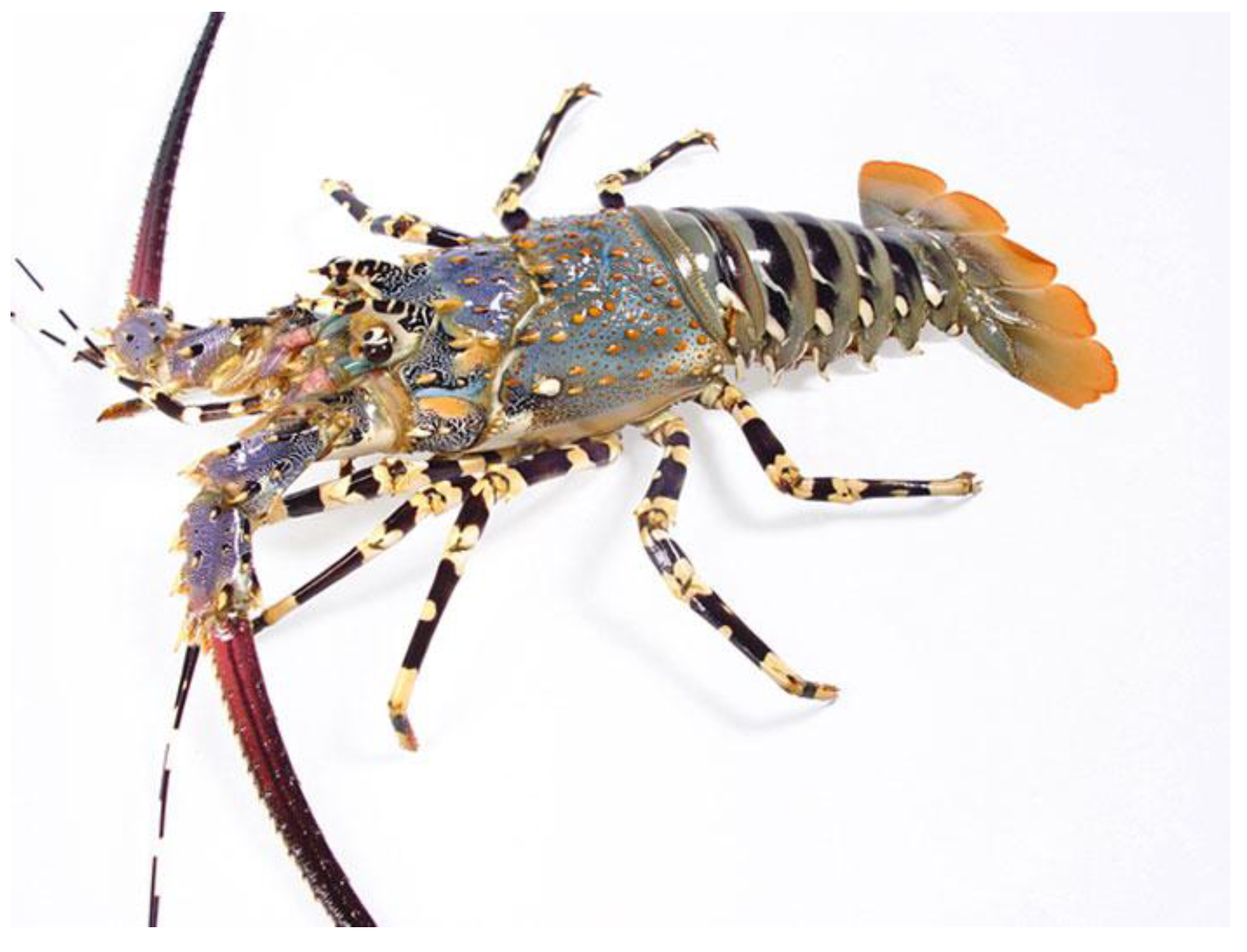
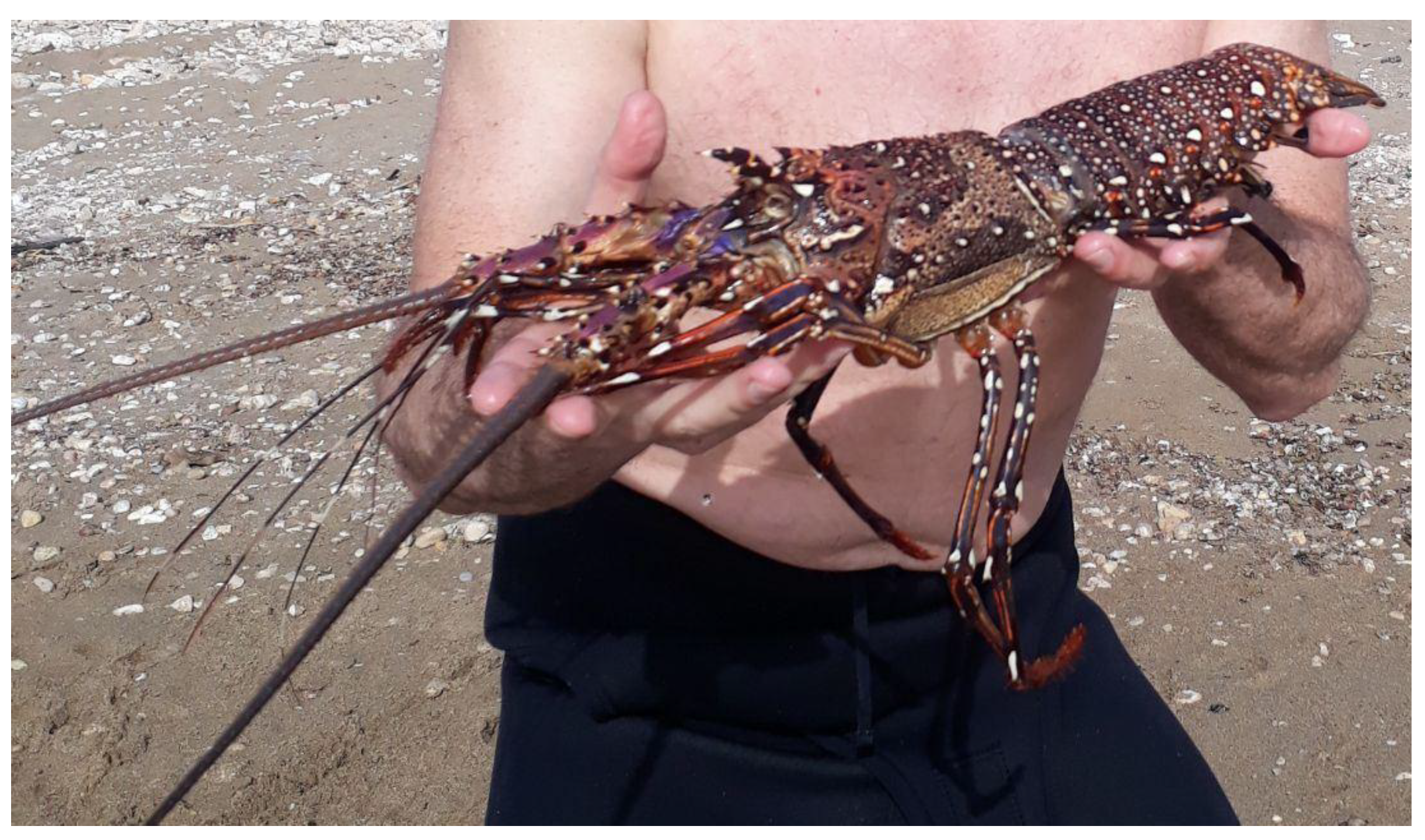
3.4. The Pronghorn Spiny Lobster
3.4.1. Reproduction and Development
3.4.2. Food and Anti-Predatory Adaptations
3.4.3. Threats, Environmental Impacts and Conservation
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holthuis, L. B. Marine lobsters of the world. FAO fisheries synopsis, /: Italy, 1991. https, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Lavalli, K. L.; Spanier, E. Infraorder Palinura Latreille, 1802. Chapter 68. In The Crustacea, Traite de Zoologie 9A – Decapoda; Forest, J., von Vaupel Klein, J.C., Eds, *!!! REPLACE !!!*, Eds.; Koninklijke Brill: Leiden, Holland, 2010; pp. 426–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanier, E. , Zviely, D. Key environmental impacts along the Mediterranean coast of Israel in the last 100 years. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanier, E; Galil, B. S. Lessepsian migrationִ a continuous biogeographical process. Endeavour 1991, 15, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galil, B.S.; Mienis, H.K.; Hoffman, R.; Goren, M. Non-indigenous species along the Israeli Mediterranean coast: tally, policy, outlook. Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 2011–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galil, B.S. A Sea, a Canal, a Disaster: The Suez Canal and the Transformation of the Mediterranean Biota. In The Suez Canal: Past Lessons and Future Challenges. Palgrave Studies in Maritime Politics and Security. Lutmar, C.; Rubinovitz, Z., Eds, *!!! REPLACE !!!*, Eds.; Palgrave Macmilla: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zittis, G.; Almazroui, M.; Alpert, P.; Ciais, P.; Cramer, W.; Dahdal, Y. . Lelieveld, J. Climate change and weather extremes in the Eastern Mediterranean and Middle East. Rev. Geophys. 2022, 60, e2021RG000762–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, F.; Valiente, J. A.; Khodayar, S. A warming Mediterranean: 38 years of increasing sea surface temperature. Remote Sen. 2020, 12, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.T.; Mostafa, A.B.; El-Naggar, M.M. Climate Change and Lessepsian Migration to the Mediterranean Sea. In Khalil, M.T., Emam, W.W.M., Negm, A., Eds; Climate Changes Impacts on Aquatic Environment. Springer Nature: London, UK, 2025; pp. 85–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eytam, Y.; Ben-Avraham, Z. Morphology and sediments of the inner shelf off northern Israel. Isr. J. Earth Sci. 1992, 41, 27–44. [Google Scholar]
- Almagor, G.; Gill. D.; Perath, I. Marine sand resources offshore Israel. Mar. Georesources Geotech. 2000, 18, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, V.; Golik, A. Sediment transport model of the southeastern Mediterranean coast. Mar. Geol. 1980, 37, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nir, Y. Offshore artificial structures and their influence on the Israel and Sinai Mediterranean beaches. Coast. Eng. 1982, 1982, 1837–1856. [Google Scholar]
- Emery, K.O.; Neev, D. Mediterranean beaches of Israel. Israel Geol. Surv. Bull. 1960, 26, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Spanier, E.; Lavalli, K.L. Natural history of Scyllarides latus (Crustacea Decapoda): a review of the contemporary biological knowledge of the Mediterranean slipper lobster. J. Nat. His. 1998, 32, 1769–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanier, E. 14. In Lobsters: Biology Management, Aquaculture and Fisheries Phillips, B. F. Ed; Part 2: Lobsters of Commercial Importance, Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 462–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, K. I. Structure and stratigraphy of the Gulf of Suez, Egypt. In Interior rift basins; Landon, S. M. Ed; AAPG Mem. 1994, 59, 57–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Avraham, Z. Structural framework of the gulf of Elat (Aqaba), northern Red Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1985, 90, 703–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, M. ; Gildor, H;, Genin, A. A coral reef refuge in the Red Sea. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 3640–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Gildor, H.; Ashkenazy, Y. Depth-dependent warming of the Gulf of Eilat (Aqaba). Clim. Change 2024, 177, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, B.; Geneid, Y. Temporal change of seagrass meadows: estimating species composition, coverage and carbon stock trends over 16 years in NIOF studied area, Hurghada, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquatic Biol. Fish. 2025, 29, 1361–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BadrElDin, A. M.; Hallock, P. Benthic foraminifers in coastal habitats of Ras Mohamed Nature Reserve, southern Sinai, Red Sea, Egypt. J. f. Micropaleontology. 2024, 43, 239–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte, G. Elements of Pelagos Biology: With Focus on the Mediterranean Sea., Springer Nature: Cham., Switzerland, 2025, 1-118 pp. [CrossRef]
- Spanier, E.; Lavalli, K.L.; Goldstein, J. S.; Groeneveld, J.C.; Jordaan G., L.; Jones, C.M.; Phillips, B. F.; Bianchini, M. L.; Kibler, R. D.; Díaz, D.; Mallol, S.; Goñi, R.; van der Meeren, G. I. ; Agnalt, A-L.; Behringer, D. C.; Keegan, W. F.; Jeffs A. A concise review of lobster utilization by worldwide human populations from pre-history to the modern era. ICES J. Mar. Sci. [CrossRef]
- Spanier, E. The utilization of lobsters by humans in the Mediterranean basin from the Prehistoric Era to the Modern Era – an interdisciplinary short review. AJMS 2015, 1, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenister, C. L. Profiling Punt: using trade relations to locate “God’s Land”. Doctoral dissertation, University of Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2008.
- Danelius, E.; Steinitz, H. The fishes and other aquatic animals on the Punt-reliefs at Deir el-Bahri. JEA 1967, 53, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, E. C. A source-book of biological names and terms; ar">CABI Charles C. Thomas: Springfield, Illinois, US,, Third Edition, Fourth Printing, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Ingle, R. Crayfishes, lobsters and crabs of Europe: an illustrated guide to common and traded species. Springer Science & Business Media, BV, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Common names of Scyllarides latus. https://www.sealifebase.se/comnames/CommonNamesList.php?ID=26141&GenusName=Scyllarides&SpeciesName=latus&StockCode=386. (accessed on 24 June 2025).
- Spanier, E. The Mediterranean Slipper Lobster - the known and the concealed in the ecology of a threatened species. Ecol. Environ. 2023, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lavalli, K. L.; Spanier, E.; Goldstein, J. S. Scyllarid Lobster Biology and Ecology, Chapter 3. In Crustacea Diarte-Plata, G.; Escamilla-Montes, R., Eds, *!!! REPLACE !!!*, Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 25–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanier, E.; Lavalli, K. L. Commercial Scyllarids. Chapter 13 In Lobsters: biology, management, aquaculture and fisheries. Phillips, B. F., Ed; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 414–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanier, E.; Tom, M.; Pisanty, S.; Almog, G. Seasonality and shelter selection by the slipper lobster Scyllarides latus in the southeastern Mediterranean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1988, 42, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessani, D.; Mura, M. The Biology of the Mediterranean Scyllarids. In The Biology and Fisheries of the Slipper Lobsters Lavalli, K. L.; Spanier, E. Eds, Ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi, H.; Booth, D.; Webber, W. R. Early life histories of slipper lobsters. In The Biology and Fisheries of the Slipper Lobsters Lavalli, K. L., Spanier, E. Eds; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2007; pp. 9–90. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, H. R. Biological studies on the exploited stock of the Mediterranean locust lobster, Scyllarides latus, (Latrielle, 1803) (Decapoda, Scyllaridae) in the Azores. J. Crustac. Biol. 1985, 5, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, H. R. Some observations on the naupliosoma and phyllosoma larvae of the Mediterranean locust lobster, Scyllarides latus, (Latrielle, 1803) from the Azores. 1985b Intl. Council for the Exploration of the Sea C.M.K. 52 (13) Shellfish Committee.
- Spanier, E.; Lavalli, K. L. First record of an early benthic juvenile likely to be that of the Mediterranean slipper lobster, Scyllarides latus (Latreille, 1802) Crustaceana 2013, 86, 259-267. 86. [CrossRef]
- Spanier, E. Mollusca as food for the slipper lobster Scyllarides latus in the coastal waters of Israel. Levantina 1987, 68, 713–716. [Google Scholar]
- Lavalli, K.L.; Spanier, E.; Grasso, F. Behavior and sensory biology of slipper lobsters. In The Biology and Fisheries of the Slipper Lobsters Lavalli, K. L. Spanier, E. Eds; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Spanier, E.; Almog-Shtayer, G. Shelter preferences in the Mediterranean slipper lobster: effects of physical properties. J. Experiment. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1992, 164, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barshaw, D. E.; Lavalli, K. L.; Spanier, E. Offense versus defense: responses of three different morphological types of lobsters to predation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 256, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarsitano, S. F.; Lavalli, K. L.; Horne, F.; Spanier, E. The constructional properties of the exoskeleton of Homarid, Palinurid, and Scyllarid Lobsters. Hydrobiologia 2006, 557, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barshaw, D.E.; Spanier, E. Anti-predator behaviors of the Mediterranean slipper lobster Scyllarides latus. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1994, 55, 375–382. [Google Scholar]
- Spanier, E.; Weihs, D.; Almog-Shtayer, G. Swimming of the Mediterranean Slipper lobster J. Experiment. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1991, 145, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanier, E.; Weihs, D. Why do shovel-nosed (slipper) lobsters have shovels? The Lobster Newsletter 1992, 5, 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lavalli, K. L.; Spanier, E. Predator adaptations of decapods, Chapter 8, In The Natural History of the Crustacea, Vol. 2: Lifestyles and Feeding Biology Thiel, M.; Watling, L, Eds, Ed.; Oxford University Press: NY, USA, 2015; pp. 190–228. [Google Scholar]
- Lavalli, K. L.; Spanier, E. Does gregariousness function as an antipredator mechanism in the Mediterranean slipper lobster, Scyllarides latus? Mar. Freshw. Res. 2001, 52, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisbaum, D.; Lavalli, K. L. Morphology and distribution of antennular setae of scyllarid lobsters (Scyllarides aequinoctialis, S. latus, and S. nodifer) with comments on their possible function. Invert. Biol. 2004, 123, 324–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S. T. F.; Spanier, E.; Meyer-Rochow, V. B. Anatomy and ultrastructural organisation of the eye of the Mediterranean slipper lobster, Scyllarides latus: preliminary results. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshwater Res. 2009, 43, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.; Spanier, E.; Diamant, R.; Yahel, R.; Spanier, E. ; Diamant, R.; Yahel R. Nature reserves facilitate the conservation of the Mediterranean slipper lobster, Scyllarides latus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2023, 714, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, L.; Lohmann, K. True navigation and magnetic maps in spiny lobsters. Nature 2003, 421, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanier, E.; Lavalli, K. L. Slipper lobster fisheries—Present status and future perspectives In The Biology and Fisheries of the Slipper Lobsters Lavalli, K. L.; Spanier, E. Eds, Ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2007; pp. 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M. , MacDiarmid, A. & Cockcroft A. Scyllarides latus, /: List of Threatened Species, 2011. . https; (accessed on 2 July 2025)2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchini, M. L.; Spanier, E.; Ragonese, S. Enzymatic variability of Mediterranean slipper lobsters, Scyllarides latus, from Sicilian waters. Ann. Ser. Hist. Nat. 2003, 13, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Faria, J.; Froufe, E.; Tuya, F.; Alexandrino, P.; Pérez-Losada, M. Panmixia in the endangered slipper lobster Scyllarides latus from the Northeastern Atlantic and Western Mediterranean. J. Crustac. Biol. 2013, 33, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehmeh, B.; Haydous, F.; Ali, H.; Hdaifi, A.; Abdlwahab, B.; Orm, M. B.; Abrahamian, Z.; Akoury, E. Emerging contaminants in the Mediterranean Sea endangering Lebanon's Palm Islands Natural Reserve. RSC adv., 2025, 15, 2034–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, R.; Gérard, J. A.; Gérard, P. Impacts of local Community perception and participation on environmental issues in integrated coastal zone Management: a case study of Tyre, southern Lebanon. IJHSS, 2024, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy-Kamal, M.; Sánchez-Lizaso, J. L.; Forcada, A. (2011). Status of marine protected areas in Egypt. Anim. Biodivers. Conser. 2011, 34, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanier, E.; Lavalli, K.L.; Edelist, D. Artificial reefs for lobsters – an overview of their application for fisheries enhancement, management, and conservation In Chapter 6 of Artificial Reefs in Fisheries Management Bortone, S.; Brandini, F. P., Fabi, G., Otake, S., Eds, *!!! REPLACE !!!*, Eds.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: NY, USA, 2011; pp. 77–109. [Google Scholar]
- Shiber, J. G. Trace metals in edible marine molluscs and crustaceans from Lebanon. Hydrobiologia 1981, 83, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanò, S.; Ragonese, S.; Bianchini, M. An anomalous specimen of Scyllarides latus (Decapoda, Scyllaridae). Crustaceana 2003, 76, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, J. S.; Spanier, E.; Spanier, E. Increasing seawater temperatures in the Levantine basin, eastern Mediterranean may elicit increased activity in slipper lobsters, Scyllarides latus (Latreille, 1803) (Decapoda: Achelata: Scyllaridae). J. Crustac. Biol. 2023, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanier, E.; Miller, E. ; Zviely. D. Winter stranding of Mediterranean slipper lobsters, Scyllarides latus. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2017, 14, 126-131. 14,. [CrossRef]
- Gennaro, G. Ampliamento delle conoscenze sulla distribuzione e sullo stato di conservazione della specie protetta Scyllarides latus nell'Area Marina Protetta" Isola di Bergeggi" e nella ZSC" Fondali Noli-Bergeggi".. Master Thesis, Universitá Delgi Studi Di Genova, Italy, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Holthuis L., B. The Indo-Pacific scyllarine lobsters (Crustacea, Decapoda, Scyllaridae). Zoosystema 2002, 24(3), 499–683. [Google Scholar]
- Alborés, I.; García-Soler, C.; Fernández, L. Reproductive biology of the slipper lobster Scyllarus arctus in Galicia (NW Spain): Implications for fisheries management. Fish. Res. 2019, 212, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, U.; Spanier, E. Occurrence of larvae of Scyllarus arctus (Crustacea, Decapoda, Scyllaridae) in the Eastern Mediterranean — preliminary results. Ann. Ser. Hist. Nat. 1999, 17, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, M.; MacDiarmid, A.; Wahle, R.; Cockcroft, A.; Chan, T.Y. (2011). Scyllarus arctus, /: List of Threatened Species. 2009 . https; (accessed on 5 July 2025)2009. [Google Scholar]
- Majdalani, S. The present status of fishery and information system in Lebanon. Enabling participation in the fishery statistics and information system in the Mediterranean (TCP/INT/2904).
- Fishelson, L. Lexicon of the Flora and Fauna of the Land of Israel, Ministry of Defense Publishing House: Raanana, Israel, 1996; Volume 3 - Aquatic Life, (in Hebrew), pp. 183-164.
- Lewinsohn, C. The occurrence of Scyllarus pygmaeus (Bate) in the eastern Mediterranean (Deacpoda, Scyllaridae) Crustaceana 1974, 27, 43–46. 27. [CrossRef]
- Lewinsohn, C.; Holthuis, L.B. The Crustacea Decapoda of Cyprus. Zool. Verh. 1986, 230, 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Guy-Haim, T.; Iakoleva, A.; Ermak, K.; Spanier, E.; Morov, A. R. First record of the phyllosoma larva of the pygmy locust lobster Scyllarus pygmaeus in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K., 2024, 104, e49, 1-4. , 104. [CrossRef]
- Wahle, R.; MacDiarmid, A.; Cockcroft, A.; Chan, T.Y.; Butler, M. Scyllarus pygmaeus, The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2009. . https://www.iucnredlist.org/search? (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Galil, B.; Pisanty, S.; Spanier, E.; Tom, M. The Indo-Pacific lobster Panulirus ornatus (Fabricius, 1798) (Crustacea: Decapoda) a new Lessepsian migrant to the Eastern Mediterranean Isr. J. Zool. 1989, 35, 241–243. [Google Scholar]
- Spanier, E.; Friedmann, E. The collection of an exuvia identified as Panulirus longipes longipes (A. Milne-Edwards, 1868) from off Haifa, Israel. Mediterr. Mar. Sci., 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
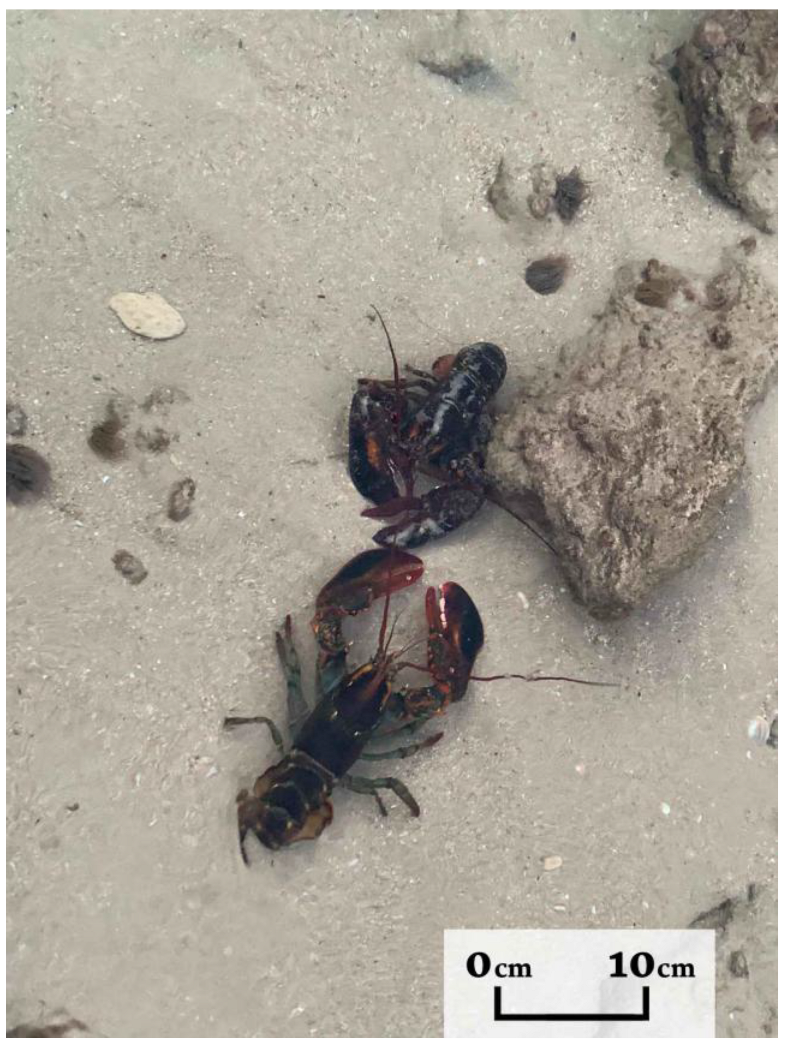
- Spanier, E. First record of the American clawed lobster, Homarus americanus (H. Milne Edwards, 1837), in the southeastern Mediterranean. Bioinvations Rec. 2023, 12, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthuis, L.B. Some new species of Scyllaridae. Proc. K. Ned. Akad. Wet. 1967, C 70, 305–308. [Google Scholar]
- Holthuis, L. The second Israel South Red Sea expedition, 1965: Report no. 7. The Palinuridae and Scyllaridae of the Red Sea. Zool. Meded. 1968, 42, 281–301. [Google Scholar]
- Kizhakudan, J. K.; Sundar, R.; Mohamed, A.A.; Anassery, A.A.; Thiagu, R. , Midhun, M. Growth, maturation and breeding of the clamkiller slipper lobster Scyllarides tridacnophaga Holthuis, 1967 in captivity. Lobster Newsletter, 2018, 31, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Herrnkind, W. Queuing behavior of spiny lobsters. Science 1969, 164, 1425-1427.–content. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDiarmid, A.; Cockcroft, A.; Butler, M. Scyllarides tridacnophaga, The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 2011. https://www.iucnredlist.org/search?query=Scyllarides%20tridacnophaga&searchType=species. (accessed on 8 July 2025).
- Holthuis, L. B. The Indo-Pacific scyllarine lobsters (Crustacea, Decapoda, Scyllaridae). Zoosystema 2002, 24, 499–683. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, T.Y. Eduarctus lewinsohni, The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 2009. https://www.iucnredlist.org/search?
- Guy-Haim, V.; Farstey, T.; Iakovleva, A.; Spanier, E.; Morov, A.R. First report of the pygmy slipper lobster Biarctus sordidus (Crustacea, Decapoda) in the Red Sea following he finding of its phyllosoma larva. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2024, 104, e110–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C. H.; Lin, C. W.; Chan, T. Y. Additional slipper lobsters of the subfamily Scyllarinae Latreille, 1825 (Crustacea, Achelata, Scyllaridae) from Taiwan. Zootaxa, /: 336-346. https, 2636. [Google Scholar]
- Sealife Base, version o4/2025. https://www.sealifebase.se/comnames/CommonNamesList.php?ID=9316&GenusName=Panulirus&SpeciesName=penicillatus&StockCode=346. (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Fishelson, L. Lexicon of the Flora and Fauna of the Land of Israel, Ministry of Defense Publishing House: Raanana, Israel, 1996; Volume 3 - Aquatic Life, (in Hebrew), p. 185.
- Vaitheeswaran, T. On rare occurrence of pronghorn spiny lobster, Panulirus penicillatus (Olivier, 1791) off Tuticorin coast, India (08 35.912’N and 78 25.327’E) (25 M). J. Agric. Sci. Bot. 2017, 1, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaut, I. Sexual maturity, reproductive season and fecundity of the spiny lobster Panulirus penicillatus from the Gulf of Eilat (Aqaba), Red Sea. Mar. Freshwater Res. 1993, 44, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, A.; Murillo, J. C. Life History of the Red Spiny Lobster, Panulirus penicillatus (Decapoda: Palinuridae), in the Galápagos Marine Reserve, Ecuador1. Pac. Sci. 2008, 62, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer-Faust, R.K.; Spanier, E. Gregariousness and sociality in spiny lobsters: implication for den habitation. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1987, 105, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, H.; Takenouchi, T.; Goldstein, J. S. The complete larval development of the pronghorn spiny lobster Panulirus penicillatus (Decapoda: Palinuridae) in culture. J. Crustac. Biol. 2006, 26, 579–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogarth, P. J.; Barratt, L. A. Size distribution, maturity and fecundity of the spiny lobster Panulirus penicillatus (Olivier 1791) in the Red Sea. Trop. Zoo. 1996, 9, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardenne, F.; Bodin, N.; Barret, L.; Blamey, L.; Govinden, R.; Gabriel, K. . Rowat, D. Diet of spiny lobsters from Mahé Island reefs, Seychelles inferred by trophic tracers. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 42, 101640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, C. D. Fecundity and reproductive rates in Indo-West Pacific spiny lobsters. Micronesica 1988, 21, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft, A.; MacDiarmid, A.; Butler, M. Panulirus penicillatus. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 2009. https://www.iucnredlist.org/search?query=Panulirus%20penicillatus.&searchType=species. (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Loya, Y. How to influence environmental decision makers? The case of Eilat (Red Sea) coral reefs. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 344, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zibdah, M. K. The Aqaba Marine Protected Area--Integration of Marine Science and Resource Management in the Gulf of Aqaba-Red Sea. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2013, 3, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanier, E. Marine protected areas – a review of their potential effects on lobster population size and structure and fisheries management Fish. Res. 2024, 275, 107025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buglass, S.; Reyes, H.; Ramirez-González, J.; Eddy, T. D.; Salinas-de-León, P. Jarrin, J. M. Evaluating the effectiveness of coastal no-take zones of the Galapagos Marine Reserve for the red spiny lobster, Panulirus penicillatus. Mar. Policy 2018, 88, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampouris, T. E.; Koutsoubas, D.; kanelopoulou, K.; Zannaki, C. , Batjakas, I. E. Informing the general public on the threat status of the European spiny lobster, Palinurus elephas (Fabricius, 1787) through Citizen-Science and social media platforms. A case study from the Aegean Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. [CrossRef]
- Galil, B.S.; Boero, F.; Campbell, M.L.; Carlton, J.T.; Cook, E.; Fraschetti, S.; Gollasch, S.; Hewitt, C.L.; Jelmert, A.; MacPherson, E.; et al. ‘Double trouble’: The expansion of the Suez Canal and marine bioinvasions in the Mediterranean Sea. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 973–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galil, B. S; Zirler, R.; Feldstein-Farkash, T.; Bronstein, O. A call to ARMS: new records of invasive alien decapods in the Mediterranean Sea. Manag. Biol. Invas. 2024, 15(4), 581–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanier, E. Why there are almost no reports on non-Indigenous lobsters? AOMB. [CrossRef]
- Albano, P.G.; Steger, J.; Bošnjak, M.; Dunne, B.; Guifarro, Z.; Turapova, E.; Hua, Q.; Kaufman, D.S.; Rilov, G.; Zuschin, M. Native biodiversity collapse in the eastern Mediterranean. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2021, 288, 20202469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savva, I.; Chartosia, N.; Antoniou, C.; Kleitou, P.; Georgiou, A.; Stern, N.; Hadjioannou, L.; Jimenez, C. ; Andreou,V.; Hall-Spencer, J. M.; Kletou, D. They are here to stay: the biology and ecology of lionfish (Pterois miles) in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Fish Biol. [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, M. I.; Chapman, J. K.; Gough, C. L.; Humber, F.; Anderson, L. G. Management implications of the influence of biological variability of invasive lionfish diet in Belize. Management of Biol. Invasions 2017, 8(1), 61-70.–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCard, M.; McCard, N.; Coughlan, N. E.; South, J.; Kregting, L.; Dick, J. T. Functional response metrics explain and predict high but differing ecological impacts of juvenile and adult lionfish. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2024, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lester, S.E.; Halpern, B.S.; Grorud-Colvert, K.; Lubchenco, J.; Ruttenberg, B.I.; Gaines, S. D.; Airam´e, S.; Warner, R.R. Biological effects within no-take marine reserves: a global synthesis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 384, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanier, E.; Tom, M.; Pisanty, S.; Almog-Shtayer, G. Artificial reefs in the low productive marine environment of the Southeastern Mediterranean. P.S.Z.N.I: Mar. Ecol. [CrossRef]
- Spanier, E.; Angel, D.L. Benthic artificial reefs and mid-water artificial substrates in the northern Gulf of Aqaba: Biodiversity and potential environmental applications. In Aqaba-Eilat, the Improbable Gulf: Environment, Biodiversity and Preservation; Por, F.D., Ed.; Hebrew University Magnes Press: Jerusalem, Israel, 2008; pp. 281–298. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, A. K.; Kotecki, S. E.; Dahl, P. H.; Bowman, V. F.; Casper, B. M.; Boerger, C.; Popper, A. N. Physical effects from underwater explosions on two fish species. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life: Principles and Practical Considerations; Popper, A.N., Sisneros, J.A., Hawkins, A.D., Thomsen, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lestang, S.; How, J.; Erbe, C.; Rushworth, K. Boom, shake the room: Seismic surveys affect behaviour and survival of western rock lobster. Fish. Res. 2024, 277, 107072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siluvaithasan, A. S.; Stokke, K. Fisheries under fire: Impacts of war and challenges of reconstruction and development in Jaffna fisheries, Sri Lanka. Nor. Geogr. Tidsskr. 2006, 60(3), 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




