Submitted:
10 April 2025
Posted:
11 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
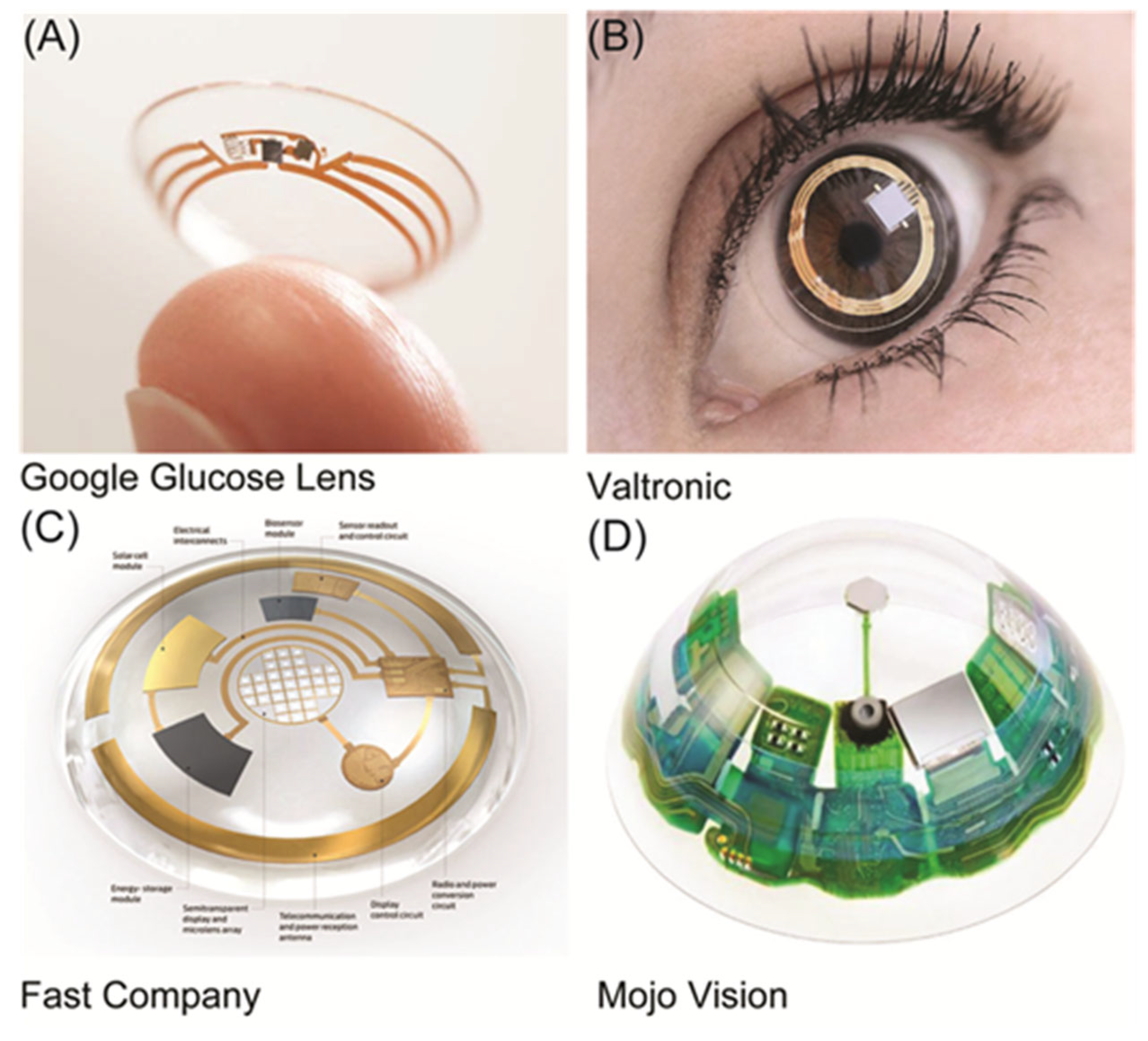
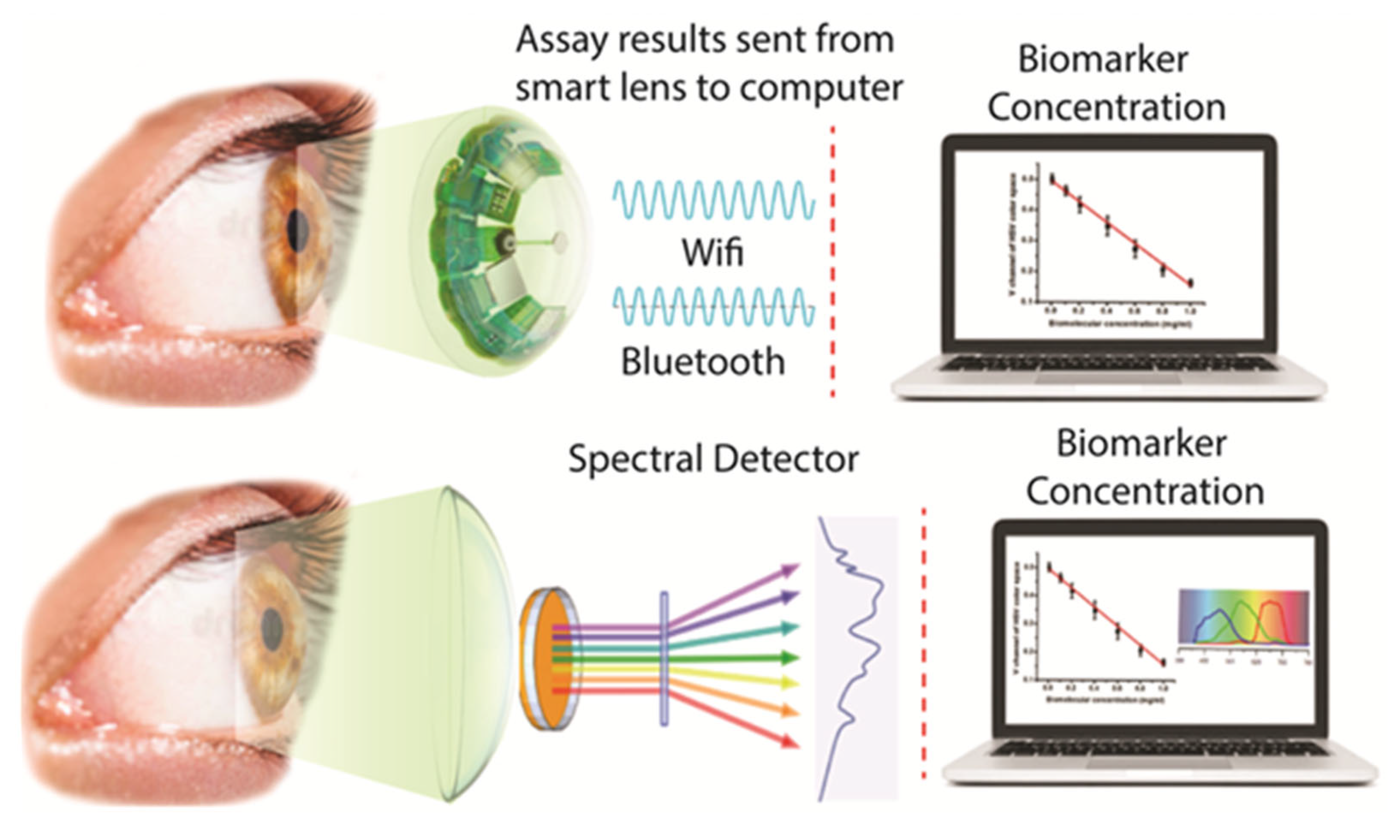
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Silicone Hydrogel (SiHG) Contact Lens
2.2. Fluorescence Measurements
3. Results
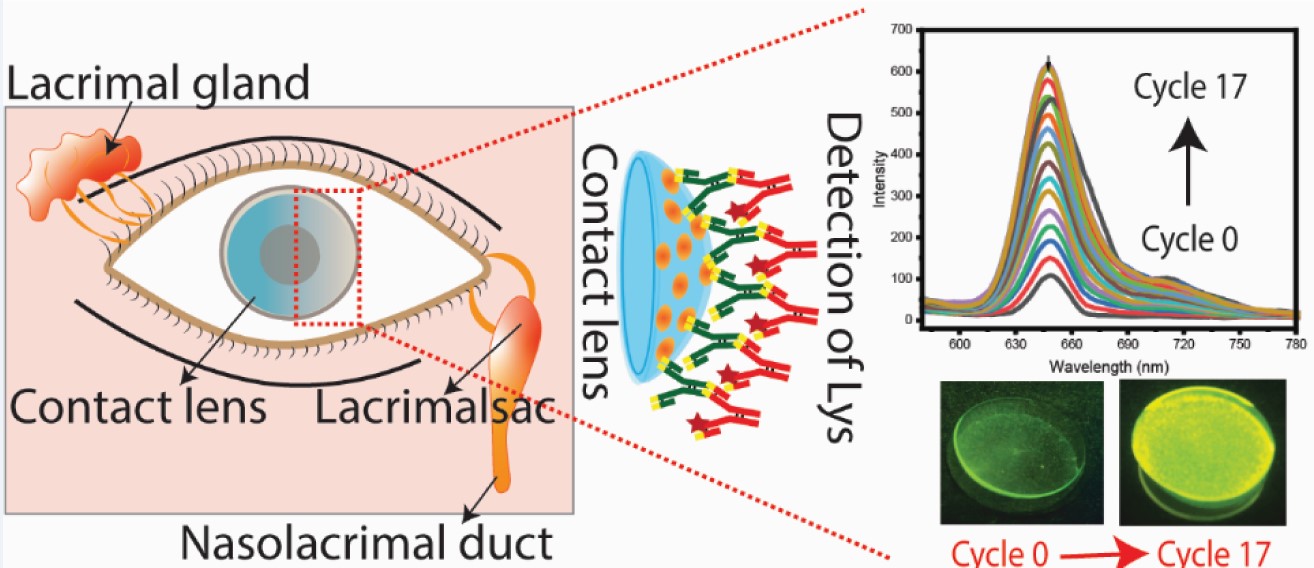
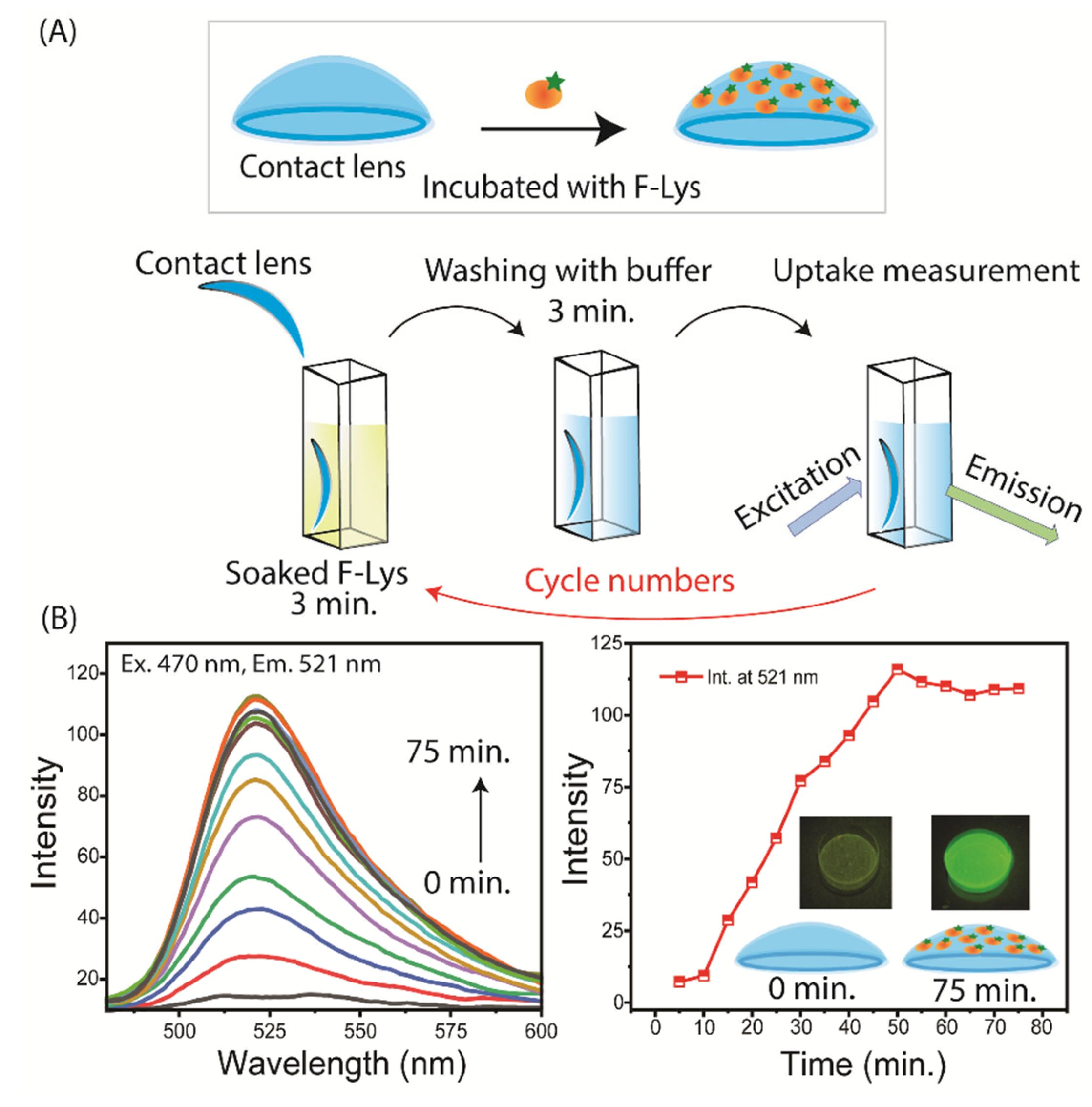
3.1. SiHG Lens Selection and Lysozyme Binding to Lenses
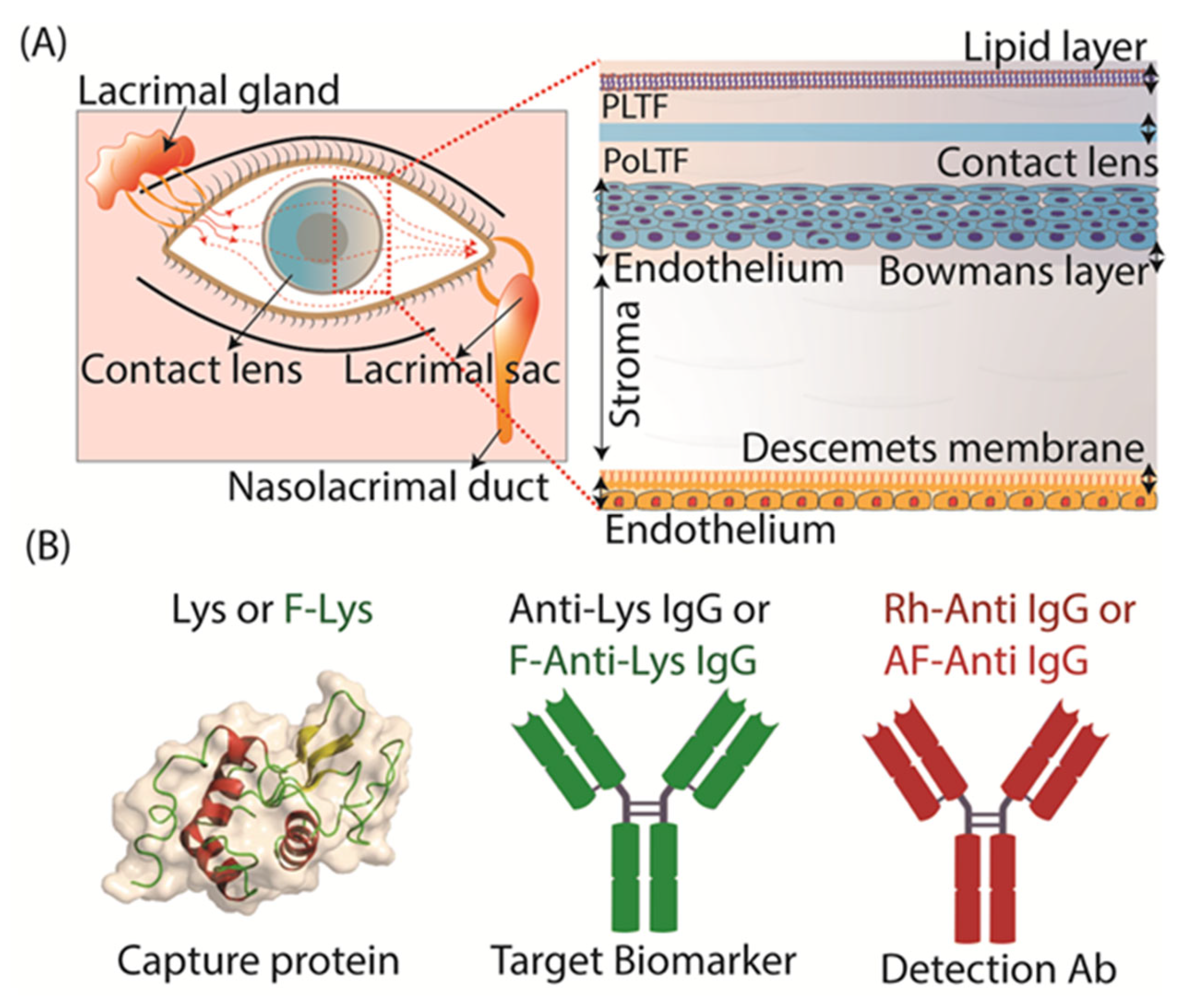
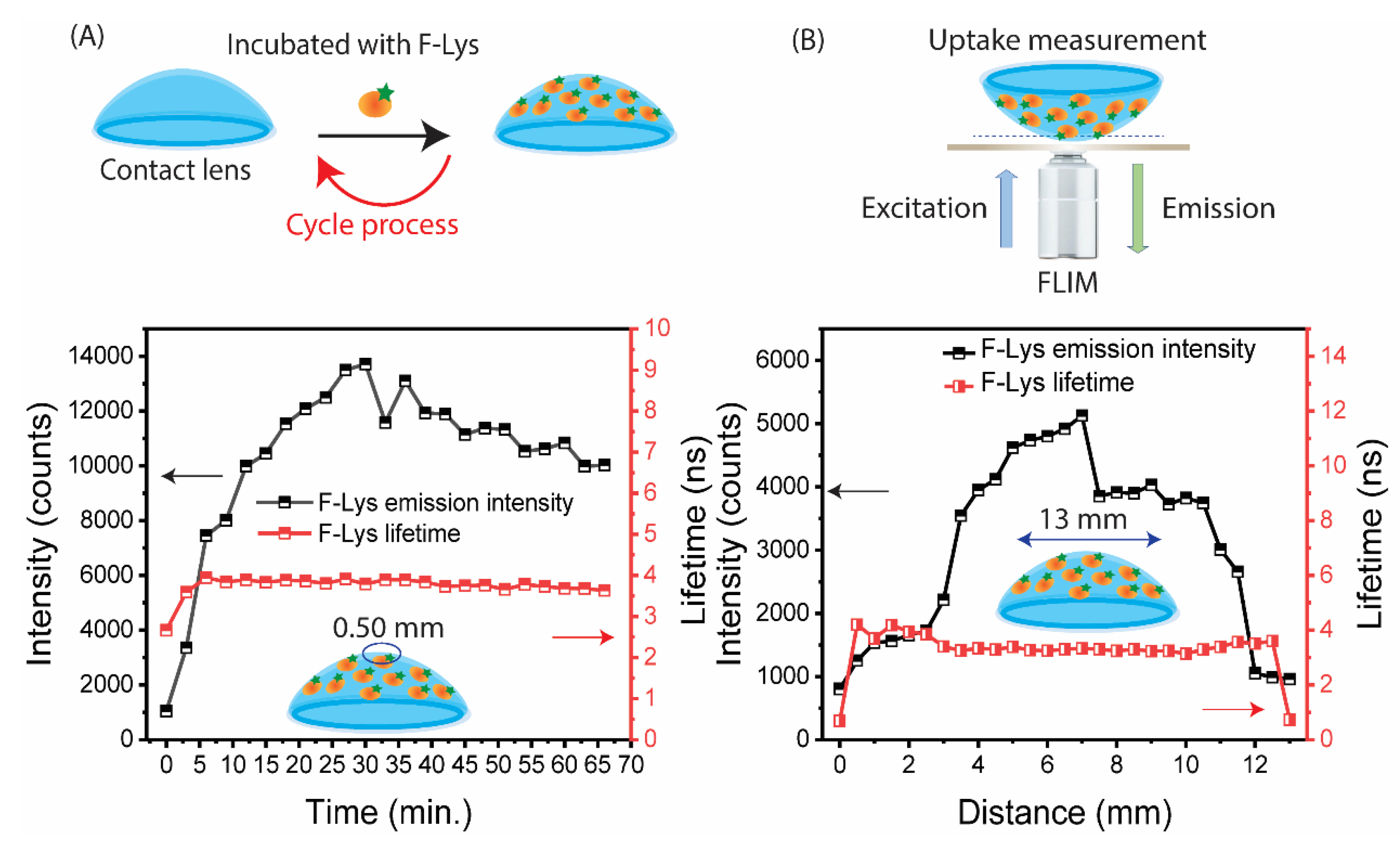
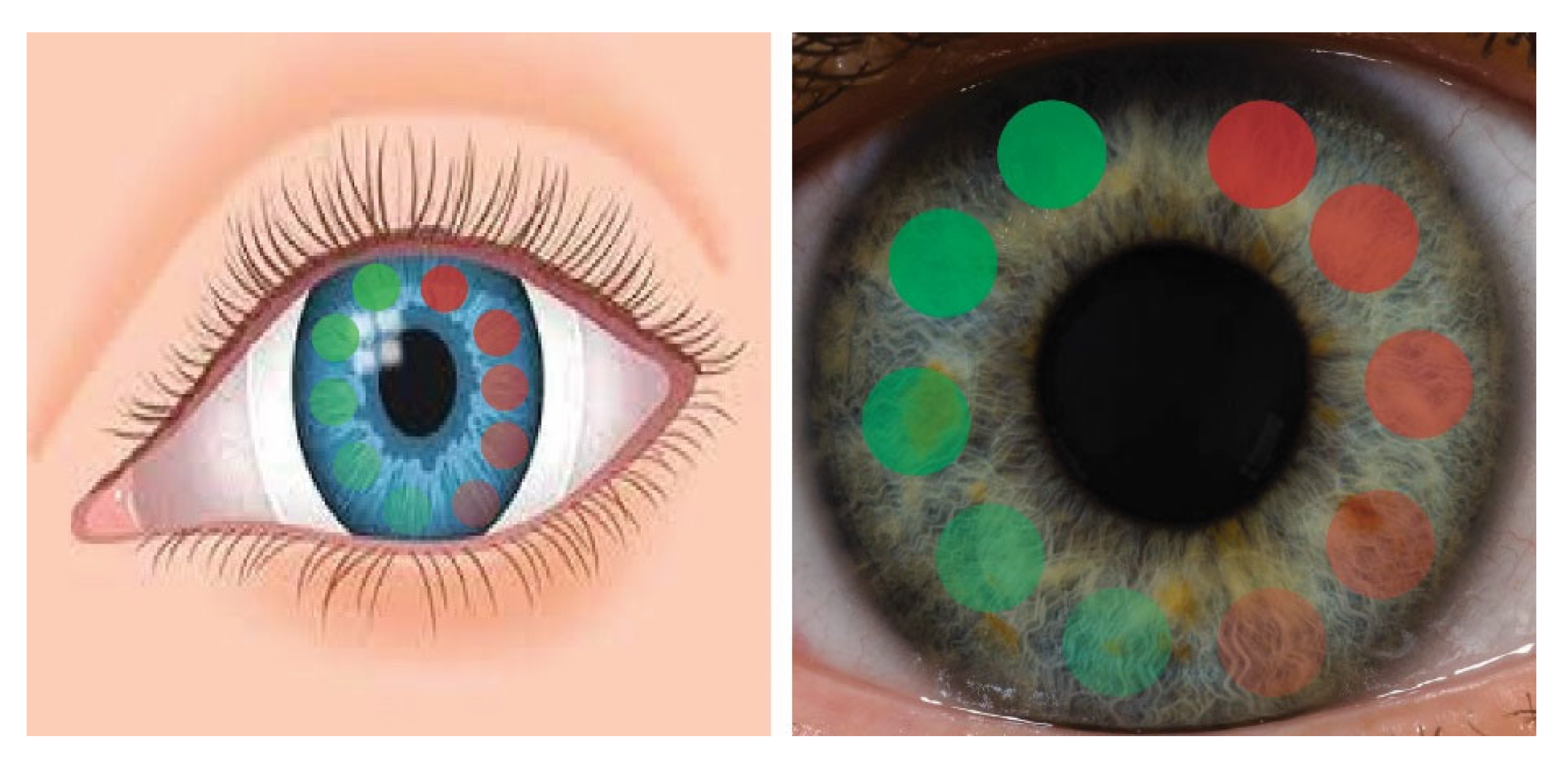
3.2. Tear Flow Across an Eye and Contact Lens
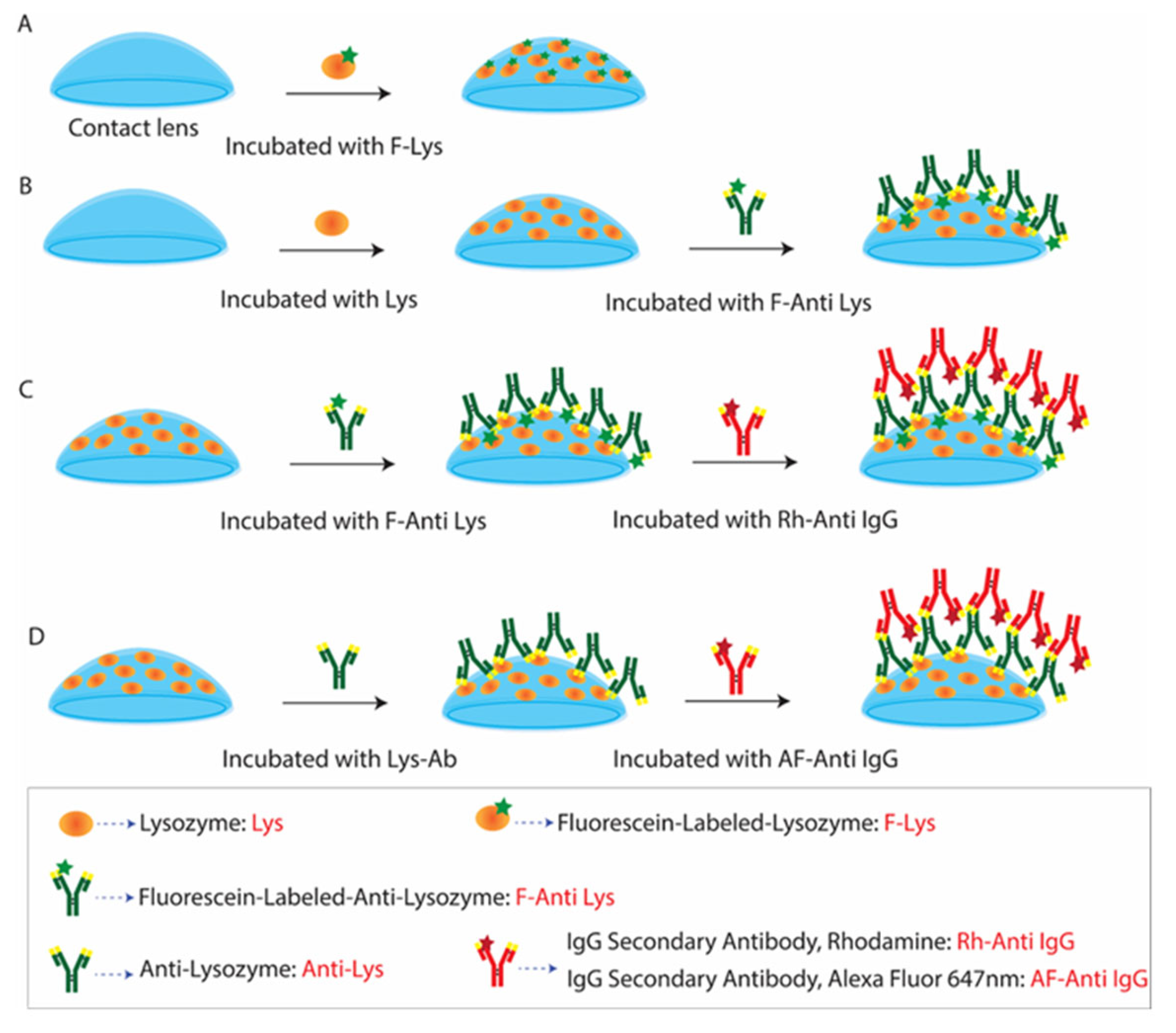
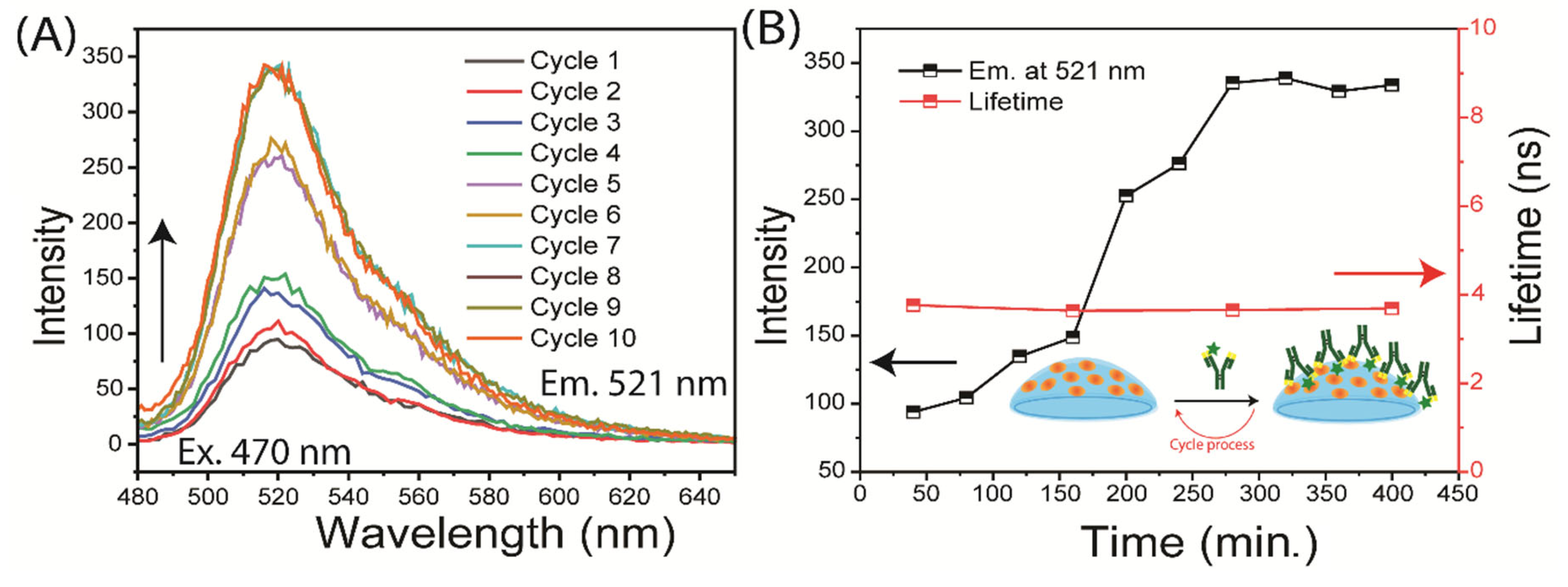
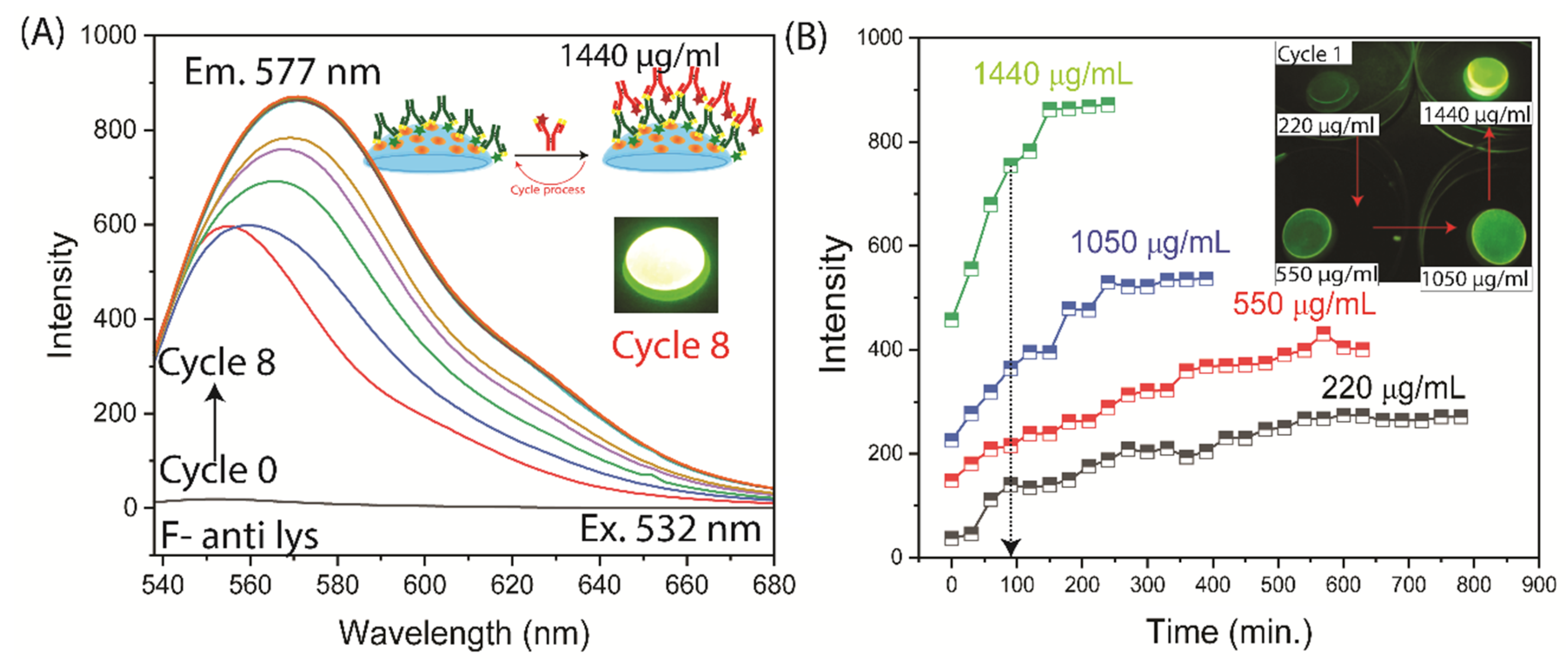
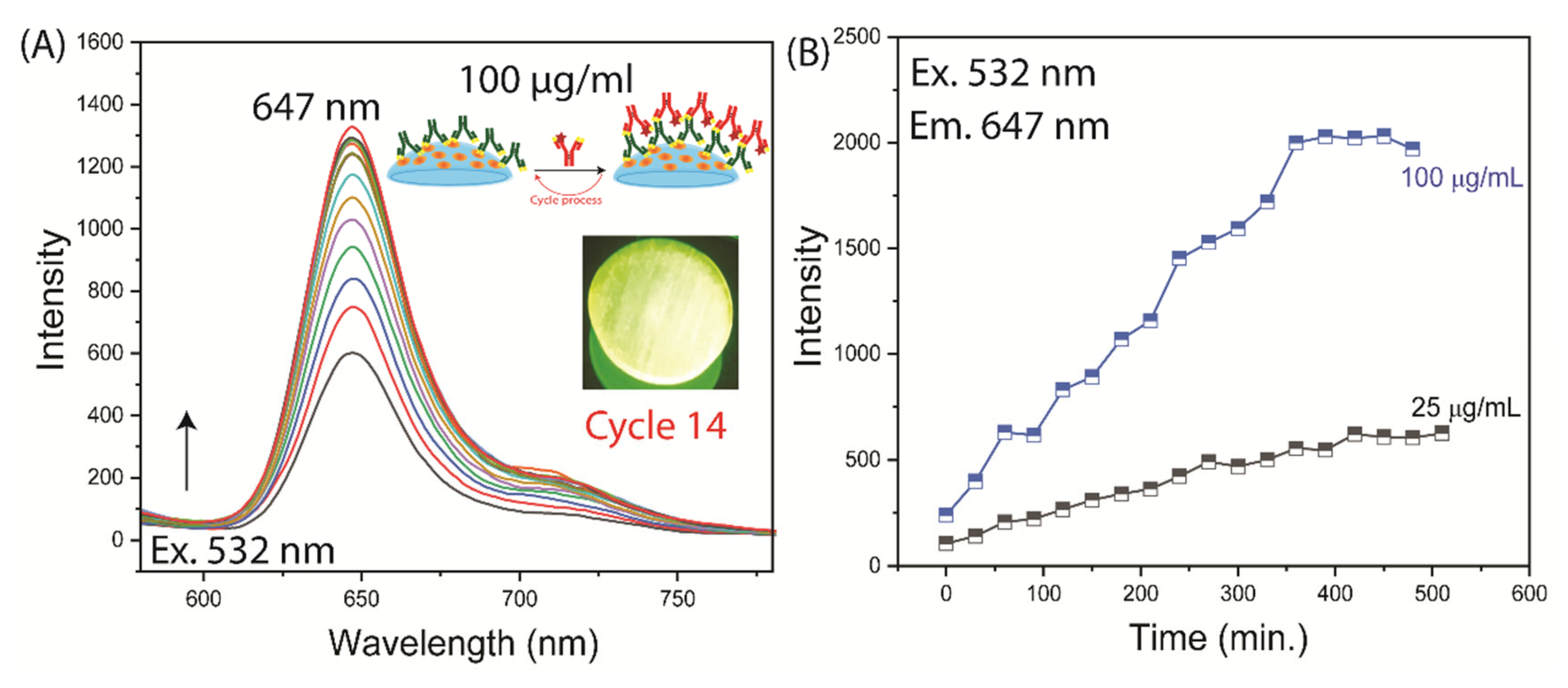
3.3. Binding of Antibodies to the Contact Lens
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- Hubbard, J.D. A Concise Review of Clinical Laboratory Science, Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins 2011, 410 pp.
- Goljan, E.F.; Sloka, K.I. Rapid Review Laboratory Testing in Clinical Medicine, Mosby Elsevier 2007, 460 pp.
- Qureshi, A.; Gurbuz, Y.; Niazi, J.H. Biosensors for cardiac biomarkers detection; A review. Sensors Actua B. 2012, 171, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.S.; Tan, W.P.; Tan, M.-Y.; Khetrapal, P.; Dong, L.; deWinter, P.; Feber, A.; Kelly, J.D. Novel urinary biomarkers for the detection of bladder cancer: A systematic review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2000, 69, 399–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi, A.; Aghaie, A.; Vahedi, E.; Quzvini, A.; Ghanei, M.; Afkhami, A.; Hajian, A.; Bagheri, H. Electrochemical biosensors for the detection of lung cancer biomarkers; A review. Talanta 2020, 206, 120251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misek, D.E.; Patwa, T.H.; Lubman, D.M.; Simeone, D.M. Early detection and biomarkers in pancreatic cancer. J. Natl. Comp. Cancer Net. 2007, 5, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, A.; Ravishankan, P.; Harms, S.; Klimberg, V.S. Using tears as a non-invasive source for easy detection of breast cancer. Plos One. 2022, 17, e0267676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csosz, E.; Boross, P.; Csutak, A.; Berta, A.; Toth, F.; Poliska, S.; Torok, Z.; Tozser, J. Quantiative analysis of proteins in the tear fluid of patients with diabetic retinopathy. Proteome J. 2012, 75, 2196–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbari, R.; Van Niewaal, J.; Bleavins, M.R. (Eds). Biomarkers in Drug Discovery and Development: Handbook of Practice, Application and Strategy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Tian, S.; Zhao, W.; Liu, K.; Ma, X.; Guo, J. Multiplexed detection of biomarkers in lateral-flow immunoassays. Analyst. 2020, 145, 2828–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishur, R.J.; Rea, S.L. Applications of mass spectrometry to metabolomics and metabonomics: Detection of biomarkers of aging and of age-related diseases. Mass Spec. Rev. 2011, 31, 70–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, P.R.; Kramer, B.S.; Srivastava, S. Trends in biomarker research for cancer detection. The Lancet Oncol. 2001, 2, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisig, B.; Gaulard, P.; deLeval, L. New biomarkers in T-cell lymphomas. Clin. Haematology. 2012, 25, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, E.; Greenhalf, W.; Neoptolemos, J.P. New biomarkers and targets in pancreatic cancer and their application to treatment. Nature Rev. 2012, 9, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, G.S.; Ahmed, T.; Heiss, L.; Walia, S.; Bhaskaran, M.; Sriram, S. Rapid and selective biomarker detection with conductometric sensors. Small. 2021, 17, 2005582–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimse, S.B.; Sonawane, M.D.; Song, K.-S.; Kim, T. Biomarker detection technologies and future directions. Analyst. 2016, 141, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haitao, J.L.; Xu, J.; Zhao, X.; Song, S.; Xue, Z.; Wu, Y.S.; Gopinath, S.C.; Lakshmipriya, T.; Zhang, H. Silica/antibody conjugated microcomb electrode sensor for cardiac biomarker analysis. Appl. Physics. 2021, 127, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Ye, X.; Cui, T. Recent progress of biomarker detection sensors. Mech. Eng. 2020, 38, 7949037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Rica, R.; Stevens, M.M. Plasmonic ELISA for the ultrasensitive detection of disease biomarkers with the naked eye. Nature Nanotech. 2012, 7, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Yi, P.; Xu, X.; Fan, Y.; Cui, B.; Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Du, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, P. Salivary protease spectrum in oral cancer. Intl. J. Oral Sci. 2019, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, S.; Davis, C.; Abrams, W.R.; Billings, P.C.; Nagashanmugam, T.; Friedman, H.; Malamud, D. Submandibular salivary proteases: lack of a role in anti-HIV activity. J. Dent. Res. 1998, 77, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roobol, M.J.; Haese, A.; Bjartell, A. Tumour markers in prostate cancer III: Biomarkers in urine. Acta Oncologica 2011, 50, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youhe, G. Urine - an untapped goldmine for biomarker discovery? Sci. China Life Sci. 2013, 56, 1145–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Corrie, S.R.; Coffey, J.W.; Islam, J.; Markey, K.A.; Kendall, M.A.F. Blood, sweat, and tears: developing clinically relevant protein biosensors for integrated body fluid analysis. Analyst. 2015, 140, 4350–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebbane, M.; Claret, P.G.; Lefebvre, S.; Mercier, G.; Rubenovitch, J.; Jreige, R.; Eledjam, J.J.; de La Coussaye, J.E. Predicting peripheral venous access difficulty in the emergency department using body mass index and a clinical evaluation of venous accessibility. J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 44, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, A.F.; Winslow, E.H. Variables influencing intravenous catheter insertion difficulty and failure: An analysis of 339 intravenous catheter insertions. Heart and Lung 2005, 34, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Guidi, C.; Mattiuzzi, C.; Plebani, M. Preanalytical variability: the dark side of the moon in laboratory testing. Clin. Chem. 2006, 44, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, S.A.; McKay, M.J.; Molloy, M.P. Evaluation of blood collection tubes using selected reaction monitoring MS: implications for proteomic biomarker studies 2010, 10, 2050–2056.
- Tamhane, M.; Cabrera-Ghayoun, S.; Abelian, G.; Viswanath, V. Review of biomarkers in ocular matrices: Challenges and opportunities. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Thun Und, H. M.; Funke, S.; Grus, F.H. Tears as a source of biomarkers for ocular and systemic diseases. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 117, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachhuber, F.; Huss, A.; Senel, M.; Tumani, H. Diagnostic biomarkers in tear fluid: from sampling to preanalytical processing. Sci. Rep., 2021, 11, 10064–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, W.G.; and Wilson, G. Essential ions for maintenance of the corneal epithelial surface. Invest. Oph. Vis. Sci. 1985, 26, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcos, M.D.P.; Argueso, P.; Georgiew, G.A.; Holopainen, J.M.; Laurie, G.W.; Millar, T.J.; Papas, E.B.; Rolland, J.P.; Schmidt, T.A.; Stahl, U.; Suarez, T.; Subbaraman, L.N.; Uçakhan, O.O.; Jones, L. TFOS DEWS II tear film report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 366–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versura, P.; Campos, E.C. TearLab osmosarity system for diagnosing dry eye. Exp. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 13, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentka, A.; Koroskenvi, K.; Harsfalvi, J.; Szekanecz, Z.; Szucs, G.; Kzodrary, P.; Kemeny-Beke, A. Evaluation of commonly used tear sampling methods and their relevance in subsequent biochemical analysis. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 54, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullard, R.J.; Snyder, C. Protein levels in nonstimulated and stimulated tears of normal human subjects. Inv. Oph. Vis. Sci., 1990, 31, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Pandit, J.C.; Nagyova, B.; Bron, A.J.; Tiffany, J.M. Physical properties of stimulated and unstimulated tears. Exp. Eye Res. 1999, 68, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullard, R.J.; Tucker, D.L. Changes in human tear protein levels with progressively increasing stimulus. Inves. Oph. Vis. Sci. 1991, 32, 2290–2301. [Google Scholar]
- Stuchell, R.N.; Feldman, J.J.; Farris, R.L.; Mandel, J.D. The effect of collection technique on tear composition. Inves. Ophthal. Vis. Sci. 1984, 25, 374–377. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, X.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Golubnitschaja, O. Mass spectrometry analysis of human tear fluid biomarkers specific for ocular and systemic diseases in the context of 3P medicine. EPMA J. 2021, 12, 449–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiarczyk, M.; Biela, K.; Michalak, K.; Winiarczyk, D.; Mackiewicz, J. Changes in tear proteomic profile in ocular diseases. Intl. J. Environ. Res. 2022, 19, 13341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzini, E.; Santambrogio, C.; DePalma, A.; Mauri, P.; Tavazzi, S.; Grandori, R. Mass spectrometry-based tear proteomics for noninvasive biomarker discovery. Mass. Spec. Rev. 2021, 41, 842–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adigal, S.S.; Rizvi, A.; Rayaroth, N.V.; John, R.V.; Barik, A.; Shandari, S. Human tear fluid analysis for clinical applications: progress and prospects. Exp. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 21, 767–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.K.; Singh, D.; Upadhay, J.; Gupta, N.; Dhiman, N.; Mittal, S.K.; Mahindroo, N. Identification of tear-based protein and non-protein biomarkers. Its application in diagnosis of human diseases using biosensors. Intl. J. Biol. Macro. 2021, 193, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zihara, M.; Kubota, N.; Kadowaki, T. Study of the correlation between tear glucose concentrations and blood glucose concentrations. Clin. Diabetes. 2018, 67, 944P. [Google Scholar]
- Baca, J.T.; Taormina, R.; Feingold, E.; Finegold, D.N.; Grabowski, J.J.; Asher, S.A. Mass spectral determination of fasting tear glucose concentrations in nondiabetic volunteers. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 1370–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aihara, M.; Kubota, N.; Minami, T.; Shirakawa, R.; Sakurai, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Iwamoto, M.; Takamoto, I.; Kubota, T.; Suzuki, R.; Usami, S.; Jinnouchi, H.; Aihara, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Sakata, T.; Kadowaki, T. Association between tear and blood glucose concentrations: Random intercept model adjusted with confounders in tear samples negative for occult blood. J. Diab. Inves. 2021, 12, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Sheng, M. , Li, J.; Yan, G.; Lin, A.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y. Tear proteomic analysis of Sjogren syndrome patients with dry eye syndrome by two-dimensional nano liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Saljyothi, A.V.; Angayarkanni, N.; Syama, C.; Utpal, T.; Shweta, A.; Bhaskar, S.; Geetha, I.K.; Vinay, P.S.; Thennarasu, M.; Sivakumar, R.M.; Prema, P. Two-dimensional electrophoretic analysis of human tears: collection method in dry eye syndrome. Electro. 2010, 31, 3420–3427. [Google Scholar]
- Bachhuber, F.; Huss, A.; Senel, M.; Tumani, H. Diagnostic biomarkers in tear fluid: from sampling to preanalytical processing. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardinois, F. Google unveils smart contact lens that diabetics measure their glucose levels 2014. https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-25771907.
- Google halts glucose sensing contact lens 2018, https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-46262520.
- McDermott, J.; Levine, B. Glucose-sensing contact lens development on hold, 2023), https://diatribe.org/glucose-sensing-contact-lens-development-hold.
- Farr, C. Alphabet stops its project to create a glucose-measuring contact lens for diabetes patients 2018, https://www.cnbc.com/2018/11/16/alphabet-verily-stops-smart-lens-glucose-measuring-contact-lens.
- Mojo Lens. The world’s first true smart contact lens 2023, https://www.mojo.vision.
- Mojo vision smart contact lenses are now “feature complete”. 2022, https://skarredghost.com/2022/03/30/mojo-vision-smart-contact-lenses-feature-complete/.
- Clark, M. Another company has stopped working on smart contact lenses, The Verge. 2023, https://www.theverge.com/2023/1/7/23543224/mojo-vision-smart-contact-lens-microled.
- Gregory, W.D. Soft Lens Material Choices and Selection. Con. Lens Spec. 2012, 27, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Badugu, R.; Reece, E.A.; Lakowicz, J.R. Glucose-sensitive silicone hydrogel contact lens toward tear glucose monitoring. J. Biomed. Optics. 2018, 23, 057005–1/9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badugu, R.; Jeng, B.H.; Reece, E.A.; Lakowicz, J.R. Contact lens to measure individual ion concentrations in tears and applications to dry eye disease. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 542, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badugu, R.; Szmacinski, H.; Reece, E.A.; Jeng, B.H.; Lakowicz, J.R. Sodium-sensitive contact lens for diagnostics of ocular pathologies. Sensors Actuators B. 2021, 331, 129434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R.; Badugu, R.; Sivashanmugan, K.; Reece, A. Remote Measurements of Tear Electrolyte Concentrations on Both Sides of an Inserted Contact Lens. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godawat, R.; Konstantinov, K.; Rohani, M.; Warikoo, V. End-to-end integrated fully continuous production of recombinant monoclonal antibodies. J. Biotech. 2015, 213, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, C.W.; Allison, D.E.; Flagella, K.; Presta, L.; Clarke, J.; Dybdal, N.; McKeever, K.; Sliwkowski. Humanization of a recombinant monoclonal antibody to produce a therapeutic HER dimerization inhibitor, pertuzumab. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006, 55, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, K.F.; Mick, J.E.; Ide, A.H.; Lima, W.C.; Sherman, L.; Schaller, K.L.; Anderson, S.M.; Zhao, N.; Stasevich, T.J.; Varma, D.; Nilsson, J.; DeLuca, J.G. Generation and diversification of recombinant monoclonal antibodies. Elife. 2021, 10, e72093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silicone hydrogels - What are they and how should they be used in everyday practice? Bausch & Lomb, CIBA Vision, Contact Lens Monthly, No. 5726, vol. 218.
- Gromacki, S.J. Compliance with daily disposable contact lenses, Contact Lens Spectrum/Special Edition 2013, p. 13.
- Gachon, A.M.; Richard, J.; Dastugue, B. Human tears: normal protein pattern and individual protein determinations in adults. Curr. Eye Res. 1983, 2, 301–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.; Willcox, M.D.; Madigan, M.C.; Wasinger, V.; Schiller, B.; Walsh, B.J.; Graham, P.H.; Kearsley, J.H.; Li, Y. Tear fluid protein biomarkers. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2013, 62, 151–96. [Google Scholar]
- Steudle, A.; Pleiss, J. Modelling of lysozyme binding to a cation exchange surface at atomic detail: the role of flexibility. Biophys J. 2011, 100, 3016–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, N.A.W.; Molloy, J.E. Microfluidic flow-cell with passive flow control for microscopy applications. PLOS One 2020, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambot, S.B.; Romauld, M.M.; Carter, G.M.; Sipior, J.; Terpetchnig, E.; Lakowicz, J.R. Sensing oxygen through skin using red diode laser and fluorescence lifetimes. Biosensors Bioelec. 1995, 10, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmacinski, H.; Lakowicz, J.R. Optical measurements of pH using fluorescence lifetimes and phase-modulation fluorometry. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Tian, W.S.; Huang, L.; Dong, L.; Guo, J. A smart-phone based biomedical sensory system. Analyst 2020, 145, 2875–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, E.; Ogawa, Y.; Yazu, H.; Aketa, N.; Yang, F.; Yamane, M.; Sato, S.; Kawakami, Y.; Tsubota, K. Smart Eye Camera: An innovative technique to evaluate tear film breakup time in murine dry eye disease model. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0215130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelleswarapu, V.R.; Jeong, H.H.; Yadavali, S.; Issadore, D. Ultra-high throughput detection of fluorescent droplets using a cell phone camera and time domain encoded optofluidics. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wargocki, P.; Deng, W.; Anwer, A.G.; Goldys, E.M. Medically relevant assays with a simple smartphone and tablet based fluorescence detection system. Sensors. 2015, 5, 11653–11664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Sun, R.; Vasile, T.; Chang, Y.C.; Li, L. High-throughput optical sensing immunoassays on smartphone. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8302–8308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamandis, E.P. Immunoassays with time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy: principles and applications. Clin. Biochem. 1988, 21, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degen, P.; Podesta, A.; Montagnoli, G. Time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay. Mol. Biotechnol. 1999, 13, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S. A short history, principles, and types of ELISA, and our laboratory experience with peptide/protein analytes using ELISA. Peptides 2015, 72, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J., Zhou. Afterflow nanoprobe-enabled quantitative lateral flow immunoassay by a palm-size device for household healthcare. Anal. Chem 2024, 96, 4891–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a cancer biomarker and MMP-9 biosensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, R.; Titlestad, I.; Lindqvist, A.; Wielders, P.; Wray, H.; Wang, M.; Samuelsson, V.; Mo, J.; Holt, A. Effects of an oral MMP-9 and -12 ihibitor, AZD1236, on biomarkers in moderate/severe COPD: a randomized controlled trial. Pul. Pharm. Therap. 2012, 25, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsen, S.B.; Christensen, S.L.; Wurtz, S.O.; Lundberg, M.; Nielsen, B.S.; Vinther, L.; Knowles, M.; Gee, N.; Fredriksson, S.; Moller, S.; Brunner, N.; Schrofl, A.-S.; Stenvang, J. Plasma levels of the MMP-9: TIMP-1 complex as prognostic biomarker in breast cancer: a retrospective study. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, H.; Woessner, J.F. Matrix metalloproteinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 21491–21494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitka, O.; Kukacka, J.; Krizkova, S.; Huska, D.; Adam, V.; Masarik, M.; Prusa, R.; Kizek, R. Matrix metalloproteinases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 3751–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creech, J.L.; Chauhan, A.; Radke, C.J. Dispersive mixing in the posterior tear film under a soft contact lens. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2001, 40, 3015–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, B.; Ziemer, K.S.; Garabino, F.A.; Carrier, R.L. Chemical and physical modifications to poly(dimethylsiloxane) surfaces affect adhesion of caco-2 cells. J. Biomed. Mater Res. A. 2010, 15, 1260–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- https://www.lens.com/eyestyle/featured/the-best-selling-contact-lenses-of-2020-bonus-the-most-popular-brands.
- Goldstein, B.; mymya, D.; He, X.; Pined, A.R.; Wofsy, C. The influence of transport on the kinetics of binding to surface receptors: application to cells and BIAcore. J. Mol. Recog. 1999, 12, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, T.M.; Messinger, R.J.; Manalis, S.R. Making it stick: convection, reaction and diffusion in surface-based biosensors. Nature Biotech. 2008, 26, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beygi, M.A.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Cornell, B. Multiple surface-based biosensors for enhanced molecular detection in fluid flow systems. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 3, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




