Submitted:
26 May 2025
Posted:
28 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Ultra-high step-up voltage gain with a low turns-ratio of the coupled inductor.
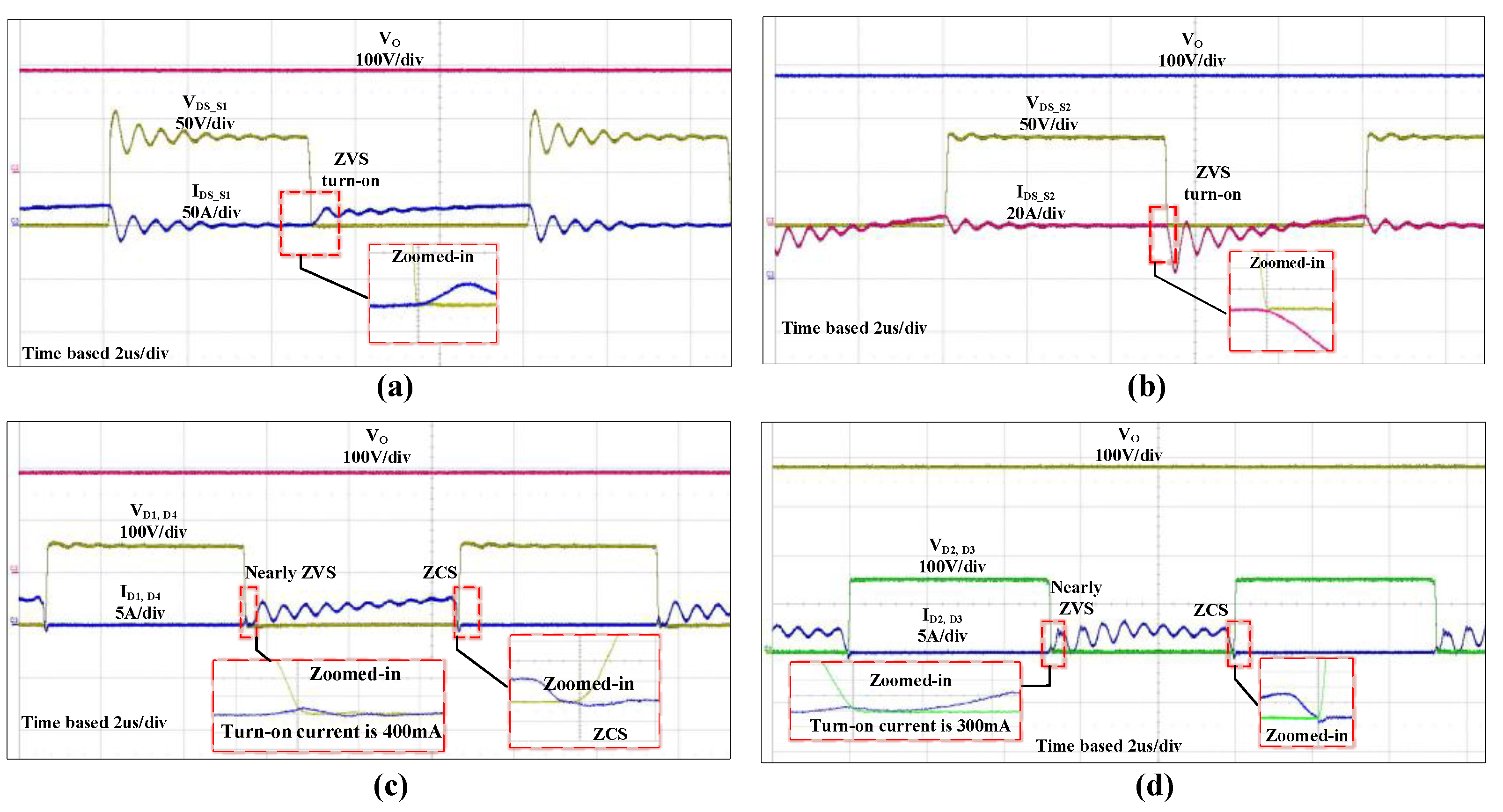
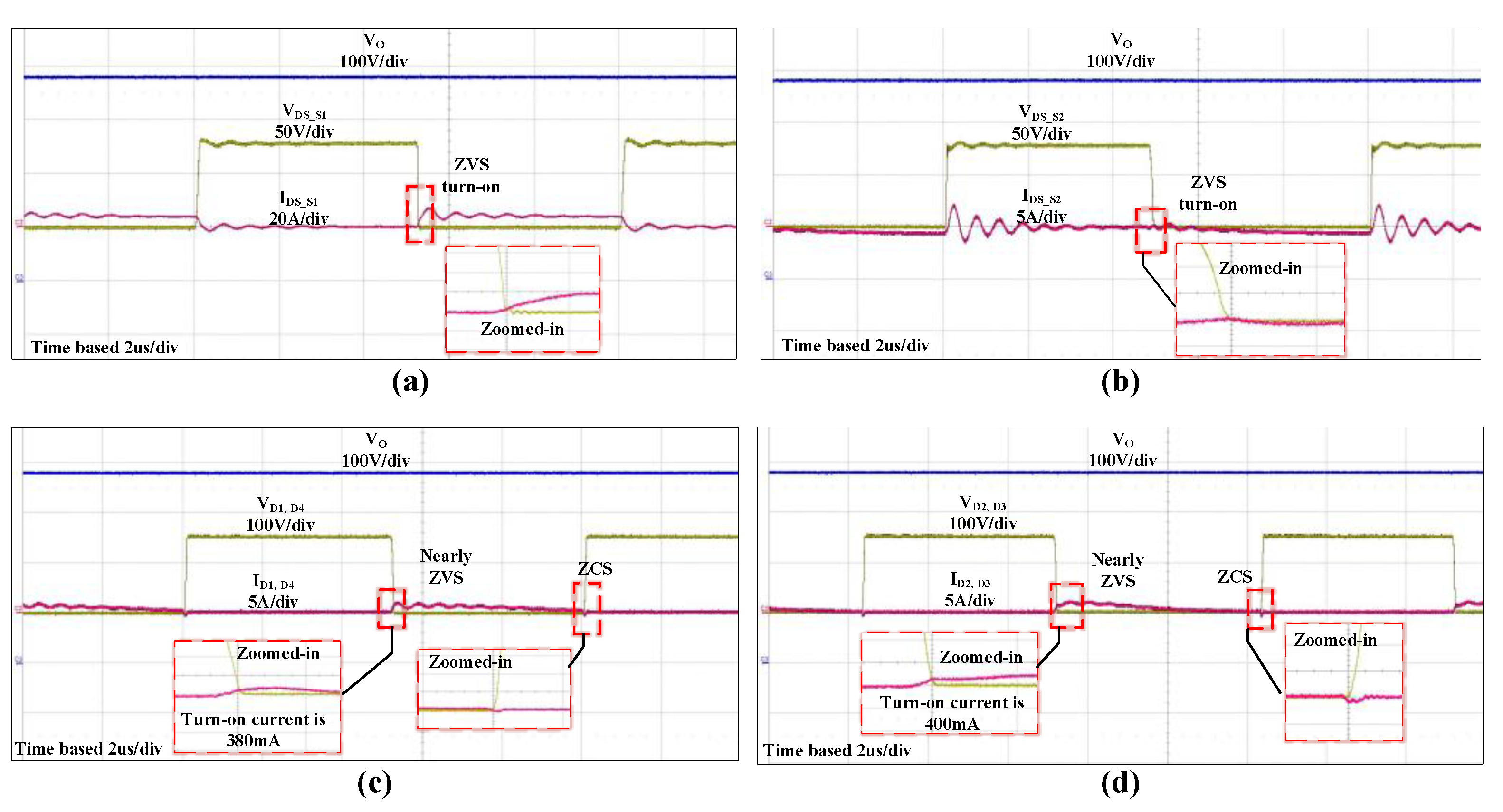
- ZVS turn-on for switches and ZCS turn-off for all diodes
- No voltage spike problem caused by leakage inductance without using an extra snubber circuit.
- Low voltage stress on all components due to the symmetrical configuration.
- Flexibly achieving higher step-up voltage gain with low duty cycle by either adjusting the turns ratio of coupled inductor or cascading a greater number of VM stages.
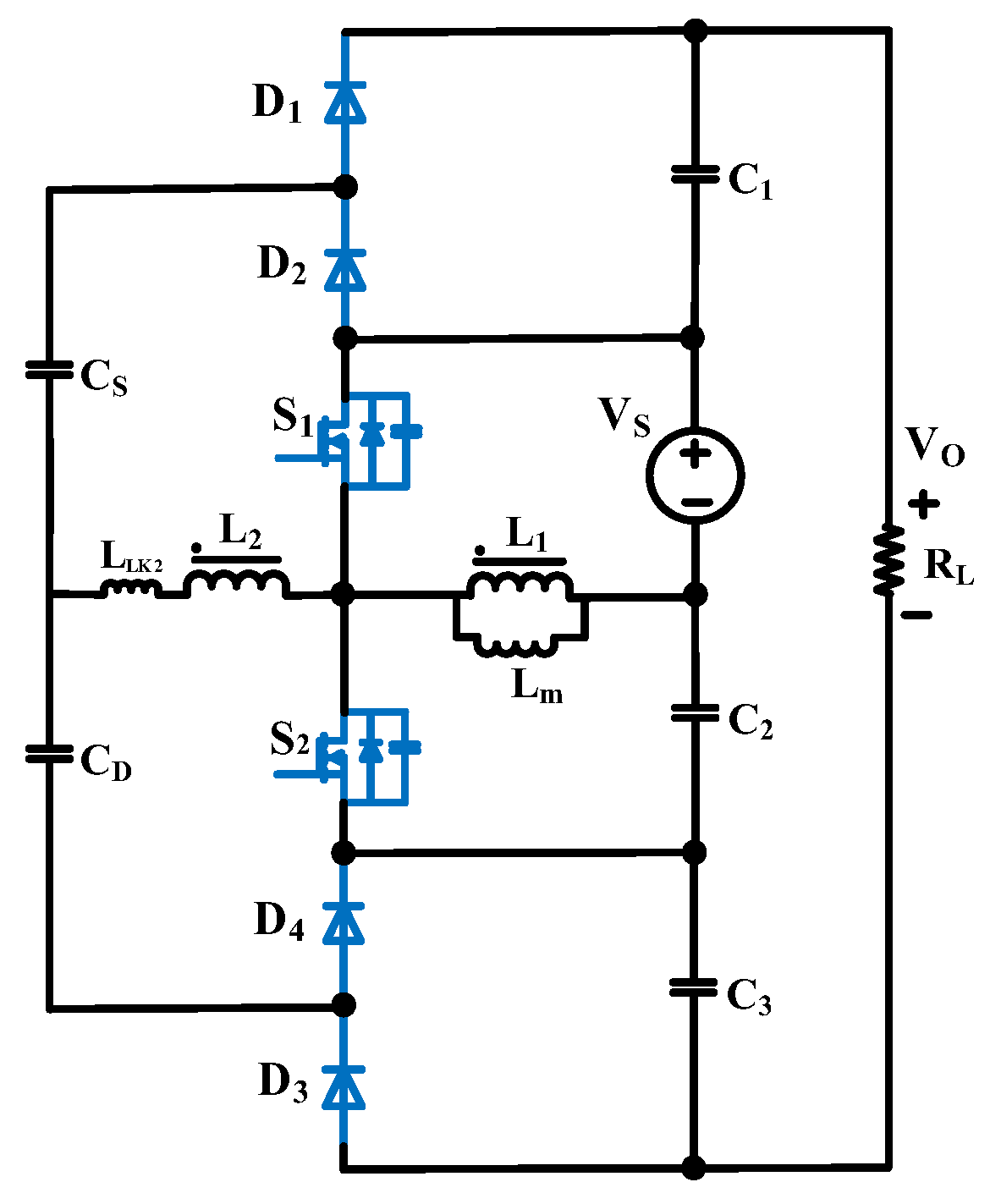
2. Proposed Converter Structure
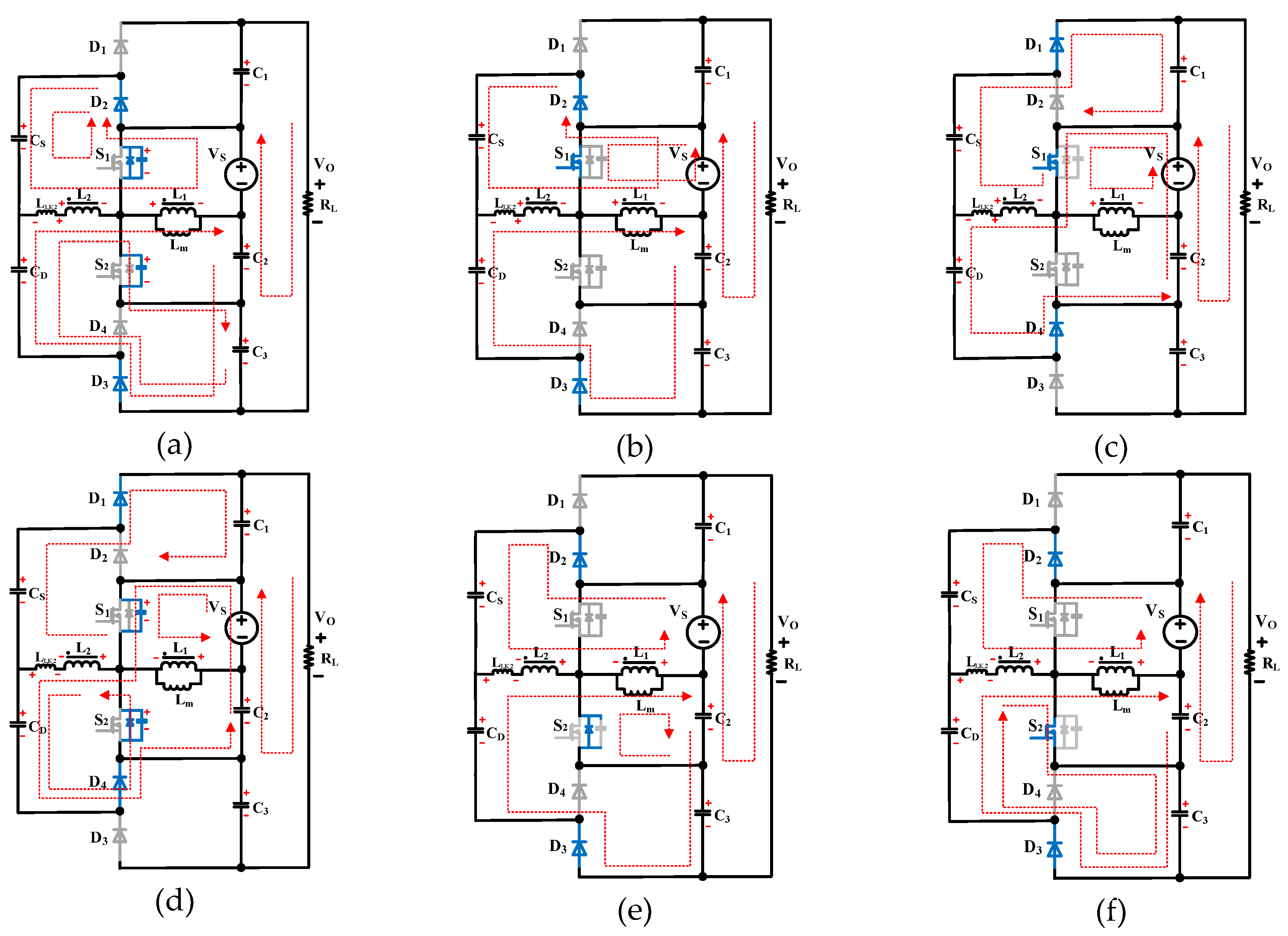
2.1. Operating Principle
- The circuit is operating in steady state mode, and the magnetizing inductor current is continuous.
- All the components are ideal, and the parasitic components are neglected.
- All the capacitors are large enough to maintain their voltages constant during a switch-off period.
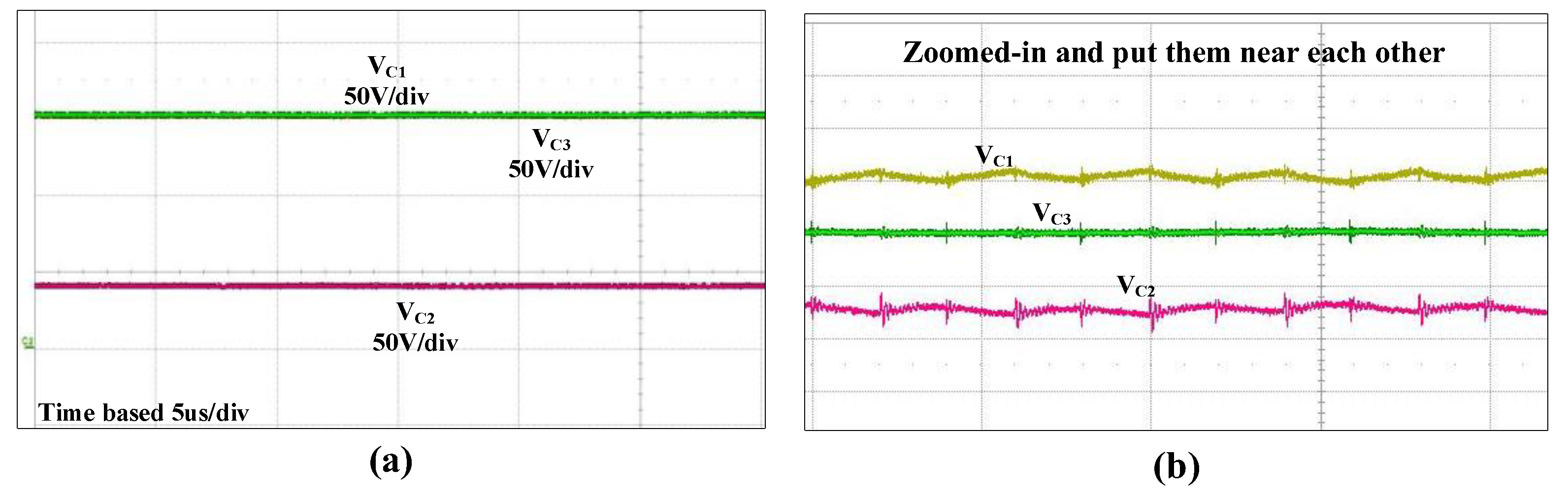
- All the output capacitors have the same value (C1 = C2 = C3), and all the blocking capacitors have the same value (CS = CD).
- The switching period is Ts; the switch S1 is closed for time DTs and open for time (1-D) Ts and vice versa.
- The turns ratio of the coupled inductor and the relationship between the voltage of each winding are defined in (1)
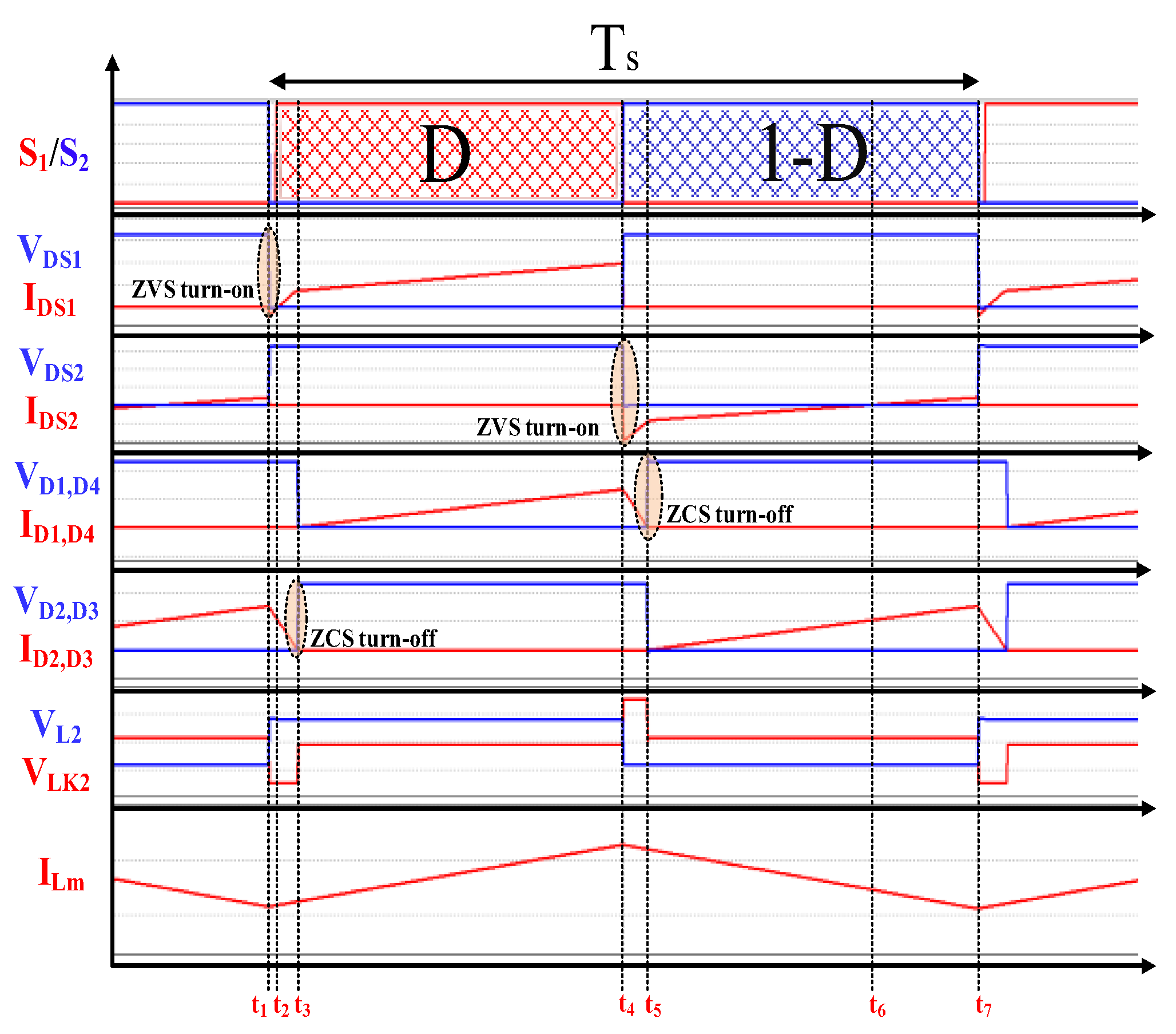
2.2. Steady State Analysis of the Proposed Converter
2.2.1. Voltage Gain and Voltage Stress on Components
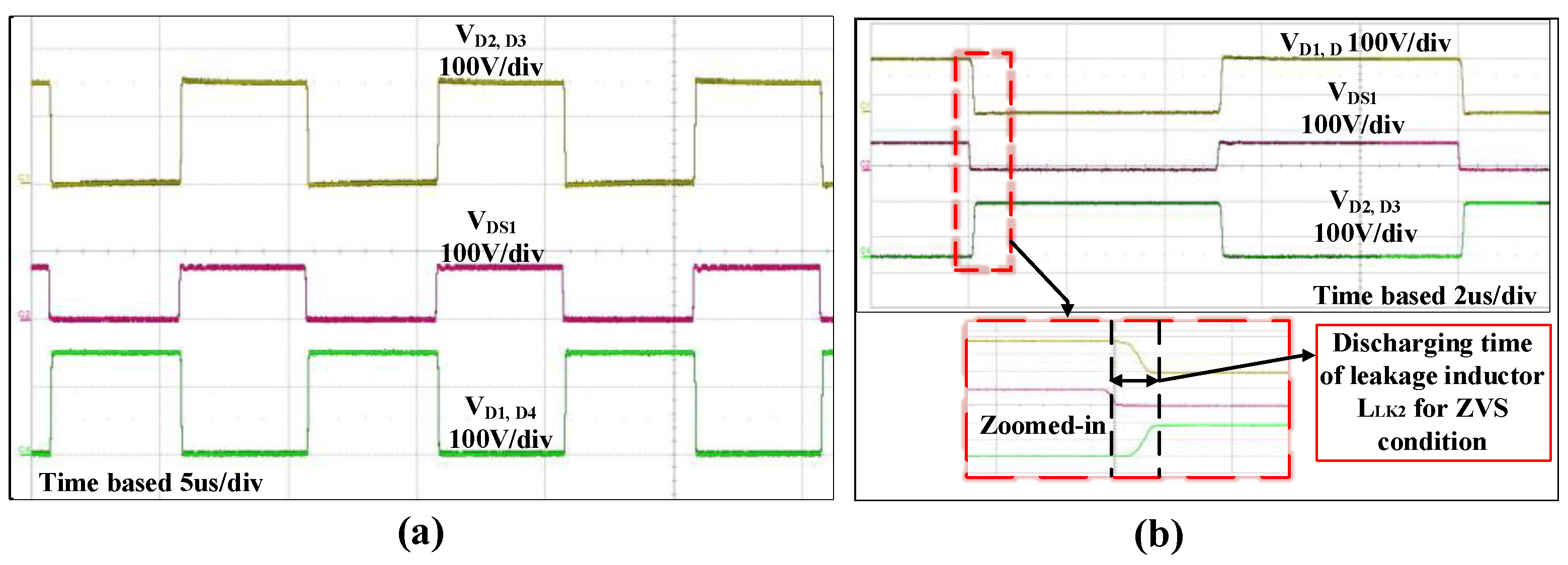
2.2.2. ZVS Condition
3. Design of the Proposed Converter
3.1. Design of the Output Capacitors
3.2. Design of the Main Inductor
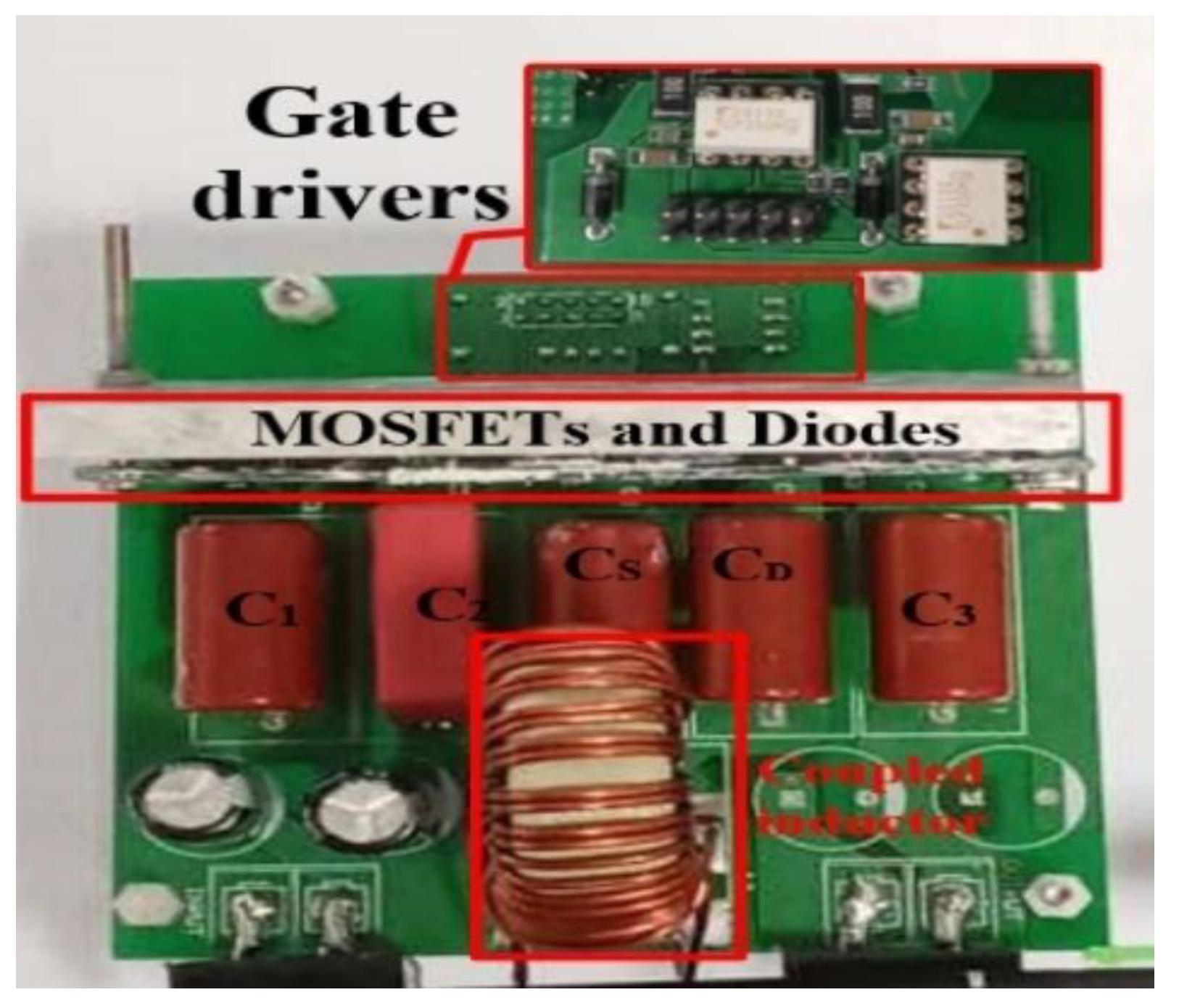
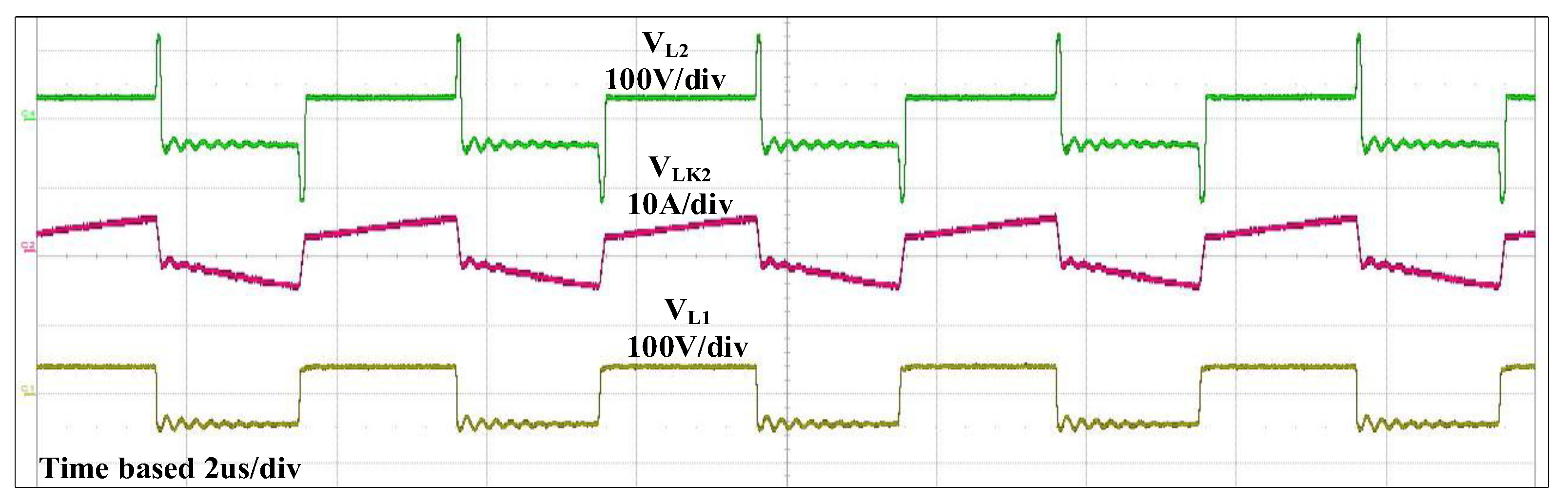
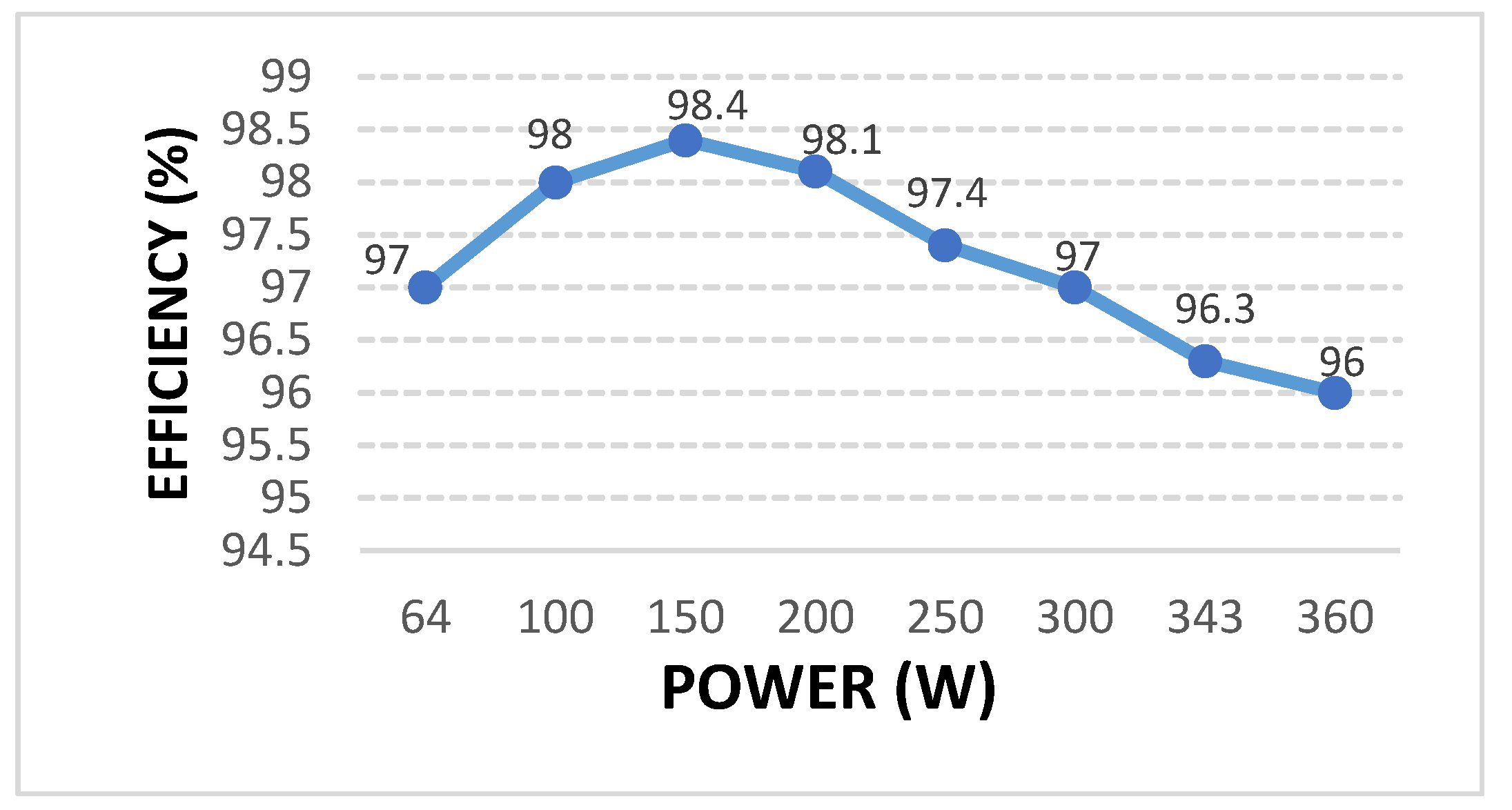
4. Experiment Results
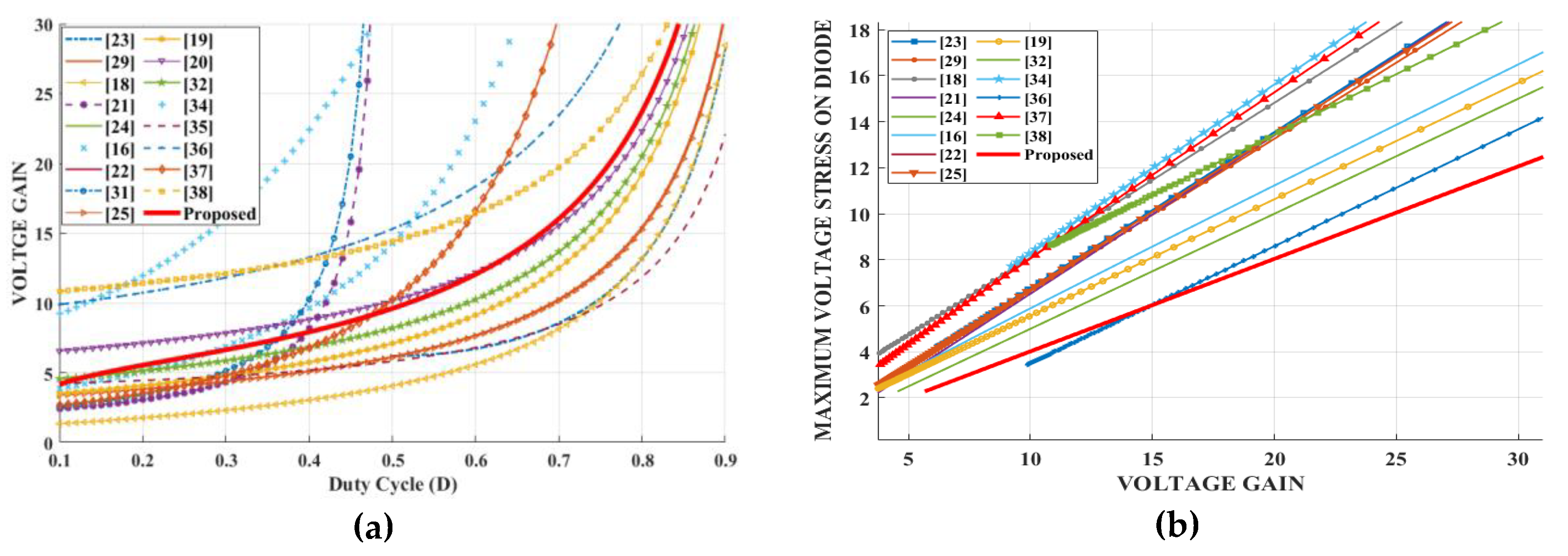
5. Comparison Study
6. Conclusions
- No spike voltage applied to semiconductor devices and hence no need for extra snubber.
- Very high efficiency with ZVS turn-on for MOSFET and ZVZCS for diodes.
- Reduced voltage stress on the components due to the symmetric configuration.
- Easy to get higher voltage gain by either choosing turns ratio of coupled inductor, duty cycle or cascading more VM stages.
References
- W. Li, D. Xu, B. Wu, Y. Zhao, H. Yang and X. He, "Zero-voltage-switching dual-boost converter with multi-functional inductors and improved symmetrical rectifier for distributed generation systems," in IET Power Electronics, vol. 5, no. 7, pp. 969-977, August 2012. [CrossRef]
- H. Cheng, K. Ma Smedley and A. Abramovitz, "A Wide-Input–Wide-Output (WIWO) DC–DC Converter," in IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 280-289, Feb. 2010. [CrossRef]
- M. Forouzesh, Y. P. Siwakoti, S. A. Gorji, F. Blaabjerg and B. Lehman, "Step-Up DC–DC Converters: A Comprehensive Review of Voltage-Boosting Techniques, Topologies, and Applications," in IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 32, no. 12, pp. 9143-9178, Dec. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zeng, H. Li, W. Wang, B. Zhang and T. Q. Zheng, "High-Efficient High-Voltage-Gain Capacitor Clamped DC–DC Converters and Their Construction Method," in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 68, no. 5, pp. 3992-4003, May 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Alzahrani, M. Ferdowsi and P. Shamsi, "A Family of Scalable Non-Isolated Interleaved DC-DC Boost Converters With Voltage Multiplier Cells," in IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 11707-11721, 2019. [CrossRef]
- G. Lin and Z. Zhang, "Low Input Ripple High Step-Up Extendable Hybrid DC-DC Converter," in IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 158744-158752, 2019. [CrossRef]
- B. Wu, S. Li, Y. Liu and K. Ma Smedley, "A New Hybrid Boosting Converter for Renewable Energy Applications," in IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 1203-1215, Feb. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Fang Lin Luo and Hong Ye, "Positive output super-lift converters," in IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 105-113, Jan. 2003. [CrossRef]
- S. Sayed, M. Elmenshawy, M. Elmenshawy, L. Ben-Brahim and A. Massoud, "Design and analysis of high-gain medium-voltage DC-DC converters for high-power PV applications," 2018 IEEE 12th International Conference on Compatibility, Power Electronics and Power Engineering (CPE-POWERENG 2018), Doha, Qatar, 2018, pp. 1-5. [CrossRef]
- E. H. Ismail, M. A. Al-Saffar, A. J. Sabzali and A. A. Fardoun, "A Family of Single-Switch PWM Converters With High Step-Up Conversion Ratio," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, vol. 55, no. 4, pp. 1159-1171, May 2008. [CrossRef]
- G. Wu, X. Ruan and Z. Ye, "Nonisolated High Step-Up DC–DC Converters Adopting Switched-Capacitor Cell," in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 62, no. 1, pp. 383-393, Jan. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.-T.; Nguyen, M.-K.; Choi, Y.-O.; Cho, G.-B. Switched-Capacitor-Based High Boost DC-DC Converter. Energies 2018, 11, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Prudente, L. L. Pfitscher, G. Emmendoerfer, E. F. Romaneli and R. Gules, "Voltage Multiplier Cells Applied to Non-Isolated DC–DC Converters," in IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 871-887, March 2008. [CrossRef]
- Y. J. A. Alcazar, D. de Souza Oliveira, F. L. Tofoli and R. P. Torrico-Bascopé, "DC–DC Nonisolated Boost Converter Based on the Three-State Switching Cell and Voltage Multiplier Cells," in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 60, no. 10, pp. 4438-4449, Oct. 2013. [CrossRef]
- M. Prudente, L. Pfitscher and R. Gules, "A Boost Converter With Voltage Multiplier Cells," 2005 IEEE 36th Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Dresden, Germany, 2005, pp. 2716-2721. [CrossRef]
- J. Ai, M. Lin and M. Yin, "A Family of High Step-Up Cascade DC–DC Converters With Clamped Circuits," in IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 35, no. 5, pp. 4819-4834, May 2020. [CrossRef]
- F. Sedaghati and S. Pourjafar, "Analysis and implementation of a boost DC–DC converter with high voltage gain and continuous input current," in IET Power Electronics, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 798-807, 18 3 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zheng and K. M. Smedley, "Analysis and Design of a Single-Switch High Step-Up Coupled-Inductor Boost Converter," in IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 535-545, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
- R. Moradpour, H. Ardi and A. Tavakoli, "Design and Implementation of a New SEPIC-Based High Step-Up DC/DC Converter for Renewable Energy Applications," in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 65, no. 2, pp. 1290-1297, Feb. 2018. [CrossRef]
- A. M. S. S. Andrade, L. Schuch and M. L. da Silva Martins, "Analysis and Design of High-Efficiency Hybrid High Step-Up DC–DC Converter for Distributed PV Generation Systems," in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 66, no. 5, pp. 3860-3868, May 2019. [CrossRef]
- B. Poorali and E. Adib, "Soft-Switched High Step-Up Quasi-Z-Source DC–DC Converter," in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 67, no. 6, pp. 4547-4555, June 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. Ye, S. Chen and Y. Yi, "Switched-Capacitor and Coupled-Inductor Based High Step-Up Converter with Improved Voltage Gain," in IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics. [CrossRef]
- K. R. Kothapalli, M. R. R. Ramteke, H. M. Suryawanshi, N. K. REDDI and R. B. Kalahasthi, "A Coupled Inductor Based High Step - up Converter for DC Microgrid Applications.," in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics. [CrossRef]
- S. Chen, S. Yang, C. Huang and Y. Chen, "High Step-Up Interleaved Converter With Three-Winding Coupled Inductors and Voltage Multiplier Cells," 2019 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Melbourne, Australia, 2019, pp. 458-463. [CrossRef]
- G. Wu, X. Ruan and Z. Ye, "High Step-Up DC–DC Converter Based on Switched Capacitor and Coupled Inductor," in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 65, no. 7, pp. 5572-5579, July 2018. [CrossRef]
- X. Hu, X. Liu, Y. Zhang, Z. Yu and S. Jiang, "A Hybrid Cascaded High Step-Up DC-DC Converter with Ultra-low Voltage Stress," in IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics. [CrossRef]
- S. Chen, S. Yang, C. Huang and Y. Chen, "High Step-Up Interleaved Converter With Three-Winding Coupled Inductors and Voltage Multiplier Cells," 2019 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Melbourne, Australia, 2019, pp. 458-463. [CrossRef]
- P. Upadhyay, R. Kumar and S. Sathyan, "Coupled-inductor-based high-gain converter utilising magnetising inductance to achieve soft-switching with low voltage stress on devices," in IET Power Electronics, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 576-591, 19 2 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Zaoskoufis and E. C. Tatakis, "An Improved Boost-based DC/DC Converter with High Voltage step-up ratio for DC Microgrids," in IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics. [CrossRef]
- A. Mirzaee and J. S. Moghani, "Coupled Inductor-Based High Voltage Gain DC–DC Converter For Renewable Energy Applications," in IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, vol. 35, no. 7, pp. 7045-7057, July 2020. [CrossRef]
- G. Wu, X. Ruan and Z. Ye, "Non-isolated high step-up DC-DC converter adopting auxiliary capacitor and coupled inductor," in Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 384-398, March 2018. [CrossRef]
- N. Molavi, E. Adib and H. Farzanehfard, "Soft-switched non-isolated high step-up DC–DC converter with reduced voltage stress," in IET Power Electronics, vol. 9, no. 8, pp. 1711-1718, 29 6 2016. [CrossRef]
- X. Ding, M. Zhou, Y. Cao, B. Li, Y. Sun and X. Hu, "A High Step-Up Coupled-Inductor-Integrated DC–DC Multilevel Boost Converter With Continuous Input Current," in IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, vol. 10, no. 6, pp. 7346-7360, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- V. Abbasi, S. Rostami, S. Hemmati and S. Ahmadian, "Ultrahigh Step-Up Quadratic Boost Converter Using Coupled Inductors With Low Voltage Stress on the Switches," in IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, vol. 10, no. 6, pp. 7733-7743, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- V. Abbasi, N. Talebi, M. Rezaie, A. Arzani and F. Y. Moghadam, "Ultrahigh Step-Up DC–DC Converter Based on Two Boosting Stages With Low Voltage Stress on Its Switches," in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 70, no. 12, pp. 12387-12398, Dec. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Maalandish, Mohammad, et al. "Ultra high step-up soft-switching DC/DC converter using coupled inductor and interleaved technique." IET Power Electronics 16.8 (2023): 1320-1338 doi.org/10.1049/pel2.12472. [CrossRef]
- R. Rahimi, S. Habibi, M. Ferdowsi and P. Shamsi, "An Interleaved Quadratic High Step-Up DC-DC Converter With Coupled Inductor," in IEEE Open Journal of Power Electronics, vol. 2, pp. 647-658, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Hashemzadeh, Seyed Majid, et al. "Design and Analysis of a New Coupled Inductor-Based Interleaved High Step-Up DC-DC Converter for Renewable Energy Applications." International Transactions on Electrical Energy Systems 2022.1 (2022): 7618242. [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Designator | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Input Voltage | 40 V | |
| Output voltage | 380 V | |
| Maximum Output voltage ripple | 0.8% | |
| Power | 360 W | |
| Switching frequency | 100 KHz |
| Component | Part # | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| MOSFETs | IPP039N10N5 | 200 V/80 A |
| Diodes (-) | DSSK10-18A | 180 V/10A |
| Capacitors | 106MMR250K | 10uF/ 250 V |
| Turns-ratio of the coupled inductor | 17:18 | |
| Leakage inductance () | 4.5uH | |
| Primary winding inductance | 103uH | |
| Secondary winding inductance | 115uH |
| Topology | Voltage gain |
Voltage stress on switches (Vs/Vin) | Maximum voltage stress on diodes (VDmax/Vin) | Maximum voltage stress on output capacitors (VCo/Vin) | S/D/CI/I/C/T | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [23] | NI | 2/3/2/0/5/12 | 96.5% | |||
| [29] | 2/3/1/1/5/12 | 96.8% | ||||
| [18] | 1/2/1/1/3/8 | 94.1% | ||||
| [21] | 2/2/1/1/4/10 | 95.6% | ||||
| [24] | NI | 2/6/2/0/6/16 | 96.7% | |||
| [16](Figure 4a) | 1/6/1/1/5/14 | 94.4% | ||||
| [22] | 1/4/1/0/4/10 | 97.1% | ||||
| [31](Figure 6b) | NI | 1/4/1/1/5/12 | 95% | |||
| [25](Figure 4) | 1/3/1/0/3/8 | 96.4% | ||||
| [19] | 1/4/1/1/5/12 | 96.2% | ||||
| [20] | 1/8/1/0/8/18 | 97.6% | ||||
| [32] | 2/4/1/0/5/12 | 96.3% | ||||
| [34] | NI | 2/5/2/5/14 | 95.2% | |||
| [35] | 2/5/1/1/5/14 | 94.2% | ||||
| [36] | NI | 2/8/2/0/8/20 | 94.6% | |||
| [37] | 2/4/2/0/4/12 | 94.4% | ||||
| [38] | NI | 2/5/3/0/5/15 | 95.96% | |||
| Proposed converter | (11) | (10d) | (10d) | 2/4/2/0/5/13 | 98.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





