Introduction
Oxygen saturation is the percentage level of oxygen that can be bound by hemoglobin (Mathar, 2018). It is important to know the condition of the body's health by looking at the amount of oxygen supply bound by the blood, patients who experience hypoxia are characterized by a lack of oxygen in the blood which causes the oxygen saturation value to decrease and other signs that can be seen if the patient is hypoxic are shortness of breath, tend to breathe. faster and faster heart rate (Asmadi, 2012). Multi-organ disorders involving disorders of the respiratory organs are usually experienced by critically ill patients (Sundana, 2018).
Data from the World Health Organization (WHO) 2016, critical patients in the ICU increase every year. There are around 9.8%-24.6% of critically ill patients treated in the ICU per 100,000 population, and deaths from critical to chronic illnesses in the world have increased by 1.1-7.4 million people. According to data from the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia in 2020, 94% of patients treated in the ICU room were available from the 16 beds available at the Riau Provincial Hospital (Kemenkes, 2021).
Decreased oxygen saturation can be caused due to respiratory failure, decreased consciousness and even fall into a coma to be one of the causes of patients experiencing multi-organ failure and requiring patients to be treated in the ICU (Dewi et al, 2020). Excessive accumulation of secretions can cause respiratory failure or decreased consciousness so that it can cause a decrease in oxygen saturation levels (Dewi et al, 2020). Signs and symptoms of a decrease in oxygen saturation are oxygen saturation levels <90%, patients experience respiratory distress such as difficulty breathing, faster breathing rate of 35x/minute, decreased level of consciousness, cyanosis, fast and shallow pulse (Hidayati et al, 2020) .
Critical patients who are treated in intensive care rooms experience airway obstruction due to excessive accumulation of secretions (Dewi et al, 2020). Things that can be done to free the airway, prevent infection in the lungs and reduce the buildup of secretions are by taking suction (Asmadi, 2012). Interventions that are often given to critically ill patients who experience excessive accumulation of secretions are by providing suction (Asmadi, 2012). Research conducted by (Kitong et al., 2014) showed that after the action suction there was a change in oxygen saturation levels. Research conducted by (Syahran et al., 2019) also showed changes before and after suctioning where the patient's oxygen saturation level changed. So it can be concluded that suction can affect oxygen saturation levels in patients who have problems with the patient's airway. Based on the phenomena and background of the problem above, the researcher is interested in analyzing the effect of action suction on oxygen saturation in patients in the ICU based on a literature review.
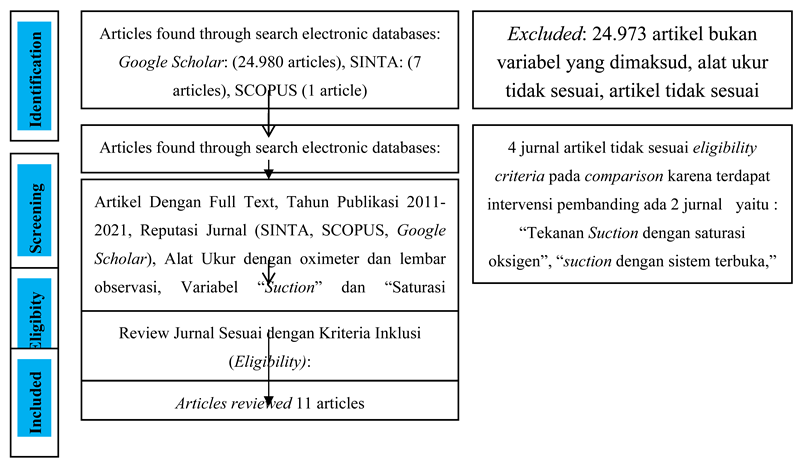
Material and Methods
The design used in this study is a literature review using a search string with the keywords: "oxygen saturation, suctioning mucus" "oxygen saturation, suction". Researchers identified data through the PICO approach (Population, Intervention, compare, and outcome) which had been adjusted for the purpose of identifying oxygen saturation in patients in the ICU based on a literature review and analyzing the effect of suction on oxygen saturation in patients in the ICU based on a literature review.. The research journals used are published in the last 10 years from 2011 to 2021. The online database source comes from Indonesian or English. The number of journal references in this literature review is 11 journals consisting of abstracts and full text indexed by SCOPUS, SINTA, Google Scholar, with articles in Indonesian and English. Researchers conducted a review research in journals using the characteristics of respondents aged 12 years and over, male and female, and all patients in the ICU, research quasi-experimental design, experiment,with a pre-post test design with a sampling technique that is total sampling, purposive sampling, consecutive sampling, accidental sampling, and quota sampling and using analytical t test, paired t test, Wilcoxon, paired sample t test, and independent t test. The measuring instruments used were observation sheets, pulse oximeters and questionnaires. The outcome measured was a change in the oxygen saturation value.
In research using this literature, researchers will only focus on discussing the effect of action
suction and oxygen saturation. It does not discuss other influences that cause changes in oxygen saturation that occur in patients and researchers determine the purpose of the study before conducting the research analysis in identifying oxygen saturation values and analyzing the effect of action
suction on oxygen saturation in patients in the ICU in each of the 11 literature reviews that are expected will produce the same results according to the research methodology carried out.
Table 1.
Analisis PICO (Population, Intervention, compare, dan outcome).
Table 1.
Analisis PICO (Population, Intervention, compare, dan outcome).
| Author |
Method |
Result |
| Sample size |
Measuring tools |
| Wanidi et al (2014) |
37 people |
Pulse oximetry and observation sheet |
|
| Sari & Ikbal(2019) |
30people |
Observation sheet |
|
| Zukhri et al (2018) |
20 people |
Pulse oximetry and observation sheet |
|
| Nizar & Haryati (2017) |
40 people |
Observation sheet |
1. Before:average 89,86 2. After: average91,65 |
| Syahran et al (2019) |
13 people |
Pulse oximetry |
|
| Septimar(2018) |
40 people |
Observation sheet |
|
| Karokaro & Hasrawi (2019) |
22 people |
Observation sheet |
|
| Kitu et al (2019) |
15 people |
Pulse oximetry and observation sheet |
|
| Kristiani et al (2020) |
35 people |
Pulse oximetry and observation sheet |
|
| Giakoumidakis et al (2011) |
103 people |
Kuisoner |
|
| Muhaji et al (2017) |
30 people |
Pulse oxymetry |
1. Before: average 95,60 at a pressure of 140 mmHg and an average of 94.73 at a pressure of 130 mmHg 2. after: averaged 98.07 at a pressure of 140 mmHg and averaged 95.87 at a pressure of 130 mmHg 3. Statistical test results p value 0.000 |
 |
Result
Results of Oxygen Saturation in Patients in the Room Based on Literature Review
Results from 11 journals obtained about oxygen saturation obtained There are 6 journals with the authors Wanidi et al (2014), Sari & Ikbal (2019), Nizar & Haryati (2017), Karokaro & Hasrawi (2019), Kitu et al (2019) and Muhaji et al (2017) revealed that the oxygen saturation value of patients in the ICU was poor or below normal, namely the saturation value pre-test ranged from 86.90 to 94.73. Furthermore, 6 journals with the authors Sari & Ikbal (2019), Zukhri et al (2018), Syahran et al (2019), Septimar (2018), Giakoumidakis et al (2011) and Muhaji et al (2017) revealed in their journals that the oxygen saturation of patients was pre-test good, namely the oxygen saturation value pre-test ranged from 95.60 to 99.48. Then 1 journal with the author Kristen et al (2020) in his journal did not disclose in the journal the oxygen saturation value pretest and patients using a ventilator in the ICU room were good or bad, only explaining that there was a change in the oxygen saturation value. There are 4 journals with the authors Zukhri et al (2018), Syahran et al (2019), Karokaro & Hasrawi (2019), and Kitu et al (2019) in the journals of respondents using ventilators and oxygen saturation values of pre-test at least 79 and the highest being 100.
The Results of the Effect of the Action of Suction on Oxygen Saturation in a Patient in the ICU is Based on Literature Review
Based on the synthesis of value measurement of oxygen saturation in patients di ruang ICU of 11 journals all imply any change subsequent to the action of suction written by Wanidi et al (2014), Syahran et al (2019), Kristen et al (2020), Sari & Ikbal (2019), Muhaji et al (2017), Zukhri et al (2018), Giakoumidakis et al (2011), Nizar & Haryati (2017), Karokaro & Hasrawi ( 2019), Septimar (2018) and (Kitu et al., 2019) in the journal using the p statistical test obtained a p value of 0.000 (p <0.05).
Discussion
Identifying Oxygen Saturation in Patients in the ICU Based on Literature Review
Based on facts from 11 journals, normal and poor oxygen saturation values were used. There are 6 journals with normal saturation values with values from 95.60 to 99.48 and poor saturation values ranging from 86.90 to 94.73. Oxygen saturation is the percentage of Hb in the blood related to oxygen in the arteries (Mathar, 2018). Normal oxygen saturation levels are 95%-100%, oxygen saturation values less than 95% indicate the patient is hypoxic (Wahid and Suprapto, 2013). Blood oxygen levels that are very low and require immediate treatment are characterized by oxygen saturation values <90%. The occurrence of other symptoms of respiratory distress can indicate low oxygen saturation (Idris et al., 2020). Factors that affect changes in oxygen saturation, namely hemoglobin, activity and suction (Zakiyah, 2015). Signs and symptoms of a decrease in oxygen saturation are oxygen saturation levels <90%, patients experience respiratory distress such as difficulty breathing, respiratory rate becomes faster 35 x/minute, decreased consciousness, cyanosis and fast and shallow pulse (Hidayati et al, 2020) . The measuring instrument used to measure oxygen saturation levels is an oximeter (pulse oximeter). Pulse oximeter or oximetry is a non-invasive method of continuous monitoring of hemoglobin oxygen saturation (SaO2). This examination is used to monitor patients for sudden changes or small changes in oxygen saturation (Wahid & Suprapto, 2013). The results of 11 journals obtained oxygen saturation values from 86.90 to 94.73 indicating poor or below normal oxygen saturation values, where the oxygen saturation value decreased which could be due to blockage in the respiratory tract due to excessive mucus buildup but the patient was unable to do so. releasing secretions that occur in patients treated in the ICU, so that the value of oxygen saturation in patients in the ICU decreases.
Analyzing the Effect of Action on Suction Oxygen Saturation in Patients in the ICU Based on the Literature Review
Results from 11 journals obtained, the administration of intervention suction proved effective on oxygen saturation in 11 journals (100%) as evidenced by changes after performed suctioning was on the results and statistical test of each research design used.action Suction needs to be carried out on patients who are unable to excrete their own secretions so that patients do not experience hypoxia, butaction suction has a relationship with changes in oxygen saturation values that occur in patients treated in the ICU so it is necessary to make observations made by nurses in the ICU. The value of oxygen saturation after action suction in patients in the ICU obtained a value of 91.65 to 98.50. Suction is an action to help patients who are unable to excrete excessive secretions which aims to maintain the airway so as to allow for an adequate gas exchange process (Timby, 2009 in Wagiran 2015). The Action is suction carried out by rotating the suction catheter for no more than 15 seconds (Gultom, 2020). The purpose of the action is suction to clean and maintain a clean airway to help meet the oxygen supply so that it remains fulfilled with an adequate airway, maintain a patent airway by maintaining a smooth airway and freeing the airway from accumulated secretions or mucus (Rakhman, 2014). . Changes in oxygen saturation, cardiac dysrhythmias, hypotension and increased intracranial pressure are the effects caused by suction in critical patients if it is not carried out with incorrect procedures (Gultom, 2020).
Based on the exposure of 11 journals were selected using a literature review their influence the action of suction on the value of the oxygen saturation in patients di ruang ICU, it is evidenced by the change in the value of oxygen saturation can be seen in the comparison of pre-test and post-test of the intervention group or the control group apart significant changes in oxygen saturation values and can be seen from the results of the observation sheet.management is Suction often performed on patients treated in the intensive care unit who have decreased consciousness and patients who are on an ETT ventilator. Based on the results of a recommended review of 11 journals used in critically ill patients with circulatory disorders to prevent hypoxia. The function of providing suction in patients with critical situations is to maintain the patient's airway due to the accumulation of excess secretions and the benefit is not only to help maintain the supply of incoming oxygen but also to help patients who experience decreased consciousness so as not to experience aspiration so that patients can help patients breathe easily. normal, although suction can make the oxygen saturation value decrease temporarily before giving hyperoxygenation but it is still done to improve the patient's critical condition. Then related to the duration of management suction according to the theory, which is <15 seconds, but in practice the 11 journals have different durations for each journal, this is due to adjusting the characteristics of respondents with varying conditions but this is not an obstacle for researchers in journals to see the effect of the action suction given, because the researchers in the 11 journals provided action suction gradually and regularly.
Conclusion
From the results of a literature review of 11 journals, it can be concluded that:
The results of the oxygen saturation value before and after the action suction changed with the average oxygen saturation value before the action suction 86.90-99.48 and the average oxygen saturation value after the action suction 91.65-98.30.
Based on the results of the literature review, it was found that there was an overall effect of action suction on the oxygen saturation value which changed in pre suction and post suction with a p value of 0.000 (p <0.05).
Suggestion
Nurses in the ICU are
Expected to carry out strict supervision in carrying out actions suction and the procedure suction must be carried out in accordance with the SOPs that are correctly applied in the hospital.
For Further Researchers Future
Researchers are expected to develop research by looking at the effect of action suction on oxygen saturation values that occur in patients treated in the ICU.
References
- Asmadi. (2012). Teknik Prosedural Keperawatan: Konsep dan Aplikasi Kebutuhan Dasar Klien. Salemba Medika.
- Dewi, A., Utomo, B., & Rachman, S. (2020). PANDUAN ASUHAN KEPERAWATAN (PAK) PADA PASIEN KRITIS DENGAN COVID-19. Airlangga University Press. https://books.google.co.id/books?id=ZVjwDwAAQBAJ.
- Giakoumidakis, K., Kostaki, Z., Patelarou, E., Baltopoulos, G., & Brokalaki, H. (2011). Oxygen saturation and secretion weight after endotracheal suctioning. British Journal of Nursing, 20(21), 1344–1351. [CrossRef]
- Gultom, N. (2020). Perbedaan Saturasi Oksigen Pada Pasien Kritis Yang Dipasang Endotracheal Tube Before Dan After Dilakukan Tindakan Suction Di Ruang ICU RSUP. H. Adam Malik Medan Tahun 2019.
- Hidayati, A. N., Akbar, M. I. A., & Rosyid, A. N. (2020). Gawat Darurat Medis dan Bedah. Airlangga University Press. https://books.google.co.id/books?id=4KmwDwAAQBAJ.
- Idris, D. N., Taviyanda, D., & Mahanani, S. (2020). Buku Ajar Keperawatan Gadar dan Kritis. Adjie Media Nusantara.
- Karokaro, T. M., & Hasrawi, L. (2019). PENGARUH TINDAKAN PENGHISAPAN LENDIR (SUCTION) ENDOTRACHEAL TUBE (ETT) TERHADAP KADAR SATURASI O2 PADA PASIEN GAGAL NAPAS DI RUANG ICU. JURNAL KEPERAWATAN DAN FISIOTERAPI (JKF), 2(1), 82–88. [CrossRef]
- Kitong, B. I., Mulyadi, N., & Malara, R. (2014). Pengaruh Tindakan Penghisapan Lendir Endotrakeal Tube (Ett) Terhadap Kadar Saturasi Oksigen Pada Pasien Yang Dirawat Di Ruang Icu Rsup Prof. Dr. Rd Kandou Manado. Jurnal Keperawatan, 2(2).
- Kitu, N. B., Rohana, N., & Widyaningsih, T. S. (2019). Pengaruh Tindakan Penghisapan Lendir Endotrakeal Tube (ETT) Terhadap Kadar Saturasi Oksigen Pada Pasien Yang Dirawat Di Ruang ICU. Jurnal Ners Widya Husada, 6 No 2, 57–64. http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:PS0JwGNsP9QJ:stikeswh.ac.id:8082/journal/index.php/jners/article/view/349&hl=id&gl=id&strip=0&vwsrc=0.
- Kristiani, A. H., Riani, S., & Supriyono, M. (2020). ANALISIS PERUBAHAN SATURASI OKSIGEN DAN FREKUENSI PERNAFASAN PADA PASIEN DENGAN VENTILATOR YANG DILAKUKAN SUCTION DIRUANG ICU RS MARDI RAHAYU KUDUS. Jurnal Perawat Indonesia, 4(3), 504–514. [CrossRef]
- Mathar, I. (2018). Manajemen Informasi Kesehatan: Pengelolaan Dokumen Rekam Medis. Deepublish. https://books.google.co.id/books?id=gCiADwAAQBAJ.
- Muhaji, M., Santoso, B., & Putrono, P. (2017). Comparison of the Effectiveness of Two Levels of Suction Pressure on Oxygen Saturation in Patients With Endotracheal Tube. Belitung Nursing Journal, 3(6), 693–696. [CrossRef]
- Nizar, A. M., & Haryati, D. S. (2017). Pengaruh Suction Terhadap Kadar Saturasi Oksigen Pada Pasien Koma Di Ruang ICU RSUD Dr. Moewardi Surakarta Tahun 2015. (JKG) Jurnal Keperawatan Global, 2(2), 62–69. [CrossRef]
- Rakhman, A. (2014). Buku Panduan Praktek Laboratorium Ketrampilan Dasar Dalam Keperawatan II (KDDK II. Deepublish. https://books.google.co.id/books?id=qGE6DAAAQBAJ.
- Sari, R. P., & Ikbal, R. N. (2019). Tindakan Suction dan Perubahan Saturasi Oksigen pada Pasien Penurunan Kesadaran Diruangan ICU Rumah Sakit. JIK (JURNAL ILMU KESEHATAN), 3(2), 85–90. [CrossRef]
- Septimar, Z. M. (2018). Pengaruh Tindakan Penghisapan Lendir (Suction) terhadap Perubahan Kadar Saturasi Oksigen pada Pasien kritis di ICU. Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan Masyarakat, 7(01), 10–14. [CrossRef]
- Sundana, K. (2018). VENTILATOR: Pendekatan Praktis Di Unit Perawatan Kritis Edisi Revisi 2018. cicu. https://books.google.co.id/books?id=j8L0AgAAQBAJ.
- Syahran, Y., Romadoni, S., & Imardiani, I. (2019). Pengaruh Tindakan Suction ETT terhadap Kadar Saturasi Oksigen pada Pasien Gagal Nafas di Ruang ICU dan IGD Rumah Sakit Umum Daerah Prabumulih Tahun 2017. Jurnal Berita Ilmu Keperawatan, 12(2), 84–90. [CrossRef]
- Wahid, A., & Suprapto, I. (2013). Keperawatan Medikal Bedah Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Gangguan Sistem Respirasi. Trans Info Media.
- Wanidi, S., Al Ummah, B., & Santoso, D. (2014). PENGARUH TINDAKAN ISAP LENDIR TERHADAP PERUBAHAN SATURASI O2 PADA PASIEN DENGAN PENURUNAN KESADARAN DI RUANG ICU RSUD WONOSOBO. Jurnal Ilmiah Kesehatan Keperawatan, 10(1).
- Zakiyah, A. (2015). Nyeri: konsep dan penatalaksanaan dalam praktik keperawatan berbasis bukti. Salemba Medika.
- Zukhri, S., Suciana, F., & Herianto, A. (2018). Pengaruh Isap Lendir (suction) Sistem Terbuka Terhadap Saturasi Oksigen Pada Pasien Terpasang Ventilator. MOTORIK Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan, 13(1), 40–54. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).






