Submitted:
09 August 2025
Posted:
13 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Nucleic Acid Aptamer
2.1. Nucleic Acid Aptamer
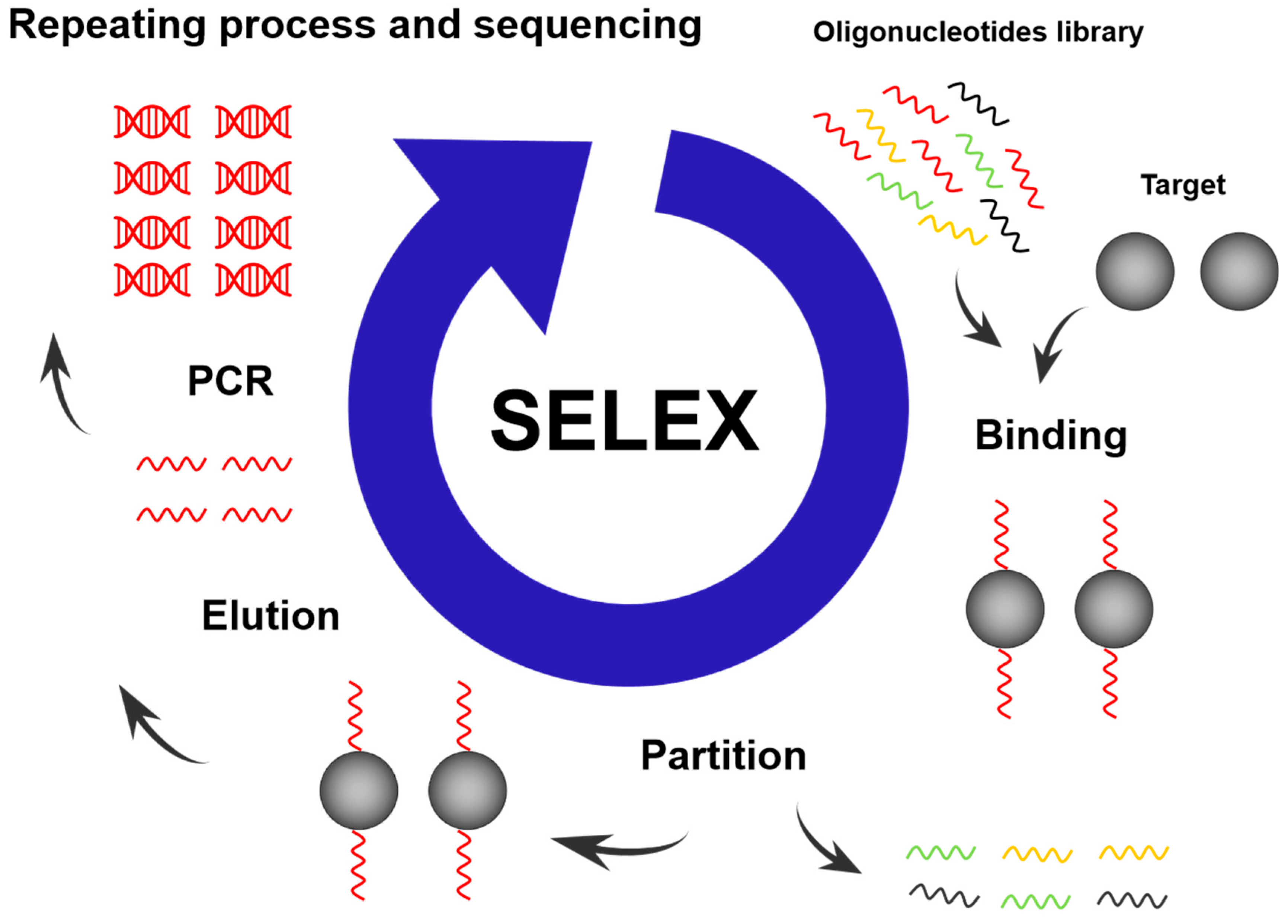
2.2. SELEX Technology
2.3. Separation of Target-Bonded and Non-Binding Aptamers
2.3.1. Capillary Electrophoresis SELEX Technology
2.3.2. Microfluidic SELEX Technology
2.3.3. Cell-SELEX Technology
3. Aptasensors
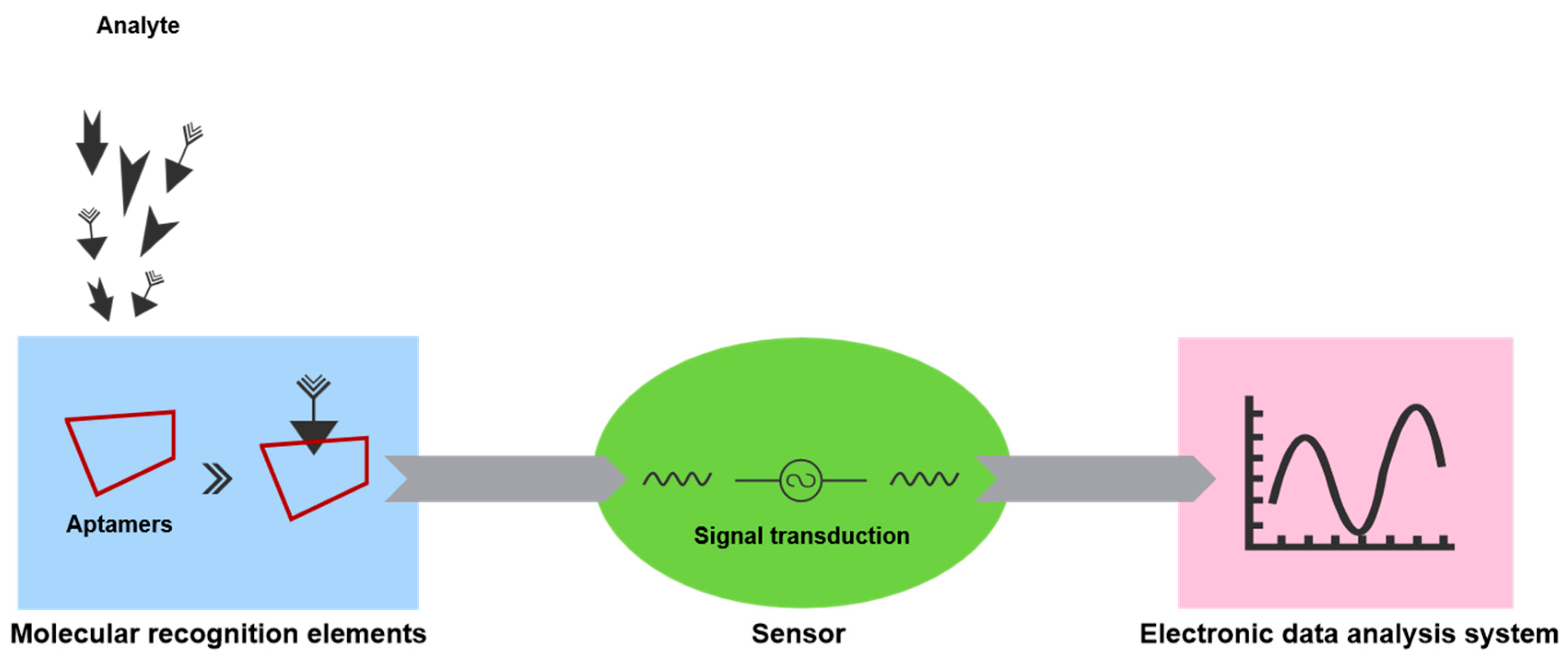
3.1. Aptasensors
3.2. Optical Aptasensors
3.2.1. Fluorescent Aptasensors
3.2.2. Colorimetric Aptasensors
3.2.3. Surface Plasmon Resonance Aptasensors
3.3. Field-Effect Transistor Aptasensors
3.4. Electrochemical Aptasensors
3.4.1. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Aptasensors
3.4.2. Voltammetric Aptasensors
3.4.3. Amperometric Aptasensors
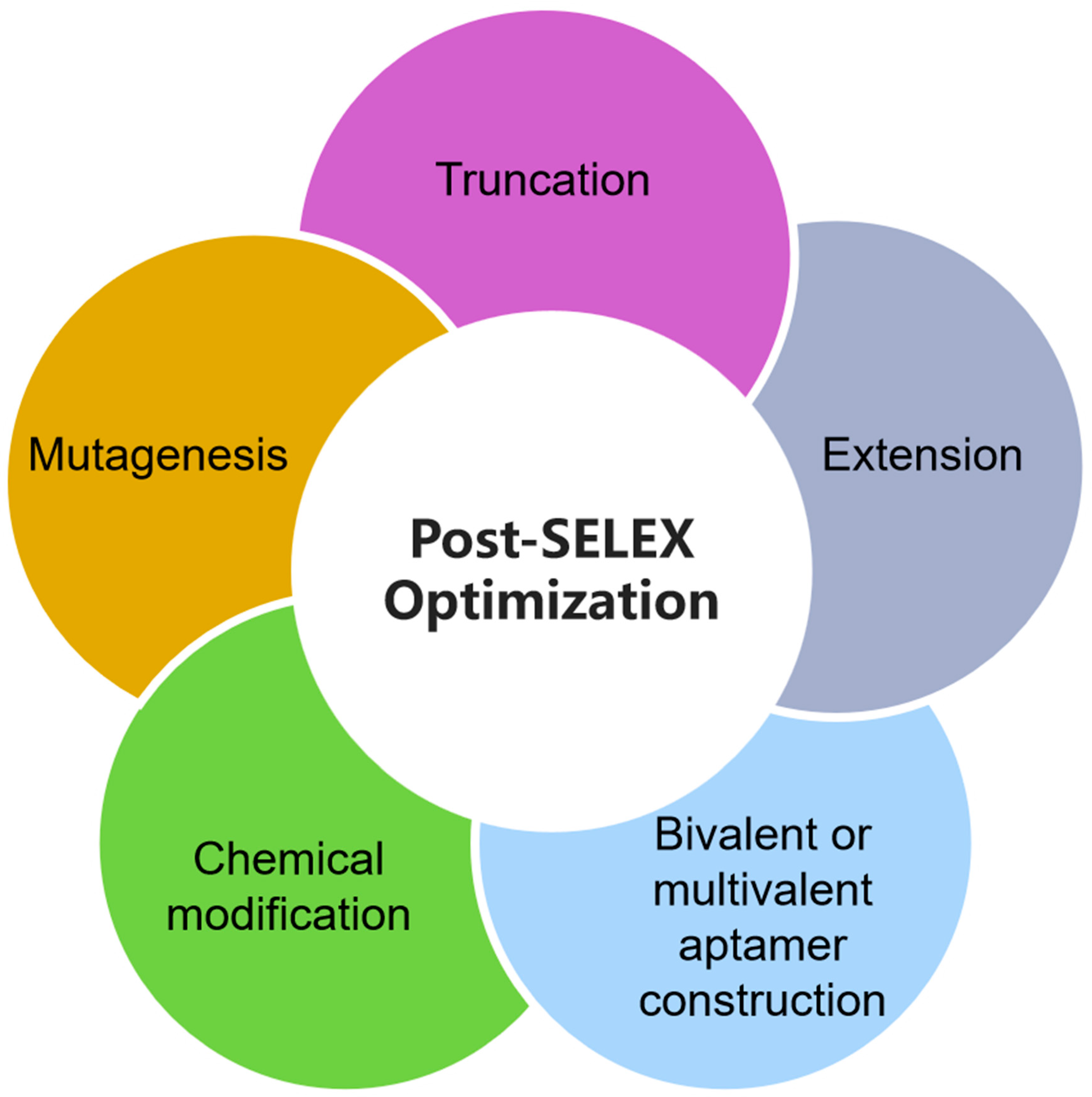
4. Post-SELEX Optimization Process of Aptamers
4.1. Truncation
4.2. Other Post-SELEX Optimization Methods
5. Conclusion and Outlook
- (1)
- It is more difficult to screen aptamers for small molecule targets than for large ones. It is worthy of highlighting a new type of SELEX technology, named as Capture-SELEX, can be used in the field of screening aptamers for small molecule targets, despite that few SELEX technologies applied in this field [220].
- (2)
- Point-of-care (POC) diagnostic systems become more and more demanded in healthcare and clinical diagnosis, aptamer-based biosensing systems have proven their feasibility, but they are still in their infancy. There is still a significant gap in affordability, standardization and commercialization [221,222,223].
- (3)
- Wearable aptasensors are a brand-new field that combines flexible materials, artificial intelligence, machine learning and aptasensors, but it is still in its infancy at present. In the future, there are still huge challenges ahead in improving the consumption of wearable devices, collection of detection data and storage of wearable aptasensors under various physiological conditions and in complex external environments [224].
- (4)
- (5)
- The discovery of aptamers and their applications in sensing have become an interdisciplinary research field across physics, chemistry, biology, materials science and computer science, and several recent aptasensors designs have demonstrated that deep learning and predictive models can effectively enhance the performance of aptasensors while significantly shorten the discovery time of the aptamers as well as running costs [227,228,229,230,231,232,233]. In the future, the development and adoption of advanced predictive algorithms and computational tools are expected to play significant impact on the development of high-performance and low-cost aptasensors,
References
- Ellington, A.D. and Szostak, J.W. (1990). In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature, 346(6287), pp.818–22. [CrossRef]
- Tuerk, C. and Gold, L. (1990). Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science, 249(4968), pp.505–510. [CrossRef]
- Farid, S. et al. (2023). Aptamer-based optical and electrochemical sensors: A Review. Chemosensors, 11(12), p. 569. [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y., Farid, S., Meshik, X., Xu, K., et al. (2018). Detection of immunoglobulin E with a graphene-based field-effect transistor aptasensor. Journal of Sensors, 2018, pp.1–8. [CrossRef]
- Famulok, M., Mayer, G. and Blind, M. (2000). Nucleic acid aptamers from selection in vitro to applications in vivo. Accounts of Chemical Research, 33(9), pp.591–599. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., Ye, Z., Ping, J., Jing, S. and Ying, Y. (2014). Development of an aptamer-based impedimetric bioassay using microfluidic system and magnetic separation for protein detection. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 59, pp.106–111. [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, I., Scarano, S., Esposito, C.L., Antoccia, A., et al. (2016). In vitro selection of RNA aptamers against CA125 tumor marker in ovarian cancer and its study by optical biosensing. Methods, 97, pp.58–68. [CrossRef]
- Villalonga, A., Pérez-Calabuig, A.M. and Villalonga, R. (2020). Electrochemical biosensors based on nucleic acid aptamers. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 412(1), pp. 55–72. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y., Yavari, K. and Liu, J. (2022). Critical evaluation of aptamer binding for biosensor designs. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 146, p.116480. [CrossRef]
- Sanford, A.A., Rangel, A.E., Feagin, T.A., Lowery, R.G., Argueta-Gonzalez, H.S. and Heemstra, J.M. (2021). RE-SELEX: restriction enzyme-based evolution of structure-switching aptamer biosensors. Chemical Science, 12(35), pp.11692–11702. [CrossRef]
- Mok, W. and Li, Y. (2008). Recent progress in nucleic acid aptamer-based biosensors and bioassays. Sensors, 8(11), pp.7050–7084. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L., Yang, G., Zhang, X. and Qu, F. (2020). Development of aptamer screening against proteins and its applications. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 48(5), pp.560–572. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G., Zhao, L., Yuan, D., Li, J., et al. (2022). A genetically encoded fluorescent biosensor for monitoring ATP in living cells with heterobifunctional aptamers. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 198, p.113827. [CrossRef]
- F. Kleinjung, Klussmann, S., Erdmann, V.A., Scheller, F.W., Fürste, J.P. and Bier, F.F. (1998). High-affinity RNA as a recognition element in a biosensor. Analytical Chemistry, 70(2), pp.328–331. [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, E.S.E., Joshi, L., Billeter, M. and Eriksson, L.A. (2014). De novo tertiary structure prediction using RNA123—benchmarking and application to Macugen. Journal of Molecular Modeling, 20(8). [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T., Oshima, H., Tsukasa Mashima, Nagata, T., Masato Katahira and Kinoshita, M. (2014). Binding of an RNA aptamer and a partial peptide of a prion protein: crucial importance of water entropy in molecular recognition. Nucleic Acids Research, 42(11), pp.6861–6875. [CrossRef]
- Kwame Sefah, Phillips, J.A., Xiong, X., Meng, L., et al. (2009). Nucleic acid aptamers for biosensors and bio-analytical applications. Analyst, 134(9), pp.1765–1765. [CrossRef]
- Byun, J. (2021). Recent progress and opportunities for nucleic acid aptamers. Life, 11(3), p.193. [CrossRef]
- Michael J.M. Fischer, Schmidt, J.T., Stanislav Koulchitsky, Klussmann, S., Vater, A. and Meßlinger, K. (2018). Effect of a calcitonin gene-related peptide-binding L-RNA aptamer on neuronal activity in the rat spinal trigeminal nucleus. Journal of Headache and Pain, 19(1). [CrossRef]
- Ruckman, J., Green, L.S., Beeson, J., Waugh, S., et al. (1998). 2′-Fluoropyrimidine RNA-based aptamers to the 165-amino acid form of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF165). Inhibition of receptor binding and VEGF-induced vascular permeability through interactions requiring the exon 7-encoded domain. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273(32), pp.20556–20567. [CrossRef]
- Savla, R., Taratula, O., Garbuzenko, O. and Minko, T. (2011). Tumor targeted quantum dot-mucin 1 aptamer-doxorubicin conjugate for imaging and treatment of cancer. Journal of Controlled Release, 153(1), pp.16–22. [CrossRef]
- Mann, D., Reinemann, C., Stoltenburg, R. and Strehlitz, B. (2005). In vitro selection of DNA aptamers binding ethanolamine. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 338(4), pp.1928–1934. [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, J., Hirofumi Imanaka, Yokota, Y. and Sugimoto, N. (2000). In vitro selection of aptamers that act with Zn2+. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 82(1-4), pp.197–206. [CrossRef]
- Hamula, C., X. Chris Le and Li, X. (2011). DNA Aptamers Binding to Multiple Prevalent M-Types of Streptococcus pyogenes. Analytical Chemistry, 83(10), pp.3640–3647. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z., Parekh, P., Turner, P., Moyer, R.W. and Tan, W. (2009). Generating Aptamers for Recognition of Virus-Infected Cells. Clinical Chemistry, 55(4), pp.813–822. [CrossRef]
- Chen, F., Hu, Y., Li, D., Chen, H. and Zhang, X.-L. (2009). CS-SELEX Generates High-Affinity ssDNA Aptamers as Molecular Probes for Hepatitis C Virus Envelope Glycoprotein E2. PLoS ONE, 4(12), p.e8142. [CrossRef]
- Gold, L. (1995). Oligonucleotides as research, diagnostic, and therapeutic agents. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 270(23), pp. 13581–13584. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., Lai, B. and Juhas, M. (2019). Recent advances in aptamer discovery and applications. Molecules, 24(5), p.941. [CrossRef]
- Fraser, L.A., Cheung, Y.K., Kinghorn, A., Guo, W., et al. (2019). Microfluidic Technology for Nucleic Acid Aptamer Evolution and Application. 3(5), pp.1900012–1900012. [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, S.C.B. (2006). Methods developed for SELEX. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 387(1), pp.171–182. [CrossRef]
- Binkley, J., Allen, P., Brown, D.M., Green, L., Tuerk, C. and Gold, L. (1995). RNA ligands to human nerve growth factor. Nucleic Acids Research, 23(16), pp.3198–3205. [CrossRef]
- Marshall, K.A. and Ellington, A.D. (2000). In vitro selection of RNA aptamers. Methods in enzymology on CD-ROM/Methods in enzymology, pp.193–214. [CrossRef]
- Uphoff, K.W., Bell, S.D. and Ellington, A.D. (1996). In vitro selection of aptamers: the dearth of pure reason. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 6(3), pp.281–288. [CrossRef]
- Famulok, M. and Szostak, J.W. (1992). In Vitro Selection of Specific Ligand-binding Nucleic Acids. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English, 31(8), pp.979–988. [CrossRef]
- Mendonsa, S.D. and Bowser, M.T. (2004). In Vitro Evolution of Functional DNA Using Capillary Electrophoresis. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 126(1), pp.20–21. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C. et al. (2019). Evolution of multi-functional capillary electrophoresis for high-efficiency selection of Aptamers. Biotechnology Advances, 37(8), p. 107432. [CrossRef]
- Yu, X. and Yu, Y. (2014). A Mathematical Analysis of the Selective Enrichment of NECEEM-Based Non-SELEX. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 173(8), pp.2019–2027. [CrossRef]
- Tok, J., Lai, J., Leung, T. and Li, S.F.Y. (2010). Selection of aptamers for signal transduction proteins by capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis, 31(12), pp.2055–2062. [CrossRef]
- Yang, G., Zhu, C., Zhao, L., Li, L., Huang, Y., Zhang, Y. and Qu, F. (2020). Pressure controllable aptamers picking strategy by targets competition. Chinese Chemical Letters, 32(1), pp.218–220. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C. et al. (2024). Recent progress of Selex methods for screening nucleic acid aptamers. Talanta, 266, p. 124998. [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y., Tsai, Y., Wang, C., and Lee, G. (2025). Aptamer slection via versatile microfluidic platforms and their diverse applications. Lab Chip, 25, pp.1047–1080. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C., Feng, Z. Qin, H., Chen, L., Yan, M., Li, L., and Qu, F. (2024). Recent progress of SELEX methods for screening nucleic acid aptamers. Talanta, 266, pp.124998. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-Y., Hsieh, I-Shan., Tung, C.-H., et al. (2022). A novel DNA aptamer targeting lung cancer stem cells exerts a therapeutic effect by binding and neutralizing Annexin A2. Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids, 27, pp.956–968. [CrossRef]
- Sun, X., Xie, L., Qiu, S., Li, H., et al. (2022). Elucidation of CKAP4-remodeled cell mechanics in driving metastasis of bladder cancer through aptamer-based target discovery. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 119(16). [CrossRef]
- Ren, M., Zhou, J., Song, Z., Mei, H., Zhou, M., Fu, Z.F., Han, H. and Zhao, L. (2021). Aptamer and RVG functionalized gold nanorods for targeted photothermal therapy of neurotropic virus infection in the mouse brain. Chemical Engineering Journal, 411, pp.128557–128557. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H. et al. (2023) Development of an aptamer-based molecular tool for specifically targeting microglia via the CD64 protein. [CrossRef]
- Sun, S. et al. (2023). Selection and identification of a novel ssDNA aptamer targeting human skeletal muscle. Bioactive Materials, 20, pp. 166–178. [CrossRef]
- Pleiko, K., Saulite, L., Parfejevs, V., Miculis, K., Vjaters, E. and Riekstina, U. (2019). Differential binding cell-SELEX method to identify cell-specific aptamers using high-throughput sequencing. Scientific Reports, 9(1). [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.I. and Song, E. (2020). Lab-on-a-Chip Systems for Aptamer-Based Biosensing. Micromachines, 11(2), p.220. [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, C.K. (2001). Aptasensors – the future of biosensing? Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 372(1), pp.44–48. [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, L. and Mazloum-Ardakani, M. (2020). Advances in Aptasensor Technology. Advances in Clinical Chemistry, pp. 237–279. [CrossRef]
- Sassolas, A., Blum, Loïc J. and Leca-Bouvier, Béatrice D. (2009). Electrochemical Aptasensors. Electroanalysis, 21(11), pp.1237–1250. [CrossRef]
- Sequeira-Antunes, B. and Ferreira, H.A. (2023). Nucleic acid aptamer-based biosensors: A Review. Biomedicines, 11(12), p. 3201. [CrossRef]
- Radi, A.-E. (2011). Electrochemical Aptamer-Based Biosensors: Recent Advances and Perspectives. International Journal of Electrochemistry, 2011, pp.1–17. [CrossRef]
- Yao, W., Shi, J., Ling, J., Guo, Y., Ding, C. and Ding, Y. (2020). SiC-functionalized fluorescent aptasensor for determination of Proteus mirabilis. Microchimica Acta, 187(7). [CrossRef]
- Song, S., Wang, L., Li, J., Fan, C. and Zhao, J. (2008). Aptamer-based biosensors. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 27(2), pp.108–117. [CrossRef]
- Hong, P., Li, W. and Li, J. (2012). Applications of Aptasensors in Clinical Diagnostics. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland), 12(2), pp.1181–1193. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z., Wilkop, T., Xu, D., Dong, Y., Ma, G. and Cheng, Q. (2007). Surface plasmon resonance imaging for affinity analysis of aptamer–protein interactions with PDMS microfluidic chips. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 389(3), pp.819–825. [CrossRef]
- So, H.-M., Won, K., Yong Hwan Kim, Kim, B.-K., Beyong Hwan Ryu, Pil Sun Na, Kim, H. and Jun Young Lee (2005). Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Biosensors Using Aptamers as Molecular Recognition Elements. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 127(34), pp.11906–11907. [CrossRef]
- Polsky, R., Gill, R., Kaganovsky, L. and Willner, I. (2006). Nucleic Acid-Functionalized Pt Nanoparticles: Catalytic Labels for the Amplified Electrochemical Detection of Biomolecules. Analytical Chemistry, 78(7), pp.2268–2271. [CrossRef]
- Zayats, M., Huang, Y., Gill, R., Ma, C. and Willner, I. (2006). Label-Free and Reagentless Aptamer-Based Sensors for Small Molecules. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 128(42), pp.13666–13667. [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.A., Xu, Y., Xia, Z., Fan, Z.H. and Tan, W. (2008). Enrichment of Cancer Cells Using Aptamers Immobilized on a Microfluidic Channel. Analytical Chemistry, 81(3), pp.1033–1039. [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, S., Obubuafo, A., Soper, S.A. and Spivak, D.A. (2007). Surface immobilization methods for aptamer diagnostic applications. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 390(4), pp.1009–1021. [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, H. and Wrenger, C. (2009). Disease-specific biomarker discovery by aptamers. Cytometry Part A, 75A(9), pp.727–733. [CrossRef]
- Jayasena, S.D. (1999). Aptamers: An Emerging Class of Molecules That Rival Antibodies in Diagnostics. Clinical Chemistry, 45(9), pp.1628–1650. [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, N., Long, F., Gao, C., He, M., Shi, H.-C. and Gu, A.Z. (2012). Aptamer-Based Optical Biosensor For Rapid and Sensitive Detection of 17β-Estradiol In Water Samples. Environmental Science & Technology, 46(6), pp.3288–3294. [CrossRef]
- Dittmer, W.U., Reuter, A. and Simmel, F.C. (2004). A DNA-Based Machine That Can Cyclically Bind and Release Thrombin. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 43(27), pp.3550–3553. [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, V., Xiao, Y., Shlyahovsky, B. and Willner, I. (2004). Aptamer-Functionalized Au Nanoparticles for the Amplified Optical Detection of Thrombin. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 126(38), pp.11768–11769. [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.-A. and Leclerc, M. (2004). Optical Sensors Based on Hybrid Aptamer/Conjugated Polymer Complexes. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 126(5), pp.1384–1387. [CrossRef]
- Feng, C., Dai, S. and Wang, L. (2014). Optical aptasensors for quantitative detection of small biomolecules: A review. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 59, pp.64–74. [CrossRef]
- Zahra, Q. ul ain, Khan, Q.A. and Luo, Z. (2021). Advances in Optical Aptasensors for Early Detection and Diagnosis of Various Cancer Types. Frontiers in Oncology, 11. [CrossRef]
- Ng, S., Lim, H.S., Ma, Q. and Gao, Z. (2016). Optical Aptasensors for Adenosine Triphosphate. Theranostics, 6(10), pp.1683–1702. [CrossRef]
- Mao, S., Yu, K., Lu, G. and Chen, J. (2011). Highly sensitive protein sensor based on thermally-reduced graphene oxide field-effect transistor. Nano Research, 4(10), pp.921–930. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S., Khan, N.I., Tsavalas, J.G. and Song, E. (2018). Selective Detection of Lysozyme Biomarker Utilizing Large Area Chemical Vapor Deposition-Grown Graphene-Based Field-Effect Transistor. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 6. [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y., Maehashi, K. and Matsumoto, K. (2010). Label-Free Biosensors Based on Aptamer-Modified Graphene Field-Effect Transistors. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 132(51), pp.18012–18013. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J., Lee, J., Seo, S.E., Kim, K.H., et al. (2020). High-Performance Conducting Polymer Nanotube-based Liquid-Ion Gated Field-Effect Transistor Aptasensor for Dopamine Exocytosis. Scientific Reports, 10(1). [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Chen, D., Huang, W., Yang, N., Yuan, Q. and Yang, Y. (2023). Aptamer-functionalized field-effect transistor biosensors for disease diagnosis and environmental monitoring. Exploration, 3:20210027, pp1-19. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.TH., Nguyen, C.M., Huynh, M.A. et al. (2023) Field effect transistor based wearable biosensors for healthcare monitoring. J Nanobiotechnol 21, 411. [CrossRef]
- Vu, C.-A. and Chen, W.-Y. (2020). Predicting future prospects of aptamers in field-effect transistor biosensors. Molecules, 25(3), p.680. [CrossRef]
- Jae Do Kwon, Lee, Y.-J., Taek Seung Lee and Ahn, J.-H. (2020). Aptamer-based field-effect transistor for detection of Avian Influenza Virus in chicken serum. Analytical Chemistry, 92(7), pp.5524–5531. [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.-T. and Mulchandani, A. (2016). Carbon nanotubes and graphene nano field-effect transistor-based biosensors. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 79, pp.222–232. [CrossRef]
- Sung Gun Kim, Jun Seop Lee, Ji Hae Jun, Dong Hoon Shin and Jang, J. (2016). Ultrasensitive bisphenol A field-effect transistor sensor using an aptamer-modified multichannel carbon nanofiber transducer. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 8(10), pp.6602–6610. [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.S., Park, S.J., Hong, J.-Y., Han, A-Reum., Lee, J.S., Lee, J.S., Oh, J.H. and Jang, J. (2012). Flexible FET-type VEGF aptasensor based on nitrogen-doped graphene converted from conducting polymer. ACS Nano, 6(2), pp.1486–1493. [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, I., Sharma, N., Vasilescu, A., Iancu, M., et al. (2018). Electrochemical aptamer-based biosensors for the detection of cardiac biomarkers. ACS Omega, 3(9), pp.12010–12018. [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.I., Maddaus, A.G. and Song, E. (2018). A low-cost inkjet-printed aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for the selective detection of lysozyme. Biosensors, 8(1), p.7. [CrossRef]
- Crulhas, B.P., Karpik, A.E., Delella, F.K., Castro, G.R. and Pedrosa, V.A. (2017). Electrochemical aptamer-based biosensor developed to monitor PSA and VEGF released by prostate cancer cells. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 409(29), pp.6771–6780. [CrossRef]
- Rohrbach, F., Karadeniz, H., Erdem, A., Famulok, M. and Mayer, G. (2012). Label-free impedimetric aptasensor for lysozyme detection based on carbon nanotube-modified screen-printed electrodes. Analytical Biochemistry, 421(2), pp.454–459. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A., Ge, B. and Yu, H.-Z. (2007). Aptamer-based biosensors for label-free voltammetric detection of lysozyme. 79(14), pp.5158–5164. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-D., Chen, Z.-B., Zhao, H.-T., Guo, L. and Mu, X. (2010). An aptamer-based biosensor for the detection of lysozyme with gold nanoparticles amplification. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 149(1), pp.110–115. [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y., He, F., Mi, X., Tong, F. and Shi, X. (2014). Lysozyme aptamer biosensor based on electron transfer from SWCNTs to SPQC-IDE. Sensors and Actuators B Chemical, 199, pp.377–383. [CrossRef]
- Liang, G. et al. (2016). Aptamer-based biosensor for label-free detection of ethanolamine by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Analytica Chimica Acta, 936, pp. 222–228. [CrossRef]
- Ikebukuro, K., Kiyohara, C. and Sode, K. (2004). Electrochemical detection of protein using a double aptamer sandwich. Analytical Letters, 37(14), pp.2901–2909. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.C., Kawde, A.-N. and Wang, J. (2005). Aptamer biosensor for label-free impedance spectroscopy detection of proteins based on recognition-induced switching of the surface charge. Chemical Communications, (34), p.4267. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z., Yang, W., Wang, J., Yang, C., Yang, F. and Yang, X. (2009). A sensitive impedimetric thrombin aptasensor based on polyamidoamine dendrimer. Talanta, 78(4-5), pp.1240–1245. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y., Li, B., Wang, X. and Duan, Y. (2014). Magnified fluorescence detection of silver(I) ion in aqueous solutions by using nano-graphite-DNA hybrid and DNase I. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 58, pp.276–281. [CrossRef]
- Ji, G. et al. (2022). Optical biosensor based on graphene and its derivatives for detecting biomolecules. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(18), p. 10838. [CrossRef]
- Lafleur, J.P., Jönsson, A., Senkbeil, S. and Kutter, J.P. (2016). Recent advances in lab-on-a-chip for biosensing applications. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 76, pp.213–233. [CrossRef]
- Kong, R.-M., Zhang, X., Ding, L., Yang, D. and Qu, F. (2017). Label-free fluorescence turn-on aptasensor for prostate-specific antigen sensing based on aggregation-induced emission–silica nanospheres. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 409(24), pp.5757–5765. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. and Guo, X. (2022). Emerging strategies in fluorescent aptasensor toward food hazard aflatoxins detection. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 129, pp.621–633. [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, H. (2011). Förster resonance energy transfer – A spectroscopic nanoruler: Principle and applications. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology C: Photochemistry Reviews, 12(1), pp.20–30. [CrossRef]
- Szöllosi, J., Damjanovich, S. and Mátyus, L. (1998). Application of fluorescence resonance energy transfer in the clinical laboratory: Routine and Research. Cytometry, 34(4), pp. 159–179. [CrossRef]
- Kocjan, B.J., Seme, K. and Poljak, M. (2008). Detection and differentiation of human papillomavirus genotypes HPV-6 and HPV-11 by FRET-based real-time PCR. Journal of Virological Methods, 153(2), pp.245–249. [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-H., Li, J., Qi, X.-J., Song, X.-R., Yang, H.-H., Chen, X. and Chen, G.-N. (2011). Multiplex detection of nucleases by a graphene-based platform. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 21(29), p.10915. [CrossRef]
- Park, Y., Dang, T.V., Jeong, U., Kim, M.I. and Kim, J. (2022). Comparison of Optical and Electrical Sensor Characteristics for Efficient Analysis of Attachment and Detachment of Aptamer. Biosensors, 12(11), p.979. [CrossRef]
- He, S., Song, B., Li, D., Zhu, C., Qi, W., Wen, Y., Wang, L., Song, S., Fang, H. and Fan, C. (2010). A Graphene Nanoprobe for Rapid, Sensitive, and Multicolor Fluorescent DNA Analysis. Advanced Functional Materials, 20(3), pp.453–459. [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.S., De, M., Luo, J., Rotello, V.M., Huang, J. and Dravid, V.P. (2012). Nanoscale graphene oxide (nGO) as artificial receptors: implications for biomolecular interactions and sensing. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 134(40), pp.16725–16733. [CrossRef]
- Xi, G., Chen, T. and Wang, X. (2016). A reduced graphene oxide-based fluorescence resonance energy transfer sensor for highly sensitive detection of matrix metalloproteinase 2. International Journal of Nanomedicine, p.1537. [CrossRef]
- Shaban, S.M. and Kim, D.-H. (2021). Recent advances in aptamer sensors. Sensors, 21(3), p.979. [CrossRef]
- Marín, M.J., Schofield, C.L., Field, R.A. and Russell, D.A. (2014). Glyconanoparticles for colorimetric bioassays. The Analyst, 140(1), pp.59–70. [CrossRef]
- Omid Heydari Shayesteh and Ghavami, R. (2019). A novel label-free colorimetric aptasensor for sensitive determination of PSA biomarker using gold nanoparticles and a cationic polymer in human serum. Spectrochimica Acta Part A Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 226, pp.117644–117644. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y., Liu, X., Li, J., Qiang, W., Sun, L., Li, H. and Xu, D. (2015). Microfluidic chip-based silver nanoparticles aptasensor for colorimetric detection of thrombin. Talanta, 150, pp.81–87. [CrossRef]
- Cate, D.M., Adkins, J.A., Mettakoonpitak, J. and Henry, C.S. (2014). Recent developments in paper-based microfluidic devices. Analytical Chemistry, 87(1), pp.19–41. [CrossRef]
- Doeven, E.H., Barbante, G.J., Kerr, E., Hogan, C.F., Endler, J.A. and Francis, P.S. (2014). Red–Green–Blue electrogenerated chemiluminescence utilizing a digital camera as detector. Analytical Chemistry, 86(5), pp.2727–2732. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W., Liang, W., Li, X., Chai, Y., Yuan, R. and Xiang, Y. (2015). MicroRNA-triggered, cascaded and catalytic self-assembly of functional ‘DNAzyme ferris wheel’ nanostructures for highly sensitive colorimetric detection of cancer cells. Nanoscale, 7(19), pp.9055–9061. [CrossRef]
- Lou, B., Zhou, Z., Du, Y. and Dong, S. (2015). Resistance-based logic aptamer sensor for CCRF-CEM and Ramos cells integrated on microfluidic chip. Electrochemistry Communications, 59, pp.64–67. [CrossRef]
- Yue, F., Li, F., Kong, Q., Guo, Y. and Sun, X. (2021). Recent advances in aptamer-based sensors for aminoglycoside antibiotics detection and their applications. Science of The Total Environment, 762, p.143129. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N., Liu, B., Cui, X., Li, Y., Tang, J., Wang, H., Zhang, D. and Li, Z. (2020). Recent advances in aptasensors for mycotoxin detection: On the surface and in the colloid. Talanta, 223, pp.121729–121729. [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, F., Abbaszadeh, H., Dolatabadi, J.E.N., Aghebati-Maleki, L. and Yousefi, M. (2019). Application of various optical and electrochemical aptasensors for detection of human prostate specific antigen: A review. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 142, p.111484. [CrossRef]
- Wei, X., Yin, M., Zhang, L., Lin, H., Wang, J., Xie, W. and Xu, D. (2022). Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) biosensor for detection of mycotoxins: A review. Journal of Immunological Methods, 510, pp.113349–113349. [CrossRef]
- Myers, F.B. and Lee, L.P. (2008). Innovations in optical microfluidic technologies for point-of-care diagnostics. Lab on a Chip, 8(12), p.2015. [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.A. (2002). Optical biosensors in drug discovery. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 1(7), pp.515–528. [CrossRef]
- Canoa, P., Simón-Vázquez, R., Popplewell, J. and África González-Fernández (2015). A quantitative binding study of fibrinogen and human serum albumin to metal oxide nanoparticles by surface plasmon resonance. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 74, pp.376–383. [CrossRef]
- Omar, N., Fen, Y., Saleviter, S., Daniyal, W., Anas, N., Ramdzan, N. and Roshidi, M. (2019). Development of a graphene-based surface plasmon resonance optical sensor chip for potential biomedical application. Materials, 12(12), p.1928. [CrossRef]
- Green, R.J., Frazier, R.A., Shakesheff, K.M., Davies, M.C., Roberts, C.J. and Tendler, S.J.B. (2000). Surface plasmon resonance analysis of dynamic biological interactions with biomaterials. Biomaterials, 21(18), pp.1823–1835. [CrossRef]
- HomolaJ., Yee, S.S. and Gauglitz, G. (1999). Surface plasmon resonance sensors: review. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 54(1-2), pp.3–15. [CrossRef]
- Kazuki Inamori, Masahiro Kyo, Yoshiaki Nishiya, Inoue, Y., Sonoda, T., Kinoshita, E., Koike, T. and Katayama, Y. (2005). Detection and quantification of on-chip phosphorylated peptides by surface plasmon resonance imaging techniques using a phosphate capture molecule. Analytical Chemistry, 77(13), pp.3979–3985. [CrossRef]
- Spadavecchia, J., Manera, M.G., Quaranta, F., Siciliano, P. and Rella, R. (2005). Surface plamon resonance imaging of DNA based biosensors for potential applications in food analysis. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 21(6), pp.894–900. [CrossRef]
- Naoki Kanoh, Masahiro Kyo, Kazuki Inamori, Ando, A., Asami, A., and Aiko Nakao and Osada, H. (2006). SPR Imaging of photo-cross-linked small-molecule arrays on gold. Analytical Chemistry, 78(7), pp.2226–2230. [CrossRef]
- Myers, F.B. and Lee, L.P. (2008). Innovations in optical microfluidic technologies for point-of-care diagnostics. Lab on a Chip, 8(12), p.2015. [CrossRef]
- Lu, G., Ocola, L.E. and Chen, J. (2009). Reduced graphene oxide for room-temperature gas sensors. Nanotechnology, 20(44), p.445502. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-W., Wu, C.-S., Chuang, C.-K., Pang, S.-T., Pan, T.-M., Yang, Y.-S. and Ko, F.-H. (2013). Real-time and label-free detection of the prostate-specific antigen in human serum by a polycrystalline silicon nanowire field-effect transistor biosensor. Analytical chemistry, 85(16), pp.7912–8. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G., Chang, J., Cui, S., Pu, H., Wen, Z. and Chen, J. (2014). Real-time, selective detection of Pb2+ in water using a reduced graphene oxide/gold nanoparticle field-effect transistor device. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 6(21), pp.19235–19241. [CrossRef]
- Mao, S. and Chen, J. (2017). Graphene-based electronic biosensors. Journal of Materials Research, 32(15), pp.2954–2965. [CrossRef]
- Mao, S., Chang, J., Pu, H., Lu, G., He, Q., Zhang, H. and Chen, J. (2017). Two-dimensional nanomaterial-based field-effect transistors for chemical and biological sensing. Chemical Society Reviews, 46(22), pp.6872–6904. [CrossRef]
- Wadhera, T., Kakkar, D., Wadhwa, G. and Raj, B. (2019). Recent advances and progress in development of the field effect transistor biosensor: A review. Journal of Electronic Materials, 48(12), pp.7635–7646. [CrossRef]
- Sedki, M., Chen, Y. and Mulchandani, A. (2020). Non-carbon 2D materials-based field-effect transistor biosensors: Recent advances, challenges, and future perspectives. Sensors, 20(17), p.4811. [CrossRef]
- Vu and Chen (2019). Field-effect transistor biosensors for biomedical applications: Recent advances and future prospects. Sensors, 19(19), p.4214. [CrossRef]
- Nehra, A. and Krishna Nand Singh (2015). Current trends in nanomaterial embedded field effect transistor-based biosensor. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 74, pp.731–743. [CrossRef]
- Poghossian, A., Yoshinobu, T., Simonis, A., Ecken, H., Lüth, H. and Schöning, M.J. (2001). Penicillin detection by means of field-effect based sensors: EnFET, capacitive EIS sensor or LAPS? Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 78(1-3), pp.237–242. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y., Feng, T., Li, Y., Ao, X., Liang, S., Yang, X., Wang, L., Xu, X. and Zhang, W. (2024). Recent advances in enhancing the sensitivity of biosensors based on field effect transistors. Advanced Electronic Materials. [CrossRef]
- Feng, X., Li, P., Xiao, M., Li, T., Chen, B., Wang, X. and Wang, L. (2023). Recent advances in the detection of pathogenic microorganisms and toxins based on field-effect transistor biosensors. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 64(25), pp.9161–9190. [CrossRef]
- Syedmoradi, L., Ahmadi, A., Norton, M.L. and Omidfar, K. (2019). A review on nanomaterial-based field effect transistor technology for biomarker detection. Mikrochimica Acta, 186(11), p.739. [CrossRef]
- Luo, X. and Davis, J.J. (2013). Electrical biosensors and the label free detection of protein disease biomarkers. Chemical Society Reviews, 42(13), p.5944. [CrossRef]
- Klinghammer, S., Voitsekhivska, T., Licciardello, N., Kim, K., Baek, C.-K., Cho, H., Wolter, K.-J., Kirschbaum, C., Baraban, L. and Cuniberti, G. (2020). Nanosensor-based real-time monitoring of stress biomarkers in human saliva using a portable measurement system. ACS Sensors, 5(12), pp.4081–4091. [CrossRef]
- Estrela, P., Paul, D., Song, Q., Stadler, L.K.J., Wang, L., Huq, E., Davis, J.J., Ferrigno, P.K. and Migliorato, P. (2010). Label-free sub-picomolar protein detection with field-effect transistors. Analytical Chemistry, 82(9), pp.3531–3536. [CrossRef]
- Costa, L., Brissos, V., Lemos, F., Ribeiro, F.R. and Cabral, J.M.S. (2008). Comparing the effect of immobilization methods on the activity of lipase biocatalysts in ester hydrolysis. Bioprocess and biosystems engineering, 31(4), pp.323–7. [CrossRef]
- Sadighbayan, D., Hasanzadeh, M. and Ghafar-Zadeh, E. (2020). Biosensing based on field-effect transistors (FET): Recent progress and challenges. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 133, p.116067. [CrossRef]
- Asai, K., Yamamoto, T., Nagashima, S., Ogata, G., Hibino, H. and Einaga, Y. (2020). An electrochemical aptamer-based sensor prepared by utilizing the strong interaction between a DNA aptamer and diamond. The Analyst, 145(2), pp.544–549. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z., Xie, M., Zhao, F. and Han, S. (2022). Application of nanomaterial modified aptamer-based electrochemical sensor in detection of heavy metal ions. Foods, 11(10), p.1404. [CrossRef]
- Willner, I. and Zayats, M. (2007). Electronic aptamer-based sensors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 46(34), pp.6408–6418. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-O., So, H.-M., Jeon, E.-K., Chang, H., Won, K. and Kim, Y.H. (2007). Aptamers as molecular recognition elements for electrical nanobiosensors. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 390(4), pp.1023–1032. [CrossRef]
- Bott, A.W. (2001). Electrochemical techniques for the characterization of redox polymers. Current Separation, 19, (3), pp. 71-75.
- Katz, E. and Willner, I. (2003). Probing biomolecular interactions at conductive and semiconductive surfaces by impedance spectroscopy: routes to impedimetric immunosensors, DNA-sensors, and enzyme biosensors. Electroanalysis, 15(11), pp.913–947. [CrossRef]
- Farzin, L., Shamsipur, M., Samandari, L. and Sheibani, S. (2018). Recent advances in designing nanomaterial based biointerfaces for electrochemical biosensing cardiovascular biomarkers. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 161, pp.344–376. [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.-G., Miao, Y.-Q. and Zhang, Q.-J. (2004). Impedimetric biosensors. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 97(4), pp.219–226. [CrossRef]
- Lisdat, F. and Schäfer, D. (2008). The use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for biosensing. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 391(5), pp.1555–1567. [CrossRef]
- Leva-Bueno, J., Peyman, S.A. and Millner, P.A. (2020). A review on impedimetric immunosensors for pathogen and biomarker detection. Medical Microbiology and Immunology, 209(3), pp.343–362. [CrossRef]
- Magar, H.S., Hassan, R.Y.A. and Mulchandani, A. (2021). Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS): principles, construction, and biosensing applications. Sensors, 21(19), p.6578. [CrossRef]
- Prodromidis, M.I. (2010). Impedimetric immunosensors - A review. Electrochimica Acta, 55(14), pp.4227–4233. [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, C., Economou, A. and Prodromidis, M.I. (2016). Electrochemical immunosensors: Critical survey of different architectures and transduction strategies. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 79, pp.88–105. [CrossRef]
- Randviir, E.P. and Banks, C.E. (2022). A review of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for bioanalytical sensors. Analytical Methods, 14(45), pp.4602–4624. [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, T.E. (1988). Voltammetric and amperometric transducers. Chemical Sensors, pp. 193–213. [CrossRef]
- Chen, A. and Shah, B. (2013). Electrochemical sensing and biosensing based on square wave voltammetry. Analytical Methods, 5(9), p.2158. [CrossRef]
- Waree Boonmee, Kritsada Samoson, Janjira Yodrak, et al. (2021). Adsorptive cathodic stripping voltammetry for quantification of Alprazolam. Molecules, 26(10), pp.2958–2958. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y., Liang, X., Niyungeko, C., Zhou, J., Xu, J. and Tian, G. (2018). A review of the identification and detection of heavy metal ions in the environment by voltammetry. Talanta, 178, pp.324–338. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H. and Shorie, M. (2019). Nanomaterial based aptasensors for clinical and environmental diagnostic applications. Nanoscale Advances, 1(6), pp.2123–2138. [CrossRef]
- Singh, A., Sharma, A., Ahmed, A., Sundramoorthy, A.K., Furukawa, H., Arya, S. and Khosla, A. (2021). Recent Advances in Electrochemical Biosensors: Applications, Challenges, and Future Scope. Biosensors, 11(9), p.336. [CrossRef]
- Ronkainen, N.J., Halsall, H.B. and Heineman, W.R. (2010). Electrochemical biosensors. Chemical Society Reviews, 39(5), p.1747. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J., Xu, Y., Liu, S., Yu, S., Yu, Z.-R. and Sze Shin Low (2022). Application and progress of chemometrics in voltammetric biosensing. Biosensors, 12(7), pp.494–494. [CrossRef]
- Kissinger, P.T. and Heineman, W.R., 1983. Cyclic voltammetry. Journal of chemical education, 60(9), p.702.
- Grieshaber, D., MacKenzie, R., Vörös, J. and Reimhult, E. (2008). Electrochemical biosensors - sensor principles and architectures. Sensors, 8(3), pp.1400–1458. [CrossRef]
- Soni, D.K., Ahmad, R. and Dubey, S.K. (2018). Biosensor for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes: emerging trends. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 44(5), pp.590–608. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q., Pan, Y., Li, W. and Yang, Z. (2023). Amperometric sensors. Elsevier eBooks, pp.123–145. [CrossRef]
- Baracu, A. and Livia Alexandra Gugoaşă (2021). Review - Recent advances in microfabrication, design and applications of amperometric sensors and biosensors. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 168(3), pp.037503–037503. [CrossRef]
- Ricci, F., Vallée-Bélisle, A., Simon, A., Alessandro Porchetta and Plaxco, K.W. (2016). Using Nature’s ‘Tricks’ to rationally tune the binding properties of biomolecular receptors. Accounts of Chemical Research, 49(9), pp.1884–1892. [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H., Savory, N., Abe, K. and Ikebukuro, K. (2016). Methods for improving aptamer binding affinity. Molecules, 21(4), p.421. [CrossRef]
- Pan, J., Xu, W., Li, W., Chen, S., Dai, Y., Yu, S., Zhou, Q. and Xia, F. (2023). Electrochemical aptamer-based sensors with tunable detection range. Analytical chemistry (Washington), 95(1), pp.420–432. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X., Xie, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, C. and Xu, W. (2020). Programmable 3D rigid clathrate hydrogels based on self-assembly of tetrahedral DNA and linker PCR products. Chemical Communications, 56(86), pp.13181–13184. [CrossRef]
- Qu, L., Xu, J., Tan, X., Liu, Z., Xu, L. and Peng, R. (2014). Dual-aptamer modification generates a unique interface for highly sensitive and specific electrochemical detection of tumor cells. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 6(10), pp.7309–7315. [CrossRef]
- Jolly, P., Formisano, N., Tkáč, J., Kasák, P., Frost, C.G. and Estrela, P. (2015). Label-free impedimetric aptasensor with antifouling surface chemistry: A prostate specific antigen case study. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 209, pp.306–312. [CrossRef]
- Duan, N., Ding, X., He, L., Wu, S., Wei, Y. and Wang, Z. (2013). Selection, identification and application of a DNA aptamer against Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control, 33(1), pp.239–243. [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-T. and DeStefano, J.J. (2012). DNA aptamers to human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase selected by a primer-free SELEX method: characterization and comparison with other aptamers. Nucleic Acid Therapeutics, 22(3), pp.162–176. [CrossRef]
- Chamorro-Garcia, A., Parolo, C., Ortega, G., Idili, A., Green, J., Ricci, F. and Plaxco, K.W. (2022). The sequestration mechanism as a generalizable approach to improve the sensitivity of biosensors and bioassays. Chemical Science, 13(41), pp.12219–12228. [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y., Hu, J. and Lu, F. (2020). Aptamers used for biosensors and targeted therapy. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 132, p.110902. [CrossRef]
- Clark, V., Waters, K., Orsburn, B., Bumpus, N.N., Kundu, N., Sczepanski, J.T., Ray, P. and Arroyo-Currás, N. (2022). Human Cyclophilin B Nuclease activity revealed via nucleic acid-based electrochemical sensors. Angewandte Chemie, 134(45). [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H., Jo, H. and Oh, S.S. (2020). Detection and beyond: challenges and advances in aptamer-based biosensors. Materials Advances, 1(8), pp.2663–2687. [CrossRef]
- Jarczewska, M. and Malinowska, E. (2020). The application of antibody–aptamer hybrid biosensors in clinical diagnostics and environmental analysis. Analytical Methods, 12(25), pp.3183–3199. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R., Pinho, E., Sousa, A.L., DeStefano, J.J., Azevedo, N.F. and Almeida, C. (2022). Improving aptamer performance with nucleic acid mimics: de novo and post-SELEX approaches. Trends in Biotechnology, 40(5), pp.549–563. [CrossRef]
- Yu, H., Zhu, J., Shen, G., Deng, Y., Geng, X. and Wang, L. (2023). Improving aptamer performance: key factors and strategies. Mikrochimica Acta, 190(7). [CrossRef]
- Wang, T., Chen, C., Larcher, L.M., Barrero, R.A. and Veedu, R.N. (2019). Three decades of nucleic acid aptamer technologies: Lessons learned, progress and opportunities on aptamer development. Biotechnology Advances, 37(1), pp.28–50. [CrossRef]
- Fallah, A., Havaei, S.A., Sedighian, H., Kachuei, R. and Fooladi, A.A.I. (2024). Prediction of aptamer affinity using an artificial intelligence approach. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 12(36), pp.8825–8842. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J., Cho, J., Lee, B.-H., Hwang, D. and Park, J.-W. (2023). Design and prediction of aptamers assisted by In Silico methods. Biomedicines, 11(2), p.356. [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T., Chumphukam, O. and Cass, A.E.G. (2014). Determination of minimal sequence for binding of an aptamer. A comparison of truncation and hybridization inhibition methods. RSC Adv., 4(88), pp.47227–47233. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.-D., Osborne, M.T., Prevot, G.T., Churcher, Z.R., Johnson, P.E., Simine, L. and Philippe Dauphin-Ducharme (2024). Truncations and in silico docking to enhance the analytical response of aptamer-based biosensors. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 265, pp.116680–116680. [CrossRef]
- Radom, F., Jurek, P.M., Mazurek, M.P., Otlewski, J. and Jeleń, F. (2013). Aptamers: molecules of great potential. Biotechnology Advances, 31(8), pp.1260–1274. [CrossRef]
- Bing, T., Yang, X., Mei, H., Cao, Z. and Shangguan, D. (2010). Conservative secondary structure motif of streptavidin-binding aptamers generated by different laboratories. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 18(5), pp.1798–1805. [CrossRef]
- Akitomi, J., Kato, S., Yoshida, Y., Horii, K., Furuichi, M. and Waga, I. (2011). ValFold: Program for the aptamer truncation process. Bioinformation, 7(1), pp.38–40. [CrossRef]
- Zuker, M. (2003). Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Research, 31(13), pp. 3406–3415. [CrossRef]
- Kilgour, M., Liu, T., Walker, B.D., Ren, P. and Simine, L. (2021). E2EDNA: simulation protocol for DNA aptamers with ligands. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 61(9), pp.4139–4144. [CrossRef]
- Reuter, J.S. and Mathews, D.H. (2010). RNAstructure: software for RNA secondary structure prediction and analysis. BMC Bioinformatics, 11(1). [CrossRef]
- Dihua Shangguan, Tang, Z., Prabodika Mallikaratchy, Xiao, Z. and Tan, W. (2007). Optimization and Modifications of Aptamers Selected from Live Cancer Cell Lines. ChemBioChem, 8(6), pp.603–606. [CrossRef]
- He, X., Guo, L., He, J., Xu, H. and Xie, J. (2017). Stepping library-based Post-SELEX strategy approaching to the minimized aptamer in SPR. Analytical Chemistry, 89(12), pp.6559–6566. [CrossRef]
- Ma, P., Ye, H., Guo, H., Ma, X., Yue, L. and Wang, Z. (2022). Aptamer truncation strategy assisted by molecular docking and sensitive detection of T-2 toxin using SYBR Green I as a signal amplifier. Food Chemistry, 381, p.132171. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C., Feng, Z., Qin, H., Chen, L., Yan, M., Li, L. and Qu, F. (2023). Recent progress of SELEX methods for screening nucleic acid aptamers. Talanta, pp.124998–124998. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X., Hu, B., Gao, S.X., Liu, D.J., Sun, M.J., Jiao, B.H. and Wang, L.H. (2015). A saxitoxin-binding aptamer with higher affinity and inhibitory activity optimized by rational site-directed mutagenesis and truncation. Toxicon, 101, pp.41–47. [CrossRef]
- Kimoto, M., Nakamura, M. and Hirao, I. (2016). Post-ExSELEX stabilization of an unnatural-base DNA aptamer targeting VEGF165 toward pharmaceutical applications. Nucleic Acids Research [Preprint]. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L., Qi, X., Yan, X., Huang, Y., Liang, X., Zhang, L., Wang, S. and Tan, W. (2019). Engineering aptamer with enhanced affinity by triple helix-based terminal fixation. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 141(44), pp.17493–17497. [CrossRef]
- Gao, S., Zheng, X., Jiao, B. and Wang, L. (2016). Post-SELEX optimization of aptamers. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 408(17), pp.4567–4573. [CrossRef]
- Prabodhika Mallikaratchy, Ruggiero, A., Gardner, J.R., Vitaly Kuryavyi, Maguire, W.F., Heaney, M.L., McDevitt, M.R., Patel, D.J. and Scheinberg, D.A. (2010). A multivalent DNA aptamer specific for the B-cell receptor on human lymphoma and leukemia. Nucleic Acids Research, 39(6), pp.2458–2469. [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W., Chen, T., Tan, W. and Fan, Z.H. (2013). Multivalent DNA Nanospheres for Enhanced Capture of Cancer Cells in Microfluidic Devices. ACS Nano, 7(8), pp.7067–7076. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-M., Cao, Z. and Tan, W. (2008). Molecular assembly for high-performance bivalent nucleic acid inhibitor. 105(15), pp.5664–5669. [CrossRef]
- Kwon, P.S., Ren, S., Kwon, S.-J., Kizer, M.E., Kuo, L., Xie, M., Zhu, D., Zhou, F., Zhang, F., Kim, D., Fraser, K., Kramer, L.D., Seeman, N.C., Dordick, J.S., Linhardt, R.J., Chao, J. and Wang, X. (2019). Designer DNA architecture offers precise and multivalent spatial pattern-recognition for viral sensing and inhibition. Nature Chemistry, 12(1), pp.26–35. [CrossRef]
- Qin, W., Chen, L., Wang, Z., Li, Q., Fan, C., Wu, M. and Zhang, Y. (2020). Bioinspired DNA nanointerface with anisotropic aptamers for accurate capture of circulating tumor cells. Advanced Science, 7(19). [CrossRef]
- Dou, B., Xu, L., Jiang, B., Yuan, R. and Xiang, Y. (2019). Aptamer-functionalized and gold nanoparticle array-decorated magnetic graphene nanosheets enable multiplexed and sensitive electrochemical detection of rare circulating tumor cells in whole blood. Analytical Chemistry, 91(16), pp.10792–10799. [CrossRef]
- Qi, L., Liu, S., Jiang, Y., Lin, J.-M., Yu, L. and Hu, Q. (2020). Simultaneous detection of multiple tumor markers in blood by functional liquid crystal sensors assisted with target-induced dissociation of aptamer. Analytical Chemistry, 92(5), pp.3867–3873. [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z., Gao, Q., Cheung, M.C., Leung, H.M., Chi, T., Sleiman, H.F., Wai, K. and Lo, P.K. (2016). A highly versatile platform based on geometrically well-defined 3D DNA nanostructures for selective recognition and positioning of multiplex targets. Nanoscale, 8(43), pp.18291–18295. [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y., Zhang, C., Wang, Y. and Chen, G. (2022). Research progress of whole-cell-SELEX selection and the application of cell-targeting aptamer. Molecular Biology Reports, 49(8), pp.7979–7993. [CrossRef]
- Ma, P., Duan, N., Ye, H., Xia, Y., Ding, Z. and Wang, Z. (2022). Selection, truncation and fluorescence polarization based aptasensor for Weissella viridescens detection. Talanta, 246, p.123499. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S., Chung, J., Song, M.Y., Jurng, J. and Kim, B.C. (2014). Aptamer cocktails: enhancement of sensing signals compared to single use of aptamers for detection of bacteria. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 54, pp.195–198. [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.Y., Lau, H.L. and Kwok, C.K. (2022). Capture-SELEX: Selection strategy, aptamer identification, and biosensing application. Biosensors, 12(12), pp.1142–1142. [CrossRef]
- Villalonga, A., Mayol, B., Villalonga, R. and Vilela, D. (2022). Electrochemical aptasensors for clinical diagnosis. A review of the last five years. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 369, pp.132318–132318. [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A., Verma, D., Mohd-Akmal Hamizan, Mukherjee, M.D., Noor Faizah Mohd-Naim and Ahmed, M.U. (2025). Trends in aptasensing and the enhancement of diagnostic efficiency and accuracy. ACS Synthetic Biology, 14(1), pp.21–40. [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.S., Wang, F., Ge, Y. and Lo, P.K. (2020). Recent developments in aptasensors for diagnostic applications. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 13(8), pp.9329–9358. [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, N. and Rabiee, M. (2024). Wearable aptasensors. Analytical Chemistry, 96, pp19160-19182. [CrossRef]
- Naresh, Varnakavi. and Lee, N. (2021). A Review on biosensors and recent development of nanostructured materials-enabled biosensors. Sensors, 21(4), p.1109. [CrossRef]
- Lino, C., Barrias, S., Chaves, R., Adega, F., Martins-Lopes, P. and Fernandes, J.R. (2022). Biosensors as diagnostic tools in clinical applications. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer, 1877(3), p.188726. [CrossRef]
- Zahra Khoshbin, Mohammad Reza Housaindokht, Izadyar, M., Mohammad Reza Bozorgmehr and Asma Verdian (2021). Recent advances in computational methods for biosensor design. 118(2), pp.555–578. [CrossRef]
- Douaki, A., Garoli, D., Inam, A.K.M.S., Angeli, M.A.C., Cantarella, G., Rocchia, W., Wang, J., Petti, L. and Lugli, P. (2022). Smart approach for the design of highly selective aptamer-based biosensors. Biosensors, 12(8), p.574. [CrossRef]
- Darmostuk, M., Rimpelova, S., Gbelcova, H. and Ruml, T. (2015). Current approaches in SELEX: An update to aptamer selection technology. Biotechnology Advances, 33(6), pp.1141–1161. [CrossRef]
- Nor Azlina Ahmad, Razauden Mohamed Zulkifli, Hussin, H. and Muhammad Helmi Nadri (2021). In silico approach for Post-SELEX DNA aptamers: A mini-review. Journal of Molecular Graphics & Modelling, 105, pp.107872–107872. [CrossRef]
- Emami, N., Pakchin, P.S. and Ferdousi, R. (2020). Computational predictive approaches for interaction and structure of aptamers. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 497, p.110268. [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, R., Leuzzi, M. and Alfinito, E. (2018). Modelling and development of electrical aptasensors: A short review. Chemosensors, 6(2), pp.20–20. [CrossRef]
- Wei, X., Ma, P., Mahmood, K.I., Zhang, Y. and Wang, Z. (2022). A review: Construction of aptamer screening methods based on improving the screening rate of key steps. Talanta, 253, pp.124003–124003. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




