Submitted:
14 June 2025
Posted:
16 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
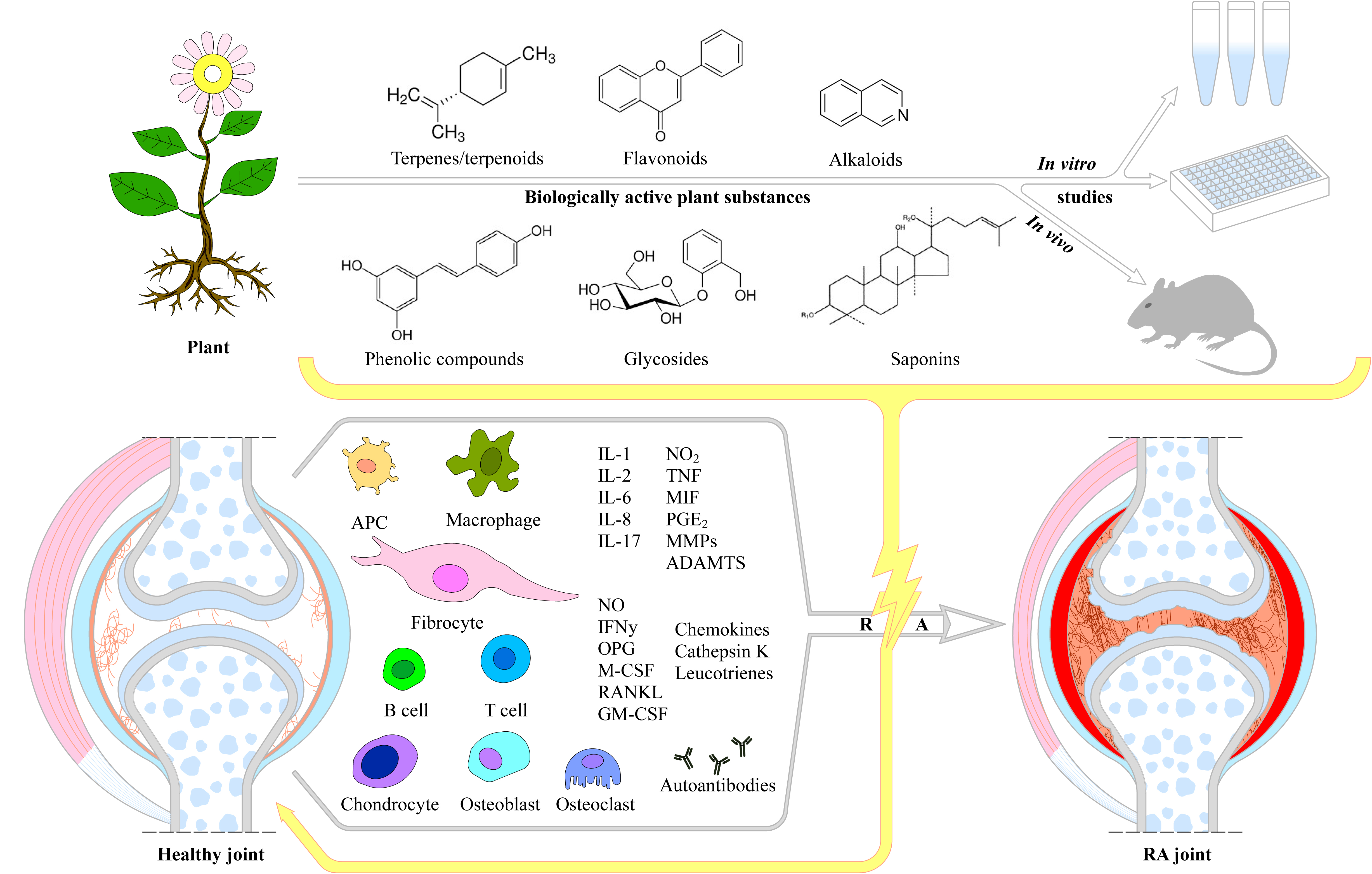
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Epidemiology Overview and Global Prevalence
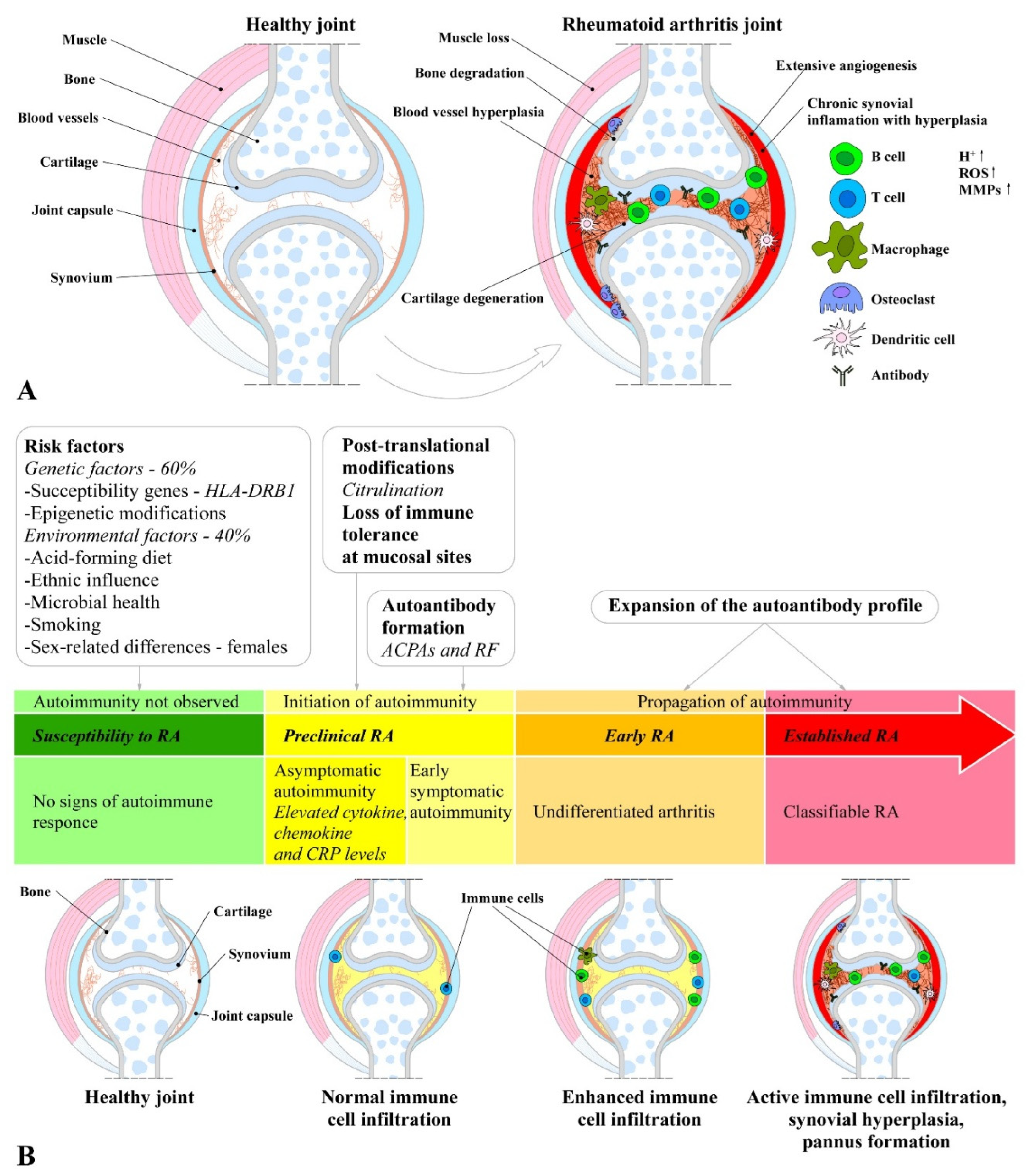
1.2. Risk factors
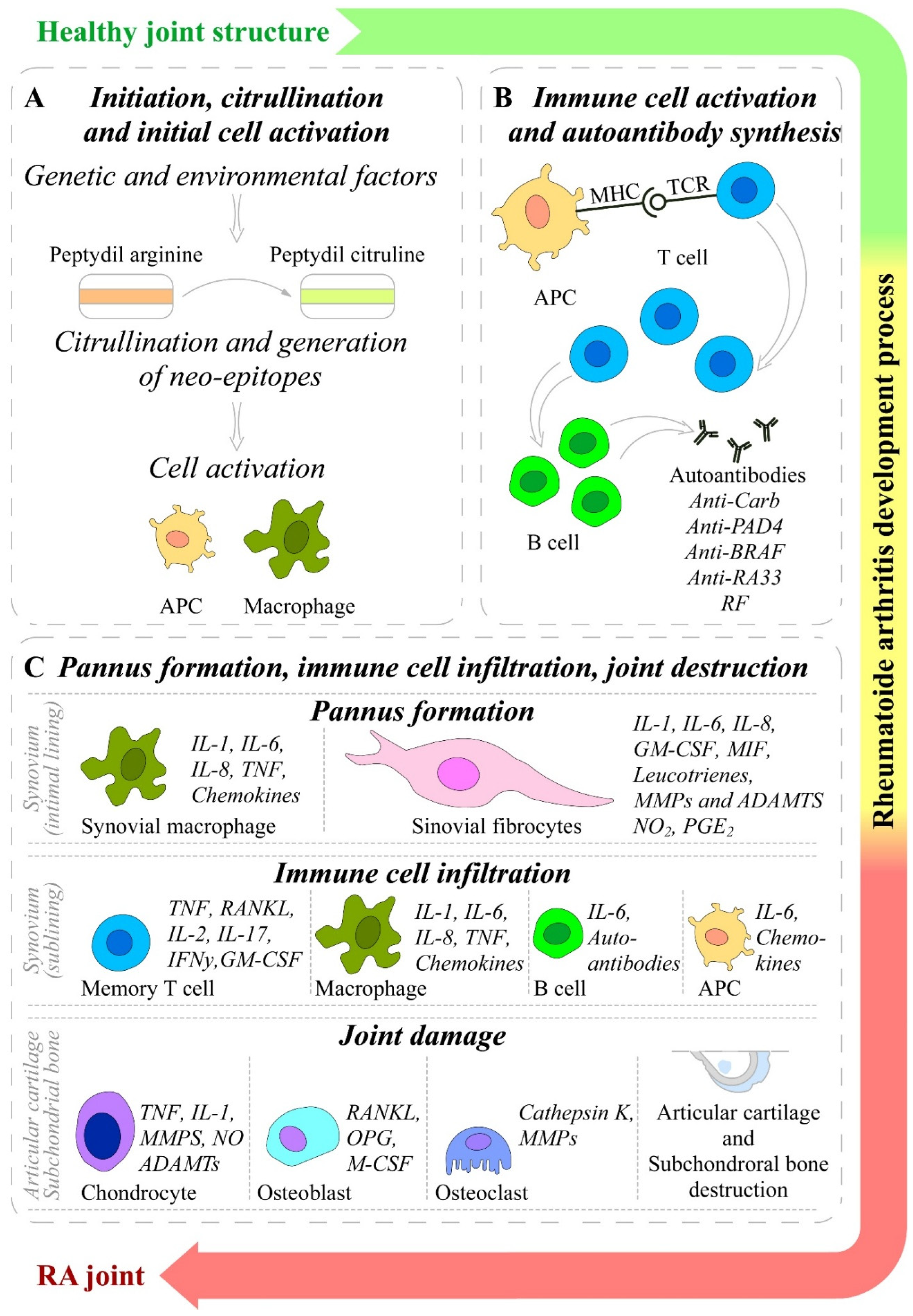
1.3. Mechanisms and (pato)etiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis Initiation, Development and Progression
2. Effectors Cells Involved in Rheumatoid Arthritis Pathology
2.1. Cytokines and the Impact on Effector Cells
2.2. The Role of Metalloproteinases
2.3. The Role of Angiogenesis
2.4. The Role of Free Radicals
3. Current Rheumatoid Arthritis Drug Treatment
3.1. Conventional Synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs)
3.2. Biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs)
3.3. Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
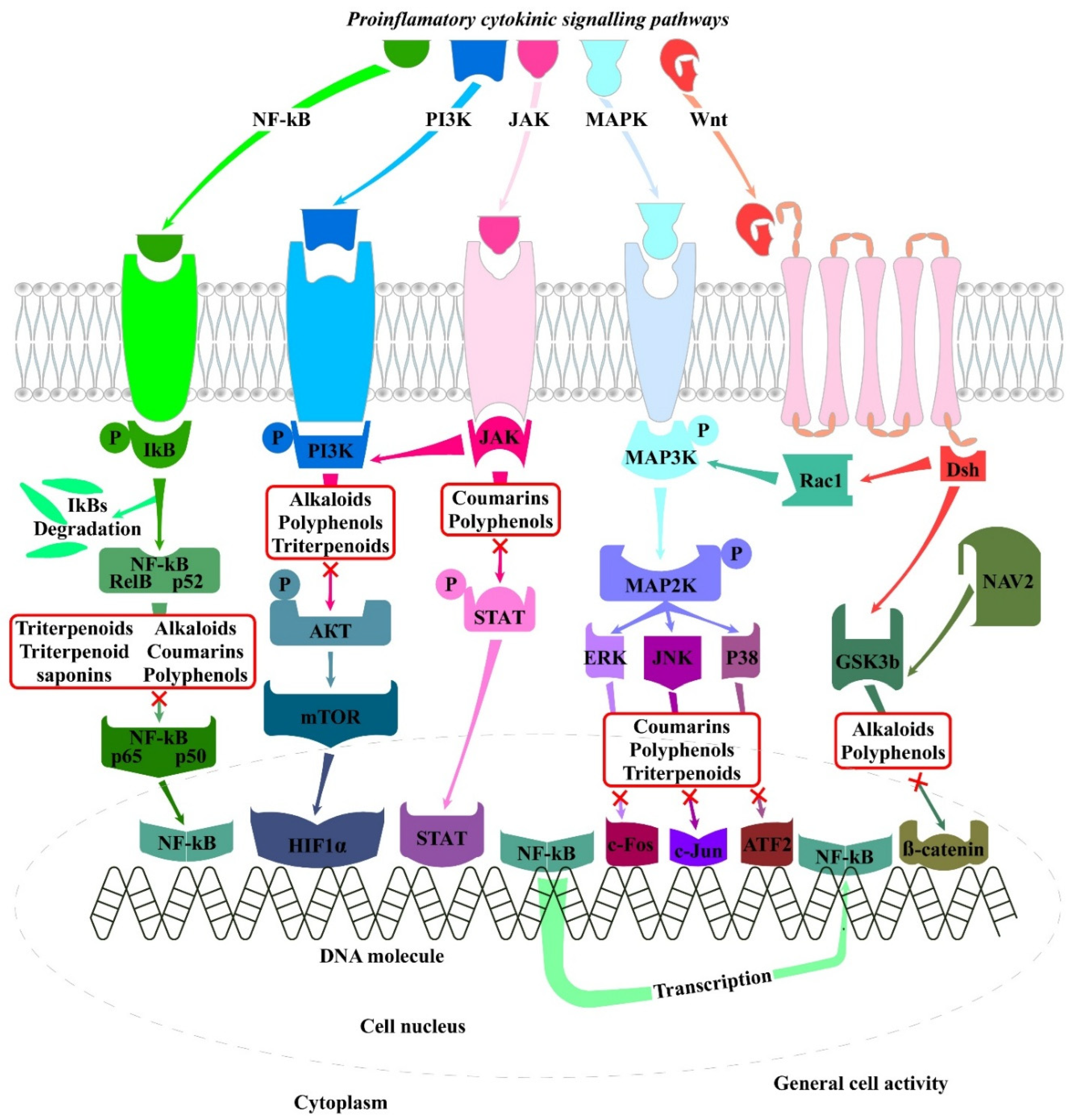
4. In Vitro Studies Using Plant-Derived Natural Products for the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Signaling Pathways
| Molecule | Dose, µM | Cell line | Targets | Main findings | Modulated pathway | Reference |
| Curcumin | 50 | MH7A | TNF-α, IL-6, IL-17 | Inhibition of migration, invasion and inflammation | PI3K/AKT | [231] |
| Emodin | 15 | L929 | IL-6, IL-1β, COX-2 | Inhibition of inflammation | NF-κB | [232] |
| Ginsenoside compound K | 30 | Isolated FLS | FLUT1, HK2, PKM1, PKM2 | Inhibition of glycolysis | NF-κB | [233] |
| Glytabastan B | 3 and 6 | SW982 | TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8, COX-2 and MMP-1 | Inhibition of inflammation and invasion | MAPK, PI3K/AKT, NF-κB | [234] |
| Isobavachalcone | 20 | MH7A | TNF-α, MAPK13, EGFR, PTGS2, MMP-3 | Inhibition of migration, invasion and inflammation | PI3K/AKT, JAK/STAT | [235] |
| Kaempferol | 10 | HFLS-RA | IL-1β, MMP-2, -9, N-cadherin, vimentin | Inhibition of inflammation and abnormal proliferation | MAPK | [236] |
| Leocarpinolide B | 20 | SW982 | IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, | Inhibition of proliferation, migration, invasion and inflammation | NF-κB | [237] |
| Magnoflorine | 10 | MH7A | iNOS, COX-2, IL-6, IL-8, MMP-1, -2, -3, -9 and -13 | Inhibition of proliferation, migration, invasion | PI3K/AKT, NF-κB, Nrf-2, | [238] |
| Nimbolide | 1 | HIG-82 | MMP-2, IL-6, iNOS, COX-2 | Reduction of inflammation | MAPK, NF-κB, Nrf-2 | [239] |
| Quercetin | 1.5 | L929, HEK293T, MH7A | COX-2, iNOS, IL-6, IL-1β | Reduction of cell apoptosis, improvement of cell injury | NF-κB | [110] |
| Sappanone A | 40 | HFLS-RA | TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17A | Inhibition of inflammation | JAK2/STAT3, PI3K/AKT, NF-κB | [240] |
| Shikonin | 1x10-7 | MH7A | VEGF, VEGFR2, TNF-α, IL-1β, PDGF and TGF-β | Inhibition of migration, invasion and adhesion | MAPK (ERK1/2, JNK, and p38) | [241] |
| Scopoletin | 30 | HFLS-RA | IL-1β, TNF-α, MMP-3, MMP-9, COX-2, Bcl-2 | Inhibition of proliferation, migration and invasion | NF-κB | [242] |
| Suberosin | 5 | RA-FLS | IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-8, MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-9, MMP-13 | Inhibition of inflammation | JAK/STAT | [243] |
| Tectoridin | 50 | HFLS-RA | IL-1β, IL-6, COX-2, iNOS | Inhibition of inflammation | MAPK (ERK1/2, JNK, and p38) | [244] |
| Umbelliferone | 20 | HFLS-RA | IL-1β, TNF-α, MMP-3, MMP-9, COX-2, Bcl-2 | Inhibition of proliferation, migration and invasion | NF-κB | [242] |
| Wilforine | 0.4 | Isolated FLS | IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, CCND1, GSK-3β, and c-Myc, MMP-3 | Inhibition of inflammation and abnormal proliferation | Wnt11/β-catenin | [245] |
5. In Vivo Studies Using Plant-Derived Natural Products for the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis
5.1. Collagen Induced Arthritis Model
5.2. Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis Model
5.3. Adjuvant Induced Arthritis Model
5.4. Pristane Induced Arthritis Model
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Abbreviations
| ACPAs | Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies |
| ADAMTS | A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase with Thrombospondin Motifs |
| Anti-CarP | Anti-carbamylated protein antibodies |
| CCR6 | Chemokine receptor 6 |
| cDMARDs | Conventional disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| CRP | C-creative protein |
| CTLA-4 | T-lymphocyte associated protein 4 |
| CXCL12 | Chemokine C-X-C motif ligand 12 |
| DALYs | Disability-adjusted life-years |
| DNMT | DNA methyltransferases |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| FGFs | Fibroblast growth factors |
| FLS | Fibroblast-like synoviocytes |
| GC | Glucocorticoids |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| HB-EGF | Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor |
| HDAC | Histone deacetylases |
| HLA-DR | Human leukocyte antigen D-related |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IRF-5 | Interferon regulatory factor 5 |
| JAK/STAT | Janus-activated kinase signal transduction and activator of transcription |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| M-CSF | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| MDC | Myeloid dendritic cells |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| MMPs | Matrix metalloproteinases |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| MTX | Methotrexate |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| NF-κβ | Nuclear factor kappa-B |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NSAIDs | Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| OPG | Osteoprotegerin |
| PADI4 | Peptidyl arginine deiminase, type IV enzyme |
| PBMCs | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| PDC | Plasmacytoid dendritic cells |
| PI3/AKT | Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase-AKT |
| PlGF | Placenta growth factor |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| RANKL | Receptor activator of nuclear factor-B ligand |
| RF | Rheumatoid factor |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SAM | S-adenosine methionine |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| SNPs | Single nucleotide polymorphisms |
| SYK/BTK | Spleen tyrosine kinase)/Bruton’s tyrosine kinase |
| TBX5 | T-box transcription factor 5 |
| Tfh | T follicular helper |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor beta |
| TIMPs | Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TRAF1 | Tumors necrosis factor-receptor associated factor 1 |
| Treg | Regulatory T cells |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| Wnt/β-catenin | Wingless/Integrated |
References
- Damerau, A.; Gaber, T. Modeling Rheumatoid Arthritis In Vitro: From Experimental Feasibility to Physiological Proximity. IJMS 2020, 21, 7916. [CrossRef]
- Kour, G.; Choudhary, R.; Anjum, S.; Bhagat, A.; Bajaj, B.K.; Ahmed, Z. Phytochemicals Targeting JAK/STAT Pathway in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Is There a Future? Biochemical Pharmacology 2022, 197, 114929. [CrossRef]
- Hosseinikhah, S.; Barani, M.; Rahdar, A.; Madry, H.; Arshad, R.; Mohammadzadeh, V.; Cucchiarini, M. Nanomaterials for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Inflammatory Arthritis. IJMS 2021, 22, 3092. [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Solomon, D.H.; Strand, V.; et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018, 4, 18001. [CrossRef]
- Jannat, A.; John, P.; Bhatti, A.; Hayat, M.Q. Tomorou Attenuates Progression of Rheumatoid Arthritis through Alteration in ULK-1 Independent Autophagy Pathway in Collagen Induced Arthritis Mice Model. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 142. [CrossRef]
- Kour, G.; Haq, S.A.; Bajaj, B.K.; Gupta, P.N.; Ahmed, Z. Phytochemical Add-on Therapy to DMARDs Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis: In Vitro and in Vivo Bases, Clinical Evidence and Future Trends. Pharmacological Research 2021, 169, 105618. [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, C.; Huo, H.; Xu, C.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, L. Prodrug-Based Nanomedicines for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Discover Nano 2024, 19, 9. [CrossRef]
- Dudics, S.; Langan, D.; Meka, R.R.; Venkatesha, S.H.; Berman, B.M.; Che, C.-T.; Moudgil, K.D. Natural Products for the Treatment of Autoimmune Arthritis: Their Mechanisms of Action, Targeted Delivery, and Interplay with the Host Microbiome. IJMS 2018, 19, 2508. [CrossRef]
- Juarez, M.; Bang, H.; Hammar, F.; Reimer, U.; Dyke, B.; Sahbudin, I.; Buckley, C.D.; Fisher, B.; Filer, A.; Raza, K. Identification of Novel Antiacetylated Vimentin Antibodies in Patients with Early Inflammatory Arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2016, 75, 1099–1107. [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.L.; Wolfe, F.; Huizinga, T.W. Rheumatoid Arthritis. The Lancet 2010, 376, 1094–1108. [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Knevel, R.; Suwannalai, P.; Van Der Linden, M.P.; Janssen, G.M.C.; Van Veelen, P.A.; Levarht, N.E.W.; Van Der Helm-van Mil, A.H.M.; Cerami, A.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; et al. Autoantibodies Recognizing Carbamylated Proteins Are Present in Sera of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Predict Joint Damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2011, 108, 17372–17377. [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, G.R.; Jothi, G.; Mohana, T.; Vasconcelos, A.B.S.; Montalvão, M.M.; Hariharan, G.; Sridharan, G.; Kumar, P.M.; Gurgel, R.Q.; Li, H.-B.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Natural Products as Potential Therapeutic Agents of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Phytomedicine 2021, 93, 153766. [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Huang, S. Nanomedicine Is More than a Supporting Role in Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy. Journal of Controlled Release 2023, 356, 142–161. [CrossRef]
- Finckh, A.; Gilbert, B.; Hodkinson, B.; Bae, S.-C.; Thomas, R.; Deane, K.D.; Alpizar-Rodriguez, D.; Lauper, K. Global Epidemiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2022. [CrossRef]
- Black, R.J.; Cross, M.; Haile, L.M.; Culbreth, G.T.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Hagins, H.; Kopec, J.A.; Brooks, P.M.; Woolf, A.D.; Ong, K.L.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Rheumatoid Arthritis, 1990–2020, and Projections to 2050: A Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. The Lancet Rheumatology 2023, 5, e594–e610. [CrossRef]
- Bahuguna, R.; Awasthi, R. Unlocking New Dimensions in Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy: Harnessing the Power of Lipid Based Vesicles beyond Traditional Therapies. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 2023, 89, 105106. [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Hu, W.; Wang, R.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Cai, J.; Rose, P.; Mao, J.; Zhu, Y.Z. Signaling Pathways in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Implications for Targeted Therapy. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2023, 8, 68. [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.; Capron, J.-P.; De Leonardis, F.; Fakhouri, W.; Rose, A.; Kouris, I.; Burke, T. The Impact of Disease Severity and Duration on Cost, Early Retirement and Ability to Work in Rheumatoid Arthritis in Europe: An Economic Modelling Study. Rheumatology Advances in Practice 2020, 4, rkaa041. [CrossRef]
- Fischer, B.D.; Adeyemo, A.; O’Leary, M.E.; Bottaro, A. Animal Models of Rheumatoid Pain: Experimental Systems and Insights. Arthritis Res Ther 2017, 19, 146. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Agarwal, S.K. Economic and Humanistic Burden of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results From the US National Survey Data 2018–2020. ACR Open Rheumatology 2024, 6, 746–754. [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Daniyal, M.; Sultana, S.; Owais, A.; Akhtar, N.; Zahid, R.; Said, F.; Bouyahya, A.; Ponomarev, E.; Ali Shariat, M.; et al. Traditional and Modern Management Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clinica Chimica Acta 2021, 512, 142–155. [CrossRef]
- Patidar, V.; Shah, S.; Kumar, R.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, S.B.; Khatri, D.K. A Molecular Insight of Inflammatory Cascades in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Anti-Arthritic Potential of Phytoconstituents. Mol Biol Rep 2022, 49, 2375–2391. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tao, T.; Yao, H.; Zheng, H.; Wang, F.; Gao, Y. Mechanism of Action of Quercetin in Rheumatoid Arthritis Models: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Animal Studies. Inflammopharmacol 2023, 31, 1629–1645. [CrossRef]
- Balendran, T.; Lim, K.; Hamilton, J.A.; Achuthan, A.A. Targeting Transcription Factors for Therapeutic Benefit in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1196931. [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Bai, L.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J. Dysregulation of lncRNAs in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Biomarkers, Pathogenesis and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 652751. [CrossRef]
- George, G.; Shyni, G.L.; Raghu, K.G. Current and Novel Therapeutic Targets in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Inflammopharmacol 2020, 28, 1457–1476. [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.-T.; Wu, Y.-J.; Yin, Q.; Chen, W.-G.; Zuo, J. The Involvement of Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Alteration in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Clinical Implication. JIR 2023, Volume 16, 1837–1852. [CrossRef]
- Németh, T.; Nagy, G.; Pap, T. Synovial Fibroblasts as Potential Drug Targets in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Where Do We Stand and Where Shall We Go? Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2022, 81, 1055–1064. [CrossRef]
- Mueller, A.-L.; Payandeh, Z.; Mohammadkhani, N.; Mubarak, S.M.H.; Zakeri, A.; Alagheband Bahrami, A.; Brockmueller, A.; Shakibaei, M. Recent Advances in Understanding the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: New Treatment Strategies. Cells 2021, 10, 3017. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.D.; Leung, S.H.; Viatte, S. Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Best Practice & Research Clinical Rheumatology 2024, 38, 101968. [CrossRef]
- Källberg, H.; Padyukov, L.; Plenge, R.M.; Rönnelid, J.; Gregersen, P.K.; Van Der Helm-van Mil, A.H.M.; Toes, R.E.M.; Huizinga, T.W.; Klareskog, L.; Alfredsson, L. Gene-Gene and Gene-Environment Interactions Involving HLA-DRB1, PTPN22, and Smoking in Two Subsets of Rheumatoid Arthritis. The American Journal of Human Genetics 2007, 80, 867–875. [CrossRef]
- Kokkonen, H.; Johansson, M.; Innala, L.; Jidell, E.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S. The PTPN221858C/T Polymorphism Is Associated with Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibody-Positive Early Rheumatoid Arthritis in Northern Sweden. Arthritis Res Ther 2007, 9, R56. [CrossRef]
- Van Der Helm-van Mil, A.H.M.; Verpoort, K.N.; Breedveld, F.C.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Toes, R.E.M.; De Vries, R.R.P. The HLA–DRB1 Shared Epitope Alleles Are Primarily a Risk Factor for Anti–Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibodies and Are Not an Independent Risk Factor for Development of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2006, 54, 1117–1121. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, L.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X. Association between Polymorphism in TRAF1/C5 Gene and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis. Mol Biol Rep 2014, 41, 317–324. [CrossRef]
- Sigurdsson, S.; Padyukov, L.; Kurreeman, F.A.S.; Liljedahl, U.; Wiman, A.; Alfredsson, L.; Toes, R.; Rönnelid, J.; Klareskog, L.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; et al. Association of a Haplotype in the Promoter Region of the Interferon Regulatory Factor 5 Gene with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2007, 56, 2202–2210. [CrossRef]
- Silman, A.J.; Pearson, J.E. Epidemiology and Genetics of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res 2002, 4, S265. [CrossRef]
- Kapitány, A.; Zilahi, E.; Szántó, S.; Szücs, G.; Szabó, Z.; Végvári, A.; Rass, P.; Sipka, S.; Szegedi, G.; Szekanecz, Z. Association of Rheumatoid Arthritis with HLA-DR1 and HLA-DR4 in Hungary. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2005, 1051, 263–270. [CrossRef]
- Becart, S.; Whittington, K.B.; Prislovsky, A.; Rao, N.L.; Rosloniec, E.F. The Role of Posttranslational Modifications in Generating Neo-Epitopes That Bind to Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated HLA-DR Alleles and Promote Autoimmune T Cell Responses. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245541. [CrossRef]
- Van Der Helm-van Mil, A.H.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Schreuder, G.M.Th.; Breedveld, F.C.; De Vries, R.R.P.; Toes, R.E.M. An Independent Role of Protective HLA Class II Alleles in Rheumatoid Arthritis Severity and Susceptibility. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2005, 52, 2637–2644. [CrossRef]
- Kanaan, S.B.; Sensoy, O.; Yan, Z.; Gadi, V.K.; Richardson, M.L.; Nelson, J.L. Immunogenicity of a Rheumatoid Arthritis Protective Sequence When Acquired through Microchimerism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2019, 116, 19600–19608. [CrossRef]
- Okada, E.; Daimon, K.; Fujiwara, H.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Nojiri, K.; Watanabe, M.; Katoh, H.; Shimizu, K.; Ishihama, H.; Fujita, N.; et al. Twenty-Year Longitudinal Follow-up MRI Study of Asymptomatic Volunteers: The Impact of Cervical Alignment on Disk Degeneration. Clinical Spine Surgery: A Spine Publication 2018, 31, 446–451. [CrossRef]
- Holoshitz, J. The Rheumatoid Arthritis HLA–DRB1 Shared Epitope. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 2010, 22, 293–298. [CrossRef]
- Viatte, S.; Massey, J.; Bowes, J.; Duffus, K.; arcOGEN Consortium; Eyre, S.; Barton, A.; Worthington, J. Replication of Associations of Genetic Loci Outside the HLA Region With Susceptibility to Anti–Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide–Negative Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatology 2016, 68, 1603–1613. [CrossRef]
- Viatte, S.; Plant, D.; Bowes, J.; Lunt, M.; Eyre, S.; Barton, A.; Worthington, J. Genetic Markers of Rheumatoid Arthritis Susceptibility in Anti-Citrullinated Peptide Antibody Negative Patients. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2012, 71, 1984–1990. [CrossRef]
- Krabben, A.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Mil, A.H.M. Biomarkers for Radiographic Progression in Rheumatoid Arthritis. CPD 2014, 21, 147–169. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Espéli, M.; Anderson, C.A.; Linterman, M.A.; Pocock, J.M.; Williams, N.J.; Roberts, R.; Viatte, S.; Fu, B.; Peshu, N.; et al. Human SNP Links Differential Outcomes in Inflammatory and Infectious Disease to a FOXO3-Regulated Pathway. Cell 2013, 155, 57–69. [CrossRef]
- Raychaudhuri, S.; Sandor, C.; Stahl, E.A.; Freudenberg, J.; Lee, H.-S.; Jia, X.; Alfredsson, L.; Padyukov, L.; Klareskog, L.; Worthington, J.; et al. Five Amino Acids in Three HLA Proteins Explain Most of the Association between MHC and Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat Genet 2012, 44, 291–296. [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Diogo, D.; Eyre, S.; Kallberg, H.; Zhernakova, A.; Bowes, J.; Padyukov, L.; Okada, Y.; González-Gay, M.A.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; et al. Fine Mapping Seronegative and Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis to Shared and Distinct HLA Alleles by Adjusting for the Effects of Heterogeneity. The American Journal of Human Genetics 2014, 94, 522–532. [CrossRef]
- Ishigaki, K.; Sakaue, S.; Terao, C.; Luo, Y.; Sonehara, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Amariuta, T.; Too, C.L.; Laufer, V.A.; Scott, I.C.; et al. Multi-Ancestry Genome-Wide Association Analyses Identify Novel Genetic Mechanisms in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat Genet 2022, 54, 1640–1651. [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.J.; Zozulya, S.; Lu, Y.-L.; Ward, K.; Gishizky, M.; Jallal, B. The Lymphoid Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Lyp Interacts with the Adaptor Molecule Grb2 and Functions as a Negative Regulator of T-Cell Activation. Experimental Hematology 2002, 30, 237–244. [CrossRef]
- Bottini, N.; Peterson, E.J. Tyrosine Phosphatase PTPN22: Multifunctional Regulator of Immune Signaling, Development, and Disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 83–119. [CrossRef]
- Vang, T.; Liu, W.H.; Delacroix, L.; Wu, S.; Vasile, S.; Dahl, R.; Yang, L.; Musumeci, L.; Francis, D.; Landskron, J.; et al. LYP Inhibits T-Cell Activation When Dissociated from CSK. Nat Chem Biol 2012, 8, 437–446. [CrossRef]
- Arechiga, A.F.; Habib, T.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Funk, A.; Buckner, J.H. Cutting Edge: The PTPN22 Allelic Variant Associated with Autoimmunity Impairs B Cell Signaling. The Journal of Immunology 2009, 182, 3343–3347. [CrossRef]
- Gardette, A.; Marzaioli, V.; Bedouhene, S.; Hayem, G.; Hurtado-Nedelec, M.; He, Y.; Dang, P.M.-C.; Dieudé, P.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Marie, J.-C.; et al. The Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Lyp/PTPN22 Drives TNFα-Induced Priming of Superoxide Anions Production by Neutrophils and Arthritis. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2025, 228, 68–78. [CrossRef]
- Nemtsova, M.V.; Zaletaev, D.V.; Bure, I.V.; Mikhaylenko, D.S.; Kuznetsova, E.B.; Alekseeva, E.A.; Beloukhova, M.I.; Deviatkin, A.A.; Lukashev, A.N.; Zamyatnin, A.A. Epigenetic Changes in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 570. [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, D.; Teng, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Z.; Yang, G.-J. Epigenetic Regulation in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 859400. [CrossRef]
- Karouzakis, E.; Trenkmann, M.; Gay, R.E.; Michel, B.A.; Gay, S.; Neidhart, M. Epigenome Analysis Reveals TBX5 as a Novel Transcription Factor Involved in the Activation of Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts. The Journal of Immunology 2014, 193, 4945–4951. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-F.; Wu, S.; Yan, Q.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Chen, H.; Yin, S.-Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Li, J. PTEN Methylation Promotes Inflammation and Activation of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 700373. [CrossRef]
- Nakano, K.; Whitaker, J.W.; Boyle, D.L.; Wang, W.; Firestein, G.S. DNA Methylome Signature in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2013, 72, 110–117. [CrossRef]
- Liebold, I.; Grützkau, A.; Göckeritz, A.; Gerl, V.; Lindquist, R.; Feist, E.; Zänker, M.; Häupl, T.; Poddubnyy, D.; Zernicke, J.; et al. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Are Hypomethylated in Active Rheumatoid Arthritis and Methylation Correlates with Disease Activity. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 1984–1995. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wu, L.-F.; Mo, X.-B.; Lu, X.; Tang, H.; Zhu, X.-W.; Xia, W.; Guo, Y.-F.; Wang, M.-J.; Zeng, K.-Q.; et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis–Associated DNA Methylation Sites in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2019, 78, 36–42. [CrossRef]
- Julià, A.; Absher, D.; López-Lasanta, M.; Palau, N.; Pluma, A.; Waite Jones, L.; Glossop, J.R.; Farrell, W.E.; Myers, R.M.; Marsal, S. Epigenome-Wide Association Study of Rheumatoid Arthritis Identifies Differentially Methylated Loci in B Cells. Human Molecular Genetics 2017, 26, 2803–2811. [CrossRef]
- Lev Maor, G.; Yearim, A.; Ast, G. The Alternative Role of DNA Methylation in Splicing Regulation. Trends in Genetics 2015, 31, 274–280. [CrossRef]
- Cribbs, A.P.; Kennedy, A.; Penn, H.; Read, J.E.; Amjadi, P.; Green, P.; Syed, K.; Manka, S.W.; Brennan, F.M.; Gregory, B.; et al. Treg Cell Function in Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Compromised by CTLA-4 Promoter Methylation Resulting in a Failure to Activate the Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Pathway. Arthritis & Rheumatology 2014, 66, 2344–2354. [CrossRef]
- Cribbs, A.; Feldmann, M.; Oppermann, U. Towards an Understanding of the Role of DNA Methylation in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Therapeutic and Diagnostic Implications. Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal 2015, 7, 206–219. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Lv, X.; Song, L.; Zhang, D.; He, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, X.; Shi, G.; et al. Reduced Activity of HDAC3 and Increased Acetylation of Histones H3 in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Journal of Immunology Research 2018, 2018, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Göschl, L.; Preglej, T.; Boucheron, N.; Saferding, V.; Müller, L.; Platzer, A.; Hirahara, K.; Shih, H.-Y.; Backlund, J.; Matthias, P.; et al. Histone Deacetylase 1 (HDAC1): A Key Player of T Cell-Mediated Arthritis. Journal of Autoimmunity 2020, 108, 102379. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Hong, K.W.; Bae, S.S.; Kim, K.; Kim, C.D. SIRT1/Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase α Signaling Enhances Macrophage Polarization to an Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1135. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hu, W.; Wang, R.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, K.; et al. Sp1 S-Sulfhydration Induced by Hydrogen Sulfide Inhibits Inflammation via HDAC6/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 732. [CrossRef]
- Mu, N.; Gu, J.; Huang, T.; Zhang, C.; Shu, Z.; Li, M.; Hao, Q.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; et al. A Novel NF-κB/YY1/microRNA-10a Regulatory Circuit in Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes Regulates Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 20059. [CrossRef]
- Stanczyk, J.; Ospelt, C.; Karouzakis, E.; Filer, A.; Raza, K.; Kolling, C.; Gay, R.; Buckley, C.D.; Tak, P.P.; Gay, S.; et al. Altered Expression of microRNA-203 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts and Its Role in Fibroblast Activation. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2011, 63, 373–381. [CrossRef]
- Gantier, M.P.; Stunden, H.J.; McCoy, C.E.; Behlke, M.A.; Wang, D.; Kaparakis-Liaskos, M.; Sarvestani, S.T.; Yang, Y.H.; Xu, D.; Corr, S.C.; et al. A miR-19 Regulon That Controls NF-κB Signaling. Nucleic Acids Research 2012, 40, 8048–8058. [CrossRef]
- Holers, V.M.; Demoruelle, M.K.; Kuhn, K.A.; Buckner, J.H.; Robinson, W.H.; Okamoto, Y.; Norris, J.M.; Deane, K.D. Rheumatoid Arthritis and the Mucosal Origins Hypothesis: Protection Turns to Destruction. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2018, 14, 542–557. [CrossRef]
- Willis, V.C.; Demoruelle, M.K.; Derber, L.A.; Chartier-Logan, C.J.; Parish, M.C.; Pedraza, I.F.; Weisman, M.H.; Norris, J.M.; Holers, V.M.; Deane, K.D. Sputum Autoantibodies in Patients With Established Rheumatoid Arthritis and Subjects at Risk of Future Clinically Apparent Disease. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2013, 65, 2545–2554. [CrossRef]
- Demoruelle, M.K.; Bowers, E.; Lahey, L.J.; Sokolove, J.; Purmalek, M.; Seto, N.L.; Weisman, M.H.; Norris, J.M.; Kaplan, M.J.; Holers, V.M.; et al. Antibody Responses to Citrullinated and Noncitrullinated Antigens in the Sputum of Subjects With Rheumatoid Arthritis and Subjects at Risk for Development of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatology 2018, 70, 516–527. [CrossRef]
- Reynisdottir, G.; Karimi, R.; Joshua, V.; Olsen, H.; Hensvold, A.H.; Harju, A.; Engström, M.; Grunewald, J.; Nyren, S.; Eklund, A.; et al. Structural Changes and Antibody Enrichment in the Lungs Are Early Features of Anti–Citrullinated Protein Antibody–Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatology 2014, 66, 31–39. [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Terao, C. The Impact of Cigarette Smoking on Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Narrative Review. Cells 2020, 9, 475. [CrossRef]
- Padyukov, L.; Silva, C.; Stolt, P.; Alfredsson, L.; Klareskog, L. A Gene–Environment Interaction between Smoking and Shared Epitope Genes in HLA–DR Provides a High Risk of Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2004, 50, 3085–3092. [CrossRef]
- Linn-Rasker, S.P.; Van Der Helm-van Mil, A.H.M.; Van Gaalen, F.A.; Kloppenburg, M.; De Vries, R.R.P.; Le Cessie, S.; Breedveld, F.C.; Toes, R.E.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J. Smoking Is a Risk Factor for Anti-CCP Antibodies Only in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Who Carry HLA-DRB1 Shared Epitope Alleles. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2006, 65, 366–371. [CrossRef]
- Källberg, H.; Ding, B.; Padyukov, L.; Bengtsson, C.; Rönnelid, J.; Klareskog, L.; Alfredsson, L. Smoking Is a Major Preventable Risk Factor for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Estimations of Risks after Various Exposures to Cigarette Smoke. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2011, 70, 508–511. [CrossRef]
- Hedström, A.K.; Klareskog, L.; Alfredsson, L. Exposure to Passive Smoking and Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk: Results from the Swedish EIRA Study. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2018, 77, 970–972. [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, A.J.; Gervin, K.; Lyle, R.; Christiansen, L.; Kyvik, K.; Junker, P.; Nielsen, C.; Houen, G.; Tan, Q. Differentially Methylated DNA Regions in Monozygotic Twin Pairs Discordant for Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Epigenome-Wide Study. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7. [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, E. Smoking, Gender and Rheumatoid Arthritis–Epidemiological Clues to Etiology. Joint Bone Spine 2003, 70, 496–502. [CrossRef]
- Too, C.L.; Muhamad, N.A.; Ilar, A.; Padyukov, L.; Alfredsson, L.; Klareskog, L.; Murad, S.; Bengtsson, C. Occupational Exposure to Textile Dust Increases the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from a Malaysian Population-Based Case–Control Study. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2016, 75, 997–1002. [CrossRef]
- Stolt, P.; Yahya, A.; Bengtsson, C.; Källberg, H.; Rönnelid, J.; Lundberg, I.; Klareskog, L.; Alfredsson, L. Silica Exposure among Male Current Smokers Is Associated with a High Risk of Developing ACPA-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2010, 69, 1072–1076. [CrossRef]
- Mehri, F.; Jenabi, E.; Bashirian, S.; Shahna, F.G.; Khazaei, S. The Association Between Occupational Exposure to Silica and Risk of Developing Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis. Safety and Health at Work 2020, 11, 136–142. [CrossRef]
- Alaya, Z.; Braham, M.; Aissa, S.; Kalboussi, H.; Bouajina, E. A Case of Caplan Syndrome in a Recently Diagnosed Patient with Silicosis: A Case Report. Radiology Case Reports 2018, 13, 663–666. [CrossRef]
- on behalf of the EIRA study group; Johansson, K.; Askling, J.; Alfredsson, L.; Di Giuseppe, D. Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. Arthritis Res Ther 2018, 20. [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Li, J.; Gan, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, L.; et al. Red Meat Intake Is Associated with Early Onset of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Cross-Sectional Study. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 5681. [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.W.; Demoruelle, M.K.; Deane, K.D.; Weisman, M.H.; Buckner, J.H.; Gregersen, P.K.; Mikuls, T.R.; O’Dell, J.R.; Keating, R.M.; Fingerlin, T.E.; et al. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Are Associated with a Lower Prevalence of Autoantibodies in Shared Epitope-Positive Subjects at Risk for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2017, 76, 147–152. [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.W.; Young, K.A.; Zerbe, G.O.; Demoruelle, M.K.; Weisman, M.H.; Buckner, J.H.; Gregersen, P.K.; Mikuls, T.R.; O’Dell, J.R.; Keating, R.M.; et al. Lower Omega-3 Fatty Acids Are Associated with the Presence of Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Autoantibodies in a Population at Risk for Future Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Nested Case-Control Study. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 367–376. [CrossRef]
- Costenbader, K.H.; Cook, N.R.; Lee, I.; Hahn, J.; Walter, J.; Bubes, V.; Kotler, G.; Yang, N.; Friedman, S.; Alexander, E.K.; et al. Vitamin D and Marine N-3 Fatty Acids for Autoimmune Disease Prevention: Outcomes Two Years After Completion of a Double-Blind , Placebo-Controlled Trial. Arthritis & Rheumatology 2024, 76, 973–983. [CrossRef]
- Karlson, E.W.; Mandl, L.A.; Aweh, G.N.; Grodstein, F. Coffee Consumption and Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2003, 48, 3055–3060. [CrossRef]
- Pattison, D.J.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Lunt, M.; Welch, A.; Luben, R.; Bingham, S.A.; Khaw, K.; Day, N.E.; Silman, A.J. Dietary Risk Factors for the Development of Inflammatory Polyarthritis: Evidence for a Role of High Level of Red Meat Consumption. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2004, 50, 3804–3812. [CrossRef]
- DeChristopher, L.R.; Uribarri, J.; Tucker, K.L. Intake of High-Fructose Corn Syrup Sweetened Soft Drinks, Fruit Drinks and Apple Juice Is Associated with Prevalent Arthritis in US Adults, Aged 20–30 Years. Nutr & Diabetes 2016, 6, e199–e199. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Costenbader, K.H.; Gao, X.; Al-Daabil, M.; Sparks, J.A.; Solomon, D.H.; Hu, F.B.; Karlson, E.W.; Lu, B. Sugar-Sweetened Soda Consumption and Risk of Developing Rheumatoid Arthritis in Women , , ,. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2014, 100, 959–967. [CrossRef]
- Radu, A.-F.; Bungau, S.G. Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview. Cells 2021, 10, 2857. [CrossRef]
- Kharlamova, N.; Jiang, X.; Sherina, N.; Potempa, B.; Israelsson, L.; Quirke, A.; Eriksson, K.; Yucel-Lindberg, T.; Venables, P.J.; Potempa, J.; et al. Antibodies to Porphyromonas Gingivalis Indicate Interaction Between Oral Infection, Smoking, and Risk Genes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Etiology. Arthritis & Rheumatology 2016, 68, 604–613. [CrossRef]
- Konig, M.F.; Abusleme, L.; Reinholdt, J.; Palmer, R.J.; Teles, R.P.; Sampson, K.; Rosen, A.; Nigrovic, P.A.; Sokolove, J.; Giles, J.T.; et al. Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans –Induced Hypercitrullination Links Periodontal Infection to Autoimmunity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8. [CrossRef]
- Alpizar-Rodriguez, D.; Lesker, T.R.; Gronow, A.; Gilbert, B.; Raemy, E.; Lamacchia, C.; Gabay, C.; Finckh, A.; Strowig, T. Prevotella Copri in Individuals at Risk for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2019, 78, 590–593. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Jia, H.; Feng, Q.; Wang, D.; Liang, D.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; et al. The Oral and Gut Microbiomes Are Perturbed in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Partly Normalized after Treatment. Nat Med 2015, 21, 895–905. [CrossRef]
- Scher, J.U.; Sczesnak, A.; Longman, R.S.; Segata, N.; Ubeda, C.; Bielski, C.; Rostron, T.; Cerundolo, V.; Pamer, E.G.; Abramson, S.B.; et al. Expansion of Intestinal Prevotella Copri Correlates with Enhanced Susceptibility to Arthritis. eLife 2013, 2, e01202. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wright, K.; Davis, J.M.; Jeraldo, P.; Marietta, E.V.; Murray, J.; Nelson, H.; Matteson, E.L.; Taneja, V. An Expansion of Rare Lineage Intestinal Microbes Characterizes Rheumatoid Arthritis. Genome Med 2016, 8, 43. [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, C.; Malspeis, S.; Orellana, C.; Sparks, J.A.; Costenbader, K.H.; Karlson, E.W. Association Between Menopausal Factors and the Risk of Seronegative and Seropositive Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results From the Nurses’ Health Studies. Arthritis Care & Research 2017, 69, 1676–1684. [CrossRef]
- Beydoun, H.A.; el-Amin, R.; McNeal, M.; Perry, C.; Archer, D.F. Reproductive History and Postmenopausal Rheumatoid Arthritis among Women 60 Years or Older: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Menopause 2013, 20, 930–935. [CrossRef]
- Kobak, S.; Bes, C. An Autumn Tale: Geriatric Rheumatoid Arthritis. Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal 2018, 10, 3–11. [CrossRef]
- Alamanos, Y.; Voulgari, P.V.; Drosos, A.A. Incidence and Prevalence of Rheumatoid Arthritis, Based on the 1987 American College of Rheumatology Criteria: A Systematic Review. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 2006, 36, 182–188. [CrossRef]
- George, M.D.; Baker, J.F. The Obesity Epidemic and Consequences for Rheumatoid Arthritis Care. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2016, 18, 6. [CrossRef]
- Alunno, A.; Carubbi, F.; Giacomelli, R.; Gerli, R. Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: New Players and Therapeutic Targets. BMC Rheumatol 2017, 1, 3. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xue, W.; Wu, Z.; Lu, D.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T. Quercetin, a Compound of the Total Flavonoids of Periploca Forrestii Schltr., Ameliorates Rheumatoid Arthritis by Targeting TNF-α. JIR 2025, Volume 18, 2879–2898. [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wu, B.; Meng, M.; Zhao, J.; Wang, D. Sesquiterpene Lactones-Enriched Fractions from Xanthium Mongolicum Kitag Alleviate RA by Regulating M1 Macrophage Polarization via NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1104153. [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Feng, Q.; Cui, M.; Fan, C.; Wang, T.; Yuan, R.; Tsering, D.; Huang, S.; Li, B. Siweixizangmaoru Decoction Ameliorated Type II Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats via Regulating JAK2–STAT3 and NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 2024, 47, 1511–1524. [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Yang, Y.; Lu, H.; Shi, H.; Jiang, L.; Liao, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, J. Network Pharmacology Combines Machine Learning, Molecular Simulation Dynamics and Experimental Validation to Explore the Mechanism of Acetylbinankadsurin A in the Treatment of Liver Fibrosis. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2024, 323, 117682. [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Cheng, M.-H.; Hu, L.-Q.; Shen, H.-H.; Tao, J.-H.; Li, X.-M.; Pan, H.-F.; Gao, J. Natural Products Action on Pathogenic Cues in Autoimmunity: Efficacy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis as Compared to Classical Treatments. Pharmacological Research 2020, 160, 105054. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Fan, X.; Qu, Y.; Tang, M.; Huang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Fu, Q. Magnoflorine Attenuates Inflammatory Responses in RA by Regulating the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB and Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 Signalling Pathways in Vivo and in Vitro. Phytomedicine 2022, 104, 154339. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, M.; Tang, Q.; Sun, H.; Yang, G.; Sun, J. Anti-Rheumatic Arthritis Efficacy of Pueraria Montana Extract against Type-II Collagen-Induced Rheumatoid Arthritis Rat Model an in Vitro and in Vivo Assessment. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2025, 340, 119175. [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.; Breedveld, F.C.; Buch, M.; Burmester, G.; Dougados, M.; Emery, P.; Gaujoux-Viala, C.; Gossec, L.; Nam, J.; et al. EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis with Synthetic and Biological Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs: 2013 Update. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2014, 73, 492–509. [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.A.; Gurish, M.F.; Marshall, J.L.; Slowikowski, K.; Fonseka, C.Y.; Liu, Y.; Donlin, L.T.; Henderson, L.A.; Wei, K.; Mizoguchi, F.; et al. Pathologically Expanded Peripheral T Helper Cell Subset Drives B Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nature 2017, 542, 110–114. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wei, K.; Slowikowski, K.; Fonseka, C.Y.; Rao, D.A.; Kelly, S.; Goodman, S.M.; Tabechian, D.; Hughes, L.B.; Salomon-Escoto, K.; et al. Defining Inflammatory Cell States in Rheumatoid Arthritis Joint Synovial Tissues by Integrating Single-Cell Transcriptomics and Mass Cytometry. Nat Immunol 2019, 20, 928–942. [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, L.J.; Kaplan, M.J. Neutrophils in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Breaking Immune Tolerance and Fueling Disease. Trends in Molecular Medicine 2019, 25, 215–227. [CrossRef]
- Rivellese, F.; Mauro, D.; Nerviani, A.; Pagani, S.; Fossati-Jimack, L.; Messemaker, T.; Kurreeman, F.A.S.; Toes, R.E.M.; Ramming, A.; Rauber, S.; et al. Mast Cells in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Associate with Disease Severity and Support B Cell Autoantibody Production. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2018, 77, 1773–1781. [CrossRef]
- Schubert, N.; Dudeck, J.; Liu, P.; Karutz, A.; Speier, S.; Maurer, M.; Tuckermann, J.; Dudeck, A. Mast Cell Promotion of T Cell–Driven Antigen-Induced Arthritis Despite Being Dispensable for Antibody-Induced Arthritis in Which T Cells Are Bypassed. Arthritis & Rheumatology 2015, 67, 903–913. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Meng, F.; Luo, M.; Chen, W.; Tian, J.; Chen, L.; Ju, Y.; Mei, Z. Anti-Inflammatory and Osteoprotective Effects of Shi-Wei-Ru-Xiang Pills on Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats via Inhibiting MAPK and STAT3 Pathways. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2023, 300, 115693. [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. The Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. N Engl J Med 2011, 365, 2205–2219. [CrossRef]
- Kondo, N.; Kuroda, T.; Kobayashi, D. Cytokine Networks in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. IJMS 2021, 22, 10922. [CrossRef]
- Cope, A.P. T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2008, 10, S1. [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.W.; Lee, K.W.; Park, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.H.; Song, J.W.; Yang, J.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, T.M.; Park, J.B.; et al. Therapeutic Effects of Anti-CD154 Antibody in Cynomolgus Monkeys with Advanced Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 2135. [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.-A.; Sim, J.H.; Park, J.A.; Kim, H.W.; Yoo, W.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, D.-S.; Kang, J.S.; Hwang, Y.-I.; Lee, W.J.; et al. Characterization of Effector Memory CD8+ T Cells in the Synovial Fluid of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Clin Immunol 2012, 32, 709–720. [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, A.H.; Zhang, F.; Dunlap, G.; Gomez-Rivas, E.; Watts, G.F.M.; Faust, H.J.; Rupani, K.V.; Mears, J.R.; Meednu, N.; Wang, R.; et al. Granzyme K+ CD8 T Cells Form a Core Population in Inflamed Human Tissue. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabo0686. [CrossRef]
- Leipe, J.; Grunke, M.; Dechant, C.; Reindl, C.; Kerzendorf, U.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Skapenko, A. Role of Th17 Cells in Human Autoimmune Arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 2010, 62, 2876–2885. [CrossRef]
- Van Baarsen, L.G.; Lebre, M.C.; Van Der Coelen, D.; Aarrass, S.; Tang, M.W.; Ramwadhdoebe, T.H.; Gerlag, D.M.; Tak, P.P. Heterogeneous Expression Pattern of Interleukin 17A (IL-17A), IL-17F and Their Receptors in Synovium of Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Osteoarthritis: Possible Explanation for Nonresponse to Anti-IL-17 Therapy? Arthritis Res Ther 2014, 16, 426. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yin, H.; Zhang, K.; Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chang, X.; Zhang, M.; Yan, X.; Ren, Y.; et al. Effector T Helper Cell Populations Are Elevated in the Bone Marrow of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients and Correlate with Disease Severity. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 4776. [CrossRef]
- Edavalath, S.; Singh, A.; Soni, N.; Mohindra, N.; Kumar, S.; Misra, R. Peripheral Blood T Helper Type 17 Frequency Shows an Inverse Correlation with Disease Activity and Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Based Osteitis and Erosions in Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug- and Steroid-Naive Established Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 2016, 186, 313–320. [CrossRef]
- Maston, L.D.; Jones, D.T.; Giermakowska, W.; Howard, T.A.; Cannon, J.L.; Wang, W.; Wei, Y.; Xuan, W.; Resta, T.C.; Gonzalez Bosc, L.V. Central Role of T Helper 17 Cells in Chronic Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 2017, 312, L609–L624. [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhu, C.; Ma, B.; Tian, J.; Baidoo, S.E.; Mao, C.; Wu, W.; Chen, J.; Tong, J.; Yang, M.; et al. Increased Frequency of Circulating Follicular Helper T Cells in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clinical and Developmental Immunology 2012, 2012, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Kondo, Y.; Yokosawa, M.; Kaneko, S.; Furuyama, K.; Segawa, S.; Tsuboi, H.; Matsumoto, I.; Sumida, T. Review: Transcriptional Regulation of CD 4+ T Cell Differentiation in Experimentally Induced Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatology 2018, 70, 653–661. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Yang, G.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Cui, D. Function and Role of Regulatory T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 626193. [CrossRef]
- Ambarus, C.A.; Noordenbos, T.; De Hair, M.J.; Tak, P.P.; Baeten, D.L. Intimal Lining Layer Macrophages but Not Synovial Sublining Macrophages Display an IL-10 Polarized-like Phenotype in Chronic Synovitis. Arthritis Res Ther 2012, 14, R74. [CrossRef]
- Soler Palacios, B.; Estrada-Capetillo, L.; Izquierdo, E.; Criado, G.; Nieto, C.; Municio, C.; González-Alvaro, I.; Sánchez-Mateos, P.; Pablos, J.L.; Corbí, A.L.; et al. Macrophages from the Synovium of Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Exhibit an Activin A-dependent Pro-inflammatory Profile. The Journal of Pathology 2015, 235, 515–526. [CrossRef]
- Kuo, D.; Ding, J.; Cohn, I.S.; Zhang, F.; Wei, K.; Rao, D.A.; Rozo, C.; Sokhi, U.K.; Shanaj, S.; Oliver, D.J.; et al. HBEGF+ Macrophages in Rheumatoid Arthritis Induce Fibroblast Invasiveness. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaau8587. [CrossRef]
- Alivernini, S.; MacDonald, L.; Elmesmari, A.; Finlay, S.; Tolusso, B.; Gigante, M.R.; Petricca, L.; Di Mario, C.; Bui, L.; Perniola, S.; et al. Distinct Synovial Tissue Macrophage Subsets Regulate Inflammation and Remission in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat Med 2020, 26, 1295–1306. [CrossRef]
- Ota, Y.; Niiro, H.; Ota, S.; Ueki, N.; Tsuzuki, H.; Nakayama, T.; Mishima, K.; Higashioka, K.; Jabbarzadeh-Tabrizi, S.; Mitoma, H.; et al. Generation Mechanism of RANKL+ Effector Memory B Cells: Relevance to the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2016, 18, 67. [CrossRef]
- Humby, F.; Durez, P.; Buch, M.H.; Lewis, M.J.; Rizvi, H.; Rivellese, F.; Nerviani, A.; Giorli, G.; Mahto, A.; Montecucco, C.; et al. Rituximab versus Tocilizumab in Anti-TNF Inadequate Responder Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (R4RA): 16-Week Outcomes of a Stratified, Biopsy-Driven, Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 4 Randomised Controlled Trial. The Lancet 2021, 397, 305–317. [CrossRef]
- Yeo, L.; Lom, H.; Juarez, M.; Snow, M.; Buckley, C.D.; Filer, A.; Raza, K.; Scheel-Toellner, D. Expression of FcRL4 Defines a Pro-Inflammatory, RANKL-Producing B Cell Subset in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2015, 74, 928–935. [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, F.; Slowikowski, K.; Wei, K.; Marshall, J.L.; Rao, D.A.; Chang, S.K.; Nguyen, H.N.; Noss, E.H.; Turner, J.D.; Earp, B.E.; et al. Functionally Distinct Disease-Associated Fibroblast Subsets in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 789. [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Cen, X.; Xie, Q. Pim-2/mTORC1 Pathway Shapes Inflammatory Capacity in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Cells Exposed to Lipid Peroxidations. BioMed Research International 2015, 2015, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Kuo, D.; Ding, J.; Cohn, I.S.; Zhang, F.; Wei, K.; Rao, D.A.; Rozo, C.; Sokhi, U.K.; Shanaj, S.; Oliver, D.J.; et al. HBEGF+ Macrophages in Rheumatoid Arthritis Induce Fibroblast Invasiveness. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaau8587. [CrossRef]
- Alivernini, S.; MacDonald, L.; Elmesmari, A.; Finlay, S.; Tolusso, B.; Gigante, M.R.; Petricca, L.; Di Mario, C.; Bui, L.; Perniola, S.; et al. Distinct Synovial Tissue Macrophage Subsets Regulate Inflammation and Remission in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat Med 2020, 26, 1295–1306. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Advances. MedComm 2024, 5, e509. [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.-S.; Jeong, G.H.; Yoo, S.-A. The Use of Animal Models in Rheumatoid Arthritis Research. J Yeungnam Med Sci 2023, 40, 23–29. [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.O.; Feldmann, M.; Maini, R.N. Cartilage Destruction and Bone Erosion in Arthritis: The Role of Tumour Necrosis Factor α. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2000, 59, i75–i80. [CrossRef]
- Horai, R.; Saijo, S.; Tanioka, H.; Nakae, S.; Sudo, K.; Okahara, A.; Ikuse, T.; Asano, M.; Iwakura, Y. Development of Chronic Inflammatory Arthropathy Resembling Rheumatoid Arthritis in Interleukin 1 Receptor Antagonist–Deficient Mice. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 2000, 191, 313–320. [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; Ortmann, R.A.; Kimpel, D. Animal Models of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Their Relevance to Human Disease. Pathophysiology 2005, 12, 167–181. [CrossRef]
- Razawy, W.; Asmawidjaja, P.S.; Mus, A.; Salioska, N.; Davelaar, N.; Kops, N.; Oukka, M.; Alves, C.H.; Lubberts, E. CD4+ CCR6+ T Cells, but Not Γδ T Cells, Are Important for the IL-23R-dependent Progression of Antigen-induced Inflammatory Arthritis in Mice. Eur J Immunol 2020, 50, 245–255. [CrossRef]
- Giant, T.T.; Mikecz, K.; Bartlett, R.R.; Deák, F.; Thonar, E.J.-M.A.; Williams, J.M.; Mattar, T.; Kuettner, K.E.; Schleyerbach, R. Immunomodulation of Proteoglycan-Induced Progressive Polyarthritis by Lefluflomide. Immunopharmacology 1992, 23, 105–116. [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Bäcklund, J.; Vestberg, M.; Holmdahl, R. Collagen Type II (CII)-Specific Antibodies Induce Arthritis in the Absence of T or B Cells but the Arthritis Progression Is Enhanced by CII-Reactive T Cells. Arthritis Res Ther 2004, 6, R544. [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H. Adaptive Immunity in the Joint of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunological Medicine 2022, 45, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Fang, Q.; Wingbro Ågren, I.; Bejmo, Z.F. Aberrant Activation of Immune and Non-Immune Cells Contributes to Joint Inflammation and Bone Degradation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. IJMS 2023, 24, 15883. [CrossRef]
- Takemura, S.; Klimiuk, P.A.; Braun, A.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. T Cell Activation in Rheumatoid Synovium Is B Cell Dependent. The Journal of Immunology 2001, 167, 4710–4718. [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, P.M.; Steiert, I.; Kötter, I.; Müller, C.A. B Cells Contribute to Heterogeneity of IL-17 Producing Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Healthy Controls. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82580. [CrossRef]
- Accelerating Medicines Partnership Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (AMP RA/SLE) Consortium; Zhang, F.; Wei, K.; Slowikowski, K.; Fonseka, C.Y.; Rao, D.A.; Kelly, S.; Goodman, S.M.; Tabechian, D.; Hughes, L.B.; et al. Defining Inflammatory Cell States in Rheumatoid Arthritis Joint Synovial Tissues by Integrating Single-Cell Transcriptomics and Mass Cytometry. Nat Immunol 2019, 20, 928–942. [CrossRef]
- Aarvak, T.; Natvig, J.B. Cell-Cell Interactions in Synovitis: Antigen Presenting Cells and T Cell Interaction in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res 2001, 3, 13–17. [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kondo, Y.; Morita, R.; Okuzono, Y.; Koga, K.; Kassai, Y.; Gamo, K.; Takiguchi, M.; Kurisu, R.; et al. Multi-Dimensional Analysis Identified Rheumatoid Arthritis-Driving Pathway in Human T Cell. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2019, 78, 1346–1356. [CrossRef]
- Fresneda Alarcon, M.; McLaren, Z.; Wright, H.L. Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Same Foe Different M.O. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 649693. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chang, Y.; Wei, W. Emerging Role of Targeting Macrophages in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Focus on Polarization, Metabolism and Apoptosis. Cell Proliferation 2020, 53, e12854. [CrossRef]
- Zec, K.; Schonfeldova, B.; Ai, Z.; Van Grinsven, E.; Pirgova, G.; Eames, H.L.; Berthold, D.L.; Attar, M.; Compeer, E.B.; Arnon, T.I.; et al. Macrophages in the Synovial Lining Niche Initiate Neutrophil Recruitment and Articular Inflammation. Journal of Experimental Medicine 2023, 220, e20220595. [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Smolen, J.S. Diagnosis and Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Review. JAMA 2018, 320, 1360. [CrossRef]
- Amarasekara, D.S.; Yun, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, N.; Kim, H.; Rho, J. Regulation of Osteoclast Differentiation by Cytokine Networks. Immune Netw 2018, 18, e8. [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Pacheco, G.A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Castruita-De La Rosa, C.; Ramirez-Acuña, J.M.; Perez-Romero, B.A.; Guerrero-Rodriguez, J.F.; Martinez-Avila, N.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. The Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Human Diseases. IJMS 2020, 21, 9739. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K. Targeting Dysregulation of Metalloproteinase Activity in Osteoarthritis.
- Del Buono, A.; Oliva, F.; Osti, L.; Maffulli, N. Metalloproteases and Tendinopathy. Muscle Ligaments and Tendons J 2019, 03, 51. [CrossRef]
- Van Den Steen, P.E.; Proost, P.; Brand, D.D.; Kang, A.H.; Van Damme, J.; Opdenakker, G. Generation of Glycosylated Remnant Epitopes from Human Collagen Type II by Gelatinase B. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 10809–10816. [CrossRef]
- Takaishi, H.; Kimura, T.; Dalal, S.; Okada, Y.; D’Armiento, J. Joint Diseases and Matrix Metalloproteinases: A Role for MMP-13.
- Burrage, P., S. Matrix Metalloproteinases: Role In Arthritis. Front Biosci 2006, 11, 529. [CrossRef]
- Montero-Melendez, T. Therapeutic Senescence via GPCR Activation in Synovial Fibroblasts Facilitates Resolution of Arthritis.
- Zeinert, I. Matrix-Mediated Activation of Murine Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes. Experimental Cell Research 2025.
- Bian, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Q.; Chen, G.; Xiang, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Pei, S.; Guo, S.; et al. Immunomodulatory Roles of Metalloproteinases in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1285455. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. et al. Functional Analysis of Discoidin Domain Receptor 2 in Synovial Fibroblasts in Rheumatoid Arthritis.
- Wang, Y.; Hao, Z.; Lu, D.; Naseem, A.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, J.; Kuang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B. Effects of Viscum Coloratum (Kom.) Nakai on Collagen-Induced Rheumatoid Arthritis. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2024, 327, 118026. [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Z.; Ji, J.; Shen, X.; Hou, X.; Mei, Z. The Antiangiogenic Effect of Total Saponins of Panax Japonicus C.A. Meyer in Rheumatoid Arthritis Is Mediated by Targeting the HIF-1α/VEGF/ANG-1 Axis. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2024, 333, 118422. [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Jin, C.; Deng, Y.; Liu, J.; Gu, C.; Wang, J.; Cai, X.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y. Exploring the Chondroprotective Effect of Chaenomeles Speciosa on Glucose-6-Phosphate Isomerase Model Mice Using an Integrated Approach of Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2023, 314, 116553. [CrossRef]
- Maybee, D.V.; Ink, N.L.; Ali, M.A.M. Novel Roles of MT1-MMP and MMP-2: Beyond the Extracellular Milieu. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022.
- Yeon, K.Y. Role of Activating Transcription Factor 3 as a Mediator of the Protective Effects of Berberine against Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated SW982 Cells and in Rheumatoid Arthritis Animal Models. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 2025.
- Zhou, W.; Cheng, H.; Fan, C.; Zhou, X.; Chen, W.; Xie, C.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, J. LAMP3-Mediated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Promotes the Invasion and Excessive Proliferation of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Journal of Autoimmunity 2025, 151, 103359. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Gao, C.; Sun, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H. Study on the Mechanism of Action of Wu Mei Pill in Inhibiting Rheumatoid Arthritis through TLR4-NF-κB Pathway. J Orthop Surg Res 2024, 19, 65. [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tang, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, F.; Zou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; He, J.; Guo, J.; et al. Leukocyte Ig-like Receptor A3 Facilitates Inflammation, Migration and Invasion of Synovial Tissue-Derived Fibroblasts via ERK/JNK Activation.
- Jin, Y.; Chang, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, P.; Wei, K.; Xu, L.; Shi, Y.; Yang, G.; Lv, X.; et al. LncRNA NONHSAT042241 Inhibits Rheumatoid Synovial Proliferation, Inflammation and Aggression via Ina.
- Lin, F.-J.; Wei, X.-L.; Liu, H.-Y.; Li, H.; Xia, Y.; Wu, D.-T.; Zhang, P.-Z.; Gandhi, G.R.; Hua-Bin Li; Gan, R.-Y. State-of-the-Art Review of Dark Tea: From Chemistry to Health Benefits. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 109, 126–138. [CrossRef]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019.
- Bruno, A.; Wang, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z. Angiogenesis Is Inhibited by Arsenic Trioxide Through Downregulation of the CircHIPK3/miR-149-5p/FOXO1/ VEGF Functional Module in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2021, 12.
- Lesturgie-Talarek, M.; Gonzalez, V.; Combier, A.; Thomas, M.; Boisson, M.; Poiroux, L.; Wanono, S.; Hecquet, S.; Carves, S.; Cauvet, A.; et al. Inflammatory and Angiogenic Serum Profile of Refractory Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci Rep 2025, 15, 7159. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M. Clematichinenoside AR Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis by Inhibiting Synovial Angiogenesis through the HIF-1α/VEGFA/ANG2 Axis. 2025.
- Wei, Y. The New Anti-Angiogenesis Perspective of Rheumatoid Arthritis with Geniposide: Reducing the Extracellular Release of HSP70 in HUVECs. International Immunopharmacology 2025.
- Wang, X.; Fan, D.; Cao, X.; Ye, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, C. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Synovial Microenvironment. 2022.
- Biniecka, M.; Fox, E.; Gao, W.; Ng, C.T.; Veale, D.J.; Fearon, U.; O’Sullivan, J. Hypoxia Induces Mitochondrial Mutagenesis and Dysfunction in Inflammatory Arthritis.
- Harty, L.C.; Biniecka, M.; O’Sullivan, J.; Fox, E.; Mulhall, K.; Veale, D.J.; Fearon, U. Mitochondrial Mutagenesis Correlates with the Local Inflammatory Environment in Arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2012, 71, 582–588. [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yu, S.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; Chen, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, N.; Chen, S.; Li, J.; Shen, B. Germline and Somatic mtDNA Mutation Spectrum of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients in the Taizhou Area, China.
- Mateen, S.; Moin, S.; Khan, A.Q.; Zafar, A.; Fatima, N. Increased Reactive Oxygen Species Formation and Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152925. [CrossRef]
- Kardeş, S.; Karagülle, M.; Durak, İ.; Avcı, A.; Karagülle, M.Z. Association of Oxidative Stress with Clinical Characteristics in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Eur J Clin Investigation 2018, 48. [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh, S.; DeGroot, J.; TeKoppele, J.M.; Tarkowski, A.; Collins, L.V. Extracellular Mitochondrial DNA and Oxidatively Damaged DNA in Synovial Fluid of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2003, 5. [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Breedveld, F.C.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.; Dougados, M.; Emery, P.; Kvien, T.K.; Navarro-Compán, M.V.; Oliver, S.; Schoels, M.; et al. Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis to Target: 2014 Update of the Recommendations of an International Task Force. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2016, 75, 3–15. [CrossRef]
- Combe, B.; Landewe, R.; Daien, C.I.; Hua, C.; Aletaha, D.; Álvaro-Gracia, J.M.; Bakkers, M.; Brodin, N.; Burmester, G.R.; Codreanu, C.; et al. 2016 Update of the EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Early Arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2017, 76, 948–959. [CrossRef]
- Hoes, J.N.; Jacobs, J.W.G.; Boers, M.; Boumpas, D.; Buttgereit, F.; Caeyers, N.; Choy, E.H.; Cutolo, M.; Da Silva, J.A.P.; Esselens, G.; et al. EULAR Evidence-Based Recommendations on the Management of Systemic Glucocorticoid Therapy in Rheumatic Diseases. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2007, 66, 1560–1567. [CrossRef]
- Cronstein, B.N.; Aune, T.M. Methotrexate and Its Mechanisms of Action in Inflammatory Arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2020, 16, 145–154. [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.M.; Pratt, A.G.; Isaacs, J.D. Mechanism of Action of Methotrexate in Rheumatoid Arthritis, and the Search for Biomarkers. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2016, 12, 731–742. [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.H.; Glynn, R.J.; Karlson, E.W.; Lu, F.; Corrigan, C.; Colls, J.; Xu, C.; MacFadyen, J.; Barbhaiya, M.; Berliner, N.; et al. Adverse Effects of Low-Dose Methotrexate: A Randomized Trial. Ann Intern Med 2020, 172, 369. [CrossRef]
- Fox, R.I.; Herrmann, M.L.; Frangou, C.G.; Wahl, G.M.; Morris, R.E.; Strand, V.; Kirschbaum, B.J. Mechanism of Action for Leflunomide in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clinical Immunology 1999, 93, 198–208. [CrossRef]
- Li, E. Leflunomide in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clinical Therapeutics 2004, 26, 447–459. [CrossRef]
- Pullar, T.; Hunter, J.A.; Capell, H.A. SULPHASALAZINE IN THE TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: RELATIONSHIP OF DOSE AND SERUM LEVELS TO EFFICACY. Rheumatology 1985, 24, 269–276. [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Smolen, J.S. Diagnosis and Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Review. JAMA 2018, 320, 1360. [CrossRef]
- Keffer, J.; Probert, L.; Cazlaris, H.; Georgopoulos, S.; Kaslaris, E.; Kioussis, D.; Kollias, G. Transgenic Mice Expressing Human Tumour Necrosis Factor: A Predictive Genetic Model of Arthritis. The EMBO Journal 1991, 10, 4025–4031. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.C.; Feldmann, M. Anti-TNF Biologic Agents: Still the Therapy of Choice for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2009, 5, 578–582. [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, S. TNF Inhibitor Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomedical Reports 2013, 1, 177–184. [CrossRef]
- Mertens, M.; Singh, J.A. Anakinra for Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. J Rheumatol 2009, 36, 1118–1125. [CrossRef]
- Konttinen, L.; Kankaanpää, E.; Luosujärvi, R.; Blåfield, H.; Vuori, K.; Hakala, M.; Rantalaiho, V.; Savolainen, E.; Uutela, T.; Nordström, D.; et al. Effectiveness of Anakinra in Rheumatic Disease in Patients Naive to Biological Drugs or Previously on TNF Blocking Drugs: An Observational Study. Clin Rheumatol 2006, 25, 882–884. [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.J. Tocilizumab: A Review in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Drugs 2017, 77, 1865–1879. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.-C.; Fettner, S.; Rowell, L.; Gott, T.; Grimsey, P.; Unsworth, A. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Tocilizumab after Subcutaneous Administration in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. CP 2013, 51, 620–630. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.D.; Keystone, E. Rituximab for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatol Ther 2015, 2, 99–111. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Bae, S.-C.; Song, G.G. The Efficacy and Safety of Rituximab for the Treatment of Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Rheumatol Int 2011, 31, 1493–1499. [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, E.M.; Le Blanc, K.; Dominici, M.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.C.; Deans, R.J.; Krause, D.S.; Keating, A. Clarification of the Nomenclature for MSC: The International Society for Cellular Therapy Position Statement. Cytotherapy 2005, 7, 393–395. [CrossRef]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.C.; Krause, D.S.; Deans, R.J.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.J.; Horwitz, E.M. Minimal Criteria for Defining Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy Position Statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [CrossRef]
- Muguruma, Y.; Yahata, T.; Miyatake, H.; Sato, T.; Uno, T.; Itoh, J.; Kato, S.; Ito, M.; Hotta, T.; Ando, K. Reconstitution of the Functional Human Hematopoietic Microenvironment Derived from Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Murine Bone Marrow Compartment. Blood 2006, 107, 1878–1887. [CrossRef]
- Bianco, P.; Robey, P.G.; Simmons, P.J. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Revisiting History, Concepts, and Assays. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 2, 313–319. [CrossRef]
- Nasef, A.; Chapel, A.; Mazurier, C.; Bouchet, S.; Lopez, M.; Mathieu, N.; Sensebé, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gorin, N.-C.; Thierry, D.; et al. Identification of IL-10 and TGF-β Transcripts Involved in the Inhibition of T-Lymphocyte Proliferation During Cell Contact With Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. gene expr 2006, 13, 217–226. [CrossRef]
- Davies, L.C.; Heldring, N.; Kadri, N.; Le Blanc, K. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Secretion of Programmed Death-1 Ligands Regulates T Cell Mediated Immunosuppression. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 766–776. [CrossRef]
- Naserian, S.; Shamdani, S.; Arouche, N.; Uzan, G. Regulatory T Cell Induction by Mesenchymal Stem Cells Depends on the Expression of TNFR2 by T Cells. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020, 11, 534. [CrossRef]
- Ansboro, S.; Roelofs, A.J.; De Bari, C. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Immune Modulation, Repair or Both? Current Opinion in Rheumatology 2017, 29, 201–207. [CrossRef]
- Maumus, M.; Guérit, D.; Toupet, K.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapies in Regenerative Medicine: Applications in Rheumatology. Stem Cell Res Ther 2011, 2, 14. [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.; Liu, D.D.; Thakor, A.S. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Homing: Mechanisms and Strategies for Improvement. iScience 2019, 15, 421–438. [CrossRef]
- Iwata, S.; Nakayamada, S.; Fukuyo, S.; Kubo, S.; Yunoue, N.; Wang, S.; Yoshikawa, M.; Saito, K.; Tanaka, Y. Activation of Syk in Peripheral Blood B Cells in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Potential Target for Abatacept Therapy. Arthritis & Rheumatology 2015, 67, 63–73. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, C.; Cai, H. Curcumin Alleviates Rheumatoid Arthritis Progression through the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B Pathway: An in Vitro and in Vivo Study. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 12899–12911. [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Tian, X.; Cao, T.; Chen, S.; Liu, C.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, M.; Peng, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, T. Emodin Mitigates Rheumatoid Arthritis through Direct Binding to TNF-α. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bao, X.; Xian, H.; Wei, F.; Song, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Glucocorticoid Receptors Involved in Ginsenoside Compound K Ameliorate Adjuvant Arthritis by Inhibiting the Glycolysis of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes via the NF-κB/HIF-1α Pathway. Pharmaceutical Biology 2023, 61, 1162–1174. [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Tan, L.; Lu, T.; Wang, K.; Wang, H.; Han, B.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Glytabastan B, a Coumestan Isolated from Glycine Tabacina, Alleviated Synovial Inflammation, Osteoclastogenesis and Collagen-Induced Arthritis through Inhibiting MAPK and PI3K/AKT Pathways. Biochemical Pharmacology 2022, 197, 114912. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Du, Q.; Sun, J.; Geng, S.; Zhang, Y. Investigation of the Mechanism of Isobavachalcone in Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis through a Combination Strategy of Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2022, 294, 115342. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lu, H.; Fan, X.; Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Gao, W. Probing the Molecular Mechanism of Kaempferol in Relieving Rheumatoid Arthritis Based on Network Pharmacology. Sci Rep 2025, 15. [CrossRef]
- Linghu, K.-G.; Zhao, G.-D.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Xiong, S.-H.; Wu, G.-P.; Shen, L.-Y.; Cui, W.-Q.; Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.-J.; Guo, B.; et al. Leocarpinolide B Attenuates Collagen Type II-Induced Arthritis by Inhibiting DNA Binding Activity of NF-κB. Molecules 2023, 28, 4241. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Teng, L.; Qu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.; Chen, S.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Song, Q.; Fu, Q. Anti-Proliferation and Anti-Inflammation Effects of Corilagin in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Downregulating NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2022, 284, 114791. [CrossRef]
- Anchi, P.; Swamy, V.; Godugu, C. Nimbolide Exerts Protective Effects in Complete Freund’s Adjuvant Induced Inflammatory Arthritis via Abrogation of STAT-3/NF-κB/Notch-1 Signaling. Life Sciences 2021, 266, 118911. [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Sun, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.; Ma, H.; Xin, P. Sappanone A Attenuates Rheumatoid Arthritis via Inhibiting PI3K/AKT/NF-κB and JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathways in Vivo and in Vitro. International Immunopharmacology 2024, 143, 113560. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; He, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Sun, C.; Li, Y.; Jia, K.; Wang, J.; Xu, T.; Ming, R.; et al. Anti-Angiogenic Effect of Shikonin in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Downregulating PI3K/AKT and MAPKs Signaling Pathways. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2020, 260, 113039. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhou, W.; Huang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wong, S.Y.; Lam, W.K.; Ying, K.Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H. Umbelliferone and Scopoletin Target Tyrosine Kinases on Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes to Block NF-κB Signaling to Combat Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Dong, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Yin, G.; Xie, Q. Suberosin Attenuates Rheumatoid Arthritis by Repolarizing Macrophages and Inhibiting Synovitis via the JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. Arthritis Res Ther 2025, 27. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Yu, J.; Yang, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Song, H.; Han, T.; Zhang, D.; Niu, X.; et al. Tectoridin Exhibits Anti-Rheumatoid Arthritis Activity through the Inhibition of the Inflammatory Response and the MAPK Pathway in Vivo and in Vitro. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 2022, 727, 109328. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chang, J.; Miao, C. Wilforine Inhibits Rheumatoid Arthritis Pathology through the Wnt11/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway Axis. Arthritis Res Ther 2023, 25. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-O.; Yang, W.S.; Park, J.G.; Jeong, D.; Kim, H.G.; Yoon, K.D.; Aravinthan, A.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, E.; Cho, J.Y. Src and Syk Contribute to the Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Achyranthes Aspera Ethanolic Extract. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2017, 206, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Prateeksha, P.; Singh, S.P.; Rao, C.V.; Singh, B.N. Nyctanthes Arbor-Tristis Bioactive Extract Ameliorates LPS-Induced Inflammation through the Inhibition of NF-κB Signalling Pathway. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2024, 320, 117382. [CrossRef]
- George, G.; Shyni, G.L.; Mohan, S.; Abraham, B.; Nisha, P.; Ranjith, S.; Rajankutty, K.; Raghu, K.G. In Vitro and in Vivo Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Arthritic Effect of Tinospora Cordifolia via Modulation of JAK/STAT Pathway. Inflammopharmacol 2023, 31, 1009–1025. [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.; John, P.; Bhatti, A.; Paracha, R.Z.; Majeed, A. Evaluation of the Inhibitory Mechanism of Pennisetum Glaucum (Pearl Millet) Bioactive Compounds for Rheumatoid Arthritis: An in Vitro and Computational Approach. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15. [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Fan, D.; Li, X.; Lu, X.; Ye, Q.; Xi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, C. Yi Shen Juan Bi Pill Regulates the Bone Immune Microenvironment via the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Vitro. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, L.-B.; Ma, R.; Wang, M.-N.; He, J.; Wang, P.-P.; Tao, Q.-W.; Xu, Y. Jolkinolide B Ameliorates Rheumatoid Arthritis by Regulating the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 124, 155311. [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Peng, T.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, R.; Meng, X.; Lu, X.; Gao, Y.; Jin, Y.; et al. Ammopiptanthus Nanus (M. Pop.) Cheng f. Stem Ethanolic Extract Ameliorates Rheumatoid Arthritis by Inhibiting PI3K/AKT/NF-κB Pathway-Mediated Macrophage Infiltration. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2025, 338, 118974. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-M.; Chung, K.-S.; Jang, D.S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, K.-T. In Vitro and in Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Effects of 5-Hydroxyconiferaldehyde via NF-κB, MAPK/AP-1, and Nrf2 Modulation. Chemico-Biological Interactions 2025, 409, 111427. [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Ma, K.; Pang, X.; Liu, Y.; Song, Z.; Zhou, R.; Tang, Z. Anti-Rheumatoid Arthritis Effects of Total Saponins from Rhizoma Panacis Majoris on Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis in Rats and Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes. Phytomedicine 2023, 119, 155021. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Jia, X.; Xuan, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Meng, X.; Su, W. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway Promotes Abnormal Activation of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes and Angiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis and the Intervention of Er Miao San. Phytomedicine 2023, 120, 155064. [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y. Total Saponins of Radix Clematis Regulate Fibroblast-Like Synoviocyte Proliferation in Rheumatoid Arthritis via the LncRNA OIP5-AS1/MiR-410-3p/Wnt7b Signaling Pathway. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2022, 2022, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Tao, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, J.; Zeng, Y.; Meng, X.; Fan, G.; Zhang, Y. Tibetan Medicine Qi-Sai-Er-Sang-Dang-Song Decoction Inhibits TNF-α-Induced Rheumatoid Arthritis in Human Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes via Regulating NOTCH1/NF-κB/NLRP3 Pathway. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2023, 310, 116402. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Lu, S.; Gao, X.; Luo, Y.; Tong, B.; Wei, Z.; Lu, T.; Xia, Y.; Chou, G.; Wang, Z.; et al. Norisoboldine, an Alkaloid Compound Isolated from Radix Linderae, Inhibits Synovial Angiogenesis in Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis Rats by Moderating Notch1 Pathway-Related Endothelial Tip Cell Phenotype. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2012, 237, 919–932. [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, R. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathophysiology, Current Therapeutic Strategies and Recent Advances in Targeted Drug Delivery System. Materials Today Communications 2023, 35, 105877. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Yang, H.-I.; Kim, K.-S. Etiology and Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Interstitial Lung Disease. IJMS 2023, 24, 14509. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-J.; Anzaghe, M.; Schülke, S. Update on the Pathomechanism, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells 2020, 9, 880. [CrossRef]
- Fraenkel, L.; Bathon, J.M.; England, B.R.; St.Clair, E.W.; Arayssi, T.; Carandang, K.; Deane, K.D.; Genovese, M.; Huston, K.K.; Kerr, G.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Care & Research 2021, 73, 924–939. [CrossRef]
- Hein, T.R.; Peterson, L.; Bartikoski, B.J.; Portes, J.; Espírito Santo, R.C.; Xavier, R.M. The Effect of Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs on Skeletal Muscle Mass in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Res Ther 2022, 24, 171. [CrossRef]
- Gehringer, C.K.; Martin, G.P.; Hyrich, K.L.; Verstappen, S.M.M.; Sergeant, J.C. Clinical Prediction Models for Methotrexate Treatment Outcomes in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 2022, 56, 152076. [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Higuchi, Y.; Kitamura, H.; Murao, N.; Saitoh, R.; Morikawa, T.; Sato, H. Novel Hyaluronic Acid–Methotrexate Conjugate Suppresses Joint Inflammation in the Rat Knee: Efficacy and Safety Evaluation in Two Rat Arthritis Models. Arthritis Res Ther 2016, 18, 79. [CrossRef]
- Simon, T.A.; Boers, M.; Hochberg, M.; Baker, N.; Skovron, M.L.; Ray, N.; Singhal, S.; Suissa, S.; Gomez-Caminero, A. Comparative Risk of Malignancies and Infections in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Initiating Abatacept versus Other Biologics: A Multi-Database Real-World Study. Arthritis Res Ther 2019, 21, 228. [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, N.; Bhatt, L.K.; Prabhavalkar, K.S. Experimental Animal Models for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunopharmacology and Immunotoxicology 2018, 40, 193–200. [CrossRef]
- Bevaart, L.; Vervoordeldonk, M.J.; Tak, P.P. Evaluation of Therapeutic Targets in Animal Models of Arthritis: How Does It Relate to Rheumatoid Arthritis? Arthritis & Rheumatism 2010, 62, 2192–2205. [CrossRef]
- Campbell, I.K.; Hamilton, J.A.; Wicks, I.P. Collagen-Induced Arthritis in C57BL/6 (H-2b) Mice: New Insights into an Important Disease Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 1568–1575. [CrossRef]
- Terato, K.; Hasty, K.A.; Reife, R.A.; Cremer, M.A.; Kang, A.H.; Stuart, J.M. Induction of Arthritis with Monoclonal Antibodies to Collagen. J Immunol 1992, 148, 2103–2108.
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R. Efficient Promotion of Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis (CAIA) Using Four Monoclonal Antibodies Specific for the Major Epitopes Recognized in Both Collagen Induced Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Journal of Immunological Methods 2005, 304, 126–136. [CrossRef]
- Khachigian, L.M. Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis. Nat Protoc 2006, 1, 2512–2516. [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R. Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis. In Arthritis Research; Cope, A.P., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Medicine; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 2007; Vol. 136, pp. 215–223 ISBN 978-1-58829-918-5.
- Pearson, C.M. Development of Arthritis, Periarthritis and Periostitis in Rats Given Adjuvants. Experimental Biology and Medicine 1956, 91, 95–101. [CrossRef]
- Negi, P.; Agarwal, S.; Garg, P.; Ali, A.; Kulshrestha, S. In Vivo Models of Understanding Inflammation (in Vivo Methods for Inflammation). In Recent Developments in Anti-Inflammatory Therapy; Elsevier, 2023; pp. 315–330 ISBN 978-0-323-99988-5.
- Ye, L.; Mingyue, H.; Feng, Z.; Zongshun, D.; Ying, X.; Xiong, C.; Liang, L. Systematic Review of Robust Experimental Models of Rheumatoid Arthritis for Basic Research. Digital Chinese Medicine 2021, 4, 262–272. [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, S.J.; Freemont, A.J.; Jayson, M.I.V. Pristane-Induced Arthritis in Balb/c Mice: I. Clinical and Histological Features of the Arthropathy. Rheumatol Int 1984, 5, 21–28. [CrossRef]
- Holmdahl, R. Experimental Models for Rheumatoid Arthritis. In Kelley and Firestein’s Textbook of Rheumatology; Elsevier, 2017; pp. 449–460 ISBN 978-0-323-31696-5.
- van den Berg, W.B. Animal Models of Arthritis. What Have We Learned? J Rheumatol Suppl 2005, 72, 7–9.
- Nho, J.-H.; Kim, A.-H.; Jung, H.-K.; Lee, M.-J.; Jang, J.-H.; Yang, B.-D.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, K.-H.; Woo, K.-W.; Cho, H.-W. Water Extract of Acori Graminei Rhizoma Attenuates Features of Rheumatoid Arthritis in DBA/1 Mice. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2019, 2019, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Tran, P.N.T. EVALUATION OF ANTI-INFLAMMATORY EFFECT OF FRUIT PEEL EXTRACTS OF ANNONA SQUAMOSA L. ON MOUSE MODELS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS. J microb biotech food sci 2021, 11, e2075. [CrossRef]
- Nho, J.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Jung, H.-K.; Jang, J.-H.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, A.-H.; Sung, T.-K.; Cho, H.-W. Effect of Saururus Chinensis Leaves Extract on Type II Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mouse Model. BMC Complement Altern Med 2019, 19, 2. [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Kim, H.; Lee, E.H.; Jo, G.; Na, C.S.; Kang, K.; Lee, T.H. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Cudrania Tricuspidata Extract and Stewartia Koreana Extract Mixture in a Collagen-Induced Arthritis Mouse Model. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 6660. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Bang, J.; Son, C.-N.; Baek, W.-K.; Kim, J.-M. Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Extract Ameliorates Murine Autoimmune Arthritis through Regulation of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Korean J Intern Med 2018, 33, 612–621. [CrossRef]
- Eor, J.Y.; Park, N.; Son, Y.J.; Kim, S.H. Therapeutic Effects of Gleditsia Sinensis Thorn Extract Fermented by Lactobacillus Casei 3260 in a Type II Collagen-Induced Rheumatoid Arthritis Mouse Model. Food Sci Anim Resour 2021, 41, 497–508. [CrossRef]
- Allam, G.; Mahdi, E.A.; Alzahrani, A.M.; Abuelsaad, A.S. Ellagic Acid Alleviates Adjuvant Induced Arthritis by Modulation of Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines. cejoi 2016, 4, 339–349. [CrossRef]
- Ulhaq, Z.S.; Hendyatama, T.H.; Alluza, H.H.D.; Aulanni’am, A. Therapeutic Effects of Durian Wood Bark Extract on a Rat Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Revista Colombiana de Reumatología 2021, 28, 118–123. [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Li, S.; Du, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, X. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Root, Stem and Leaf Extracts of Chloranthus Serratus on Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis in Rats. Pharmaceutical Biology 2020, 58, 528–537. [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Wang, S.; Zhu, H.; Yin, T.; Zhou, R.; Hu, W.; Lu, C. Core Constituents of Caragana Sinica Root for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment and the Potential Mechanism. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 2586–2595. [CrossRef]
| Antibody | Molecular structure | Administration and dose |
| Infliximab (IFX, Remicade) | Chimeric IgG1 monoclonal antibody | Intravenous injections 3-10 mg/kg every 4-8 weeks |
| Etanercept (ETN, Enbrel) | Recombinant human fusion protein (TNF-α receptor bound to Fc fragment) | Subcutaneous injections 50 mg/week or 25 mg/twice a week |
| Adalimumab (ADA, Humira) | Recombinant human IgG monoclonal antibody | Subcutaneous injections 25 mg/twice a week |
| Golimumab (GOL, Simponi) | Human IgG monoclonal antibody | Subcutaneous injections 50 mg/month |
| Certolizumab Pegol (CZP, Cimzia) | Recombinant humanized Fab fragment |
Subcutaneous injections 400 mg at weeks 0, 2 and 4 followed by 200 mg/ every 2 weeks |
| Host | Biological agent | Mode of action | Reference |
| Mouse | Acori Graminei | Reduction of inflammation indicators including IL-6 and TNF-α | 96 |
| Mouse | Fruit peel extracts of Annona Squamosa L. |
Decrease in the leukocytes in the serum | 97 |
| Mouse | Saururus chinensis | Reduction of inflammatory cytokines | 98 |
| Mouse | Cudrania tricuspidata and Stewartia koreana | Decrease in inflammatory cytokine levels, NOS inhibitors | 99 |
| Mouse | Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract | Inhibition of TLR4/ MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. | 100 |
| Mouse |
Gleditsia sinensis thorn extract fermented by Lactobacillus |
Reduction of inflammatory cytokine levels | 101 |
| Mouse | Ellagic acid | Downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and upregulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines |
102 |
| Rat | Duran wood bark extract | iNOS suppression/NOS inhibitor | 103 |
| Rat | Chloranthus serratus | Inhibition of the releases of inflammatory cytokines and amelioration of antioxidant capacity |
104 |
| Rat | Caragana sinica | Negative regulation of the NF-κB pathway |
105 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





