Submitted:
21 July 2025
Posted:
22 July 2025
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Mitochondrial Suffocation as the Origin of Sulfur Deficiency
4. The Sulfur Insulin Deformation Hypothesis: A Transformative Framework
5. Targeting Sulfur Homeostasis: A Revolutionary Therapeutic Approach for Type 2 Diabetes
6. Evidence for Sulfur-Driven Insulin Dysfunction: Linking Cysteine Deficiency to Disulfide Bond Disruption in Type 2 Diabetes
7. Limitations
8. Discussion
9. Conclusion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei J, Fan L, He Z, Liu Y, Zhang X, Wang Q, Chen H, Li M, Zhang J, Yang C, Zhao W. The global, regional, and national burden of type 2 diabetes mellitus attributable to low physical activity from 1990 to 2021: a systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2021. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 2025;22:8. [CrossRef]
- Vinther TN, Norrman M, Ribel U, Huus K, Schlein M, Steensgaard DB, Pedersen TÅ, Pettersson I, Ludvigsen S, Kjeldsen T, Jensen KJ, Hubálek F. Insulin analog with additional disulfide bond has increased stability and preserved activity. Protein Sci 2013;22(3):296–305. [CrossRef]
- Comas F, Moreno-Navarrete JM. The impact of H2S on obesity-associated metabolic disturbances. Antioxidants 2021;10(5):633. [CrossRef]
- Sbodio JI, Snyder SH, Paul BD. Regulators of the transsulfuration pathway. Br J Pharmacol 2019;176(4):583–593. [CrossRef]
- Stipanuk MH, Ueki I. Dealing with methionine/homocysteine sulfur: cysteine metabolism to taurine and inorganic sulfur. J Inherit Metab Dis 2011;34(1):17–32. [CrossRef]
- Murphy B, Bhattacharya R, Mukherjee P. Hydrogen sulfide signaling in mitochondria and disease. FASEB J 2019;33(12):13098–13125. [CrossRef]
- Jiang H, Thapa P, Hao Y, Ding N, Alshahrani A, Wei Q. Protein disulfide isomerases function as the missing link between diabetes and cancer. Antioxid Redox Signal 2022;37(16-18):1191–1205. [CrossRef]
- Isakoff SJ, Taha C, Rose E, Marcusohn J, Klip A, Skolnik EY. The inability of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation to stimulate GLUT4 translocation indicates additional signaling pathways are required for insulin-stimulated glucose uptake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1995;92(22):10247–10251. [CrossRef]
- Sergi D, Naumovski N, Heilbronn LK, Abeywardena M, O’Callaghan N, Lionetti L, Luscombe-Marsh N. Mitochondrial (dys)function and insulin resistance: from pathophysiological molecular mechanisms to the impact of diet. Front Physiol 2019;10:532. [CrossRef]
- Masenga SK, Kabwe LS, Chakulya M, Kirabo A. Mechanisms of oxidative stress in metabolic syndrome. Int J Mol Sci 2023;24(9):7898. [CrossRef]
- Yung JHM, Giacca A. Role of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Cells 2020;9(3):706. [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty S, Herkenham M. Toll-like receptor 4 on nonhematopoietic cells sustains CNS inflammation during endotoxemia, independent of systemic cytokines. J Neurosci 2005;25(7):1788–1796. [CrossRef]
- Kumar AR, Nair B, Kamath AJ, Nath LR, Calina D, Sharifi-Rad J. Impact of gut microbiota on metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma: pathways, diagnostic opportunities and therapeutic advances. Eur J Med Res 2024;29(1):485. [CrossRef]
- Haque PS, Kapur N, Barrett TA, Theiss AL. Mitochondrial function and gastrointestinal diseases. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2024;21(8):537–555. [CrossRef]
- Guerbette T, Boudry G, Lan A. Mitochondrial function in intestinal epithelium homeostasis and modulation in diet-induced obesity. Mol Metab 2022;63:101546. [CrossRef]
- Pinti MV, Fink GK, Hathaway QA, Durr AJ, Kunovac A, Hollander JM. Mitochondrial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus: an organ-based analysis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2019;316(2):E268–E285. [CrossRef]
- Iheagwam FN, Joseph AJ, Adedoyin ED, Iheagwam OT, Ejoh SA. Mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetes: shedding light on a widespread oversight. Pathophysiology 2025;32(1):9. [CrossRef]
- Chen TH, Wang HC, Chang CJ, Lee SY. Mitochondrial glutathione in cellular redox homeostasis and disease manifestation. Int J Mol Sci 2024;25(2):1314. [CrossRef]
- Zhao RZ, Jiang S, Zhang L, Yu ZB. Mitochondrial electron transport chain, ROS generation and uncoupling. Int J Mol Med 2019;44(1):3–15. [CrossRef]
- Aoyama K, Nakaki T. Glutathione in cellular redox homeostasis: association with the excitatory amino acid carrier 1 (EAAC1). Molecules 2015;20(5):8742–8758. [CrossRef]
- Fujii J, Osaki T, Soma Y, Matsuda Y. Critical roles of the cysteine-glutathione axis in the production of γ-glutamyl peptides in the nervous system. Int J Mol Sci 2023;24(9):8044. [CrossRef]
- Aryal B, Kwakye J, Ariyo OW, Ghareeb AFA, Milfort MC, Fuller AL, Khatiwada S, Rekaya R, Aggrey SE. Major oxidative and antioxidant mechanisms during heat stress-induced oxidative stress in chickens. Antioxidants 2025;14(4):471. [CrossRef]
- Blom HJ, Smulders Y. Overview of homocysteine and folate metabolism. With special references to cardiovascular disease and neural tube defects. J Inherit Metab Dis 2011;34(1):75–81. [CrossRef]
- Parra M, Stahl S, Hellmann H. Vitamin B6 and its role in cell metabolism and physiology. Cells 2018;7(7):84. [CrossRef]
- Badawy AA. Multiple roles of haem in cystathionine β-synthase activity: implications for hemin and other therapies of acute hepatic porphyria. Biosci Rep 2021;41(7):BSR20210935. [CrossRef]
- Xiao T, Chen S, Yan G, Zheng J, Qiu Q, Lin S, Zong Y, Chang H, Yu Chang AC, Wu Y, Hou C. Cystathionine γ-lyase inhibits mitochondrial oxidative stress by releasing H2S nearby through the AKT/NRF2 signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol 2024;15:1374720. [CrossRef]
- Carelli S, Ceriotti A, Cabibbo A, Fassina G, Ruvo M, Sitia R. Cysteine and glutathione secretion in response to protein disulfide bond formation in the ER. Science 1997;277(5332):1681–1684. [CrossRef]
- Yu X, Long Y. Crosstalk between cystine and glutathione is critical for the regulation of amino acid signaling pathways and ferroptosis. Sci Rep 2016;6:30033. [CrossRef]
- Lingappan K. NF-κB in oxidative stress. Curr Opin Toxicol 2018;7:81–86. [CrossRef]
- Checa J, Aran JM. Reactive oxygen species: drivers of physiological and pathological processes. J Inflamm Res 2020;13:1057–1073. [CrossRef]
- Sykiotis GP, Papavassiliou AG. Serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate-1: a novel target for the reversal of insulin resistance. Mol Endocrinol 2001;15(11):1864–1869. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh S, Whitley CS, Haribabu B, Jala VR. Regulation of intestinal barrier function by microbial metabolites. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;11(5):1463–1482. [CrossRef]
- Page MJ, Kell DB, Pretorius E. The role of lipopolysaccharide-induced cell signalling in chronic inflammation. Chronic Stress 2022;6:24705470221076390. [CrossRef]
- Berbudi A, Khairani S, Tjahjadi AI. Interplay between insulin resistance and immune dysregulation in type 2 diabetes mellitus: implications for therapeutic interventions. ImmunoTargets Ther 2025;14:359–382. [CrossRef]
- Jia XY, Guo ZY, Wang Y, Xu Y, Duan SS, Feng YM. Peptide models of four possible insulin folding intermediates with two disulfides. Protein Sci 2003;12(11):2412–2419. [CrossRef]
- Vinther TN, Kjeldsen TB, Jensen KJ, Hubálek F. The road to the first, fully active and more stable human insulin variant with an additional disulfide bond. J Pept Sci 2015;21(10):797–806. [CrossRef]
- Weil-Ktorza O, Rege N, Lansky S, Shalev DE, Shoham G, Weiss MA, Metanis N. Substitution of an internal disulfide bridge with a diselenide enhances both foldability and stability of human insulin. Chem Eur J 2019;25(36):8513–8521. [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C. Kicking off the insulin cascade. Nature 444, 833–834 (2006). [CrossRef]
- Xu R, Jap E, Gubbins B, Hagemeyer CE, Karas JA. Semisynthesis of A6-A11 lactam insulin. J Pept Sci 2024;30(2):e3542. [CrossRef]
- Arai K, Okumura M, Lee YH, Takei M, Tsutsumi H, Miyakawa M, Koizumi M, Inaba K. Diselenide-bond replacement of the external disulfide bond of insulin increases its oligomerization leading to sustained activity. Commun Chem 2023;6:258. [CrossRef]
- Liu M, Wright J, Guo H, Xiong Y, Arvan P. Proinsulin entry and transit through the endoplasmic reticulum in pancreatic beta cells. Vitam Horm 2014;95:35–62. [CrossRef]
- Rocha AG, Knight SAB, Pandey A, Yoon H, Pain J, Pain D, Dancis A. Cysteine desulfurase is regulated by phosphorylation of Nfs1 in yeast mitochondria. Mitochondrion 2018;40:29–41. [CrossRef]
- Roman JV, Mascarenhas R, Ceric K, Ballou DP, Banerjee R. Disease-causing cystathionine β-synthase linker mutations impair allosteric regulation. J Biol Chem 2023;299(12):105449. [CrossRef]
- Zuhra K, Augsburger F, Majtan T, Szabo C. Cystathionine-β-synthase: molecular regulation and pharmacological inhibition. Biomolecules 2020;10(5):697. [CrossRef]
- Rahman NSA, Zahari S, Syafruddin SE, Firdaus-Raih M, Low TY, Mohtar MA. Functions and mechanisms of protein disulfide isomerase family in cancer emergence. Cell Biosci 2022;12(1):129. [CrossRef]
- Yang M, Chiu J, Scartelli C, Ponzar N, Patel S, Patel A, Ferreira RB, Keyes RF, Carroll KS, Pozzi N, Hogg PJ, Smith BC, Flaumenhaft R. Sulfenylation links oxidative stress to protein disulfide isomerase oxidase activity and thrombus formation. J Thromb Haemost 2023;21(8):2137–2150. [CrossRef]
- De Meyts P, Sajid W, Palsgaard J, Theede AM, Gauguin L, Aladdin H, Whittaker J. Insulin and IGF-I receptor structure and binding mechanism. Madame Curie Biosci Database 2013;NBK6192.
- Wilden PA, Siddle K, Haring E, Backer JM, White MF, Kahn CR. The role of insulin receptor kinase domain autophosphorylation in receptor-mediated activities. Analysis with insulin and anti-receptor antibodies. J Biol Chem 1992;267(19):13719–13727.
- Martínez Báez A, Ayala G, Pedroza-Saavedra A, González-Sánchez HM, Chihu Amparan L. Phosphorylation codes in IRS-1 and IRS-2 are associated with the activation/inhibition of insulin canonical signaling pathways. Curr Issues Mol Biol 2024;46(1):634–649. [CrossRef]
- Liu P, Cheng H, Roberts TM, Zhao JJ. Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2009;8(8):627–644. [CrossRef]
- Wang Q, Somwar R, Bilan PJ, Liu Z, Jin J, Woodgett JR, Klip A. Protein kinase B/Akt participates in GLUT4 translocation by insulin in L6 myoblasts. Mol Cell Biol 1999;19(6):4008–4018. [CrossRef]
- Ahn SW, Gang GT, Tadi S, Nedumaran B, Kim YD, Park JH, Kweon GR, Koo SH, Lee K, Ahn RS, Yim YH, Lee CH, Harris RA, Choi HS. Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and glucose-6-phosphatase are required for steroidogenesis in testicular Leydig cells. J Biol Chem 2012;287(50):41875–41887. [CrossRef]
- Zhao X, An X, Yang C, Sun W, Ji H, Lian F. The crucial role and mechanism of insulin resistance in metabolic disease. Front Endocrinol 2023;14:1149239. [CrossRef]
- Szablewski L. Changes in cells associated with insulin resistance. Int J Mol Sci 2024;25(4):2397. [CrossRef]
- Cao R, Tian H, Zhang Y, Liu G, Wang H, Dong W, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Zhao J. Signaling pathways and intervention for therapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus. MedComm 2023;4:e283. [CrossRef]
- Zhang H, Huang Y, Chen S, Tang C, Wang G, Du J, Jin H. Hydrogen sulfide regulates insulin secretion and insulin resistance in diabetes mellitus, a new promising target for diabetes mellitus treatment? A review. J Adv Res 2020;27:19–30. [CrossRef]
- Paul BD, Sbodio JI, Snyder SH. Cysteine metabolism in neuronal redox homeostasis. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2018;39(5):513–524. [CrossRef]
- Negm A, Mersal EA, Dawood AF, Abd El-Azim AO, Hasan O, Alaqidi R, Alotaibi A, Alshahrani M, Alheraiz A, Shawky TM. Multifaceted cardioprotective potential of reduced glutathione against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via modulating inflammation–oxidative stress axis. Int J Mol Sci 2025;26(7):3201. [CrossRef]
- Guo Q, Jin Y, Chen X, Ye G, Zhao L, Hou X, Liu Z, Bao T, Yang F, Liu Z, Zhang S, Fan X, Wang W. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: new insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2024;9:53. [CrossRef]
- Li R, Yan X, Zhao Y, Liu H, Wang J, Yuan Y, Li Q, Su J. Oxidative stress induced by nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) dysfunction aggravates chronic inflammation through the NAD+/SIRT3 axis and promotes renal injury in diabetes. Antioxidants 2025;14(3):267. [CrossRef]
- Rui L, Aguirre V, Kim JK, Shulman GI, Lee A, Corbould A, Dunaif A, White MF. Insulin/IGF-1 and TNF-alpha stimulate phosphorylation of IRS-1 at inhibitory Ser307 via distinct pathways. J Clin Invest 2001;107(2):181–189. [CrossRef]
- Bloch-Damti A, Potashnik R, Gual P, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Tanti JF, Rudich A, Bashan N. Differential effects of IRS1 phosphorylated on Ser307 or Ser632 in the induction of insulin resistance by oxidative stress. Diabetologia 2006;49(10):2463–2473. [CrossRef]
- Yadav PK, Vitvitsky V, Carballal S, Seravalli J, Banerjee R. Thioredoxin regulates human mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase at physiologically-relevant concentrations. J Biol Chem 2020;295(19):6299–6311. [CrossRef]
- Yang B, Lin Y, Huang Y, Shen YQ, Chen Q. Thioredoxin (Trx): a redox target and modulator of cellular senescence and aging-related diseases. Redox Biol 2024;70:103032. [CrossRef]
- Velloso LA, Folli F, Saad MJ. TLR4 at the crossroads of nutrients, gut microbiota, and metabolic inflammation. Endocr Rev 2015;36(3):245–271. [CrossRef]
- Hassan I, Gaines KS, Hottel WJ, Wishy RM, Miller SE, Powers LS, Rutkowski DT, Monick MM. Inositol-requiring enzyme 1 inhibits respiratory syncytial virus replication. J Biol Chem 2014;289(11):7537–7546. [CrossRef]
- Hetz C, Zhang K, Kaufman RJ. Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2020;21(8):421–438. [CrossRef]
- He Z, Liu Q, Wang Y, Zhao B, Zhang L, Yang X, Wang Z. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in type 2 diabetes mellitus mechanisms and impact on islet function. PeerJ 2025;13:e19192. [CrossRef]
- Watt NT, McGrane A, Roberts LD. Linking the unfolded protein response to bioactive lipid metabolism and signalling in the cell non-autonomous extracellular communication of ER stress. BioEssays 2023;45:e2300029. [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee A, Morales-Scheihing D, Butler PC, Soto C. Type 2 diabetes as a protein misfolding disease. Trends Mol Med 2015;21(7):439–449. [CrossRef]
- Vilas-Boas EA, Almeida DC, Roma LP, Ortis F, Carpinelli AR. Lipotoxicity and β-cell failure in type 2 diabetes: oxidative stress linked to NADPH oxidase and ER stress. Cells 2021;10(12):3328. [CrossRef]
- Takeda H, Murakami S, Liu Z, Sawa T, Takahashi M, Izumi Y, Bamba T, Sato H, Akaike T, Sekine H, Motohashi H. Sulfur metabolic response in macrophage limits excessive inflammatory response by creating a negative feedback loop. Redox Biol 2023;65:102834. [CrossRef]
- Chiang FF, Chao TH, Huang SC, Cheng CH, Tseng YY, Huang YC. Cysteine regulates oxidative stress and glutathione-related antioxidative capacity before and after colorectal tumor resection. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23(17):9581. [CrossRef]
- Mowla SN, Perkins ND, Jat PS. Friend or foe: emerging role of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells in cell senescence. OncoTargets Ther 2013;6:1221–1229. [CrossRef]
- Termite F, Archilei S, D’Ambrosio F, Petrucci L, Viceconti N, Iaccarino R, Liguori A, Gasbarrini A, Miele L. Gut microbiota at the crossroad of hepatic oxidative stress and MASLD. Antioxidants 2025;14(1):56. [CrossRef]
- Guijarro-Muñoz I, Compte M, Álvarez-Cienfuegos A, Álvarez-Vallina L, Sanz L. Lipopolysaccharide activates Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway and proinflammatory response in human pericytes. J Biol Chem 2014;289(4):2457–2468. [CrossRef]
- Sen U, Givvimani S, Abe OA, Lederer ED, Tyagi SC. Cystathionine β-synthase and cystathionine γ-lyase double gene transfer ameliorate homocysteine-mediated mesangial inflammation through hydrogen sulfide generation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2011;300(1):C155–C163. [CrossRef]
- Zavala-Valencia AC, Velasco-Hidalgo L, Martínez-Avalos A, Castillejos-López M, Torres-Espíndola LM. Effect of N-acetylcysteine on cisplatin toxicity: a review of the literature. Biologics 2024;18:7–19. [CrossRef]
- Lu SC. Glutathione synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013;1830(5):3143–3153. [CrossRef]
- Atkuri KR, Mantovani JJ, Herzenberg LA, Herzenberg LA. N-Acetylcysteine—a safe antidote for cysteine/glutathione deficiency. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2007;7(4):355–359. [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Banaclocha M. N-Acetyl-cysteine: modulating the cysteine redox proteome in neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants 2022;11(2):416. [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto S, Gon Y, Matsumoto K, Takeshita I, Horie T. N-acetylcysteine attenuates TNF-alpha-induced p38 MAP kinase activation and p38 MAP kinase-mediated IL-8 production by human pulmonary vascular endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol 2001;132(1):270–276. [CrossRef]
- Lee YH, Giraud J, Davis RJ, White MF. c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) mediates feedback inhibition of the insulin signaling cascade. J Biol Chem 2003;278(5):2896–2902. [CrossRef]
- Sampson SR, Cooper DR. Specific protein kinase C isoforms as transducers and modulators of insulin signaling. Mol Genet Metab 2006;89(1-2):32–47. [CrossRef]
- Abdelbagi O, Taha M, Al-Kushi AG, Alobaidy MA, Baokbah TAS, Sembawa HA, Azher ZA, Obaid R, Babateen O, Bokhari BT, Qusty NF, Malak HA. Ameliorative effect of N-acetylcysteine against 5-fluorouracil-induced cardiotoxicity via targeting TLR4/NF-κB and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. Medicina 2025;61(2):335. [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Li C, Peng M, Wang L, Zhao D, Wu T, Yi D, Hou Y, Wu G. N-Acetylcysteine improves intestinal function and attenuates intestinal autophagy in piglets challenged with β-conglycinin. Sci Rep 2021;11(1):1261. [CrossRef]
- Ciesielska A, Matyjek M, Kwiatkowska K. TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci 2021;78(4):1233–1261. [CrossRef]
- Kawiak A, Kostecka A. Regulation of Bcl-2 family proteins in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer and their implications in endocrine therapy. Cancers 2022;14(2):279. [CrossRef]
- Butawan M, Benjamin RL, Bloomer RJ. Methylsulfonylmethane: applications and safety of a novel dietary supplement. Nutrients 2017;9(3):290. [CrossRef]
- du Preez HN, Aldous C, Kruger HG, Johnson L. N-Acetylcysteine and other sulfur-donors as a preventative and adjunct therapy for COVID-19. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci 2022;2022:4555490. [CrossRef]
- Sekhar RV, McKay SV, Patel SG, Guthikonda AP, Reddy VT, Balasubramanyam A, Jahoor F. Glutathione synthesis is diminished in patients with uncontrolled diabetes and restored by dietary supplementation with cysteine and glycine. Diabetes Care 2011;34(1):162–167. [CrossRef]
- Jain S, Micinski D, Huning L, Quinn J, Dupre J, Storey KB. Vitamin D and L-cysteine levels correlate positively with GSH and negatively with insulin resistance levels in the blood of type 2 diabetic patients. Eur J Clin Nutr 2014;68(10):1148–1153. [CrossRef]
- Lutchmansingh FK, Hsu JW, Bennett FI, Badaloo AV, McFarlane-Anderson N, Gordon-Strachan GM, Wright-Pascoe RA, Jahoor F, Boyne MS. Glutathione metabolism in type 2 diabetes and its relationship with microvascular complications and glycemia. PLoS One 2018;13(6):e0198626. [CrossRef]
- Kalamkar S, Acharya J, Kolappurath Madathil A, Gajjar V, Divate U, Karandikar-Iyer S, Ghaskadbi S, Goel P. Randomized clinical trial of how long-term glutathione supplementation offers protection from oxidative damage and improves HbA1c in elderly type 2 diabetic patients. Antioxidants 2022;11(5):1026. [CrossRef]
- Tuell D, Ford G, Los E, Stone W. The role of glutathione and its precursors in type 2 diabetes. Antioxidants 2024;13(2):184. [CrossRef]
- Gawlik K, Naskalski JW, Fedak D, Pawlica-Gosiewska D, Grudzień U, Dumnicka P, Małecki MT, Solnica B. Markers of antioxidant defense in patients with type 2 diabetes. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016;2016:2352361. [CrossRef]
- van Lierop B, Ong SC, Belgi A, Delaine C, Andrikopoulos S, Haworth NL, Menting JG, Lawrence MC, Forbes BE, Wade JD. Insulin in motion: the A6-A11 disulfide bond allosterically modulates structural transitions required for insulin activity. Sci Rep 2017;7:17239. [CrossRef]
- Vinther TN, Pettersson I, Huus K, Schlein M, Steensgaard DB, Sørensen A, Jensen KJ, Kjeldsen T, Hubálek F. Additional disulfide bonds in insulin: prediction, recombinant expression, receptor binding affinity, and stability. Protein Sci 2015;24(5):779–788. [CrossRef]
- Jarosinski MA, Dhayalan B, Chen YS, Chatterjee D, Varas N, Weiss MA. Structural principles of insulin formulation and analog design: a century of innovation. Mol Metab 2021;52:101325. [CrossRef]
- Chang SG, Choi KD, Jang SH, Shin HC. Role of disulfide bonds in the structure and activity of human insulin. Mol Cells 2003;16(3):323–330. [CrossRef]
- Ong SC, Belgi A, van Lierop B, Delaine C, Andrikopoulos S, MacRaild CA, Norton RS, Haworth NL, Robinson AJ, Forbes BE. Probing the correlation between insulin activity and structural stability through introduction of the rigid A6–A11 bond. J Biol Chem 2018;293(30):11928–11943. [CrossRef]
- Hubálek F, Cramer CN, Helleberg H, Johansson E, Nishimura E, Schluckebier G, Steensgaard DB, Sturis J, Kjeldsen TB. Enhanced disulphide bond stability contributes to the once-weekly profile of insulin icodec. Nat Commun 2024;15(1):6124. [CrossRef]
- Zheng N, Karra P, VandenBerg MA, Kim JH, Webber MJ, Holland WL, Chou DH. Synthesis and characterization of an A6-A11 methylene thioacetal human insulin analogue with enhanced stability. J Med Chem 2019;62(24):11437–11443. [CrossRef]
- Weil-Ktorza O, Rege N, Lansky S, Shalev DE, Shoham G, Weiss MA, Metanis N. Substitution of an internal disulfide bridge with a diselenide enhances both foldability and stability of human insulin. Chem Eur J 2019;25(36):8513–8521. [CrossRef]
- Yoshinaga T, Nakatome K, Nozaki J, Naitoh M, Hoseki J, Kubota H, Nagata K, Koizumi A. Proinsulin lacking the A7-B7 disulfide bond, Ins2Akita, tends to aggregate due to the exposed hydrophobic surface. Biol Chem 2005;386(11):1077–1085. [CrossRef]
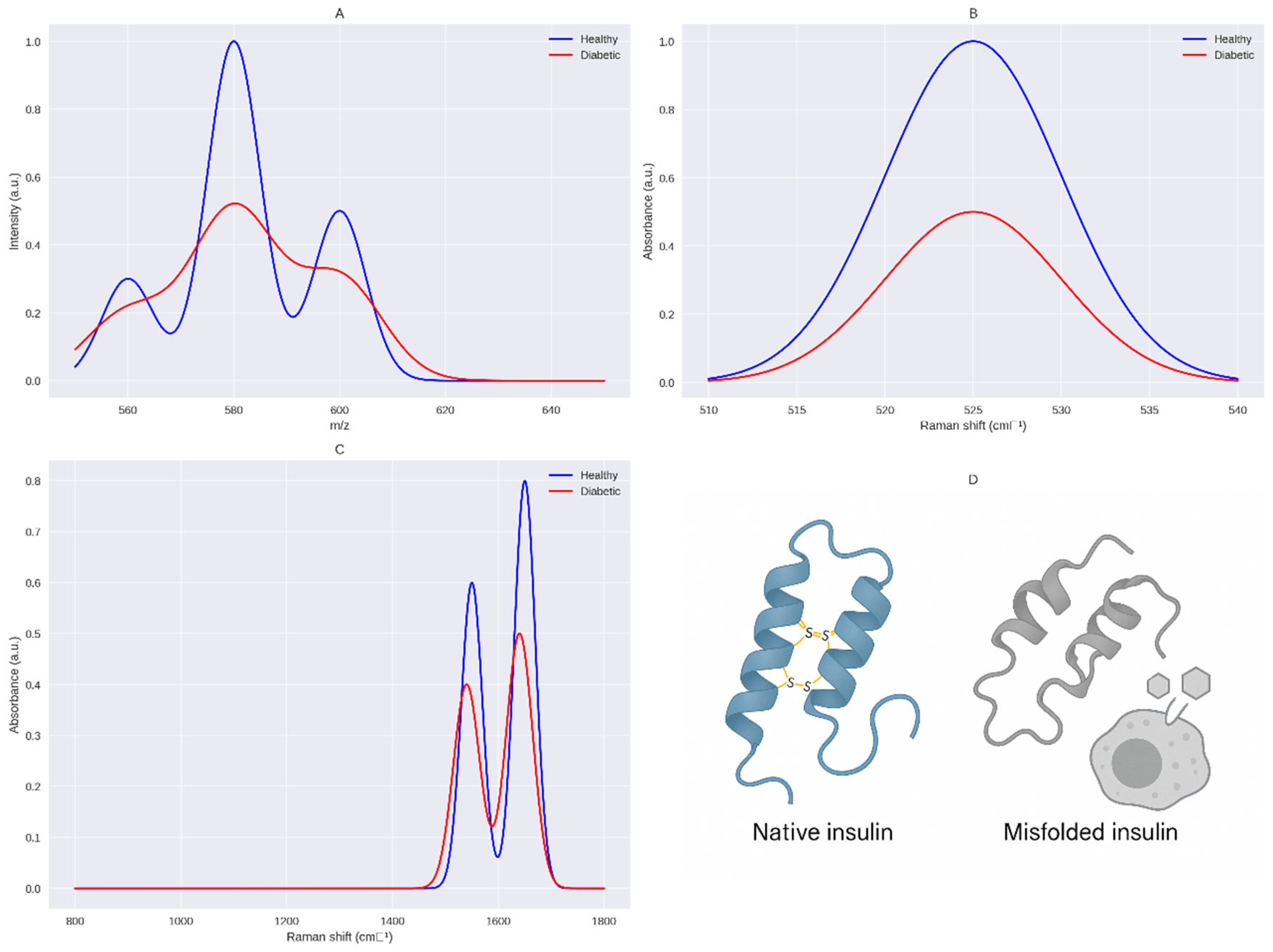
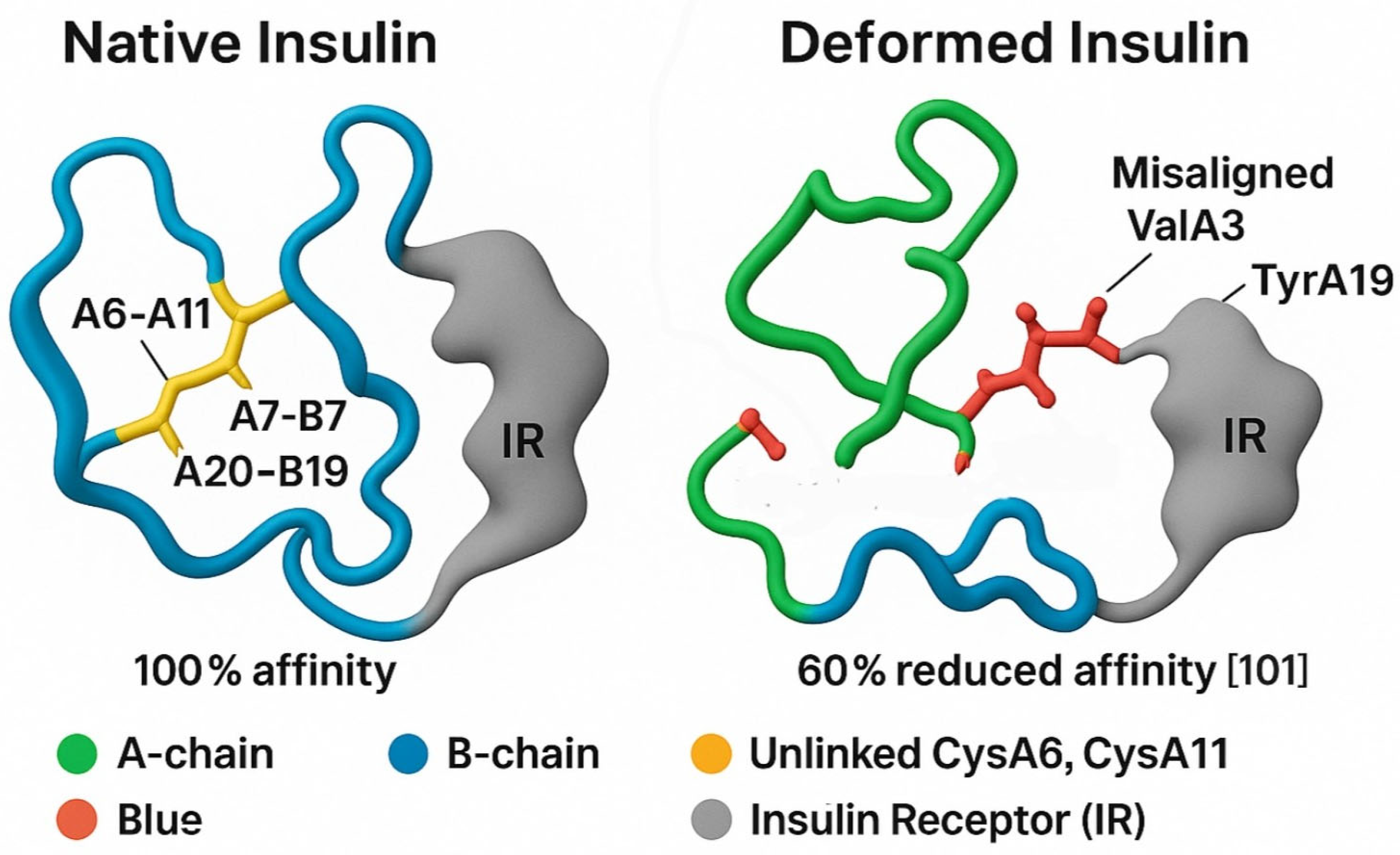
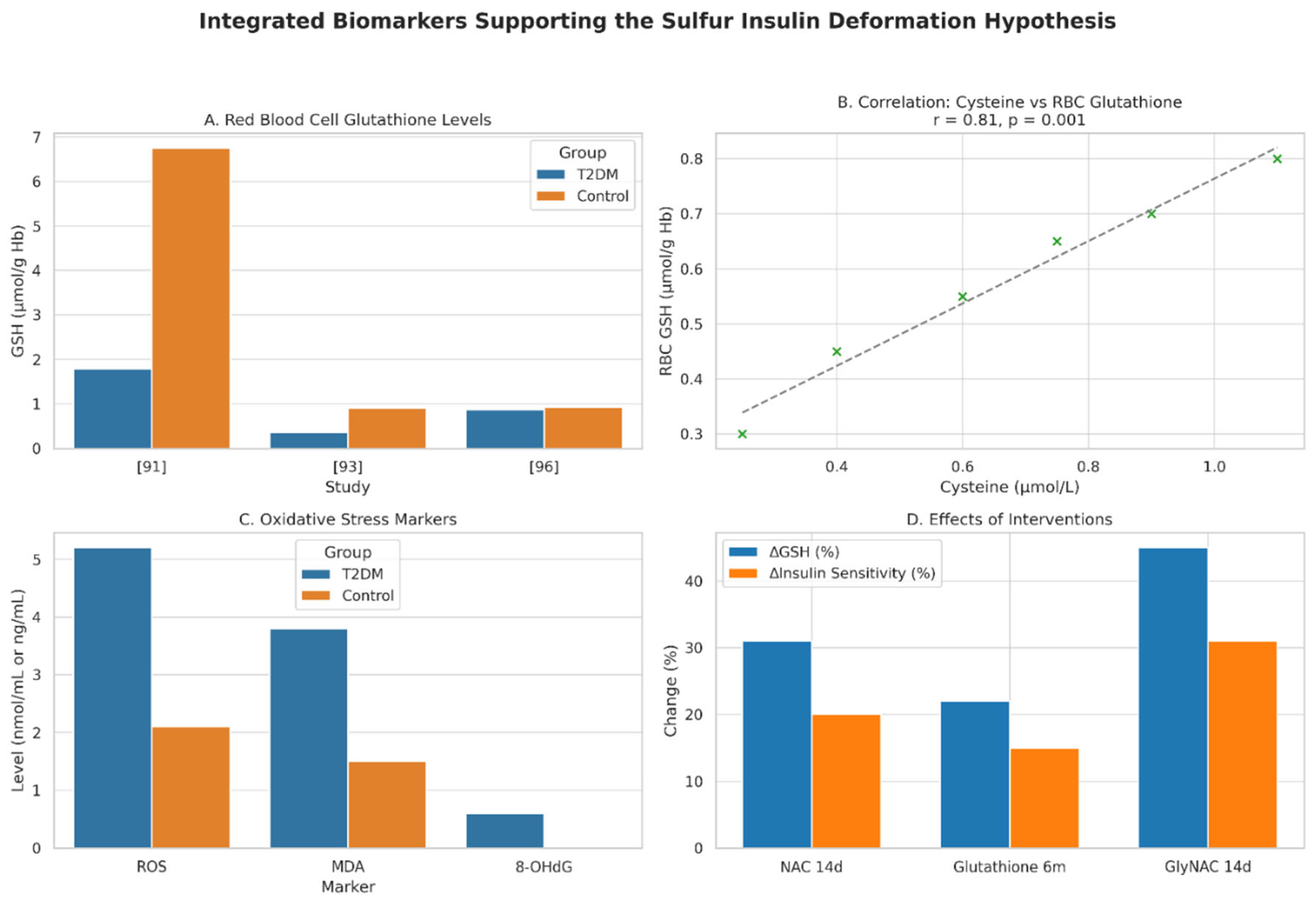
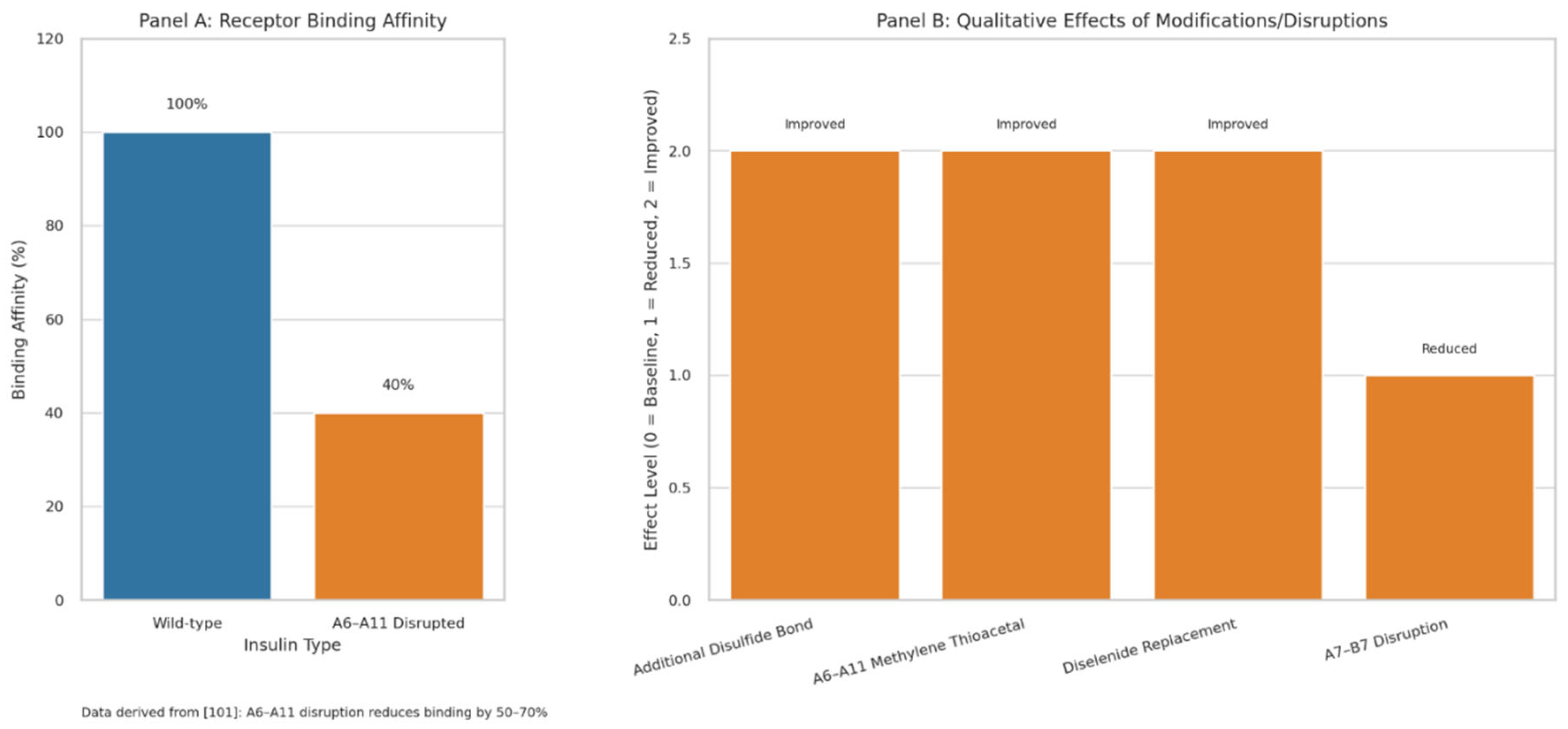
| Comparative Dimension | Traditional Paradigm of T2DM | Sulfur-Dependent Misfolding Hypothesis |
| Root Cause | Peripheral insulin resistance driven by obesity, lipotoxicity, and inflammation. | Structural misfolding of insulin due to disulfide bond disruption caused by organic sulfur deficiency. |
| Initiation Site | Skeletal muscle, liver, and adipose tissue. | Mitochondrial dysfunction in intestinal epithelial cells impairing sulfur metabolism. |
| Pathophysiological Focus | Post-receptor signaling defects (IRS, PI3K, Akt). | Primary insulin deformation with reduced receptor affinity due to disrupted disulfide bonds. |
| Explanation of Hyperinsulinemia + Hyperglycemia Paradox | Compensatory hypersecretion due to peripheral resistance. | Endogenous insulin is misfolded and non-functional; exogenous insulin remains effective due to intact structure. |
| Immunological Mechanism | Chronic inflammation from adipose tissue and macrophage activation. | Glutathione depletion induces NF-κB and JNK pathways via oxidative stress and endotoxemia. |
| Role of the Gut | Secondary influence via microbiome and inflammation. | Primary site of dysfunction initiating mitochondrial suffocation, impaired sulfur metabolism, and mucosal barrier breakdown. |
| Insulin Signaling Defect | Impaired receptor signaling due to inflammation and phosphorylation of IRS. | Insulin fails to initiate signaling due to misfolded structure with up to 70% loss in receptor affinity. |
| Therapeutic Strategy | Blood glucose control via metformin, GLP-1 agonists, or exogenous insulin. | Sulfur restoration through NAC, MSM, and dietary methionine/cysteine to stabilize insulin structure. |
| Experimental Accessibility | HOMA-IR index and indirect measures of resistance. | Direct structural assessment of insulin via LC-MS/MS and Raman spectroscopy. |
| Biochemical Depth | Focuses downstream of the insulin receptor. | Traces the issue upstream to insulin biosynthesis and protein folding integrity. |
| Innovation Potential | Incremental improvements to a saturated model. | A paradigm shift introducing sulfur metabolism as a central therapeutic and diagnostic axis. |
| Philosophical Reframing | The body becomes resistant to insulin. | The body produces dysfunctional insulin; the issue lies at the source. |
| Potentially paradigm-shifting | Unlikely due to conceptual saturation. | Potentially transformative discovery redefining T2DM pathogenesis and therapy. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





