Submitted:
28 July 2025
Posted:
30 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
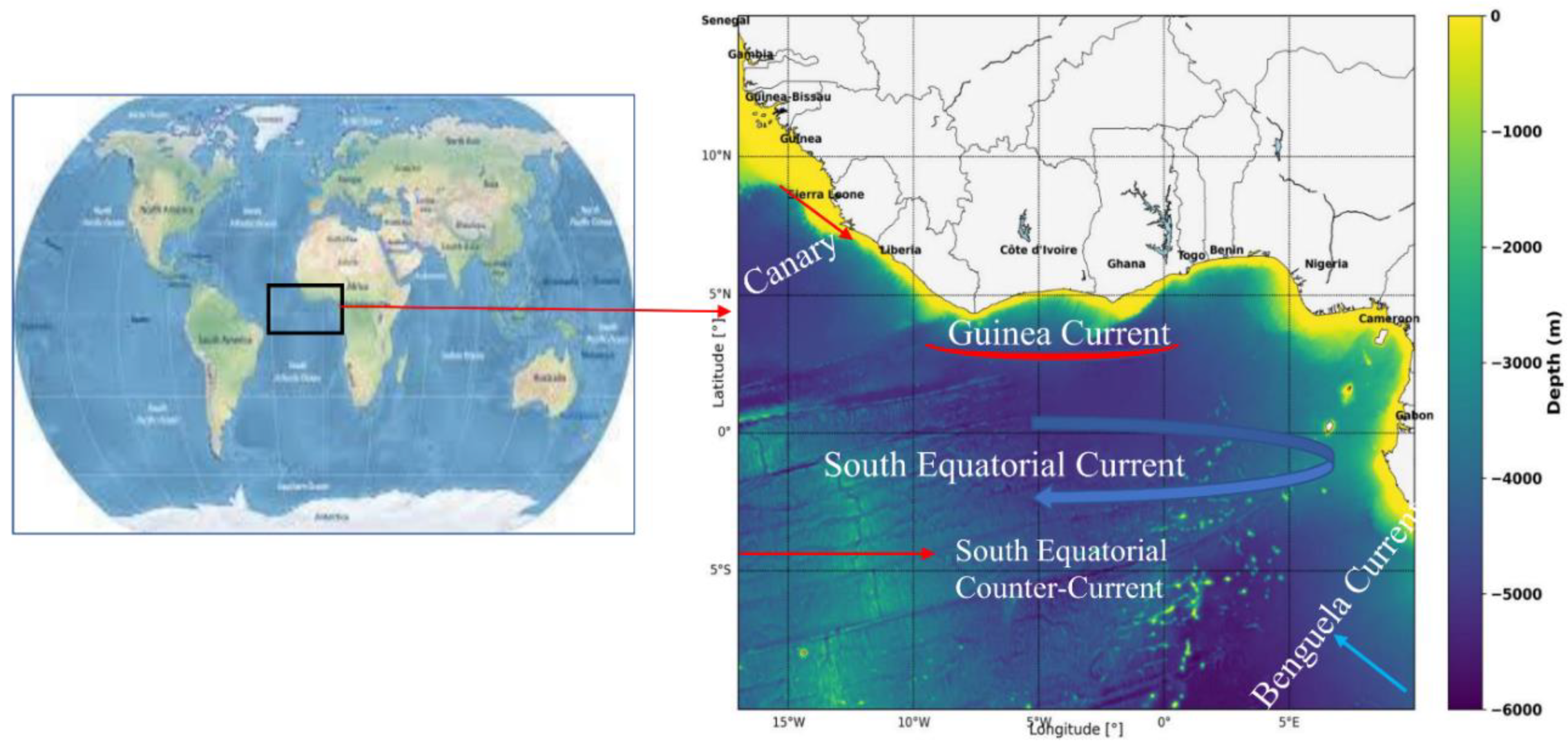
1 Introduction
2 Data and Methods
2.1 Decomposition of Sea Level Signal
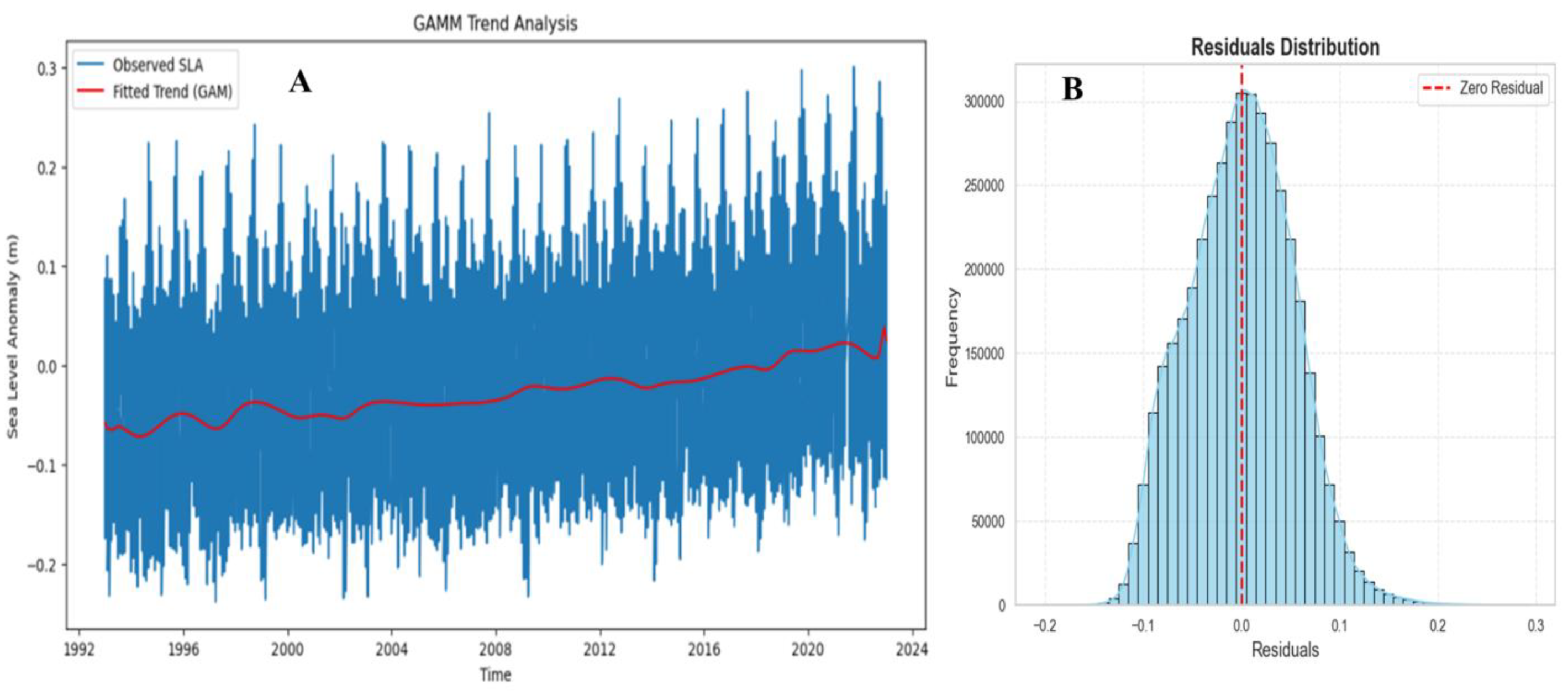
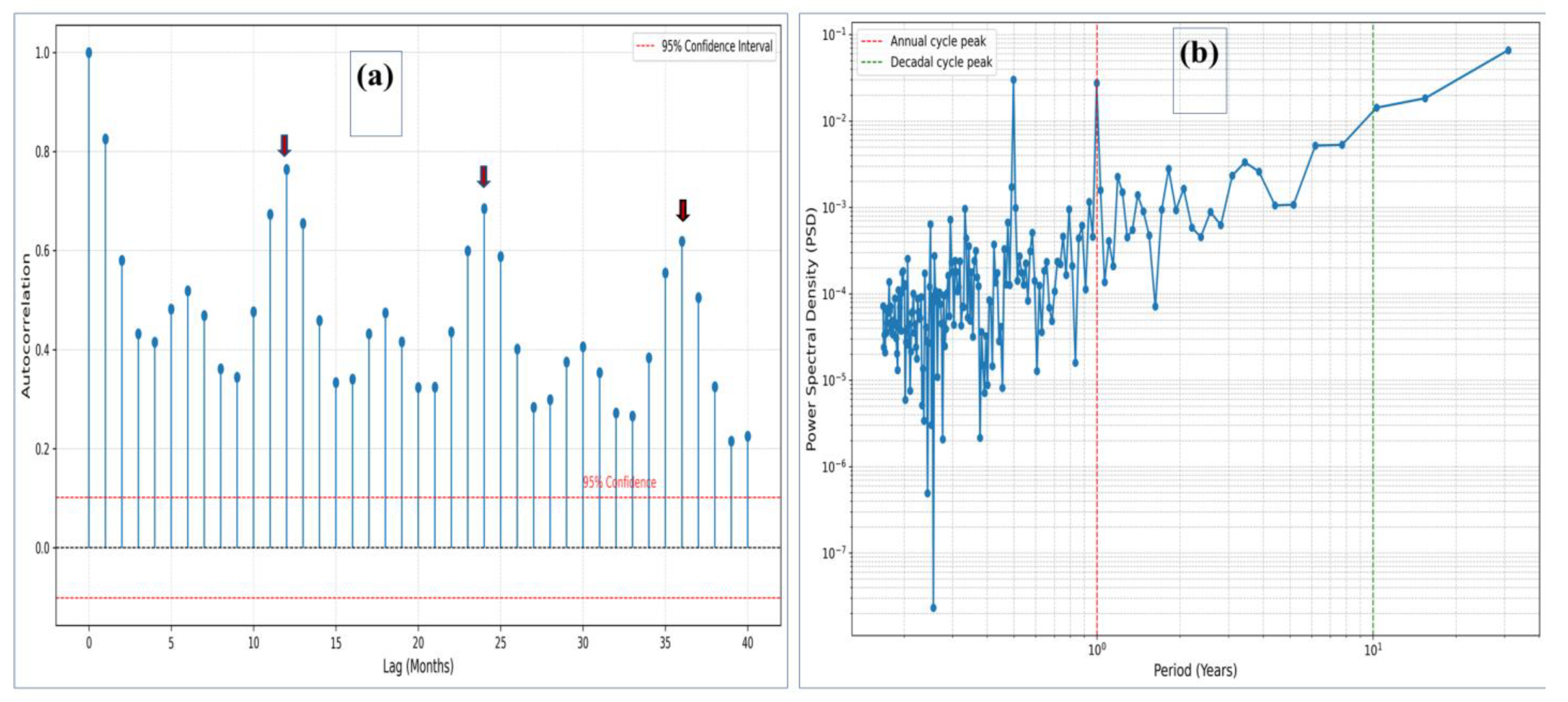
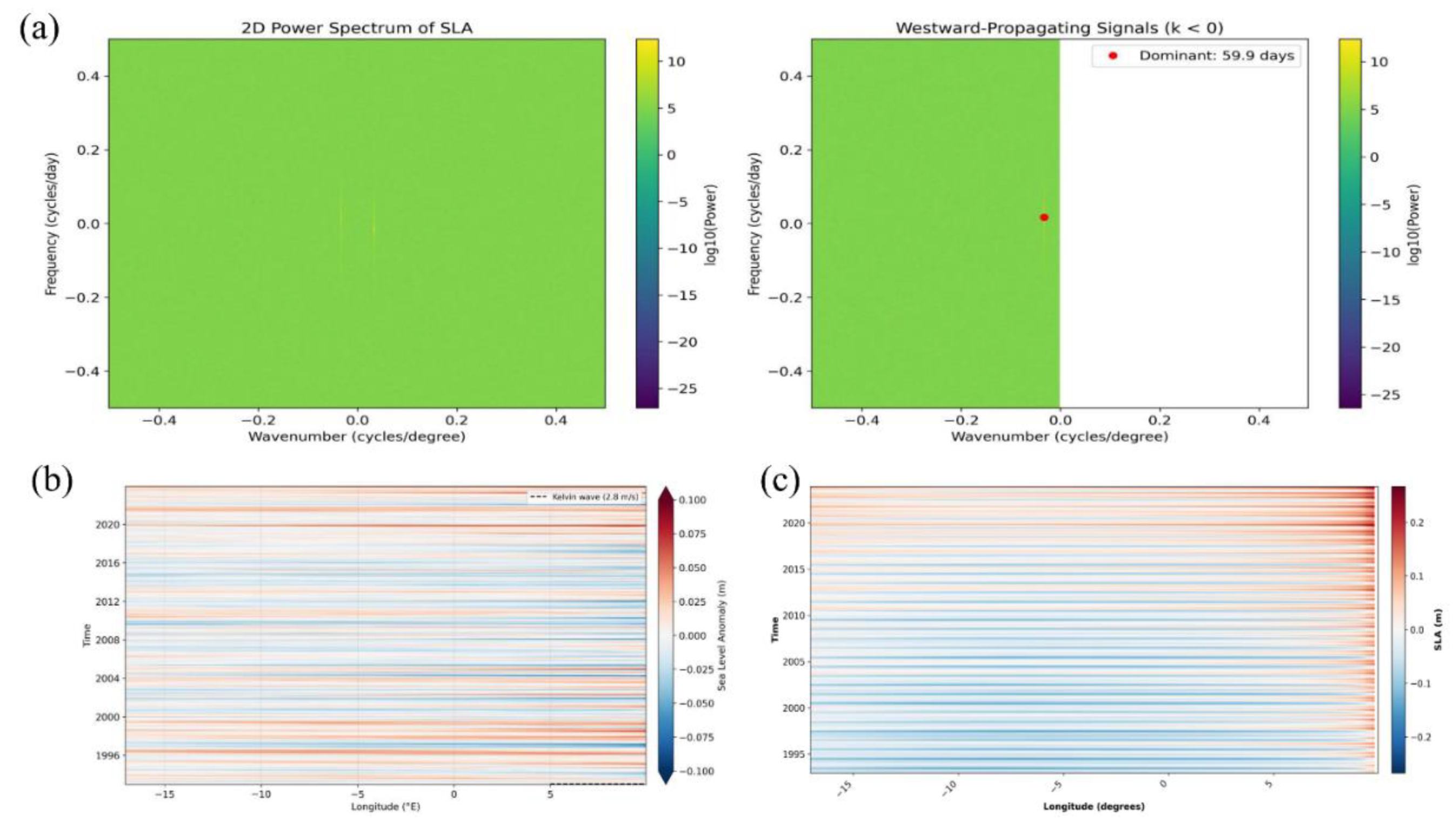
2.2 Spatiotemporal and Frequency Analysis of SLA
2.3 Nonlinear Modeling and Machine Learning of SLA
2.4 Ocean Mass Change and Regional Sea Level Budget Closure
3 Results
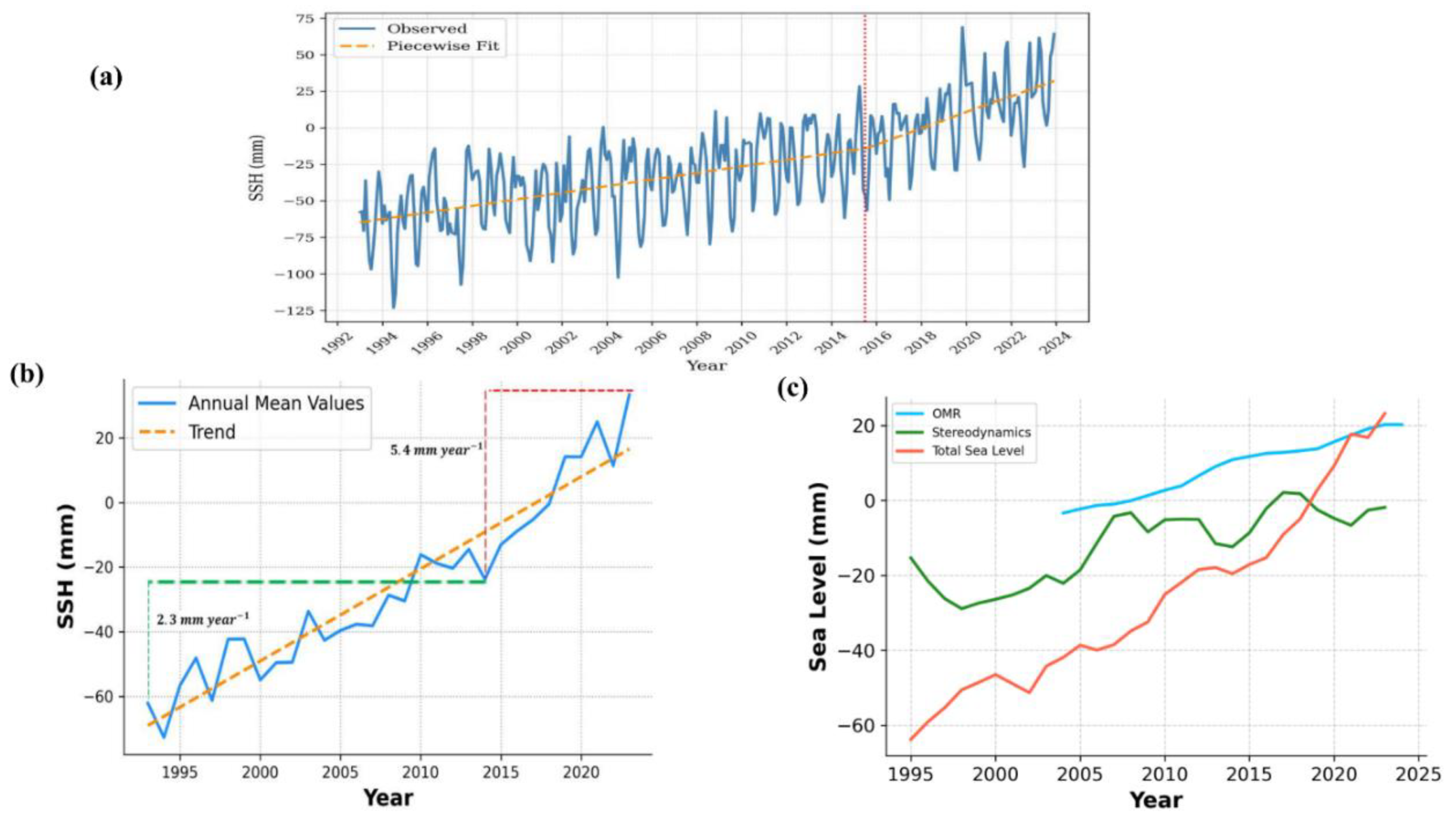
3.1 Temporal Trends and Physical Attribution
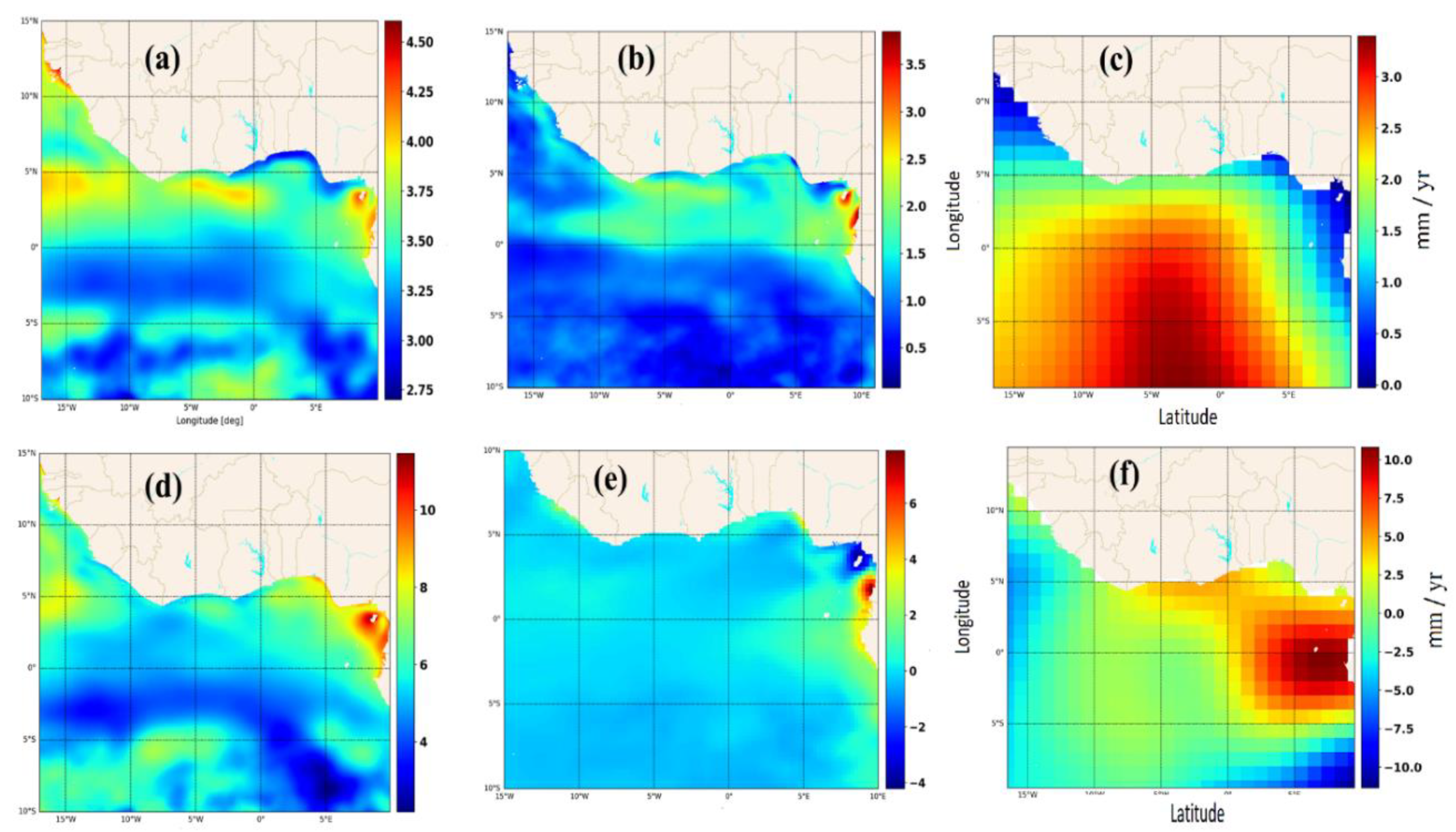
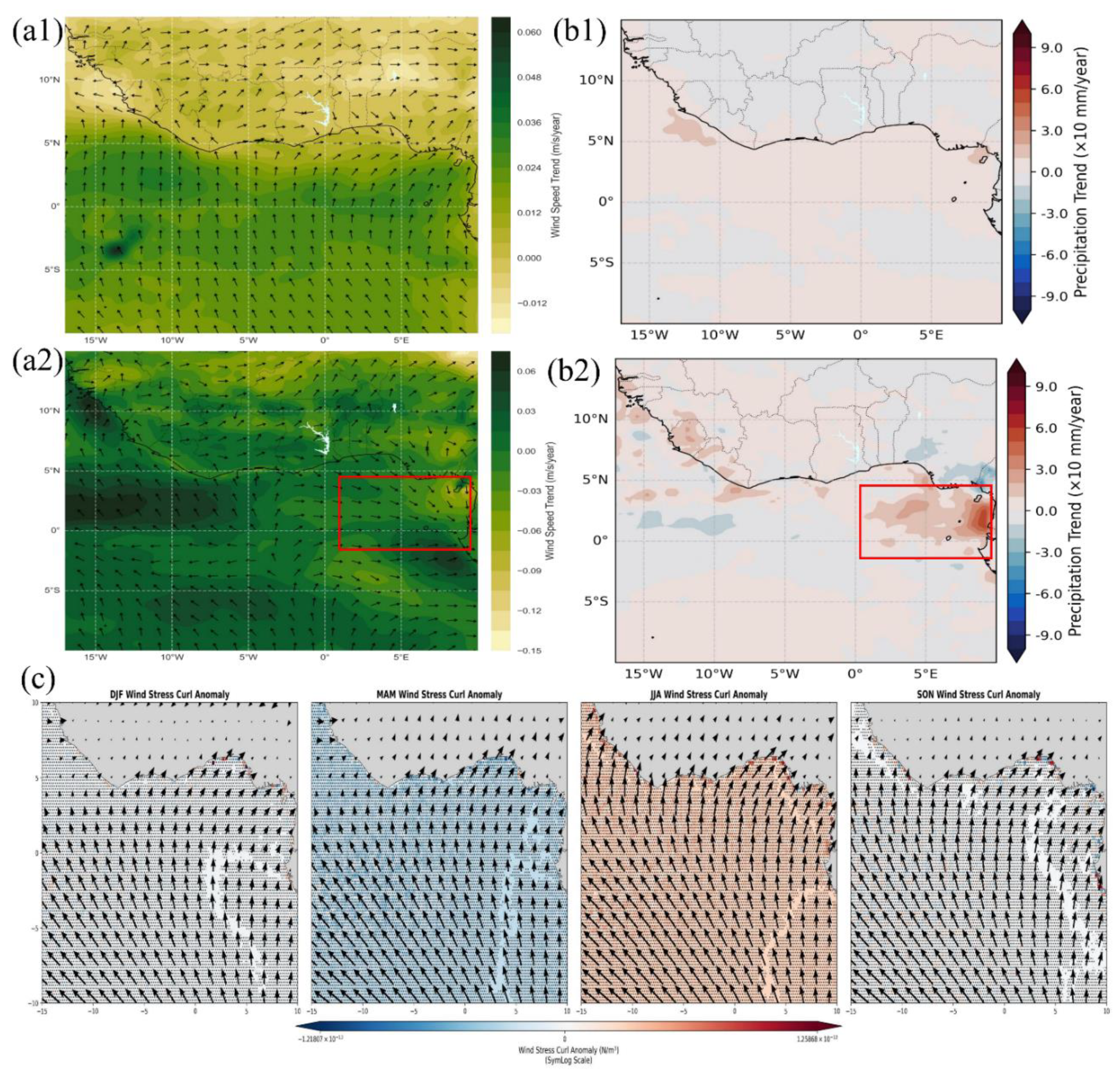
3.2 Spatial Disaggregation and Forcing Shifts
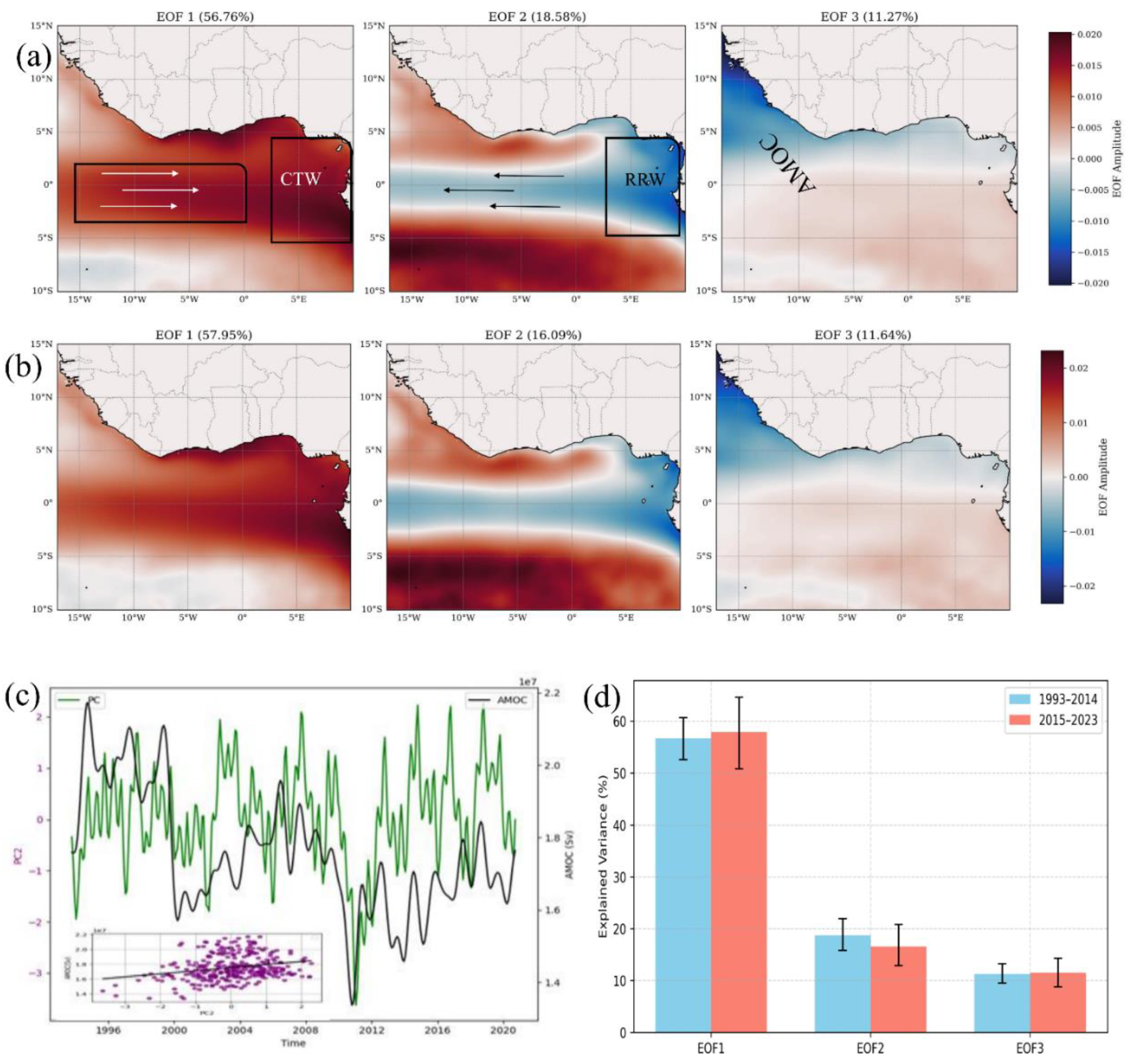
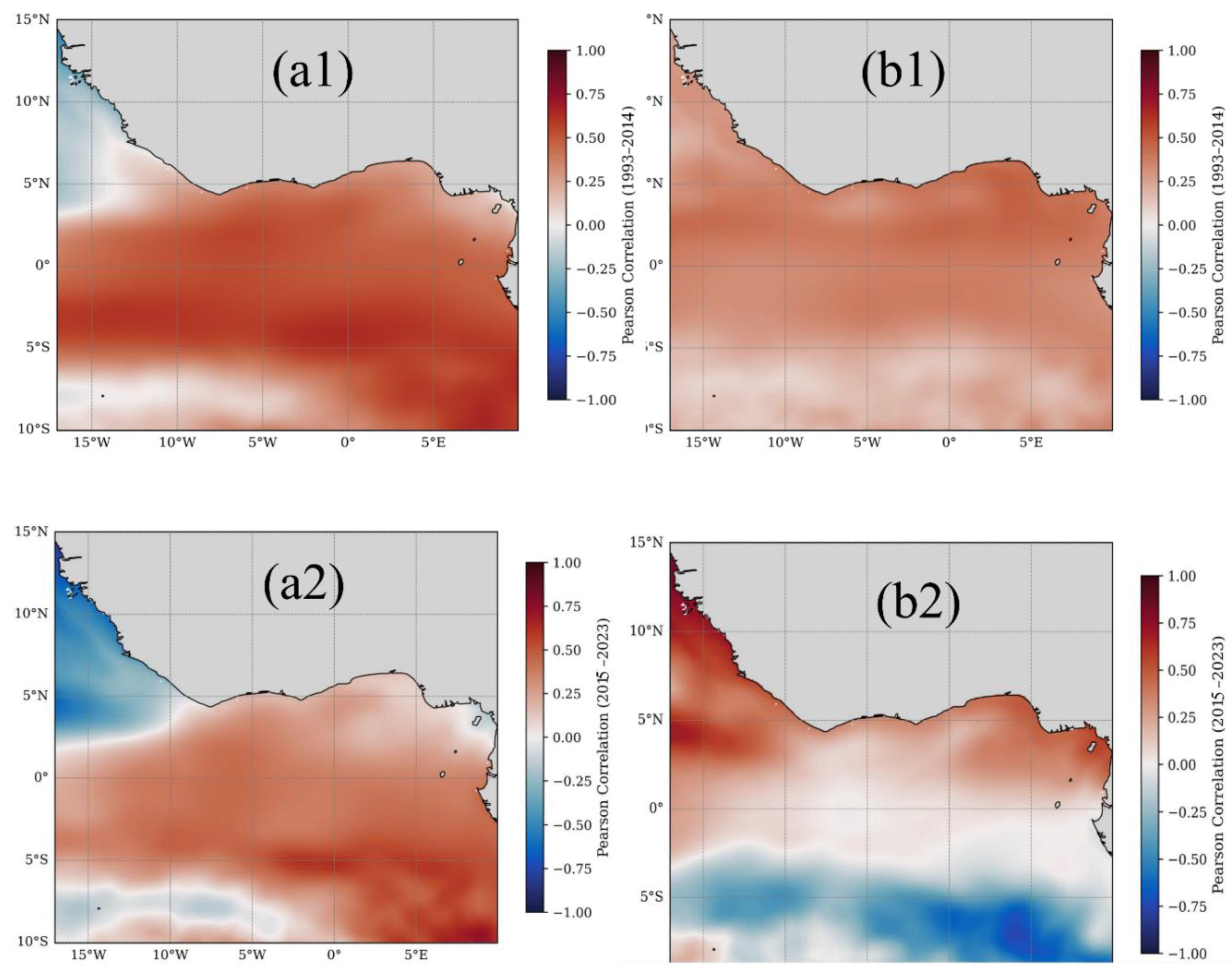
3.4 Climate Variability and Regional Teleconnections
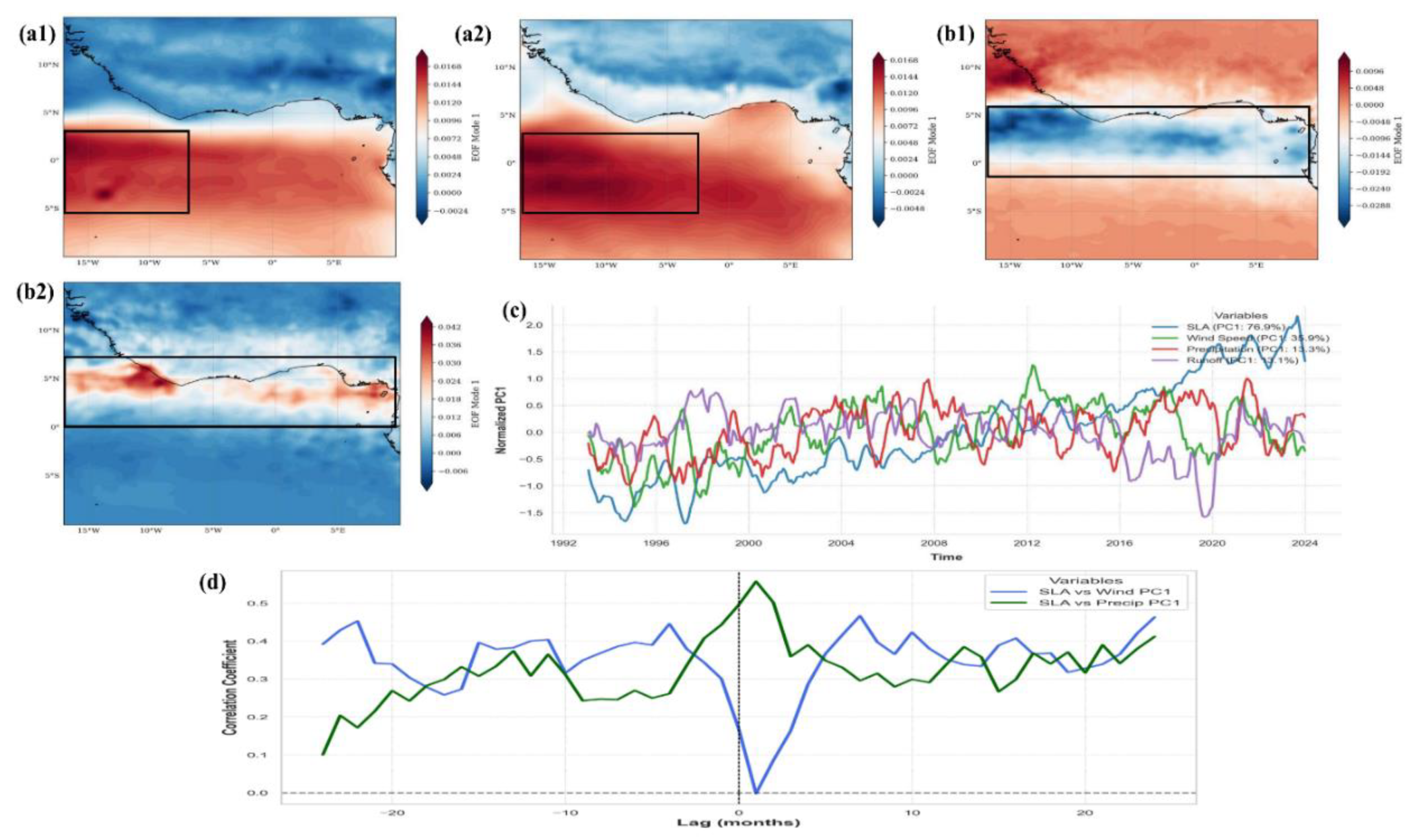
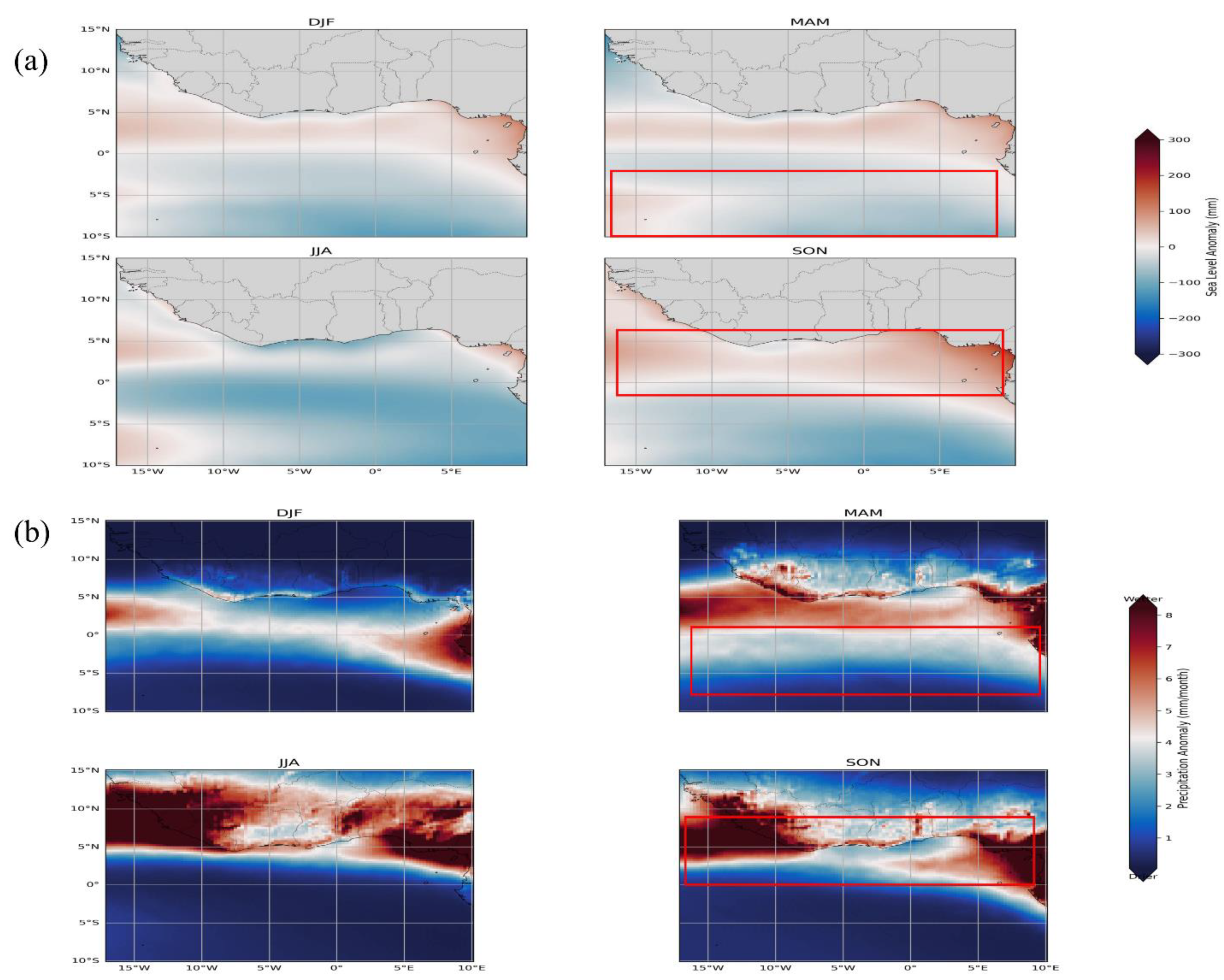
3.4.1 Seasonal SLA Variability and Hydroclimatic Forcing
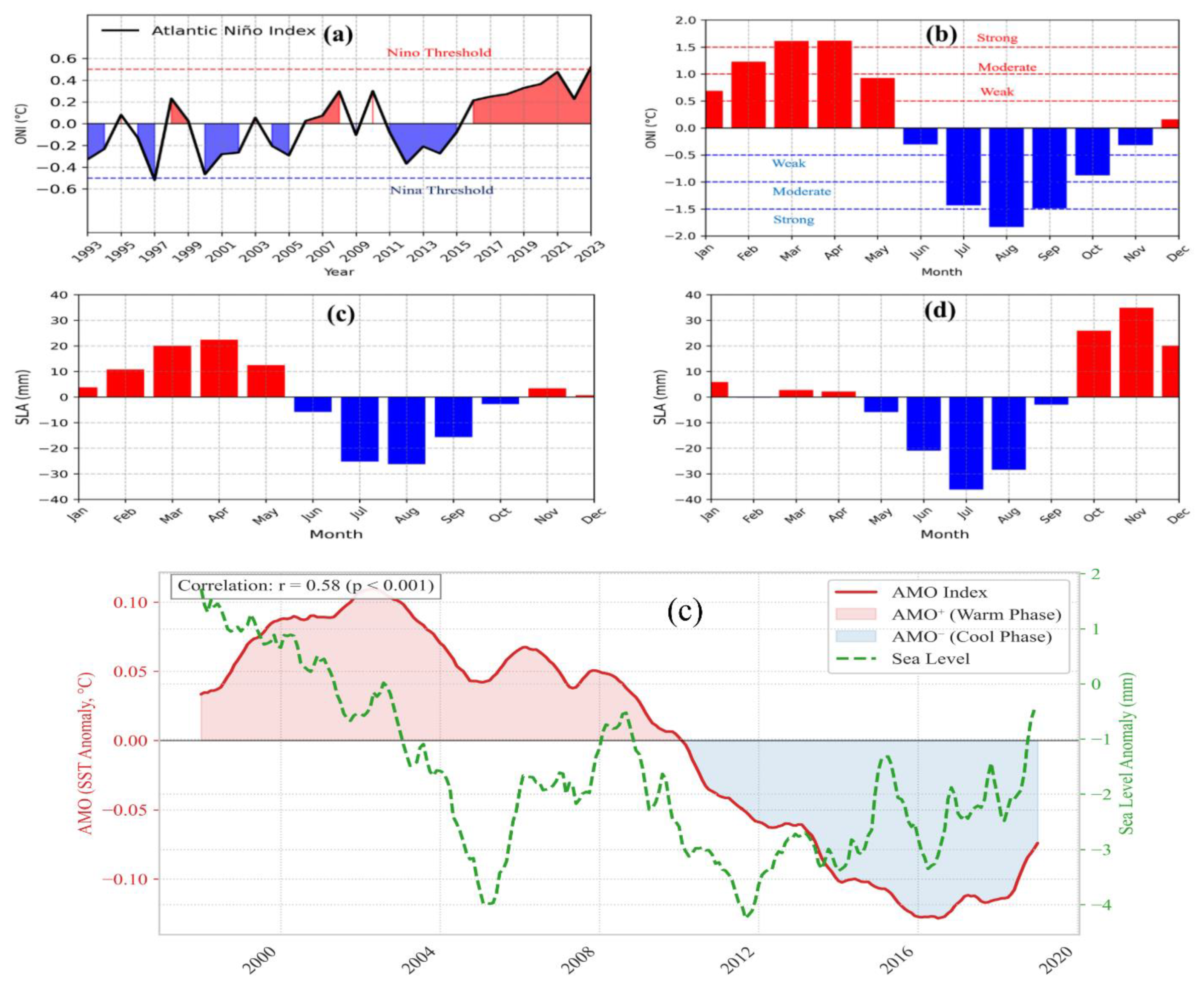
3.4.2 ENSO and AMO Teleconnections
4. Discussion and Conclusion
References
- Adamec, D.; O’Brien, J.J. The seasonal upwelling in the Gulf of Guinea due to remote forcing. Journal of Physical Oceanography 1978, 8, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, A.; Testut, L.; Woodworth, P.L.; Aarup, A.; Dixon, D.J. Seasonal sea level variability in the Gulf of Guinea from altimetry and tide gauge. Revue Ivoirienne des Sciences et Technologie 2007, 9, 105–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ayinde, A.S.; Yu, H.; Wu, K. Sea level variability and modeling in the Gulf of Guinea using supervised machine learning. Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 21318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelton, D.B.; DeSzoeke, R.A.; Schlax, M.G.; El Naggar, K.; Siwertz, N. Geographical variability of the first baroclinic Rossby radius of deformation. Journal of Physical Oceanography 1998, 28, 433–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Church, J. A. , Watson, C. S., King, M. A., Monselesan, D., Legresy, B.; Harig, C. The increasing rate of global mean sea-level rise during 1993–2014. Nature Climate Change 2017, 7, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangendorf, S.; Hay, C.; Calafat, F. M., et al. Persistent acceleration in global sea-level rise since the 1960s. Nature Climate Change 2019, 9, 705–710. [CrossRef]
- Dieng, H.B.; Dadou, I.; Léger, F.; Morel, Y.; Jouanno, J.; Lyard, F.; Allain, D. Sea level anomalies using altimetry, model and tide gauges along the African coasts in the Eastern Tropical Atlantic Ocean: Inter-comparison and temporal variability. Advances in Space Research 2021, 68, 534–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evadzi, P.I.K.; Zorita, E.; Hünicke, B. West African sea level variability under a changing climate: What can we learn from the observational period? Journal of Coastal Conservation 2019, 23, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox-Kemper, B.; Hewitt, H.T.; Xiao, C.; Aðalgeirsdóttir, G.; Drijfhout, S.S.; Edwards, T.L.; Golledge, N.R.; Hemer, M.; Kopp, R.E.; Krinner, G. and Mix, A., 2021. Ocean, cryosphere and sea level change. Climate change 2021: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change. Ghomsi, K. F. E., Raj, R. P., Bonaduce, A., Halo, I., Nyberg, B., Cazenave, A., ... & Johannessen, O. M. (2024). Sea level variability in the Gulf of Guinea from satellite altimetry. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 4759.
- Fox-Kemper, B.; Hewitt, H.T.; Xiao, C.; Aðalgeirsdóttir, G.; Drijfhout, S.S.; Edwards, T.L.; Golledge, N.R.; Hemer, M.; Kopp, R.E.; Krinner, G.; Mix, A. Ocean, cryosphere and sea level change. Climate change 2021: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Good, S.A.; Martin, M.J. and Rayner, N.A. EN4: Quality controlled ocean temperature and salinity profiles and monthly objective analyses with uncertainty estimates. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 2013, 118, 6704–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iler, A.M.; Inouye, D.W.; Schmidt, N.M.; Høye, T.T. Detrending phenological time series improves climate–phenology analyses and reveals evidence of plasticity. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC (2023). Lee, H., Calvin, K., Dasgupta, D., Krinner, G., Mukherji, A., Thorne, P., Trisos, C., Romero, J., Aldunce, P., Barret, K., and Blanco, G., 2023. Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report, Summary for Policymakers. Contribution of Working Groups I, II, and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Core Writing Team, H. Lee and J. Romero (eds.)]. IPCC, Geneva, Switzerland.
- Longhurst, A.R. A review of the oceanography of the Gulf of Guinea. Bulletin de l’Institut Français d’Afrique Noire Série A Sciences Naturelles 1962, 24, 633–663. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, E.N., 1956. Empirical orthogonal functions and statistical weather prediction. (No Title).
- Kendall, M. G., 1975. Rank correlation methods. Griffin, London.
- Kemgang Ghomsi, F.E.; Raj, R.P.; Bonaduce, A.; Halo, I.; Nyberg, B.; Cazenave, A.; Rouault, M.; Johannessen, O.M. Sea level variability in Gulf of Guinea from satellite altimetry . Scientific Reports 2024, 14, 4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H. B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGirr, R.; Tregoning, P.; Purcell, A.; McQueen, H. Significant local sea level variations caused by continental hydrology signals. Geophysical Research Letters 2024, 51, e2024GL108394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyssignac, B.; Slangen, A.A.; Melet, A.; Church, J.A.; Fettweis, X.; Marzeion, B.; Agosta, C.; Ligtenberg, S.R.M.; Spada, G.; Richter, K. and Palmer, M.D. Evaluating model simulations of twentieth-century sea-level rise. Part II: Regional sea-level changes. Journal of Climate 2017, 30, 8565–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, G.R.; Bell, T.L.; Cahalan, R.F.; Moeng, F.J. Sampling errors in the estimation of empirical orthogonal functions. Monthly weather review 1982, 110, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, M.; Glavovic, B.; Hinkel, J.; Van de Wal, R.; Magnan, A.K.; Abd-Elgawad, A.; Cai, R.; Cifuentes-Jara, M.; Deconto, R.M.; Ghosh, T.; Hay, J. Sea level rise and implications for low lying islands, coasts and communities.
- Peltier, W.R.; Argus, D.F.; Drummond, R. Space geodesy constrains ice age terminal deglaciation: The global ICE-6G_C (VM5a) model. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 2015, 120, 450–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Fonseca, B.; Polo, I.; García-Serrano, J.; Losada, T.; Mohino, E.; Mechoso, C.R. and Kucharski, F., 2009. Are Atlantic Niños enhancing Pacific ENSO events in recent decades? . Geophysical Research Letters 2009, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. Journal of the American Statistical Association 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slangen, A.B.; Meyssignac, B.; Agosta, C.; Champollion, N.; Church, J.A.; Fettweis, X.; Ligtenberg, S.R.; Marzeion, B.; Melet, A.; Palmer, M.D. and Richter, K. Evaluating model simulations of twentieth-century sea level rise. Part I: Global mean sea level change. Journal of Climate 2017, 30, 8539–8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spall, M.A.; Pedlosky, J. Reflection and transmission of equatorial Rossby waves. Journal of physical oceanography 2005, 35, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.; Chambers, D.; Wahr, J. Estimating geocenter variations from a combination of GRACE and ocean model output. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theil, H. A rank-invariant method of linear and polynomial regression analysis. In Proceedings of the Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (Vol. 1950). Springer.
- Thorncroft, C.D.; Nguyen, H.; Zhang, C.; Peyrillé, P. Annual cycle of the West African monsoon: regional circulations and associated water vapour transport. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society 2011, 137, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellinga, M.; Arribas, A. and Graham, R., 2013. Seasonal forecasts for regional onset of the West African monsoon. Climate Dynamics 2013, 40, 3047–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, J.M. The seasonal upwellings in the Gulf of Guinea. Progress in Oceanography 1992, 29, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Storch, H. and Zwiers, F.W. Statistical analysis in climate research. Cambridge university press.
- Wahr, J.; Molenaar, M.; Bryan, F. Time variability of the Earth’s gravity field: Hydrological and oceanic effects and their possible detection using GRACE. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 1998, 103, 30205–30229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.P.; Carton, J.A. Tropical Atlantic variability: Patterns, mechanisms, and impacts. Earth’s Climate: The Ocean–Atmosphere Interaction, Geophys. Monogr 2004, 147, pp. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



