Submitted:
07 April 2025
Posted:
07 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Laboratory Study
2.1.1. Investigation of MicroRNA-192
2.1.2. Purification of RNA and Reverse Transcriptase
2.1.3. Real-Time PCR
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahin DHH: Sultana R, Farooq J, Taj T, Khaiser UF, Alanazi N, Alshammari MK, Alshammari MN, Alsubaie FH, Asdaq SMB, Alotaibi AA, Alamir AA, Imran M and Jomah S. Insights into the uses of traditional plants for diabetes nephropathy: a review. Curr Issues Mol Biol 2022, 44, 2887–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma X, Lu C, Lv C, et al. The expression of miR-192 and its significance in diabetic nephropathy patients with different urine albumin creatinine ratio. J Diabetes Res. 7894.
- Martinez-Hernandez R, Marazuela M. MicroRNAs in autoimmune thyroid diseases and their role as biomarkers. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2023, 37, 101741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krattinger R, Bostrom A, Schioth HB, Thasler WE, Mwinyi J, Kullak-Ublick GA. 13microRNA-192 suppresses the expression of the farnesoid X receptor. Am J PhysiolGastrointest Liver Physiol 2016, 310, G1044–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishan MA, Tabari M, Parnian J, Fallahi J, Mahrooz A, Bagheri A. Functional mechanisms of miR-192 family in cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer (2020). [CrossRef]
- Ren FJ, Yao Y, Cai XY, Fang GY. Emerging role of MiR-192-5p in human diseases. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 614068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan X, Liao J, Lai H, Zhang S, Cui J, Chen C. Roles of microRNA-192 in diabetic nephropathy: the clinical applications and mechanisms of action. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023, 14, 1179161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Diabetes Work Group. KDIGO 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, S1–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang F, Li C, Han J, Wang L. Diagnostic Value of Combination of MicroRNA-192 in Urinary Sediment and B-Ultrasound for Bladder Cancer. Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment. [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, A.G.A. , Badr, D.F., El Kheir, N.Y.A. et al. Prevalence of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase and molecular detection of blaTEM, blaSHV, and blaCTX-M genotypes among gram-negative Bacilli isolates from hospital acquired infections in pediatrics, one institutional study. Ital J Pediatr 2024, 50, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbazian H and Rezaii I: Diabetic kidney disease; review of the current knowledge. J Renal Inj Prev. 2013, 2, 73–80.
- Dronavalli S, Duka I and Bakris GL: The pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2008, 4, 444–452. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu C, Sun L, Xiao L, Han Y, Fu X, Xiong X, Xu X, Liu Y, Yang S, Liu F and Kanwar YS: Insight into the mechanisms involved in the expression and regulation of extracellular matrix proteins in diabetic nephropathy. Curr Med Chem. 2015, 22, 2858–2870. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora MK and Singh UK: Molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy: An update. Vascul Pharmacol. 58:259–271.
- Chang AS, Hathaway CK, Smithies O and Kakoki M: Transforming growth factor-β1 and diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016, 310, F689–F696. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutale JJ, Thordarson H, Abbas ZG and Vetvik K: Microalbuminuria among type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients of African origin in Dar Es Salaam, Tanzania. BMC Nephrol. 8:22007.
- Sun Y, Koo S, White N, Peralta E, Esau C, Dean NM, Perera RJ. Development of a micro-array to detect human and mouse microRNAs and characterization of expression in human organs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kafaji G, Al-Muhtaresh HA. Expression of microRNA-377 and microRNA-192 and their potential as blood-based biomarkers for early detection of type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Mol Med Rep. 2018, 18, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang J, Yao D, Yan H, Chen X, Wang L, Zhan H. The Role of MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Nephropathy. Int J Endocrinol. 2019, 2019, 8719060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Krupa A, Jenkins R, Luo DD, Lewis A, Phillips A and Fraser D: Loss of microRNA-192 promotes fibrogenesis in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010, 21, 438–447. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma X, Lu C, Lv C, Wu C, Wang Q. The Expression of miR-192 and Its Significance in Diabetic Nephropathy Patients with Different Urine Albumin Creatinine Ratio. J Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 6789402. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang B, Herman-Edelstein M, Koh P, Burns W, Jandeleit-Dahm K, Watson A, Saleem M, Goodall GJ, Twigg SM, Cooper ME, Kantharidis P. E-cadherin expression is regulated by miR-192/215 by a mechanism that is independent of the profibrotic effects of transforming growth factor-β. Diabetes. 2010, 59, 1794–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong Z, Banchs PAP, Liu Y, Fu H, Arena VC, Forno E, Libman I, Ho J, Muzumdar R. Serum α-KL, a potential early marker of diabetes complications in youth with T1D, is regulated by miRNA 192. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022, 13, 937093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jia Y, Guan M, Zheng Z, Zhang Q, Tang C, Xu W, Xiao Z, Wang L and Xue Y: miRNAs in urine extracellular vesicles as predictors of early-stage diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Res. 2016, 79327652016.
- El-Monem A, A. , Mahfouz M H., Mohamed M A., Abd El-Aziz H G, Hussien N. Microrna 192 Gene Expression in Type II Diabetic Nephropathy. The Egypt J of Hosp Med 2017, 68, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group III (n=50) |
Group I (n=50) |
Group II (n=50) |
P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex Male Female |
34 16 |
29 21 |
32 18 |
0.58 |
| age | 51.8 ± 7.37 | 52.28± 7 6.15 | 53.34± 7 5.47 | 0.47 |
| BUN | 26.38± 7 2.77 | 27.68± 7 2.83 | 56.8± 7 4.73 | 0.001 |
| creatinine | 0.92± 7 0.2 | 1.02± 7 0.13 | 4.1± 7 0.6 | 0.001 |
| Fasting blood glucose | 90.1± 7 11.4 | 150.4 ± 740.4 | 158.2± 7 60.4 | 0.001 |
| HB1c | 4.4± 7 0.6 | 8.9 ± 7 2.01 | 8.5 ± 71.8 | 0.001 |
| duration | 5.23 ± 72.8 | 7.7± 7 3.3 | 0.001 | |
| Albumin | 4.04± 7 0.45 | 3.9 ± 7 0.2 | 3.7 ± 70.35 | 0.001 |
| Albumin in urine | 11.0± 7 4.9 | 17.01 ± 73.6 | 83.3 ± 716.6 | 0.001 |
| Urinary creatinine | 1. 71 ±0.4 | 1.1± 7 0.3 | 0.7± 7 0.13 | 0.001 |
| Albumin/creatinine ratio | 12.5± 7 7.4 | 16.0± 71 5.0 | 117.6± 7 27.23 | 0.001 |
| eGFR | 90.2 ± 719.2 | 69.6 ± 710.33 | 17.3± 7 4.02 | 0.001 |
| MicroRNA-192 | Group III (n=50) |
Group I (n=50) |
Group II (n=50) |
P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MicroRNA-192 | 0.83± 7 0.3 | 1.35± 7 0.5 | 0.65± 7 0.2 | P=0.001 P1=0.004 P2=0.001 P3=0.001 |
| MicroRNA-192 | |
|---|---|
| Creatinine R P |
-.651 0.001 |
| eGFR R P |
0.744 0.001 |
| Urinary creatinine R P |
0.488 0.001 |
| Urinary albumin R P |
-.616 0.001 |
| Duration R P |
-0.302 0.001 |
| Urinary albumin/creatinine ratio R P |
-.624 0.001 |
| eGFR R P |
.354** .000 |
| BUN R P |
-.419-** .000 |
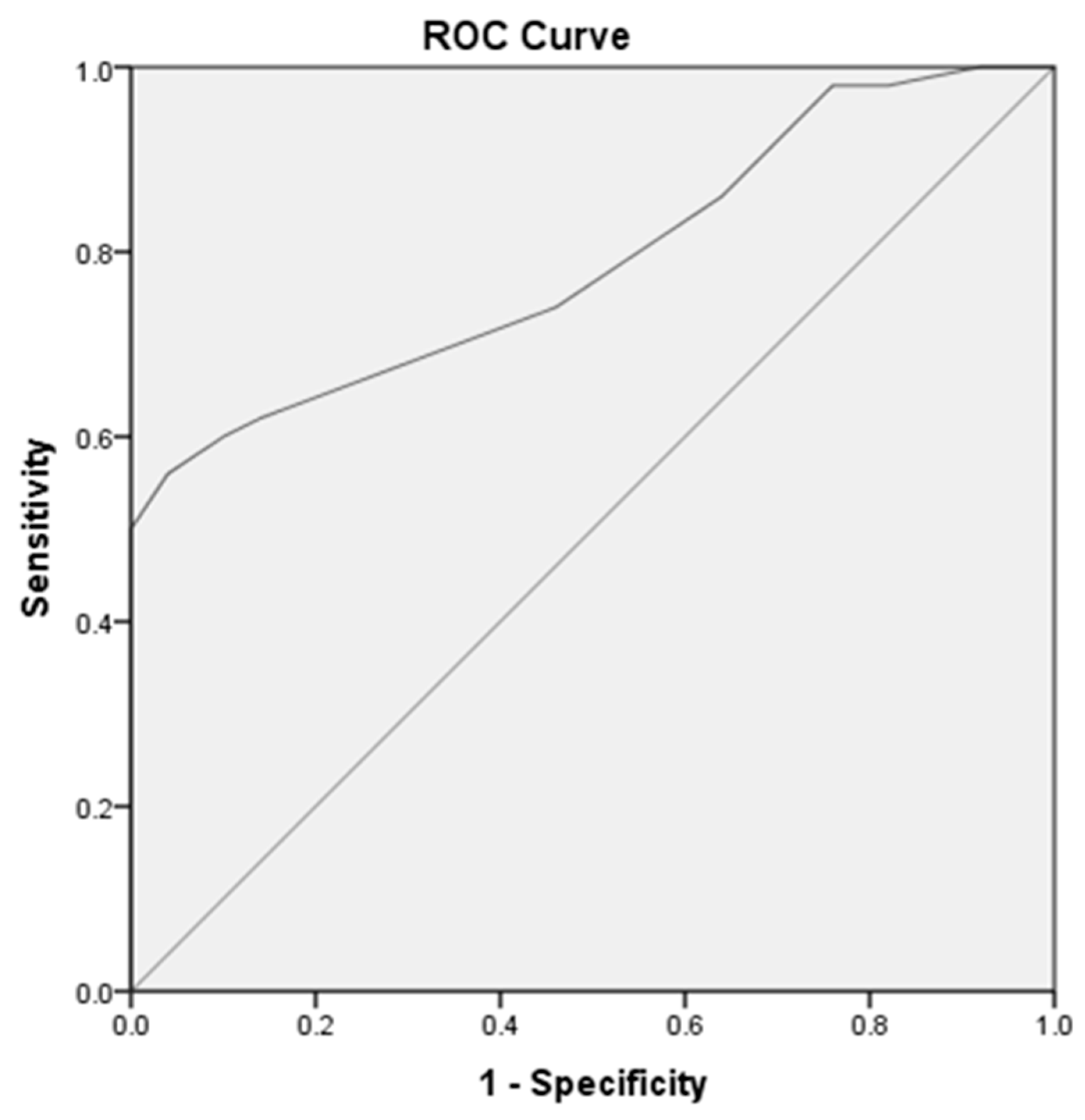
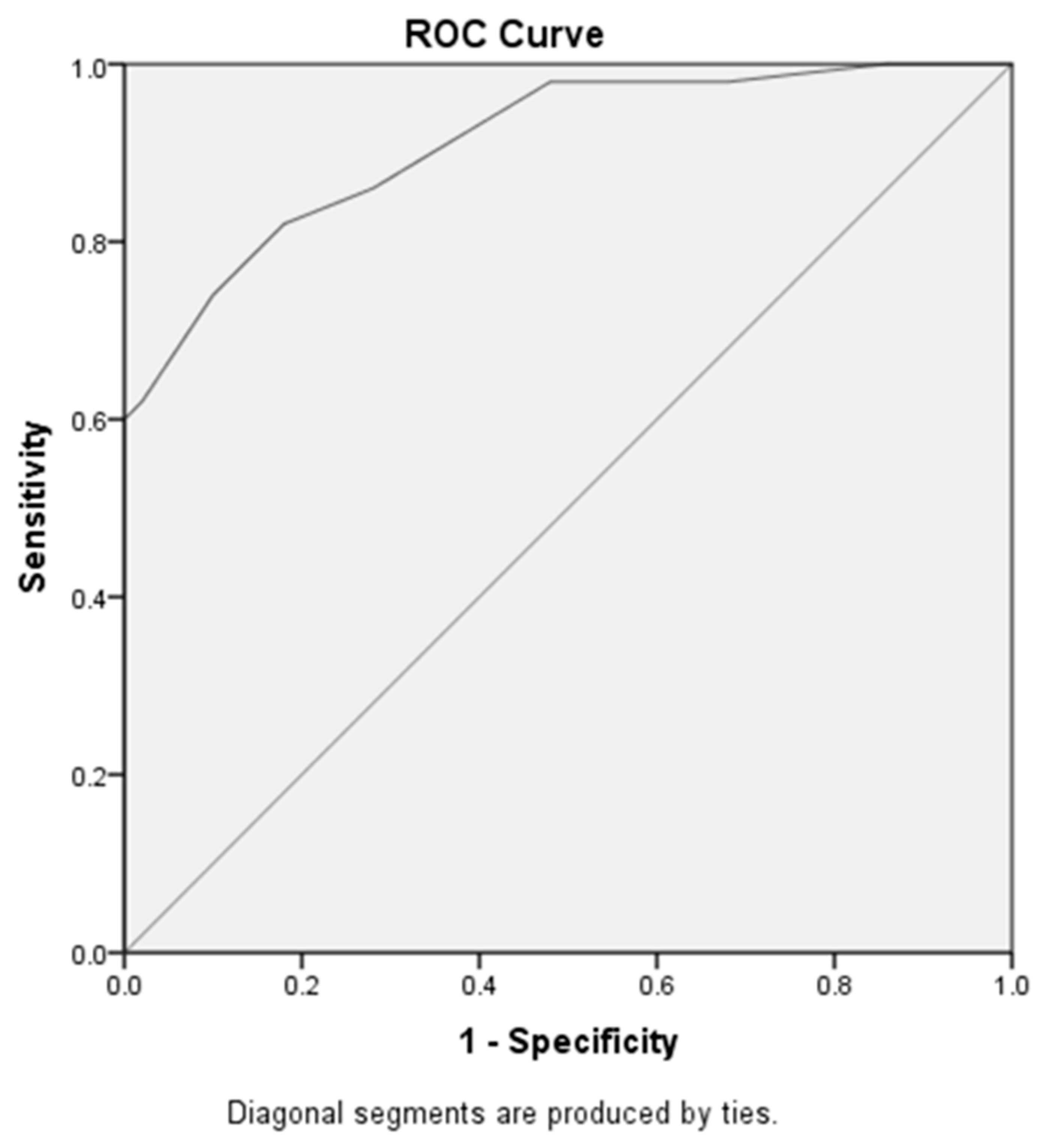
| Area under curve | Cut off value | Sensitivity | Specificity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MicroRNA-192 at early diabetic nephropathy versus control subjects | 0.79 | 1,05 | 62% | 86% | |
| MicroRNA-192 at early diabetic nephropathy versus late diabetic nephropathy | .91 |
0.85 |
82% | 82% |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





