Submitted:
25 June 2025
Posted:
26 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
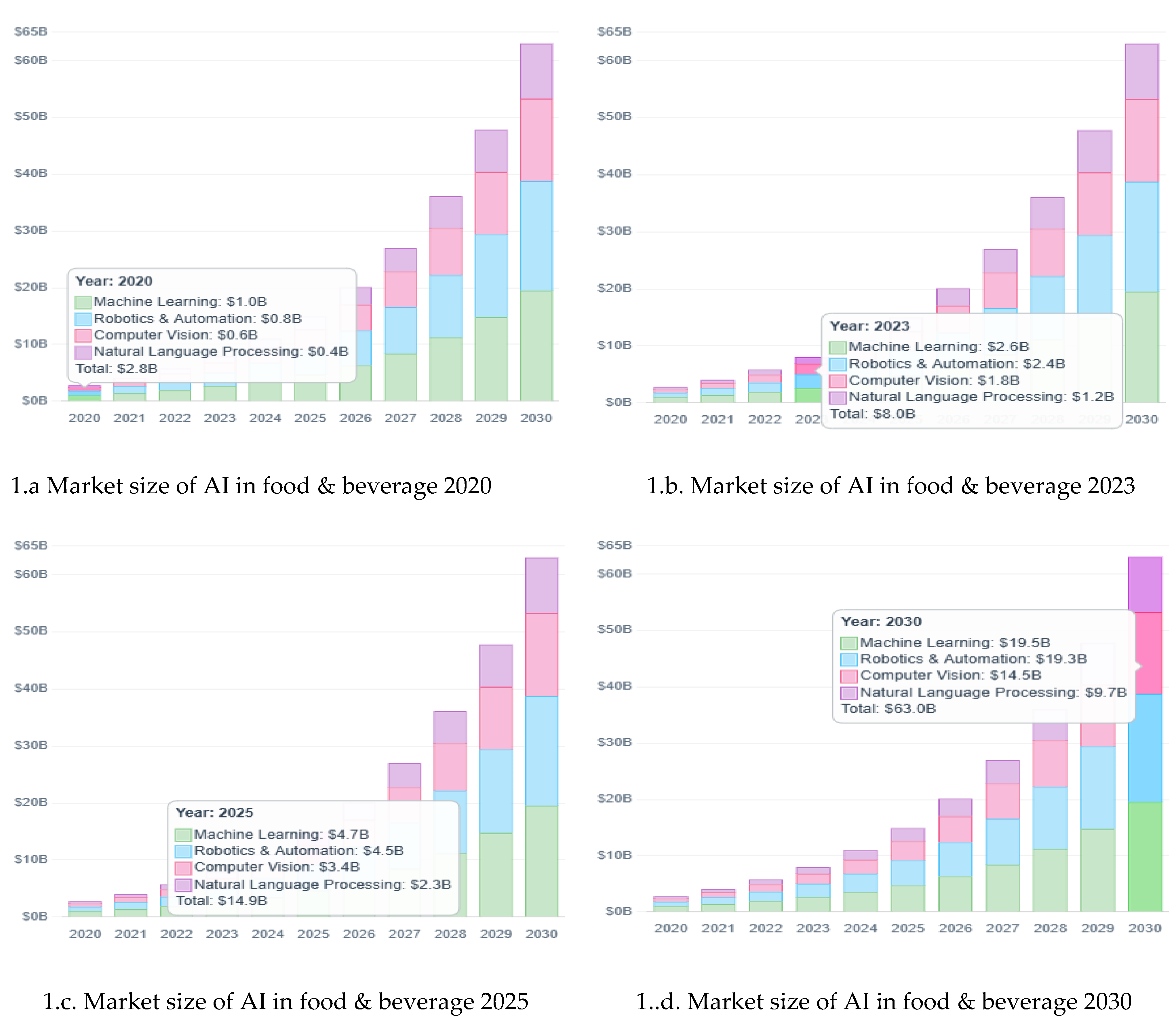
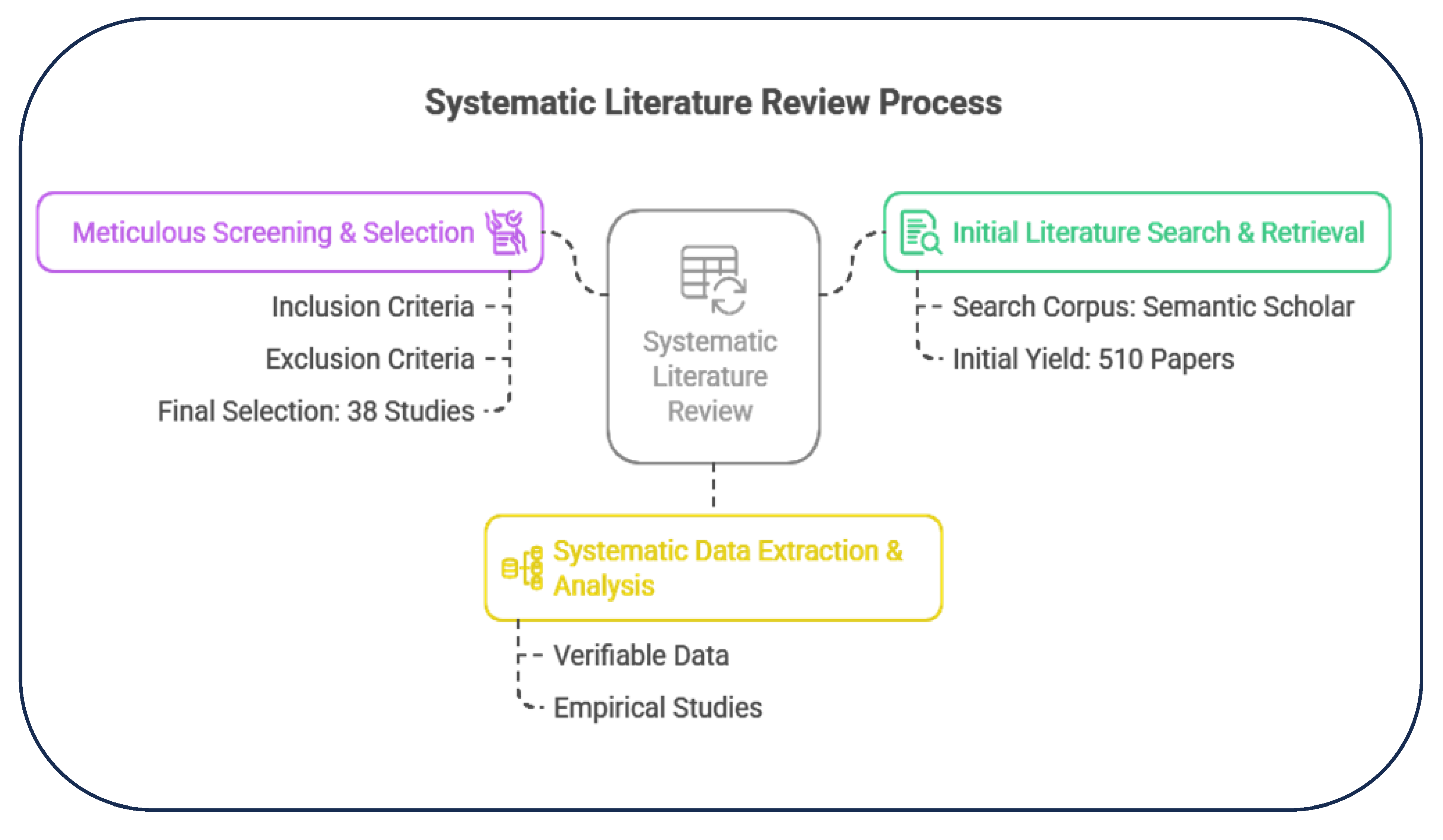
2. Materials and Methods
| Study | Study Design | Domain | Core AI Technologies | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carlson et al., 2022[4] | Theoretical/conceptual study | Wine, Beer | Transformer neural network (generative artificial intelligence) | Machine-generated reviews, review synthesis, marketing innovation |
| Yu et al., 2022 [5] | Systematic review (not explicitly stated as such) | Traditional fermented alcoholic beverages | Artificial intelligence and machine learning (not generative) | Trends, challenges, artificial intelligence in supply chain |
| Schreurs et al., 2024[6] | Empirical study | Beer | Gradient boosting (machine learning) | Flavor prediction, product innovation |
| Basile et al., 2023[7] | Systematic review | Plant-based foods/beverages | Artificial intelligence and machine learning (artificial neural networks, chemometrics) | Sensory analysis, product innovation |
| Addanki et al., 2022[8] | Review (type not specified in the paper) | Food industry (dairy, bakery, beverages) | Artificial intelligence and machine learning | Applications in quality, shelf life, robotics |
| Tardáguila et al., 2021[9] | Systematic review | Viticulture (wine) | Artificial intelligence, digital technology | Sensing, decision support, sustainability |
| Brown et al., 2024[10] | Theoretical/conceptual study | Multiple (including beverage) | ChatGPT, generative artificial intelligence | Workplace transformation, marketing, business models |
| Patil et al., 2021[11] | Bibliometric analysis | Tea | Artificial intelligence and machine learning, sensors | Digital flavor recognition, marketing |
| Kessler et al., 2020[12] | Systematic review | Beverages | Automated facial expression analysis (AFEA) | Consumer emotion, sensory evaluation |
| Tan et al., 2022[3] | Systematic review | Food & beverage | Deep learning | Quality assessment, product innovation |
| Wang et al., 2024[13] | Review (type not specified in the paper) | Alcoholic beverages | Artificial intelligence, biometrics | Sensory analysis, production |
| McDonagh et al., 2020[14] | Theoretical/conceptual study | Formulated products | Artificial intelligence and machine learning, simulation | Research and development transformation, digital modeling |
| Gao et al., 2022[15] | Exploratory artificial intelligence-based study | Wine tourism | Deep neural networks | Value creation, sentiment analysis |
| Ta et al., 2024[16] | Systematic review | Food value chain | Artificial intelligence (image-based) | Sustainability, quality control, marketing |
| Liao et al., 2023[17] | Systematic review | Alcoholic beverages | Artificial intelligence, intelligent monitoring | Safety, hazard mitigation |
| Queiroz et al., 2024[18] | Systematic review | Flavor engineering | Artificial intelligence (general) | Flavor development, industry perspective |
| Doanh et al., 2023[19] | Critical review | Manufacturing | ChatGPT, DALL-E | Product/process innovation, marketing |
| Kanbach et al., 2023[20] | Scoping review, qualitative | Software, healthcare, finance | ChatGPT, DALL-E | Business model innovation, content creation |
| Chintalapati and Pandey, 2021[21] | Systematic review | Marketing (general) | Artificial intelligence (general) | Artificial intelligence in marketing, use cases |
| Misra et al.,2020[22] | Systematic review | Agriculture, food | Internet of Things, artificial intelligence and machine learning | Process control, automation |
| Mariani et al., 2023[23] | Systematic review, bibliometric | Innovation (general) | Artificial intelligence (general) | Types of innovation, research agenda |
| Bahoo et al., 2023[24] | Systematic review | Corporate innovation | Artificial intelligence (general) | Taxonomy, innovation fields |
| Sedkaoui and Benaichouba, 2024[25] | Systematic review | Multiple sectors | Generative artificial intelligence | Innovation, creativity, ethics |
| Nicoletti and Appolloni, 2023[26] | Systematic review | Manufacturing, servitization | Generative artificial intelligence | Business model, regulatory, financial innovation |
| Anayat and Rasool, 2022[27] | Bibliometric analysis | Marketing | Artificial intelligence (general) | Science mapping, research gaps |
| Torrico et al., 2022[28] | Systematic review | Sensory evaluation | Artificial intelligence, biometrics | Novel sensory methods |
| Kler et al., 2022[29] | Systematic review | Food industry | Artificial intelligence and machine learning | Supply chain, optimization |
| Nunes et al., 2023[30] | Systematic review | Food sensory/consumer | Artificial intelligence (general) | Sensory/consumer studies |
| Liao et al., 2022[17] | Theoretical/conceptual study | Microbial engineering | Machine learning | Design-build-test-learn cycle optimization |
| Ganeshkumar et al., 2021[31] | Systematic review, qualitative | Agriculture value chain | Artificial intelligence and machine learning | Value chain actors, adoption |
| Naeem et al., 2024[32] | Bibliometric + systematic review | Product-service innovation | Artificial intelligence (general) | Business models, innovation clusters |
| Kyaw et al., 2022[33] | Theoretical/conceptual study | Milk, beverages | Artificial intelligence (general) | Food safety, automation |
| Violino et al., 2020[34] | Systematic review | Beer | Internet of Things, smart technology | Production, logistics, traceability |
| Madanchian, 2024[35] | Systematic review | E-commerce, energy, public health | Generative adversarial networks, variational autoencoders, transformers | Consumer behavior prediction, marketing |
| Singh et al., 2024[36] | Theoretical/conceptual study | Organizations (general) | Generative artificial intelligence (general) | Innovation, ethics, performance |
| Gupta and Khan, 2024[37] | Systematic review, bibliometric | Marketing/customer engagement | Artificial intelligence (general) | Customer engagement, value creation |
| Liu and Yu, 2021[38] | Systematic review | E-commerce, video | Artificial intelligence-powered video generation (generative video artificial intelligence) | Video generation, marketing |
| Cui et al., 2025[[2] | Systematic review | Food flavor | Artificial intelligence (general) | Flavor development, product innovation |
| Yoo et al., 2024[39] | Mixed-methods | Customer relationship management (general) | Generative artificial intelligence, machine learning | Customer relationship management features, competitive advantage |
3. Generative AI Applications in Beverages
4.1. AI-Driven Product Ideation and Conceptualization
4.2. Process Optimization and Quality Control Enhancement
4.3. Digital Product Development Evolution
4.4. Smart Manufacturing Integration for Enhanced Efficiency
4.5. Marketing Strategy Revolution through AI Insights
4.6. Personalized Consumer Engagement and Digital Platforms
4. Challenges and Solutions
5.1. Technical Implementation Challenges and Solutions
5.2. Business Adaptation Challenges and Solutions
5.3. Ethical and Regulatory Considerations and Solutions
5. Future Directions and Research Agenda
6.1. Multimodal AI for Holistic Beverage Design
6.2. Culturally Adaptive Sensory Models
6.3. Sustainable AI for SME Adoption
6.4. Robust Regulatory and Ethical Frameworks
6.5. Human-AI Collaboration Paradigms
6.5. Implementation Roadmap
| Timeframe | Focus Area | Key Milestones |
| 2024–2025 | Technical Validation | Development of standardized benchmark datasets specifically for beverage AI (e.g., a comprehensive "BevNet-1M" dataset). Release of open-source foundational formulation models (e.g., under an MIT License) to encourage widespread adoption and collaborative development. |
| 2026–2028 | Industry Scaling | Widespread implementation of AI-augmented HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) systems across beverage production facilities. Establishment of cross-company data trusts to facilitate secure and collaborative data sharing, particularly for rare or specialized ingredients. |
| 2029–2030 | Policy Integration | Development and adoption of global standards for AI in food and beverage safety, ensuring harmonized regulatory environments. Pilot programs for carbon-negative AI-optimized breweries, showcasing advanced sustainability through GenAI. |
6.6. Critical Gaps Requiring Immediate Attention:
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ray, D.P., Shrivastava, P., Das, I. and Roy, S.B. Business Opportunities for Food and Beverages from Natural Fibre Plant Materials. Econ. Aff., 2024, 69(01):p. 531-539.
- Cui, Z., et al., Artificial intelligence and food flavor: How AI models are shaping the future and revolutionary technologies for flavor food development. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 2025. 24(1). [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.K., et al., Recent technology for food and beverage quality assessment: a review. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2022. 60(6): p. 1681–1694. [CrossRef]
- Carlson, K., et al., Complementing human effort in online reviews: A deep learning approach to automatic content generation and review synthesis. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 2023. 40(1): p. 54–74. [CrossRef]
- Yu, H., et al., Artificial intelligence-based approaches for traditional fermented alcoholic beverages’ development: review and prospect. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2022. 64(10): p. 2879–2889. [CrossRef]
- Schreurs, M., et al., Predicting and improving complex beer flavor through machine learning. Nature Communications, 2024. 15(1). [CrossRef]
- Basile, T., D. Mallardi, and M.F. Cardone, Spectroscopy, a Tool for the Non-Destructive Sensory Analysis of Plant-Based Foods and Beverages: A Comprehensive Review. Chemosensors, 2023. 11(12): p. 579. [CrossRef]
- Addanki, M., P. Patra, and P. Kandra, Recent advances and applications of artificial intelligence and related technologies in the food industry. Applied Food Research, 2022. 2(2): p. 100126. [CrossRef]
- Tardaguila, J., et al., Smart applications and digital technologies in viticulture: A review. Smart Agricultural Technology, 2021. 1: p. 100005. [CrossRef]
- Brown, O., et al., Theory-Driven Perspectives on Generative Artificial Intelligence in Business and Management. British Journal of Management, 2024. 35(1): p. 3–23. [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.B., M.R. Bachute, and K. Kotecha, Artificial Perception of the Beverages: An In-Depth Review of the Tea Sample. IEEE Access, 2021. 9: p. 82761–82785. [CrossRef]
- Kessler, S.J., F. Jiang, and R.A. Hurley, The State of Automated Facial Expression Analysis (AFEA) in Evaluating Consumer Packaged Beverages. Beverages, 2020. 6(2): p. 27. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., et al., From Traditional to Intelligent, A Review of Application and Progress of Sensory Analysis in Alcoholic Beverage Industry. Food Chemistry: X, 2024. 23: p. 101542.
- McDonagh, J.L., et al., What can digitisation do for formulated product innovation and development? Polymer International, 2020. 70(3): p. 248–255.
- Gao, D., et al., Value creation in wine tourism – an exploration through deep neural networks. Journal of Vacation Marketing, 2022. 30(3): p. 376–391. [CrossRef]
- Ta, M.D.-P., S. Wendt, and T.O. Sigurjonsson, Applying Artificial Intelligence to Promote Sustainability. Sustainability, 2024. 16(12): p. 4879. [CrossRef]
- Liao, H., et al., Mitigation of microbial nitrogen-derived metabolic hazards as a driver for safer alcoholic beverage choices: An evidence-based review and future perspectives. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 2023. 22(6): p. 5020–5062. [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, L.P., I.B.R. Nogueira, and A.M. Ribeiro, Flavor Engineering: A comprehensive review of biological foundations. Food Research International, 2024. 196: p. 115100. [CrossRef]
- Doanh, D.C., et al., Generative AI in the Manufacturing Process: Theoretical Considerations. Engineering Management in Production and Services, 2023. 15(4): p. 76–89. [CrossRef]
- Kanbach, D.K., et al., The GenAI is out of the bottle: generative artificial intelligence from a business model innovation perspective. Review of Managerial Science, 2023. 18(4): p. 1189–1220. [CrossRef]
- Chintalapati, S. and S.K. Pandey, Artificial intelligence in marketing: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Market Research, 2021. 64(1): p. 38–68. [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.N., et al., IoT, Big Data, and Artificial Intelligence in Agriculture and Food Industry. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022. 9(9): p. 6305–6324. [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.M., I. Machado, and S. Nambisan, Types of innovation and artificial intelligence: A systematic quantitative literature review and research agenda. Journal of Business Research, 2023. 155: p. 113364. [CrossRef]
- Bahoo, S., M. Cucculelli, and D. Qamar, Artificial intelligence and corporate innovation: A review and research agenda. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2023. 188: p. 122264. [CrossRef]
- Sedkaoui, S. and R. Benaichouba, Generative AI as a transformative force for innovation: a review of opportunities, applications and challenges. European Journal of Innovation Management, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, B. and A. Appolloni, Artificial Intelligence for the Management of Servitization 5.0. Sustainability, 2023. 15(14): p. 11113.
- Anayat, S. and G. Rasool, Artificial intelligence marketing (AIM): connecting-the-dots using bibliometrics. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 2022. 32(1): p. 114–135. [CrossRef]
- Torrico, D.D., A. Mehta, and A.B. Borssato, New methods to assess sensory responses: a brief review of innovative techniques in sensory evaluation. Current Opinion in Food Science, 2023. 49: p. 100978. [CrossRef]
- Kler, R., et al., Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in the Food Industry: A Sustainable Approach. Journal of Food Quality, 2022. 2022: p. 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Nunes, C.A., et al., Artificial intelligence in sensory and consumer studies of food products. Current Opinion in Food Science, 2023. 50: p. 101002. [CrossRef]
- Ganeshkumar, C., et al., Artificial intelligence in agricultural value chain: review and future directions. Journal of Agribusiness in Developing and Emerging Economies, 2021. 13(3): p. 379–398. [CrossRef]
- Naeem, R., M. Kohtamäki, and V. Parida, Artificial intelligence enabled product–service innovation: past achievements and future directions. Review of Managerial Science, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Kyaw, K.S., et al., Toward in-process technology-aided automation for enhanced microbial food safety and quality assurance in milk and beverages processing. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2022. 64(6): p. 1715–1735. [CrossRef]
- Violino, S., et al., Internet of Beer: A Review on Smart Technologies from Mash to Pint. Foods, 2020. 9(7): p. 950. [CrossRef]
- Madanchian, M., Generative AI for Consumer Behavior Prediction: Techniques and Applications. Sustainability, 2024. 16(22): p. 9963. [CrossRef]
- Singh, K., S. Chatterjee, and M. Mariani, Applications of generative AI and future organizational performance: The mediating role of explorative and exploitative innovation and the moderating role of ethical dilemmas and environmental dynamism. Technovation, 2024. 133: p. 103021. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, Y. and F.M. Khan, Role of artificial intelligence in customer engagement: a systematic review and future research directions. Journal of Modelling in Management, 2024. 19(5): p. 1535–1565. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C. and H. Yu, AI-Empowered Persuasive Video Generation: A Survey. ACM Computing Surveys, 2023. 55(13s): p. 1–31. [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.W., J. Park, and H. Park, the impact of AI-enabled CRM systems on organizational competitive advantage: A mixed-method approach using BERTopic and PLS-SEM. Heliyon, 2024. 10(16): p. e36392. [CrossRef]
- César, I., et al., A Systematic Review on Responsible Multimodal Sentiment Analysis in Marketing Applications. IEEE Access, 2024. 12: p. 111943–111961. [CrossRef]
- Gosavi, A.A., et al., Exploring the Potential of Artificial Intelligence as a Facilitating Tool for Formulation Development in Fluidized Bed Processor: a Comprehensive Review. AAPS PharmSciTech, 2024. 25(5). [CrossRef]
- Gündüzyeli, B., Artificial Intelligence in Digital Marketing Within the Framework of Sustainable Management. Sustainability, 2024. 16(23): p. 10511. [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A., et al., From Food Industry 4.0 to Food Industry 5.0: Identifying technological enablers and potential future applications in the food sector. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 2024. 23(6). [CrossRef]
- Qin, J., P. Zheng, and X. Wang, Product Redesign and Innovation Based on Online Reviews: A Multistage Combined Search Method. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 2024. 36(3): p. 742–765. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D. and V. Ratten, Artificial intelligence and family businesses: a systematic literature review. Journal of Family Business Management, 2024. 15(2): p. 373–392. [CrossRef]
- Varriale, V., et al., Critical analysis of the impact of artificial intelligence integration with cutting-edge technologies for production systems. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2023. 36(1): p. 61–93. [CrossRef]
- Ozgit, H. and A. Öztüren, Themed editorial: The impact and usage of automation and AI in the hospitality and tourism industry. Worldwide Hospitality and Tourism Themes, 2024. 16(2): p. 125–126. [CrossRef]
- Passmore, J. and D. Tee, The library of Babel: assessing the powers of artificial intelligence in knowledge synthesis, learning and development and coaching. Journal of Work-Applied Management, 2023. 16(1): p. 4–18. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X., et al., Teaching large language models to self-debug. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.05128, 2023.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





