Submitted:
02 July 2025
Posted:
03 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Ether Relativity
2.1. Reintroduction of Ether
2.2. Relativistic Rate of Clocks and Energy Density of Ether
2.3. Space Dragging Effects and Ether
2.4. Ether Is Multidimensional and Time-Invariant
3. Ether Cosmology
3.1. Gravity and Time-Invariant Ether
3.2. CMB and Ether
3.3. Expansion of the Universe and Ether
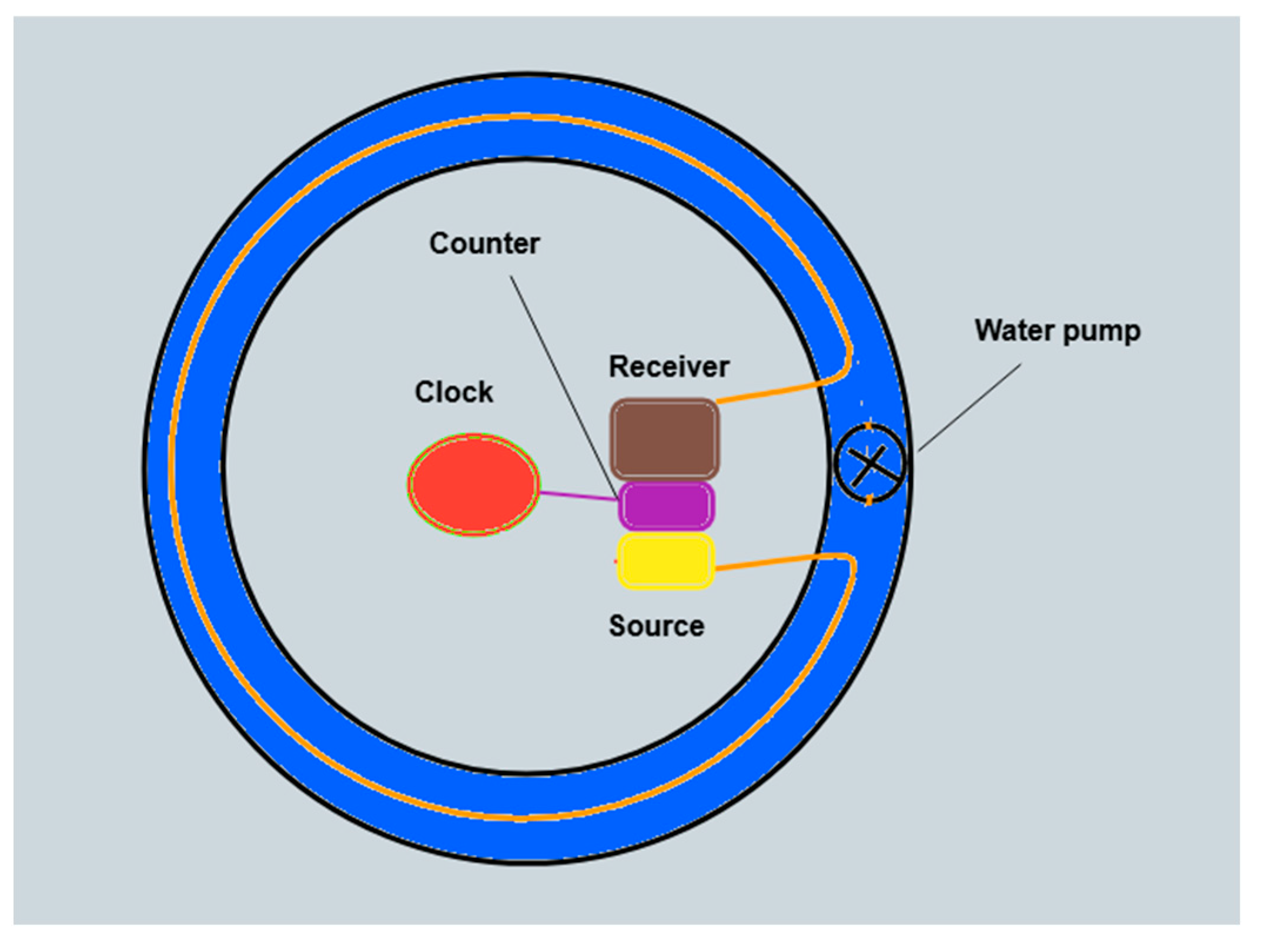
4. Experimental Verification of Ether
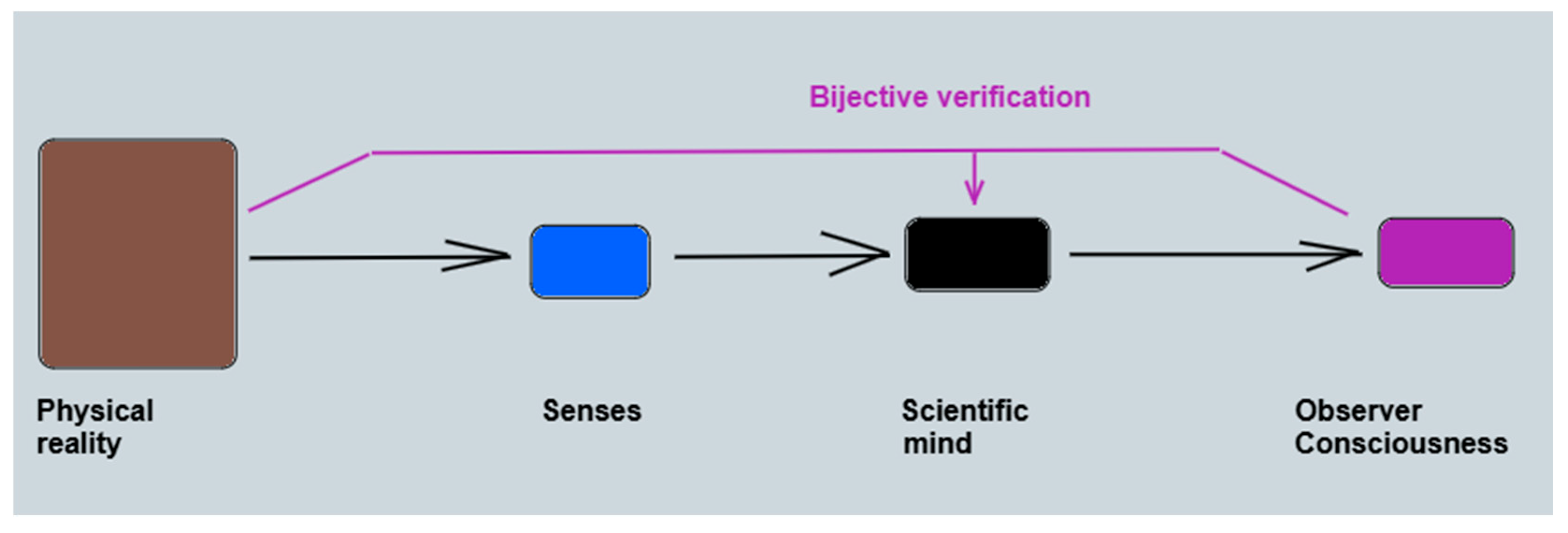
5. Ether Theory of Everything
- -
- Dark energy is the energy of the ether and represents 95% of the energy of the universe; 5% of the energy is in the form of matter
- -
- Ether is dynamic; it moves and rotates with stellar objects, and is the answer to the dark matter
- -
- A photon is a wave of the 4-dimensional layer of ether
- -
- Elementary particles are vortexes of the 4-dimensional layer of ether
- -
- The gravitational force is carried by the variable energy density of the ether
- -
- The Platonic world and the Mathematical universe of Max Tegmark [46] are carried by the higher-dimensional structures of the ether. The multidimensional ether model explains the physical origin with Max Tegmark’s mathematical universe model. Higher levels of ether carry information of a mathematical code that governs the physical universe.
- -
- Consciousness is the Planck frequency of an n-dimensional layer of ether, see Eq. (15) below:
6. Conclusions
References
- Einstein, A. (2007). Ether and the Theory of Relativity. In: Janssen, M., Norton, J.D., Renn, J., Sauer, T., Stachel, J. (eds) The Genesis of General Relativity. Boston Studies in the Philosophy of Science, vol 250. Springer, Dordrecht. [CrossRef]
- Chris Ormel, Einstein Field Equations, NASA https://spsweb.fltops.jpl.nasa.gov/portaldataops/mpg/MPG_Docs/Source%20Docs/Einstein’s%20Field%20Equations.pdf (2001).
- P G L Porta Mana, Dimensional analysis in relativity and in differential geometry, European Journal of Physics, 42 (2021), no. 4. [CrossRef]
- A. Sorli, N. Gorjup, R. Gorjup, Replacement of space-time with superfluid space and restoration of Newton’s dynamic ether, Rep. Adv. Phys. Sci., 7 (2023), 2350005. [CrossRef]
- Michael F. L’Annunziata, Radioactivity, Chapter 7 - Hall of Fame: Part III, Elsevier (2014) . [CrossRef]
- Amrit Sorli, Stefan Celan, Niko Gorjup, Physical origin of the relative rate of clocks in GPS and errors of relative motion concept, Advanced Studies in Theoretical Physics, Vol. 16, 2022, no. 4, 191-200 https://www.m-hikari.com/astp/astp2022/astp1-4-2022/91893.html.
- E. F. Taylor, J. A. Wheeler: Spacetime Physics: Introduction to Special Relativity, 2nd ed. (Freeman, New York 1992) pp. 250-251.
- Schlatter and R E Kastner, Gravity from transactions: fulfilling the entropic gravity program, Journal of Physics Communications (2025). https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/2399-6528/acd6d7.
- I. Newton, The Third Book of Optics (1718). https://www.newtonproject.ox.ac.uk/view/texts/normalized/NATP00051.
- Amrit Srecko Sorli, Rado Gorjup, Niko Gorjup, Tomaz Makovec, Akash Saroj, Akash Ranjan, Piyush Singh, Re-examination of Penrose’s and Kerr’s singularities and the origin of protons in astrophysical jets, Advanced Studies in Theoretical Physics, Vol. 18, 2024, no. 2, 61-82 https://www.m-hikari.com/astp/astp2024/astp1-4-2024/92117.html.
- Mayeul Arminjon, Gravitation as a pressure force: a scalar ether theory (2011) . [CrossRef]
- Wang, XS. The New Concepts of Ether and Calculation of the Cosmological Constant. Phys. Part. Nuclei 54, 991–996 (2023). [CrossRef]
- V. I. Sbitnev, Hydrodynamics of the Physical Vacuum: II. Vorticity Dynamics. Found. Phys. 46 (2016) 1238–1252. [CrossRef]
- Sbitnev, Hydrodynamics of the Physical Vacuum: I. Scalar Quantum Sector. Found. Phys. 46 (2016) 606–619. [CrossRef]
- Amrit Sorli, Stefan Celan, Temporal and timeless cognition in physics Physics Essays, Volume 35, Number 3, September 2022, pp. 305-308(4) . [CrossRef]
- Amrit Sorli, Implications of Time-Invariant Superfluid Quantum Space Model in Fundamental Physics and Cosmology, Applied Physics Research (2025) https://ccsenet.org/journal/index.php/apr/article/view/0/51593.
- Paul Marmet, The GPS and the constant velocity of light, Acta Scientiarum, 22 (2000), no. 5, 1269-1279. https://periodicos.uem.br/ojs/index.php/ActaSciTechnol/article/view/3062/2214.
- Lense, J.; Thirring, H. (1918). “Über den Einfluss der Eigenrotation der Zentralkörper auf die Bewegung der Planeten und Monde nach der Einsteinschen Gravitationstheorie”. Physikalische Zeitschrift. 19: 156–163. Bibcode:1918PhyZ...19..156L. [On the Influence of the Proper Rotation of Central Bodies on the Motions of Planets and Moons According to Einstein’s Theory of Gravitation].
- Niko Gorjup, Amrit Sorli, SMBH relativistic mass and missing dark matter, Advanced Studies in Theoretical Physics, Vol. 16, 2022, no. 4, 291-297 https://www.m-hikari.com/astp/astp2022/astp1-4-2022/91963.html.
- Sagnac, Georges (1913), ”L’éther lumineux démontré par l’effet du vent relatif d’éther dans un interféromètre en rotation uniforme” [The demonstration of the luminiferous aether by an interferometer in uniform rotation], Comptes Rendus, 157: 708–710.
- Irwin I. Shapiro (1964). “Fourth Test of General Relativity”. Physical Review Letters. 13 (26): 789-791. Bibcode:1964PhRvL..13..789S. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.13.789.
- Luis A. Anchordoqui, Alek Bedroya, Dieter Lüst, Primordial Black Holes are 5D (2025) https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.14874.
- Amrit Sorli, Bio-cosmology. Integration of life and consciousness into cosmology Advanced Studies in Theoretical Physics, Vol. 17, 2023, no. 1, 9-20 https://www.m-hikari.com/astp/astp2023/astp1-4-2023/91969.html.
- Clare Burrage et al JCAP07(2012)004. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1475-7516/2012/07/004.
- Niko Gorjup, Rado Gorjup, Amrit Srecko Sorli, End of time travel, Advanced Studies in Theoretical Physics, Vol. 18, 2024, no. 3, 109-116 https://www.m-hikari.com/astp/astp2024/astp1-4-2024/92131.html.
- Hu, W., Farrell, J.A. Derivation of the Sagnac (Earth-rotation) correction and analysis of its accuracy for GNSS applications. J Geod 98, 102 (2024). [CrossRef]
- Bracco, “Einstein and Besso: From Zurich to Milano,” e-print https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1412/1412.6981.pdf (2014).
- Saulson, P., (2021) “THE NATURE OF TIME AS A PUZZLE FOR NATURALISM”, Zygon: Journal of Religion and Science 56(4), 922–942. doi: . [CrossRef]
- The End of Time: The Next Revolution in Physics, Oxford University Press, 1999, ISBN 0-297-81985-2.
- The End of Time (Konec časa), self-publishing, CIP 18417920, Slovenia, 1990.
- Sorli, A., Jafari, S., Fiscaletti, D., Gorjup, N., Gorjup, R., & Makovec T. (2023). Evidence-Based Cosmology – Black holes are rejuvenating systems of the universe. Reports in Advances of Physical Sciences, 7, 2350012. [CrossRef]
- Šorli, A.S. & Čelan Š., Time-Invariant Superfluid Quantum Space as the Unified Field Theory, Reports in Advances of Physical Sciences, 4 (2020), no. 3, 20050007. [CrossRef]
- Rado Gorjup, Amrit Srecko Sorli, Planck’s energy density of intergalactic space and gravitational constant G, Advanced Studies in Theoretical Physics, Vol. 18, 2024, no. 4, 163-172 https://www.m-hikari.com/astp/astp2024/astp1-4-2024/92135.html.
- Penrose, R. Gravitational collapse and space-time singularities, Physical Review Letters, 14 (1965), no. 3, 57. [CrossRef]
- J. B. Hartle and S. W. Hawking, Wave function of the Universe, Phys. Rev. D 28 (1983) 2960. [CrossRef]
- 36. Oscar del Barco, An accurate equation for the gravitational bending of light by a static massive object, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Volume 535, Issue 3, December 2024, Pages 2504–2510, . [CrossRef]
- Bruce Allen and Joseph D. Romano, Detecting a stochastic background of gravitational radiation: Signal processing strategies and sensitivities, Phys. Rev. D 59, 102001 – Published 31 March 1999, . [CrossRef]
- Amrit Sorli, Gravity as a vector of superfluid space and universe expansion, Advanced Studies in Theoretical Physics, Vol. 19, 2025, no. 1, 21-29. https://www.m-hikari.com/astp/astp2025/astp1-4-2025/92245.html.
- Adam G. Riess et al., ApJ, 977 (2024), 120. https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-4357/ad8c21.
- A. Einstein, On the influence of gravitation on the propagation of light, Annalen der Physik, 35, pp. 898-908 (1911) http://eotvos.dm.unipi.it/documents/EinsteinPapers/Einstein1911English.pdf.
- Paul S. Wesson, FUNDAMENTAL UNSOLVED PROBLEMS IN PHYSICS AND ASTROPHYSICS (2025) http://www.calphysics.org/problems.pdf.
- Sagnac, Georges (1913), ”L’éther lumineux démontré par l’effet du vent relatif d’éther dans un interféromètre en rotation uniforme” [The demonstration of the luminiferous aether by an interferometer in uniform rotation], Comptes Rendus, 157: 708–710.
- Sagnac, Georges (1913), ”Sur la preuve de la réalité de l’éther lumineux par l’expérience de l’interférographe tournant” [On the proof of the reality of the luminiferous aether by the experiment with a rotating interferometer], Comptes Rendus, 157: 1410–1413.
- Fizeau, H. (1851). ”Sur les hypothèses relatives à l’éther lumineux”. Comptes Rendus. 33: 349–355. English: Fizeau, H. (1851). ”The Hypotheses Relating to the Luminous Aether, and an Experiment which Appears to Demonstrate that the Motion of Bodies Alters the Velocity with which Light Propagates itself in their Interior” . Philosophical Magazine. 2: 568–573.
- Fizeau, H. (1859). ”Sur les hypothèses relatives à l’éther lumineux”. Ann. Chim. Phys. 57: 385–404. English: Fizeau, H. (1860). ”On the Effect of the Motion of a Body upon the Velocity with which it is traversed by Light” . Philosophical Magazine. 19: 245–260.
- Tegmark, Max (November 1998). “Is “the Theory of Everything” Merely the Ultimate Ensemble Theory?”. Annals of Physics. 270 (1): 1–51. arXiv:gr-qc/9704009. Bibcode:1998AnPhy.270....1T. doi:10.1006/aphy.1998.5855. S2CID 41548734.
- NASA, Our Universe https://wmap.gsfc.nasa.gov/universe/uni shape.html (2014).
- Farnes, J.S. (2018). “A Unifying Theory of Dark Energy and Dark Matter: Negative Masses and Matter Creation within a Modified ΛCDM Framework”. Astronomy & Astrophysics. 620: A92. arXiv:1712.07962. Bibcode:2018A&A...620A..92F. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201832898. S2CID 53600834.
- Daniela Angulo et al., Experimental evidence that a photon can spend a negative amount of time in an atom cloud (2024) . [CrossRef]
- Šorli, Amrit S., Čelan, Štefan, Inconsistency of time-symmetry model, Physics Essays, Volume 34, Number 4, December 2021, pp. 470-471(2) . [CrossRef]
- Geoffrey A. Landis, Negative Mass in Contemporary Physics and its Application to Propulsion (2019) https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/20200000366/downloads/20200000366.pdf.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




