Submitted:
30 June 2025
Posted:
02 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- motor rotational speed 3000 rpm
- circumferential speed 16.6 m/s
- run duration 7 min. 30 s
- maximum load stage 12
- maximum loading torque 535 N·m
- maximum Hertzian stress 2.6 GPa
- initial lubrication oil temperature 90oC (uncontrolled after starting the run)
- type of lubrication dip lubrication (oil quantity ca. 1.5 dm3)
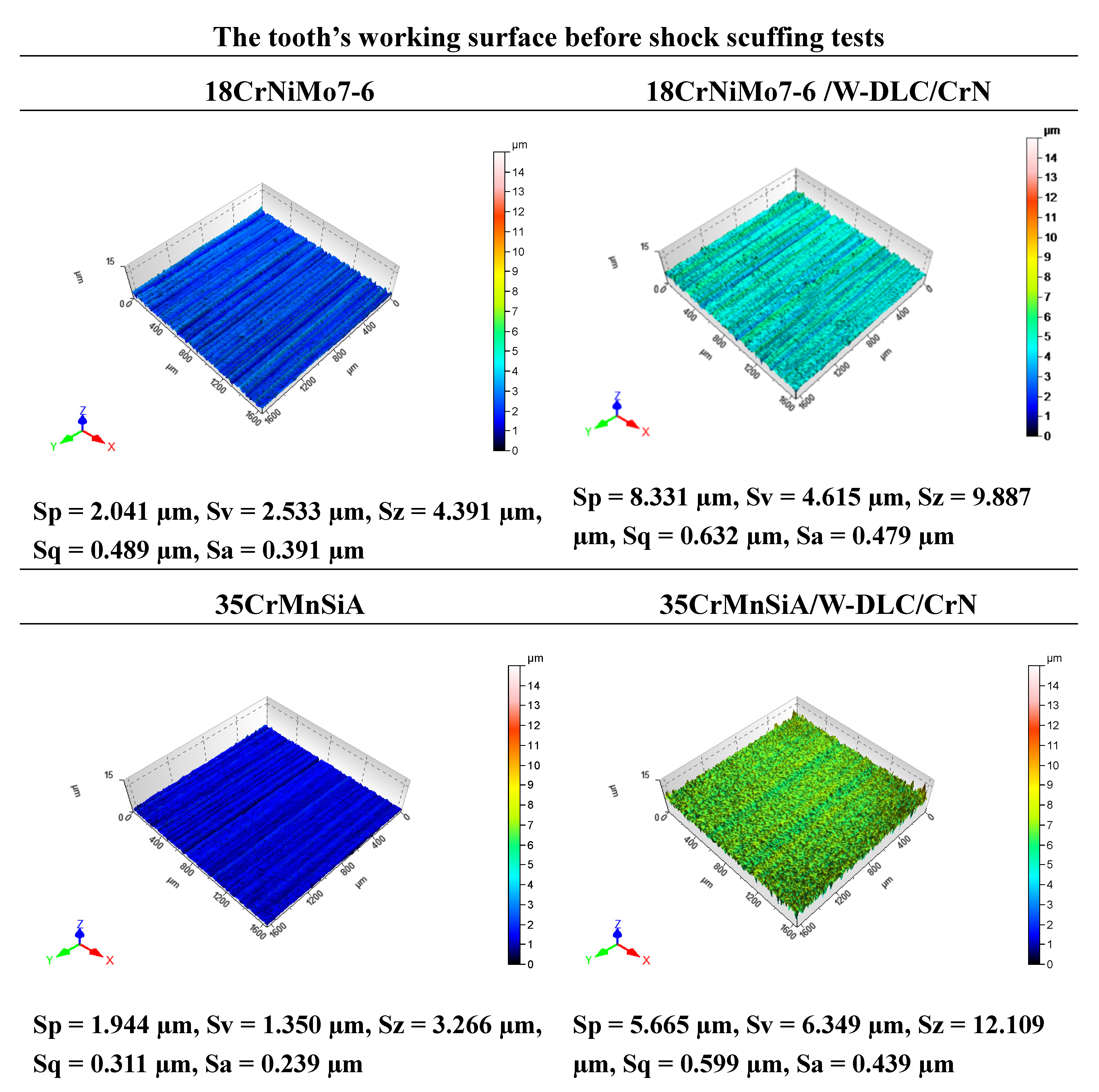
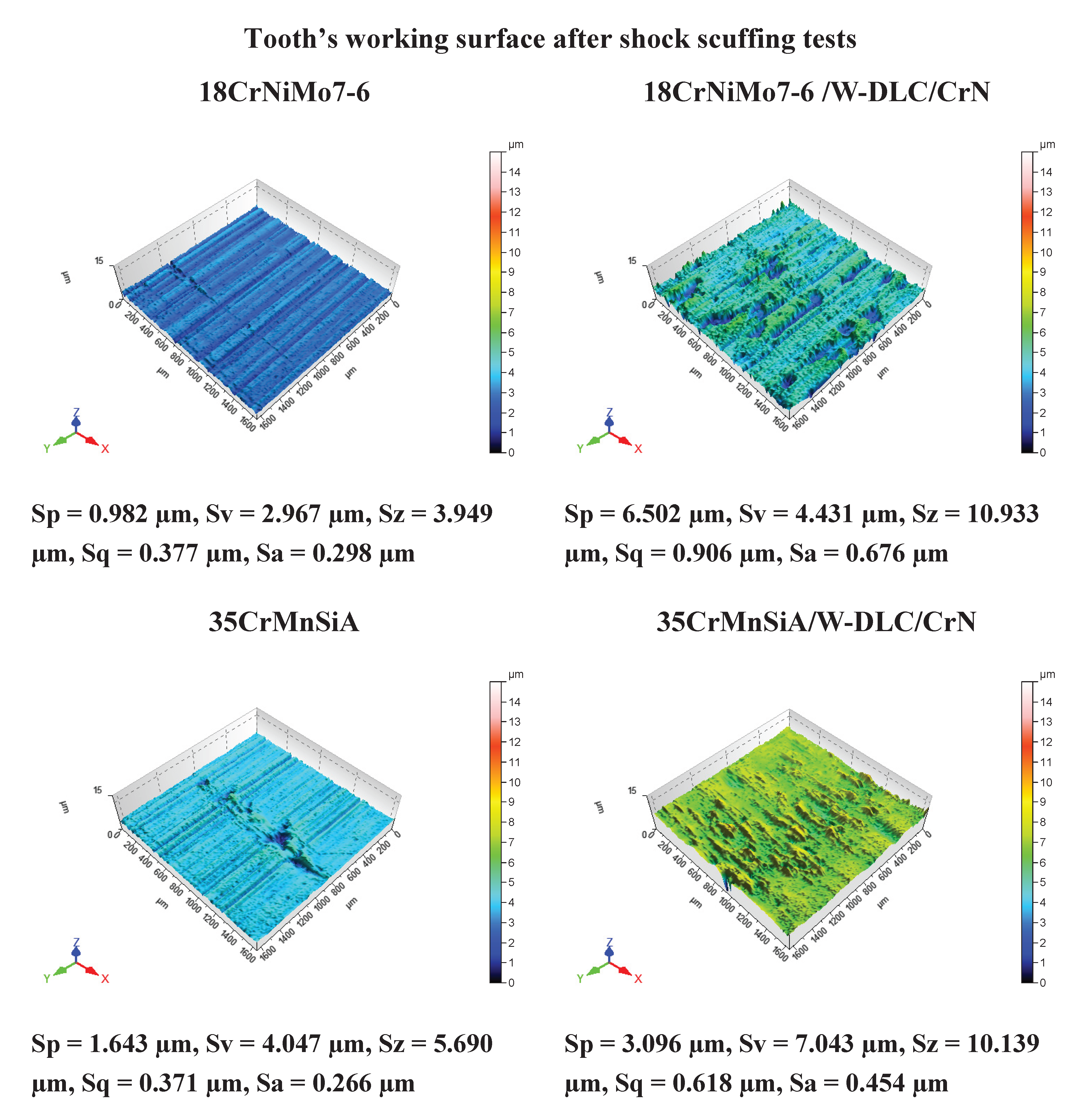
3. Results
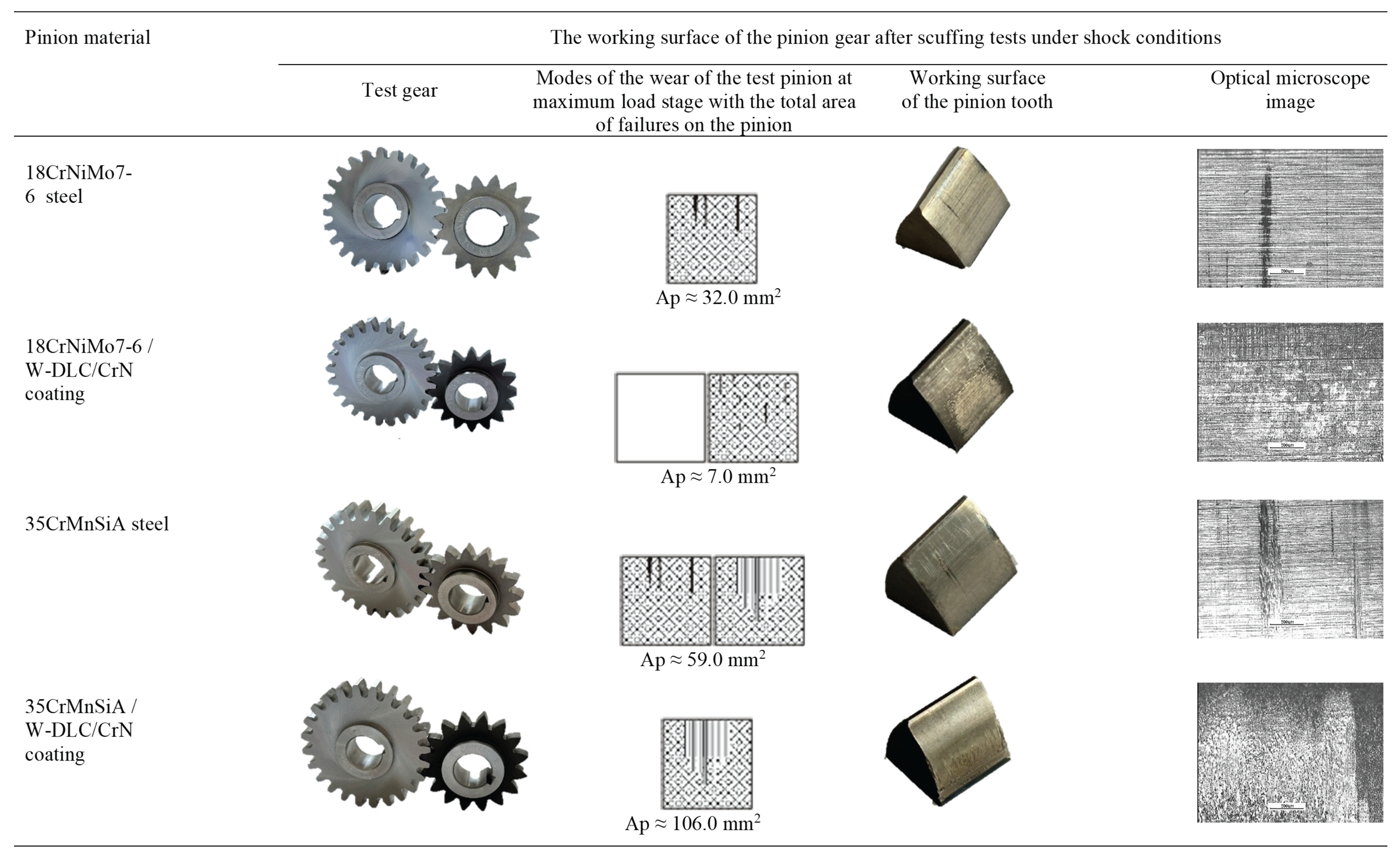 |
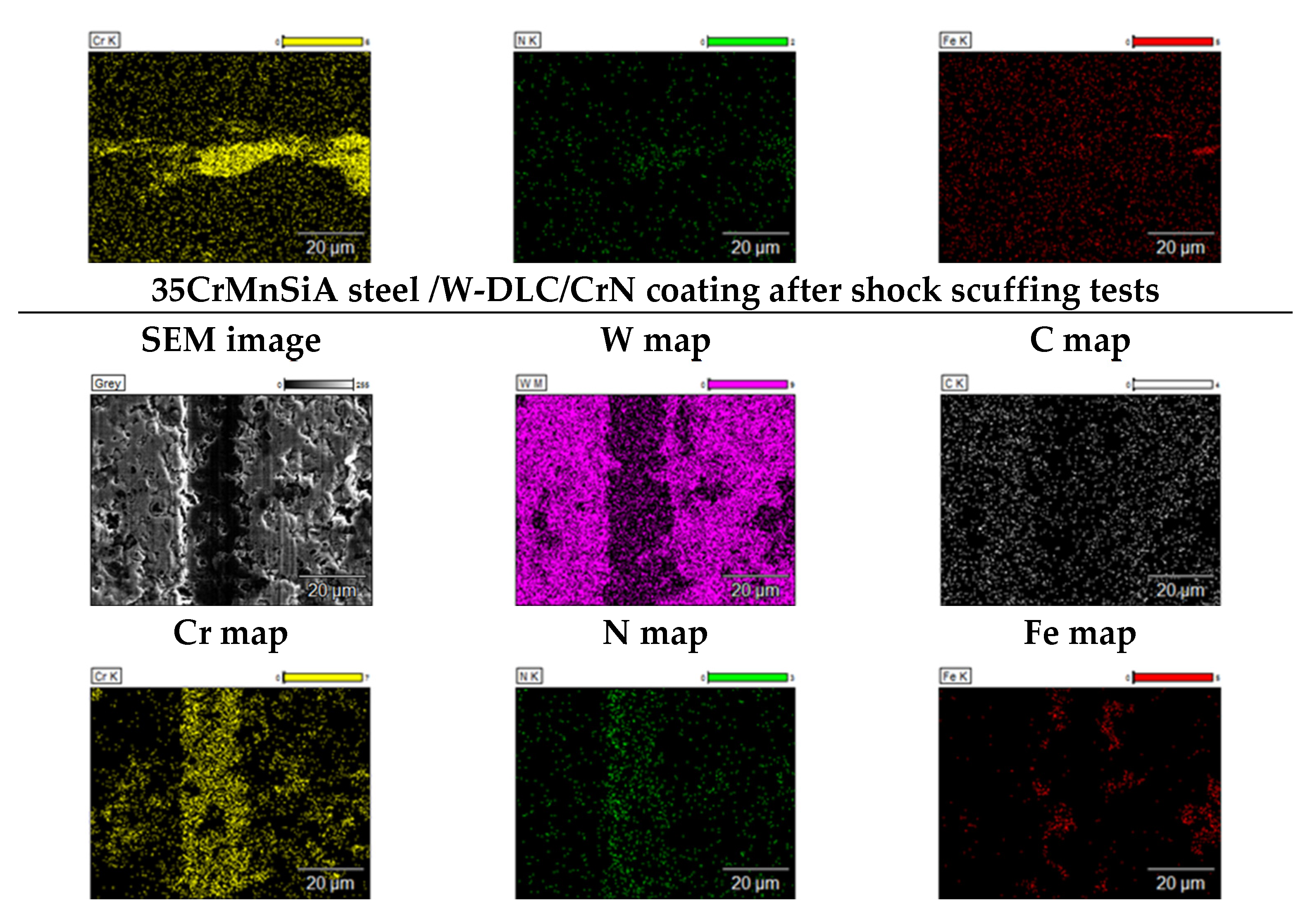
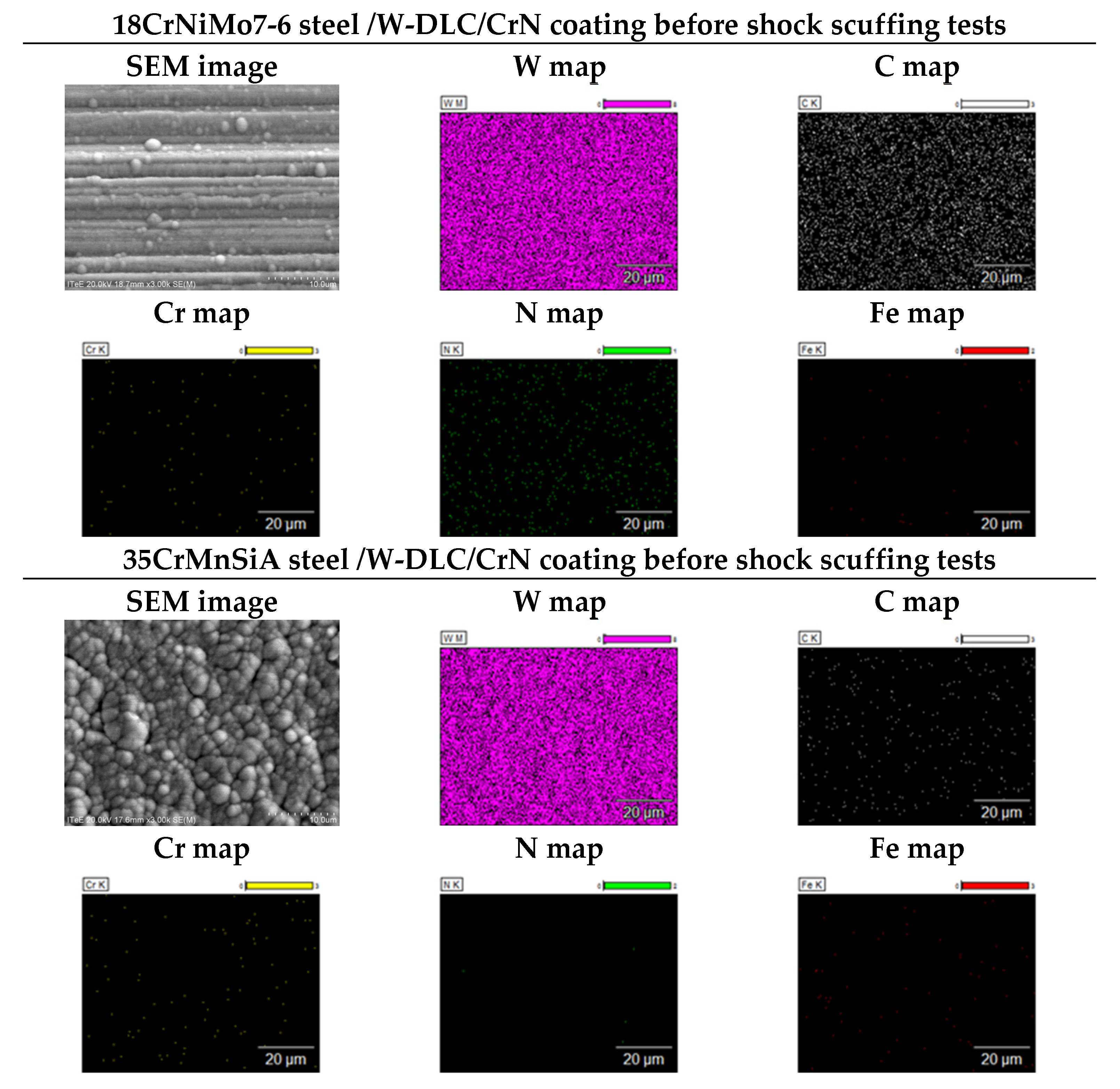
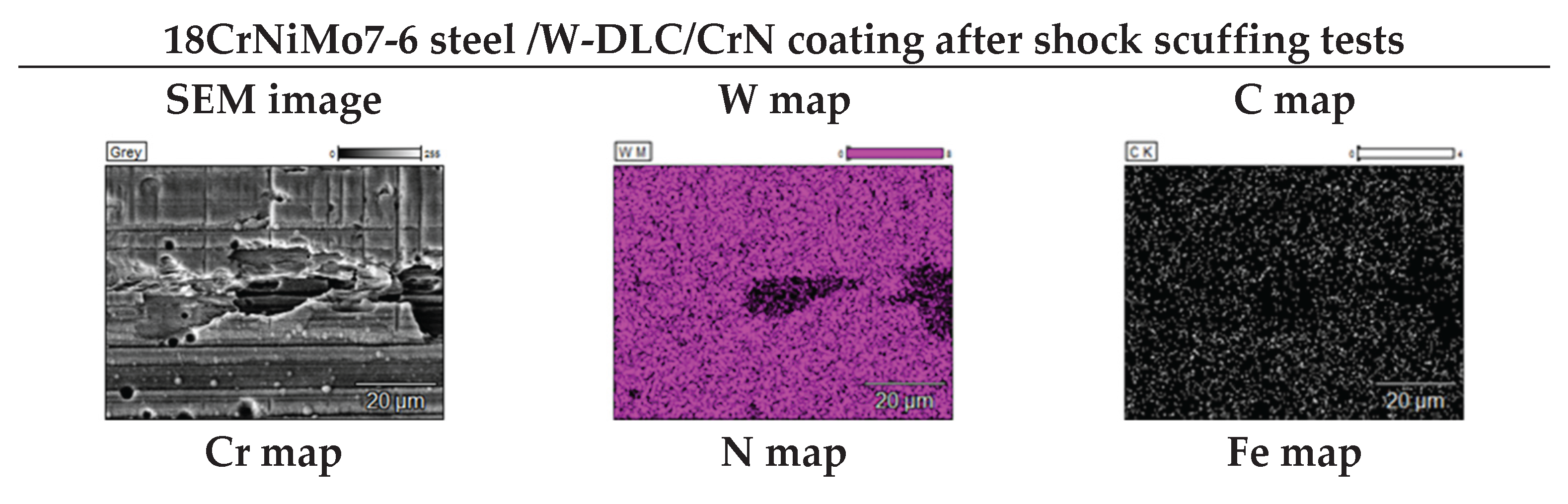

4. Conclusions
- 35CrMnSiA steel pinions with W-DLC/CrN coating were seizured under shock loading. The coating proved insufficient under extreme overloading conditions.
- Scuffing areas were observed on the 35CrMnSiA steel tooth’s surface.
- 18CrNiMo7-6 steel pinions without the coating were not seizured even under the highest, 12th stage of loading. This proves a much higher material resistance of this steel to scuffing compared with 35CrMnSiA steel.
- 18CrNiMo7-6 steel teeth’s surfaces, coated with -DLC/CrN, did not show any signs of scuffing under the maximal loading either. The combination of a high-quality base material and a coating proved effective under shock scuffing conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FLS | failure load stage |
| FZG | the Gear Research Centre (Forschungsstelle fur Zahnrader und Getriebebau, FZG) of the Technical University of Munich |
| DLC | Diamond – Like Carbon coating |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscope |
| EDS | Energy Dispersive Spectrometer |
| WLI | White Light Interferometer Microscope |
| AFM | Atomic Force Microscope |
| Ra | profile roughness [µm] |
| Sa | surface roughness [µm] |
| Sp | maximum peak height [µm] |
| Sv | maximum indentation depth [µm] |
| Sz | maximum surface height [µm] |
| Sq | mean square deviation of the surface roughness [µm] |
| Ap | wear surface area [mm2] |
References
- Evaristo, M.; Fernandes, F.; Cavaleiro, A. Influence of the alloying elements on thetribological performance of DLC coatings in different sliding conditions. Wear 2023, 526-527, 204880. [CrossRef]
- Forsberg, P.; Gustavsson, F. Renman,, V.; Hieke A.; Jacobson, S. Performance of DLC coatings in heated commercial engine oils. Wear 2013, 304(1-2), 211-222. [CrossRef]
- Rincon, C.; Zambrano, G.; Carvajal, A.; Prieto, P.; Galindo, H.; Martinez, E.; Lousa, A.; Esteve, J. Tungsten carbide/diamond-like carbon multilayer coatings on steel for tribological applications. Surface and Coatings Technology 2001, 148, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goti, E.; Mura, A.; Gautier di Confiengo, G.M.; Casalegno, V. The tribological performance of super-hard Ta:C DLC coatings obtained by low-temperature PVD. Ceramics International 2023, 49, 40193–40210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, D. K.; Kumar, A.; Behera, A.; Menezes, P. Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) Coatings: Classification, Properties, and Applications, Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.; Sadeghi, M.; Cruz, S.; Ferreira, F. Recent Progress on the Tribology of Pure/Doped Diamond-like Carbon Coatings and Ionic Liquids, Coatings 2024, 14(1), 71. [CrossRef]
- Radoń-Kobus, K.; Madej, M.; Kowalczyk, J.; Piotrowska, K. Properties of Diamond-like Tungsten-Doped Carbon Coatings Lubricated with Cutting Fluid, Coatings 2024, 14(3), 342. [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.; Amaro, R.; Seabra, J. Influence of low friction coatings on the scuffing load capacity and efficiency of gears, Tribol. Int. 2008, 41, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vengudusamy, B.; Mufti, R. A.; Lamb, G. D.; Green, J. H.; Spikes, H. A. Friction properties of DLC/DLC contacts in base oil, Tribol. Int. 2011, 44 (7-8), 922–932. [CrossRef]
- Kalin, M.; Vižintin, J. The tribological performance of DLC-coated gears lubricated with biodegradable oil in various pinion/gear material combinations, Wear 2005, 259, 1270–1280. [CrossRef]
- Tuszyński, W.; Michalczewski, R.; Osuch-Słomka, E.; Snarski-Adamski, A.; Kalbarczyk, M.; Wieczorek, A.; Nędza, J. Abrasive wear, scuffing and rolling contact fatigue of DLC-coated 18CrNiMo7-6 steel lubricated by a pure and contaminated gear oil, Materials 2021, 14(22), 7086. [CrossRef]
- Tuszyński, W.; et al. The effect of WC/C coating on the wear of bevel gears used in coal mines. Materials Science (Medžiagotyra) 2015, 21, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, Y. J.; Sagraloff, N.; Egger, G.; Tobie, T.; Stahl, K. Investigations on Ways to Improve the Scuffing and Wear Behavior of Oil-Free Water-Based Lubricants for Gear Applications, J. Tribol. 2024, 146, (5), 054601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronkainen, H.; Elomaa, O.; Varjus, S.; Kilpi, L.; Jaatinen, T.; Koskinen, J. The influence of carbon based coatings and surface finishon the tribological performance in high-load contacts, Tribology International 2016, 96, 402–409. [CrossRef]
- Beilicke, R.; Bobach, L.; Bartel, D. Transient thermal elastohydrodynamic simulation of a DLC coated helical gear pair considering limiting shear stress behavior of the lubricant, Tribology International 2016, 97, 136–150. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, Ch. Tribological evaluation of a coated spur gear pair, Tribology International 2016, 99, 117–126. [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Seki, M.; Yoshida, A. Surface durability of WC/C-coated case-hardened steel gear, J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2010, 24, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalczewski, R.; Kalbarczyk, M.; Piekoszewski, W.; Szczerek, M.; Tuszynski, W. The rolling contact fatigue of WC/C-coated spur gears, J. Eng. Tribol. 2013, 227, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuch-Słomka, E.; Michalczewski, R.; Mańkowska-Snopczyńska, A.; Kalbarczyk, M.; Wieczorek, A.; Skołek, E. Wear mechanisms of the working surface of gears after scuffing tests, Materials 2024, 17(14), 3552. [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Diez, O.; Aristizábal-Sierra, R.; Serna-Giraldo, C.; Jimenez, J. A.; Garcia-Mateo, C. Development of nanobainitic microstructures in carbo-austempered cast steels: Heat treatment, microstructure and properties, Metals 2020, 10(5), 635. [CrossRef]
- Rementeria, R.; Morales-Rivas, L.; Kuntz, M.; Garcia-Mateo, C.; Kerscher, E.; Sourmail, T.; Caballero, F. G. On the role of microstructure in governing the fatigue behaviour of nanostructured bainitic steels, Material Scence Engineering A 2015, 630, 71–77. [CrossRef]
- Solano-Alvarez, W.; Pickering, E.; Bhadeshia, H. K. D Degradation of nanostructured bainitic steel under rolling contact fatigue, Material Scence Engineering A 2014, 617, 156–164. [CrossRef]
- Łukaszewicz, G.; Szczygieł, M.; Wesierska-Hinca, M.; Chmielarz, K.; Wierzbicka, E.; Wasiak, K. Interrupted quenching and bainitising below Ms temperature of EN X37CrMoV5-1 hot-work tool steel: Bainitic transformation kinetics, microstructure and mechanical properties, Material Scence Engineering A 2023, 869, 144740. [CrossRef]
- Morales-Rivas, L.; Azadi, A.; Kerscher, E. Fatigue behavior of nanostructured bainite: A morphological study of crack path, Procedia Struct. Integr. 2022, 39, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FVA Information Sheet, no. 243, Status June 2000, Method to Assess the Scuffing Load Capacity of Lubricants with High EP Performance Using an FZG Gear Test Rig, 2000. 20 June.
- Höhn, B. R.; Michaelis, K.; Eberspächer, C.; Schlenk, L. A scuffing load capacity test with the FZG gear test rig for gear lubricants with high EP performance, Tribotest Journal 1999, 5, 383–390. ,.
- Michaelis, K.; Höhn, B. R.; Graswald, C. Scuffing tests for API GL-1 to GL-5 gear lubricants”, In: Proc. 13th international colloquium tribology 2002, p. 1133-1137.
- Michaelis, K.; Höhn, B. R.; Oster, P. Influence of lubricant on gear failures-test methods and application to gearboxes in practice, Tribotest Journal 2004, 11-1, 43-56.
- Van De Velde, F.; Willen, P.; De Baets, P.; Van Geetruyen, C. Substitution of inexpensive bench tests for the FZG scuffing test - Part I: Calculations, Tribol. Trans. 1999, 42, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Velde, F.; Willen, P.; De Baets, P.; Van Geeteruyen, C. Substitution of inexpensive bench tests for the FZG scuffing test - Part II: Oil tests, Tribol. Trans. 1999, vol. 42, pp. 71-75.
- Tuszynski, W. , Michalczewski R., Szczerek M., Kalbarczyk M.: A new scuffing shock test method for the determination of the resistance to scuffing of coated gears. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering (ACME), 2012, vol. 12 (4), s. 436-445. [CrossRef]
- Michalczewski, R.; Kalbarczyk, M.; Mańkowska-Snopczyńska, A.; Osuch-Słomka, E.; Piekoszewski, W.; Snarski-Adamski, A.; Szczerek, M.; Tuszynski, W.; Wulczyński, J.; Wieczorek, A. The effect of a gear oil on abrasion, scuffing, and pitting of theDLC-coated 18CrNiMo7-6 steel, Coatings 2019, 9(1), 2. [CrossRef]
- Szczerek, M.; Kalbarczyk, M.; Mańkowska-Snopczyńska, A.; Osuch-Słomka, E.; Piekoszewski, W.; Snarski-Adamski, A.; Tuszyński, W.; Wieczorek, A. N. The correlated selection of a thin coating and gear oil to increase the resistance of 18CrNiMo7-6 gears to pitting - Part 1, ASIATRIB 2018, 133, 293-295. ISBN 978-967-13625-2-5.
- Tuszyński, W.; Michalczewski, R.; Osuch-Słomka, E.; Wieczorek, A. N.; Wulczyński, J. The correlated selection of a thin coating and gear oil to increase the resistance of 18CrNiMo7-6 gears to abrasion and scuffing - Part 2, ASIATRIB 2018, 204, 450-452. ISBN 978-967-13625-2-5.
- Michalczewski, R.; Piekoszewski, W.; Szczerek, M.; Tuszynski, W. The lubricant-coating interaction in rolling and sliding contacts. Tribol. Int. 2009, 42, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Polishing | Scratches | Scoring | Scuffing |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





