1. Introduction
Orofacial clefts (OFCs) are the most prevalent craniofacial anomalies globally, characterized by complex genetic and environmental interactions as risk factors. The formation of craniofacial structures involves complex molecular pathways, including bone morphogenetic proteins, sonic hedgehog, and wingless-related integration sites [
1]. Numerous genes have been identified in etiologic studies on OFCs. These include
IRF6,
TBX22,
MAFB,
ARHGAP29,
VAX1, and
PAX7, highlighting the genetic complexity associated with these conditions [
2]. The classification of OFCs includes various presentations, primarily comprising isolated cleft lip (CL), isolated cleft palate (CP), or their combinations [
3]. These abnormalities may manifest unilaterally or bilaterally and can arise as isolated defects (non-syndromic) or as components of wider syndromes. Syndromic types encompass well-documented diseases such as Pierre Robin Sequence, Trisomy 13, Trisomy 18, Apert Syndrome, Stickler Syndrome, and Waardenburg Syndrome [4,5].
Global epidemiological data indicate that OFCs occur in 1 to 2.2 per 1,000 births [
6]. The incidence exhibits considerable diversity among many people, affected by genetic factors and environmental exposures. Environmental risk factors encompass maternal exposure to teratogens, infections, pharmaceuticals, tobacco use, alcohol intake, radiation, and nutritional deficiencies, especially folate deficiency [
3]. Environmental factors interact with genetic predispositions, resulting in differing severities of facial developmental anomalies. Research indicates that newborns with OFCs frequently encounter difficulty in sucking and swallowing, as well as challenges with speech development and social interaction [
7]. Dental growth is often impaired, with delays in tooth eruption usually noted in these patients [
8].
Despite the surgical treatment of OFCs, patients in sub-Saharan Africa consume a range of medications, including analgesics, antimalarials, antibacterials, and antiretrovirals; which may culminate in adverse drug reactions (ADRs) due to the generation of reactive metabolites during drug biotransformation. Drug biotransformation occurs in various phases. Phase I reactions primarily involving cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver. These enzymes enable the integration of polar structures by oxidation, reduction, and hydrolysis of pharmaceutical substances [
9]. Phase II activities encompass many transferase enzymes that conjugate modified pharmaceuticals to improve their aqueous solubility and promote excretion [
10]. Cytochrome P450 enzymes are pivotal in drug metabolism, accounting for over 75% of enzymatic drug metabolism activities [
14]. The CYP superfamily comprises several significant enzymes, including CYP1A2, CYP2C18, CYP27A1, and CYP2B6; each characterized by unique substrate specificities and regulatory mechanisms [
15]. Moreover, drug transporters such as SLC6A2 and ABCC3 are essential for the distribution and removal of drugs.
Pharmacogenomics holds substantial importance in clinical practice, explaining more than 80% of the diversity in pharmacological effectiveness and safety profiles [
11]. Genetic polymorphisms can markedly affect pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, resulting in various metabolizer phenotypes: extensive metabolizers (EM), ultra-rapid metabolizers (UM), intermediate metabolizers (IM), and poor metabolizers (PM) [
12]. ADRs constitute a significant healthcare issue in Sub-Saharan Africa, especially in Ghana and Nigeria. From 2000 to 2012, Ghana recorded 343 ADRs in children aged 0 to 17 years, leading to 23 fatalities. Whereas Nigeria reported 473 cases with 21 deaths [
13]. These figures underscore the pressing necessity for extensive pharmacogenomic research in African populations, particularly among families impacted by OFCs.
This study aimed to discover and characterize genetic variations in drug-metabolizing and drug-transporting genes in Ghanaian and Nigerian families affected by OFCs. We employed an integrated methodology combining whole genome sequencing (WGS), protein structure modeling and molecular docking to assess the structural and functional effects of the variants. This study enhances our understanding of pharmacogenetic diversity in Sub-Saharan African populations and holds significant implications for personalizing pharmacological therapy in patients with OFCs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
This cross-sectional study investigated variations in drug metabolism and transporting genes across families impacted by OFCs. We recruited 130 case parent trios (104 from Ghana and 26 from Nigeria) from the Komfo Anokye Teaching Hospital (Ghana), Lagos University Teaching Hospital, and Obafemi Awolowo University Teaching Hospital (Nigeria). The sample included 51 cases of cleft lip and 79 cases of cleft lip and palate.
2.2. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
Saliva samples were obtained from parents and probands using Oragene Saliva Kits (DNA GenoTek, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada). Cheek swab samples were obtained from younger probands employing cotton swabs. DNA extraction followed the Oragene Saliva Protocol, with DNA quantified using the Qubit 4 Fluorometer (
http://www.invitrogen.com/site/us/en/home/brands/Product-Brand/Qubit.html; ThermoFisher Scientific, Grand Island, NY). As a quality control step, the sexes of participants were verified through TaqMan XY genotyping. The detailed protocols have been published elsewhere [
16].
2.3. Whole Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
The protocols for WGS, quality control checks and bioinformatics analysis have been published elsewhere [
16], but a summary is given here. DNA samples that met quality control standards were sequenced at the Broad Institute through the Gabriella Miller Kids First Paediatric Research Consortium (
https://kidsfirstdrc.org/). The WGS was conducted at the Broad Institute with the entire genome sequenced at an average read depth of 30 (30X). Sequence alignment map (SAM) files were obtained after the sequence data were aligned to the Human genome assembly GRCh38 (hg38) and converted them into binary alignment map (BAM) file format. Alternate alleles (i.e., variants from the reference genome), were called using the GenomeAnalysisToolKit (GATK) pipelines by the Broad Institute (
https://software.broadinstitute.org/gatk/best-practices/workflow). Briefly, single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and insertions or deletions (Indels) were called using the HaplotypeCaller in GVCF mode for single-sample variant calling and in GenotypeGVCFs for the multiple-sample joint variant calling. Variants were stored in a variant call format (VCF) file, which was used for further analyses. Quality control of VCF files has been published [
16]. We filtered for variants with minor allele frequency (MAF <1%) using databases including the 1000 Genomes Project, Exome Variant Server, dbSNP and gnomAD [
17].
2.4. Selection of Genes
We focused on 50 clinically relevant pharmacogenes for Africans (Supplemental
Table S1), including
CYP2A6,
CYP2B6,
CYP2C8,
CYP2C9,
CYP2C19,
CYP2D6,
CYP3A4,
CYP3A5,
NAT,
UGT,
ABC, and
SLC families. These genes were selected based on their classification as Very Important Pharmacogenes by PharmGKB [
18] and their documented genetic variability in African populations [
19].
2.5. Variant Classification and Structural Analysis
Variants were classified according to American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) recommendations [
20], using ClinVar and other eleven variant effect predictive tools embedded in dbNSFP [
21]. Pathogenicity of missense variants were assessed using twelve tools including SIFT, PolyPhen-2, Mutation Taster, Mutation Assessor, MetaRNN, REVEL, MutPred, BayesDel_addAF, ClinPred, CADD, ClinVar, and AlphaMissense. Misssense variants were considered pathogenic if at least six of these tools, in addition to ClinVar, predicted so (
Supplementary Table S2 and
Table S3). Loss-of-function (LOF) variants were evaluated based on CADD and REVEL, whereas SpliceAI was used to evaluate splice site variants. Selected variants were subjected to further investigation using segregation analysis and functional assessment.
The HOPE [
22] analysis toolkit was utilized for
in silico modeling of protein tertiary structure to evaluate how gene variants influence the structure and function of affected proteins. The HOPE methodology begins with inputting the protein sequence in FASTA format or as an accession code through an easy-to-use web interface. A BLAST analysis is then conducted to identify similar sequences in the UniProt [
23] database and search for 3D structures or templates in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) for homology modeling. If no direct structure is available, Yasara software [
24] is employed for homology modeling to generate a 3D model automatically. The analysis proceeds with data collection, where structural characteristics such as residue accessibility, secondary structure, and ligand interactions are examined using WHAT IF web services [
25]. Functional information, including active sites, domains, and motifs, is retrieved from UniProt annotations. Additionally, Reprof [
26] predictions are used to provide additional insights into secondary structure and solvent accessibility if necessary. The data gathered is then integrated through a decision tree, which prioritizes the most reliable sources, such as real protein structures, UniProt annotations, and Reprof predictions. This synthesized information is used to generate a report that assesses the impact of the variant on structural contacts, functional regions, post-translational modifications, variations, and amino acid properties. The final output is presented in an accessible and user-friendly format [
22].
Molecular docking simulations were performed using protein structures derived from AlphaFold [
27] and ligands sourced from PubChem [
28]. Protein preparation was performed using Discovery Studio [
29] to ensure structural optimization and minimization. Mutant protein variants were generated using Chimera [
30], utilizing its mutagenesis tools to simulate single nucleotide polymorphisms and assess their structural effects. Ligand libraries were curated and refined in Spartan ‘14 [
31] using its quantum chemical calculation features to optimize molecular geometries and electronic characteristics. Docking simulations were performed globally with PyRx [
32], enabling the screening and ranking of ligands based on their binding affinities to both the wildtype and mutant proteins. The top protein-ligand complexes with the best docking poses were visualized and analyzed using Discovery Studio [
29] and Chimera [
30]. Key structural interactions were identified to offer insights into binding modes and potential functional consequences of the variant.
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Characterization of Pathogenic Variants in Drug-Metabolizing and Drug-Transporting Genes
Our thorough analyses of WGS data from families with OFCs identified several pathogenic variations in genes essential for drug metabolism and transport. Fifty-seven (57) variants in fifty (50) drug-metabolizing and transporting genes were observed (
Table 1, Supplemental
Table S5). The pathogenicity of the variant was meticulously evaluated utilizing twelve prediction tools: SIFT, PolyPhen-2, Mutation Taster, Mutation Assessor, MetaRNN, REVEL, MutPred, BayesDel_addAF, ClinPred, CADD, ClinVar, and AlphaMissense. We established stringent standards whereby missense variants were designated pathogenic only when over five tools consistently predicted so (Supplemental
Table S2). Supplemental
Table 3 outlines the syndromes, metabolic pathways and commonly used drugs or substrates metabolised by the genes with pathogenic variants.
3.2. Structural and Functional Impact Analysis
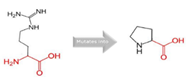
3.2.1. CYP1A2 Variants
In the
CYP1A2 gene, we detected two pathogenic variants (
Table 2): rs45565238 (c.217G>A, p.Gly73Arg) and a novel variant (c.269G>C, p.Arg90Pro). This gene is linked to many diseases, including Porphyria Cutanea Tarda and Hepatocellular Adenoma, exhibiting autosomal dominant inheritance (
Table S4). The comprehensive HOPE analysis (
Table 2) indicated that the p.Gly73Arg mutation in
CYP1A2 considerably affected protein flexibility at a highly conserved site. The mutation introduced a larger, positively charged residue, compromising the protein's structural stability. The p.Arg90Pro variant modified hydrogen bonding patterns and hydrophobicity, presumably influencing substrate identification and binding.
3.2.2. CYP2C18 Variants
Two variants in
CYP2C18 were identified: rs59636573 (c.988G>T, p.Val330Leu) and rs60181876 (c.896C>T, p.Thr299Ile),
Table 1. This gene is associated with Danubian Endemic Familial Nephropathy and Coumarin Resistance, exhibiting an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern (
Table S4). The p.Val330Leu variant caused alterations in secondary structure preferences. However, the projected protein damage was minor. The p.Thr299Ile variant, situated near a highly conserved site, introduced a bigger, more hydrophobic residue, which may influence protein-substrate interactions (
Table 2).
3.2.3. CYP27A1 Variants
In
CYP27A1, we detected rs145722193 (c.1102G>T, p.Val368Leu) and rs151117761 (c.1564G>A, p.Val522Met),
Table 1. This gene is linked to metabolic illnesses, including Xanthomatosis and Lipid Storage Disease, exhibiting autosomal recessive inheritance (
Table S4). The p.Val368Leu and p.Val522Met variants in
CYP27A1 influenced β-strand preferences and introduced larger residues, possibly leading to structural perturbations.
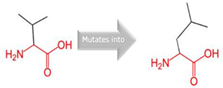
3.2.4. CYP2B6 Variants
The
CYP2B6 gene had two variants: rs764288403 (c.1301G>A, p.Arg434Gln) and rs372295360 (c.293G>A, p.Arg98Gln),
Table 1. This gene has been associated with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome which exhibits X-linked dominant inheritance (
Table S4). The
CYP2B6 variants (p.Arg434Gln and p.Arg98Gln) had substantial impacts on ligand binding and protein stability, with the Arg434Gln variant loss of positive charge disrupting protein electrostatic interaction with negatively charged residue or co-factors (
Table 2).
3.3. Molecular Docking Analysis and Drug-Binding Implications
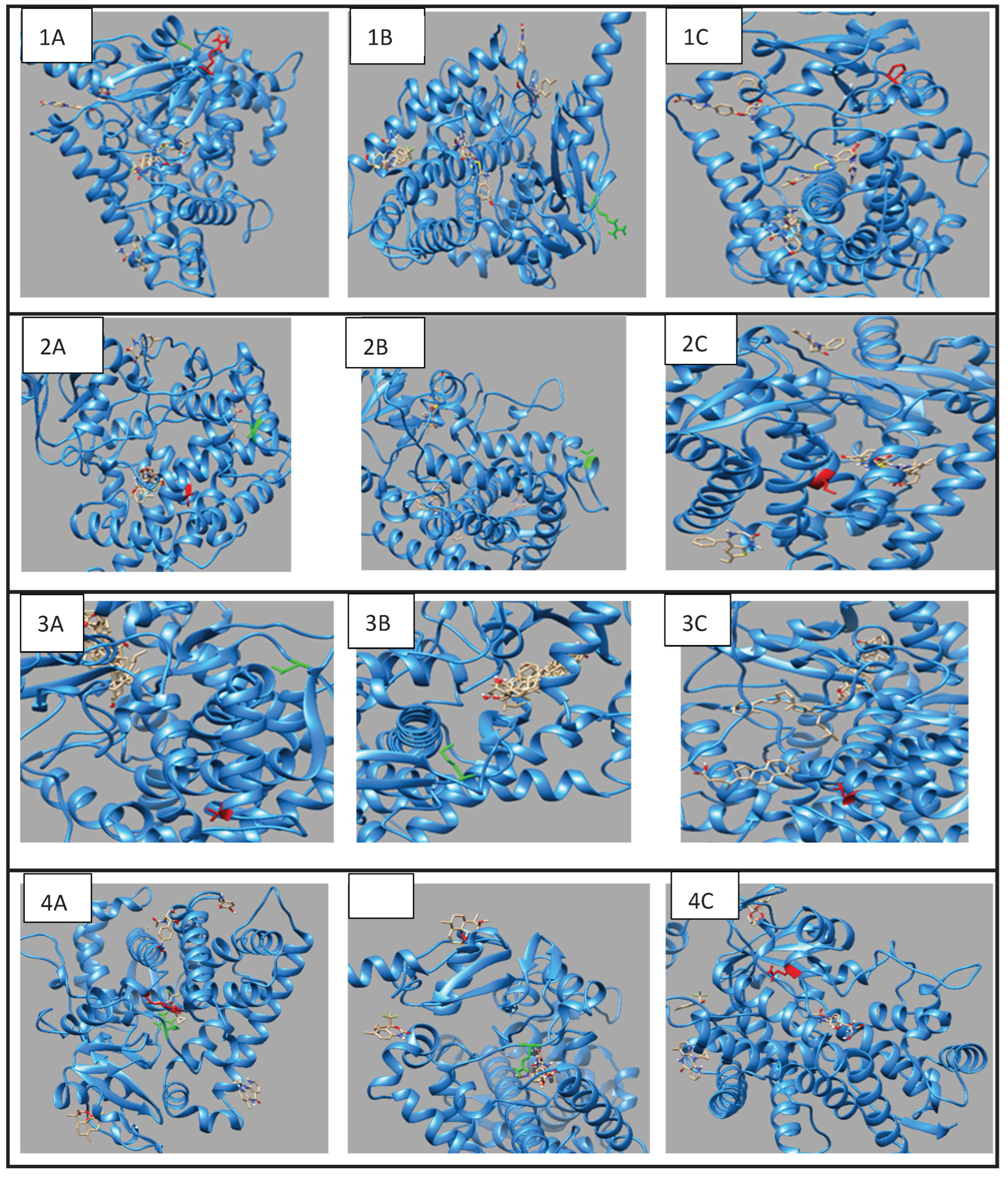
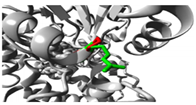
3.3.1. CYP1A2 Drug Interactions
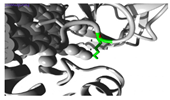
Molecular docking investigations demonstrated substantial alterations in substrate binding (
Figure 1,
Table S6). The wild-type
CYP1A2 exhibited optimal binding with omeprazole (-8.5), but the Gly73Arg mutant had enhanced affinity (-9.0). Both variants exhibited decreased affinity for caffeine (wild-type: -7.2; Gly73Arg: -6.9; Arg90Pro: -6.0) and fluvoxamine (wild-type: -7.7; Gly73Arg: -6.2 and Arg90Pro: -6.0).
3.3.2. CYP2C18 Substrate Binding
The Val330Leu variant showed altered binding patterns with key substrates (
Figure 1,
Table S7). Notable changes included reduced affinity for omeprazole (wild-type: -7.7; Val330Leu: -6.9) and tolbutamide (wild-type: -6.1; Val330Leu: -5.9). The Thr299Ile variant maintained similar binding affinities for most substrates but showed enhanced binding to tolbutamide (-6.9).
3.3.3. CYP27A1 Metabolic Effects
Docking studies demonstrated complex impacts on substrate binding (
Figure 1,
Table S8). The Val368Leu variant exhibited diminished affinity for chenodeoxycholic acid (-7.7 compared to wild-type -8.8) but enhanced affinity for ergocalciferol (-9.9 compared to wild-type -9.6). The Val522Met variant exhibited increased binding affinity to cholecalciferol (-9.4 compared to wild-type -9.1).
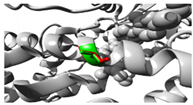
3.3.4. CYP2B6 Metabolic Effects
Docking studies demonstrated distinct impacts on substrate binding (
Figure 1,
Table S9).
CYP2B6 showed significant changes in binding affinities, particularly with efavirenz, where affinity decreased from -8.3 (wild-type) to -7.3 (Arg434Gln) and -7.2 (Arg98Gln), while nevirapine showed improved binding in the Arg98Gln variant (-8.4) compared to wild-type (-6.6).
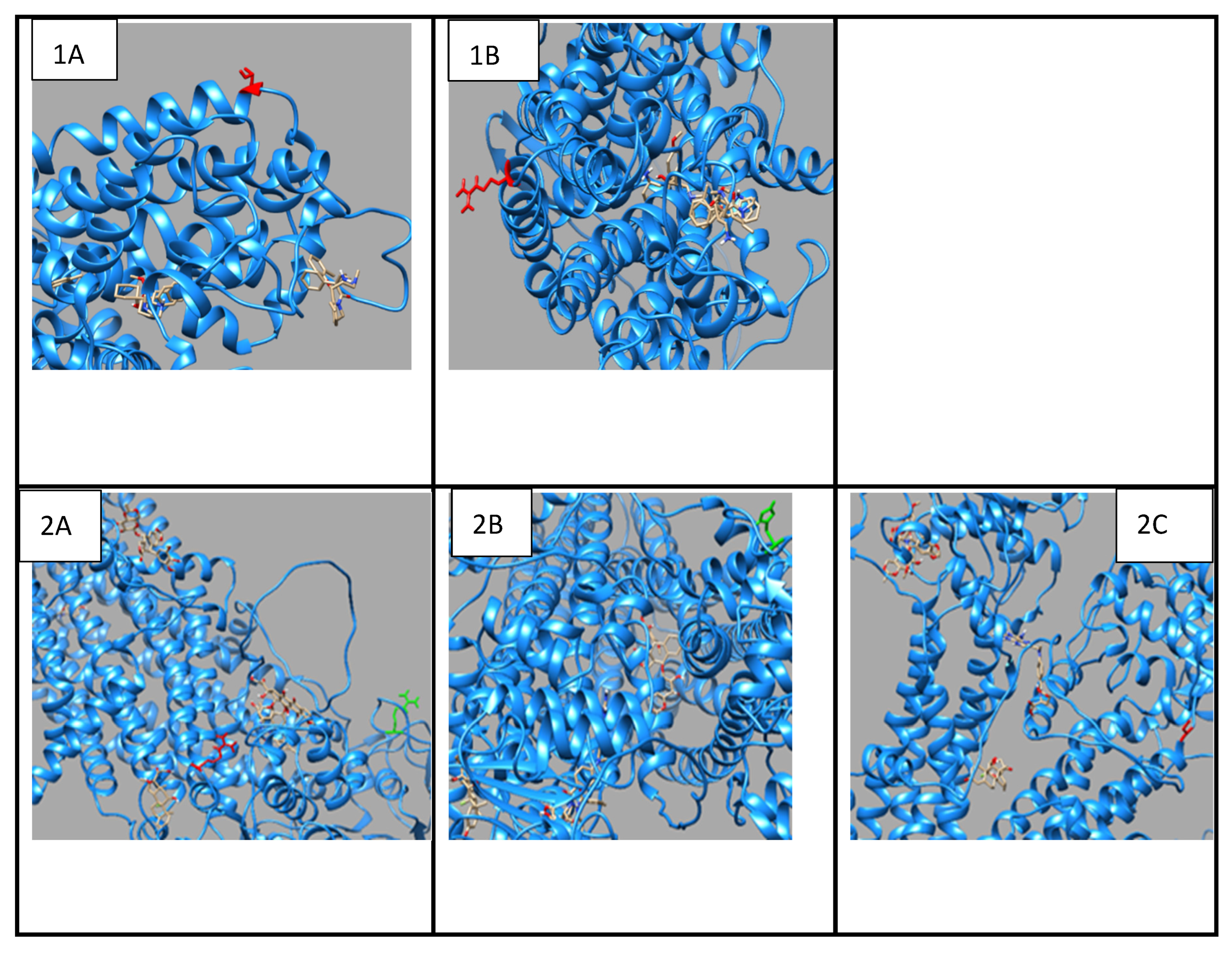
3.4. Drug Transport Gene Variants
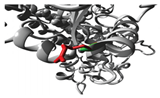
The p.Thr283Arg variant of
SLC6A2 exhibited notably constant binding affinities for inhibitors of neurotransmitter transport, indicating preserved functionality despite the mutation (
Figure 2;
Table S10). Conversely,
ABCC3 variants (
Figure 2,
Table S11), exhibited substrate-specific effects, with the p.Arg1166Cys variant revealing significantly altered binding patterns for different drugs, particularly enhanced affinity for dexamethasone (-8.6 compared to wild-type -8.0) and diminished affinity for methotrexate (-8.4 compared to wild-type -8.9). The findings indicate that genetic differences in drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters might substantially influence drug-protein interactions, potentially impacting therapeutic efficacy and metabolism in persons with OFCs. The noted alterations in binding affinities and protein conformation offer significant insights for personalised medicine strategies for treating patients with these genetic variants.
4. Discussion
The identification and characterization of genetic variants in genes encoding drug-metabolizing enzymes and drug-transporting proteins within Ghanaian and Nigerian families with OFCs provides essential insights into the molecular foundations of pharmacogenetic diversity in Sub-Saharan African populations. Our findings indicate diverse genetic variations that may substantially influence medication metabolism and transport, carrying considerable implications for medical treatments in this population. The
CYP1A2 variants observed in our study can potentially modify drug metabolism patterns. The p.Gly73Arg variant, located adjacent to a highly conserved area, induces structural alterations that our modelling indicates may diminish the protein's catalytic effectiveness. This finding supports earlier research by others [
33], which revealed that mutations closer to conserved areas of
CYP1A2 can substantially influence its metabolic capacity. The p.Arg90Pro variant is an undocumented alteration for which our structural study indicates may significantly affect protein function by altering hydrogen bonding networks and hydrophobicity patterns.
Our findings regarding
CYP2B6 variants are particularly relevant due to the enzyme's function in the metabolism of antiretroviral medicines often used in African populations. The p.Arg434Gln and p.Arg98Gln variants may modify the metabolism of medicines like efavirenz and nevirapine, which are frequently employed in treatments of HIV. These findings expand upon the research conducted by others [
34], who highlighted the significance of
CYP2B6 polymorphisms in the outcomes of antiretroviral therapy. Our molecular docking investigations indicate that these variants may influence drug-binding affinity, possibly requiring dose modifications in afflicted people.
The identified variants in
CYP27A1 are significant due to their possible effects on vitamin D metabolism and cholesterol regulation. The p.Val368Leu and p.Val522Met variants exhibit modified binding affinities for critical substrates, indicating possible implications for endogenous metabolism and pharmacokinetics. These findings strengthen the research conducted by others [
35], which identified the function of CYP27A1 in cholesterol metabolism and vitamin D activation. Variants observed in transport proteins such as
SLC6A2 and
ABCC3 indicate possible effects on medication distribution and cellular efflux. The p.Thr283Arg variant in
SLC6A2 may influence the transport of many medicinal drugs, whereas
ABCC3 mutations may alter the efflux of conjugated drug metabolites. These findings align with the studies conducted elsewhere [
36], which illustrated the significance of these transporters in drug disposal and therapeutic results.
Our structural analyses offer mechanistic insights into the possible impact of these variants on protein function. The identified alterations in amino acid characteristics, protein structure, and ligand interaction indicate various methods by which these variants may affect drug metabolism and transport. These findings expand sequence variation to offer a comprehensive understanding of potential functional implications, facilitating the advancement of more targeted therapeutic strategies. The implications of these findings for therapeutic treatment in Sub-Saharan Africa are substantial. The prevalence of potentially functional variants in essential drug-metabolizing enzymes and drug-transporting proteins indicates the necessity for pharmacogenetic screening prior to starting particular pharmacological therapy, especially for drugs with narrow therapeutic parameters. This method may mitigate the occurrence of ADRs, which is recognised as a major contributor to morbidity in African populations [
37].
The molecular docking analyses provide valuable insights into substrate-specific effects of these variants. The observed changes in binding affinities for common therapeutic agents suggest that certain drugs may require dosage adjustments in individuals carrying these variants. For instance, the altered binding patterns observed with antiepileptic drugs like carbamazepine in
CYP1A2 variants align with clinical observations elsewhere [
38], which reported variable drug responses in populations with similar genetic variations. These findings emphasize the importance of considering genetic variation in drug metabolism when designing treatment protocols for patients with OFCs. Of particular concern is the impact of these variants on commonly prescribed medications in African populations. The reduced binding affinity observed for efavirenz in
CYP2B6 variants supports findings by others [
39], who reported altered drug metabolism in patients with
CYP2B6 polymorphisms. Similarly, the modified interactions between
ABCC3 variants and various substrates, including acetaminophen and methotrexate, suggest potential implications for the safety and efficacy of these widely used medications. These observations are particularly relevant given the findings of a study [
13] that documented significant numbers of ADRs in Ghanaian and Nigerian paediatric populations.
Our findings significantly explain how genetic variants, such as those in CYP1A2, affect drug metabolism, highlighting the complexity of genotype-phenotype relationships. Reduced binding affinities for some ligands suggest a loss-of-function effect, whereas increased affinity for others points to potential gain-of-function scenarios. Such duality emphasizes the importance of comprehensive functional assays to fully characterize the molecular pathological basis of variants of pharmagenomics interest, such as those in CYP1A2.
Identifying novel variants and previously unreported functional impacts highlights the genetic diversity within African populations and underscores the importance of population-specific pharmacogenetic studies. A study [
40] noted that understanding population-specific genetic variation is crucial for developing effective and efficient precision medicine approaches. Our findings contribute to this knowledge base and suggest that current drug dosing guidelines, often developed based on studies in non-African populations, may need revision for optimal application in Sub-Saharan African contexts. The structural changes observed in these proteins also broadly affect our understanding of protein-drug interactions. The detailed characterization of how specific amino acid substitutions affect protein structure and function provides valuable insights for predicting the impacts of other variants in these and related proteins. This knowledge could be particularly valuable for future drug development efforts, as suggested by a study [
15], which emphasized the importance of structural understanding in drug design and optimization.
The study had several limitations that highlight areas for future research and improvement. Firstly, the relatively small cohort of 130 families may limit the generalizability of the findings, necessitating a larger sample size to enhance statistical power and better estimate the prevalence of genetic variants linked to ADRs. In silico modelling techniques, such as HOPE analysis and PyRx docking simulations, were instrumental in predicting structural and functional impacts of genetic variants. However, these tools have inherent limitations. These include reliance on theoretical predictions, exclusion of post-translational modifications, and lack of consideration for complex physiological environments. Additionally, the study concentrated on specific drug-metabolizing and drug-transporting genes, potentially overlooking other relevant genetic factors. Its focus on drugs commonly used in Ghana and Nigeria limits applicability to other healthcare contexts.
5. Conclusion
Our study provides a comprehensive molecular characterization of genetic variants affecting drug metabolism and transport in Ghanaian and Nigerian families with OFCs. The identified structural and functional impacts of these variants have significant implications for drug therapy in this population. These findings support the need for pharmacogenetic screening in clinical practice and suggest opportunities for optimizing drug therapy through genotype-guided dosing approaches. Implementation of these insights could contribute to reduced ADRs and improved therapeutic outcomes in Sub-Saharan African populations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.,
Table S1: Prioritized pharmacogenes for the study;
Table S2: Variant annotation to test deleteriousness of variants using various bioinformatics tools;
Table S3: Range and Predictive threshold of tools for testing variant deleteriousness;
Table S4: Syndromes, metabolic pathways and common substrates associated with genes with pathogenic variants;
Table S5: Other Variants observed in the 50 genes of interest;
Table S6: Binding affinity of ligands to
CYP1A2 wildtype and variants;
Table S7: Binding affinity of
CYP2C18 wildtype and variants to ligands;
Table S8: Binding affinity of
CYP27A1 wildtype and variants to ligands;
Table S9: Binding affinity of
CYP2B6 wildtype and variants to ligands;
Table S10: Binding affinity of
SLC6A2 wildtype and variant to ligands;
Table S11: Binding affinity of
ABCC3 wildtype and variants to ligands.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.P.A., A.B. and L.J.J.G.; methodology, E.P.A., G.O.M., C.O.A., B.T., T.D.B., L.S.B., A.B. and L.J.J.G.; software, G.O.M., C.O.A., B.T., L.S.B., L.J.J.G.; validation, E.P.A., G.O.M., C.O.A., B.T., H.A., A.S.D., S.B.Y., T.D.B., L.S.B., P.D., A.B. and L.J.J.G.; formal analysis, E.P.A., G.O.M., C.O.A., B.T., T.D.B., L.S.B., A.B. and L.J.J.G..; investigation, E.P.A., A.B. and L.J.J.G.; resources, A.B. and L.J.J.G.; data curation, E.P.A., G.O.M., C.O.A., B.T., H.A., A.S.D., S.B.Y., T.D.B., L.S.B., P.D., A.B. and L.J.J.G.; writing—original draft preparation, E.P.A.; writing—review and editing, E.P.A., G.O.M., C.O.A., B.T., H.A., A.S.D., S.B.Y., T.D.B., L.S.B., P.D., A.B. and L.J.J.G.; visualization, E.P.A., G.O.M., C.O.A., B.T., T.D.B., L.S.B., A.B. and L.J.J.G.; supervision, A.B. and L.J.J.G.; project administration, L.J.J.G.; funding acquisition, A.B. and L.J.J.G.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Institutes of Health, K43DE029427 and R01DE028300, and The APC was funded by L.J.J.G.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology (CHRPE/RC/018/130), Lagos University Teaching Hospital (ADM/DCST/HREC/VOL.XV/321), Obafemi Awolowo University Teaching Hospital (ERC/2011/12/01), and the University of Iowa (IRB ID #: 201101720).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are openly available in Gabriella Miller Kids First Pediatric Research program at
https://kidsfirstdrc.org.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the families who participated in the research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ADR |
Adverse drug reaction |
| ACMG |
American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics |
| CL |
Cleft lip |
| CP |
Cleft palate |
| GoF |
Gain-of-function |
| LoF |
Loss-of-function |
| OFC |
Orofacial clefts |
| WGS |
Whole genome sequencing |
References
- Manlove, K.R., Johnson, C.K., Hayes, B.H., 2020. Molecular mechanisms of craniofacial development. Dev. Biol. 460, 132-145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.10.002.
- Khan, N.E., Smith, M.H., Johnson, D.R., 2020. Role of genetic factors in orofacial clefts. Gene 752, 144793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.144793.
- Ghenwa, K., Naji, M.A., Saheb, A., Abdulkhaliq, S.R., 2021. Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors for cleft lip and/or palate in Iraq. BMC Pediatr. 21, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-021-02623-2.
- Lu, X., Chen, Y., Wang, R., 2019. Syndromic forms of orofacial clefts. Clin. Genet. 96, 402-414. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.13675.
- Jackson, R.M., Wilson, K.L., Chen, T.H., 2020. Epidemiology of orofacial clefts: A global perspective. Epidemiol. Rev. 42, 58-71. https://doi.org/10.1093/epirev/mxz017.
- Cladiu, R.T., Thompson, J.K., Richards, M.L., 2018. Orofacial clefts prevalence worldwide. Global Birth Defects J. 3, 77-89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gbdj.2018.03.006.
- Alighieri, D., Martinez, K.L., Singh, P., 2019. Functional challenges in orofacial cleft patients. Oral Health J. 24, 65-72. https://doi.org/10.1097/ohj.2019.24.1.065.
- Van Dyck, E., Roberts, L.M., Chen, K., 2019. Dental anomalies in cleft patients. J. Dent. Res. 98, 855-860. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034519858560.
- Mingzhe, H., Johnson, K.L., Roberts, M.P., 2021. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in clinical practice. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 175, 113-128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2021.01.004.
- Testa, B., Richardson, K.L., Chen, P.R., 2012. Drug biotransformation and conjugation pathways. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 25, 197-224. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx200455m.
- Shoshi, N., Thompson, M.L., Roberts, K.P., 2017. Pharmacogenomics in clinical therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 18, 293-310. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2017.15.
- Zhao, X., Chen, K.L., Thompson, M.R., 2021. Pharmacogenetic variation and drug metabolism. Front. Genet. 12, 637159. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.637159.
- Obebi, M., Thompson, K.L., Richards, M.P., 2015. Adverse drug reactions in pediatric populations. Afr. Pharmacol. J. 9, 240-248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.afjph.2015.08.009.
- Rendic, S., Guengerich, F.P., 2015. Contributions of human cytochrome P450 enzymes to carcinogen metabolism. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 28, 603-616. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00077.
- Manikandan, P., Nagini, S., 2018. Cytochrome P450 structure, function and clinical significance: A review. Curr. Drug Targets 19, 38-54. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389450117666160728142444.
- Awotoye W, Mossey PA, Hetmanski JB, Gowans LJJ, Eshete MA, Adeyemo WL, Alade A, Zeng E, Adamson O, Naicker T, Anand D, Adeleke C, Busch T, Li M, Petrin A, Aregbesola BS, Braimah RO, Oginni FO, Oladele AO, Oladayo A, Kayali S, Olotu J, Hassan M, Pape J, Donkor P, Arthur FKN, Obiri-Yeboah S, Sabbah DK, Agbenorku P, Plange-Rhule G, Oti AA, Gogal RA, Beaty TH, Taub M, Marazita ML, Schnieders MJ, Lachke SA, Adeyemo AA, Murray JC, Butali A. Whole-genome sequencing reveals de-novo mutations associated with nonsyndromic cleft lip/palate. Sci Rep. 2022 July 11;12(1):11743. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15885-1. PMID: 35817949; PMCID: PMC9273634.
-
Anderson, D., & Lassmann, T. (2022). An expanded phenotype centric benchmark of variant prioritization tools. Human Mutation, 43(5), 539–546.
- PharmGKB Knowledgebase.
-
Sistonen, J., Fuselli, S., Bentall, A., Sajantila, A., & Terwilliger, J. D. (2009). CYP2D6 genetic variability and personalized medicine in Africa. Pharmacogenomics, 10(5), 769–780.
-
National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). (n.d.). Gene summaries for CYP450 enzymes and transporters. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
-
Richards, S., Aziz, N., Bale, S., Bick, D., Das, S., Gastier-Foster, J., Grody, W. W., Hegde, M., Lyon, E., Spector, E., Voelkerding, K., Rehm, H. L., & ACMG Laboratory Quality Assurance Committee. (2015). Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genetics in Medicine, 17(5), 405–424.
-
Venselaar, H., Te Beek, T. A., Kuipers, R. K., Hekkelman, M. L., & Vriend, G. (2010). Protein structure analysis of mutations causing inheritable diseases: An e-Science approach with life scientist friendly interfaces. BMC Bioinformatics, 11, 548.
- The UniProt Consortium. (2021). UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Research, 49(D1), D480–D489.
- Krieger, E., & Vriend, G. (2014). YASARA View—molecular graphics for all devices—from smartphones to workstations. Bioinformatics, 30(20), 2981–2982.
- Bordoli, L., Kiefer, F., Arnold, K., Benkert, P., Battey, J., & Schwede, T. (2009). Protein structure homology modeling using SWISS-MODEL workspace. Nature Protocols, 4(1), 1–13.
- Bordoli, L., Kiefer, F., Arnold, K., Benkert, P., Battey, J., & Schwede, T. (2009). Protein structure homology
modeling using SWISS-MODEL workspace. Nature Protocols, 4(1), 1–13.
- AlphaFold Database, EMBL-EBI. (2024). AlphaFold protein structure database. Retrieved from https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk.
-
Kim, S., Chen, J., Cheng, T., et al. (2023). PubChem 2023 update: New tools, improved functionality and enhanced ability to explore chemical space. Nucleic Acids Research, 51(D1), D1373–D1380.
-
Biovia, D. S. (2019). Discovery Studio Visualizer. San Diego, CA: Dassault Systèmes.
-
Pettersen, E. F., Goddard, T. D., Huang, C. C., Couch, G. S., Greenblatt, D. M., Meng, E. C., & Ferrin, T. E. (2004). UCSF Chimera: A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 25(13), 1605–1612.
- Hehre, W.J. and Ohlinger, W.A. (2014) Spartan ’14. Wavefunction, Inc., Irvine.
-
Dallakyan, S., & Olson, A. J. (2015). Small-molecule library screening by docking with PyRx. In S. R. Ahmed (Ed.), Methods in Molecular Biology (Vol. 1263, pp. 243–250). Humana Press.
- Zhou, S.F., Liu, J.P., Chowbay, B., 2009. Clinical pharmacogenetics and potential application in personalized medicine. Curr. Drug Metab. 10, 803-829. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920009789375409.
- Zanger, U.M., Schwab, M., 2018. Cytochrome P450 enzymes in drug metabolism: Regulation of gene expression, enzyme activities, and impact of genetic variation. Pharmacol. Ther. 138, 103-141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.12.001.
- Pikuleva, I.A., 2002. Cholesterol-metabolizing cytochromes P450: Implications for cholesterol lowering. Physiol. Rev. 82, 101-130. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00004.2001.
- van de Steeg, E., Wagenaar, E., van der Kruijssen, C.M., 2009. Role of multidrug resistance protein 3 (MRP3/ABCC3) in hepatobiliary and enteric transport of bile salts. Mol. Pharmacol. 75, 154-160. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.108.051078.
- Adedapo, A.D.A., Adedeji, W.A., Adedapo, I.A., Adedapo, K.S., 2021. Cohort study on adverse drug reactions in adults admitted to the medical wards of a tertiary hospital in Nigeria: Prevalence, incidence, risk factors, and fatality. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 87, 1878-1889. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.14577.
- Pascale, A., Marino, S., Esposito, M., 2019. Liver metabolism: The core of drug biotransformation. J. Hepatic Pharmacol. 16, 45-58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-019-01234-y.
- Ribaudo, H.J., Haas, D.W., Tierney, C., 2010. CYP2B6 genotypes and efavirenz pharmacokinetics. The J. Infect. Dis. 202, 711-720. https://doi.org/10.1086/655827.
- Weinshilboum, R.M., Wang, L., 2017. Pharmacogenomics: Precision medicine and drug response. Mayo Clin. Proc. 92, 1711-1722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2017.09.001.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).