Submitted:
12 June 2025
Posted:
13 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
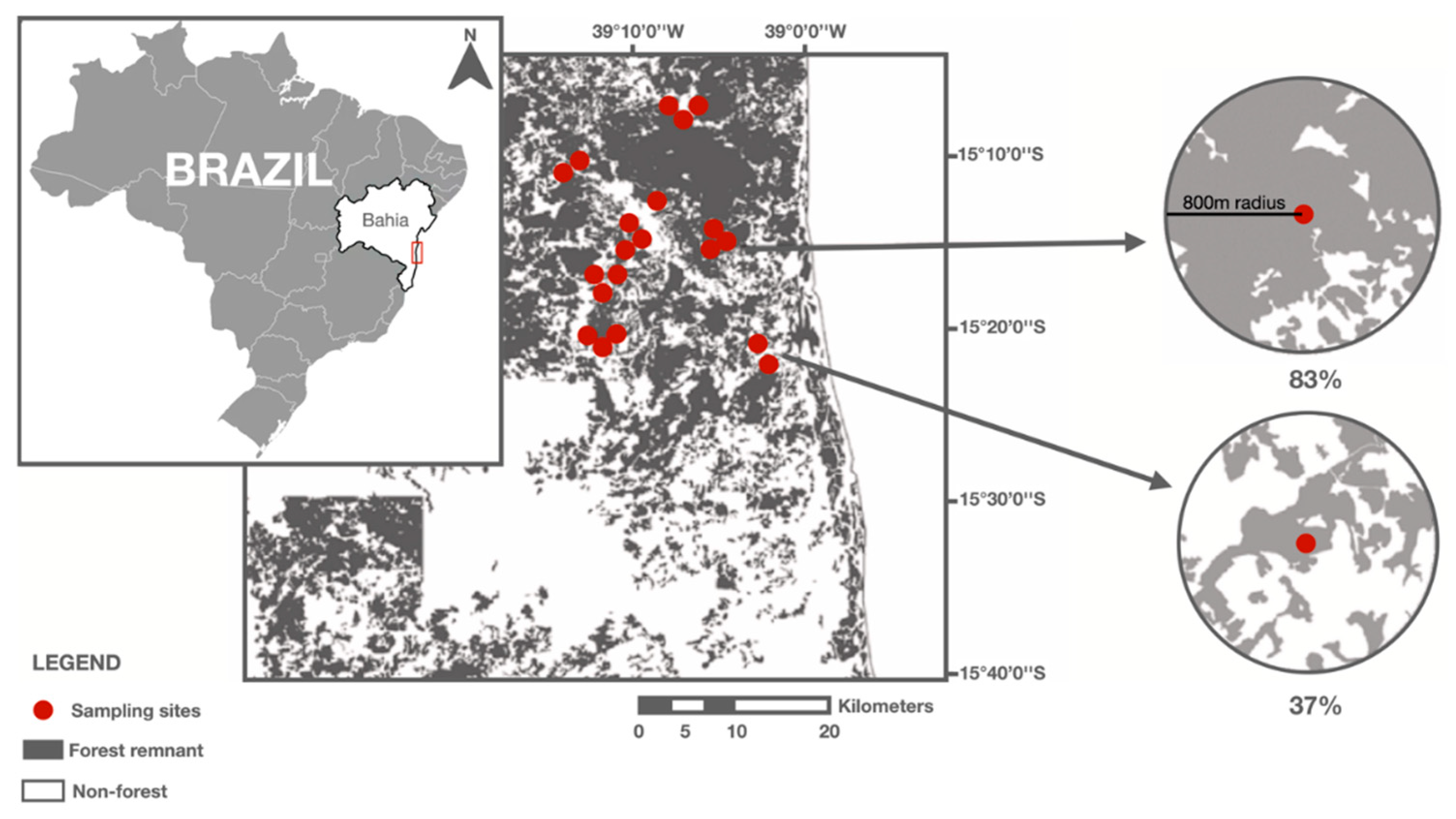
2. Materials and Methods
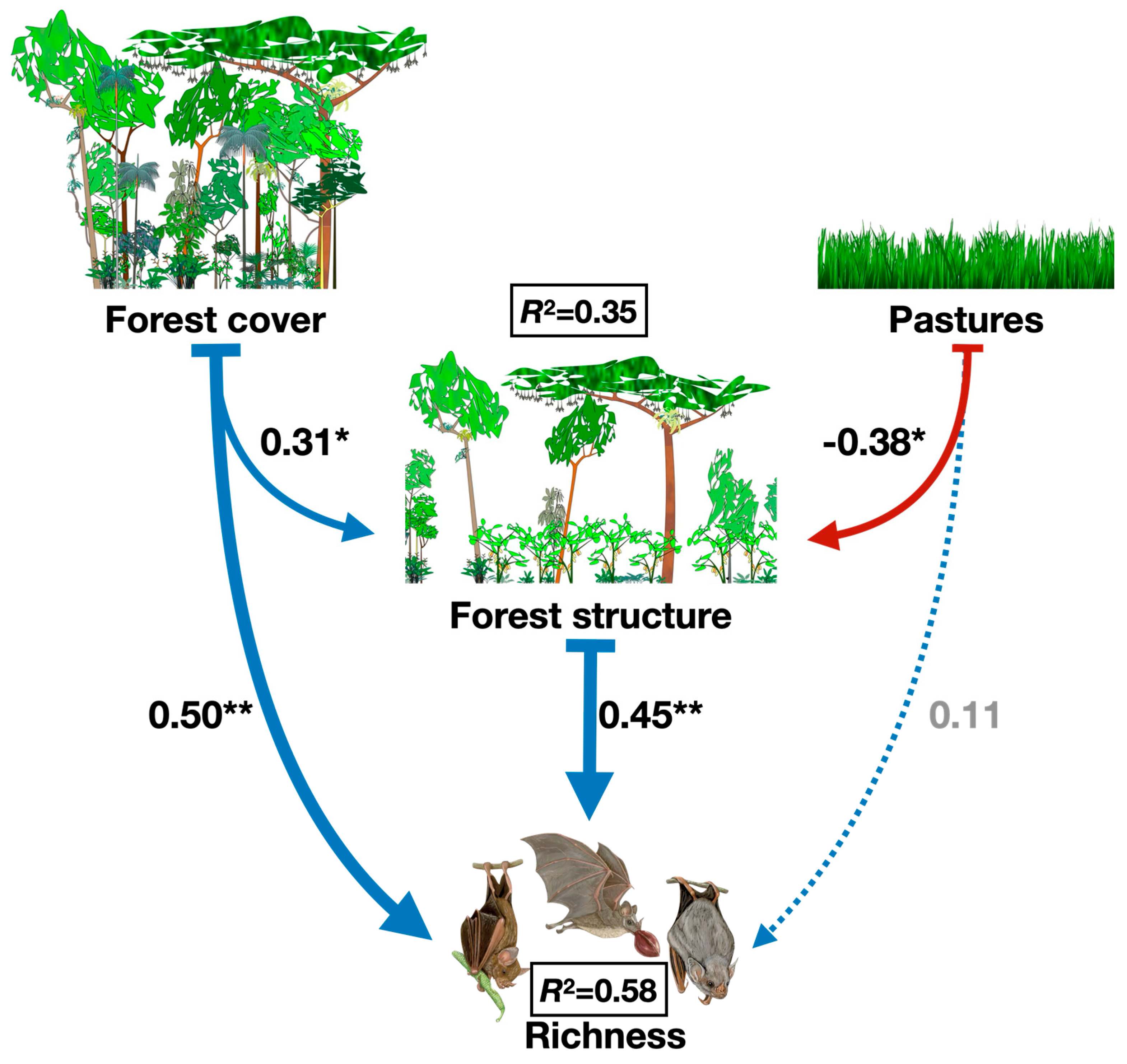
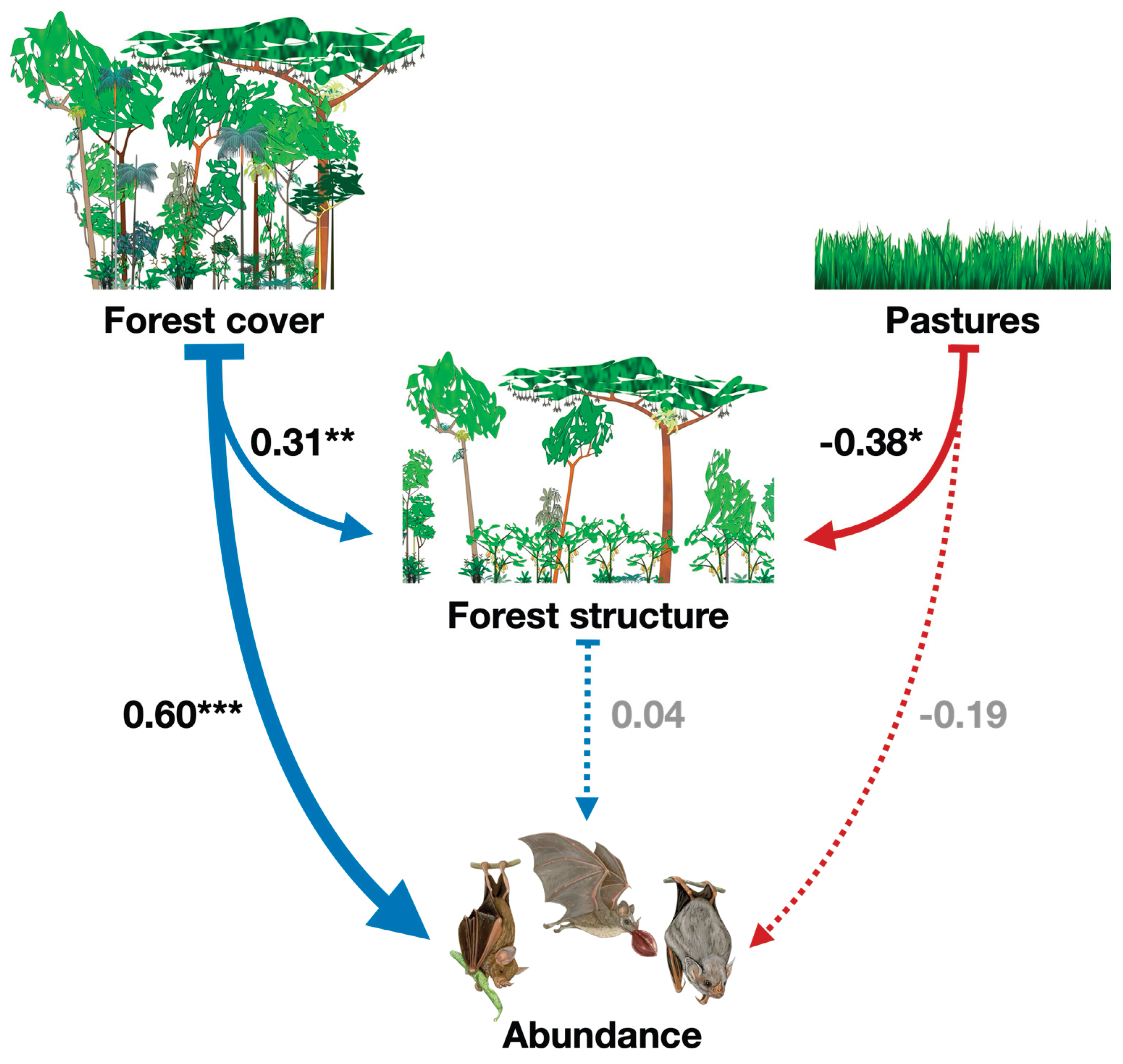
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
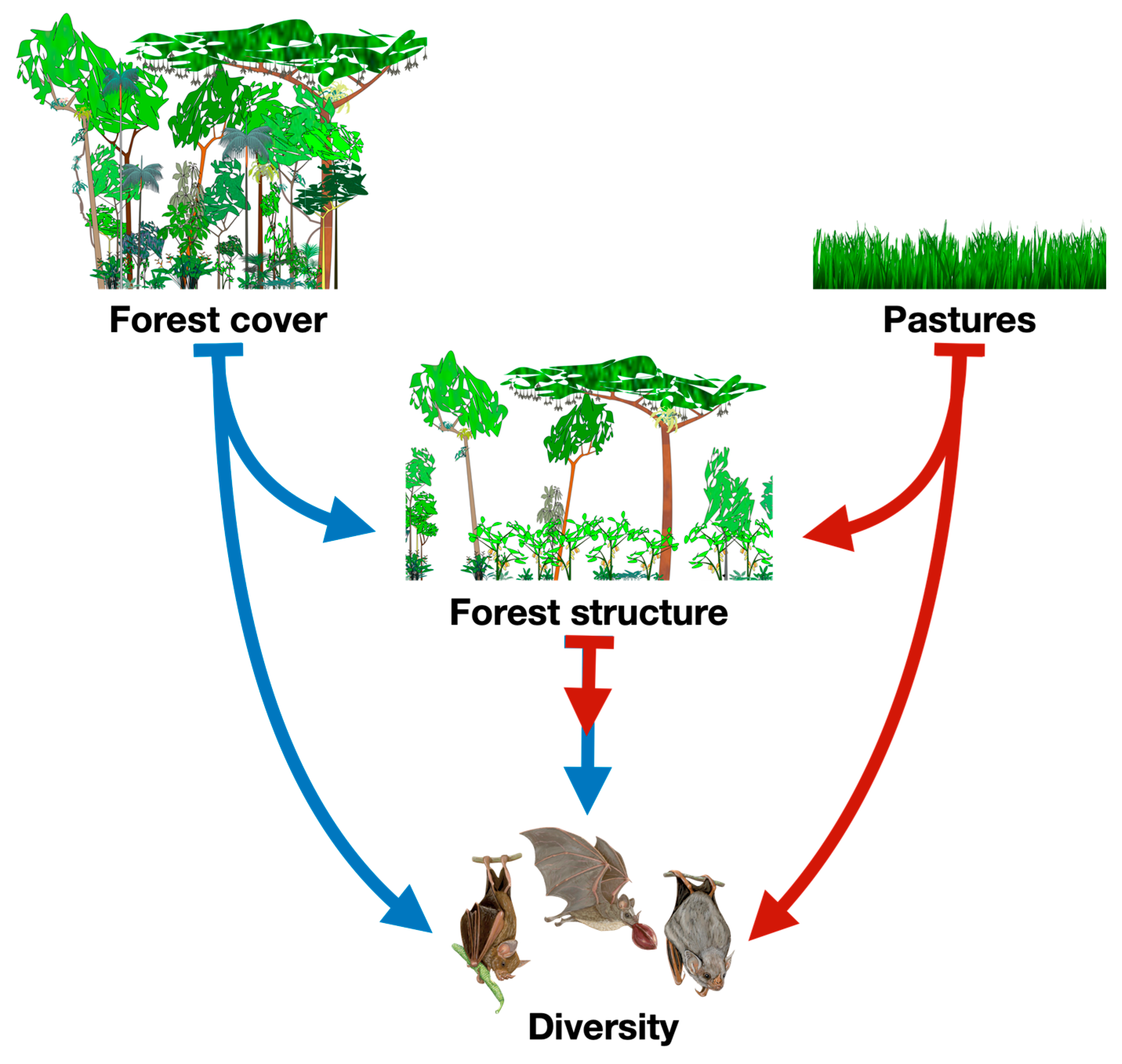
Appendix A.1. The Script Models Used Structural Equation Models (SEM) to Investigate the Direct and Indirect Effects of Landscape Factors (Forest Cover and Pasture) and Local Factors (Forest Structure) on the Diversity (Richness and Abundance) of Phyllostomid Bats Across 20 Forest Fragments in the Atlantic Forest of Southern Bahia, Brazil
References
- Maxwell, S.L.; Fuller, R.A.; Brooks, T.M.; Watson, J.E. Biodiversity: The ravages of guns, nets and bulldozers. Nature 2016, 536, 143–145. [CrossRef]
- Newbold, T.; Hudson, L.N.; Hill, S.; Contu, S.; Lysenko, I.; Senior, R.A.; Börger, L.; Bennett, D.; Choimes, A.; Collen, B. Global land-use impacts on local terrestrial biodiversity. Nature 2015, 520, 45–50.
- Sala, O.E.; Chapin, F.S., 3rd; Armesto, J.J.; Berlow, E.; Bloomfield, J.; Dirzo, R.; Huber-Sanwald, E.; Huenneke, L.F.; Jackson, R.B.; Kinzig, A.; et al. Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science 2000, 287, 1770–1774. [CrossRef]
- Chazdon, R.L.; Lindenmayer, D.; Guariguata, M.R.; Crouzeilles, R.; Benayas, J.M.R.; Chavero, E.L. Fostering natural forest regeneration on former agricultural land through economic and policy interventions. Environmental Research Letters 2020, 15, 043002. [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Rodríguez, V.; Fahrig, L.; Tabarelli, M.; Watling, J.I.; Tischendorf, L.; Benchimol, M.; Cazetta, E.; Faria, D.; Leal, I.R.; Melo, F.P. Designing optimal human-modified landscapes for forest biodiversity conservation. Ecology letters 2020, 23, 1404–1420. [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, S.A.; Willis, K.J.; Birks, H.J.B.; Whittaker, R.J. Agroforestry: a refuge for tropical biodiversity? Trends in ecology & evolution 2008, 23, 261–267.
- Schroth, G.; Jeusset, A.; Gomes, A.d.S.; Florence, C.T.; Coelho, N.A.P.; Faria, D.; Läderach, P. Climate friendliness of cocoa agroforests is compatible with productivity increase. Mitigation and adaptation strategies for global change 2016, 21, 67–80. [CrossRef]
- Fahrig, L. Rethinking patch size and isolation effects: the habitat amount hypothesis. Journal of biogeography 2013, 40, 1649–1663. [CrossRef]
- Pardini, R.; Faria, D.; Accacio, G.M.; Laps, R.R.; Mariano-Neto, E.; Paciencia, M.L.B.; Dixo, M.; Baumgarten, J. The challenge of maintaining Atlantic forest biodiversity: A multi-taxa conservation assessment of specialist and generalist species in an agro-forestry mosaic in southern Bahia. Biological Conservation 2009, 142, 1178–1190. [CrossRef]
- Faria, D.; Morante-Filho, J.C.; Baumgarten, J.; Bovendorp, R.S.; Cazetta, E.; Gaiotto, F.A.; Mariano-Neto, E.; Mielke, M.S.; Pessoa, M.S.; Rocha-Santos, L.; et al. The breakdown of ecosystem functionality driven by deforestation in a global biodiversity hotspot. Biological Conservation 2023, 283. [CrossRef]
- Faria, D. Phyllostomid bats of a fragmented landscape in the north-eastern Atlantic forest, Brazil. Journal Of Tropical Ecology 2006, 22, 531–542. [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Santos, L.; Pessoa, M.S.; Cassano, C.R.; Talora, D.C.; Orihuela, R.L.; Mariano-Neto, E.; Morante-Filho, J.C.; Faria, D.; Cazetta, E. The shrinkage of a forest: Landscape-scale deforestation leading to overall changes in local forest structure. Biological Conservation 2016, 196, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Bovendorp, R.S.; Brum, F.T.; McCleery, R.A.; Baiser, B.; Loyola, R.; Cianciaruso, M.V.; Galetti, M. Defaunation and fragmentation erode small mammal diversity dimensions in tropical forests. Ecography 2018, 42, 23–35. [CrossRef]
- Banks-Leite, C.; Pardini, R.; Tambosi, L.R.; Pearse, W.D.; Bueno, A.A.; Bruscagin, R.T.; Condez, T.H.; Dixo, M.; Igari, A.T.; Martensen, A.C.; et al. Using ecological thresholds to evaluate the costs and benefits of set-asides in a biodiversity hotspot. Science 2014, 345, 1041–1045. [CrossRef]
- Morante-Filho, J.C.; Arroyo-Rodríguez, V.; Faria, D. Patterns and predictors of β-diversity in the fragmented Brazilian Atlantic forest: a multiscale analysis of forest specialist and generalist birds. Journal of Animal Ecology 2016, 85, 240–250. [CrossRef]
- Kunz, T.H.; de Torrez, E.B.; Bauer, D.; Lobova, T.; Fleming, T.H. Ecosystem services provided by bats. In Year in Ecology and Conservation Biology, Ostfeld, R.S., Schlesinger, W.H., Eds.; Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences; 2011; Volume 1223, pp. 1–38. [CrossRef]
- Fleming, T.H.; Martino, A.M.; Dávalos, L.; Mello, M. Population biology; The University of Chicago Press Chicago and London: 2020.
- Bredt, A.; Uieda, W.; Pedro, W.A. Plantas e morcegos: na recuperação de áreas degradadas e na paisagem urbana; Rede de sementes do Cerrado: 2012.
- Cleveland, C.J.; Betke, M.; Federico, P.; Frank, J.D.; Hallam, T.G.; Horn, J.; López Jr, J.D.; McCracken, G.F.; Medellín, R.A.; Moreno-Valdez, A. Economic value of the pest control service provided by Brazilian free-tailed bats in south-central Texas. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 2006, 4, 238–243. [CrossRef]
- Cassano, C.R.; Silva, R.M.; Mariano-Neto, E.; Schroth, G.; Faria, D. Bat and bird exclusion but not shade cover influence arthropod abundance and cocoa leaf consumption in agroforestry landscape in northeast Brazil. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2016, 232, 247–253. [CrossRef]
- Medellín, R.A.; Equihua, M.; Amin, M.A. Bat diversity and abundance as indicators of disturbance in Neotropical rainforests. Conservation biology 2000, 14, 1666–1675.
- Meyer, C.F.; Kalko, E.K. Assemblage-level responses of phyllostomid bats to tropical forest fragmentation: land-bridge islands as a model system. Journal of Biogeography 2008, 35, 1711–1726. [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Rodríguez, V.; Rojas, C.; Saldaña-Vázquez, R.A.; Stoner, K.E. Landscape composition is more important than landscape configuration for phyllostomid bat assemblages in a fragmented biodiversity hotspot. Biological Conservation 2016, 198, 84–92. [CrossRef]
- Rezende, C.L.; Scarano, F.R.; Assad, E.D.; Joly, C.A.; Metzger, J.P.; Strassburg, B.B.N.; Tabarelli, M.; Fonseca, G.A.; Mittermeier, R.A. From hotspot to hopespot: An opportunity for the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Perspectives in ecology and conservation 2018, 16, 208–214. [CrossRef]
- Vancine, M.H.; Muylaert, R.L.; Niebuhr, B.B.; Oshima, J.E.d.F.; Tonetti, V.; Bernardo, R.; De Angelo, C.; Rosa, M.R.; Grohmann, C.H.; Ribeiro, M.C. The Atlantic Forest of South America: Spatiotemporal dynamics of the vegetation and implications for conservation. Biological Conservation 2024, 291. [CrossRef]
- Benchimol, M.; Talora, D.C.; Mariano-Neto, E.; Oliveira, T.L.; Leal, A.; Mielke, M.S.; Faria, D. Losing our palms: The influence of landscape-scale deforestation on Arecaceae diversity in the Atlantic forest. Forest Ecology and Management 2017, 384, 314–322. [CrossRef]
- Faria, D.; Paciencia, M.L.B.; Dixo, M.; Laps, R.R.; Baumgarten, J. Ferns, frogs, lizards, birds and bats in forest fragments and shade cacao plantations in two contrasting landscapes in the Atlantic forest, Brazil. Biodiversity And Conservation 2007, 16, 2335–2357. [CrossRef]
- Melo, R.S.; Alexandrino, E.R.; de Paula, F.R.; Boscolo, D.; de Barros Ferraz, S.F. Promoting bird functional diversity on landscapes with a matrix of planted Eucalyptus spp. in the Atlantic Forest. Environmental Management 2024, 73, 395–407. [CrossRef]
- GARCÍA-MORALES, R.; Badano, E.I.; Moreno, C.E. Response of Neotropical bat assemblages to human land use. Conservation Biology 2013, 27, 1096–1106. [CrossRef]
- Estrada, A.; Coates-Estrada, R. Bats in continuous forest, forest fragments and in an agricultural mosaic habitat-island at Los Tuxtlas, Mexico. Biological conservation 2002, 103, 237–245. [CrossRef]
- Quesada, M.; Stoner, K.E.; Rosas-Guerrero, V.; Palacios-Guevara, C.; Lobo, J.A. Effects of habitat disruption on the activity of nectarivorous bats (Chiroptera: Phyllostomidae) in a dry tropical forest: implications for the reproductive success of the neotropical tree Ceiba grandiflora. Oecologia 2003, 135, 400–406. [CrossRef]
- Falcão, F.; Dodonov, P.; Caselli, C.B.; dos Santos, J.S.; Faria, D. Landscape structure shapes activity levels and composition of aerial insectivorous bats at different spatial scales. Biodiversity and Conservation 2021, 30, 2545–2564. [CrossRef]
- Orihuela, R.L.; Peres, C.A.; Mendes, G.; Jarenkow, J.A.; Tabarelli, M. Markedly Divergent Tree Assemblage Responses to Tropical Forest Loss and Fragmentation across a Strong Seasonality Gradient. Plos One 2015, 10, e0136018. [CrossRef]
- Avila-Cabadilla, L.D.; Sanchez-Azofeifa, G.A.; Stoner, K.E.; Alvarez-Anorve, M.Y.; Quesada, M.; Portillo-Quintero, C.A. Local and landscape factors determining occurrence of phyllostomid bats in tropical secondary forests. Plos One 2012, 7, e35228. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Petric, R.; Alazzawi, Z.; Kauzlarich, J.; Mahmoud, R.H.; McFadden, R.; Perslow, N.; Rodriguez Flores, A.; Soufi, H.; Morales, K. Four years continuous monitoring reveals different effects of urban constructed wetlands on bats. Land 2021, 10, 1087. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Filho, A.T.; Fontes, M.A.L. Patterns of floristic differentiation among Atlantic forests in southeastern Brazil and the influence of climate. Biotropica 2000, 32, 793 – 810. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.W.; CARVALHO, A.M.D.; Amorim, A.M.; Garrison, J.; ARBELA´ EZ, A.L. Plant endemism in two forests in southern Bahia, Brazil. Biodiversity & Conservation 1998, 7, 311–322. [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.A.; Boom, B.M.; Decarvalho, A.M.; Dossantos, T.S. Southern Bahian Moist Forests. Botanical Review 1983, 49, 155–232. [CrossRef]
- Morante-Filho, J.C.; Faria, D.; Mariano-Neto, E.; Rhodes, J. Birds in Anthropogenic Landscapes: The Responses of Ecological Groups to Forest Loss in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Plos One 2015, 10, e0128923. [CrossRef]
- QGIS, D.T. QGIS, Geographic Information System, Open Source Geospatial Foundation: 2017.
- Eigenbrod, F.; Hecnar, S.J.; Fahrig, L. Sub-optimal study design has major impacts on landscape-scale inference. Biological Conservation 2011, 144, 298–305. [CrossRef]
- Huais, P.Y. multifit: an R function for multi-scale analysis in landscape ecology. Landscape Ecology 2018, 33, 1023–1028. [CrossRef]
- Muylaert, R.L.; Stevens, R.D.; Ribeiro, M.C. Threshold effect of habitat loss on bat richness in cerrado-forest landscapes. Ecological Applications 2016, 26, 1854–1867. [CrossRef]
- Bergallo, H.G.; Esberard, C.E.L.; Mello, M.A.R.; Lins, V.; Mangolin, R.; Melo, G.G.S.; Baptista, M. Bat species richness in Atlantic forest: What is the minimum sampling effort? Biotropica 2003, 35, 278–288. [CrossRef]
- Vizotto, L.; Taddei, V.A. Chave para determinação de quirópteros brasileiros; 1973.
- Simmons, N.B.; Voss, R.S. The mammals of Paracou, French Guiana, a Neotropical lowland rainforest fauna. 1998.
- Gardner, A. Mammals of South America, Volume 1: Marsupials, Xenarthrans, Shrews, and Bats; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2009; Volume Volume 1, pp. 1–690.
- Simmons, N.B. Order chiroptera. Mammal species of the world 2005, 1, 337.
- Nogueira, M.R.; Lima, I.P.d.; Moratelli, R.; Tavares, V.d.C.; Gregorin, R.; Lúcio, P. Checklist of Brazilian bats, with comments on original records. Volume 10, Número 4, Pags. 808-821 2014.
- Dale, M.R.; Fortin, M.-J. Spatial analysis: a guide for ecologists; Cambridge University Press: 2014.
- Bolker, B.; Skaug, H.; Magnusson, A.; Nielsen, A. Getting started with the glmmADMB package. 2012.
- Muggeo, V. segmented: an R package to fit regression models with broken-line relationships. R News, 2008; pp. 20–25.
- Team, R.C. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Retrived from http://www.R-project.org/, 2024.12.1; 2024.
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.; Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’hara, R.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.; Szoecs, E. vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.6-4. 2022. 2023.
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; DebRoy, S.; Sarkar, D.; Team, R.C. nlme: linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. R package version 3. 2017, 1–131. https://CRAN.R–project.org/package=nlme.
- Sanchez, G. PLS path modeling with R. Berkeley: Trowchez Editions 2013, 383, 551.
- Wickham, H.; Bryan, J. R packages; " O'Reilly Media, Inc.": 2023.
- Faria, D. Phyllostomid bats of a fragmented landscape in the north-eastern Atlantic forest, Brazil. Journal of Tropical Ecology 2006, 22, 531–542. [CrossRef]
| Species | Trophic guilds | N | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Family Phyllostomidae | |||
| Subfamily Desmodontinae | |||
| Desmodus rotundus (E. Geoffroy,1810) | H | 4 | 0.67 |
| Subfamily Glossophaginae | |||
| Glossophaga soricina (Pallas, 1766) | N | 7 | 1.17 |
| Lonchophyla sp. | N | 1 | 0.17 |
| Subfamily Phyllostominae | |||
| Chrotopterus auritus (Peters, 1856) | C | 3 | 0.50 |
| Micronycteris megalotis (Gray, 1842) | Ic | 1 | 0.17 |
| Micronycteris sp. | Ic | 1 | 0.17 |
| Phylloderma stenops (Peters 1865) | O | 3 | 0.50 |
| Phyllostomus discolor Wagner, 1843 | O | 3 | 0.50 |
| Gardenericterys crenulatum (É. Geoffroy, 1803) | Ic | 1 | 0.17 |
| Lophostoma brasiliensis Peters, 1866 | Ic | 2 | 0.34 |
| Subfamily Carolliinae | |||
| Carollia brevicauda (Linnaeus, 1758) | F | 12 | 2.01 |
| Carollia perspicillata (Linnaeus, 1758) | F | 268 | 44.97 |
| Subfamily Rhinophyllinae | |||
| Rhinophylla fischerae Carter, 1966 | F | 3 | 0.50 |
| Rhinophylla pumilio Peters, 1865 | F | 142 | 23.83 |
| Subfamily Stenodermatinae | |||
| Artibeus lituratus (Olfers, 1818) | F | 33 | 5.54 |
| Artibeus planirostris (Spix, 1823) | F | 10 | 1.68 |
| Artibeus obscurus (Schinz, 1821) | F | 57 | 9.56 |
| Dermanura cinerea (Gervais, 1856) | F | 40 | 6.71 |
| Platyrrhinus lineatus (É. Geoffroy, 1810) | F | 1 | 0.17 |
| Sturnira lilium (E. Geoffroy, 1810) | F | 4 | 0.67 |
| TOTAL: | 596 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





