Submitted:
14 May 2025
Posted:
14 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
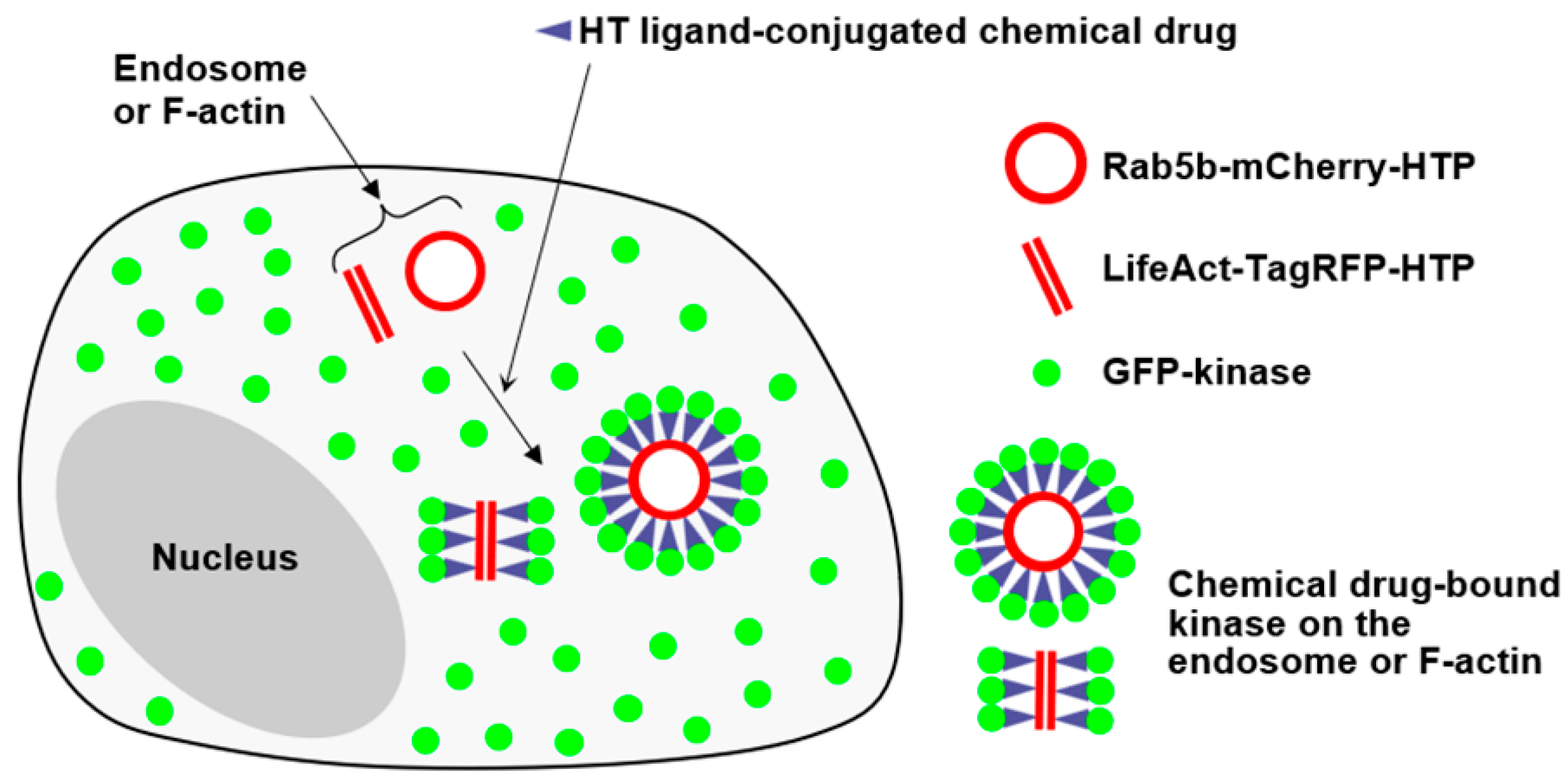
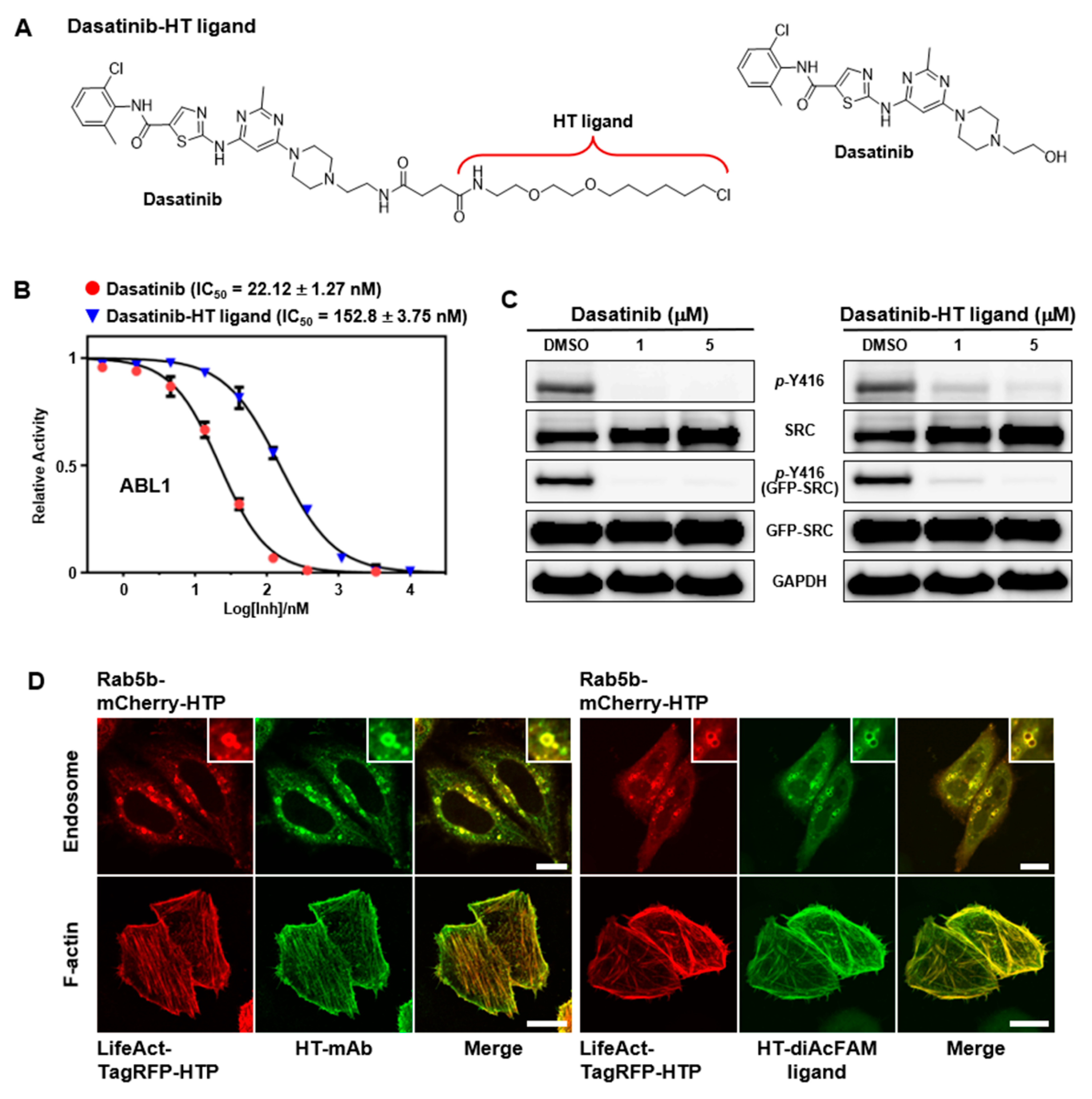
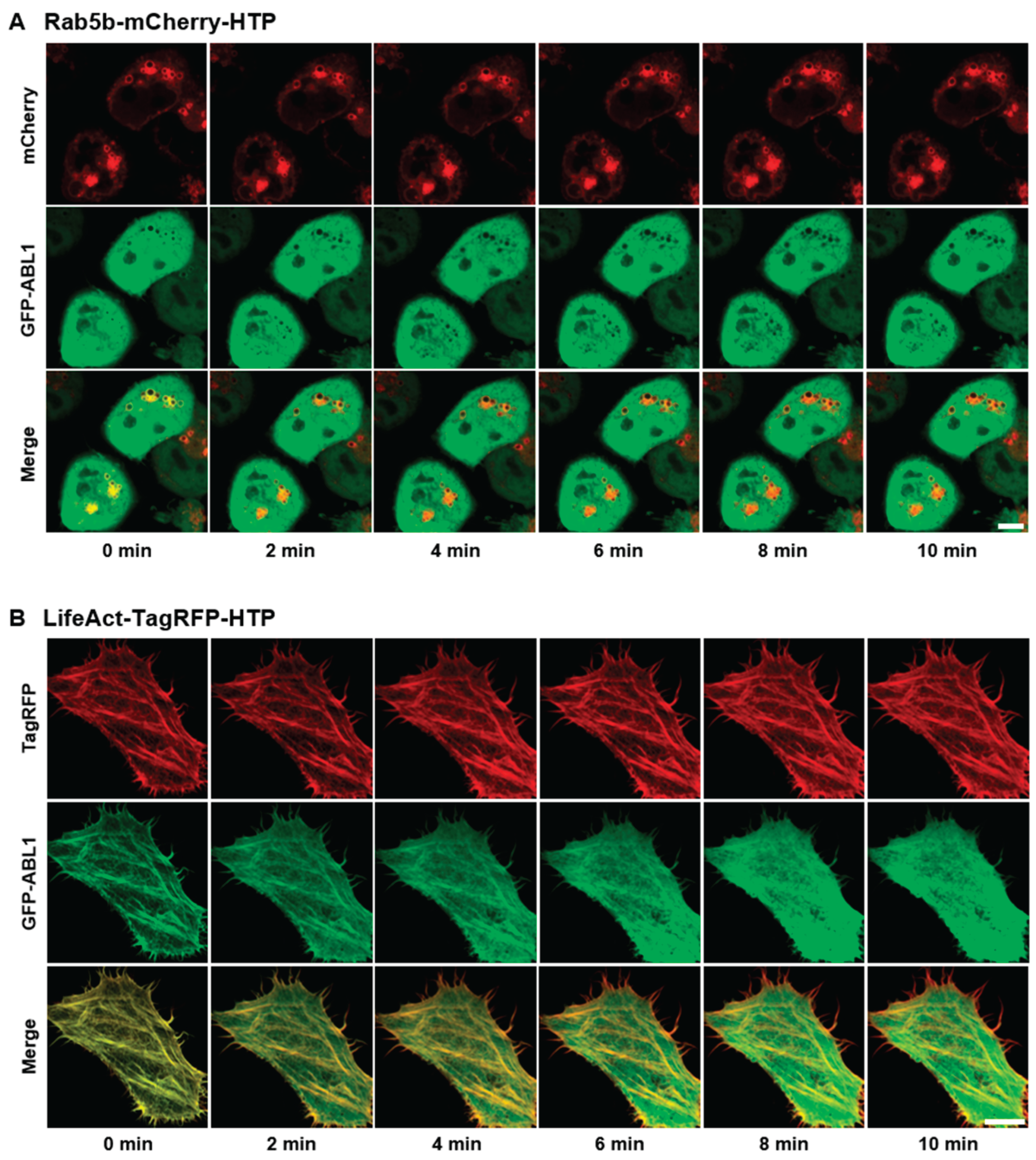
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of HT Ligand-Conjugated Dasatinib (Dasatinib−HT Ligand)
3.2. In Vitro Kinase Assay
3.3. SRC Kinase Inhibition Assay in Cells
3.4. Construction of Rab5b−mCherry−HTP and LifeAct−TagRFP−HTP Expression Vectors
3.5. Construction of EGFP−Kinase Expression Vectors
3.6. Validation of HaloTag−Fusion Proteins
3.7. Confocal Imaging
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Simple Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.J.; Yi, Y.W.; Kim, J.H. In situ monitoring of bindings between dasatinib and its target protein kinases using magnetic nanoparticles in live cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16466–16467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubach, J.M.; Vinegoni, C.; Mazitschek, R.; Fumene Feruglio, P.; Cameron, L.A.; Weissleder, R. In vivo imaging of specific drug-target binding at subcellular resolution. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Huang, X.; Ren, J. In situ study of the drug-target protein interaction in single living cells by combining fluorescence correlation spectroscopy with affinity probes. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 7020–7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhao, H.; Hu, L.; Shao, X.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ling, P.; Li, Y.; Zeng, K.; Chen, Q. Enhanced optical imaging and fluorescent labeling for visualizing drug molecules within living organisms. Acta. Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 2428–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, L.; Hahn, F.; Grau, B.W.; Wild, M.; Niesar, A.; Wangen, C.; Kataev, E.; Marschall, M.; Tsogoeva, S.B. Autofluorescent artemisinin−benzimidazole hybrids via organo−click Reaction: Study of antiviral properties and mode of action in living cells. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202301194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, C.; Cornish, V.W. A fluorogenic TMP-tag for high signal-to-background intracellular live cell imaging. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 1704–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, W.Y.; Yang, H.W.; Heo, W.D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2010, 107, 3412–3417. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.B.; Hwang, J.M.; Choi, I.S.; Rho, J.R.; Choi, J.-S.; Kim, G.H.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, S.; Lee, Z.W. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1314–1317. [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.C.; Cho, M.; Hwang, J.M.; Myung, K.; Kweon, H.S.; Lee, Z.W.; Seong, H.A.; Lee, K.B. Imaging the Raf–MEK–ERK signaling cascade in living cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgania, H.K.; Metz, J.; Jeske, M. ReLo is a simple and rapid colocalization assay to identify and characterize direct protein–protein interactions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.R.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, Y.J.; Chae, D.E.; Kim, K.A.; Lee, Z.W.; Kim, N.D.; Choi, J.S.; Choi, I.S.; Lee, K.B. A bioorthogonal approach for imaging the binding between dasatinib and its target proteins inside living cells. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11764–11767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, J.; Kühn, S.; Tarnawski, M.; Gotthard, G.; Tünnermann, J.; Tänzer, T.; Karpenko, J.; Mertes, N.; Xue, L.; Uhrig, U.; Reinstein, J.; Hiblot, J.; Johnsson, K. Kinetic and structural characterization of the self-labeling protein tags HaloTag7, SNAP-tag, and CLIP-tag. Biochemistry 2021, 60, 2560–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelzel, C.A.; Zhang, X. Visualizing and manipulating biological processes by using HaloTag and SNAP-Tag technologies. ChemBioChem 2020, 21, 1935–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los, G.V.; Encell, L.P.; McDougall, M.G.; Hartzell, D.D.; Karassina, N.; Zimprich, C.; Wood, M.G.; Learish, R.; Ohana, R.F.; Urh, M.; Simpson, D.; Mendez, J.; Zimmerman, K.; Otto, P.; Vidugiris, G.; Zhu, J.; Darzins, A.; Klaubert, D.H.; Bulleit, R.F.; Wood, K.V. HaloTag: A novel protein labeling technology for cell imaging and protein analysis. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- England, C.G.; Luo, H.; Cai, W. HaloTag technology: A versatile platform for biomedical applications. Bioconjugate Chem. 2015, 26, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brave, M.; Goodman, V.; Kaminskas, E.; Farrell, A.; Timmer, W.; Pope, S.; Harapanhalli, R.; Saber, H.; Morse, D.; Bullock, J.; Men, A.; Noory, C.; Ramchandani, R.; Kenna, L.; Booth, B.; Gobburu, J.; Jiang, X.; Sridhara, R.; Justice, R.; Pazdur, R. Sprycel for chronic myeloid leukemia and Philadelphia chromosome−positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia resistant to or intolerant of imatinib mesylate. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhang, C.J.; Chen, G.Y.J.; Yao, S.Q. Cell−based proteome profiling of potential dasatinib targets by use of affinity-based probes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3001–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurty, R.; Brigham, J.L.; Leonard, S.E.; Ranjitkar, P.; Larson, E.T.; Dale, E.J.; Merritt, E.A.; Maly, D.J. Active site profiling reveals coupling between domains in SRC−family kinases. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 19, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.E.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Du, J.; Luo, X.; Deshmukh, V.; Kim, C.H.; Lawson, B.R.; Tremblay, M.S.; Young, T.S.; Kazane, S.A.; Wang, F.; Schultz, P.G. An immunosuppressive antibody−drug conjugate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3229–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, R. A small molecule nanodrug consisting of pH-sensitive ortho ester–dasatinib conjugate for cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 163, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedl, J.; Crevenna, A.H.; Kessenbroch, K.; Yu, J.H.; Neukirchen, D.; Bista, M.; Bradke, F.; Jenne, D.; Holak, T.A.; Werb, Z.; Sixt, M.; Wedlich-Soldner, R. Lifeact: a versatile marker to visualize F-actin. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 605–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greuber, E.K.; Smith-Pearson, P.; Wang, J.; Pendergast, A.M. Role of ABL family kinases in cancer: from leukaemia to solid tumors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




