Submitted:
20 May 2025
Posted:
20 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background of the study
3. Objectives
- ➢
- To review the types of enzymes used in food safety and quality improvement.
- ➢
- To compare different enzymatic approaches and their effectiveness in enhancing food safety and quality.
- ➢
- To identify challenges and limitations in enzyme applications in the food industry.
- ➢
- To propose future directions for research and industrial application.
4. Methodology
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Types of Enzymes and Their Roles in Food Safety and Quality
| Enzyme Type | Function in Food System | Impact on Safety and Quality | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proteases | Hydrolyze proteins, tenderize meat, remove allergens | Improve texture, reduce allergenic proteins, enhance digestibility | (Li et al., 2021) |
| Lipases | Breakdown lipids to improve flavor and reduce rancidity | Enhance flavor, extend shelf life | (Ahmed & Khan, 2020) |
| Oxidases | Catalyze oxidation reactions, degrade pesticides | Detoxify food contaminants, reduce microbial load | (Garcia et al., 2022) |
| Amylases | Break down starch into sugars | Improve sweetness, texture, and fermentability | (Zhao et al., 2019) |
| Laccases | Oxidize phenolic compounds | Reduce browning, improve color stability | (Fernandez et al., 2023) |
5.2. Comparative Analysis of Enzymatic Applications
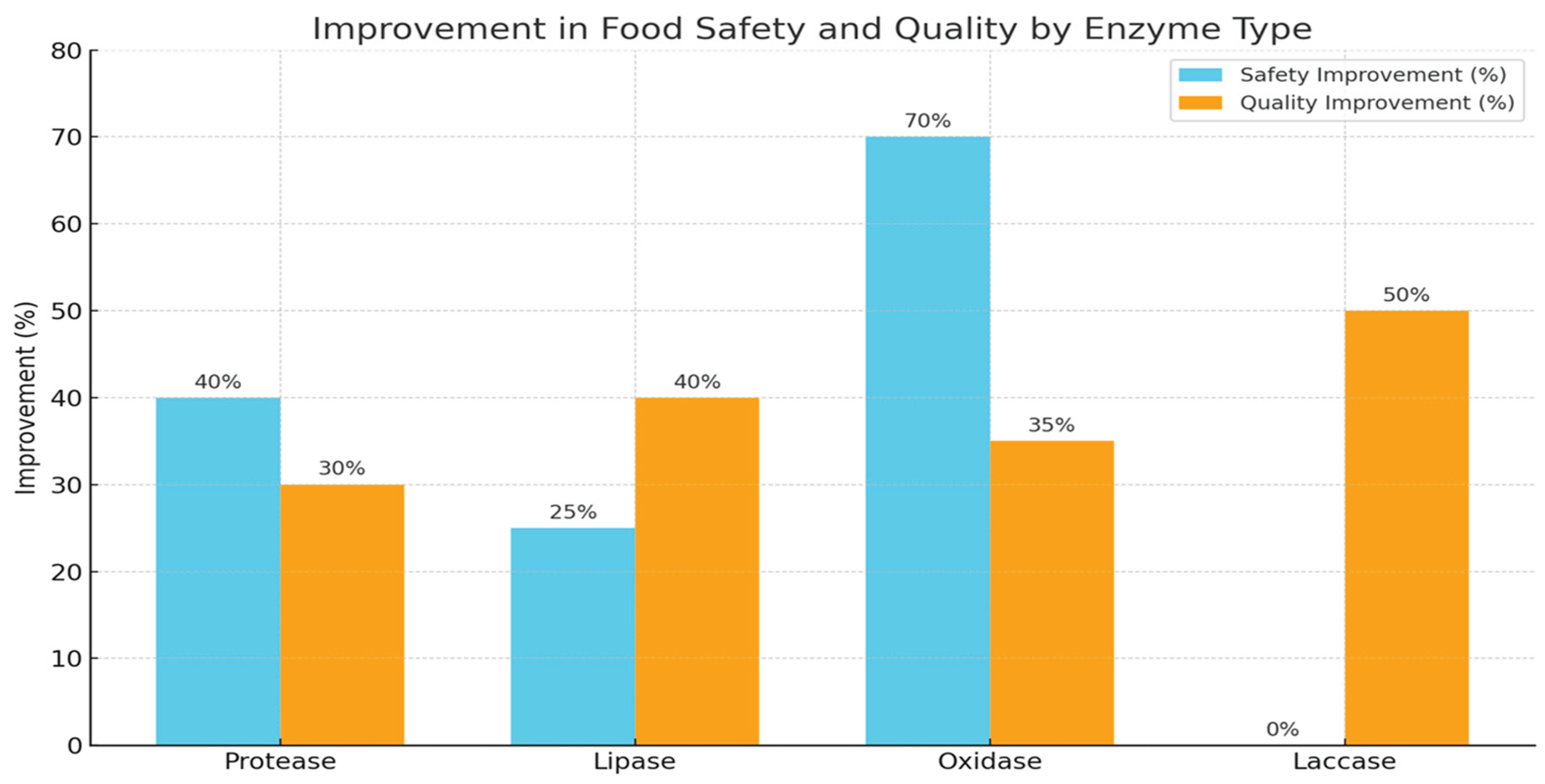
| Study | Enzyme Used | Food Matrix | Safety Improvement | Quality Enhancement | Outcome Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li et al. (2021) | Protease | Meat | Decreased allergenicity by 40% | Improved tenderness by 30% | Enhanced safety and sensory quality |
| Ahmed & Khan (2020) | Lipase | Dairy products | Reduced lipid oxidation by 25% | Increased flavor profile | Prolonged shelf life |
| Garcia et al. (2022) | Oxidase | Fruits and vegetables | Detoxified pesticide residues by 70% | Reduced microbial spoilage | Significantly safer fresh produce |
| Fernandez et al. (2023) | Laccase | Fruit juices | Lower enzymatic browning | Improved color retention | Extended visual appeal and consumer acceptance |
5.3. Mechanisms Underlying Safety and Quality Improvement
- 1)
- Detoxification of Contaminants: Oxidative enzymes such as oxidases and laccases are effective in degrading harmful chemical residues, including mycotoxins and pesticide residues that may be present in raw agricultural produce. These enzymes catalyze redox reactions that break down toxic molecules into less harmful or inert compounds, thereby reducing public health risks associated with foodborne toxins (Garcia et al., 2022; Fernandez et al., 2023).
- 2)
- Antimicrobial Activity: Enzymatic interventions can also exert antimicrobial effects either by degrading the structural components of microbial cells or through the production of antimicrobial peptides. For instance, lysozymes and certain proteases disrupt microbial cell walls, while engineered enzymes can generate peptides with bacteriostatic properties (Bhushan et al., 2020; Singh et al., 2023).
- 3)
- Texture Modification: Proteolytic enzymes such as papain, bromelain, and trypsin hydrolyze protein structures, enhancing the tenderness and texture of meat and dairy products. This enzymatic tenderization is particularly valuable in the meat industry to improve palatability and reduce processing time (Li et al., 2021).
- 4)
- Flavor Enhancement: Lipases contribute significantly to flavor development by catalyzing the release of free fatty acids, which serve as flavor precursors in dairy, baked goods, and fermented products. These enzymes help create complex and desirable flavor profiles without the need for artificial additives (Ahmed & Khan, 2020).
- 5)
- Shelf Life Extension: By reducing lipid oxidation and microbial proliferation, enzymes such as catalases and peroxidases contribute to prolonged shelf life. Their ability to degrade reactive oxygen species and suppress spoilage microorganisms enhances product stability and safety (Kumar et al., 2022; Singh & Sharma, 2021).
6. Challenges and Limitations
- ➢
- Enzyme stability: Many enzymes are sensitive to temperature, pH, and food matrix conditions, limiting industrial use (Singh & Sharma, 2021).
- ➢
- Cost: High production and purification costs can be a barrier for widespread application.
- ➢
- Allergenicity: Some enzyme sources may induce allergic reactions.
- ➢
- Regulatory hurdles: Approval processes for enzyme use vary globally and can delay commercialization.
- ➢
- Interaction with food components: Enzymes may produce unwanted by-products or affect sensory qualities negatively if not carefully controlled.
7. Future Recommendations
8. Summary and Conclusion
References
- Ahmed, S., & Khan, M. (2020). Role of lipases in improving dairy product quality and shelf life. Food Chemistry, 318, 126467. [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B., Dubey, K. K., & Singh, D. (2020). Enzyme-based approaches for food allergen mitigation: Recent trends and future prospects. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 55(8), 2741–2750. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J., Martinez, A., & Lopez, S. (2023). Application of laccase enzymes in fruit juice preservation: A review. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 58(2), 342–356.
- Garcia, P., Rivera, M., & Soto, R. (2022). Oxidases for detoxification of pesticides in fruits and vegetables: A sustainable approach. Environmental Science & Technology, 56(7), 4301–4310.
- Kumar, R., Singh, A., & Patel, M. (2022). Advances in enzymatic food processing for quality enhancement: A comprehensive review. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 123, 234–248. [CrossRef]
- Li, X., Zhang, Y., & Chen, H. (2021). Protease applications in meat processing: Improving tenderness and reducing allergenicity. Meat Science, 179, 108538. [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, N. K., & Nayak, C. A. (2022). Enzyme applications in emerging food processing technologies. Current Opinion in Food Science, 46, 100839. [CrossRef]
- Singh, P., & Sharma, R. (2021). Role of enzymes in food processing: An overview. Journal of Food Biochemistry, 45(2), e13523. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R., Kumar, M., Mittal, A., & Mehta, P. K. (2023). Enzymatic strategies for enhancing food safety and nutrition. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 63(3), 456–471.
- Zhao, Y., Xu, J., & Wang, Y. (2019). Functional role of amylases in modern food industry: Current applications and future perspectives. Food Science and Human Wellness, 8(4), 223–229. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





