Submitted:
09 October 2025
Posted:
14 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
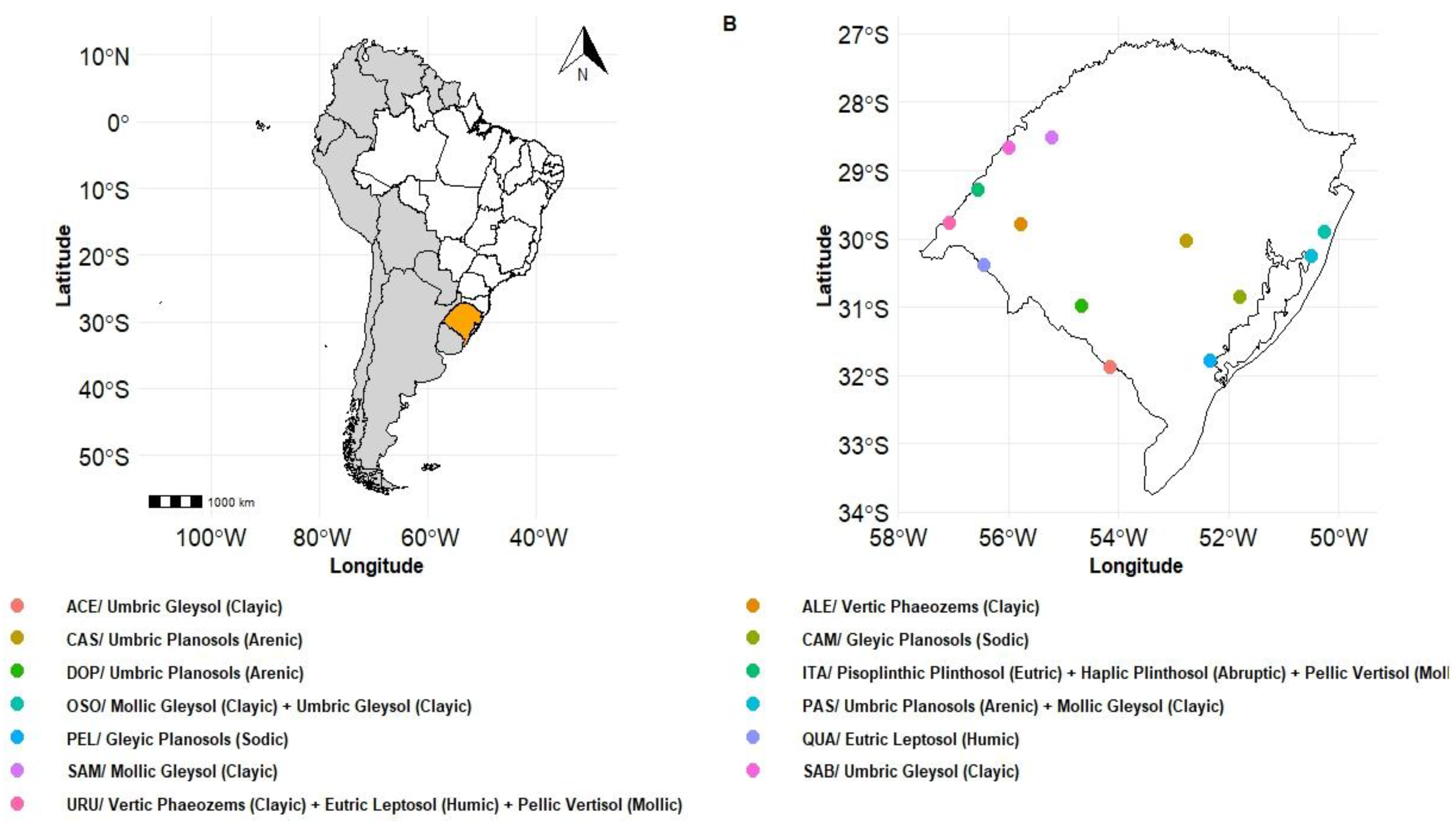
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Soil Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
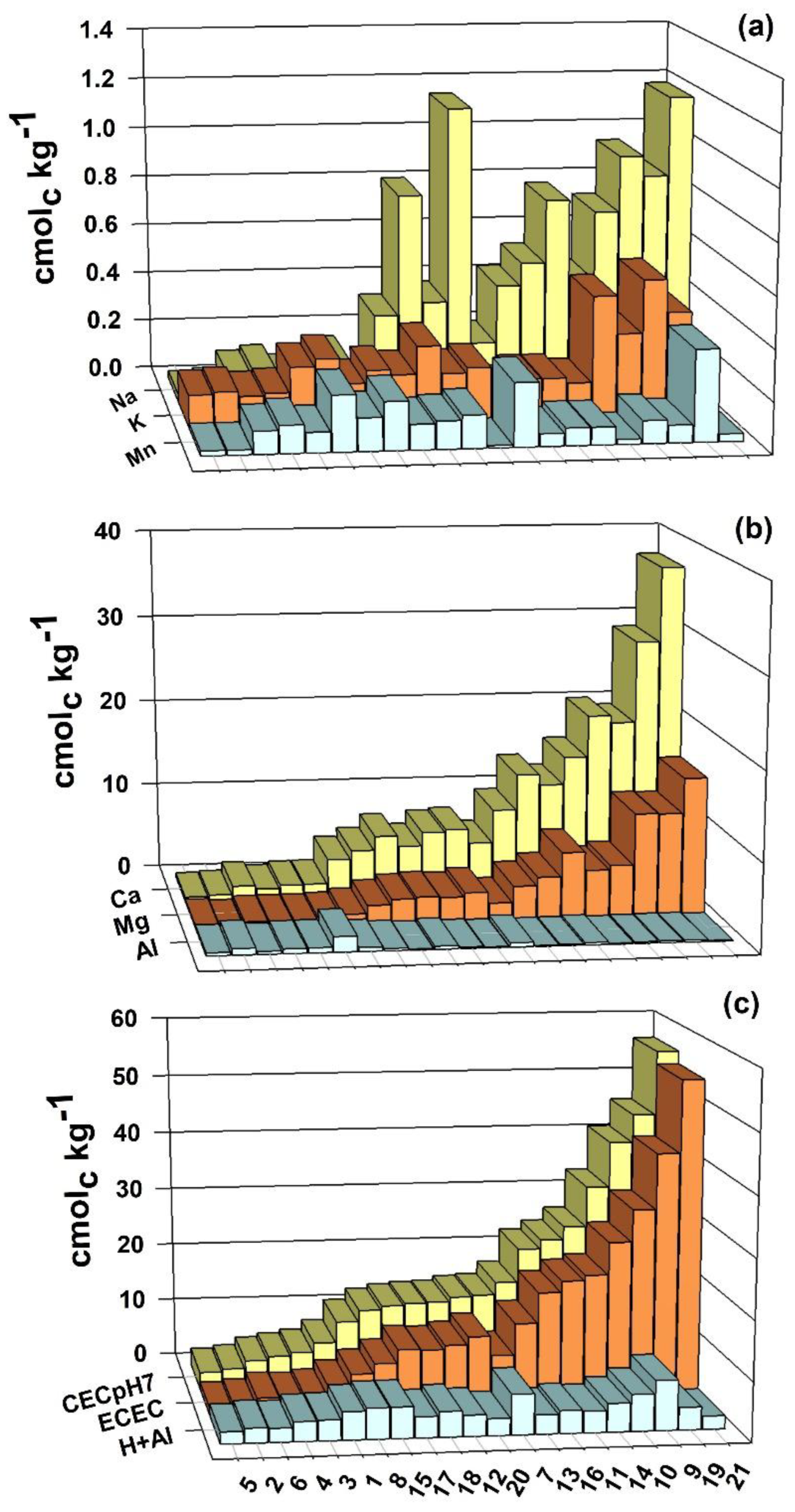
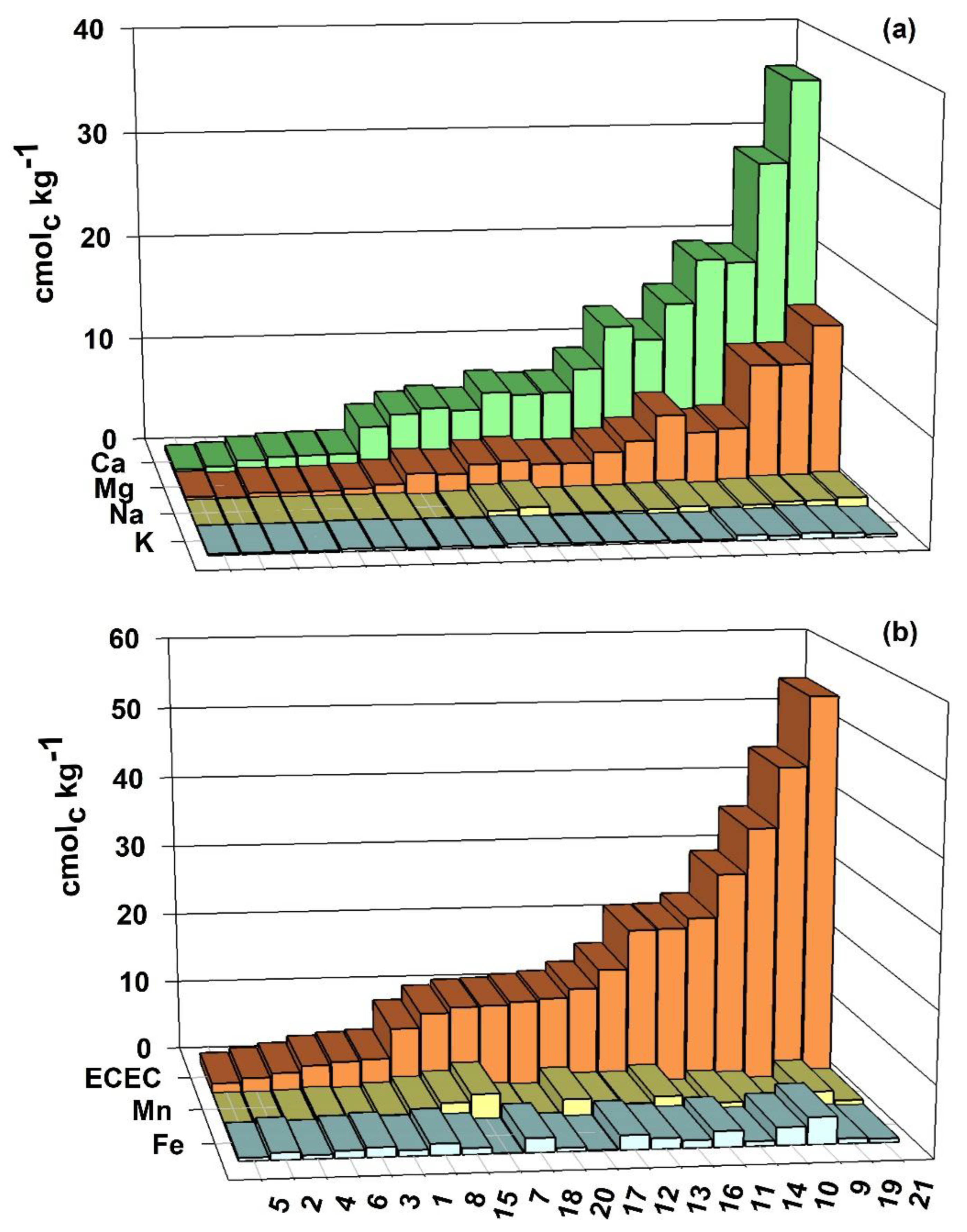
3.2. Exchangeable Cation Contents, ECEC and CEC at pH 7.0
3.3. CEC and Fe2+ Estimates
4. Discussion
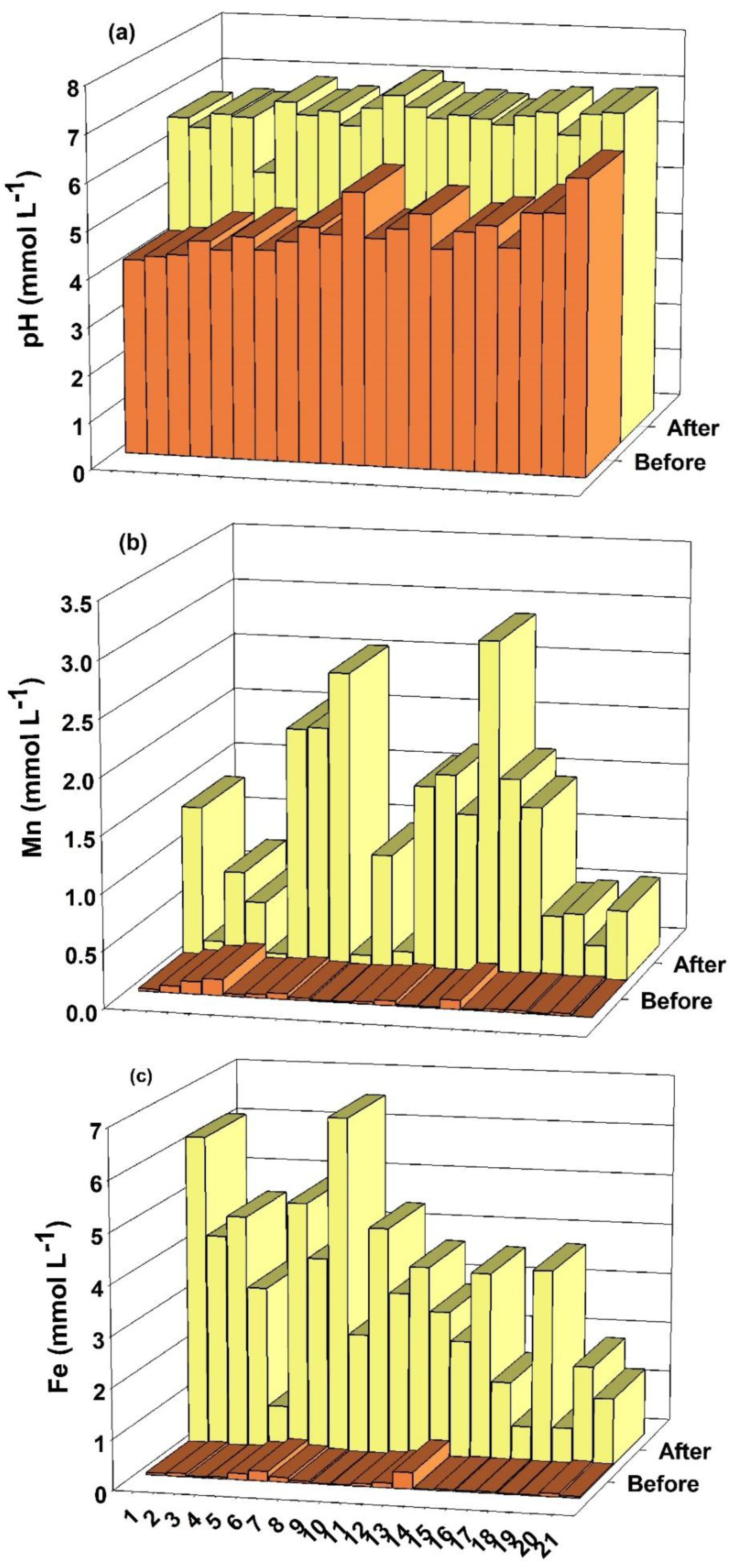
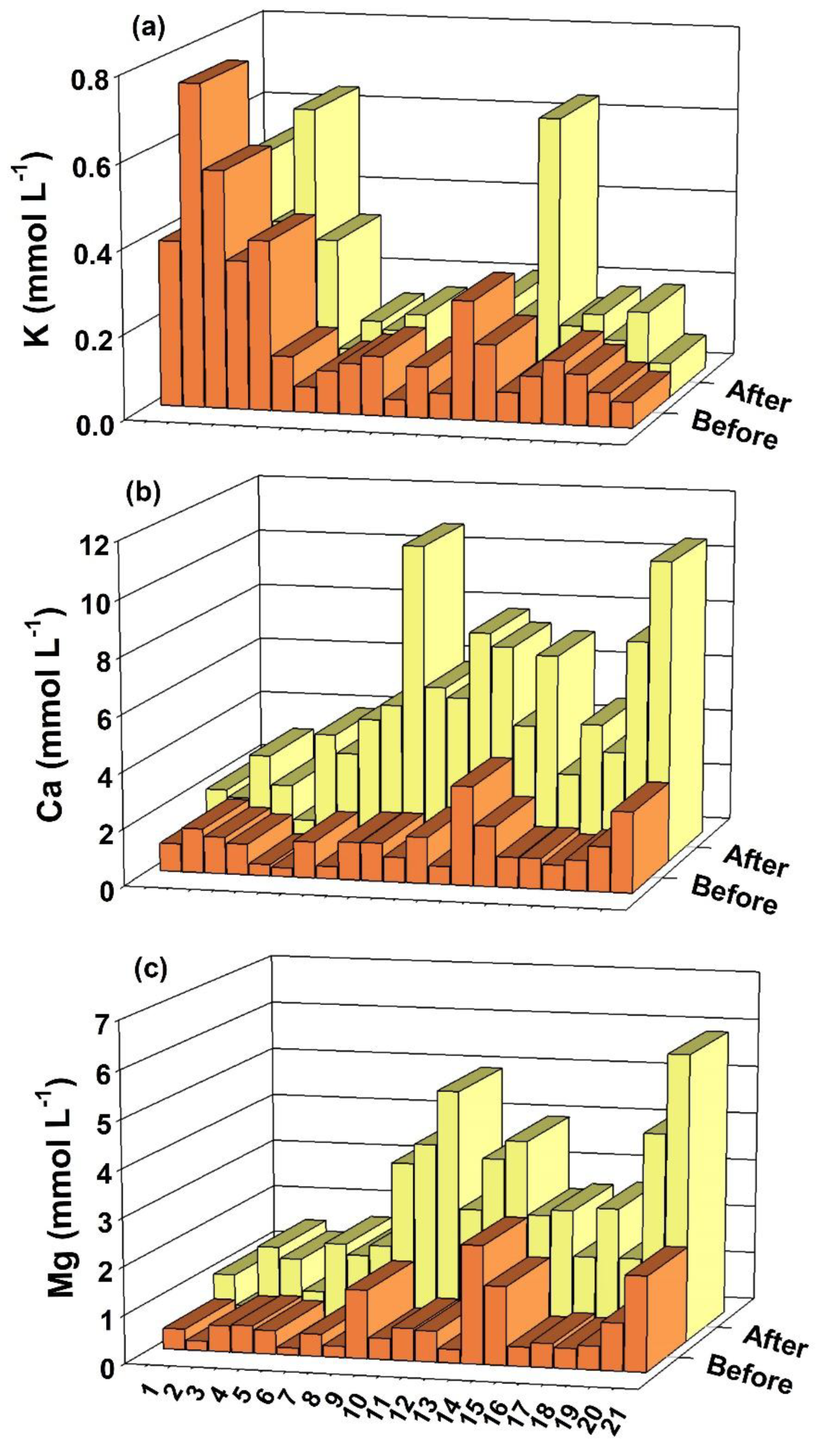
4.1. pH, Mn, Fe, K, Ca and Mg in Soil Solution
4.2. Exchangeable Cation Contents, ECEC and CEC at pH 7.0
4.3. CEC and Fe2+ Estimate
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CEC | Cation Exchange Capacity |
| ECEC | Effective Cation Exchange Capacity |
References
- SOSBAI. (2022). Arroz Irrigado - Recomendações técnicas da pesquisa para o Sul do Brasil. In Sociedade Sul brasileira de arroz irrigado.
- Sousa, R. O. de, Carlos, F. S., Silva, L. S. da, Scivittaro, W. B., Ribeiro, P. L., & Lima, C. L. R. de. (2021). No-tillage for flooded rice in Brazilian subtropical paddy fields: history, challenges, advances and perspectives. Revista Brasileira de Ciência Do Solo, 45. [CrossRef]
- Freitas, A. S. de, Carlos, F. S., Martins, G. L., Monteiro, G. G. T. N., & Roesch, L. F. W. (2024). Bacterial Resilience and Community Shifts Under 11 Draining-Flooding Cycles in Rice Soils. Microbial Ecology, 87(1), 149. [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R. O. de; Bohnen, H.; Meurer, E. J. Composição da solução de um solo alagado conforme a profundidade e o tempo de alagamento, utilizando novo método de coleta. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, [S.L.], v. 26, n. 2, p. 343-348, jun. 2002. FapUNIFESP (SciELO). [CrossRef]
- Carmona, F. de C., Adamski, J. M., Wairich, A., Carvalho, J. B., Lima, G. G., Anghinoni, I., Jaeger, I. R., Silva, P. R. F., Terra, T. de F., Fett, J. P., & Carlos, F. S. (2021). Tolerance mechanisms and irrigation management to reduce iron stress in irrigated rice. Plant and Soil, 469(1–2), 173–191. [CrossRef]
- Suriyagoda, L. D. B., Sirisena, D. N., Somaweera, K. A. T. N., Dissanayake, A., De Costa, W. A. J. M., & Lambers, H. (2017). Incorporation of dolomite reduces iron toxicity, enhances growth and yield, and improves phosphorus and potassium nutrition in lowland rice (Oryza sativa L). Plant and Soil, 410(1–2), 299–312. [CrossRef]
- Sparrow, L. A., Uren, N. C. (2014). Manganese oxidation and reduction in soils: effects of temperature, water potential, pH and their interactions. Soil Research, 52(5), 483–494. [CrossRef]
- Nel, T., Bruneel, Y., & Smolders, E. (2023). Comparison of five methods to determine the cation exchange capacity of soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 186(3), 311–320. [CrossRef]
- Martins, A. P., Denardin, L. G. de O., Tiecher, T., Borin, J. B. M., Schaidhauer, W., Anghinoni, I., Carvalho, P. C. de F., & Kumar, S. (2020). Nine-year impact of grazing management on soil acidity and aluminum speciation and fractionation in a long-term no-till integrated crop-livestock system in the subtropics. Geoderma, 359, 113986. [CrossRef]
- Barrow, N. J., & Hartemink, A. E. (2023). The effects of pH on nutrient availability depend on both soils and plants. Plant and Soil, 487(1–2), 21–37. [CrossRef]
- Borin, J. B. M., Carmona, F. de C., Anghinoni, I., Martins, A. P., Jaeger, I. R., Marcolin, E., Hernandes, G. C., & Camargo, E. S. (2016). Soil solution chemical attributes, rice response and water use efficiency under different flood irrigation management methods. Agricultural Water Management, 176, 9–17. [CrossRef]
- Carlos, F. S., Denardin, L. G. de O., Martins, A. P., Anghinoni, I., Carvalho, P. C. F., Rossi, I., Buchain, M. P., Cereza, T., Carmona, F. C., & Camargo, F. A. de O. C. (2020). Integrated crop–livestock systems in lowlands increase the availability of nutrients to irrigated rice. Land Degradation & Development, 31(18), 2962–2972. [CrossRef]
- Holzschuh, M. J., Carlos, F. S., Carmona, F. C., Bohnen, H., & Anghinoni, I. (2014). Iron oxidation on the surface of adventitious roots and its relation to aerenchyma formation in rice genotypes | Oxidação do Fe na superfície de raízes adventícias e sua relação com a formação de aerênquima em genótipos de arroz. Revista Brasileira de Ciencia Do Solo, 38(1). [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F., Fortes, M. de Á., Wesz, J., Buss, G. L., & Sousa, R. O. de. (2013). The impact of water management on iron toxicity in flooded rice. Revista Brasileira de Ciência Do Solo, 37(5), 1226–1235. https://doi.org/. [CrossRef]
- Sahrawat, K.L. (2004) Iron Toxicity in Wetland Rice and the Role of Other Nutrients. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 27, 1471-1504. [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H., Ahmed, S. F., Santiago-Arenas, R., Himanshu, S. K., Mansour, E., Cha-um, S., & Datta, A. (2023). Tolerance mechanism and management concepts of iron toxicity in rice: A critical review. Advances in Agronomy, 177, 215–257. [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. (2022). World reference base for soil resources. International soil classification system for naming soils and creating legends for soil maps ( 4th ed.). International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS). https://www3.ls.tum.de/boku/?id=1419.
- Tedesco, M., Gianello, C., Bissani, C., Bohnen, H., & Volkwiess, S. (1995). Análises de solo, plantas e outros materiais (2nd ed.).
- Ding, C., Du, S., Ma, Y., Li, X., Zhang, T., & Wang, X. (2019). Changes in the pH of paddy soils after flooding and drainage: Modeling and validation. Geoderma, 337, 511–513. [CrossRef]
- Ponnamperuma, F. N. (1972). The Chemistry of Submerged Soils. Advances in Agronomy, 24(C), 29–96. [CrossRef]
- Saeki, K.; Wada, S.; Shibata, M. Ca2+-Fe2+ and Ca2+-Mn2+ exchange selectivity of kaolinite, montmorillonite, and ilite. Soil Science 169(2):p 125-132, February 2004. [CrossRef]
- Orucoglu, E., Grangeon, S., Gloter, A., Robinet, J. C., Madé, B., & Tournassat, C. (2022). Competitive Adsorption Processes at Clay Mineral Surfaces: A Coupled Experimental and Modeling Approach. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 6(1), 144–159. [CrossRef]
- Silva, L. S., Ranno, S, K., Rhoden, A. C., Santos, D. R., Graupe, F. A. Avaliação de métodos para estimativa da disponibilidade de fósforo para arroz em solos de Várzea do Rio Grande do Sul. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, v. 32, p. 207-216, 2008. [CrossRef]
- REIS, Cecília Estima Sacramento dos. Caracterização química e disponibilidade de enxofre em solos de várzea do Rio Grande do Sul. Orientador: Rogério Oliveira de Sousa. Dissertação (Mestrado em Agronomia) - Faculdade de Agronomia Eliseu Maciel, Pelotas-RS, 2008. p. 88.
- Streck, E. V., Kampf, N., Dalmolin, R. S. D., Klamt, E., Nascimento, P. C. do, Schneider, P., Giasson, E., Pinto, L. F. S. (2008). Solos do Rio Grande do Sul (2nd ed.).
| ID No. | County | Classification (WRB) | Organic C (g kg-1) |
CECpH7 (cmolc kg-1) |
| 1 | Cachoeira do Sul | Umbric Planosols (Arenic) | 9.2 | 7.59 |
| 2 | Dom Pedrito | Umbric Planosols (Arenic) | 8.2 | 3.44 |
| 3 | Camaquã | Gleyic Planosols (Sodic) | 11.4 | 5.98 |
| 4 | Pelotas | Gleyic Planosols (Sodic) | 12.9 | 5.42 |
| 5 | Palmares do Sul | Umbric Planosols (Arenic) | 7.7 | 2.93 |
| 6 | Itaqui | Pisoplinthic Plinthosol (Eutric) | 10.9 | 4.77 |
| 7 | Itaqui | Haplic Plinthosol (Abruptic) | 20.0 | 15.24 |
| 8 | Itaqui | Haplic Plinthosol (Abruptic) | 19.5 | 11.15 |
| 9 | Osório | Mollic Gleysol (Clayic) | 24.5 | 41.23 |
| 10 | Alegrete | Vertic Phaeozems (Clayic) | 17.3 | 33.62 |
| 11 | Osório | Umbric Gleysol (Clayic) | 18.2 | 24.63 |
| 12 | Uruguaiana | Vertic Phaeozems (Clayic) | 46.8 | 14.26 |
| 13 | Uruguaiana | Vertic Phaeozems (Clayic) | 19.2 | 17.37 |
| 14 | Quaraí | Eutric Leptosol (Humic) | 18.8 | 26.84 |
| 15 | Uruguaiana | Eutric Leptosol (Humic) | 11.8 | 13.07 |
| 16 | Uruguaiana | Pellic Vertisol (Mollic) | 18.2 | 23.10 |
| 17 | Itaqui | Vertic Phaeozems (Clayic) | 11.5 | 13.75 |
| 18 | Aceguá | Umbric Gleysol (Clayic) | 26.4 | 14.08 |
| 19 | São Borja | Umbric Gleysol (Clayic) | 39.1 | 45.87 |
| 20 | Palmares do Sul | Mollic Gleysol (Clayic) | 32.3 | 14.98 |
| 21 | Santo Antônio das Missões | Mollic Gleysol (Clayic) | 29.4 | 56.54 |
| ID No | ECECanalysed | ECEC estimated | Fe2+analysed | Fe2+ estimated |
| --------------------------- cmolc kg-1 ------------------------------- | ||||
| 1 | 4.25 | 7.12 | 0.81 | 3.68 |
| 2 | 1.97 | 3.03 | 1.00 | 2.06 |
| 3 | 3.98 | 5.61 | 1.33 | 2.96 |
| 4 | 2.59 | 4.96 | 0.53 | 2.90 |
| 5 | 1.34 | 1.93 | 0.43 | 1.02 |
| 6 | 3.54 | 4.75 | 1.00 | 2.21 |
| 7 | 11.39 | 14.49 | 0.04 | 3.14 |
| 8 | 8.55 | 10.76 | 1.58 | 3.79 |
| 9 | 35.88 | 39.26 | 3.76 | 7.14 |
| 10 | 29.52 | 33.34 | 2.49 | 6.31 |
| 11 | 21.94 | 25.14 | 2.19 | 5.39 |
| 12 | 13.64 | 14.21 | 2.02 | 2.59 |
| 13 | 16.27 | 16.96 | 1.46 | 2.15 |
| 14 | 23.37 | 26.36 | 0.65 | 3.64 |
| 15 | 10.61 | 12.57 | 0.86 | 2.82 |
| 16 | 21.83 | 22.46 | 1.06 | 1.69 |
| 17 | 12.36 | 13.52 | 0.10 | 1.26 |
| 18 | 11.54 | 14.01 | 1.98 | 4.45 |
| 19 | 44.41 | 44.70 | 0.70 | 0.99 |
| 20 | 11.98 | 14.91 | 0.54 | 3.47 |
| 21 | 54.25 | 56.57 | 0.52 | 2.84 |
| Cations | Relative ratios | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil solution | ECEC | Estimated ECEC | |
| K | 0.02A | 0.03A | 0.02A |
| Na | 0.15A | 0.03B | 0.02B |
| Ca | 0.34C | 0.51A | 0.43B |
| Mg | 0.17A | 0.20A | 0.17A |
| Fe | 0.24A | 0.14B | 0.28A |
| Mn | 0.08A | 0.10A | 0.08A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





