Submitted:
23 July 2025
Posted:
28 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Key Herbal Ingredients
1.1.1. Neem (Azadirachta indica)
- Common Names: Neem, Indian Lilac, Margosa Tree.
- Botanical Source: Obtained from dried leaves and bark of Azadirachta indica.
- Family: Meliaceae.
-
Ecology and Habitat:
- ○
- Climate: Tropical to subtropical; drought-resistant.
- ○
- Soil: Well-drained sandy or loamy soils.
- ○
- Tolerance: Poor, dry, and rocky soils.
-
Plant Description:
- ○
- Type: Evergreen tree.
- ○
- Height: Typically grows 15–20 meters tall, can reach up to 35–40 meters in ideal conditions.
- ○
- Leaves: Pinnate leaves with 8–19 leaflets, bright green, serrated edges.
- ○
- Flowers: Small, white, fragrant flowers in clusters.
- ○
- Fruit: Smooth, olive-like drupe; green when unripe and yellow when mature [4].
- Preparation and Dental Application: Azadirachta indica was collected in Kale plant center, Nagpur and identified by Prof. Acharya Botany Dep., Wardha. RTMNU, Nagpur. Neem bark extract is used in dental gels due to its strong antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects. The process begins by cleaning, drying, and grinding the bark into a fine powder. This powder is then subjected to solvent extraction—commonly with ethanol, methanol, or water—to draw out beneficial compounds such as nimbin and nimbidin. Once filtered and concentrated by removing the solvent, the extract is incorporated into dental gel formulations. Its inclusion helps fight harmful oral microbes, soothe gum irritation, and promote better oral health.
1.1.2. Clove Oil (Eugenia caryophyllata)
- Common Name: Clove Oil.
- Botanical Source: Obtained from dried flower buds of Eugenia caryophyllata.
- Family: Myrtaceae.
- Oil Extraction Method: Steam distillation.
- Part Used for Oil Extraction: Dried flower buds, leaves, and stems are used.
- Major Constituents of Clove Oil: Eugenol (70–90%) – primary active compound, Eugenyl acetate, Caryophyllene, Humulene.
- Aroma: Strong, spicy, warm, and woody scent.
- Plant Description: Clove is a medium-sized evergreen tree that grows up to 8–12 meters tall. It has large green leaves and clusters of aromatic flower buds that start pale, then turn green, and finally develop into a bright red when ready for harvesting [5].
- Medicinal Properties and Dental Application: Clove oil, primarily composed of the active compound eugenol, is widely used in dental care due to its potent analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. When incorporated into dental gels, clove oil offers several therapeutic benefits including pain relief, antibacterial effects, and anti-inflammatory effects [6].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Gel Formulations
2.2. Evaluation of Formulated Gel
2.2.1. Physical Stability
2.2.3. Spreadability
- S = Spreadability
- M = Mass attached with the slide
- L = Length moved by the glass slide
- T = Time required to travel a distance by the slid
2.2.4. Homogeneity
2.2.5. Extrudability Study
2.2.6. Content Uniformity
2.2.7. Viscosity Measurement
3. Antimicrobial Assay
3.1. Bacterial Strain and Maintenance
3.2. Well Diffusion Method
Zone of Inhibition
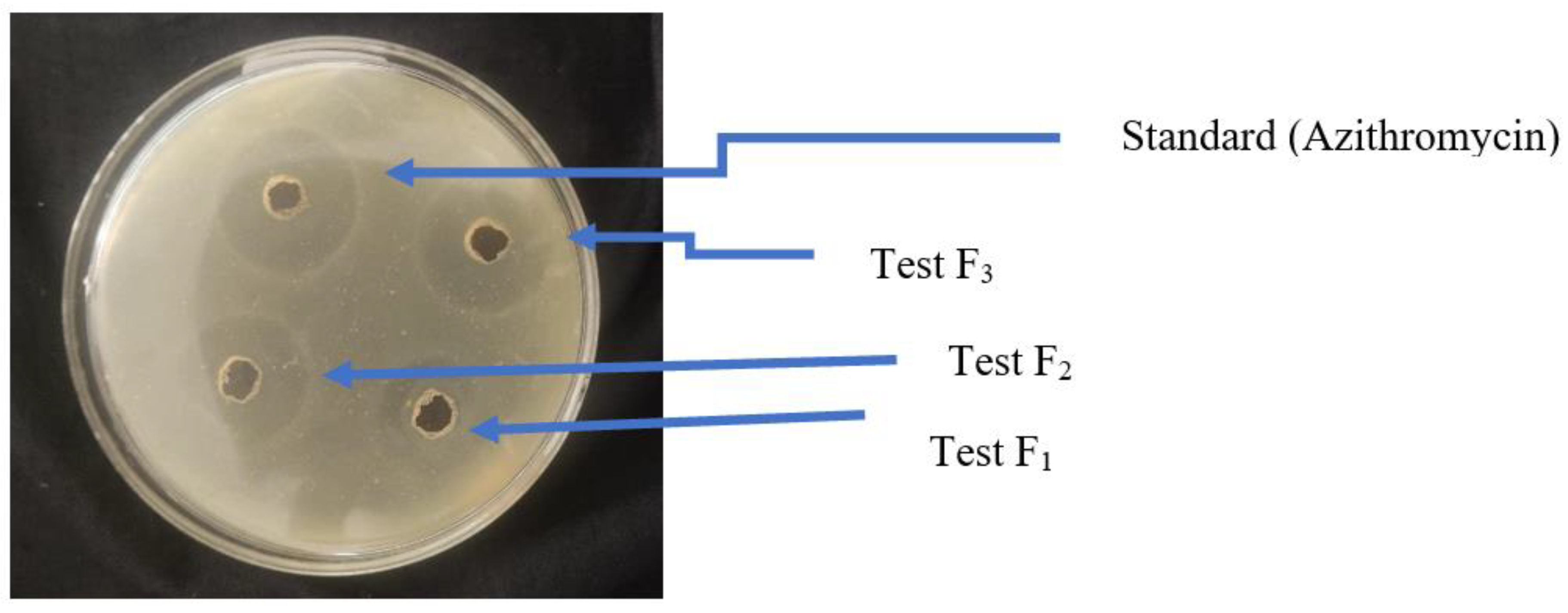
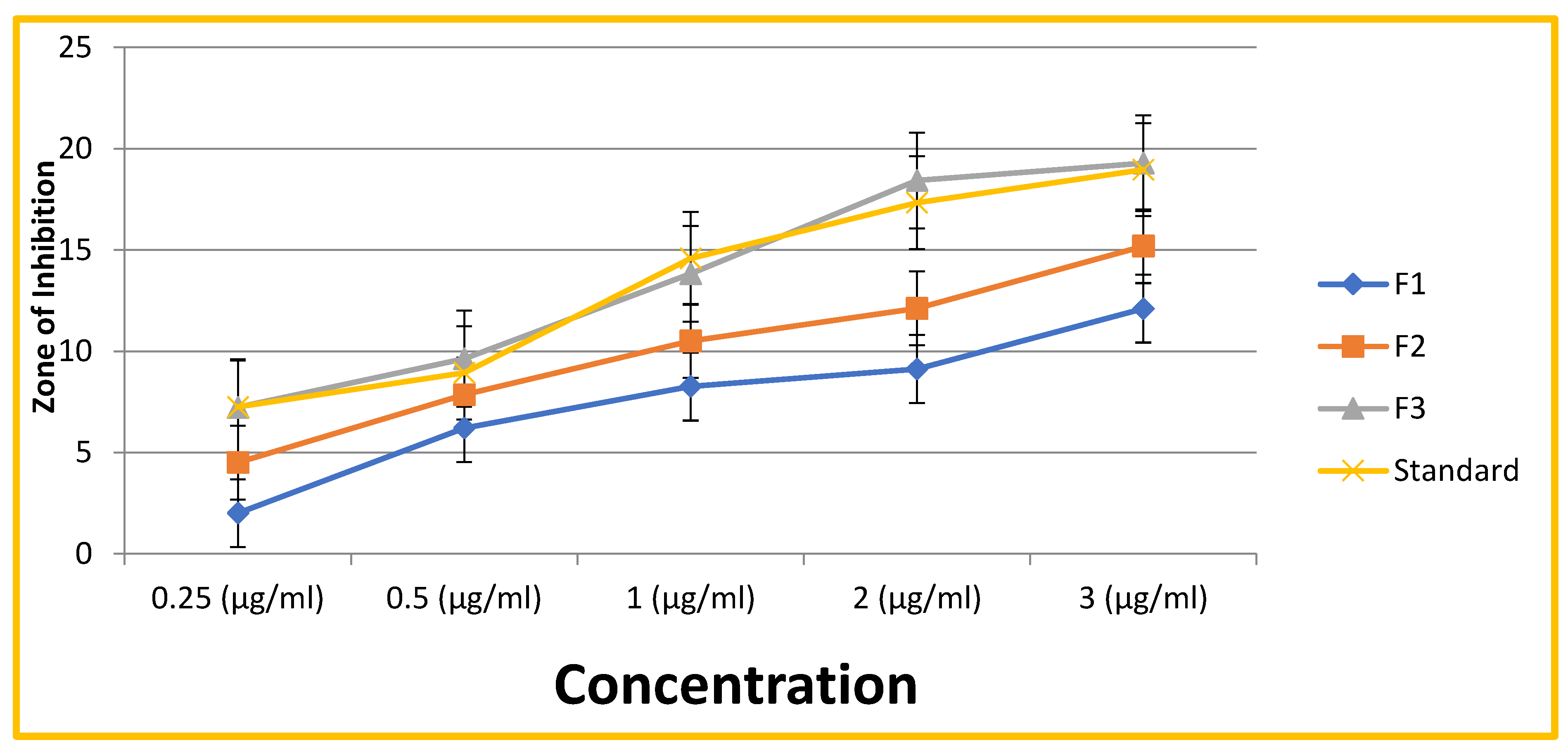
3.3. Determination of MIC (Minimum Inhibitory Concentration)
| Formulation | Different Concentrations (µg/ml) | ||||
| Concentration | 0.25 (µg/ml) | 0.5 (µg/ml) | 1 (µg/ml) | 2 (µg/ml) | 3 (µg/ml) |
| F1 | 2.00±0.22 | 6.21±0.56 | 8.25±0.46 | 9.12±0.98 | 12.10±0.50 |
| F2 | 4.52±0.25 | 7.85±1.85 | 10.50±1.52 | 12.11±0.82 | 15.18±0.45 |
| F3 | 7.23±0.55 | 9.63±0.61 | 13.82±0.44 | 18.42±0.66 | 19.28±1.75 |
| Standard | 7.25± 0.21 | 8.93±0.50 | 14.58±0.71 | 17.33±0.51 | 18.96±0.84 |
4. Results & Discussion
5. Discussion
- pH: Formulations F2 and F3 showed a neutral pH of 7.0, which is generally considered suitable for oral application, minimizing irritation to oral tissues. F1 had a slightly acidic pH of 6.0.
- Appearance and Odor: F1 and F2 were slightly opaque, while F3 had a brownish appearance, likely due to the higher concentration of herbal extracts. The odor increased from mild in F1 to strong in F3, correlating with the increased herbal content.
- Spreadability: F3 demonstrated significantly higher spreadability (26.08 gms.cm/sec) compared to F1 and F2, indicating better applicability and ease of use. This is crucial for a dental gel to ensure proper coverage of oral surfaces.
- Viscosity: F3 exhibited the highest viscosity (9632 cps), which is consistent with its enhanced spreadability. An optimal viscosity is important for retaining the gel at the site of application and allowing for sustained release of active ingredients.
- Skin Irritation: All three formulations were found to be non-irritant, suggesting they are safe for topical application on oral mucosal membranes.
- Extrudability: F3 showed the best Extrudability (+++), indicating it can be easily dispensed from a tube, which is a key factor for user convenience.
- Antimicrobial Activity: All formulations exhibited antimicrobial activity against Streptococcus mutans. Crucially, F3 demonstrated the most significant antimicrobial activity, aligning with its higher concentrations of neem extract and clove oil. This superior efficacy is further supported by the MIC data presented in Table 2, where F3 showed the lowest MIC values across various concentrations, indicating its greater potency in inhibiting bacterial growth compared to F1, F2, and even the standard drug at some concentrations. The synergistic effects of neem, clove oil, honey, and vitamin E likely contribute to the enhanced performance of F3.
6. Summary
7. Conclusions
References
- Dörfer C, Benz C, Aida J, Campard G. The relationship of oral health with general health and NCDs: a brief review. International dental journal. 2017 Oct; 67:14-8.
- Alzohairy, MA. Therapeutics role of Azadirachta indica (Neem) and their active constituents in diseases prevention and treatment. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2016;2016 (1):7382506.
- Tashkandi, H. Honey in wound healing: An updated review. Open life sciences. 2021 Oct 6;16(1):1091-100.
- Biswas K, Chattopadhyay I, Banerjee RK, Bandyopadhyay U. Biological activities and medicinal properties of neem (Azadirachta indica). Current science. 2002 Jun 10:1336-45.
- Haro-González JN, Castillo-Herrera GA, Martínez-Velázquez M, Espinosa-Andrews H. Clove essential oil (Syzygium aromaticum L. Myrtaceae): Extraction, chemical composition, food applications, and essential bioactivity for human health. Molecules. 2021 Oct 22;26(21):6387.
- Dhakad AK, Kumar R, Choudhary R, Singh S, Khan S, Poonia PK. Traditional to modern perspectives on Neem (Azadirachta indica): A gateway to bioactive compounds, sustainable agrochemicals and industrial applications. Industrial Crops and Products. 2025 Sep 1;231:121155.
- Voleti VK, Shaik SB, Konduru C, Peyam S, Yaramsetti CK, Pasala S, Pitchaimuthu SP. Formulation and development of dental gel containing clove oil for the treatment of human periodontal diseases. J Com pr Pharm. 2016;3:1-7.
- Raj PG, Ranjeetha AR, Aishwarya KS, Ananya MS, Anjana NK. Formulation And Evaluation Of Topical Gel Containing Econazole Nitrate. IJP. 2024;11(11):636-40.
- Dantas MG, Reis SA, Damasceno CM, Rolim LA, Rolim-Neto PJ, Carvalho FO, Quintans-Junior LJ, Almeida JR. Development and evaluation of stability of a gel formulation containing the monoterpene borneol. The Scientific World Journal. 2016;2016(1):7394685.
- Traynor B, Uvegi H, Olivetti E, Lothenbach B, Myers RJ. Methodology for pH measurement in high alkali cementitious systems. Cement and Concrete Research. 2020 Sep 1;135:106122.
- Raj PG, Ranjeetha AR, Aishwarya KS, Ananya MS, Anjana NK. Formulation And Evaluation Of Topical Gel Containing Econazole Nitrate. IJP. 2024;11(11):636-40.
- Patel H, Panchal MS, Shah S, Vadalia KR. Formulation and evaluation of transdermal gel of sildenafil citrate. Int J Pharm Res Allied Sci. 2012 Mar 5;1(3):103-8.
- Raj PG, Ranjeetha AR, Aishwarya KS, Ananya MS, Anjana NK. Formulation And Evaluation Of Topical Gel Containing Econazole Nitrate. IJP. 2024;11(11):636-40.
- Nematpour N, Moradipour P, Zangeneh MM, Arkan E, Abdoli M, Behbood L. The application of nanomaterial science in the formulation a novel antibiotic: Assessment of the antifungal properties of mucoadhesive clotrimazole loaded nanofiber versus vaginal films. Materials Science and Engineering: C. 2020 May 1; 110:110635.
- Panwar A, Upadhyay N, Bairagi M, Gujar S, Darwhekar G, Jain D. Emulgel: A review. Asian J Pharm Life Sci. 2011;2231:4423.
- Abdelkader HS, Alayafi AA, Ahmed HE, Bin Osail RA. The antibacterial activity of nanosilver coupled edible plant extracts against Streptococcus mutans, the cause of dental caries. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2021;33:167-86.
- Finn, RK. Theory of agar diffusion methods for bioassay. Analytical Chemistry. 1959 Jun 1;31(6):975-7.
- Schantz EJ, Lauffer MA. Diffusion measurements in agar gel. Biochemistry. 1962 Jul 1;1(4):658-63.
- Hossain TJ. Methods for screening and evaluation of antimicrobial activity: A review of protocols, advantages, and limitations. European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology. 2024 May 14;14(2):97-115.
- Barnes L, Heithoff DM, Mahan SP, House JK, Mahan MJ. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing to evaluate minimum inhibitory concentration values of clinically relevant antibiotics. STAR protocols. 2023 Sep 15;4(3):102512.
| Sr. No | Ingredients | Functions | F1 | F2 | F3 |
| 1. | Carbopol 940 | Gelling agent | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| 2. | Neem extract | Antibacterial | 2.0 | 3.5 | 5.0 |
| 3. | Clove oil | Analgesic, Antiseptic | 0.5 | 0.75 | 1.0 |
| 4. | Peppermint oil | Flavour, mild antiseptic | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.50 |
| 5. | Honey | Healing, Humectant | 2.0 | 3.5 | 5.0 |
| 6. | Vitamin E oil | Antioxidant | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 7. | Propylene glycol | Humectant, Solvent | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| 8. | Triethanolamine | pH adjuster | - | - | - |
| 9. | Methyl Paraben | Preservative | 0.1 g | 0.1 g | 0.1 g |
| FORMULATION | CLARITY | pH | SPREADABILITY (gms.cm/sec)* | VISCOSITY (cps) | SKIN IRRITATION | EXTRDURABILITY | ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY |
| F1 | ++ | 6.0 | 20.66 ±0.1159 | 7954 | NI | ++ | Shows Antimicrobial Activity |
| F2 | ++ | 7.0 | 20.01 ±0.0152 | 8122 | NI | ++ | Shows Antimicrobial Activity |
| F3 | +++ | 7.0 | 26.08 ±0.0152 | 9632 | NI | +++ | Shows Most Significant Antimicrobial activity |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




