Submitted:
15 May 2025
Posted:
16 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
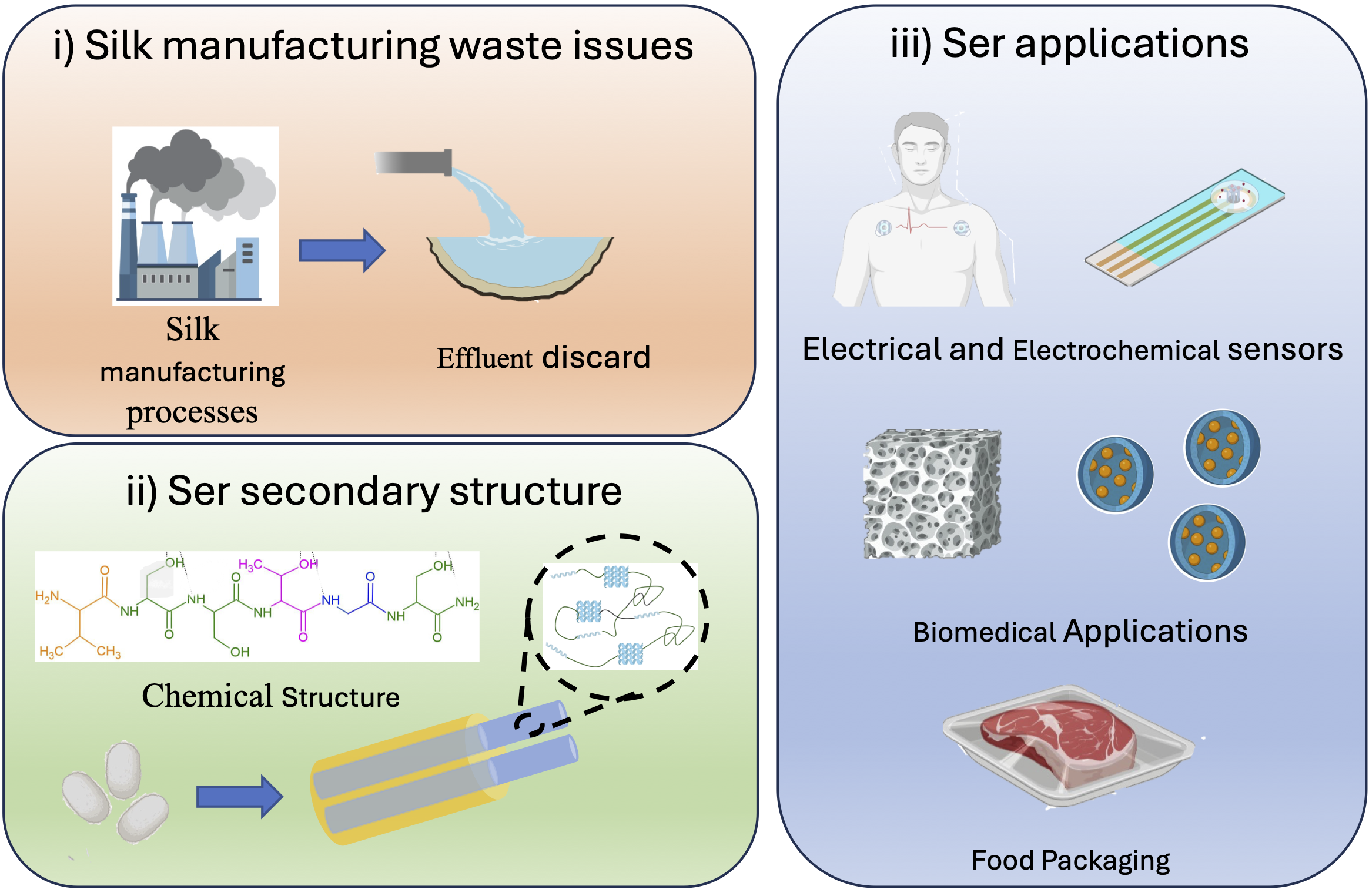
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Structure and Composition of Silk
2.1. Ser Structure and Phisico-Chemical Properties
3. Ser Extraction Process
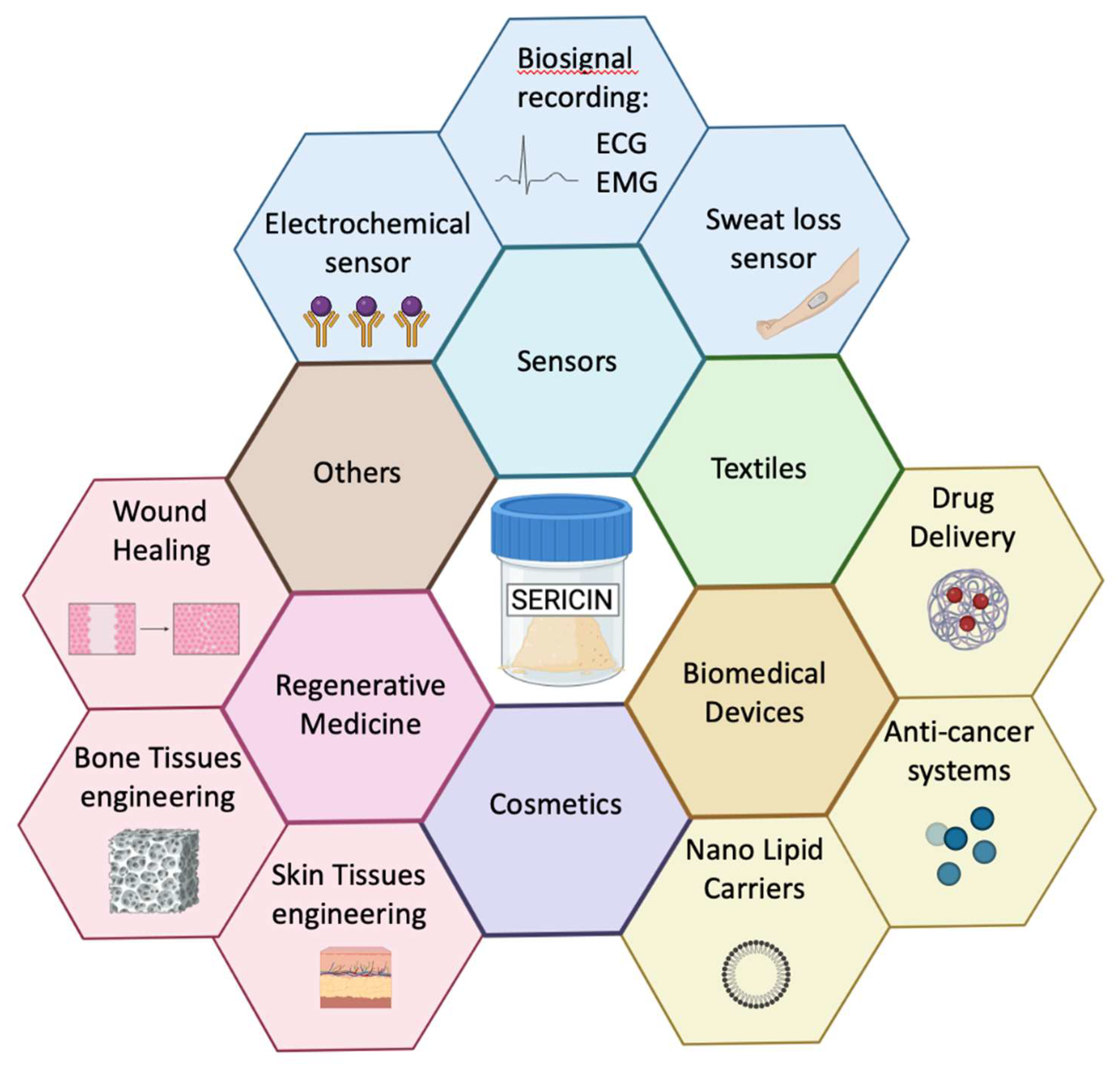
4. Applications of Ser
4.1. Advances in Bioelectronic Devices for Sensing
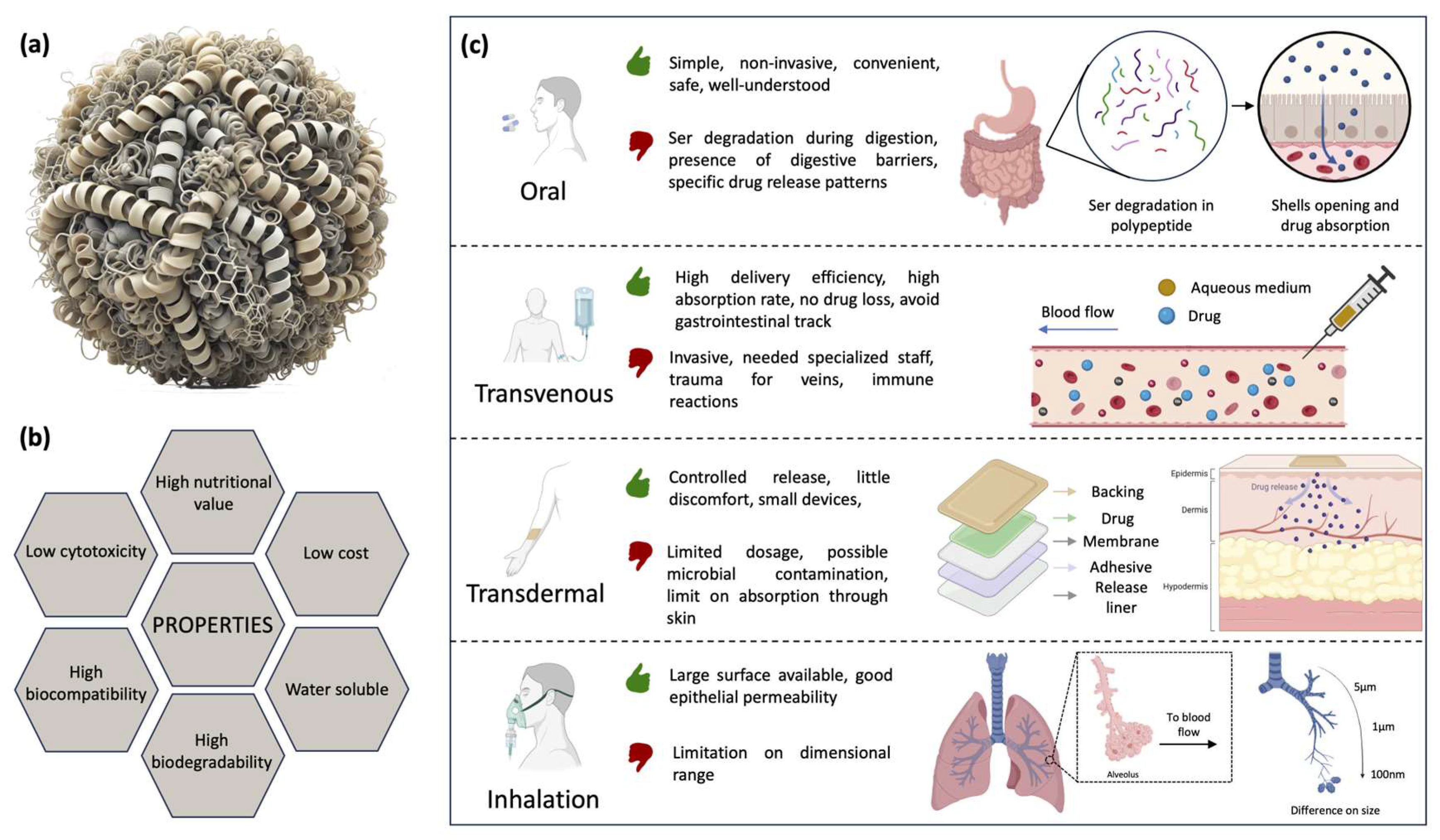
4.2. Drug Delivery Applications of Protein-Based Materials
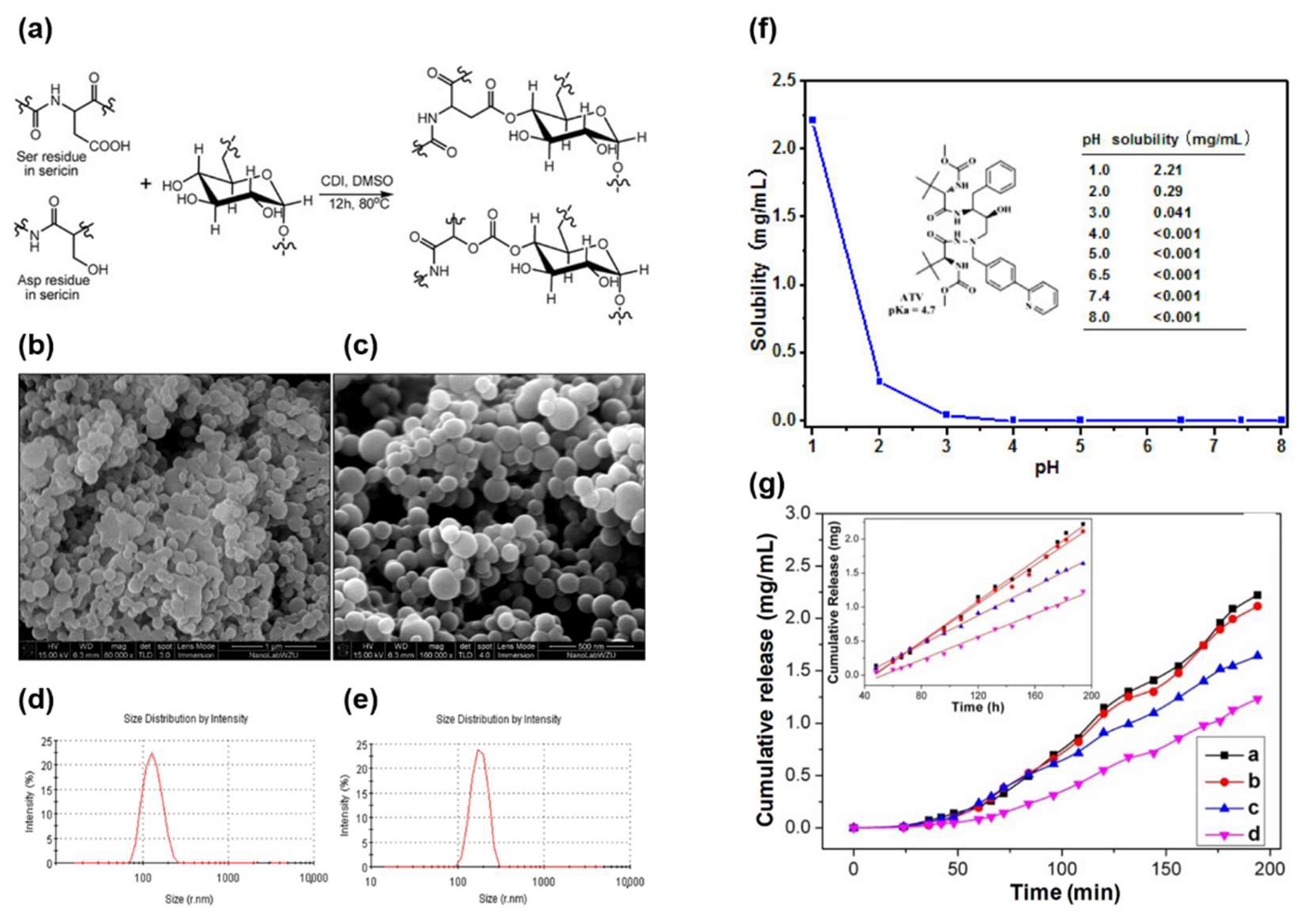
4.2.1. Ser in Drug Delivery Applications
4.3. Ser in Biotechnology Field; Beyond Drug Delivery
4.3.1. Ser Anticancer Effect
4.3.2. Ser Metabolic Effect
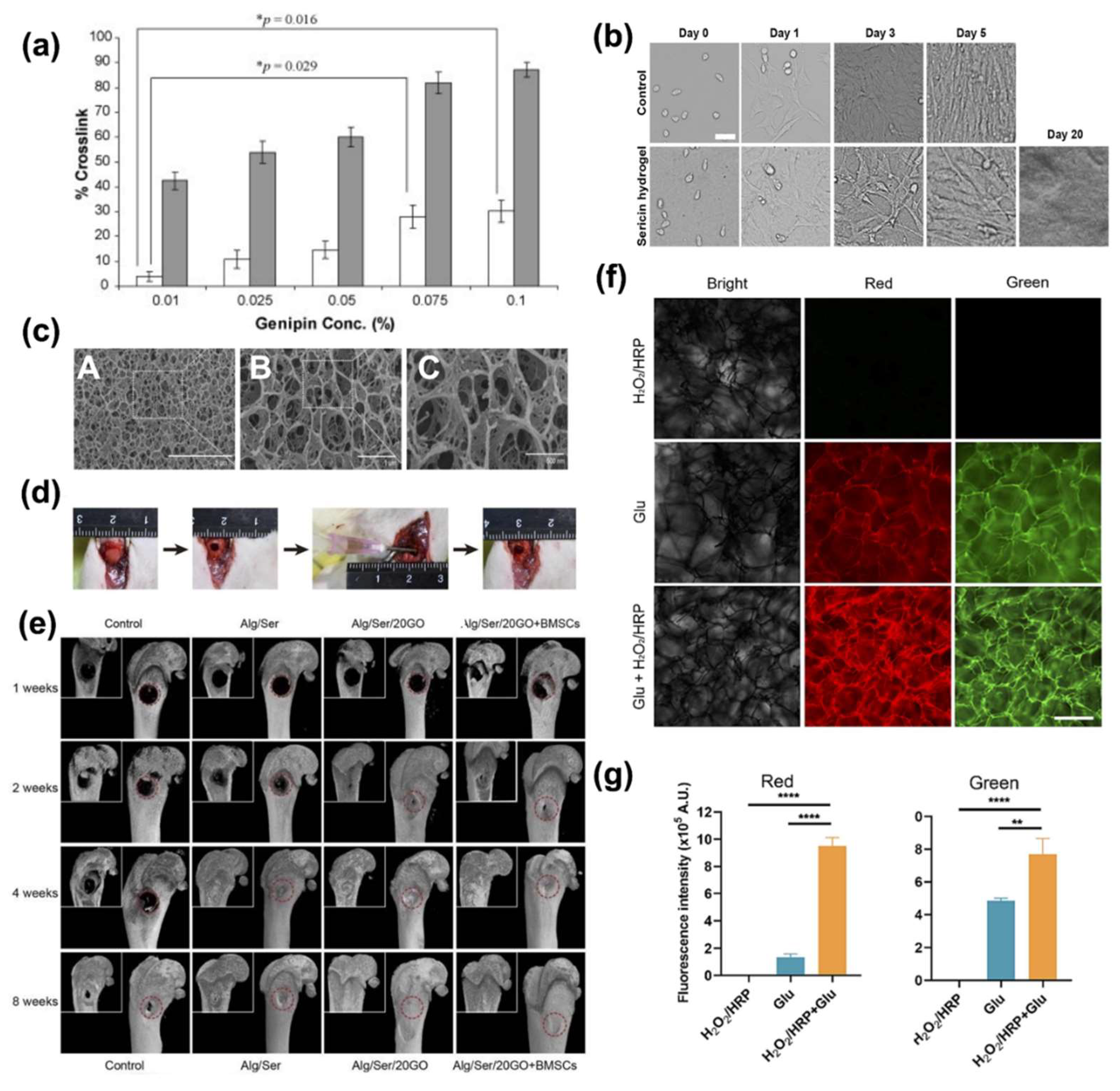
4.3.3. Ser in Tissue Engineering
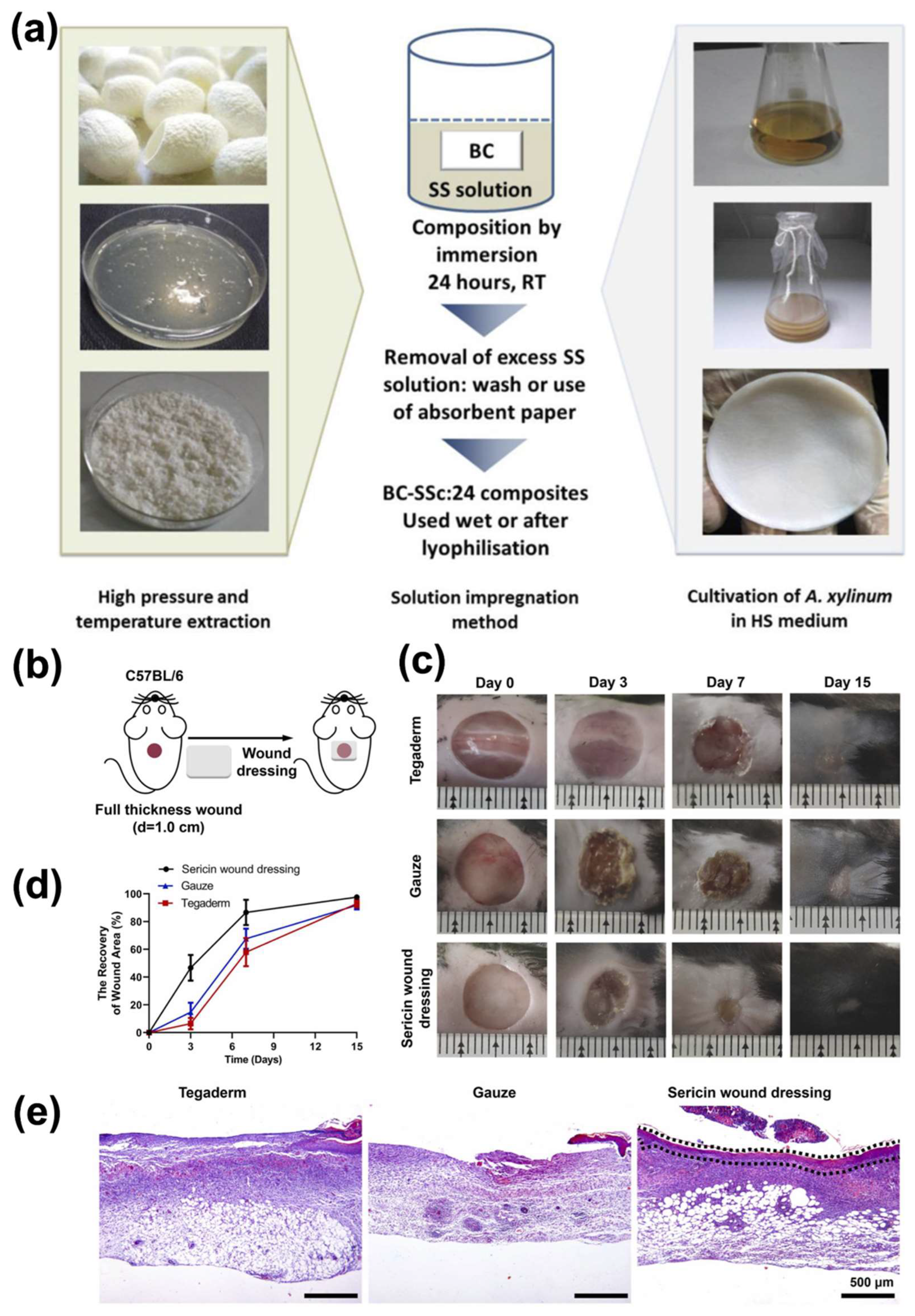
4.3.4. Wound Healing Applications
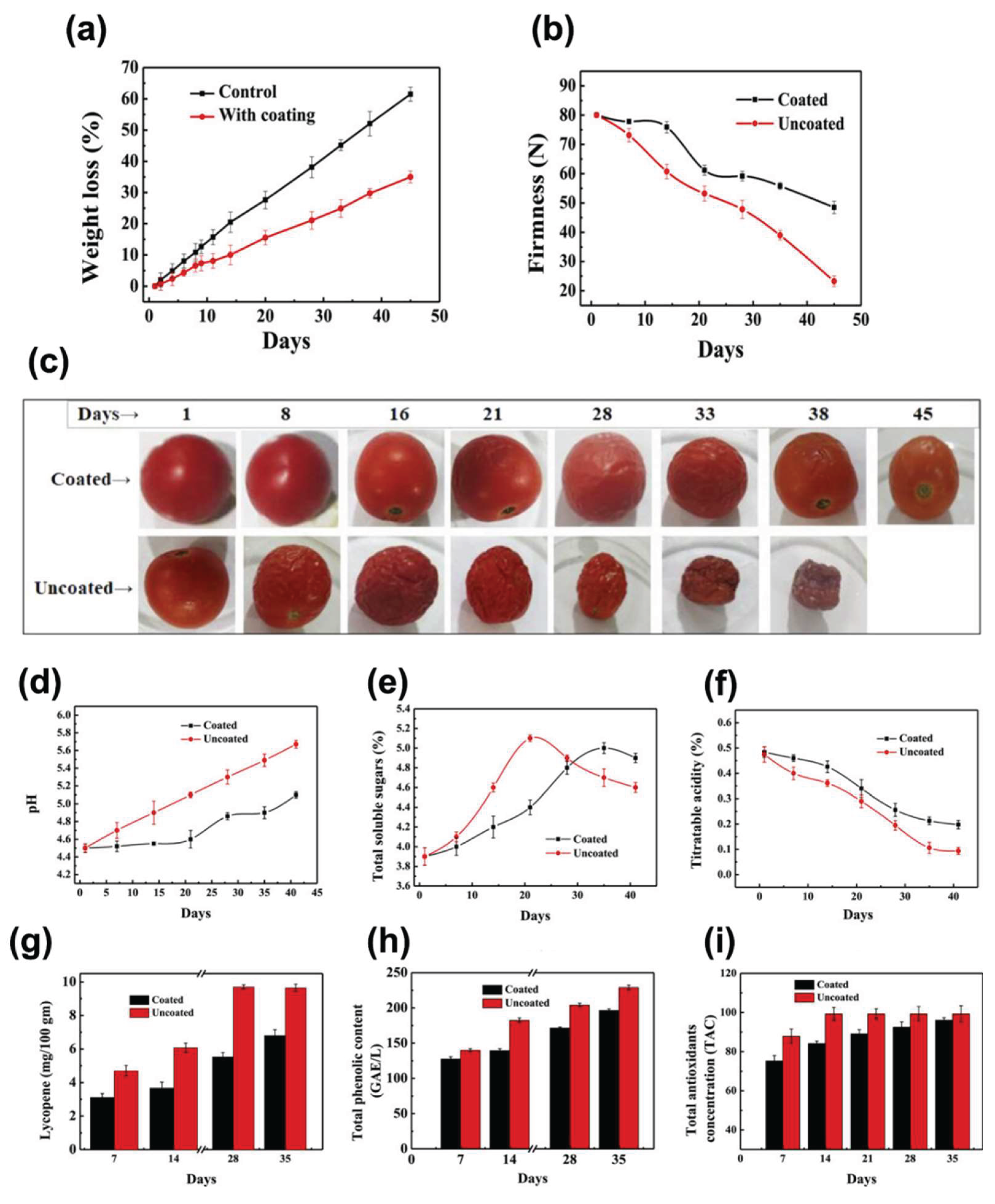
4.3.5. Ser for Food Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bandh, S.A.; Malla, F.A.; Wani, S.A.; Hoang, A.T. Waste Management and Circular Economy. In Waste Management in the Circular Economy; Springer, Cham, 2024; pp. 1–17 ISBN 9783031424267.
- Chouhan, D.; Mandal, B.B. Silk Biomaterials in Wound Healing and Skin Regeneration Therapeutics: From Bench to Bedside. Acta Biomater 2020, 103, 24–51. [CrossRef]
- Fagnani, D.E.; Tami, J.L.; Copley, G.; Clemons, M.N.; Getzler, Y.D.Y.L.; McNeil, A.J. 100th Anniversary of Macromolecular Science Viewpoint: Redefining Sustainable Polymers. ACS Macro Lett 2021, 10, 41–53. [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhu, L. Recent Advances and Challenges in Enzymatic Depolymerization and Recycling of PET Wastes. ChemBioChem 2023, 25, e202300578. [CrossRef]
- Marques, G.G.; Couffin, A.; Hajji, P.; Inoubli, R.; Bounor-Legaré, V.; Fulchiron, R. A Review on the Formulation and Rupture Properties of Polyethylene Terephthalate in a Mechanical Recycling Context. Ind Eng Chem Res 2023, 63. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Lindqvist, K.; de la Motte, H. An Efficient Recycling Process of Glycolysis of PET in the Presence of a Sustainable Nanocatalyst. J Appl Polym Sci 2018, 135, 46285. [CrossRef]
- Ügdüler, S.; Van Geem, K.M.; Denolf, R.; Roosen, M.; Mys, N.; Ragaert, K.; De Meester, S. Towards Closed-Loop Recycling of Multilayer and Coloured PET Plastic Waste by Alkaline Hydrolysis. Green Chemistry 2020, 22, 5376–5394. [CrossRef]
- Galstyan, V.; D’Angelo, P.; Tarabella, G.; Vurro, D.; Djenizian, T. High Versatility of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Waste for the Development of Batteries, Biosensing and Gas Sensing Devices. Chemosphere 2024, 359, 142314. [CrossRef]
- El Seoud, O.A.; Kostag, M.; Jedvert, K.; Malek, N.I. Cellulose Regeneration and Chemical Recycling: Closing the “Cellulose Gap” Using Environmentally Benign Solvents. Macromol Mater Eng 2020, 305, 1900832. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, T.; Liu, T.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H. Eco-Friendly Post-Consumer Cotton Waste Recycling for Regenerated Cellulose Fibers. Carbohydr Polym 2019, 206, 141–148. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Naresh Dholakiya, R.; Anil Kumar, M.; Mody, K.H. Recycling of Starch Processing Industrial Wastewater as a Sole Nutrient Source for the Bioflocculant Production. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 2017, 36, 1458–1465. [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Yu, X.; Yang, Y. Sustainable and Green Process for Recycling Waste Wool Textiles into High-Quality Protein Fibers on a Pilot Scale. Resour Conserv Recycl 2023, 198. [CrossRef]
- Giaveri, S.; Schmitt, A.M.; Roset Julià, L.; Scamarcio, V.; Murello, A.; Cheng, S.; Menin, L.; Ortiz, D.; Patiny, L.; Bolisetty, S.; et al. Nature-Inspired Circular-Economy Recycling for Proteins: Proof of Concept. Advanced Materials 2021, 33. [CrossRef]
- Calleja-Agius, J.; England, K.; Calleja, N. The Effect of Global Warming on Mortality. Early Hum Dev 2021, 155, 3–5. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wen, P.; Qin, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, P.; Ye, Y. Toxicological Evaluation of Water-Extract Sericin from Silkworm (Bombyx Mori) in Pregnant Rats and Their Fetus during Pregnancy. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 982841. [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, C.; Pizzichini, M.; Spadoni, M.; Zeddita, G. Treatment of Waste Water from Silk Degumming Processes for Protein Recovery and Water Reuse. Desalination 1996, 105, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; He, H.; Cai, R.; Tao, G.; Yang, M.; Zuo, H.; Umar, A.; Wang, Y. Cross-Linking of Dialdehyde Carboxymethyl Cellulose with Silk Sericin to Reinforce Sericin Film for Potential Biomedical Application. Carbohydr Polym 2019, 212, 403–411. [CrossRef]
- Sonjan, S.; Ross, · G M; Mahasaranon, · S; Sinkangam, · B; Intanon, · S; Ross, · S Biodegradable Hydrophilic Film of Crosslinked PVA/Silk Sericin for Seed Coating: The Effect of Crosslinker Loading and Polymer Concentration. J Polym Environ 2021, 29, 323–334. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Supaweera, N.; Nwabor, O.F.; Chaichompoo, W.; Suksamrarn, A.; Chittasupho, C.; Chunglok, W. Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)-Gelatin-Sericin Copolymerized Film Fortified with Vesicle-Entrapped Demethoxycurcumin/Bisdemethoxycurcumin for Improved Stability, Antibacterial, Anti-Inflammatory, and Skin Tissue Regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol 2024, 258, 129071. [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X. Channel Structure Design and Biological Properties of Silk Fibroin/Sericin Sponge Nerve Scaffolds. Polymer (Guildf) 2024, 306, 127212. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, W.; Ming, P.Y.; Jiang, X.; Yang, B.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Multi-Functional Carboxymethyl Chitosan/Sericin Protein/Halloysite Composite Sponge with Efficient Antibacterial and Hemostatic Properties for Accelerating Wound Healing. Int J Biol Macromol 2023, 234, 123357. [CrossRef]
- Siavashani, A.Z.; Mohammadi, J.; Rottmar, M.; Senturk, B.; Nourmohammadi, J.; Sadeghi, B.; Huber, L.; Maniura-Weber, K. Silk Fibroin/Sericin 3D Sponges: The Effect of Sericin on Structural and Biological Properties of Fibroin. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 153, 317–326. [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo-Quiceno, N.; Rueda-Mira, S.; Marín, J.F.S.; Álvarez-López, C. Development of a Novel Silk Sericin-Based Hydrogel Film by Mixture Design. Journal of Polymer Research 2023, 30, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Li, X.; Tian, X.; Fu, D. an; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Cai, B.; Wang, J.; Su, Q.; et al. A Degradable and Biocompatible Supercapacitor Implant Based on Functional Sericin Hydrogel Electrode. Adv Energy Mater 2023, 13, 2203814. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, M.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ming, P.; Li, S.; Zhou, P.; Cai, R.; Yu, K.; et al. Biocompatible Gellan Gum/Sericin Hydrogels Containing Halloysite@polydopamine Nanotubes with Hemostasis and Photothermal Antibacterial Properties for Promoting Infectious Wound Repair. Mater Des 2023, 227, 111744. [CrossRef]
- Kumar Dan, A.; Aamna, B.; De, S.; Pereira-Silva, M.; Sahu, R.; Cláudia Paiva-Santos, A.; Parida, S. Sericin Nanoparticles: Future Nanocarrier for Target-Specific Delivery of Chemotherapeutic Drugs. J Mol Liq 2022, 368. [CrossRef]
- Suktham, K.; Koobkokkruad, T.; Wutikhun, T.; Surassmo, S. Efficiency of Resveratrol-Loaded Sericin Nanoparticles: Promising Bionanocarriers for Drug Delivery. Int J Pharm 2018, 537, 48–56. [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.J.; Im, K.-J.; Shin, H.-S.; Das, G.; Patra, J.K. Application of Sericin-Based Materials in Food Packaging: An Overview. In Proceedings of the Biology and Life Sciences Forum 2021, Vol. 6, Page 40; Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute, October 13 2022; Vol. 6, p. 40. [CrossRef]
- Byram, P.K.; Mukherjee, M.; Rahaman, M.; Bora, H.; Kaushal, M.; Dhara, S.; Chakravorty, N. Bioactive Self-Assembling Silk Fibroin–Sericin Films for Skin Tissue Engineering. Biomedical Materials 2024, 19, 025009. [CrossRef]
- Dash, R.; Mandal, M.; Ghosh, S.K.; Kundu, S.C. Silk Sericin Protein of Tropical Tasar Silkworm Inhibits UVB-Induced Apoptosis in Human Skin Keratinocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 2008, 311, 111–119. [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Luo, Q.; Wu, W.; Mao, Z.; Ma, W. Screen-Printed Carbon Black/Recycled Sericin@Fabrics for Wearable Sensors to Monitor Sweat Loss. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2022, 14, 11813–11819. [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Lu, Y. Silk Sericin As a Green Adhesive to Fabricate a Textile Strain Sensor with Excellent Electromagnetic Shielding Performance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2021, 13, 28832–28842. [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, H.; Hu, E.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, P.; Xu, F.; Sheng, Y.; et al. Artificial Neurons Using Ag−In−Zn−S/Sericin Peptide-Based Threshold Switching Memristors for Spiking Neural Networks. Adv Electron Mater 2023. [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, F.; Qin, H.; Hu, E.; Wang, X.; Chen, P.; Sheng, Y.; Tong, Y.; et al. Realization of Dual-Functional Resistive Switching Characteristics in Ag−In−Zn−S/Sericin Peptide-Based Memristive Device. Appl Phys Lett 2023, 123. [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhao, P. Compliant Immune Response of Silk-Based Biomaterials Broadens Application in Wound Treatment. Front Pharmacol 2025, 16, 1548837. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ge, Z.; Wang, Y.; Toh, S.L.; Sutthikhum, V.; Goh, J.C.H. Modification of Sericin-Free Silk Fibers for Ligament Tissue Engineering Application. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 2007, 82, 129–138. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, L.; Deng, Y.; Zou, M.; Cai, B.; Song, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Silk Sericin-Based Materials for Biomedical Applications. Biomaterials 2022, 287, 121638. [CrossRef]
- Meerasri, J.; Kongsin, K.; Chollakup, R.; Sothornvit, R. Characterization and Functional Properties of Novel Nanocomposite Sericin-Based Films Incorporated with Sericin Nanoparticles. Chemical Engineering Journal Advances 2023, 16, 100542. [CrossRef]
- Purwar, R.; Sharma, S.; Sahoo, P.; Srivastava, C.M. Flexible Sericin/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Clay Blend Films. Fibers and Polymers 2015, 16, 761–768. [CrossRef]
- Gün Gök, Z. Preparation of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Silk Sericin Blend Membranes with Solvent Casting Method For Effective Removal of Remazol Black B. Fibers and Polymers 2023, 24, 4099–4110. [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Yuan, J.; Yang, X.; Cheng, X.; Li, J. Interaction Study of Collagen and Sericin in Blending Solution. Int J Biol Macromol 2016, 93, 468–475. [CrossRef]
- De Giorgio, G.; Matera, B.; Vurro, D.; Manfredi, E.; Galstyan, V.; Tarabella, G.; Ghezzi, B.; D’Angelo, P. Silk Fibroin Materials: Biomedical Applications and Perspectives. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 167. [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.S.; Costa, E.C.; Reis, S.; Spencer, C.; Calhelha, R.C.; Miguel, S.P.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Barros, L.; Vaz, J.A.; Coutinho, P. Silk Sericin: A Promising Sustainable Biomaterial for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications. Polymers (Basel) 2022, 14, 4931. [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.; El-Samad, L.M.; Gomaa, R.A.; Augustyniak, M.; Hassan, M.A. A Comprehensive Review of Recent Advances in Silk Sericin: Extraction Approaches, Structure, Biochemical Characterization, and Biomedical Applications. Int J Biol Macromol 2023, 250, 126067. [CrossRef]
- Kunz, R.I.; Brancalhão, R.M.C.; Ribeiro, L.D.F.C.; Natali, M.R.M. Silkworm Sericin: Properties and Biomedical Applications. Biomed Res Int 2016, 2016, 8175701. [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H. Silk Sericin Retards the Crystallization of Silk Fibroin. Macromol Rapid Commun 2004, 25, 1792–1796. [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Guo, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, S.; Chang, H.; Tang, M.; An, L.; Xia, Q.; et al. Identification of Bombyx Mori Sericin 4 Protein as a New Biological Adhesive. Int J Biol Macromol 2019, 132, 1121–1130. [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, D.; Qin, L.; Jiang, W.; Hu, W.; Liu, X.; Xia, Q.; Dong, Z.; Zhao, P. Identification and Characterization of Sericin5 Reveals Non-Cocoon Silk Sericin Components with High β-Sheet Content and Adhesive Strength. Acta Biomater 2022, 150, 96–110. [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.B.; Wu, L.P.; Chen, L.S.; Mao, X.Y.; Ren, F.Z. Antioxidant Activities of Silk Sericin from Silkworm Bombyx Mori. J Food Biochem 2009, 33, 74–88. [CrossRef]
- Padamwar, M.N.; Pawar, A.P. Silk Sericin and Its Applications: A Review. J Sci Ind Res (India) 2004, 63, 323–329.
- Wang, Y.J.; Zhag, Y.Q. Three-Layered Sericins around the Silk Fibroin Fiber from Bombyx Mori Cocoon and Their Amino Acid Composition. In Proceedings of the Advanced Materials Research; 2011; Vol. 175–176, pp. 158–163. [CrossRef]
- Das, P. A REVIEW ON PHYSICOCHEMICAL, STRUCTURAL AND BIOMEDICAL PROPERTIES OF SILK WORM SERICIN. Current Trends in Pharmaceutical Research 2022, 8.
- Jena, K.; Pandey, J.P.; Kumari, R.; Sinha, A.K.; Gupta, V.P.; Singh, G.P. Free Radical Scavenging Potential of Sericin Obtained from Various Ecoraces of Tasar Cocoons and Its Cosmeceuticals Implication. Int J Biol Macromol 2018, 120, 255–262. [CrossRef]
- Chlapanidas, T.; Faragò, S.; Lucconi, G.; Perteghella, S.; Galuzzi, M.; Mantelli, M.; Avanzini, M.A.; Tosca, M.C.; Marazzi, M.; Vigo, D.; et al. Sericins Exhibit ROS-Scavenging, Anti-Tyrosinase, Anti-Elastase, and in Vitro Immunomodulatory Activities. Int J Biol Macromol 2013, 58, 47–56. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.P.; Mandal, B.B. Antioxidant Potential of Mulberry and Non-Mulberry Silk Sericin and Its Implications in Biomedicine. Free Radic Biol Med 2017, 108, 803–818. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Rajkhowa, R.; Tsuzuki, T.; Millington, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Photoprotection by Silk Cocoons. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3660–3667. [CrossRef]
- Millington, K.R. Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy of Fibrous Proteins. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 1277–1285. [CrossRef]
- Ratchamak, R.; Ratsiri, T.; Kheawkanha, T.; Vongpralub, T.; Boonkum, W.; Chankitisakul, V. Evaluation of Cryopreserved Boar Semen after Supplementation Sericin Form Silkworm (Bombyx Mori) in Semen Extender. Animal Science Journal 2020, 91, e13428. [CrossRef]
- Shu, W.H.; Yang, S.H.; Wei, M.; Liu, X.C.; Chen, Z.X.; Wei, C.Y.; Zhang, X.; Si, L.N.; Chen, Z.H.; Qiao, Y.B.; et al. Effects of Sericin on Oxidative Stress and PI3K/AKT/MTOR Signal Pathway in Cryopreserved Mice Ovarian Tissue. Cryobiology 2023, 111, 16–25. [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Oishi, K.; Yukawa, H.; Noguchi, H.; Sasaki, M.; Iwata, H.; Hayashi, S. Cryopreservation of Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem/Progenitor Cells Using the Silk Protein Sericin. Cell Transplant 2012, 21, 617–622. [CrossRef]
- Baust, J.G.; Gao, D.; Baust, J.M. Cryopreservation: An Emerging Paradigm Change. Organogenesis 2009, 5, 90–96. [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M.J.; Baumber, J.; Kass, P.H.; Meyers, S.A. Osmotic Stress Induces Oxidative Cell Damage to Rhesus Macaque Spermatozoa. Biol Reprod 2010, 82, 644–651. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, F.; Pan, Y.; Miao, L.; Zhu, Q.; Tan, S. The Feasibility of Antioxidants Avoiding Oxidative Damages from Reactive Oxygen Species in Cryopreservation. Front Chem 2021, 9. [CrossRef]
- Cavaillon, J.M.; Adib-Conquy, M.; Fitting, C.; Adrie, C.; Payen, D. Cytokine Cascade in Sepsis. Scand J Infect Dis 2003, 35, 535–544. [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Park, J.; Nam, J.; Hyun, Y.; Jin, H.J.; Kwak, H.W. Antioxidant and UV-Blocking Glucose-Crosslinked Sericin Films with Enhanced Structural Integrity. React Funct Polym 2021, 165. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, C. Electrospun Chitosan/Sericin Composite Nanofibers with Antibacterial Property as Potential Wound Dressings. Int J Biol Macromol 2014, 68, 92–97. [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.; Hyun, Y.; Oh, S.; Park, J.; Jin, H.J.; Kwak, H.W. Effect of Cross-Linkable Bacterial Cellulose Nanocrystals on the Physicochemical Properties of Silk Sericin Films. Polym Test 2021, 97. [CrossRef]
- Vaithanomsat, P.; Kitpreechavanich, V. Sericin Separation from Silk Degumming Wastewater. Sep Purif Technol 2008, 59, 129–133. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Tao, M.L.; Shen, W. De; Zhou, Y.Z.; Ding, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, W.L. Immobilization of L-Asparaginase on the Microparticles of the Natural Silk Sericin Protein and Its Characters. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 3751–3759. [CrossRef]
- Gaviria, A.; Jaramillo-Quiceno, N.; Motta, A.; Restrepo-Osorio, A. Silk Wastes and Autoclaved Degumming as an Alternative for a Sustainable Silk Process. Sci Rep 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Terada, S.; Nishimura, T.; Sasaki, M.; Yamada, H.; Miki, M. Sericin, a Protein Derived from Silkworms, Accelerates the Proliferation of Several Mammalian Cell Lines Including a Hybridoma. In Proceedings of the Cytotechnology; 2002; Vol. 40, pp. 3–12. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Pan, Y.; Gong, K.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, T.; Li, Q. A Comparative Study of Ultrasonic Degumming of Silk Sericin Using Citric Acid, Sodium Carbonate and Papain. Coloration Technology 2019, 135, 195–201. [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, S.; Kandasubramanian, B. Processing Trends of Silk Fibers: Silk Degumming, Regeneration and Physical Functionalization. Journal of the Textile Institute 2020, 111, 1794–1810. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ye, C.; Zheng, K.; Zhong, J.; Tang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Buehler, M.J.; Ling, S.; Kaplan, D.L. Tensan Silk-Inspired Hierarchical Fibers for Smart Textile Applications. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 6968–6977. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Nasri, M.; Manayi, A.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Jeon, T.J.; Kang, L. Sericin Coats of Silk Fibres, a Degumming Waste or Future Material? Mater Today Bio 2024, 29, 101306. [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.R.; Ribani, M.; Gimenes, M.L.; Scheer, A.P. High Molecular Weight Sericin Obtained by High Temperature and Ultrafiltration Process. In Proceedings of the Procedia Engineering; Elsevier Ltd., 2012; Vol. 42, pp. 833–841. [CrossRef]
- Dragojlov, I.; Aad, R.; Ami, D.; Mangiagalli, M.; Natalello, A.; Vesentini, S. Silk Sericin-Based Electrospun Nanofibers Forming Films for Cosmetic Applications: Preparation, Characterization, and Efficacy Evaluation. Molecules 2025, 30, 715. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Saurav, S.; Tabassum, Z.; Sood, B.; Kumar, A.; Malik, T.; Mohan, A.; Girdhar, M. Applications and Interventions of Polymers and Nanomaterials in Alveolar Bone Regeneration and Tooth Dentistry. RSC Adv 2024, 14, 36226–36245. [CrossRef]
- Uyen, T.N.T.; Thao, H.T.; Huong, B.M. Study on the Influence of Degumming Technological Parameters on Self-Dyed Silk. Journal of Science and Technology Issue on Information and Communications Technology 2023, 34–37. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.D.P.K.D.P.T.L.T.D.B.L.Q.N.Q. INVESTIGATE THE CHARACTERISTICS AND ABILITY TO EXTRACT SERICIN FROM SILKWORM COCOONS USING HIGH TEMPERATURE.
- Yoo, Y.J.; Um, I.C. Effect of Extraction Time on the Rheological Properties of Sericin Solutions and Gels. Int J Indust Entomol 2013, 27, 180–184. [CrossRef]
- Gimenes, M.L.; Silva, V.R.; Vieira, M.G.A.; Silva, M.G.C.; Scheer, A.P. High Molecular Sericin from Bombyx Mori Cocoons: Extraction and Recovering by Ultrafiltration. International Journal of Chemical Engineering and Applications 2014, 5, 266–271. [CrossRef]
- Atay, I.; Asad, E.; Yagci, M.B.; Sürme, S.; Kavakli, I.H.; Yilgör, E.; Yilgör, I. Simple and Green Process for Silk Fibroin Production by Water Degumming. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 272–280. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Tian, C.; Jing, X.; Zhao, P.; Xia, Q. A Novel Method for Silkworm Cocoons Self-Degumming and Its Effect on Silk Fibers. J Adv Res 2023, 53, 87–98. [CrossRef]
- Nultsch, K.; Bast, L.K.; Näf, M.; Yakhlifi, S. El; Bruns, N.; Germershaus, O. Effects of Silk Degumming Process on Physicochemical, Tensile, and Optical Properties of Regenerated Silk Fibroin. Macromol Mater Eng 2018, 303, 1800408. [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.J.; Das, G.; Shin, H.S.; Patra, J.K. Silk Sericin Protein Materials: Characteristics and Applications in Food-Sector Industries. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 4951. [CrossRef]
- Dragojlov, I.; Aad, R.; Ami, D.; Mangiagalli, M.; Natalello, A.; Vesentini, S. Silk Sericin-Based Electrospun Nanofibers Forming Films for Cosmetic Applications: Preparation, Characterization, and Efficacy Evaluation. Molecules 2025, 30, 715. [CrossRef]
- Roblin, N. V.; DeBari, M.K.; Shefter, S.L.; Iizuka, E.; Abbott, R.D. Development of a More Environmentally Friendly Silk Fibroin Scaffold for Soft Tissue Applications. J Funct Biomater 2023, 14, 230. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, L.; Fan, Y. Preparation of Natural Amphoteric Silk Nanofibers by Acid Hydrolysis. J Mater Chem B 2019, 7, 1450–1459. [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ma, Q.; Zhou, H.T.; Zhao, J.M.; Cao, M.; Wang, S.D. Review on Fabrication and Application of Regenerated Bombyx Mori Silk Fibroin Materials. Autex Research Journal 2023, 23, 164–183. [CrossRef]
- Gulrajanid, M.L.; Sethi, S.; Gupta, S. Some Studies in Degumming of Silk with Organic Acids. Journal of the Society of Dyers and Colourists 1992, 108, 79–86. [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.C.; Prasannan, A.; Hong, P. Da; Chiang, M.Y. Silk-Sericin Degummed Wastewater Solution-Derived and Nitrogen Enriched Porous Carbon Nanosheets for Robust Biological Imaging of Stem Cells. Int J Biol Macromol 2018, 107, 2122–2130. [CrossRef]
- Kurioka, A.; Kurioka, F.; Yamazaki, M. Characterization of Sericin Powder Prepared from Citric Acid-Degraded Sericin Polypeptides of the Silkworm, Bombyx Mori. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 2004, 68, 774–780. [CrossRef]
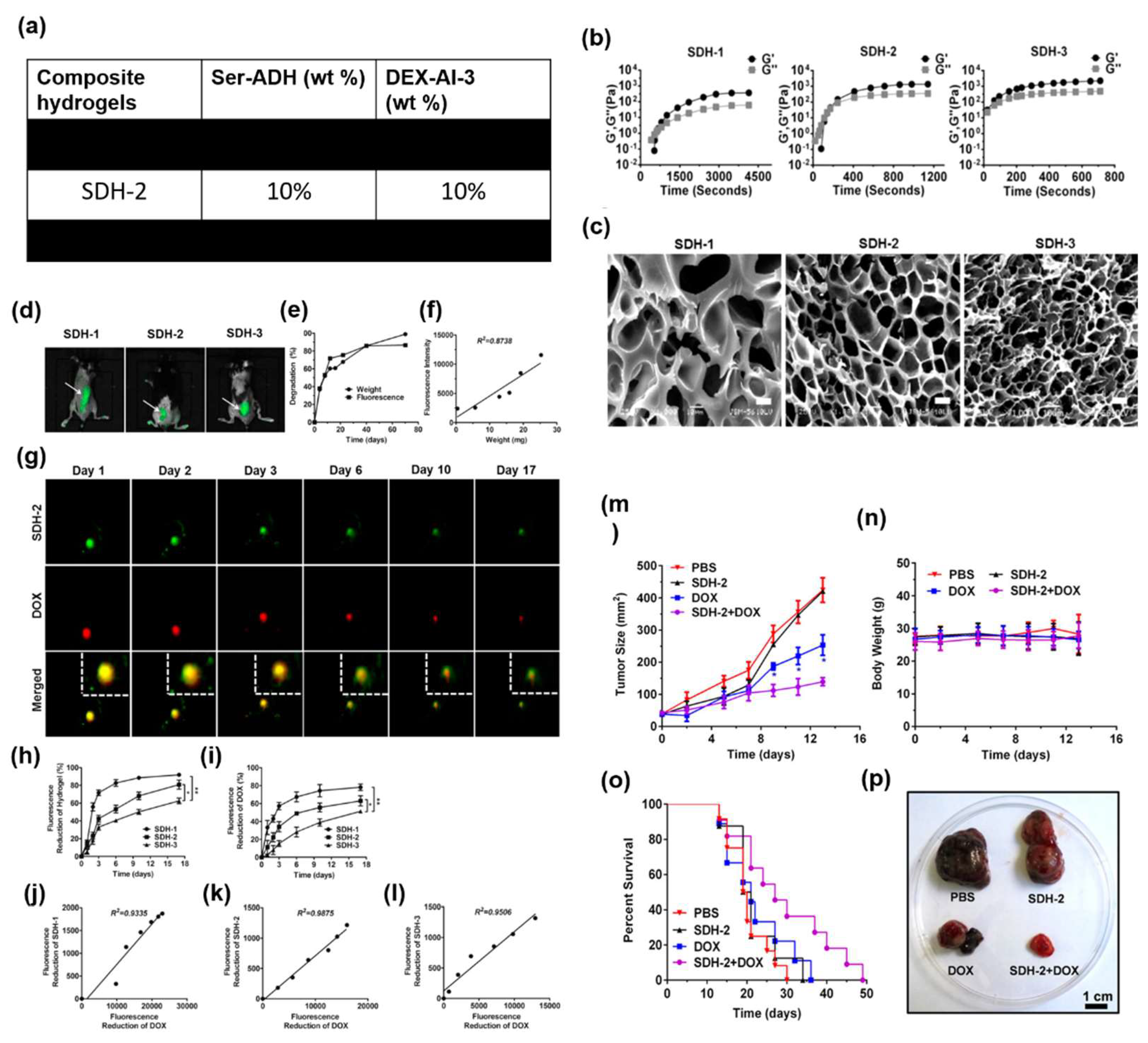
- Song, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, N.; Huang, K.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Huang, K.; Wang, L. An Injectable Silk Sericin Hydrogel Promotes Cardiac Functional Recovery after Ischemic Myocardial Infarction. Acta Biomater 2016, 41, 210–223. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, W.; Xie, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. CNT/Sericin Conductive Nerve Guidance Conduit Promotes Functional Recovery of Transected Peripheral Nerve Injury in a Rat Model. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2020, 12, 36860–36872. [CrossRef]
- More, S. V.; Chavan, S.; Prabhune, A.A. Silk Degumming and Utilization of Silk Sericin by Hydrolysis Using Alkaline Protease from Beauveria Sp. (MTCC 5184): A Green Approach. Journal of Natural Fibers 2018, 15, 373–383. [CrossRef]
- Suwannaphan, S.; Fufeungsombut, E.; Promboon, A.; Chim-anage, P. A Serine Protease from Newly Isolated Bacillus Sp. for Efficient Silk Degumming, Sericin Degrading and Colour Bleaching Activities. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 2017, 117, 141–149. [CrossRef]
- Prathumpai, W.; Promboon, A.; Werapan, B.; Nutaratat, P.; Chim-Anek, P.; Ninpetch, U. Pilot-Scale Protease Production by Bacillus Sp. C4 for Silk Degumming Processes. Journal of Natural Fibers 2020, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Vyas, S.K.; Shukla, S.R. Comparative Study of Degumming of Silk Varieties by Different Techniques. Journal of the Textile Institute 2016, 107, 191–199. [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, D.; Chakraborty, A.; Chatterjee, S.M. Studies on Degumming of Eri Silk Cocoons. Journal of the Textile Institute 2017, 108, 1327–1339. [CrossRef]
- More, S. V.; Khandelwal, H.B.; Joseph, M.A.; Laxman, R.S. Enzymatic Degumming of Silk with Microbial Proteases. Journal of Natural Fibers 2013, 10, 98–111. [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, H.; Mowafi, S.; El-Fiky, A.F.; Khalil, E.M. Low Temperature Water-Saving Bio-Degumming of Natural Silk Using Thermophilic Protease. Sustain Chem Pharm 2022, 27. [CrossRef]
- Gulrajani, M.L.; Sinha, S. Studies in Degumming of Silk with Aliphatic Amines. Journal of the Society of Dyers and Colourists 1993, 109, 256–260. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Rather, L.J.; Gong, K.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, T.; Li, Q. Effects of Ultrasonic Treatment on Hydrophilicity and Thermal Stability of Silk. Macromol Mater Eng 2019, 304. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. Sericin from Fibroin-Deficient Silkworms Served as a Promising Resource for Biomedicine. Polymers (Basel) 2023, 15, 2941. [CrossRef]
- Aramwit, P.; Damrongsakkul, S.; Kanokpanont, S.; Srichana, T. Properties and Antityrosinase Activity of Sericin from Various Extraction Methods. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 2010, 55, 91–98. [CrossRef]
- Aramwit, P.; Kanokpanont, S.; Nakpheng, T.; Srichana, T. The Effect of Sericin from Various Extraction Methods on Cell Viability and Collagen Production. Int J Mol Sci 2010, 11, 2200–2211. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Wang, Z.; Xu, S.Y. Preparation and Characterization of Sericin Powder Extracted from Silk Industry Wastewater. Food Chem 2007, 103, 1255–1262. [CrossRef]
- Das, G.; Shin, H.S.; Campos, E.V.R.; Fraceto, L.F.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Mariano, K.C.F.; de Araujo, D.R.; Fernández-Luqueño, F.; Grillo, R.; Patra, J.K. Sericin Based Nanoformulations: A Comprehensive Review on Molecular Mechanisms of Interaction with Organisms to Biological Applications. J Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Suktham, K.; Koobkokkruad, T.; Saesoo, S.; Saengkrit, N.; Surassmo, S. Physical and Biological Characterization of Sericin-Loaded Copolymer Liposomes Stabilized by Polyvinyl Alcohol. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2016, 148, 487–495. [CrossRef]
- Aramwit, P.; Palapinyo, S.; Srichana, T.; Chottanapund, S.; Muangman, P. Silk Sericin Ameliorates Wound Healing and Its Clinical Efficacy in Burn Wounds. Arch Dermatol Res 2013, 305, 585–594. [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.N.; Um, I.C. Effects of Solvent on the Solution Properties, Structural Characteristics and Properties of Silk Sericin. Int J Biol Macromol 2015, 78, 287–295. [CrossRef]
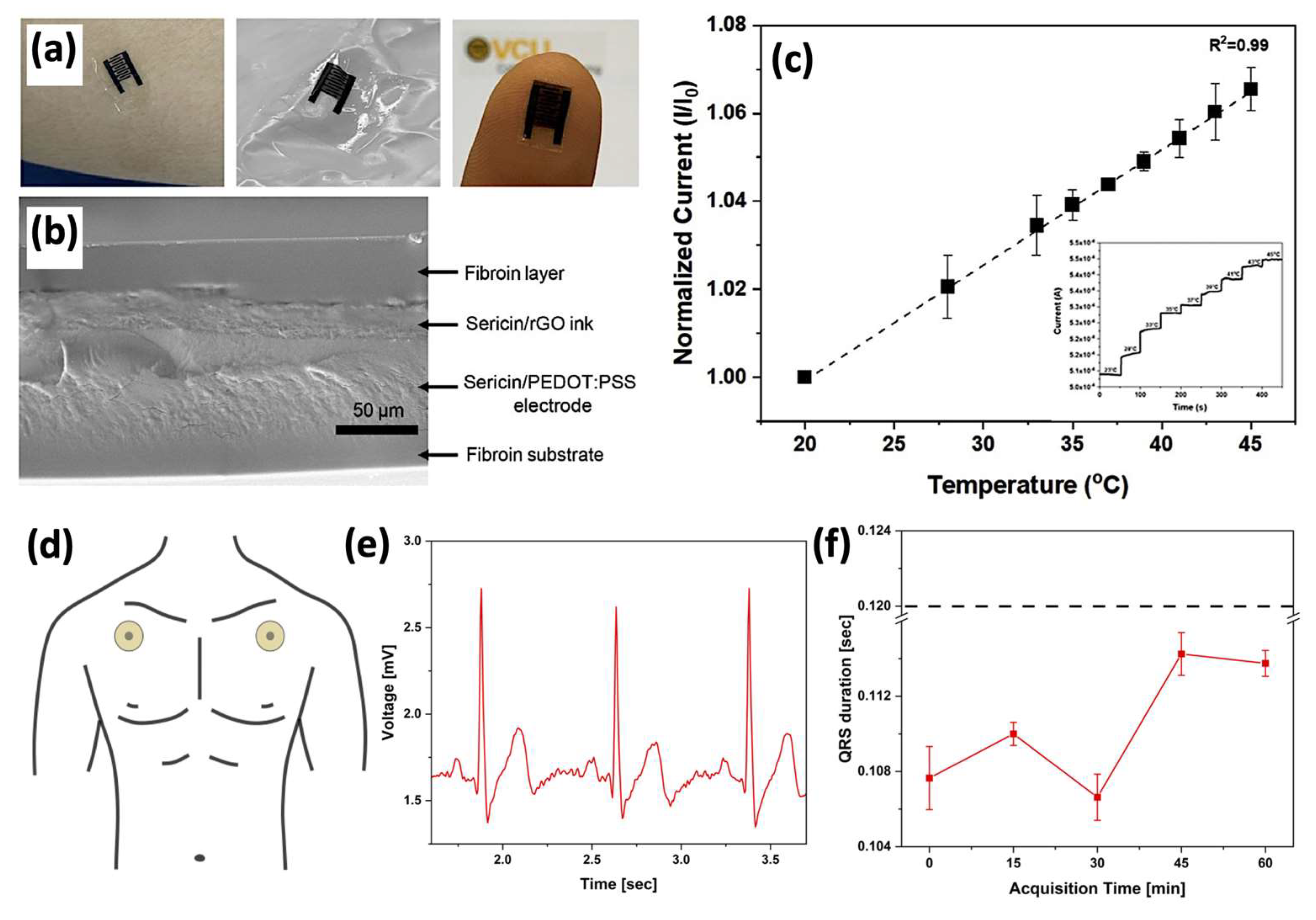
- Vurro, D.; Liboà, A.; D’Onofrio, I.; De Giorgio, G.; Scaravonati, S.; Crepaldi, M.; Barcellona, A.; Sciancalepore, C.; Galstyan, V.; Milanese, D.; et al. Sericin Electrodes with Self-Adhesive Properties for Biosignaling. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2025. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, L.; Yang, M.; Min, S.; Yang, L.; Zhu, L. Enhancing Effect of Glycerol on the Tensile Properties of Bombyx Mori Cocoon Sericin Films. Int J Mol Sci 2011, 12, 3170–3181. [CrossRef]
- Mabey, D.; Peeling, R.W.; Ustianowski, A.; Perkins, M.D. Diagnostics for the Developing World. Nat Rev Microbiol 2004, 2, 231–240. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, T.; Ramana, L.N.; Sharma, T.K. Current Advancements and Future Road Map to Develop ASSURED Microfluidic Biosensors for Infectious and Non-Infectious Diseases. Biosensors (Basel) 2022, 12, 357. [CrossRef]
- Vurro, D.; Pasquardini, L.; Borriello, M.; Foresti, R.; Barra, M.; Sidoli, M.; Pontiroli, D.; Fornasini, L.; Aversa, L.; Verucchi, R.; et al. Inflammatory Biomarker Detection in Saliva Samples by Printed Graphene Immunosensors. Sensors and Actuators Reports 2024, 8, 100211. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Chen, K.; Dong, L.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Q.; Jin, M.; Zeng, S.; Chen, X.; Xing, J.; Yang, G.; et al. A Biodegradable and Recyclable Piezoelectric Macrofiber Based on Imidazole Perchlorate Crystallized in Bacterial Cellulose for Mechanical Sensing Fabrics. Chemical Engineering Journal 2025, 509, 161034. [CrossRef]
- Soleimani Dinani, H.; Reinbolt, T.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, G.; Gerald, R.E.; Yan, Z.; Huang, J. Miniaturized Wearable Biosensors for Continuous Health Monitoring Fabricated Using the Femtosecond Laser-Induced Graphene Surface and Encapsulated Traces and Electrodes. ACS Sens 2025, 10, 761–772. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Vurro, D.; Jiang, Y.; Xue, L.; Gong, Y.; Qin, Y. A Miniaturized Flexible Patch Based on CNT Fiber Sensors and Highly Integrated SoC for Analysis of Sweat. IEEE Sens J 2024. [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Fan, A.; Li, Z.; Wei, N.; Fan, W.; Liang, H.; Wang, H.; Bi, P.; Li, S.; Wu, X.E.; et al. Highly Regulatable Heat Conductance of Graphene–Sericin Hybrid for Responsive Textiles. Adv Funct Mater 2022, 32, 2111121. [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ying, L.; Wang, Y.; Farooq, A.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z. Versatile, Durable Conductive Networks Assembled from MXene and Sericin-Modified Carbon Nanotube on Polylactic Acid Textile Micro-Etched via Deep Eutectic Solvent. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Siddika, A.; Hossain, M.M.; Harmon, J. Hemp-Based Electronic Textiles for Sustainable and Wearable Applications. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2023, 11, 14913–14920. [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Afroj, S.; Yin, J.; Novoselov, K.S.; Chen, J.; Karim, N. Advances in Printed Electronic Textiles. Advanced Science 2024, 11. [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Li, H.; Dou, J.; Wang, Q.; He, W.; Wang, C.; Li, D.; Lin, J.M.; Zhang, Y. Stable and Biocompatible Carbon Nanotube Ink Mediated by Silk Protein for Printed Electronics. Advanced Materials 2020, 32. [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhu, M.; Li, H.; Dou, J.; Jian, M.; Xia, K.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Hydrophilic, Breathable, and Washable Graphene Decorated Textile Assisted by Silk Sericin for Integrated Multimodal Smart Wearables. Adv Funct Mater 2022, 32. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hao, L. Effect of Modified Sericin on the Alkaline Anti-Wrinkle Finishing of Cottonfabric by FAP. Cellulose 2023, 30, 6667–6677. [CrossRef]
- Dang, W.; Manjakkal, L.; Navaraj, W.T.; Lorenzelli, L.; Vinciguerra, V.; Dahiya, R. Stretchable Wireless System for Sweat PH Monitoring. Biosens Bioelectron 2018, 107, 192–202. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, S.; Tu, X.; Zhang, X. Skin-Attachable Tb-MOF Ratio Fluorescent Sensor for Real-Time Detection of Human Sweat PH. Biosens Bioelectron 2024, 263, 116606. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Sun, P.; Dong, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, D.; Xu, X. A Sweat-PH-Enabled Strongly Adhesive Hydrogel for Self-Powered e-Skin Applications. Mater Horiz 2023, 10, 2271–2280. [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Yadavalli, V.K. Photolithographically Printed Flexible Silk/PEDOT:PSS Temperature Sensors. ACS Appl Electron Mater 2021, 3, 21–29.
- Huang, J.; Xie, G.; Wei, Q.; Su, Y.; Xu, X.; Jiang, Y. Degradable MXene-Doped Polylactic Acid Textiles for Wearable Biomonitoring. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2023, 15, 5600–5607. [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Hai, W.; Wang, L.; Xu, K.; Chen, Q.; Chen, C.; Yu, Q.; Chen, C.; Li, M.; Shao, H.; et al. Green One-Step Strategy of Conductive Ink for Active Health Monitoring in Rehabilitation and Early Care. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Mecerreyes, D.; Porcarelli, L. Green Electrolyte-Based Organic Electronic Devices. In Sustainable Strategies in Organic Electronics; Woodhead Publishing, 2022; pp. 281–295 ISBN 9780128231470. [CrossRef]
- Nishida, A.; Yamada, M.; Kanazawa, T.; Takashima, Y.; Ouchi, K.; Okada, H. Sustained-Release of Protein from Biodegradable Sericin Film, Gel and Sponge. Int J Pharm 2011, 407, 44–52. [CrossRef]
- Ren, A.; Hu, J.; Qin, C.; Xia, N.; Yu, M.; Xu, X.; Yang, H.; Han, M.; Zhang, L.; Ma, L. Oral Administration Microrobots for Drug Delivery. Bioact Mater 2024, 39, 163–190. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Zhong, H.; Pi, J.; Chen, G.; Chen, Z. Oral Sericin Ameliorates Type 2 Diabetes through Passive Intestinal and Bypass Transport into the Systemic Circulation. J Ethnopharmacol 2024, 332, 118342. [CrossRef]
- Jao, D.; Xue, Y.; Medina, J.; Hu, X. Protein-Based Drug-Delivery Materials. Materials 2017, 10. [CrossRef]
- Jain, K.K. An Overview of Drug Delivery Systems. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana, New York, NY, 2020; Vol. 2059, pp. 1–54 ISBN 978-1-4939-9798-5. [CrossRef]
- Dash, R.; Acharya, C.; Bindu, P.C.; Kundu, S.C. Antioxidant Potential of Silk Protein Sericin against Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress in Skin Fibroblasts. BMB Rep 2008, 41, 236–241. [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, I.; De Giorgio, G.; Sajapin, R.; Vurro, D.; Liboà, A.; Dembech, E.; Trevisi, G.; Botti, M.; Galstyan, V.; Tarabella, G.; et al. Inhalable Drug-Loaded Silk Fibroin Carriers for Pulmonary Drug Delivery. RSC Adv 2024, 14, 27288–27297. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xia, D.; Shi, T.; Li, B.; Wang, D.; Liang, C.; Dong, M. Thermo-Responsive Microneedles Patch for Transdermal Drug Delivery via Squeezing in Diabetic Foot Ulcers. J Mater Sci Technol 2025, 205, 299–314. [CrossRef]
- Phatale, V.; Vaiphei, K.K.; Jha, S.; Patil, D.; Agrawal, M.; Alexander, A. Overcoming Skin Barriers through Advanced Transdermal Drug Delivery Approaches. Journal of Controlled Release 2022, 351, 361–380. [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.F.; Ang, K.P.; Sethi, G.; Looi, C.Y. Recent Advancement of Medical Patch for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Medicina (Lithuania) 2023, 59, 778. [CrossRef]
- CS, J.; Haider, M.; Rawas-Qalaji, M.; Sanpui, P. Curcumin-Loaded Zein Nanoparticles: A Quality by Design Approach for Enhanced Drug Delivery and Cytotoxicity against Cancer Cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2025, 245, 114319. [CrossRef]
- Argitekin, E.; Erez, O.; Cakan-Akdogan, G.; Akdogan, Y. Periodate-Mediated Cross-Linking for the Preparation of Catechol Conjugated Albumin Nanoparticles Used for in Vitro Drug Delivery. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2025. [CrossRef]
- Jalilian, S.; Bahremand, K.; Arkan, E.; Jaymand, M.; Aghaz, F. A Comparative Study of Sericin and Gluten for Magnetic Nanoparticle-Mediated Drug Delivery to Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Aad, R.; Dragojlov, I.; Vesentini, S. Sericin Protein: Structure, Properties, and Applications. J Funct Biomater 2024, 15, 322. [CrossRef]
- Mandal, B.B.; Kundu, S.C. Self-Assembled Silk Sericin/Poloxamer Nanoparticles as Nanocarriers of Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Drugs for Targeted Delivery. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 355101. [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Sheikh, S.A.; Singh, S.A.; Shetty, N.P. Improvement of Storage Stability and Bioaccessibility of Microencapsulated Black Carrot (Daucus Carota Ssp. Sativus) Anthocyanins Using Maltodextrin and Sericin Protein Combinations as Wall Material. Food Biosci 2024, 61, 104666. [CrossRef]
- Kalepu, S.; Nekkanti, V. Insoluble Drug Delivery Strategies: Review of Recent Advances and Business Prospects. Acta Pharm Sin B 2015, 5, 442–453. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Feng, X.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Gao, W.; Miao, Q.; Wu, H. Microparticles of Sericin-Dextran Conjugate for Improving the Solubility of Antiviral Drug. J Funct Biomater 2023, 14, 292. [CrossRef]
- Beloqui, A.; Solinís, M.Á.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A.; Almeida, A.J.; Préat, V. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: Promising Drug Delivery Systems for Future Clinics. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 143–161. [CrossRef]
- Elmowafy, M.; Al-Sanea, M.M. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs) as Drug Delivery Platform: Advances in Formulation and Delivery Strategies. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal 2021, 29, 999–1012. [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Xu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Hu, B.; Yang, M.; Zhu, L. PH-Triggered Charge-Reversal Silk Sericin-Based Nanoparticles for Enhanced Cellular Uptake and Doxorubicin Delivery. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2017, 5, 1638–1647. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qi, C.; Tao, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, Q.; et al. Sericin/Dextran Injectable Hydrogel as an Optically Trackable Drug Delivery System for Malignant Melanoma Treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2016, 8, 6411–6422. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Kundu, S.C.; Wang, L. Exploring Natural Silk Protein Sericin for Regenerative Medicine: An Injectable, Photoluminescent, Cell-Adhesive 3D Hydrogel. Sci Rep 2014, 4. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Young, D.J.; Loh, X.J. Fluorescent Gels: A Review of Synthesis, Properties, Applications and Challenges. Mater Chem Front 2019, 3, 1489–1502. [CrossRef]
- Ko, B.; Jeon, N.; Kim, J.; Kang, H.; Seong, J.; Yun, S.; Badloe, T.; Rho, J. Hydrogels for Active Photonics. Microsyst Nanoeng 2024, 10, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, M.; Yan, H.; Li, Y. A Novel Injectable Sericin Hydrogel with Strong Fluorescence for Tracing. Int J Biol Macromol 2024, 258, 129000. [CrossRef]
- Ratanabunyong, S.; Siriwaseree, J.; Wanaragthai, P.; Krobthong, S.; Yingchutrakul, Y.; Kuaprasert, B.; Choowongkomon, K.; Aramwit, P. Exploring the Apoptotic Effects of Sericin on HCT116 Cells through Comprehensive Nanostring Transcriptomics and Proteomics Analysis. Sci Rep 2024, 14. [CrossRef]
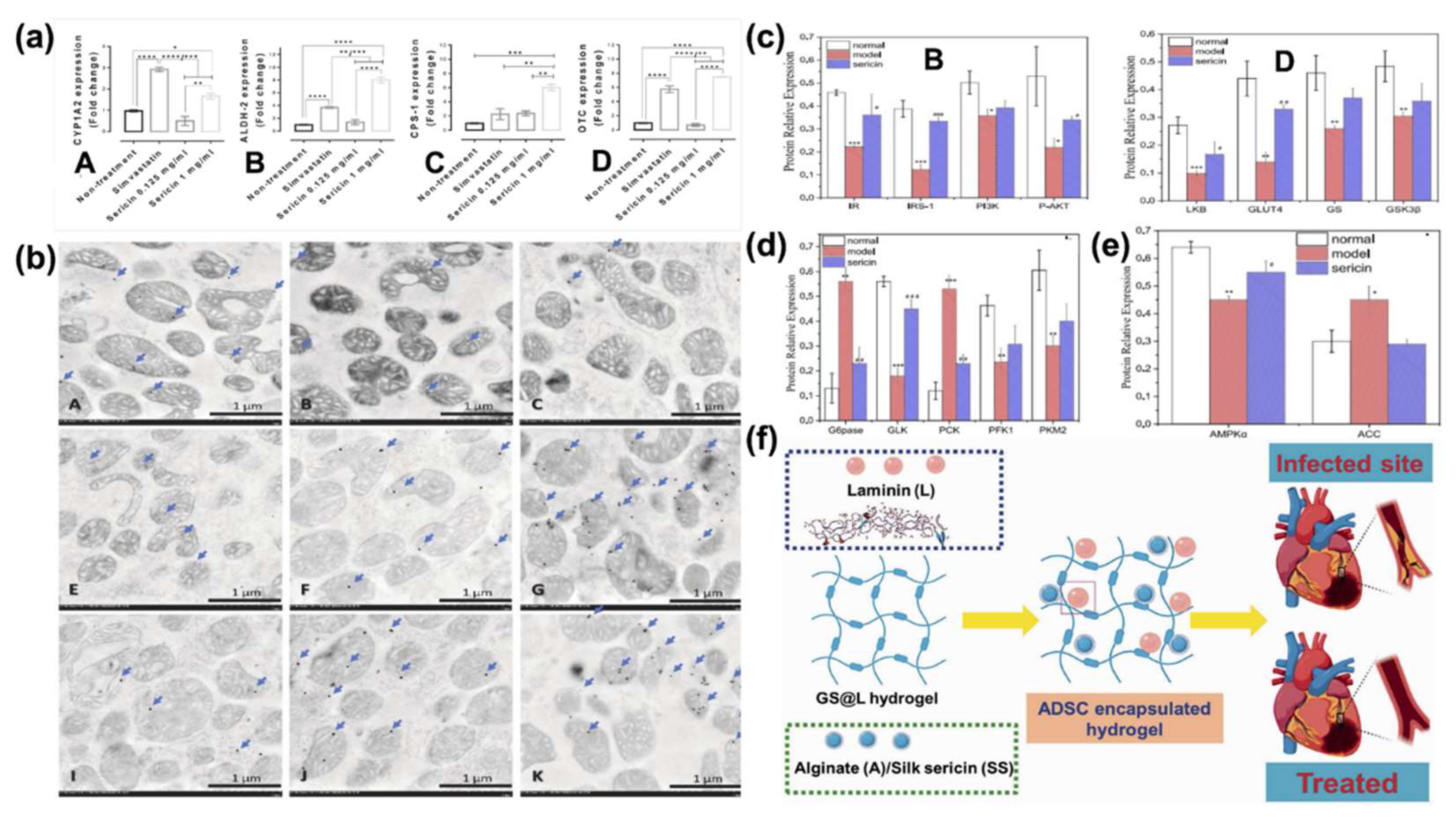
- Ampawong, S.; Tirawanchai, N.; Kanjanapruthipong, T.; Fongsodsri, K.; Tuentam, K.; Isarangkul, D.; Aramwit, P. Sericin Enhances Ammonia Detoxification by Promotes Urea Cycle Enzyme Genes and Activates Hepatic Autophagy in Relation to CARD-9/MAPK Pathway. Heliyon 2023, 9. [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhao, S.X.; Yin, X.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Wei, Z.G.; Zhang, Y.Q. Silk Sericin Has Significantly Hypoglycaemic Effect in Type 2 Diabetic Mice via Anti-Oxidation and Anti-Inflammation. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 150, 1061–1071. [CrossRef]
- Long, G.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Tao, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X. Engineering of Injectable Hydrogels Associate with Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Delivery for Anti-Cardiac Hypertrophy Agents. Drug Deliv 2021, 28, 1334–1341. [CrossRef]
- Kunz, R.I.; Capelassi, A.N.; Alegre-Maller, A.C.P.; Bonfleur, M.L.; Ribeiro, L. de F.C.; Costa, R.M.; Natali, M.R.M. Sericin as Treatment of Obesity: Morphophysiological Effects in Obese Mice Fed with High-Fat Diet. Einstein (Sao Paulo) 2020, 18, eAO4876. [CrossRef]
- Dash, R.; Mandal, M.; Ghosh, S.K.; Kundu, S.C. Silk Sericin Protein of Tropical Tasar Silkworm Inhibits UVB-Induced Apoptosis in Human Skin Keratinocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 2008, 311, 111–119. [CrossRef]
- Ampawong, S.; Isarangkul, D.; Aramwit, P. Sericin Improves Heart and Liver Mitochondrial Architecture in Hypercholesterolaemic Rats and Maintains Pancreatic and Adrenal Cell Biosynthesis. Exp Cell Res 2017, 358, 301–314. [CrossRef]
- Ampawong, S.; Isarangkul, D.; Aramwit, P. Sericin Ameliorated Dysmorphic Mitochondria in High-Cholesterol Diet/Streptozotocin Rat by Antioxidative Property. Exp Biol Med 2017, 242, 411–421. [CrossRef]
- Langer, R.; Tirrell, D.A. Designing Materials for Biology and Medicine; 2004. [CrossRef]
- Goksen Tosun, N.; Ozer, A.; Bektas, T.; Oksuz, K.E.; Erden Tayhan, S.; Ozdemir, T. Silk Sericin-Hydroxyapatite Nanoribbons toward Structurally Stable Osteogenic Scaffolds. Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society 2023. [CrossRef]
- Aramwit, P.; Siritientong, T.; Kanokpanont, S.; Srichana, T. Formulation and Characterization of Silk Sericin-PVA Scaffold Crosslinked with Genipin. Int J Biol Macromol 2010, 47, 668–675. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.B.; Ding, S.L.; Ding, W.; Su, D.H.; Zhang, F.X.; Zhang, T.W.; Yin, X.F.; Xiao, L.; Li, Y.L.; Yuan, F.L.; et al. Injectable Sericin Based Nanocomposite Hydrogel for Multi-Modal Imaging-Guided Immunomodulatory Bone Regeneration. Chemical Engineering Journal 2021, 418. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cui, T.; Xu, X.; Du, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Pang, J. Robust Alcohol Soluble Polyurethane/Chitosan/Silk Sericin (APU/CS/SS) Nanofiber Scaffolds Toward Artificial Skin Extracellular Matrices via Microfluidic Blow-Spinning. Advanced Fiber Materials 2023, 5, 349–361. [CrossRef]
- Lungu, A.; Albu, M.G.; Stancu, I.C.; Florea, N.M.; Vasile, E.; Iovu, H. Superporous Collagen-Sericin Scaffolds. J Appl Polym Sci 2013, 127, 2269–2279. [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, M.G.; van Baar, M.E.; Choudhry, M.A.; Chung, K.K.; Gibran, N.S.; Logsetty, S. Burn Injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2020, 6, 1–25. [CrossRef]
- Lian, A.A.; Yamaji, Y.; Kajiwara, K.; Takaki, K.; Mori, H.; Liew, M.W.O.; Kotani, E.; Maruta, R. A Bioengineering Approach for the Development of Fibroblast Growth Factor-7-Functionalized Sericin Biomaterial Applicable for the Cultivation of Keratinocytes. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [CrossRef]
- Rujimongkon, K.; Ampawong, S.; Reamtong, O.; Buaban, T.; Aramwit, P. The Therapeutic Effects of Bombyx Mori Sericin on Rat Skin Psoriasis through Modulated Epidermal Immunity and Attenuated Cell Proliferation. J Tradit Complement Med 2021, 11, 587–597. [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Talukdar, S.; Kundu, S.C. Potential of 2D Crosslinked Sericin Membranes with Improved Biostability for Skin Tissue Engineering. Cell Tissue Res 2012, 347, 783–794. [CrossRef]
- Sapru, S.; Das, S.; Mandal, M.; Ghosh, A.K.; Kundu, S.C. Sericin-Chitosan-Glycosaminoglycans Hydrogels Incorporated with Growth Factors for in Vitro and in Vivo Skin Repair. Carbohydr Polym 2021, 258, 117717. [CrossRef]
- Akturk, O.; Tezcaner, A.; Bilgili, H.; Deveci, M.S.; Gecit, M.R.; Keskin, D. Evaluation of Sericin/Collagen Membranes as Prospective Wound Dressing Biomaterial. J Biosci Bioeng 2011, 112, 279–288. [CrossRef]
- Czaja, W.; Krystynowicz, A.; Bielecki, S.; Brown, R.M. Microbial Cellulose - The Natural Power to Heal Wounds. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 145–151. [CrossRef]
- Lamboni, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, G. Silk Sericin-Functionalized Bacterial Cellulose as a Potential Wound-Healing Biomaterial. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 3076–3084. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhang, G.; Fang, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Yan, H.; Liang, P.; Lian, J.; Zhang, Y. A Native Sericin Wound Dressing Spun Directly from Silkworms Enhances Wound Healing. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2023, 225, 113228. [CrossRef]
- European Commission Circular Economy Action Plan - European Commission Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/strategy/circular-economy-action-plan_en (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Vijayakumar, N.; Sanjay, A.V.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Nicoletti, M.; Baskar, G.; Kumar, R.; Govindarajan, M. Development of Biodegradable Bioplastics with Sericin and Gelatin from Silk Cocoons and Fish Waste. Toxics 2024, 12, 453. [CrossRef]
- Tufariello, M.; Iammarino, M.; Licciardello, F.; Mentana, A. Novel Approaches in Food Preservation and Their Impact on the Food System. Foods 2023, 12. [CrossRef]
- GRAS Letter 1026 | FDA Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/163217/download (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Seo, S.J.; Das, G.; Shin, H.S.; Patra, J.K. Silk Sericin Protein Materials: Characteristics and Applications in Food-Sector Industries. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [CrossRef]
- Adel, A.M.; Ibrahim, A.A.; El-Shafei, A.M.; Al-Shemy, M.T. Inclusion Complex of Clove Oil with Chitosan/β-Cyclodextrin Citrate/Oxidized Nanocellulose Biocomposite for Active Food Packaging. Food Packag Shelf Life 2019, 20. [CrossRef]
- Ormanli, E.; Amca Uluturk, B.; Bozdogan, N.; Bayraktar, O.; Tavman, S.; Kumcuoglu, S. Development of a Novel, Sustainable, Cellulose-Based Food Packaging Material and Its Application for Pears. Food Chem 2023, 429. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, G.; Kurita, H.; Nagasawa, A.; Hori, M.; Narita, F. Enhanced Mechanical Qualities of Sericin-Removed Silk by Direct Feeding of Silkworms with Cellulose Nanofiber. J Appl Polym Sci 2024, 141, e55512. [CrossRef]
- Iammarino, M. Recent Advances in Meat Products Quality & Safety Improvements and Assurance: Editorial. Int J Food Sci Technol 2020, 55, 917–918. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.A.A.; El-Sakhawy, M.; El-Sakhawy, M.A.M. Polysaccharides, Protein and Lipid -Based Natural Edible Films in Food Packaging: A Review. Carbohydr Polym 2020, 238. [CrossRef]
- Suhag, R.; Kumar, N.; Petkoska, A.T.; Upadhyay, A. Film Formation and Deposition Methods of Edible Coating on Food Products: A Review. Food Research International 2020, 136. [CrossRef]
- Jayasekhar Babu, P.; Suamte, L. Applications of Silk-Based Biomaterials in Biomedicine and Biotechnology. Engineered Regeneration 2024, 5, 56–69. [CrossRef]
- Tarangini, K.; Kavi, P.; Jagajjanani Rao, K. Application of Sericin-Based Edible Coating Material for Postharvest Shelf-Life Extension and Preservation of Tomatoes. eFood 2022, 3. [CrossRef]
- Miguel, G.A.; Álvarez-López, C. Extraction and Antioxidant Activity of Sericin, a Protein from Silk. Brazilian Journal of Food Technology 2020, 23. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, J.H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J. hua; Geng, X. qing; Wang, Z.W.; Wang, S.Y. Investigation of the Physiochemical Properties, Cryoprotective Activity and Possible Action Mechanisms of Sericin Peptides Derived from Membrane Separation. LWT 2017, 77, 532–541. [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.T.; Zhang, Y.Q. The Potential of Silk Sericin Protein as a Serum Substitute or an Additive in Cell Culture and Cryopreservation. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 1029–1039. [CrossRef]
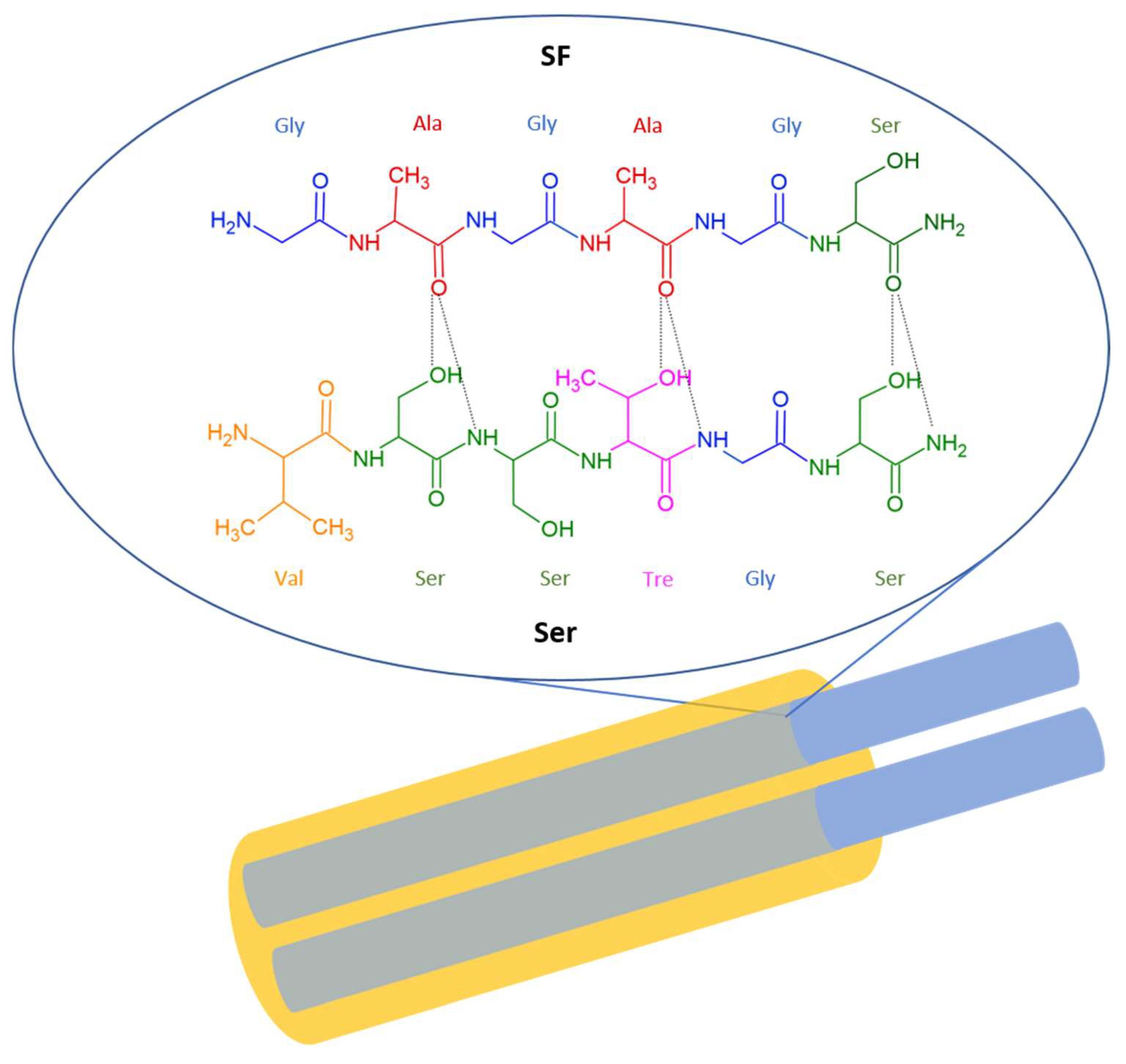
| Silk Fibers | SF (70-80%) | Ser (20- 30%) | ||
| H chain | L chain | P25 Glycoprotein | Glue-Like protein | |
| Molecular Weight (kDa) | 325 | 26 | 30 | 20-400 |
| Polarity | Hydrophobic/hydrophilic | Hydrophilic | Hydrophobic/hydrophilic | Hydrophilic |
| Structure | Silk I (random coil) Silk II (crystalline structure) Silk II (unstable phase) |
No crystalline structure | ||
| Function | Core of silk fibers | Wrapped two filaments Coating Protein Protection of pupae from UV radiation and external ambient detrimental effects |
||
| Amino Acid | Content Percentage |
|---|---|
| Aspartic acid (Asp) | 18.71 |
| Serine (Ser) | 32.16 |
| Glutamic acid (Glu) | 3.83 |
| Glycine (Gly) | 16.43 |
| Histidine (His) | 1.46 |
| Arginine (Arg) | 3.74 |
| Threonine (Thr) | 8.04 |
| Alanine (Ala) | 4.35 |
| Proline (Pro | 0.97 |
| Cysteine (Cys) | 0.13 |
| Tyrosine (Tyr) | 3.14 |
| Valine (Val) | 2.56 |
| Methionine (Met) | 0.64 |
| Lysine (Lys) | 1.79 |
| Isoleucine (Ile) | 0.66 |
| Leucine (Leu) | 0.80 |
| Phenylalaline (Phe) | 0.64 |
| Extraction techniques | Peptide weight | Secondary structure % | Advantages | Limitations | Ref. | ||||
| α-helix | β-sheet | Turns | Random coils | ||||||
| Chemical-based approach | Soaps | 15-75 kDa | 28.8 | 0.0 | 35.1 | 36.1 | Maximum extraction Fast process Cost-effective High efficiency Strong process Brings silk whiteness High strength and elasticity |
High Ser degradation Degummed Ser difficult to recover Energy consuming Effluent problem Presence of metal ions on soaps can produce insoluble metal soaps on the fiber surface Decrease the fiber strength Degumming bath cannot be repeatedly used |
[55,70,72] |
| Alkaline solutions | 15-75 kDa | 28.5 | 0.0 | 33.8 | 37.8 | Improved productivity Low processing cost Easy to handle |
Impart yellowish color to degummed fibers when used alone | [55] | |
| Acidic solutions | 50-150 kDa | 14.9 | 34.8 | 17.0 | 33.3 | Improve tensile strength Reusable degumming bath |
Dye uptake slightly decreased Limited hydrolytic action |
[73] | |
| Urea | 10–225 kDa | 2.8 | 54.5 | 4.0 | 38.7 | Little SF degradation Cheaper than Marseille soap |
Purification is needed to remove impurities Toxic to cells |
[74] | |
| Salt solutions | 24-400 kDa | NA | NA | NA | NA | Mild process Low degradation |
May cause water pollution Expensive |
[75] | |
| Physical processes (heat, pressure) | Boiling | 25-150 kDa | NA | NA | NA | NA | No purification process necessary Low-cost Environmentally friendly Simple process |
Time-consuming SF damaged and Ser degradation Low efficiency Remove only outer layer |
[72,75] |
| Autoclaving | 25-150 kDa | 0.0 | 56.2 | 2.5 | 41.3 | No purification process necessary Low-cost Environmentally friendly High efficiency Avoid contamination |
Time-consuming Affects fiber whiteness and absorbency Removes only the outer layer of Ser Incomplete extraction |
[76,77] | |
| Enzymatic | 5-2 kDa | NA | NA | NA | NA | Avoids uneven dyeing Improved dye affinity (particularly with reactive dyes) |
Easy to deactivate High cost Possible overreaction to fibers Time consuming |
[72] | |
| Ammine degumming | NA | NA | NA | NA | Low weighting rate Brings silk bright whiteness Low strength loss |
Difficult to apply in industries Unpleasant smell |
[73] | ||
| CO2 supercritical fluid degumming | NA | NA | NA | NA | Keeps Ser clean Avoid contamination |
High cost Necessity of demanding equipment |
[72] | ||
| Ultrasonication | NA | NA | NA | NA | Less chemical needed Environmentally friendly |
Necessity of demanding equipment Fine tuning necessary |
[72] | ||
| Device | Role of Ser | Sensors | Sensing mechanism | Output | Ref. |
| Electronic textile | Carbon black ink stabilizer enhancement of humidity absorption and enhancement of Ph sensitivity | Strain sensor | Change in resistivity | Sweat loss (increasing water volume, good sensitivity in acid media) | [31] |
| Electronic textile | Graphene stabilizer and chemical site for functionalization | Sweat loss sensor | Electrical mechanism | EMG and hand movement | [126] |
| Electronic textile | SCNT ink stabilizer | ECG sensor | Electrical mechanism | ECG | [125] |
| Electronic textile | SCNT ink stabilizer | Breath sensors | Change in resistance | Increase in resistance due to swelling | [125] |
| Screen printed electrode | SCNT ink stabilizer | Electrochemical sensor | Amperometric measurement | H2O2 concentration (linear range from 0.6 to 1.7 mM) | [125] |
| Electronic textile | Enhancement of MXenes dispersion in water, oxidation inhibitory | Breath sensor | Change in resistance | Humidity level (linear relationship between resistance and RH level from 33% to 97%) | [122] |
| Electronic textile | SCNT ink stabilizer, reductant of silver ions and graphene oxide | Electrochemical sensor | Amperometric measurement | H2O2 concentration (linear range from 0.1 to 10 mM) | [133] |
| Interdigitated electrode | Photoactive matrix to pattern rGO and PEDOT:PSS, biodegradation under proteolysis. |
Temperature sensor | Linear voltammetry | Linear increase of current in the range from 20 to 50°C | [131] |
| Flexible electrode | Ser as skin adhesion layer and electrolyte | ECG sensor | Electrical mechanism | ECG | [113] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





