Submitted:
13 August 2025
Posted:
13 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Fish, Cells and Virus
2.3. Cell Treatment
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assays
2.5. Virus Infection Assay In Vitro
2.6. RNA Isolation and qRT-PCR Analysis
2.7. Western Blotting Analysis
2.8. Annexin V-FITC/PI Apoptosis Assay
2.9. Antiviral Activity of EUG In Vivo
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
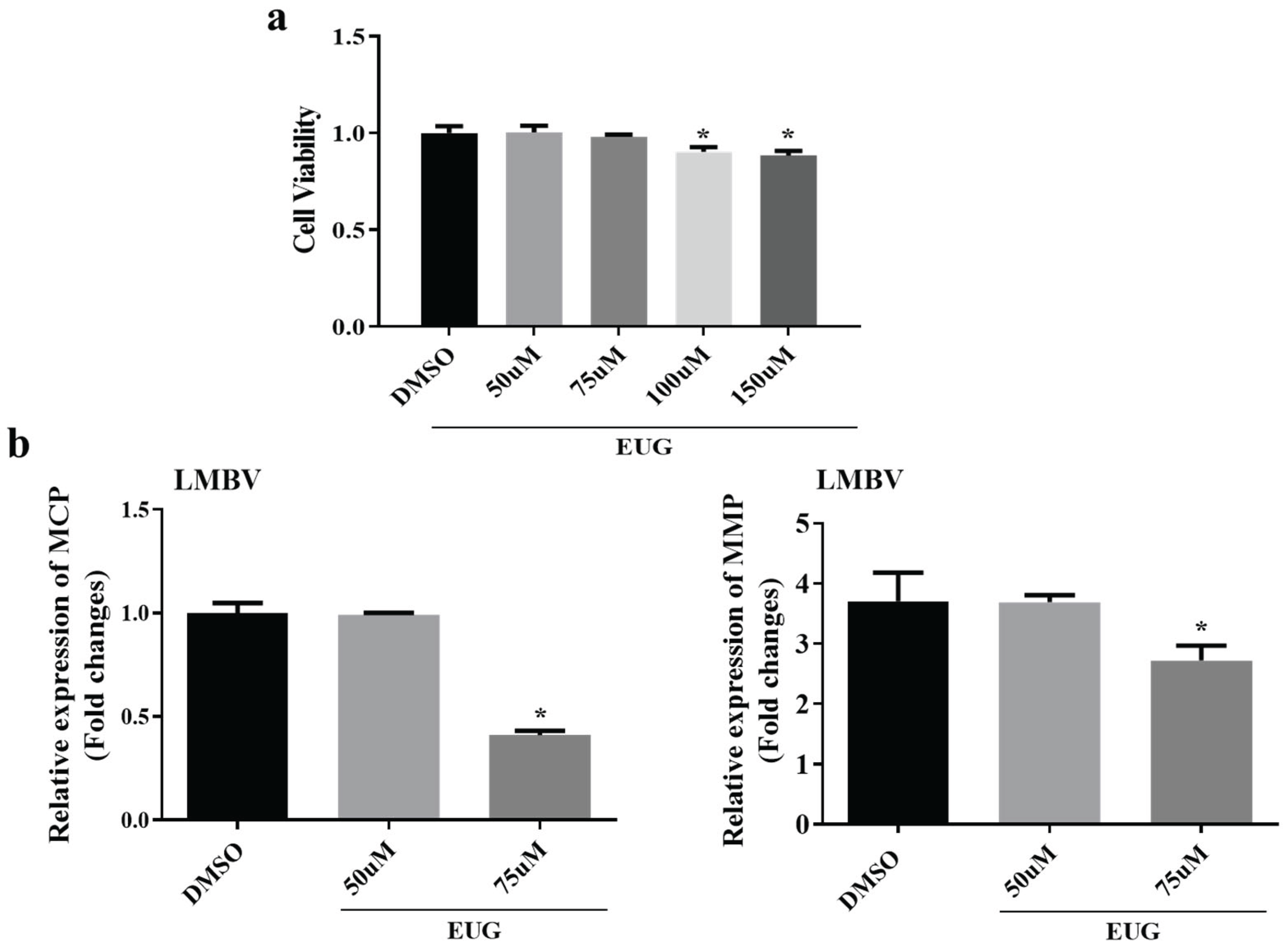
3.1. Effect of EUG in Different Concentrations on LMBV Infection
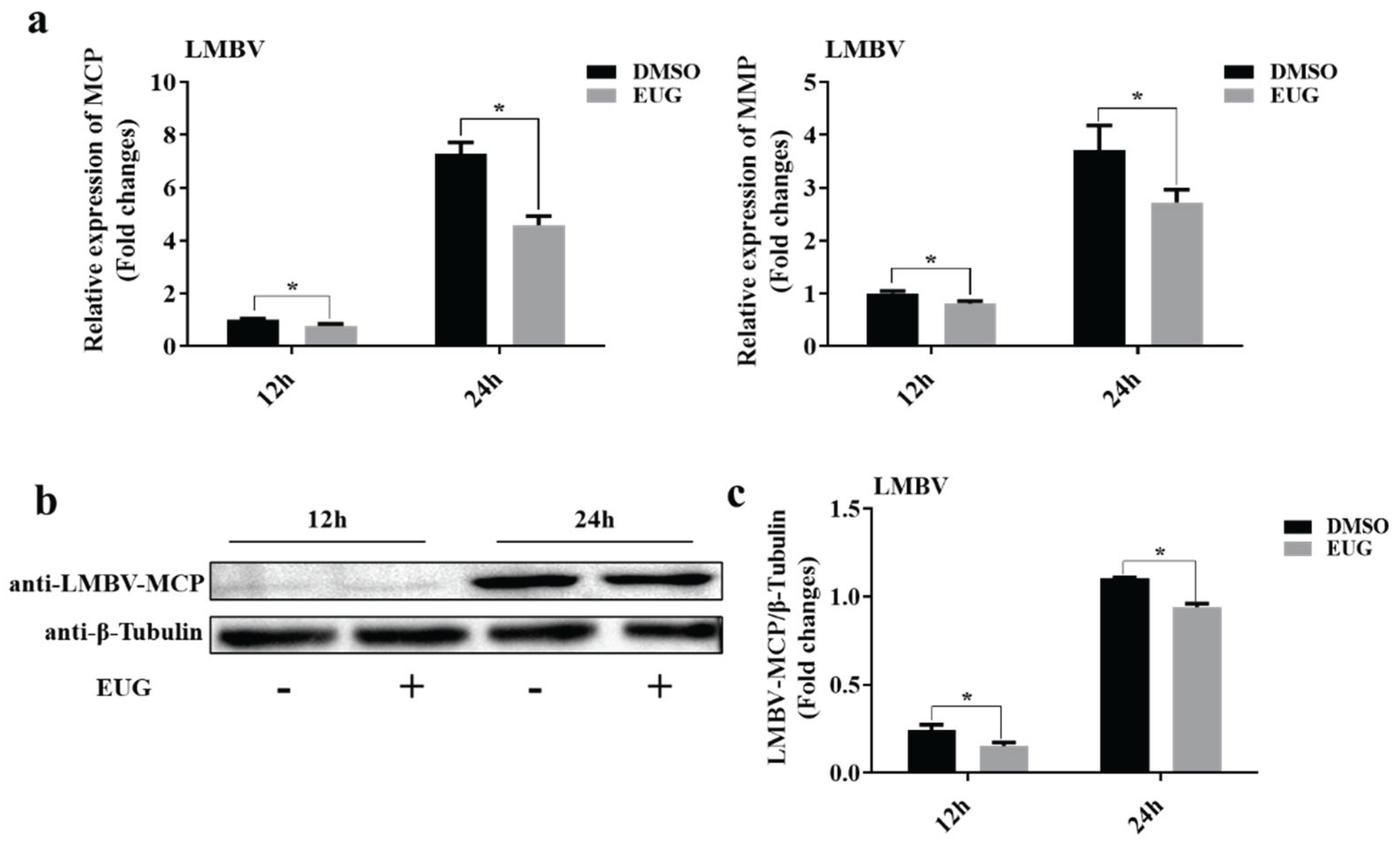
3.2. EUG inhibits LMBV Infection at Different Time Points
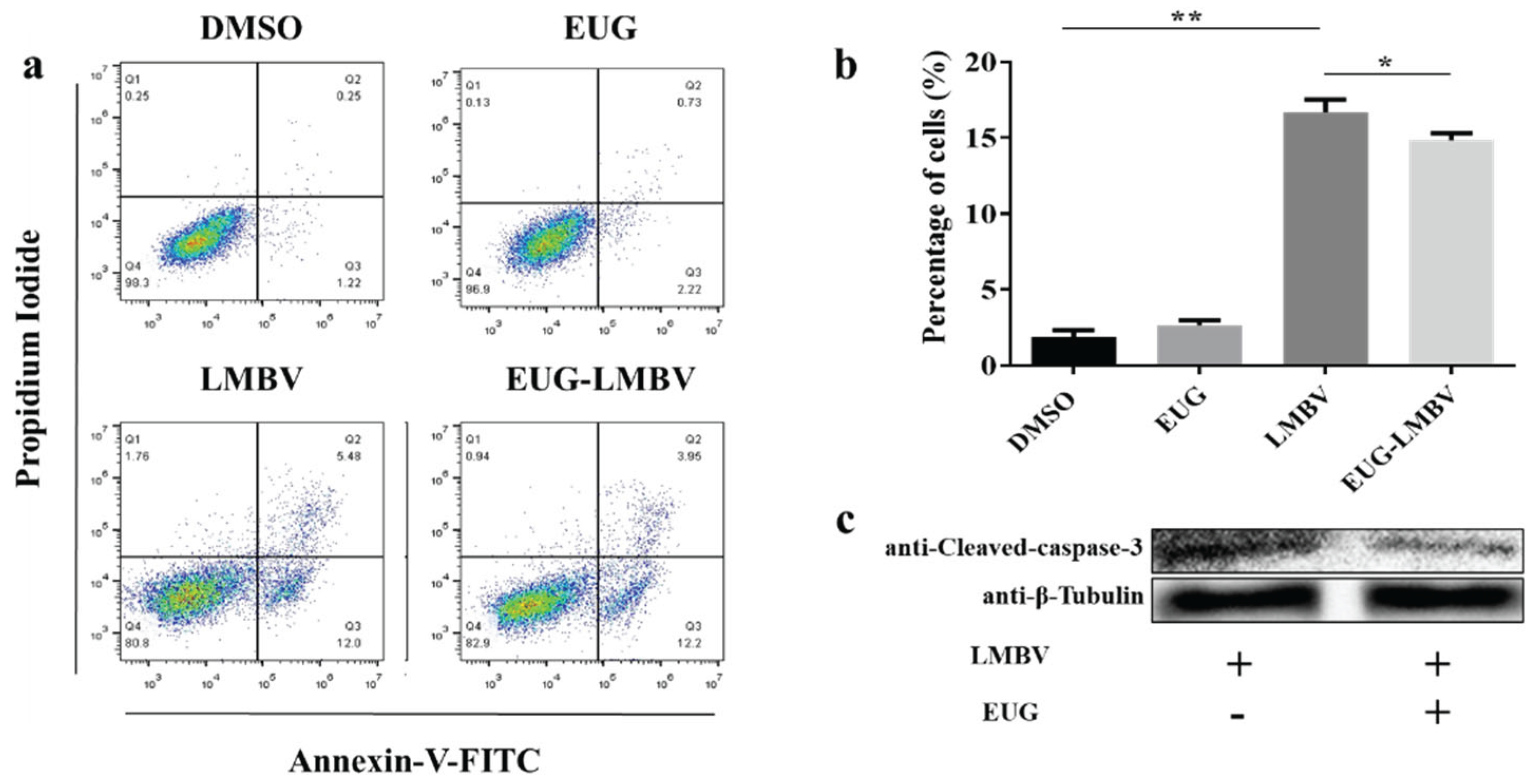
3.3. EUG Inhibits Apoptosis In Cells Infected by LMBV
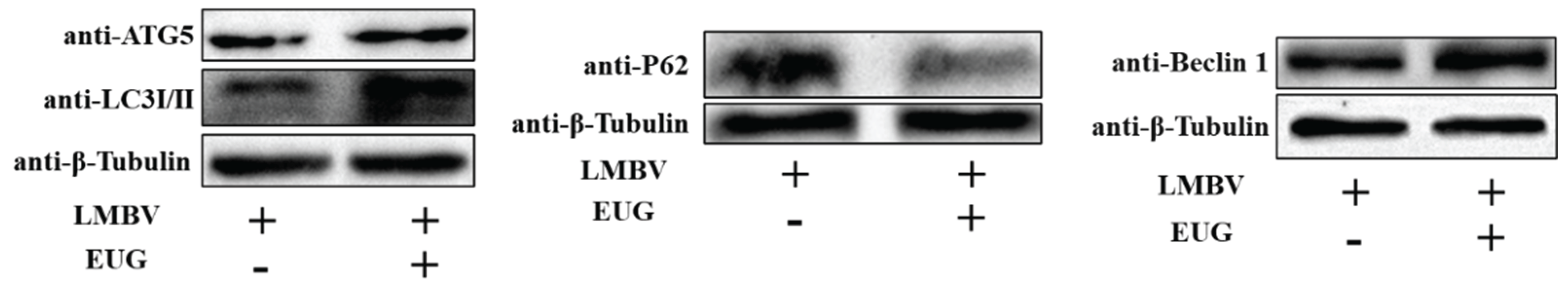
3.4. EUG Promotes Cellular Autophagy in LMBV Infection
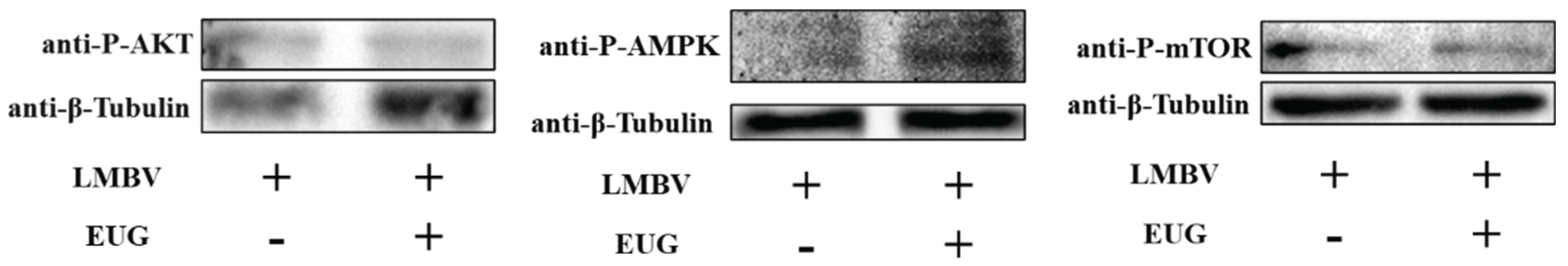
3.5. EUG regulates AMPK and AKT/mTOR Pathway in LMBV Infection
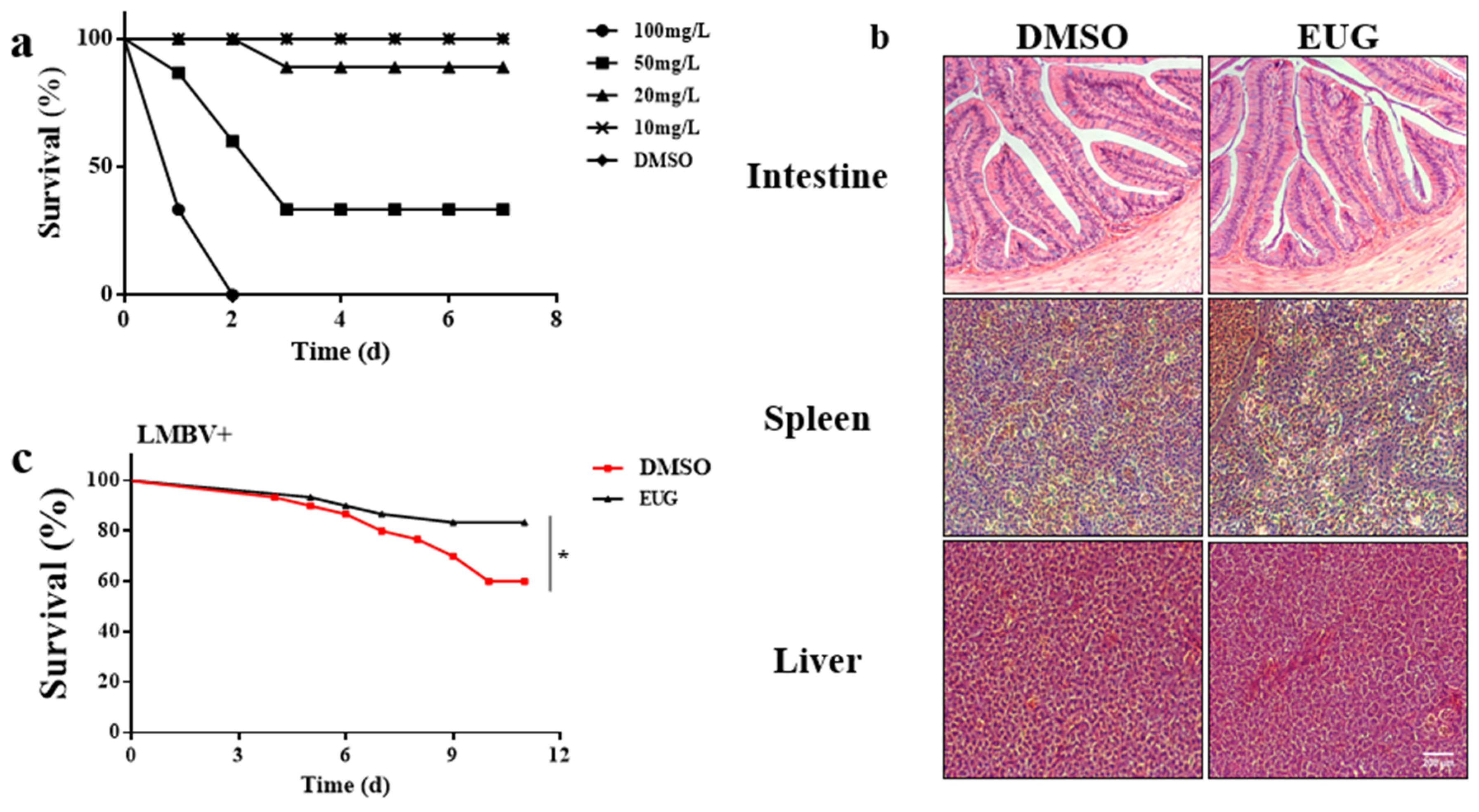
3.6. EUG Reduces Mortality in LMBV-Infected Largemouth Bass
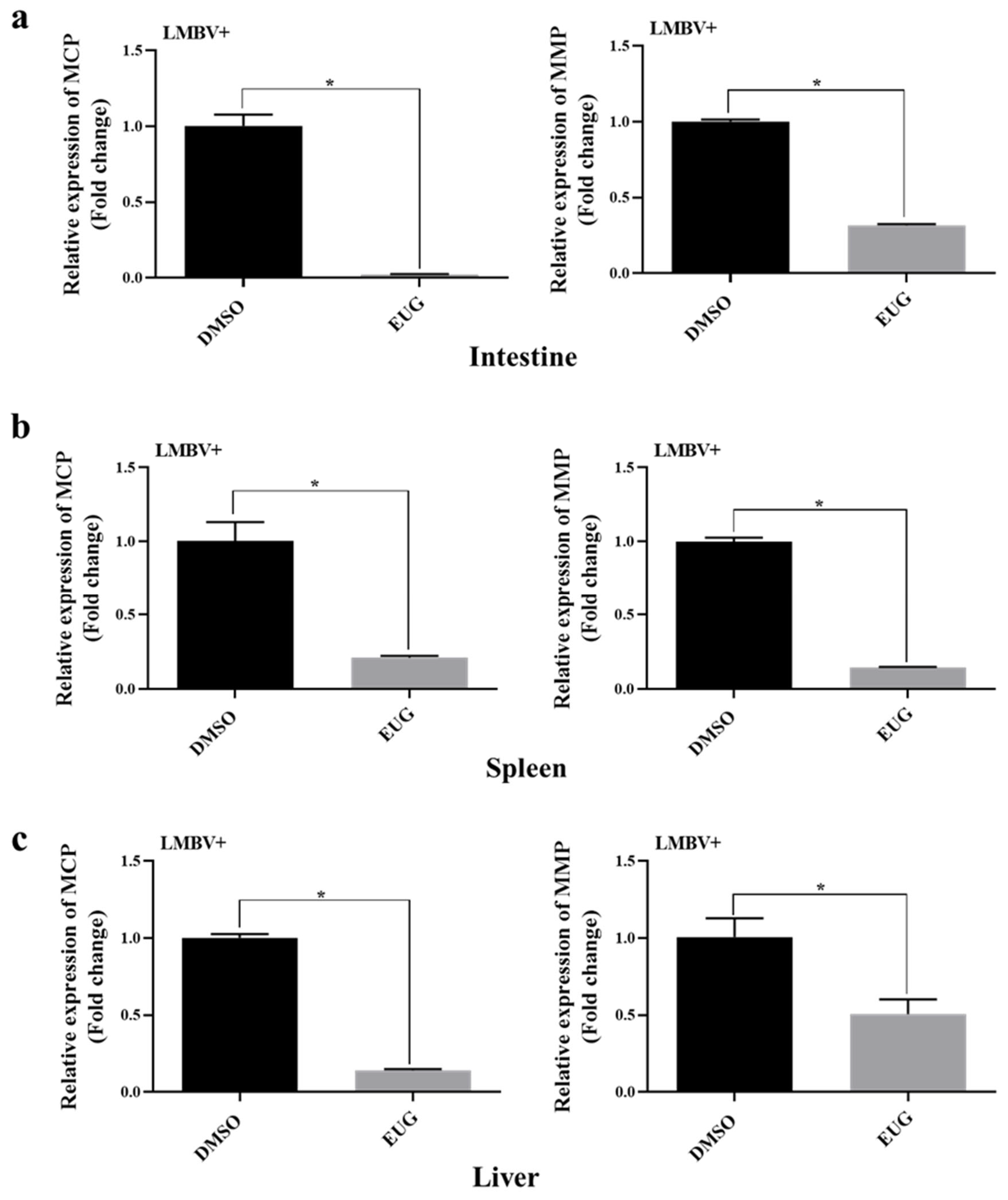
3.7. EUG Inhibits LMBV Infection in Tissues
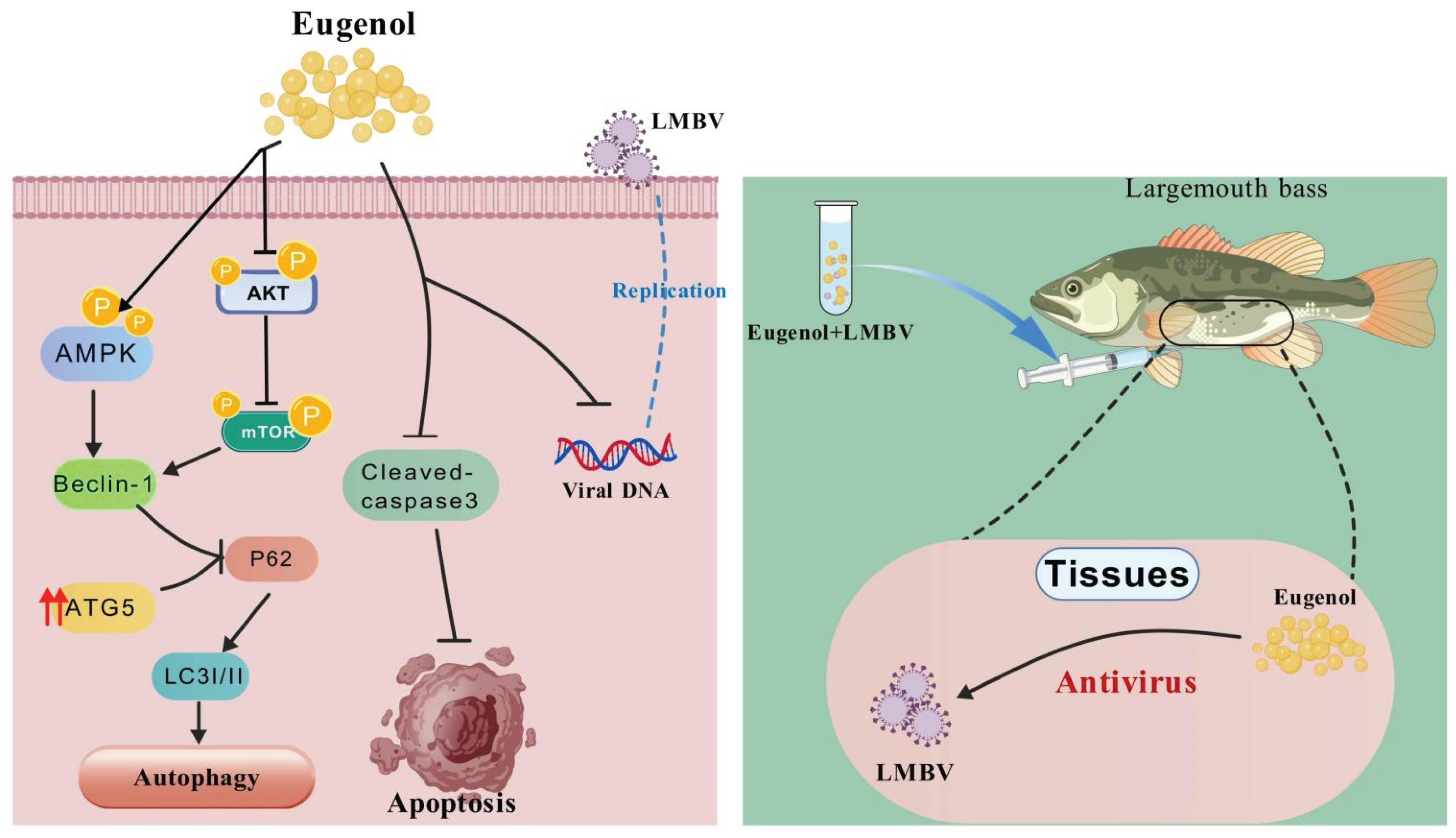
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salazar, V.; Koch, J.D.; Neely, B.C.; Steffen, C.J.; Flores, E.; Steffen, S.F. The effect of largemouth bass virus on bass populations in Kansas impoundments. J. Aquat. Anim. Health. 2022, 34, 38-44. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhong, Y.; Luo, M.; Zheng, G.; Huang, J.; Wang, G.; Geng, Y.; Qian, X. Largemouth bass ranavirus: Current status and research progression. Aquacult. Rep. 2023, 32, 101706. [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Deng, G.; Bai, J.; Li, S.; Yu, L.; Quan, Y.; Yang, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Ye, X. A strain of Siniperca chuatsi rhabdovirus causes high mortality among cultured largemouth bass in South China. J. Aquat. Anim. Health. 2013, 25, 197-204. [CrossRef]
- Fogelson, S.B.; Petty, B.D.; Reichley, S.R.; Ware, C.; Bowser, P.R.; Crim, M.J.; Getchell, R.G.; Sams, K.L.; Marquis, H.; Griffin, M.J. Histologic and molecular characterization of Edwardsiella piscicida infection in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2016, 28, 338-344. [CrossRef]
- Chinchar, V.G. Ranaviruses (family Iridoviridae): Emerging cold-blooded killers. Arch. Virol. 2002, 147, 447-470. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; An, Z.; Zhang, X.; Vakharia, V.N.; Lin, L. Isolation, identification and the pathogenicity characterization of a Santee-Cooper ranavirus and its activation on immune responses in juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 135, 108641. [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, C.;Yuan, X.; Huang, L.; Hu, D.; Yu, Z.; Yin, W.; Lin, L.; Pan, X.; Yang, G.; Wang, C.; Shen, J.; et al. Oral vccination with recombinant pichia pastoris expressing iridovirus major capsid protein elicits protective immunity in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Front Immunol. 2022, 13, 852300. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Chen, J.; He, X.; He, H.; Qin, Q.; Yang, M. The role of largemouth bass NF-kappa B/p65: Inhibition of LMBV and activator of IL-18 promoter. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025, 158, 110120. [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Feng, Y.; OuYang, P.; Chen, D.; Huang, X.; Guo, H.; Deng, H.; Fang, J.; Lai, W.; Geng, Y. Autophagy induced by largemouth bass virus inhibits virus replication and apoptosis in Epithelioma papulosum cyprini cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 123, 489-495. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, W.; Pan, Z.; Qin, Q.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y. Largemouth bass virus infection induced non-apoptotic cell death in MsF cells. Viruses 2022, 14, 1568. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Xu, L.; Qin, Q. Involvement of the PI3K and ERK signaling pathways in largemouth bass virus-induced apoptosis and viral replication. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 371-379. [CrossRef]
- D', A.F.M.; Oliveira, P.S.; Dutra, F.S.; Fernandes, T.J.; De Pereira, C.M.; De Oliveira, S.Q.; Stefanello, F.M.; Lencina, C.L.; Barschak, A.G. Eugenol derivatives as potential anti-oxidants: Is phenolic hydroxyl necessary to obtain an effect? J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 733-746. [CrossRef]
- Amangeldinova, M.; Ersatir, M.; Necip, A.; Yilmaz, M.A.; Cimentepe, M.; Kudrina, N.; Terletskaya, N.V.; Ozturk, C.O.; Yildirim, M. Simultaneous quantitative screening of 53 phytochemicals from Rheum tataricum L. roots: A comparative study of supercritical CO2, subcritical ethanol, and ultrasound-assisted extraction for enhanced antioxidant, antibacterial activities, and molecular docking study. Front. Plant. Sci. 2024, 15, 1513875. [CrossRef]
- Benencia, F.; Courreges, M.C. In vitro and in vivo activity of eugenol on human herpesvirus. Phytother. Res. 2000, 14, 495-500. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, J.; Gong, H.; Qin, Q.; Wei, S. In vitro antiviral activity of eugenol on Singapore grouper iridovirus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 151, 109748. [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, J.; Wan, Q.; Yang, J.; Li, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, G.; Li, K. Drug screening for autophagy inhibitors based on the dissociation of Beclin1-Bcl2 complex using BiFC technique and mechanism of eugenol on anti-influenza A virus activity. PLoS. One. 2013, 8, e61026. [CrossRef]
- Imre, G. Cell death signalling in virus infection. Cell. Signal. 2020, 76, 109772. [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.L.; Al-Shabanah, O.; Hassan, Z.K.; Hafez, M.M. Eugenol-induced autophagy and apoptosis in breast cancer cells via PI3K/AKT/FOXO3a pathway inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9243. [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.; Shisi, H.U.; Zhenduo, Y.; Xiaodan, C. Eugenol attenuates the inflammation of Fusarium-induced keratitis through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int. Eye Sci. 2024, 1194-1199.
- Saleh, D.O.; Baraka, S.M.; Jaleel, G.; Hassan, A.; Ahmed-Farid, O.A. Eugenol alleviates acrylamide-induced rat testicular toxicity by modulating AMPK/p-AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and blood-testis barrier remodeling. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1910. [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zang, S.; Xu, M.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, X.; Qin, Q. TRAF6 is a critical factor in fish immune response to virus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 60, 6-12. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Cai, J.; Wei, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Qin, Q. Molecular cloning, expression and functional analysis of ISG15 in orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 1094-1102. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yao, H.; Li, Y.H.; Xu, Y.J.; Ma, X.F.; Wang, H.P. Global diversity and genetic landscape of natural populations and hatchery stocks of largemouth bass micropterus salmoides across American and Asian regions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16697. [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, A.D.; Gould, A.R.; Zupanovic, Z.; Cunningham, A.A.; Hengstberger, S.; Whittington, R.J.; Kattenbelt, J.; Coupar, B.E. Comparative studies of piscine and amphibian iridoviruses. Arch. Virol. 2000, 145, 301-331. [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.; Ting, J.; Wu, M.; Wu, M.; Guo, I.; Chang, C. Complete genome sequence of the grouper iridovirus and comparison of genomic organization with those of other iridoviruses. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2010-2023. [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Jian, J.; Niu, B.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Xu, X. Germplasm resources evaluation of cultured largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) in China based on whole genome resequencing. Genes (Basel) 2024, 15, 1307. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Feng, J. Rapid diagnosis of largemouth bass ranavirus in fish samples using the loop-mediated isothermal amplification method. Mol. Cell. Probes. 2020, 52, 101569. [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Wang, J.; Chinchar, G.D.; Chinchar, V.G. Molecular characterization of a ranavirus isolated from largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 1999, 37, 107-114. [CrossRef]
- Zilberg, D.; Grizzle, J.M.; Plumb, J.A. Preliminary description of lesions in juvenile largemouth bass injected with largemouth bass virus. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2000, 39, 143-146. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Xue, M.; Jiang, N.; Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, N.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Oral vaccination of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) against largemouth bass ranavirus (LMBV) using yeast surface display technology. Animals (Basel) 2023, 13, 1183. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, C.; He, H.; Chen, J.; He, X.; Qin, Q.; Yang, M. Largemouth bass Rel exerts antiviral role against fish virus and regulates the expression of interleukin-10. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 142, 109117. [CrossRef]
- Ohlemeyer, S.; Holopainen, R.; Tapiovaara, H.; Bergmann, S.M.; Schutze, H. Major capsid protein gene sequence analysis of the Santee-Cooper ranaviruses DFV, GV6, and LMBV. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2011, 96, 195-207. [CrossRef]
- Kvansakul, M. Viral infection and apoptosis. Viruses 2017, 9, 356. [CrossRef]
- Micoli, K.J.; Pan, G.; Wu, Y.; Williams, J.P.; Cook, W.J.; McDonald, J.M. Requirement of calmodulin binding by HIV-1 gp160 for enhanced FAS-mediated apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1233-1240. [CrossRef]
- Clarke, P.; Leser, J.S.; Quick, E.D.; Dionne, K.R.; Beckham, J.D.; Tyler, K.L. Death receptor-mediated apoptotic signaling is activated in the brain following infection with West Nile virus in the absence of a peripheral immune response. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1080-1089. [CrossRef]
- Souza, B.S.; Sampaio, G.L.; Pereira, C.S.; Campos, G.S.; Sardi, S.I.; Freitas, L.A.; Figueira, C.P.; Paredes, B.D.; Nonaka, C.K.; Azevedo, C.M.; et al. Zika virus infection induces mitosis abnormalities and apoptotic cell death of human neural progenitor cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39775. [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.S.; Chiou, P.P.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, C.W.; Chiu, I.S.; Chen, S.D.; Cheng, Y.H.; Chang, C.Y. Characterization of apoptosis induced by grouper iridovirus in two newly established cell lines from barramundi, Lates calcarifer (Bloch). J. Fish. Dis. 2008, 31, 825-834. [CrossRef]
- Al-Sharif, I.; Remmal, A.; Aboussekhra, A. Eugenol triggers apoptosis in breast cancer cells through E2F1/survivin down-regulation. BMC. Cancer. 2013, 13, 600. [CrossRef]
- Pisano, M.; Pagnan, G.; Loi, M.; Mura, M.E.; Tilocca, M.G.; Palmieri, G.; Fabbri, D.; Dettori, M.A.; Delogu, G.; Ponzoni, M.; et al. Antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic activity of eugenol-related biphenyls on malignant melanoma cells. Mol. Cancer. 2007, 6, 8. [CrossRef]
- Asadi, M.; Taghizadeh, S.; Kaviani, E.; Vakili, O.; Taheri-Anganeh, M.; Tahamtan, M.; Savardashtaki, A. Caspase-3: Structure, function, and biotechnological aspects. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 1633-1645. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, L.; Mostowy, S.; Sancho-Shimizu, V. Autophagy-virus interplay: From cell biology to human disease. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 155. [CrossRef]
- Levine, B.; Mizushima, N.; Virgin, H.W. Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature 2011, 469, 323-335. [CrossRef]
- Nardacci, R.; Amendola, A.; Ciccosanti, F.; Corazzari, M.; Esposito, V.; Vlassi, C.; Taibi, C.; Fimia, G.M.; Del, N.F.; Ippolito, G.; et al. Autophagy plays an important role in the containment of HIV-1 in nonprogressor-infected patients. Autophagy 2014, 10, 1167-1178. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Torresilla, C.; Rassart, E.; Barbeau, B. Implication of different HIV-1 genes in the modulation of autophagy. Viruses 2017, 9, 389. [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Wang, J.; Jin, Q.; Zhao, Z. The interplays between autophagy and apoptosis induced by enterovirus 71. PLoS One. 2013, 8, e56966. [CrossRef]
- Joubert, P.E.; Werneke, S.W.; de la Calle, C.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Giodini, A.; Peduto, L.; Levine, B.; Schwartz, O.; Lenschow, D.J.; Albert, M.L. Chikungunya virus-induced autophagy delays caspase-dependent cell death. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1029-1047. [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.H.; Kleeman, L.K.; Jiang, H.H.; Gordon, G.; Goldman, J.E.; Berry, G.; Herman, B.; Levine, B. Protection against fatal Sindbis virus encephalitis by beclin, a novel Bcl-2-interacting protein. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 8586-8596. [CrossRef]
- Yeganeh, B.; Ghavami, S.; Rahim, M.N.; Klonisch, T.; Halayko, A.J.; Coombs, K.M. Autophagy activation is required for influenza A virus-induced apoptosis and replication. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Mol. Cell. Res. 2018, 1865, 364-378. [CrossRef]
- Ariosa, A.R.; Klionsky, D.J. Autophagy core machinery: Overcoming spatial barriers in neurons. J. Mol. Med (Berl). 2016, 94, 1217-1227. [CrossRef]
- Aita, V.M.; Liang, X.H.; Murty, V.V.; Pincus, D.L.; Yu, W.; Cayanis, E.; Kalachikov, S.; Gilliam, T.C.; Levine, B. Cloning and genomic organization of beclin 1, a candidate tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 17q21. Genomics 1999, 59, 59-65. [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.H.; Jackson, S.; Seaman, M.; Brown, K.; Kempkes, B.; Hibshoosh, H.; Levine, B. Induction of autophagy and inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature 1999, 402, 672-676. [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Waguri, S.; Koike, M.; Sou, Y.S.; Ueno, T.; Hara, T.; Mizushima, N.; Iwata, J.; Ezaki, J.; Murata, S.; et al. Homeostatic levels of p62 control cytoplasmic inclusion body formation in autophagy-deficient mice. Cell 2007, 131, 1149-1163. [CrossRef]
- Nezis, I.P.; Simonsen, A.; Sagona, A.P.; Finley, K.; Gaumer, S.; Contamine, D.; Rusten, T.E.; Stenmark, H.; Brech, A. Ref(2)P, the Drosophila melanogaster homologue of mammalian p62, is required for the formation of protein aggregates in adult brain. J. Cell. Biol. 2008, 180, 1065-1071. [CrossRef]
- Hardie, D.G.; Schaffer, B.E.; Brunet, A. AMPK: An energy-sensing pathway with multiple inputs and outputs. Trends. Cell. Biol. 2016, 26, 190-201. [CrossRef]
- Bowman, C.J.; Ayer, D.E.; Dynlacht, B.D. Foxk proteins repress the initiation of starvation-induced atrophy and autophagy programs. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2014, 16, 1202-1214. [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Zhang, M.; Marshall, B.; Smith, S.; Covar, J.; Atherton, S. Interplay of autophagy and apoptosis during murine cytomegalovirus infection of RPE cells. Mol. Vis. 2014, 20, 1161-1173.
- Li, Q.; Rao, R.; Vazzana, J.; Goedegebuure, P.; Odunsi, K.; Gillanders, W.; Shrikant, P.A. Regulating mammalian target of rapamycin to tune vaccination-induced CD8(+) T cell responses for tumor immunity. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3080-3087. [CrossRef]
- Dazert, E.; Hall, M.N. mTOR signaling in disease. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 2011, 23, 744-755. [CrossRef]
- O'Reilly, K.E.; Rojo, F.; She, Q.B.; Solit, D.; Mills, G.B.; Smith, D.; Lane, H.; Hofmann, F.; Hicklin, D.J.; Ludwig, D.L.; et al. mTOR inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and activates Akt. Cancer. Res. 2006, 66, 1500-1508. [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.I.; Lickteig, R.L.; Estes, R.; Rundell, K.; Walter, G.; Mumby, M.C. Control of protein phosphatase 2A by simian virus 40 small-t antigen. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 1988-1995. [CrossRef]
| Primer | Sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| FHM-β-Actin-RT-F | TACGAGCTGCCTGACGGACA |
| FHM-β-Actin-RT-R | GGCTGTGATCTCCTTCTGCA |
| MS-β-Actin-RT-F | CCACCACAGCCGAGAGGGAA |
| MS-β-Actin-RT-R | TCATGGTGGATGGGGCCAGG |
| LMBV-MCP-RT-F | CTCGCCACTTATGACAGCCTTGAC |
| LMBV-MCP-RT-R | AACCCACGGGATAATGCTCTTTGAC |
| LMBV-MMP-RT-F | GCGTATTTCGCACCCTCTG |
| LMBV-MMP-RT-R | TAAGCGTCGCCCTTGTCTG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





