Submitted:
27 April 2025
Posted:
28 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. POME Emulsion Preparation
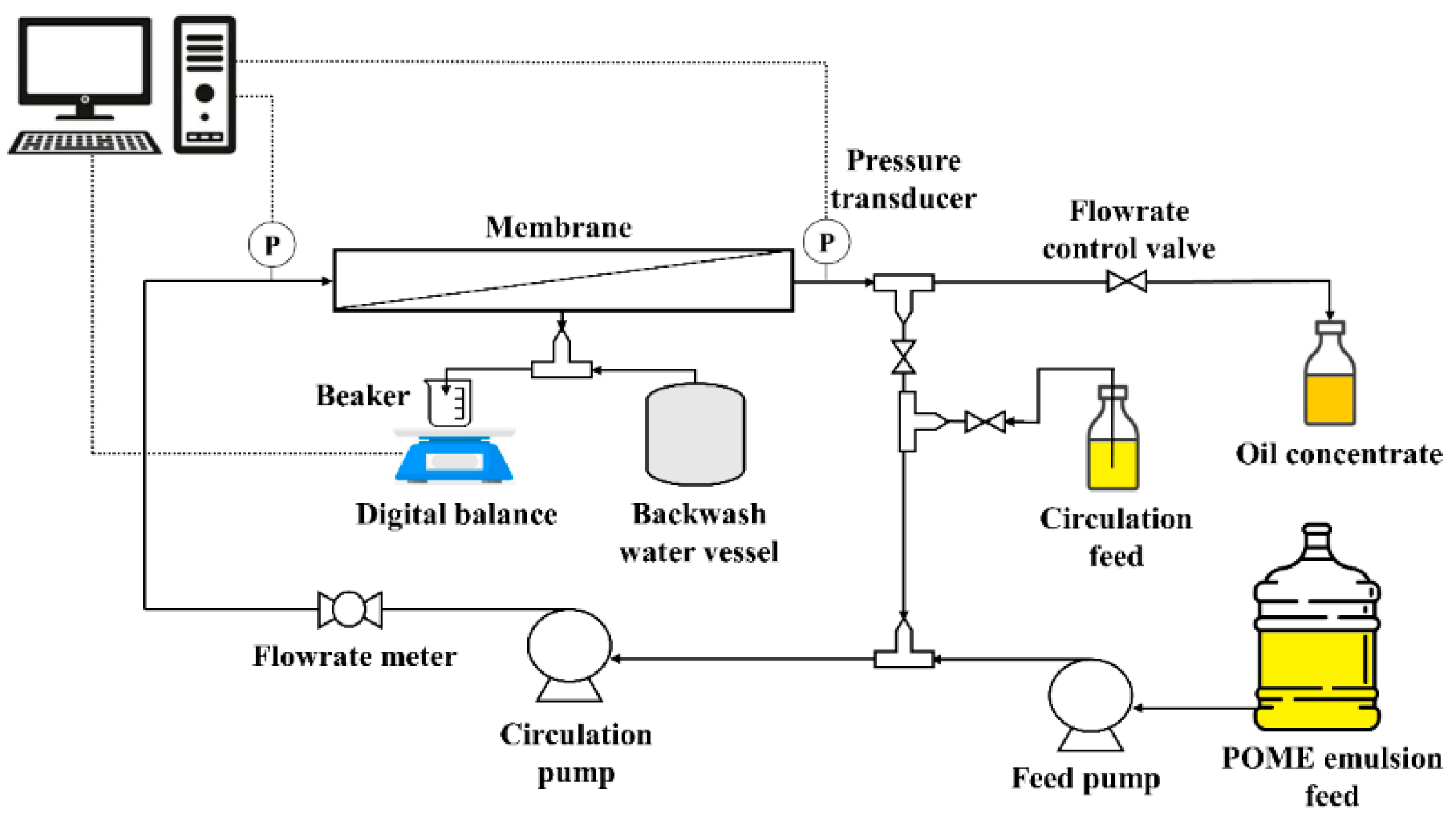
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Experimental Design
2.3.1. Constant Permeate Flux Crossflow Experiments
| Parameter / membrane | CFV(m/s) | Flux 1 (LMH) |
Flux 2 (LMH) |
Flux 3 (LMH) |
Flux 4 (LMH) |
| PVDF | 0.8 | 20 | 40 | 50 | - |
| α-Al2O3 | 0.8 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 70 |
2.3.2. Membrane Conditioning and Cleaning
2.3.3. Membrane Performance Evaluation Methods
2.3.3.1. Rejection Capacity (Rj)
2.3.3.2. Oil Concentration Factor (Fo)
2.3.3.3. Water Recovery (Rw)
2.3.3.4. Normalized Transmembrane Pressure (TMPn)
2.3.4. Membrane Fouling Evaluation
2.3.4.1. Hydraulic Permeability
2.4. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. POME Emulsion Characteristics
| Parameters | POME emulsion | Raw POME [18,63] |
| pH | 5.4 | 3.4 – 5.5 |
| Electrical Conductivity (µS/cm) | 18.3 ± 0.1 | 137 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 580.7 ± 9.0 | (65.6 – 69.4) × 103 |
| CODt (g/L) | 15.0 ± 0.2 | 15 – 100 |
| CODs (g/L) | 2.1 | - |
| TS (g/L) | 3.7 ± 0.1 | 11.5 – 79.0 |
| TDSa (g/L) | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 20.6 – 41.1 |
| TSS (g/L) | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 5 – 71.3 |
| FOGb (g/L) | 5.5 ± 0.1 | 2.2 – 27.2 |
| Total nitrogen (g TN/L) | (5.9 ± 0.1) × 10-3 | 0.2 – 1.7 |
| Ammoniacal nitrogen (g NH4-N/L) | 0.2 × 10-3 | (17 – 254) × 10-3 |
| Particle size distribution (PSD) (µm, % v/v) | 1.54 (61.5 %), 0.04 (38.5 %) |
- |
3.2. Comparison on the Quality of Oil and Water Recovery
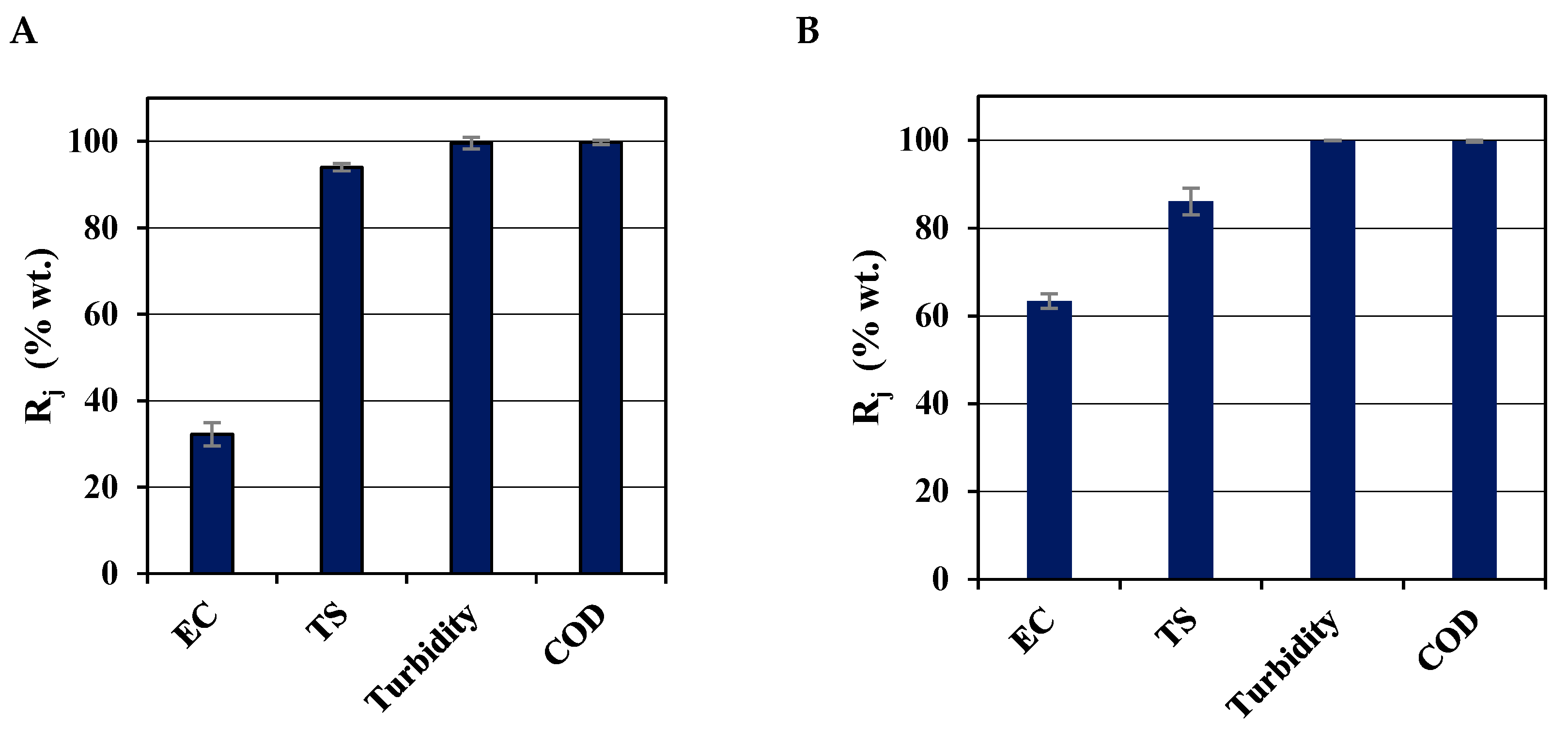
3.2.1. Rejection Capacity (Rj)
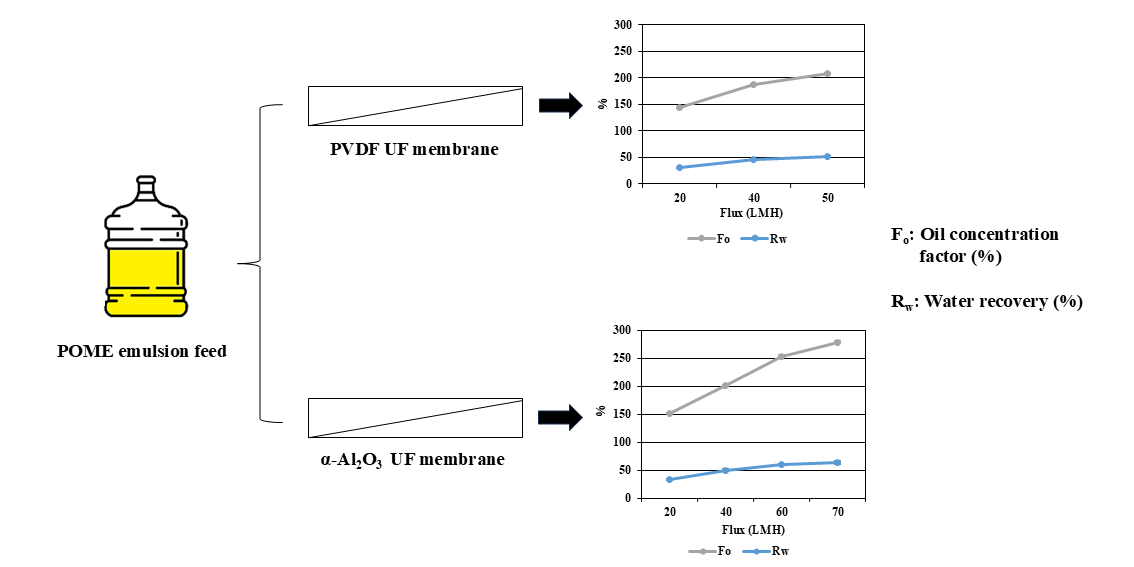
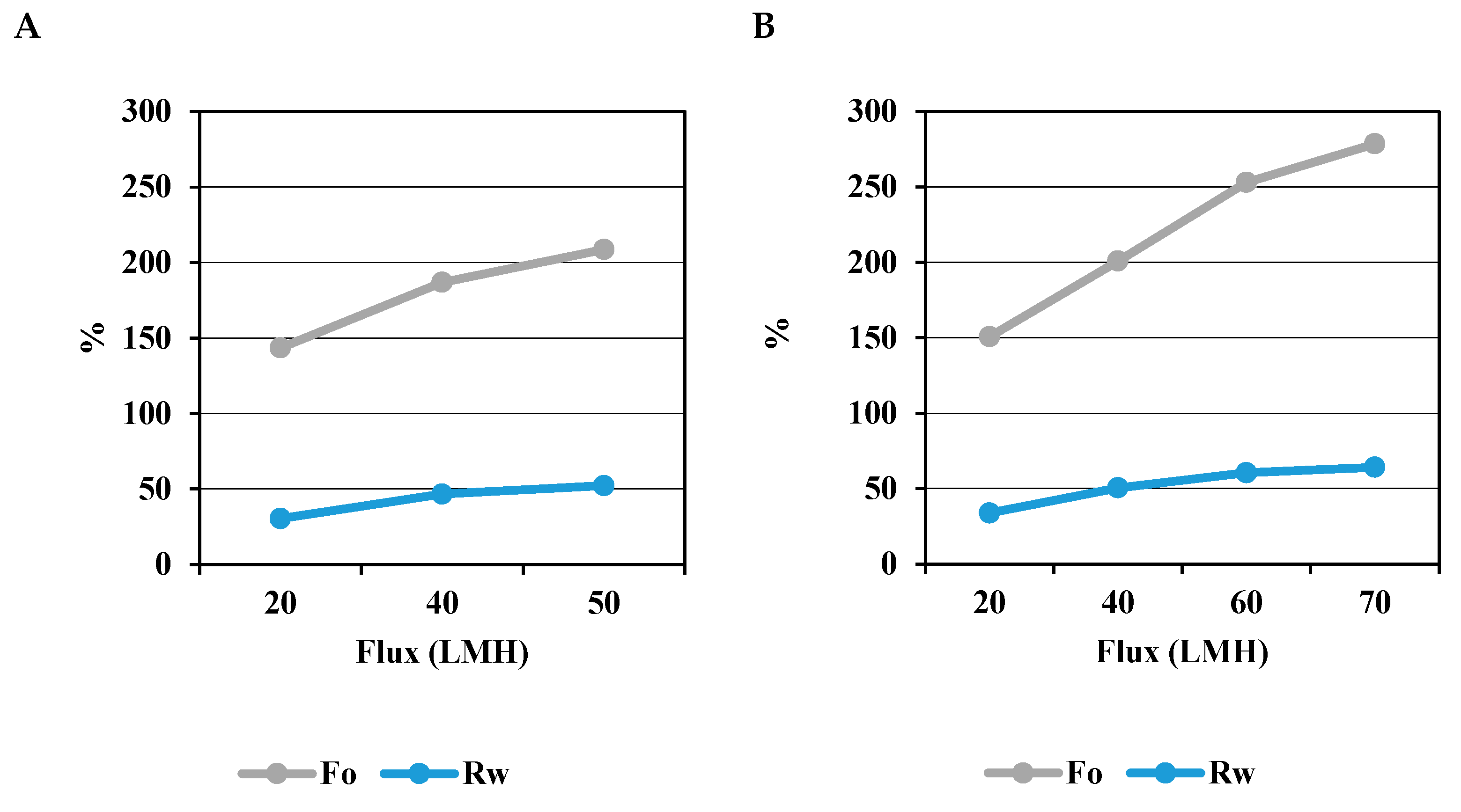
3.2.2. Oil Concentration Factor (Fo) and Water Recovery (Rw)
3.2.3. Permeate Water Characteristics
| Parameters | Permeate water characteristics | Industrial water discharge requirements |
POME discharge standards [14,69] |
|
| PVDF membrane |
α-Al2O3 membrane |
|||
| pH | 5.4 ± 0.20 | 6.0 ± 0.1 | 6.5 – 8.5 [59,70] | 5 - 9 |
| EC (µS/cm) | 12.4 ± 0.1 | 6.7 ± 0.1 | 260 [59] | - |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 2.5 ± 0.04 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | < 5 [59] | - |
| COD (mg/L) | 35.7 ± 1.5 | 33.1 ± 1.8 | < 50 [59] | < 1000 |
| TS (mg/L) | 219.3 ± 50.0 | 509.0 ± 43 | < 1000 [59] | < 1500 |
| TSS (mg/L) | 33.3 ± 5.8 | 20.3 ± 0.6 | < 400 [70] | < 400 |
| TDSa (mg/L) | 186.0 ± 44.2 | 488.5 ± 42.4 | - | - |
| FOGb (mg/L) | 13.2 ± 0.6 | 12.2 ± 0.7 | < 50 [70] | < 50 |
| Ammoniacal nitrogen (mg NH4-N/L) |
< 0.001 | < 0.001 | - | < 100 |
| Total nitrogen (mg TN/L) | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | < 150 [70] | - |
3.3. Comparison on the Rate of Oil and Water Recovery
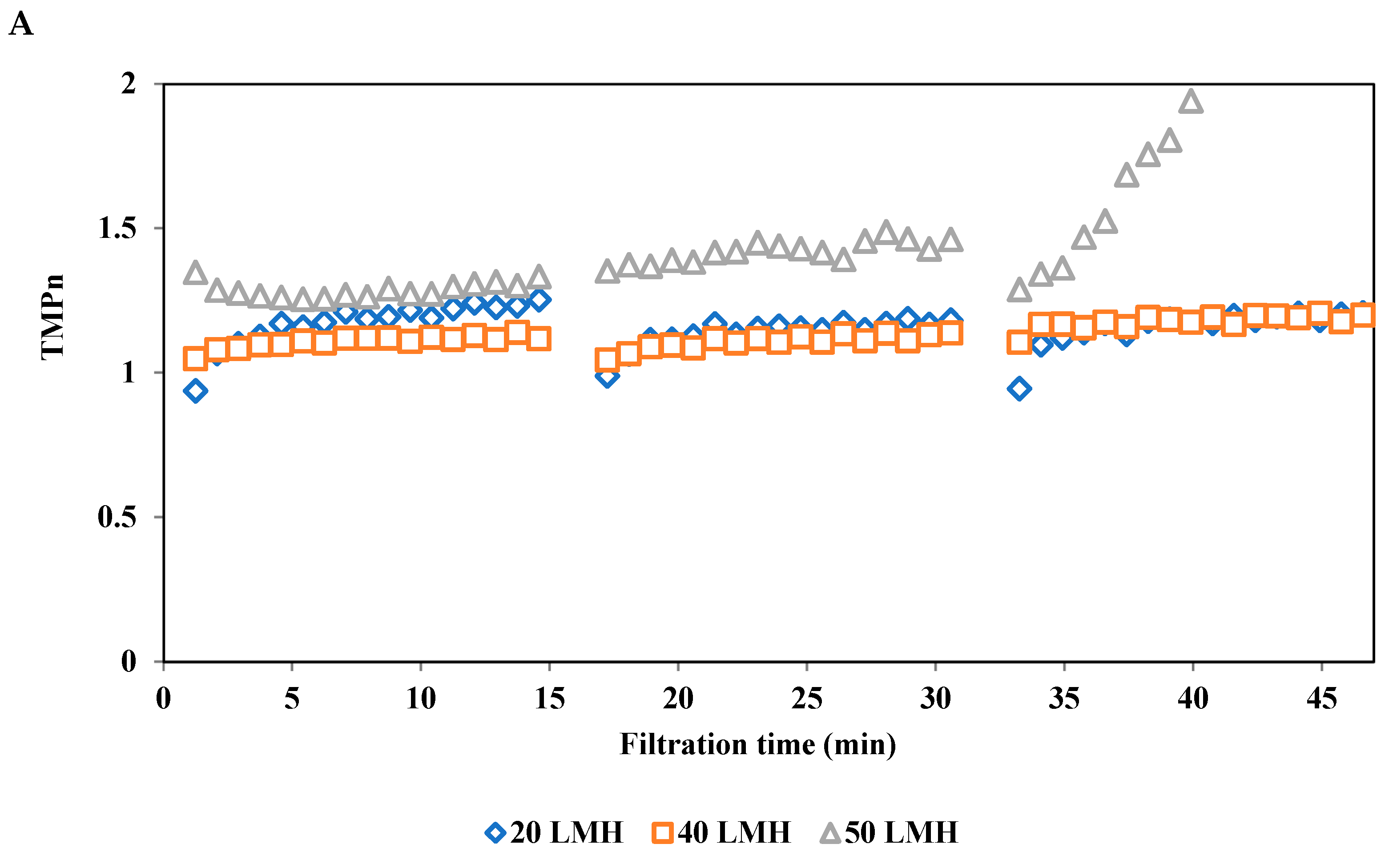
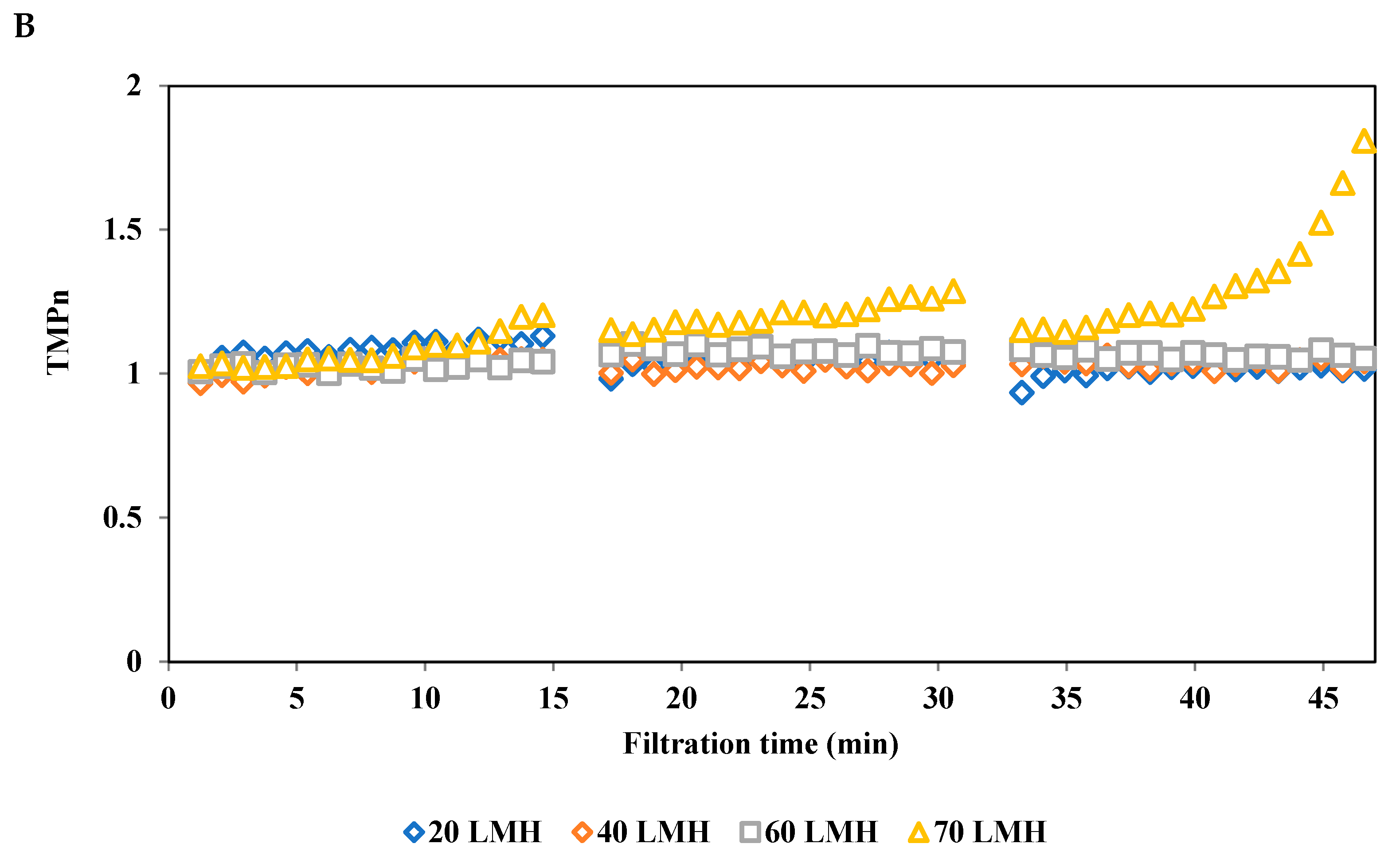
3.3.1. Effect of Permeate Flux on Normalized Transmembrane Pressure (TMPn)
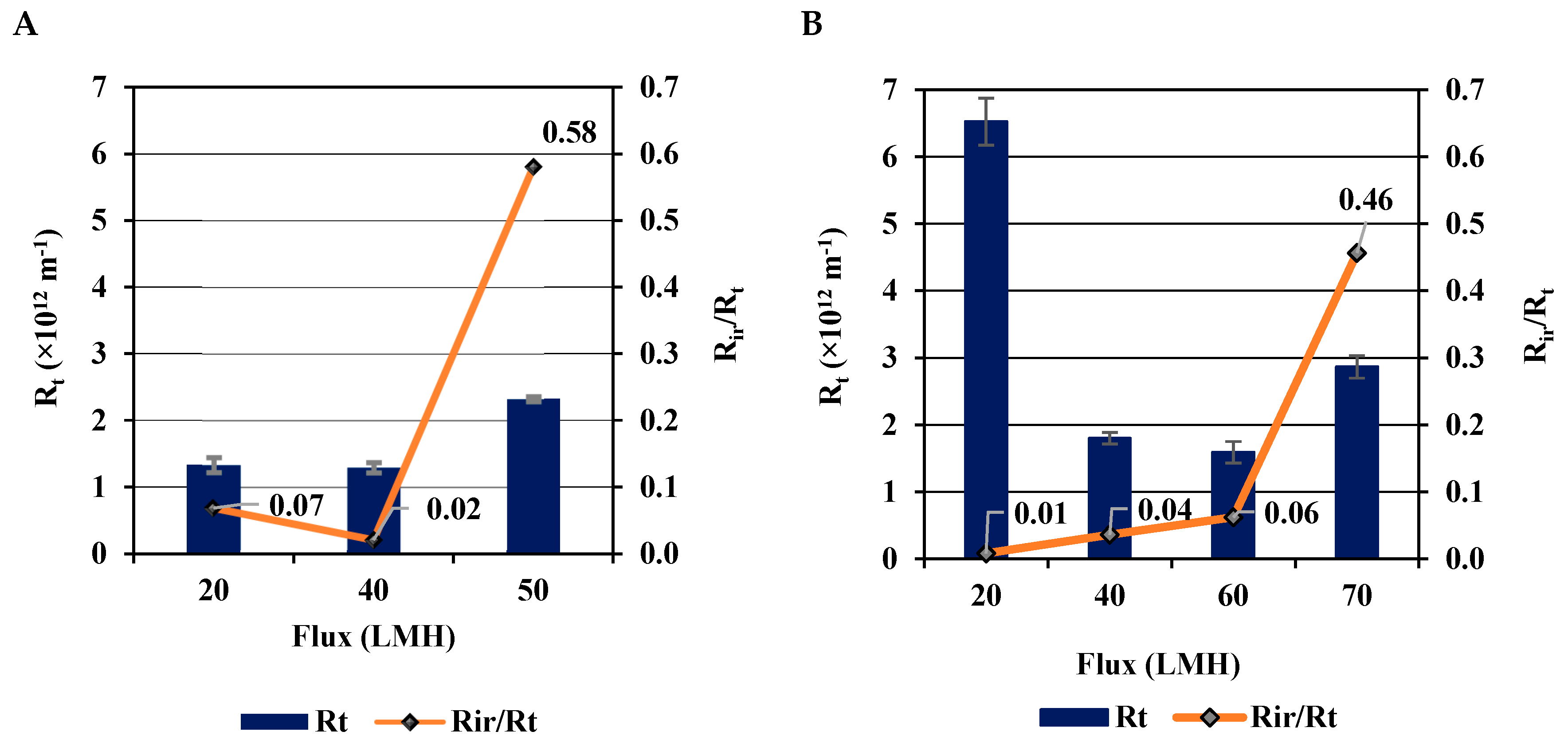
3.3.2. Effect of Permeate Flux on Fouling Resistances (R)
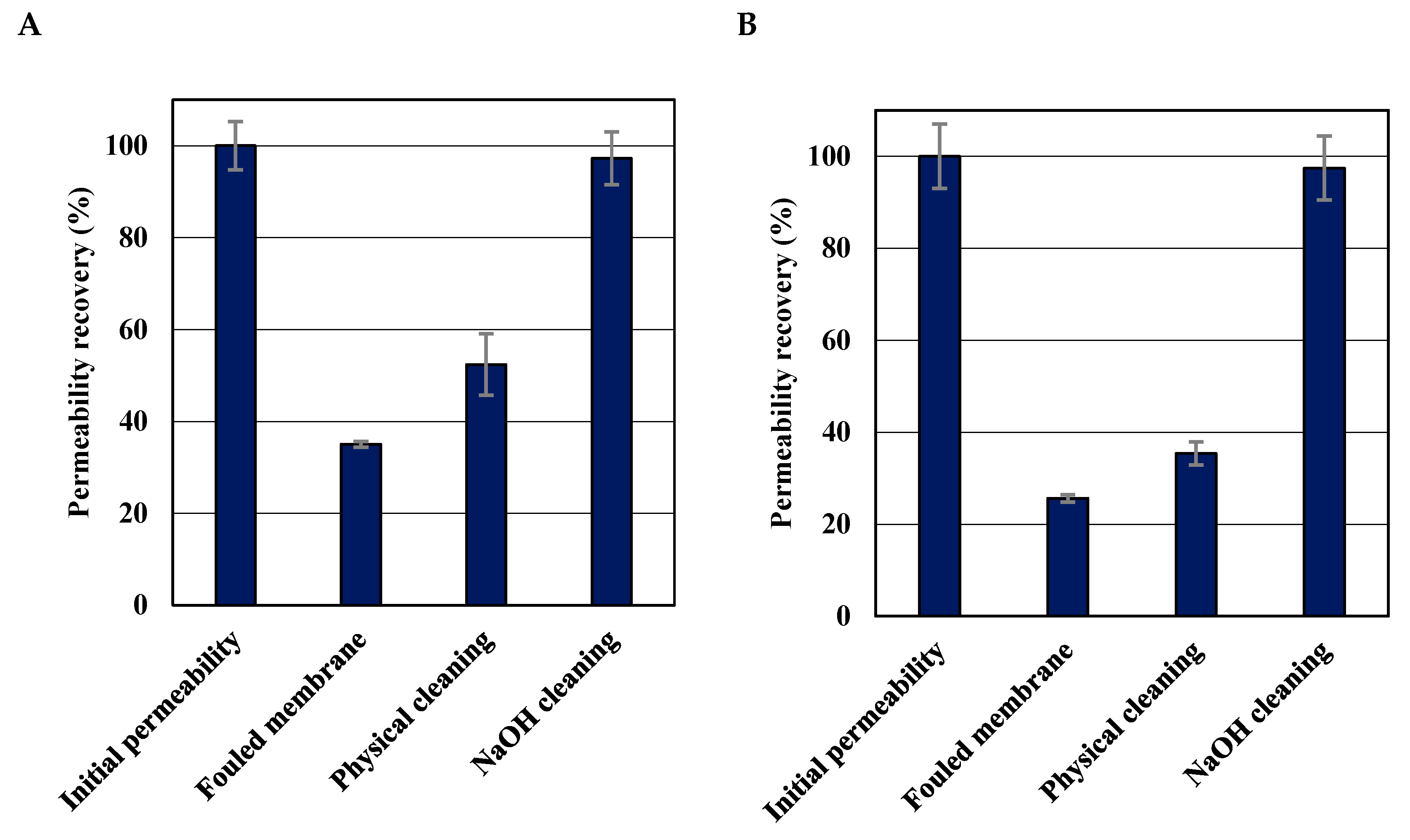
3.4. Efficiency of Membrane Cleaning
3.5. Comparison Summary of PVDF and α-Al2O3 Membranes Performance
| Performance variables | Experimental results | Key findings | |
| PVDF membrane | α-Al2O3 membrane | ||
| Normalized transmembrane pressure (TMPn) | 1.2 | 1.08 | α-Al2O3 membrane showed more stability and slightly less in magnitude of TMPn at a higher flux than PVDF membrane. At similar fluxes, α-Al2O3 membrane had TMPn that is lower and more stable than those of PVDF membrane. |
| Total resistance (Rt) | 1.3 ×1012 m-1 | 1.59 ×1012 m-1 | Both membranes showed relatively low total resistance at their respective optimum conditions. |
| Irreversible to total resistances ratio (Rir/Rt) | 0.02 | 0.06 | Both membranes demonstrated minimum irreversible fouling at their respective optimum conditions. |
| COD rejection (Rj) | 99.8 % | 99.8 % | Both membranes illustrated efficient removal of COD at their respective optimum conditions. |
| Oil concentration factor (Fo) | 186.8 % | 253.0 % | α-Al2O3 membrane achieved higher concentration of oil per filtration cycle than PVDF membrane. |
| Water recovery (Rw) | 46.6 % | 60.5 % | α-Al2O3 membrane recovered more water per filtration cycle than PVDF membrane. |
| Membrane cleaning efficiency | 97.3 % | 97.4 % | Cleaning methods used in this study achieved an efficient recovery of hydraulic permeability. |
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cifuentes-Cabezas, M.; Carbonell-Alcaina, C.; Vincent-Vela, M.C.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A.; Álvarez-Blanco, S. Comparison of different ultrafiltration membranes as first step for the recovery of phenolic compounds from olive-oil washing wastewater. Process Safety and Environmental Protection 2021, 149, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muraisy, S.A.; Soares, L.A.; Chuayboon, S.; Ismail, S.B.; Abanades, S.; van Lier, J.B.; Lindeboom, R.E. Solar-driven steam gasification of oil palm empty fruit bunch to produce syngas: Parametric optimization via central composite design. Fuel Processing Technology 2022, 227, 107118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avornyo, A.; Chrysikopoulos, C.V. Applications of graphene oxide (GO) in oily wastewater treatment: Recent developments, challenges, and opportunities. Journal of Environmental Management 2024, 353, 120178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihsanullah, I.; Bilal, M.; Sajid, M.; Mohammad, A.W.; Atieh, M.A.; Ghaffour, N. Emerging MXenes: Revolutionizing oily wastewater treatment-a comprehensive and critical review. Separation and Purification Technology 2024, 329, 125181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murić, A.; Petrinić, I.; Christensen, M.L. Comparison of ceramic and polymeric ultrafiltration membranes for treating wastewater from metalworking industry. Chemical Engineering Journal 2014, 255, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Guria, C.; Mandal, A. A review of oily wastewater treatment using ultrafiltration membrane: A parametric study to enhance the membrane performance. Journal of Water Process Engineering 2020, 36, 101289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, A.S.; Innocentini, M.D.; Oliveira, J.V.; Lider, A.; Fey, T.; Travitzky, N.; Hotza, D. Unveiling the potential of silicon carbide as a support material and membranes for oily wastewater remediation. Separation and Purification Technology 2024, 354, 129044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, B.; Qiu, F.; Zhang, T. A dual wastes-based aerogel with inverse beetles-like structure for enhanced oily wastewater treatment. Separation and Purification Technology 2024, 333, 125896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidabutar, R.; Trisakti, B.; Michael, M.; Vanness, V.; Alexander, V.; Natasya, Y.; Alamsyah, V.; Zaiyat, M.Z.Z.; Syafriandy, S.; Al Fath, M.T. Synergistic integration of zeolite engineering and fixed-bed column design for enhanced biogas upgrading: Adsorbent synthesis, CO2/CH4 separation kinetics, and regeneration assessment. Separation and Purification Technology 2025, 355, 129772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.S.; Wirzal, M.D.H.; Putra, Z.A. Review on current approach for treatment of palm oil mill effluent: Integrated system. Journal of Environmental Management 2021, 286, 112209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semilin, V.; Janaun, J.; Chung, C.H.; Touhami, D.; Haywood, S.K.; Chong, K.P.; Yaser, A.Z.; Zein, S.H. Recovery of oil from palm oil mill effluent using polypropylene micro/nanofiber. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2021, 404, 124144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.A.; Farid, M.A.A.; Zakaria, M.R.; Ariffin, H.; Andou, Y.; Shirai, Y. Palm oil expansion in Malaysia and its countermeasures through policy window and biorefinery approach. Environmental Science & Policy 2024, 153, 103671. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.E.; Bagheri, G.; Wahid, M.A.; Saat, A. Clean fuel, clean energy conversion technology: Experimental and numerical investigation of palm oil mill effluent biogas flameless combustion. BioResources 2015, 10, 6597–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmod, S.S.; Takriff, M.S.; AL-Rajabi, M.M.; Abdul, P.M.; Gunny, A.A.N.; Silvamany, H.; Jahim, J.M. Water reclamation from palm oil mill effluent (POME): Recent technologies, by-product recovery, and challenges. Journal of Water Process Engineering 2023, 52, 103488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhukhan, J.; Martinez-Hernandez, E.; Murphy, R.J.; Ng, D.K.; Hassim, M.H.; Ng, K.S.; Kin, W.Y.; Jaye, I.F.M.; Hang, M.Y.L.P.; Andiappan, V. Role of bioenergy, biorefinery and bioeconomy in sustainable development: Strategic pathways for Malaysia. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2018, 81, 1966–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, P.L.; Bashir, M.J.; Wong, L.-P. Recent advancements in the treatment of palm oil mill effluent (POME) using anaerobic biofilm reactors: Challenges and future perspectives. Journal of Environmental Management 2022, 320, 115750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, P.; Felgueiras, F.; Mourão, Z.; Fernandes, E.D.O.; Moreira, A.; Gabriel, M.F. Predicting health risk from exposure to trihalomethanes in an Olympic-size indoor swimming pool among elite swimmers and coaches. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part A 2019, 82, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.W.; Chong, C.C.; Lam, M.K.; Leong, W.H.; Chuah, L.F.; Yusup, S.; Setiabudi, H.D.; Tang, Y.; Lim, J.W. Identification of microbial inhibitions and mitigation strategies towards cleaner bioconversions of palm oil mill effluent (POME): A review. Journal of Cleaner Production 2021, 280, 124346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, M.; Brodie, J. Nutrients and eutrophication, in: Marine pollution–monitoring, management and mitigation, Springer, 2023, pp. 75–100.
- Yusof, M.A.B.M.; Chan, Y.J.; Chong, C.H.; Chew, C.L. Effects of operational processes and equipment in palm oil mills on characteristics of raw Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME): A comparative study of four mills. Cleaner Waste Systems 2023, 5, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samavati, Z.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Lau, W.J.; Samavati, A.; Ng, B.C.; Abdullah, M.S. Advancements in membrane technology for efficient POME treatment: A comprehensive review and future perspectives. Journal of Environmental Sciences 2024, 155, 730–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskandar, M.J.; Baharum, A.; Anuar, F.H.; Othaman, R. Palm oil industry in South East Asia and the effluent treatment technology—A review. Environmental technology & innovation 2018, 9, 169–185. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.W.; Chong, C.C.; Lam, M.K.; Ayoub, M.; Cheng, C.K.; Lim, J.W.; Yusup, S.; Tang, Y.; Bai, J. Holistic process evaluation of non-conventional palm oil mill effluent (POME) treatment technologies: A conceptual and comparative review. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2021, 409, 124964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo-Corbacho, M.A.; Pacheco-Ruiz, S.; Míguez, D.; Hooijmans, C.M.; García, H.A.; Brdjanovic, D.; van Lier, J.B. Impact of solids retention time on the biological performance of an AnMBR treating lipid-rich synthetic dairy wastewater. Environmental Technology 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohimain, E.I.; Izah, S.C. A review of biogas production from palm oil mill effluents using different configurations of bioreactors. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2017, 70, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choong, Y.Y.; Chou, K.W.; Norli, I. Strategies for improving biogas production of palm oil mill effluent (POME) anaerobic digestion: A critical review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2018, 82, 2993–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izah, S.; Oduah, A.; Ohimain, E. Effects of temperature and fermentation period on the recovery of second grade palm oil from palm press fiber. International Journal of Engineering Science and Innovative Technology 2014, 3, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Padaki, M.; Murali, R.S.; Abdullah, M.S.; Misdan, N.; Moslehyani, A.; Kassim, M.; Hilal, N.; Ismail, A. Membrane technology enhancement in oil–water separation. A review. Desalination 2015, 357, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.O.; Azizli, K.A.M.; Isa, M.H.; Ezechi, E.H. Treatment of POME using Fenton oxidation process: Removal efficiency, optimization, and acidity condition. Desalination and Water Treatment 2016, 57, 23750–23759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahrim, A.; Dexter, Z.; Joseph, C.; Hilal, N. Effective coagulation-flocculation treatment of highly polluted palm oil mill biogas plant wastewater using dual coagulants: Decolourisation, kinetics and phytotoxicity studies. Journal of water process engineering 2017, 16, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.J.; Han, T.M.; Wei, L.J.; Aun, N.C.; Amr, S.S.A. Polishing of treated palm oil mill effluent (POME) from ponding system by electrocoagulation process. Water Science and Technology 2016, 73, 2704–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.P.; Sharma, M.; Purkait, M.K. Recent progress on electrocoagulation process for wastewater treatment: A review. Separation and Purification Technology 2022, 292, 121058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, N.S.; Yunos, K.F.M. Wastewater treatment of palm oil mill effluent (POME) by ultrafiltration membrane separation technique coupled with adsorption treatment as pre-treatment. Agriculture and Agricultural Science Procedia 2014, 2, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.E.; Wahid, M.A. Pollutant in palm oil production process. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association 2015, 65, 773–781. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Han, M.; He, F. A review of treating oily wastewater. Arabian journal of chemistry 2017, 10, S1913–S1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcinkaya, F.; Boyraz, E.; Maryska, J.; Kucerova, K. A review on membrane technology and chemical surface modification for the oily wastewater treatment. Materials 2020, 13, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, M.C.S.; Lebron, Y.; Moreira, V. Oily wastewater treatment by membrane-assisted technologies. In Advanced Technologies in Wastewater Treatment; Elsevier, 2023, pp. 213–255.
- Salahi, A.; Abbasi, M.; Mohammadi, T. Permeate flux decline during UF of oily wastewater: Experimental and modeling. Desalination 2010, 251, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asatekin, A.; Mayes, A.M. Oil industry wastewater treatment with fouling resistant membranes containing amphiphilic comb copolymers. Environmental science & technology 2009, 43, 4487–4492. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Tu, W.; Wee, K.-H.; Bai, R. Effective and low fouling oil/water separation by a novel hollow fiber membrane with both hydrophilic and oleophobic surface properties. Journal of membrane science 2014, 466, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alresheedi, M.T.; Barbeau, B.; Basu, O.D. Comparisons of NOM fouling and cleaning of ceramic and polymeric membranes during water treatment. Separation and Purification Technology 2019, 209, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadekar, S.S.; Vidic, R.D. Comparison of ceramic and polymeric nanofiltration membranes for treatment of abandoned coal mine drainage. Desalination 2018, 440, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Dilaver, M.; Park, P.-K.; Kim, J.-H. Comparative analysis of fouling characteristics of ceramic and polymeric microfiltration membranes using filtration models. Journal of Membrane Science 2013, 432, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, M.; Goh, P.; Lau, W.; Tan, Y.; Ng, B.; Ismail, A. Hydrophilic hollow fiber PVDF ultrafiltration membrane incorporated with titanate nanotubes for decolourization of aerobically-treated palm oil mill effluent. Chemical Engineering Journal 2017, 316, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.J.; Kasemset, S.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B.D. Comparison of membrane fouling at constant flux and constant transmembrane pressure conditions. Journal of Membrane Science 2014, 454, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Feng, H.; Ding, Y.; Pan, S.; Qiao, H. Comparison of the formation, filtration performance, and structural characteristic of self-forming dynamic membranes under constant transmembrane pressure and constant filtration flux. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2022, 10, 108691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, P.; Ismail, A. A review on inorganic membranes for desalination and wastewater treatment. Desalination 2018, 434, 60–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadaroo, S.N.; Grassia, P.; Gouwanda, D.; Poh, P.E. Is the dewatering of Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) feasible? Effect of temperature on POME’s rheological properties and compressive behavior. Chemical Engineering Science 2019, 202, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Xing, W.; Zhang, B. Fabrication of ceramic membranes with controllable surface roughness and their applications in oil/water separation. Ceramics International 2013, 39, 4355–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Hou, Y. Reducing ultrafiltration membrane fouling during recycled paper mill wastewater treatment using pretreatment technologies: A comparison between coagulation and Fenton. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology 2019, 94, 804–811. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, P.B.; Ricci, B.C.; Reis, B.G.; Neta, L.S.; Cerqueira, A.C.; Amaral, M.C. Effect of MBR-H2O2/UV Hybrid pre-treatment on nanofiltration performance for the treatment of petroleum refinery wastewater. Separation and Purification Technology 2018, 192, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhady, S.; Bassyouni, M.; Mansour, R.A.; Elzahar, M.H.; Abdel-Hamid, S.; Elhenawy, Y.; Saleh, M.Y. Oily wastewater treatment using polyamide thin film composite membrane technology. Membranes 2020, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.; Loulergue, P.; Karpel, N.; Teychene, B. Electron beam irradiation of polyvinylidene fluoride/polyvinylpyrrolidone ultrafiltration membrane in presence of zwitterions molecules evaluation of filtration performances. Radiation Physics and Chemistry 2019, 159, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Yasuda, Y.; Morita, T. Low-temperature synthesis of α-alumina based on sol-gel processes. Advances in Materials and Processing Technologies 2020, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Shang, R.; Sberna, P.M.; Luiten-Olieman, M.W.; Rietveld, L.C.; Heijman, S.G. Highly permeable silicon carbide-alumina ultrafiltration membranes for oil-in-water filtration produced with low-pressure chemical vapor deposition. Separation and Purification Technology 2020, 253, 117496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Liang, H.; Chuah, C.J.; Bao, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Snyder, S.A. Insight into Fe (II)/UV/chlorine pretreatment for reducing ultrafiltration (UF) membrane fouling: Effects of different natural organic fractions and comparison with coagulation. Water research 2019, 167, 115112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmaleh, S.; Abdelmoumni, L. Cross-flow filtration of an anaerobic methanogenic suspension. Journal of Membrane Science 1997, 131, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Chen, X.; Yumminaga, Y.; Wang, N.; Yan, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Shi, J. Effect of operating conditions on the performance of multichannel ceramic ultrafiltration membranes for cattle wastewater treatment. Journal of Water Process Engineering 2021, 41, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, K.; Muro, C.; Ortega, R.E.; Velazquez, S.; Riera, F. Water recovery by treatment of food industry wastewater using membrane processes. Environmental technology 2021, 42, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA, Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. APHA, American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rupani, P.F.; Singh, R.P.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Esa, N. Review of current palm oil mill effluent (POME) treatment methods: Vermicomposting as a sustainable practice. World Applied Sciences Journal 2010, 11, 70–81. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Ismail, S.; Bhatia, S. Water recycling from palm oil mill effluent (POME) using membrane technology. Desalination 2003, 157, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okogbenin, O.; Anisiobi, G.; Okogbenin, E.; Okunwaye, T.; Ojieabu, A. Microbiological assessment and physiochemical parameters of palm oil mill effluent collected in a local mill in Ovia North East area of Edo State, Nigeria. Herald Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 2014, 1, 001–009. [Google Scholar]
- Kanani, D.M.; Sun, X.; Ghosh, R. Reversible and irreversible membrane fouling during in-line microfiltration of concentrated protein solutions. Journal of Membrane Science 2008, 315, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennani, C.F.; Ousji, B.; Ennigrou, D.J. Reclamation of dairy wastewater using ultrafiltration process. Desalination and Water Treatment 2015, 55, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoluzzi, A.C.; Faitão, J.A.; Di Luccio, M.; Dallago, R.M.; Steffens, J.; Zabot, G.L.; Tres, M.V. Dairy wastewater treatment using integrated membrane systems. Journal of environmental chemical engineering 2017, 5, 4819–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Gu, H.; Xiao, K.; Qu, F.; Yu, H.; Wei, C. Fouling mechanisms analysis via combined fouling models for surface water ultrafiltration process. Membranes 2020, 10, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Chang, H.; Liu, B.; He, Q.; Xiong, B.; Kumar, M.; Zydney, A.L. A combined ultrafiltration–reverse osmosis process for external reuse of Weiyuan shale gas flowback and produced water. Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology 2018, 4, 942–955. [Google Scholar]
- Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S.; Din, M.F.M.; Rezania, S.; Khademi, T.; Kumar, A. Palm oil mill effluent as an environmental pollutant. Palm oil 2018, 13, 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Azmi, N.S.; Yunos, K.F.M.; Baharuddin, A.S.; Dom, Z.M. The effect of operating parameters on ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis of palm oil mill effluent for reclamation and reuse of water. BioResources 2013, 8, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Miller, D.J.; Kasemset, S.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B.D. The effect of permeate flux on membrane fouling during microfiltration of oily water. Journal of membrane science 2017, 525, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoller, M.; Ochando-Pulido, J.M. About merging threshold and critical flux concepts into a single one: The boundary flux. The Scientific World Journal 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Luo, J.; Guo, S.; Hang, X.; Chen, X.; Wan, Y. Threshold flux in concentration mode: Fouling control during clarification of molasses by ultrafiltration. Journal of Membrane Science 2019, 586, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Wee, C.; Benjamin, M.M. Fouling mechanisms in low-pressure membrane filtration in the presence of an adsorbent cake layer. Journal of Membrane Science 2013, 433, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Kim, Y.; Jin, Y.; Hong, S.; Park, C. Comparison of filtration and treatment performance between polymeric and ceramic membranes in anaerobic membrane bioreactor treatment of domestic wastewater. Separation and Purification Technology 2018, 199, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, C.; Yang, F. Improvement of antifouling performances for modified PVDF ultrafiltration membrane with hydrophilic cellulose nanocrystal. Applied Surface Science 2018, 440, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ognier, S.; Wisniewski, C.; Grasmick, A. Membrane bioreactor fouling in sub-critical filtration conditions: A local critical flux concept. Journal of membrane Science 2004, 229, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereli, R.K.; Heffernan, B.; Grelot, A.; van der Zee, F.P.; van Lier, J.B. Influence of high lipid containing wastewater on filtration performance and fouling in AnMBRs operated at different solids retention times. Separation and Purification Technology 2015, 139, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PVDF membrane | α-Al2O3 membrane | |
| Inner diameter (mm) | 5.2 | 7.0 |
| Pore size (nm)a | 30 | 70 |
| Length (mm) | 640.0 | 600.0 |
| Cross-sectional area (m2) | 21.2×10-6 | 38.5×10-6 |
| Membrane surface area (m2) | 1.05×10-2 | 1.3×10-2 |
| Maximum TMPb (kPa) | 500.0 | 800.0 |
| MWCOc (kDa) | 300.0 | 500.0 |
| Operating pH range | 2-10 | 2-12 |
| Iso Electric Point | 3-4 [53] | 8.6–9.8 [54] |
| InitialPermeabilitya,d (LMH·bar) | ≥ 750 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





